Abstract
This study focuses on producing asphalt with improved rheological properties that differ from the original asphalt and are less affected by aging conditions. The rheological properties of Qayara asphalt were enhanced by modifying the asphalt using spent rubber tire (SRT) with different percentages of anhydrous aluminum chloride. Percentages ranging from 1.0% by weight of the spent tire rubber were added after proceeding with the thermal crushing process. The percentages of anhydrous aluminum chloride catalyst were 0.4 and 0.8%, respectively. This mixture was microwaved at 270 watt of power for 4, 8, and 12 min, respectively. The measurements performed are plasticity, penetration, softening point, and penetration index. The previously mentioned measurements were also made on the modified asphalt one year after the modification process to understand the effect of aging conditions. The microstructure and thermodynamics have been characterized by FE-SEM and EDX measurements. This study provides good rheological properties of the modified bitumen binder that is aging-resistant.
1. Introduction
The asphalt industry is one of the most important industries that exist today. Asphalt is a thermoplastic material and keeps its condition very well. At normal temperatures, asphalt is a liquid or semi-solid material with a high viscosity and works as an excellent insulator from water that is not affected by any factors such as salts or even acids [1,2,3,4]. It can be black or dark brown in color. Asphalt is a heavy hydrocarbon component derived from the direct distillation of crude oil, and it is one of the best materials used in the process of paving roads in streets, airfields roads, and others [5]. It also consists of three main layers that serve as the basic layers, namely, the base layer, the bonding layer, and the third layer is the surface layer. The first layer consists of ordinary gravel or crushed gravel, as well as sand and filler. The second layer, consisting of crushed gravel, its proportion is about 90%, and the thickness of that layer is 5 cm up to 8 cm. The last layer, which is the surface layer, consists of the same components that make up the second layer but with different sizes and thicknesses, from 6 cm to 8 cm in thickness [6,7,8,9,10]. Obtaining asphalt with rheological properties and resistance to aging factors is an important and necessary issue to ensure the longest possible period for asphalt use in the most important area, which is paving [3,11]. Asphaltic materials are heterogeneous hydrocarbon materials produced by direct distillation that contain sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen (S, N, O), in addition to cyclic and non-cyclic compounds [12]. One of the most important methods for obtaining asphalt with rheological properties that exceed those of the original asphalt is the rheological modification of asphalt processes using polymeric materials [13]. Chemical modification with polymers was chosen over other methods because the produced asphalt has compatible properties [14,15,16,17]. Due to the importance of asphalt and its use in the field of paving and its availability in large quantities, many researchers have modified asphalt and improved its rheological properties by using various additives, such as Mashaan and Nikraz, who studied the engineering properties of asphalt binder modified with local waste of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a common type used for local road surfaces in Australia [12,18]. Several tests were conducted through dynamic shearing, thin film furnace, and aging tests for modified asphalt, and it was found through the study that the best percentage of re-polymer is (6.0–8.0%) of the weight of the mixture, which can improve the properties of the concrete paving mixture [18,19].
Cunha et al. studied the rheological properties of modified asphalt containing natural fibers sourced from Amazon rain forests, discovering that these additives significantly improve physical properties, such as fluidity, using TG and DSR tests [20,21]. Saleh studied the effect of adding the different ratios of asphaltene to Begi and Qayara asphalt [22]. He measured the rheological properties, and the results obtained after 18 months of aging, compared with those of untreated asphalt, showed an increase in the homogeneity system for both Qayara and Begi asphalt, with improvement in the aging specifications for Qayara asphalt only [23,24,25]. Anjan and Veeragavan found that the mixing of asphalt with certain additives caused to improve the mechanical properties of the studied asphalt [26]. Hamedi and Joubani studied the effect of styrene-butadiene rubber-modified asphalt (SBR) on improving the moisture susceptibility of asphalt mixtures. Repeated loading tests were performed in wet and dry conditions side by side, and the study showed that the presence of this polymer in the mixture caused a positive change, as it increased the strength of the mixture against moisture damage [27]. Nikraz and Mashaan studied the engineering properties of the asphalt with local points (Ethylene Terephthalate) evaluated from tests, dynamic shear test, and aging test, and the study showed that the best percentage of re-polymer is (2.0 to 6.0%) of the best possible modification [28]. Pakenari and Hamidi were also able to study some of the rheological properties of a warm recycled asphalt mixture (WAM). The results showed that the increase in the time of placing the mixture in the kiln increased the hardness coefficient, which reduced the stress life and increased the adhesion between the asphalt binders and rubble [29,30]. Due to the urgent need to produce materials of great feasibility and economic value, the production of asphalt with specifications differing from the specifications of the basis of traditional asphalt materials and suitable for use in areas not commensurate with the normal use of conventional asphalt is necessary.
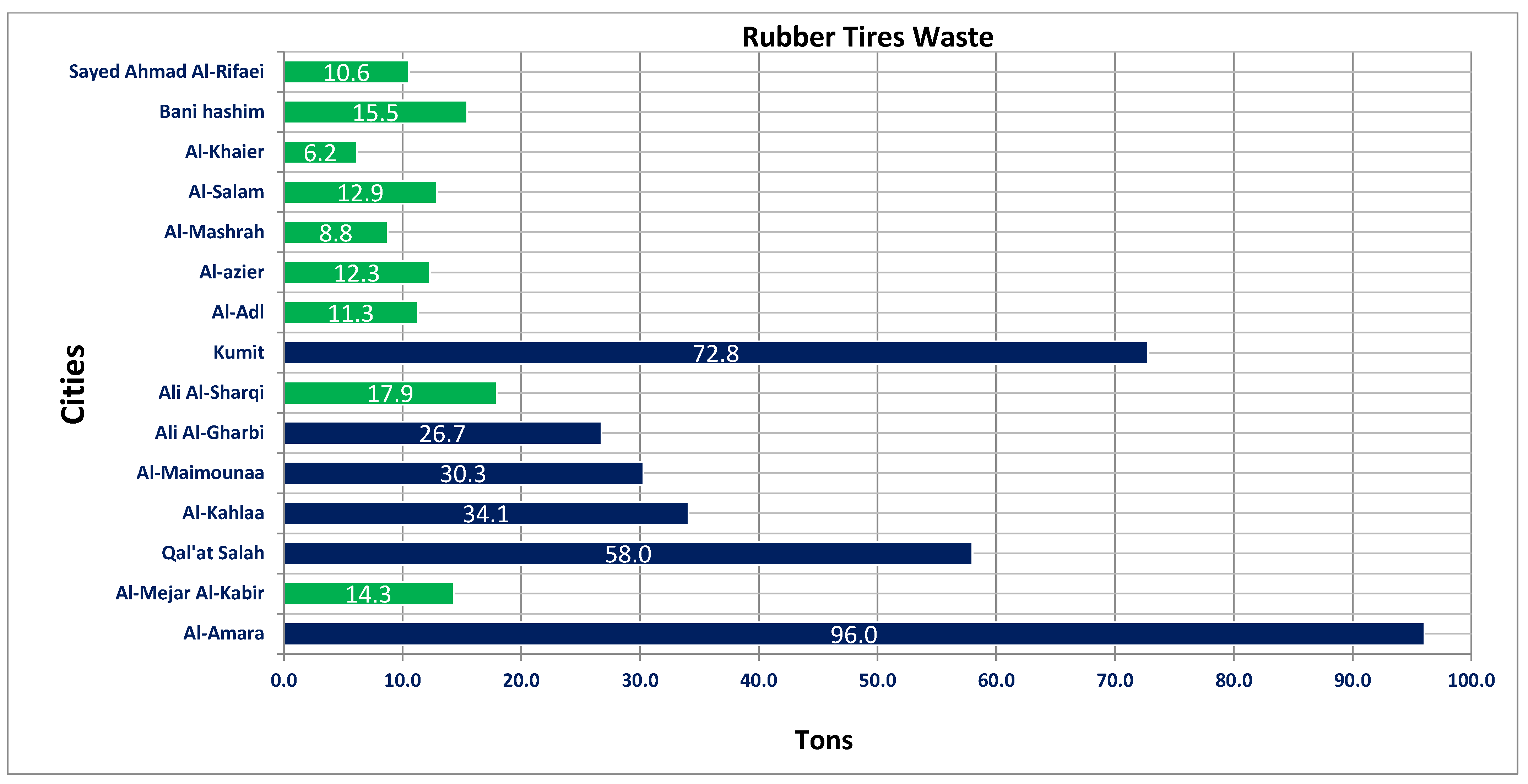
The main objective of the current research was to evaluate the rheological properties of modified asphalt binders. Recycling old rubber tires reduces the amount of new bitumen needed in the paving process, reducing reliance on or importing new bitumen. Recycling reduces waste tire rubber, as the recycled material is no longer sent to the landfill as a huge accumulated quantity. Accordingly, with regard to the issue of estimating the amount of waste rubber tires in the province of Iraq, we attempted to develop an approach based on the principle of tons and proportionality—a process between the aforementioned in terms of approximate tons, shown in Figure 1, as an indicator of the expected percentage of the amount of waste rubber tires generated, which amounts to the total waste percentage for one year (2020), during the time period [31]. Cities with high RTW consumption are represented in the blue column, while those with low consumption are represented in the green bars. The green bars are the cities that spent less than 20 tons of SRT, and the blue bars are the cities that have the most.
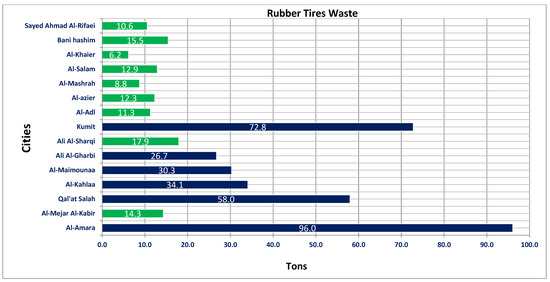
Figure 1.
Accumulations of spent rubber tires for each Iraqi city.
Recycling the spent rubber tires and the asphalt pavement recycling process helps conserve natural resources and be sustainable. The use of modified asphalt by polymers is increasing at the present time because this method very useful for the environment because it uses polymeric solid wastes, which are polluting the environment. The aim of this study is to change these harmful substances into useful ones. Therefore, asphalt without modification is not climate resistant and needs improvement. Accordingly, asphalt modified by such means has considerable resistance to the process of aging.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
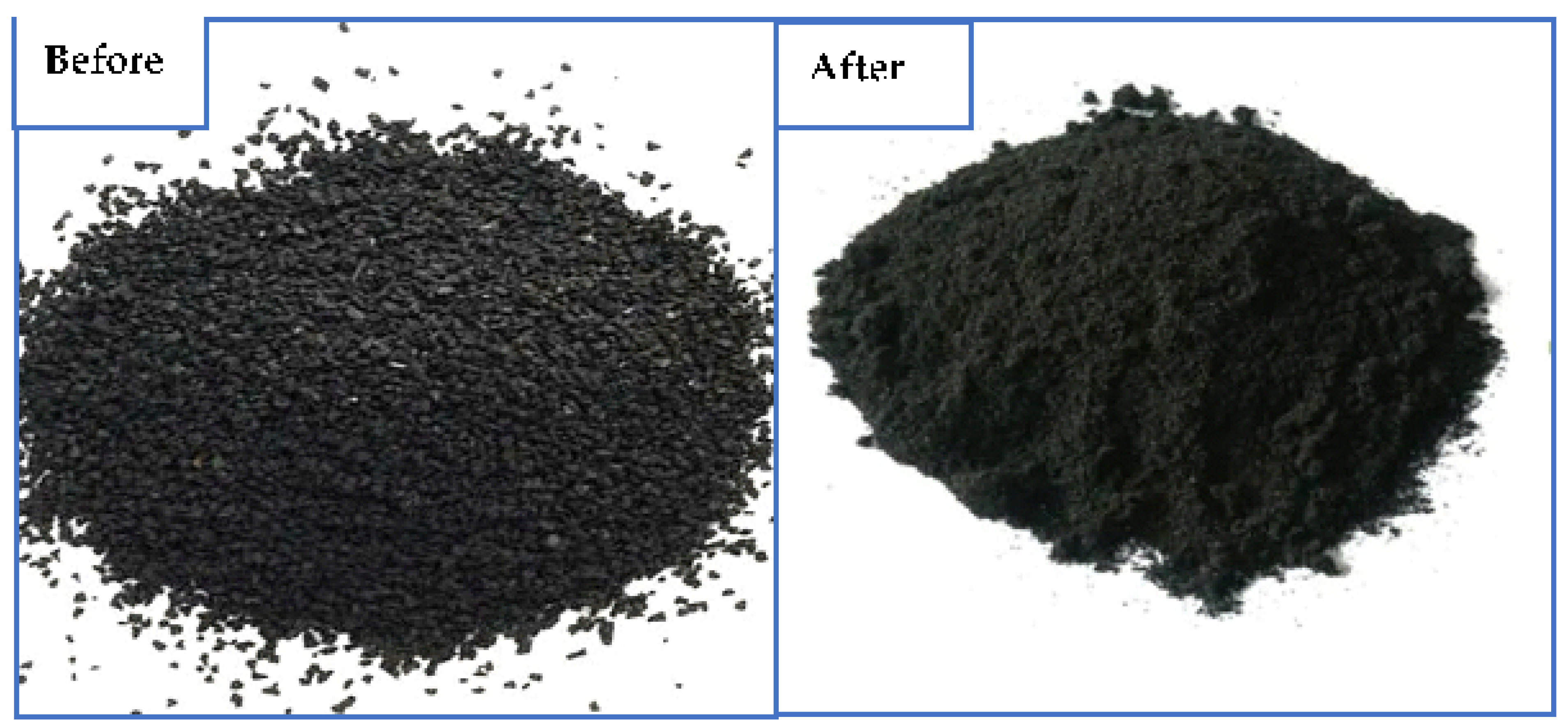
The main raw materials were provided from Qayara crude asphalt, with the specs tabulated in Table 1. Bitumen binder was produced in Al-Qayara refinery Co., about 50 km south of Mosul city (North Baghdad, Iraq). Figure 2 shows the visual inspection of milled rubber tires (before and after), which were ground up to 1.0 µm mesh size (the content of isoprene rubber is 40%). The reclaimed rubber tires were provided by the General Company of the Babylon tire industry (Babylon, Iraq) [32]. Anhydrous aluminum chloride was supplied by Fluka Company (Darmstadt, Germany) for chemicals. Table 2 reports the specifications for Anhyd-AlCl3. Twenty kilograms were collected from Qayara crude asphalt followed by homogeneity and dried at 105 °C for 24 h before practical work. Additionally, the Rheological properties of Qayara crude asphalt vs. the standard testing measurements (JTG E20, 2011) are detailed in Table 3 [33].

Table 1.
Rheological properties of bitumen binder (Qayara).

Figure 2.
Visual inspection of milled rubber tires (before and after milling).

Table 2.
Technical specification of anhydrous aluminium chloride (as received).

Table 3.
Rheological properties of Qayara crude asphalt vs. the standard testing measurements (JTG E20,2011).
2.2. Materials Preparation and Methods
We developed six suggested mixtures for the current laboratory work. A total of 250 gm asphalt was thermally treated at 100 °C. Crushed reclaimed rubber tires at 1.0% wt. and catalyst ratios of both 0.5% and 1.0% were totally mixed with bitumen binder; mix proportions are shown in Table 4. The prepared samples were placed in an oven at 360 °C for 5, 10, and 15 min, respectively, for thermal homogeneity.

Table 4.
Mix proportions of SRT incorporated with asphalt patches at different AlCl3 ratios.
In order to obtain a polymer with lower molecular weight, reclaimed rubber tires were exposed to mechanical and thermal crushing conditions before interaction with bitumen binder material. The process was conducted based on the thermo-gravimetric analysis of the rubber tires by placing rubber tires in an oven at 360 °C, followed by cooling at ambient temperature and crushing by manual mortar. The specimen’s rheological properties were measured, e.g., ductility test at 25 °C [34], penetration [35], softening point [36], and penetration index [37], as clearly identified elsewhere [38]. Two ratios were taken from reclaimed crushed rubber tires, with granules 1.0 mm mesh size, placed in a ceramic crucible, and covered with aluminum foil, then the crucible was thermally treated. As the temperature increased, the weight loss increased and vice versa; the weight loss increased from 39.03% (100 °C) to 99.07% (600 °C). The effect of aging under atmospheric conditions was carefully evaluated by measuring the penetration, ductility test at 25 °C, softening point, and penetration index; the cured specimen was kept for 365 days, and the measurement was repeated after a year. Figure 3 shows the specimen after curing for one year. In our study, a Marshal examination of the original model was conducted, in addition to one of the best samples before and after the aging procedure, which confirmed the specifications of the standard testing measurements (JTG E20, 2011) [33].

Figure 3.
The specimen after curing for one year.
2.3. Instrumentation
A microwave oven (900 Watt, 2500 MHz- German, Tokiwa) was used to conduct the rheological modification of bitumen binder with SRT. The Ductility measurement was conducted according to the US standards of ASTM (D5-83) [39]. The measurement of the asphalt penetration was performed according to the ASTM (D36-70), using a penetrometer to comply with the norm explained elsewhere [35]. A ring and ball apparatus was used to measure the softening point in accordance with the specifications of ASTM (D5-85) universally adopted [40]. The morphology, e.g., FSEM of the specimen, was conducted with (FEI Company, The Netherlands) integrated with EDXA, namely, “an energy dissipation X-ray analyzer”.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Use of 0.5% Catalyst as Rheological Modifier of Asphalt
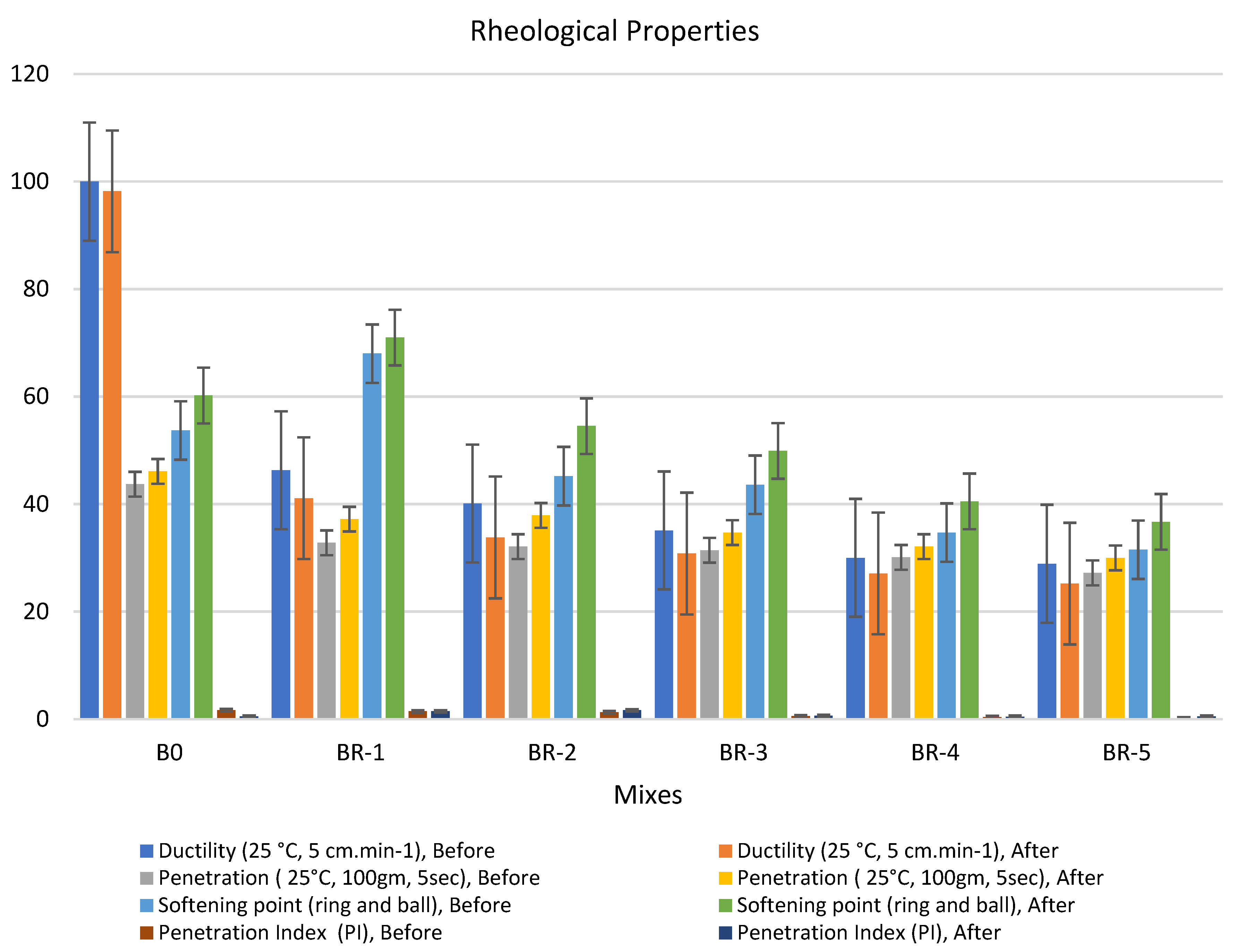
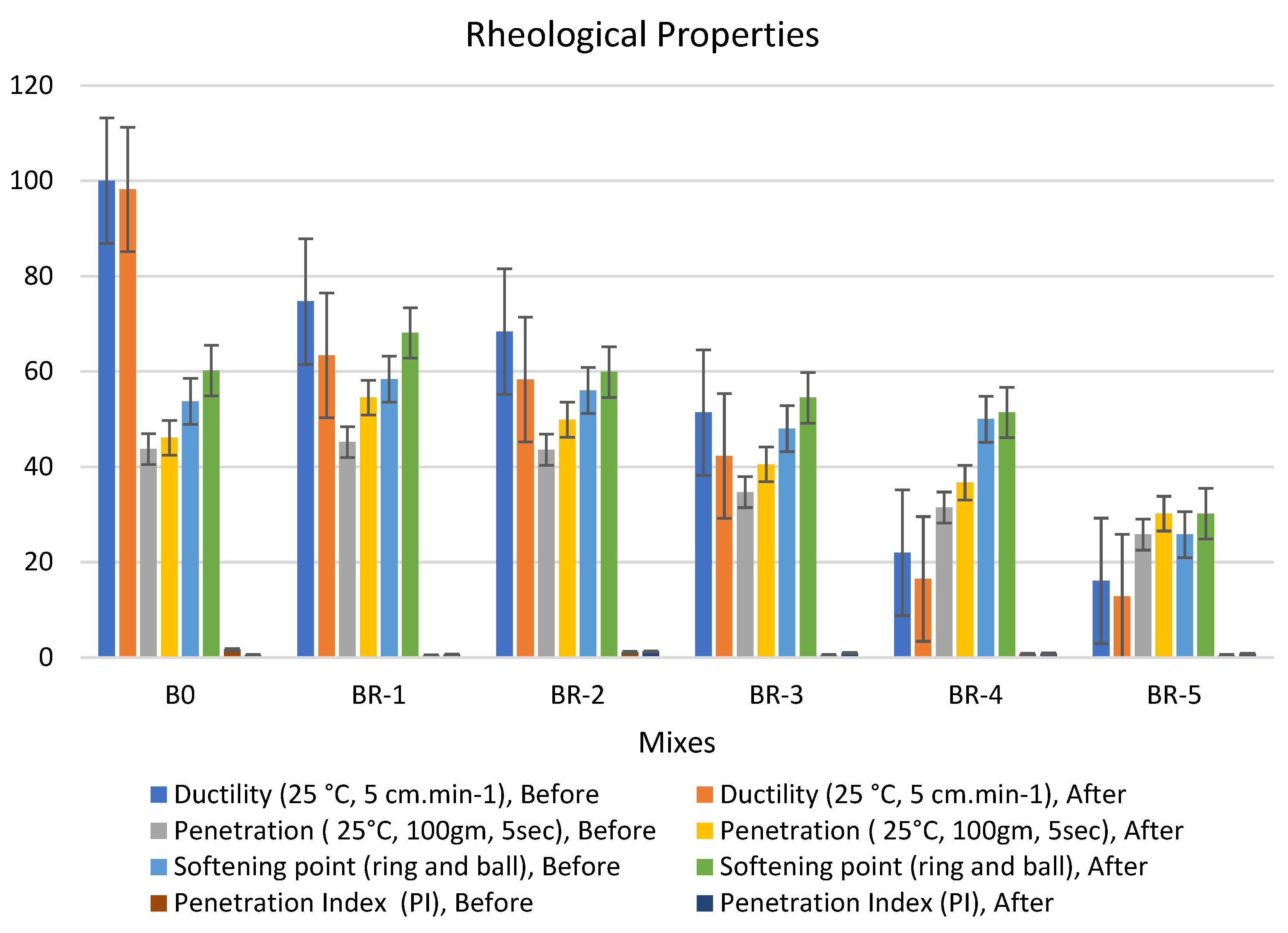
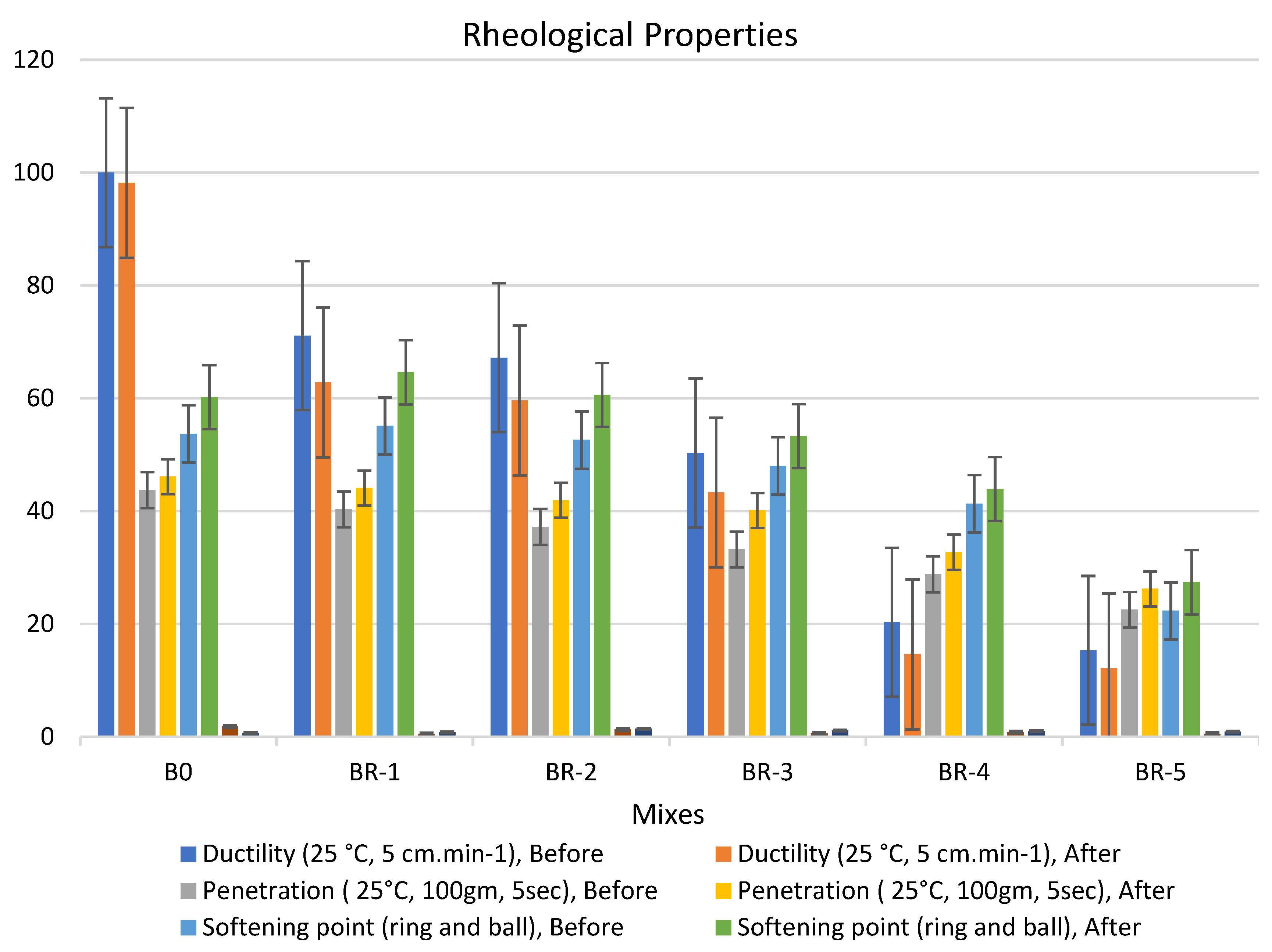
SRT incorporated with asphalt in the presence of a catalyzed amount of anhydrous aluminum chloride by 0.5% ratio is shown in Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6. Three patches were tested for each examined mix, and the mean value was recorded. The rheological properties of the modified bitumen pastes catalyzed by 0.5% from anhydrous aluminum chloride at different times (5, 10, 15 min), respectively; 0.5% by weight of catalyst made the asphalt system more homogenous. The anhydrous aluminum chloride (AlCl3) was selected as one of the Lewis acid catalysts for such interactions based on previous findings in the literature for the active role played by the catalyst in various industrial processes, such as the alkylation process and the stimulating effect in such operations [41].
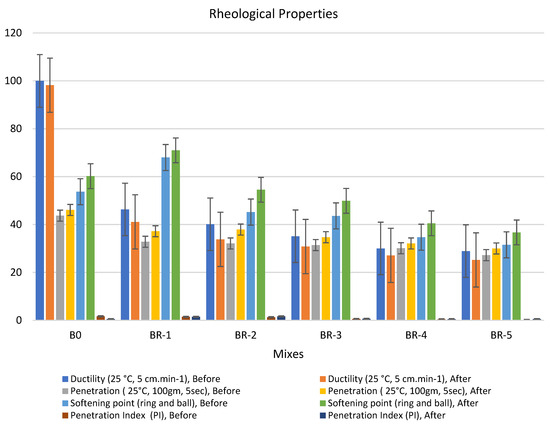
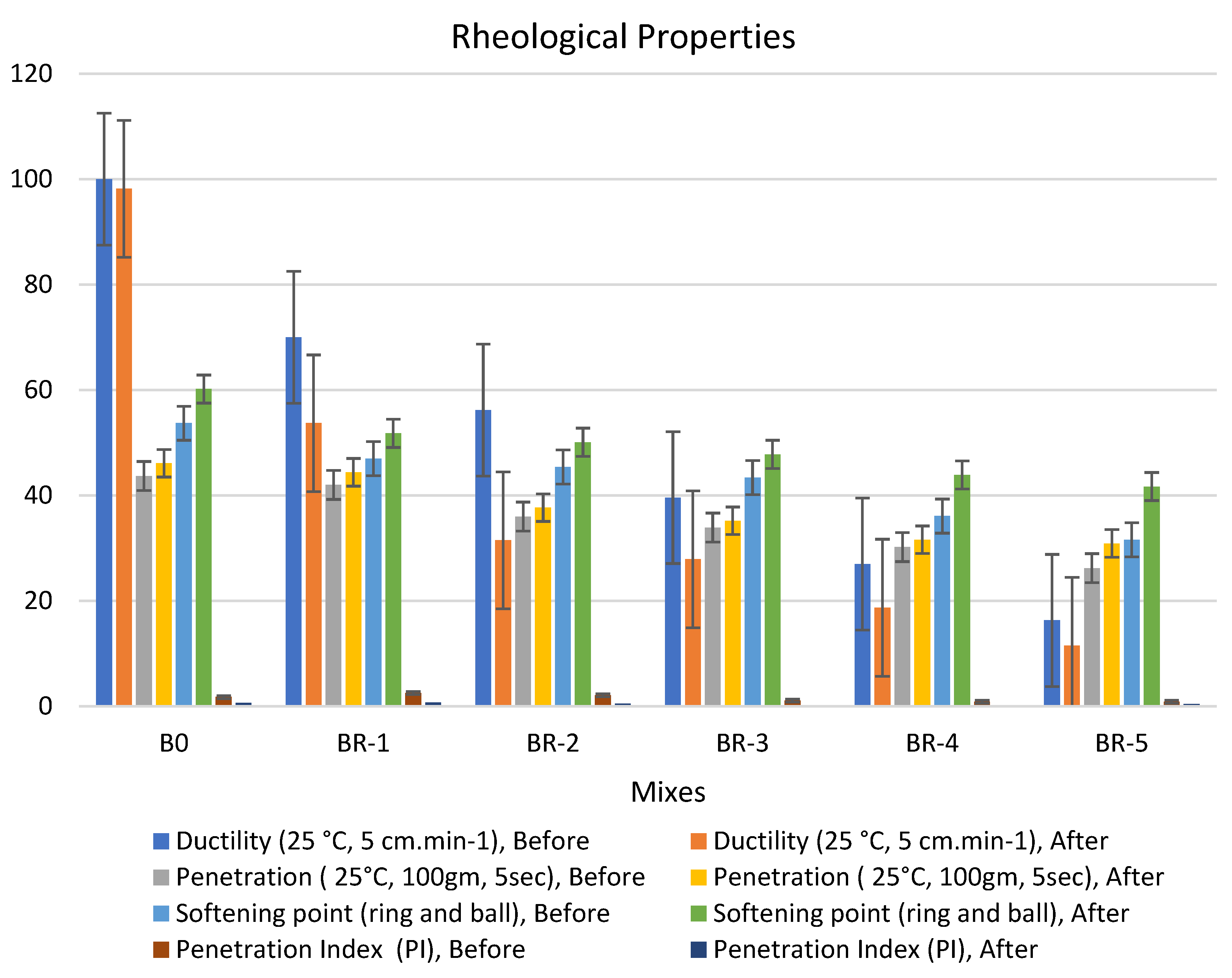
Figure 4.
Properties of asphalt modified by 0.5% by weight of AlCl3, using 1.0% of SRT before and after the aging procedure (at 5 min), treated at 360 °C.
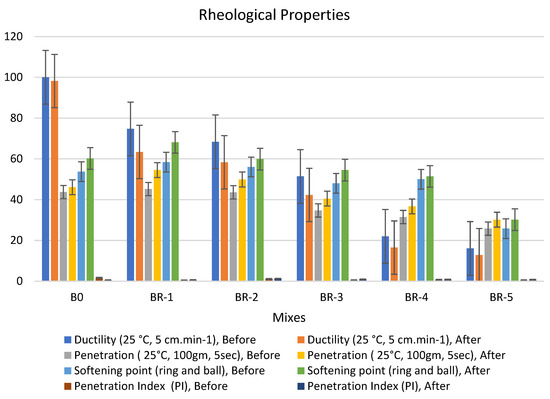
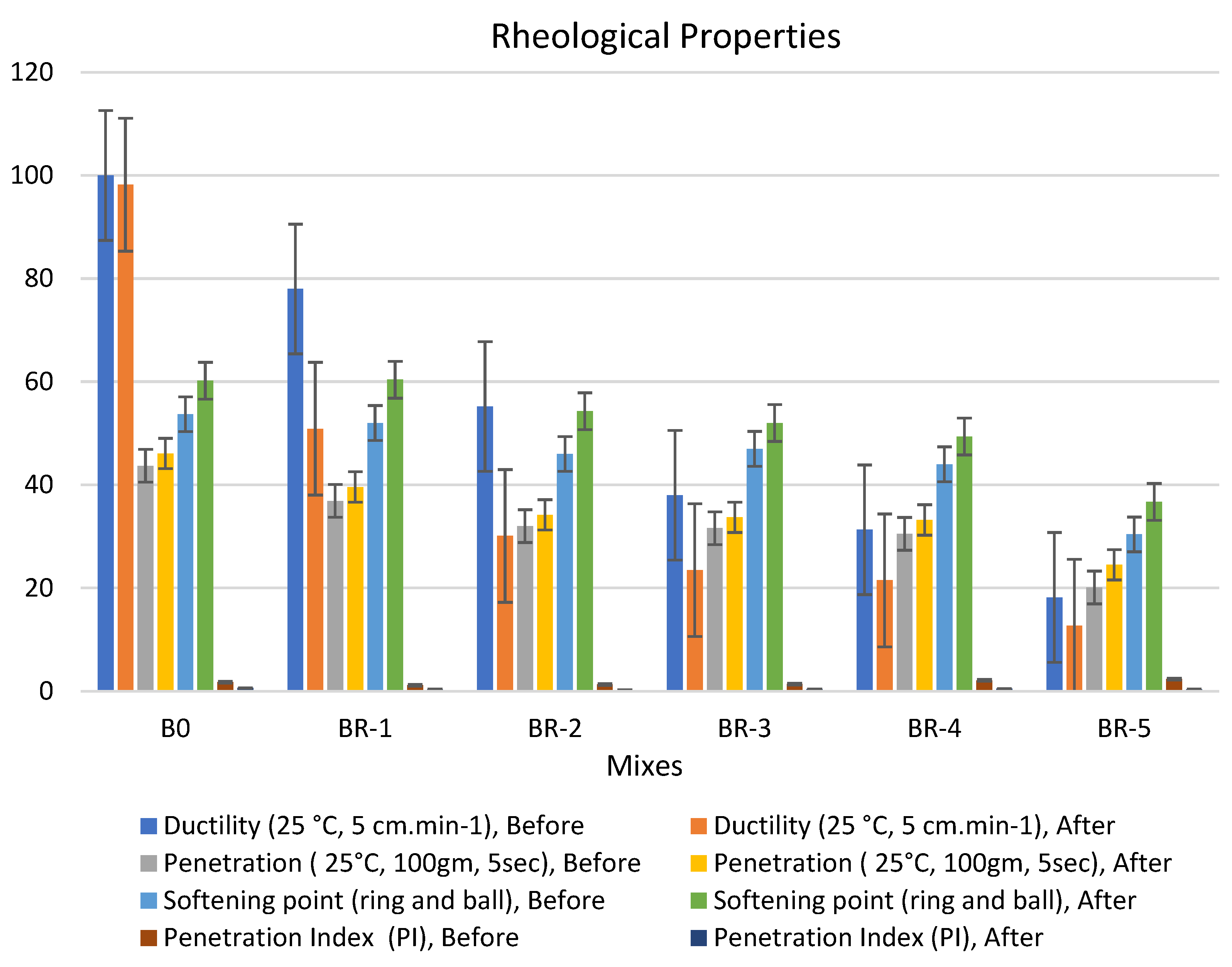
Figure 5.
Properties of asphalt modified by 0.5% by weight of AlCl3, using 1.0% of SRT before and after the aging procedure (at 10 min), treated at 360 °C.
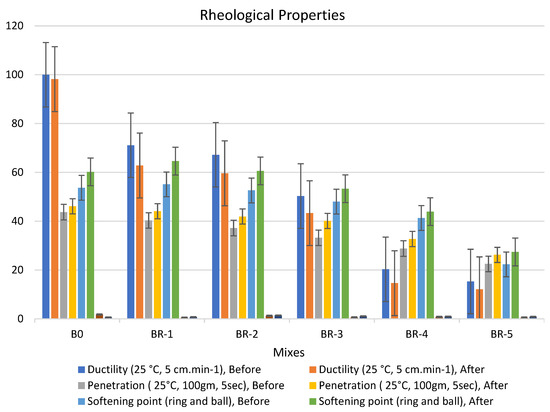
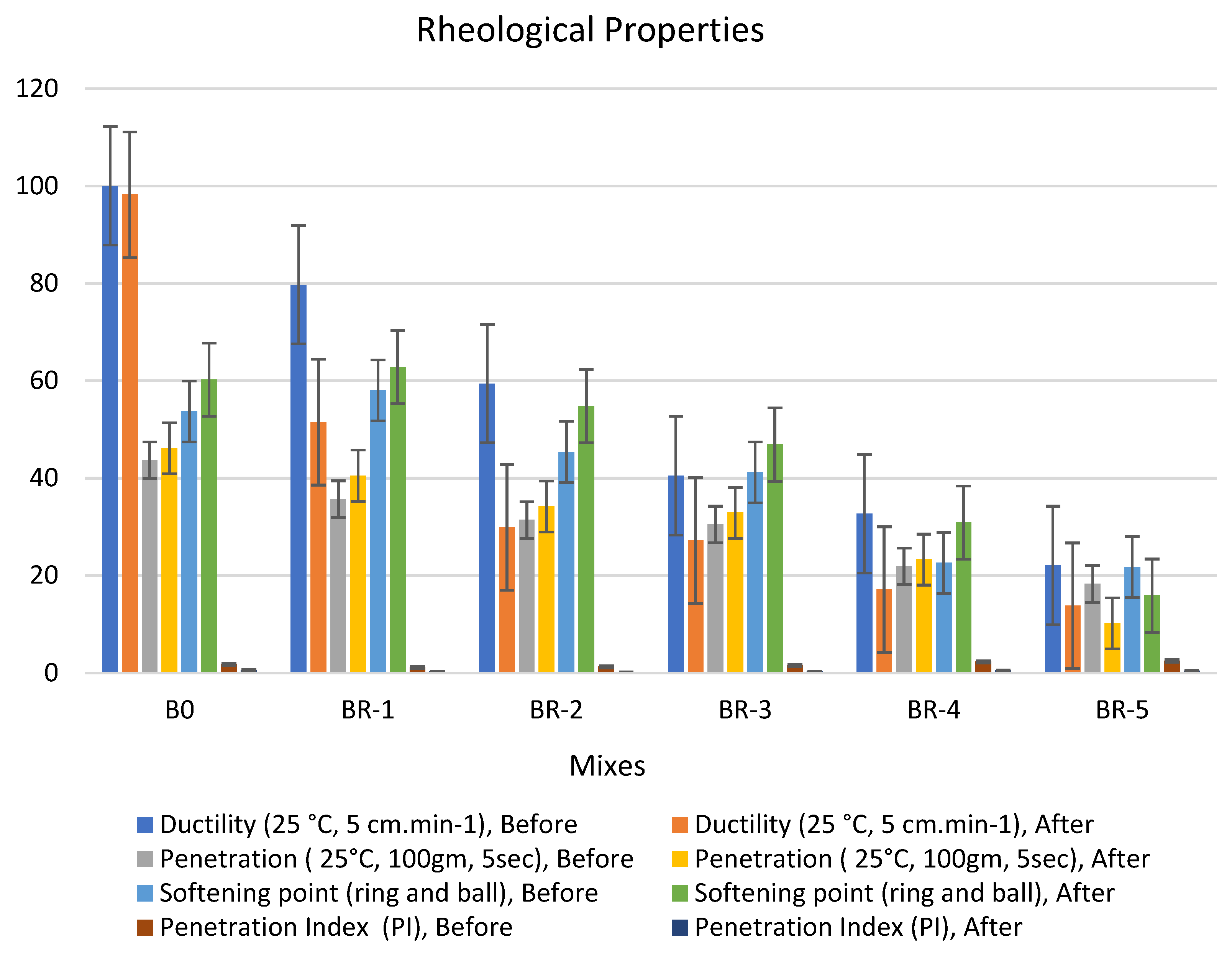
Figure 6.
Properties of asphalt modified by 0.5% by weight of AlCl3, using 1.0% of SRT before and after the aging procedure (at 15 min), treated at 360 °C.
Adding 0.5% of the AlCl3 catalyst to the bitumen binder modified its physical properties due to the filling effect of SRT fine powder and increased the viscosity of the samples. The rheological properties of the specimens had the following order: BR1 > B0 > BR2 > BR3 > BR4 > BR5. The modified samples showed an increase in softening point values after aging (10 min), e.g., BR1 (68.1) > B0 (60.8) > BR2 (59.9) > BR3 (54.5) > BR4 (51.4) > BR5 (30.2). In addition, low values of penetration were detected after aging (10 s), BR1 (54.5) > B0 (46.1) < BR2 (49.6) > BR3 (40.5) > BR4 (36.7) > BR5 (35.2). Ductility decreased due to the filling effect. The penetration index was reduced because of the low penetration of BR1 compared to B0 due to increased bulk density and decreasing total porosity. Ductility (25 °C, 5 cm·min−1) after aging (10 min) sharply decreased with an increase in SRT powder and decreasing the bitumen content, e.g., BR1 (63.4) < B0 (98.2) > BR2 (58.3) > BR3 (42.3) > BR4 (16.5) > BR5 (12.8). Rheological properties after aging at 5 min and 15 min reported low workability and operating performance because 5 min was not sufficient time to modify the properties, and at 15 min, most physical bonds of N-S-C were destroyed, weakening the specimen flexure pressure.
3.2. Use of 1.0% Catalyst as Rheological Modifier of Asphalt
SRT incorporated with asphalt in the presence of a catalyzed amount of anhydrous aluminum chloride in a 1.0% ratio is shown in Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9. The rheological properties of the modified bitumen catalyzed by 1.0% from anhydrous aluminum chloride at different times (5, 10, 15 min), respectively.
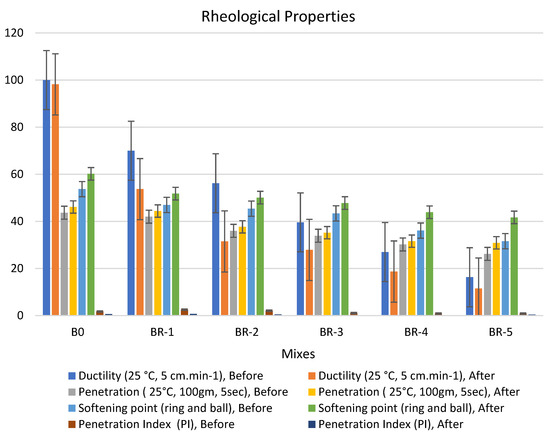
Figure 7.
Properties of asphalt modified by 1.0% by weight of AlCl3, using 1.0% of SRT before and after the aging procedure (at 5 min), treated at 360 °C.
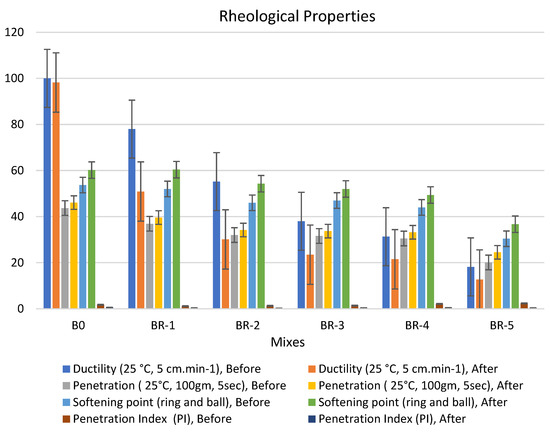
Figure 8.
Properties of asphalt modified by 1.0 by weight of AlCl3, using 1.0% of SRT before and after the aging procedure (at 10 min), treated at 360 °C.
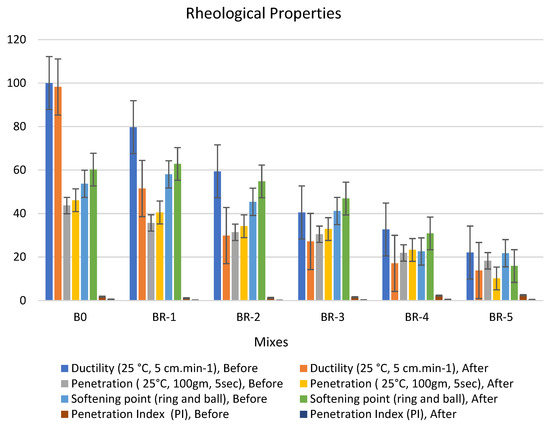
Figure 9.
Properties of asphalt modified by 1.0% by weight of AlCl3, using 1.0% of SRT before and after the aging procedure (at 15 min), treated at 360 °C.
Furthermore, the AlCl3 catalyst was increased to 1.0% of the bitumen binder to enhance the physical properties. The filling effect of SRT fine powder increased the viscosity of the proposed samples. The rheological properties of the specimens have the same following order: BR1 > B0 > BR2 > BR3 > BR4 > BR5. The modified samples show an increase in softening point values after aging (10 s), e.g., BR1 (60.4) > B0 (60.2) > BR2 (54.3) > BR3 (52.0) > BR4 (49.4) > BR5 (36.7). In addition, low values of penetration were detected after aging (10 min), BR1 (39.6) < B0 (46.1) < BR2 (34.2) > BR3 (33.7) > BR4 (33.2) > BR5 (24.5). Ductility decreased due to the filling effect. The penetration index was reduced because of the low penetration of BR1 compared to B0 due to increased paste bulk density and decreasing total porosity. Ductility (25 °C, 5 cm·min−1), after aging (10 s), sharply decreased with an increase in SRT powder and decreasing the bitumen content, e.g., BR1 (50.9) < B0 (98.2) > BR2 (30.1) > BR3 (23.5) > BR4 (21.5) > BR5 (12.7). Rheological properties after aging at 5 min and 15 min report low workability and operating performance because 5 min is not sufficient time to modify the properties, and at 15 min, most physical bonds of N-S-C are destroyed, leading to weak specimen flexure pressure.
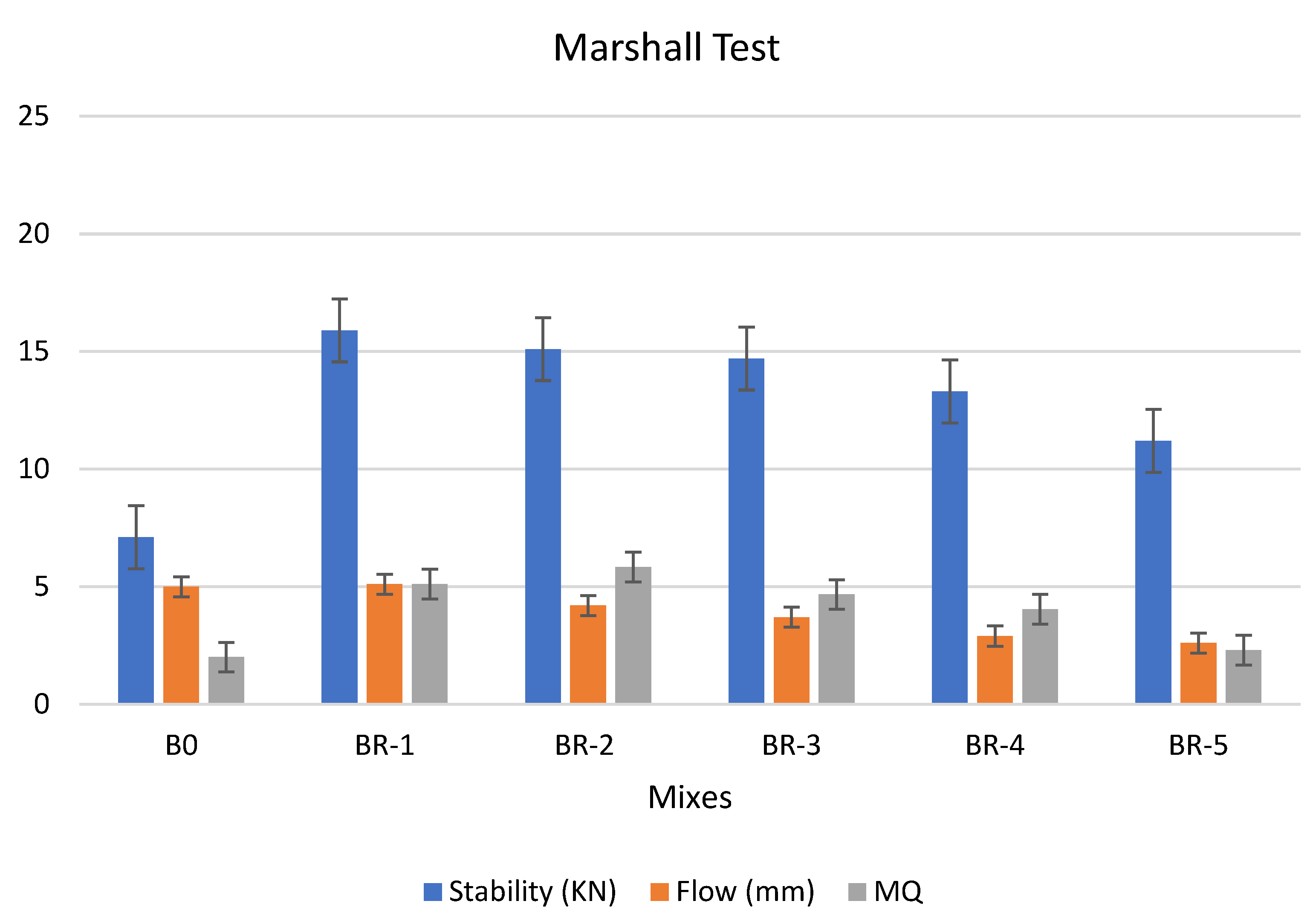
3.3. Marshall Test
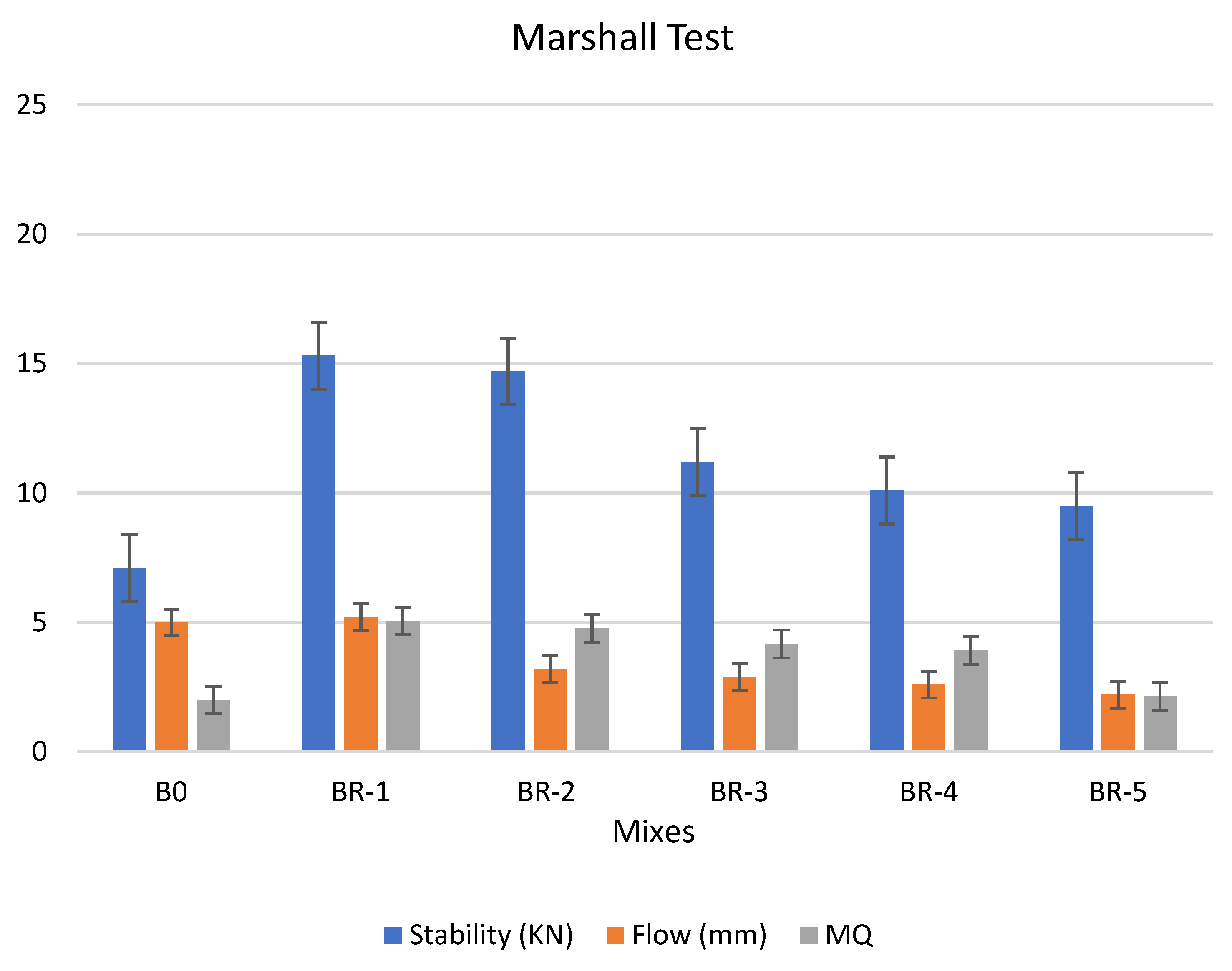
A group of three samples was tested for each composite. Figure 10 and Figure 11 report the Marshall test results for selected specimens show better rheological properties. Three patches were tested for each examined mix, and the mean values were recorded. The examination indicated the suitability of the bitumen binder for paving by applying pressure (mechanical stress) on the specimen to be tested, and when the specimen began to deform, the stability and flow measurements were taken through certain gradients present in the device [42,43,44,45]. We noted that mixtures of asphalt modified by 0.5% and 1.0% by weight of catalyst AlCl3, using 1.0% of SRT after the aging procedure (at 10 min), treated at 360 °C, reported good rheological properties.
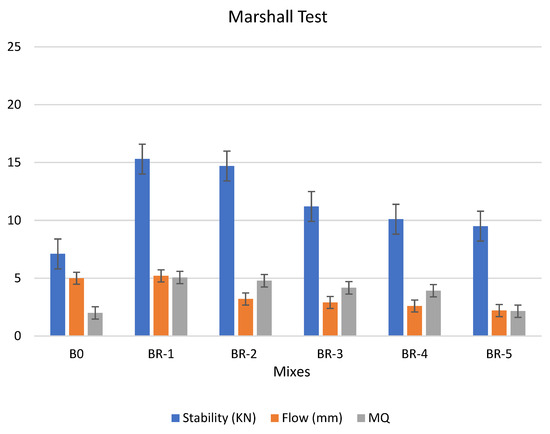
Figure 10.
Marshall test of asphalt modified by 0.5% by weight of AlCl3, using 1.0% of SRT after the aging procedure (at 10 min), treated at 360 °C.
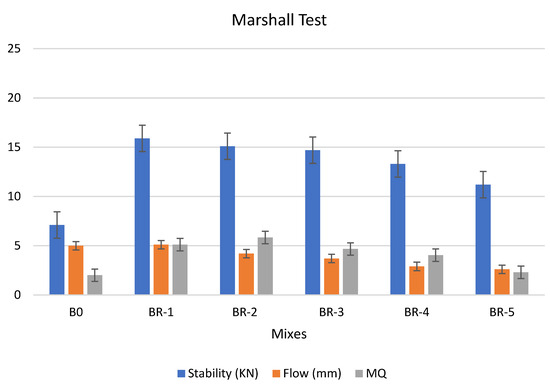
Figure 11.
Marshall test of asphalt modified by 1.0% by weight of AlCl3, using 1.0% of SRT after the aging procedure (at 10 min), treated at 360 °C.
It is clear from the above figure that the modified specimen is better than the original asphalt (#B0) in terms of stability and creep values if they could be used in asphalt paving. Additionally, we also noted that the specimen was more stable and unaffected by the aging conditions through the values of stability and creep, which were measured according to the Marshall test. This is a good indication of the pavement’s ability to resist deformation and distortion caused by climate change and repeated transportation loads on the roads.
We concluded that the modified specimen by 0.5% and 1.0% with weight of AlCl3, using 1.0% of SRT after the aging procedure (at 10 min), treated at 360 °C, are better than the original asphalt (#B0), in terms of stability and flow values if they could be used in asphalt paving. The Marshall test of the specimens had the same following order: BR1 > B0 > BR2 > BR3 > BR4 > BR5. 0.5% by weight of AlCl3-catalyst after the aging procedure (at 10 min) shows higher performance than 1.0% by weight of AlCl3 at the same aging conditions; this may be attributed to 1.0% catalyst is sufficient for enhancing the physical properties of the mixture after 365 days of curing [44]. The specimen was more stable and unaffected by the aging conditions at 0.5% catalyst, through the values of stability: BR1 (15.3) > B0 (7.1) > BR2 (14.7) > BR3 (11.2) > BR4 (10.1) > BR5 (9.5). Regarding the followability, which was measured according to the Marshall test, shows the following order BR1 (5.2) > B0 (5.0) > BR2 (3.2) > BR3 (2.9) > BR4 (2.6) > BR5 (2.2). This is a good indication of the pavement’s creep and ability to resist deformation and distortion caused by climate change and repeated transportation loads on the roads.
3.4. The Conventional Performance
Eventually, as tabulated in Table 5, the degree of ductility, penetration, softening point, and extension values for the asphalt modified by 0.5% and 1.0% by weight of AlCl3, respectively, using 1.0% of SRT after the aging procedure at different periods, treated at 360 °C. Composites recorded results within the limits of specification for bitumen shown in Section 2.1. The ductility values decrease at 0.5% and 1.0% by weight of AlCl3, respectively, by weight of the SRT additive. Nevertheless, it remained within acceptable limits [46,47]. As the replacement ratio of SRT increases, it reduces the conventional performance of asphalt with aging. Friction should be as little as possible with the asphalt to improve age ability. High bulk density and low porosity process increase the extension effect, but with the SRT addition effect, reduce the extension effect and penetration results. It is reported that the penetration results of the modified asphalt composites, in the order AS > BR-1 < BR-2, have better results because the extra addition of SRT from either source or bio-fuel shows a negative performance when added to modified asphalt.

Table 5.
Conventional properties of asphalt modified by 0.5% and 1.0% by weight of AlCl3, using 1.0% of SRT after the aging procedure (at 10 min), treated at 360 °C.
3.5. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy
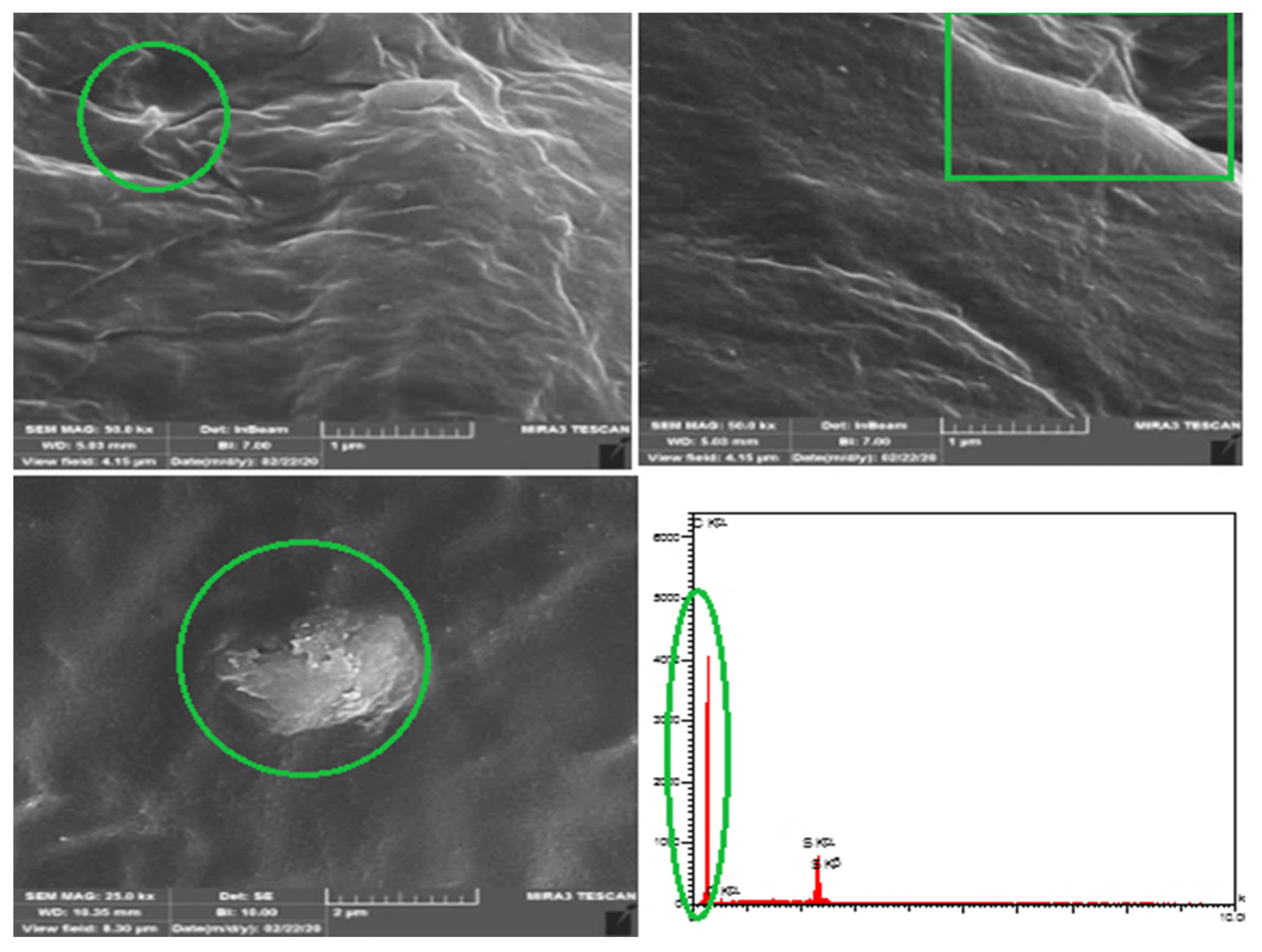
Figure 12 FE-SEM of the asphalt sample as received from Qayara Refinery Company. The grade of asphalt depends on the raw source and chemical compositions, especially the carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) content. The physical properties of the asphalt were determined by the chemical composition of green circle hydrocarbon, which was substantiated by EDX analysis [48,49,50]. The green circle shows the sulfur content, as proven by EDX analysis. The content of sulfur shows the high purity of crude used and less contaminant present in the delivered mixes.
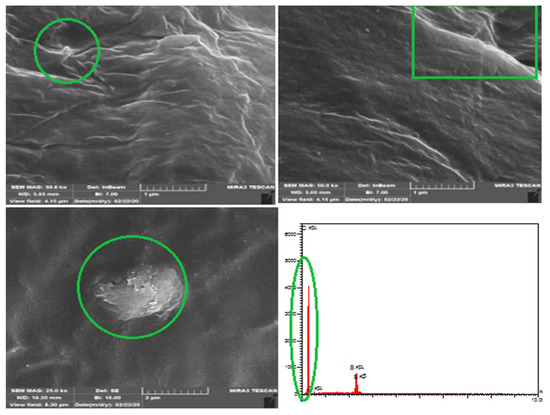
Figure 12.
FE-SEM and EDX for asphalt (as received).
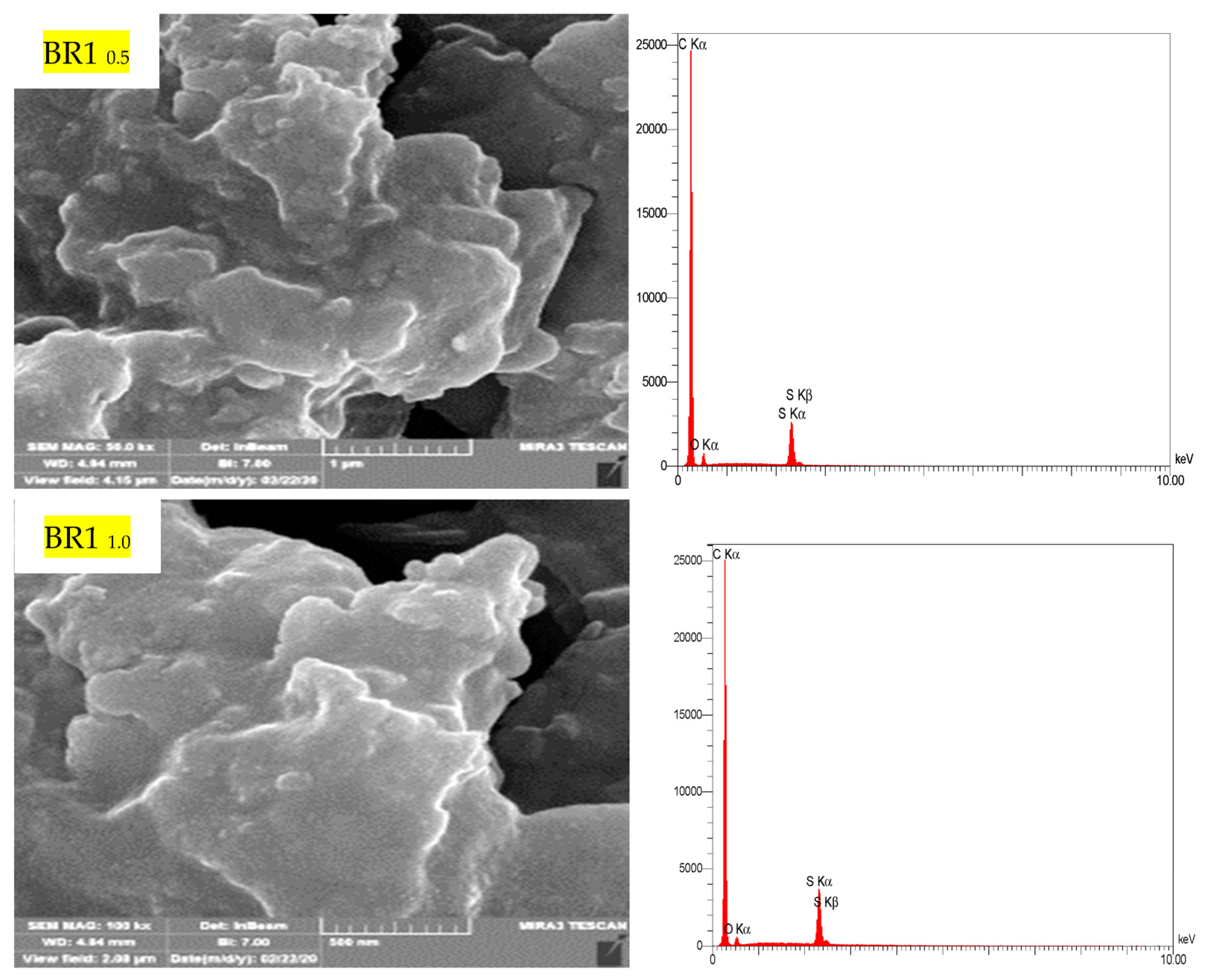
Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM) was additives. Figure 13 report the microstructure for BR1 samples modified by 0.5% and 1.0% conducted on some selected samples obtained from modulating asphalt with polymeric catalyst after aging (10 min). The incorporation of polymer into the microstructure of the asphalt system further complicates the study of the internal structure of the modified asphalt and its effect on the rheological and morphological properties of asphalt because the shape and rheological properties of asphalt result from the interactions of polymer and asphalt [51,52]. In BR10.5 morphology is a more compact surface and has less porosity; there is a difference in the structural form of the conventional asphalt through SEM and EDX examination. BRT1.0 morphologies have a distortion in the internal skeleton structure, which decreases the compression pressure and MQ results.
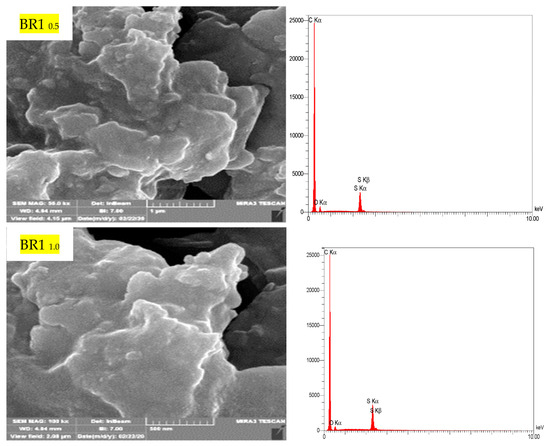
Figure 13.
FE-SEM and EDX for BR-1 sample modified by 0.5% and 1.0% by weight of AlCl3, using 1.0% of SRT before and after the aging procedure (at 10 min), treated at 360 °C.
4. Conclusions
The rheological properties of Qayara asphalt were improved by using spent rubber tires (SRT) with different percentages of anhydrous aluminum chloride. All required measurements were made on the modified asphalt one year after the modification process to understand the effect of aging conditions, which provided good rheological properties of the modified bitumen binder that is aging resistant. Eventually, the microwave energy was used to reduce the modification time from hours to minutes. Spent tire rubbers (STR) show a positive impact on the rheological properties of asphalt composites due to the filling effect and improve the microstructure of new proposed mixtures. In addition, microwave energy decreases the pollutant gas content that may evolve during the treatment and reduces environmental air pollution, leading to better life cycle assessment. It was clear that thermal sensitivity enhanced the penetration index (PI), which was a good value between −2.0 and +2.0. The increase in the thermal stability of output shows better workability during curing ages. The substation of a small amount of rubber 1.0% wt. percentage into asphalt composites with 0.5% catalyst (BR1) makes the system more homogenous and processing, fundamentally for asphalt resistance to weather condition improvement. More research is needed to reach sustainability in raw materials, as asphalt is a high-consumption material worldwide.
Author Contributions
Data curation, K.A.O. and R.Y.G.; Formal analysis, K.A.O.; Investigation, R.Y.G. and M.A.A.; Methodology, M.A.A.; Resources, K.A.O., R.Y.G. and M.A.A.; Writing—original draft, M.A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, Y.; Su, P.; Li, M.; You, Z.; Zhao, M. Review on evolution and evaluation of asphalt pavement structures and materials. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2020, 7, 573–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkash, S. Petroleum Fuels Manufacturing Handbook: Including Specialty Products and Sustainable Manufacturing Techniques; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Owaid, K.A.; Hamdoon, A.A.; Matti, R.R.; Saleh, M.Y.; Abdelzaher, M.A. Waste Polymer and Lubricating Oil Used as Asphalt Rheological Modifiers. Materials 2022, 15, 3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Chen, J.; Han, Z.; Liu, W. A review on solutions for improving rutting resistance of asphalt pavement and test methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 168, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Dong, Z.J.; Tan, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.Y. Investigating the interactions of the saturate, aromatic, resin, and as-phaltene four fractions in asphalt binders by molecular simulations. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 112–121. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelzaher, M.A. Performance and hydration characteristic of dark white evolution (DWE) cement composites blended with clay brick powder. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Leng, Z.; Jiang, J.; Ni, F.; Zhao, Z. Nondestructive prediction of rutting resistance of in-service middle asphalt layer based on gene expression programing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 293, 123481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z. Interlaminar shear fatigue and damage characteristics of asphalt layer for asphalt overlay on rigid pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 68, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z. Effects of interlayer bonding conditions between semi-rigid base layer and asphalt layer on mechanical responses of asphalt pavement structure. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2017, 10, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Cerdas, S.F.; Qiu, Y. Numerical determination for optimal location of sub-track asphalt layer in high-speed rails. J. Mod. Transp. 2013, 21, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Park, H.M. Performance evaluation of high modulus asphalt mixtures for long life asphalt pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaan, N.S.; Chegenizadeh, A.; Nikraz, H.; Rezagholilou, A. Investigating the engineering properties of asphalt binder modified with waste plastic polymer. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaan, N.; Chegenizadeh, A.; Nikraz, H. Laboratory Properties of Waste PET Plastic-Modified Asphalt Mixes. Recycling 2021, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.M.; Kabir, S.; Alhussain, M.A.; Almansoor, F.F. Asphalt Design Using Recycled Plastic and Crumb-rubber Waste for Sustainable Pavement Construction. Procedia Eng. 2016, 145, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantawy, M.A.; El-Roudi, A.M.; Abdalla, E.M.; Abdelzaher, M.A. Fire Resistance of Sewage Sludge Ash Blended Cement Pastes. J. Eng. 2013, 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Huang, W.; Lin, P.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Q. Chemical and rheological evaluation of aging properties of high content SBS polymer modified asphalt. Fuel 2019, 252, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, W.M.; Hamdoon, A.A.; Abeed, F.; Saleh, M.Y.; Abdelzaher, M.A. Polymer Wastes Reinforced the Rheological Properties of Bitumen Composites Pastes. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Z.; Padhan, R.K.; Sreeram, A. Production of a sustainable paving material through chemical recycling of waste PET into crumb rubber modified asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, A.; Enieb, M.; Singh, D. Influence of aging on properties of polymer-modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 196, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.A.; Veeraragavan, A. Performance based binder type selection using mixed integer programming technique. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2091–2100. [Google Scholar]
- Veeraragavan, A. Rheological and Rutting Characterization of Asphalt Mixes with Modified Binders. J. Test. Eval. 2012, 40, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, G.H.; Sahraei, A.; Esmaeeli, M.R. Investigate the effect of using polymeric anti-stripping additives on moisture damage of hot mix asphalt. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2021, 25, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, G.H.; Pirbasti, Z.R.; Esmaeili, N. Laboratory investigation of the effect of ABS polymer on moisture susceptibility of asphalt mixtures. Aust. J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 17, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abandansari, H.F.; Modarres, A. Investigating effects of using nanomaterial on moisture susceptibility of hot-mix asphalt using mechanical and thermodynamic methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 131, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakenari, M.M.; Hamedi, G.H. Investigating the Effective Laboratory Parameters on the Stiffness Modulus and Fatigue Cracking of Warm Mix Asphalt. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 19, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavussi, A.; Qorbani, M.; Khodaii, A.; Haghshenas, H. Moisture susceptibility of warm mix asphalt: A statistical analysis of the laboratory testing results. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 52, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelzaher, M.A.; Farahat, E.M.; Abdel-Ghafar, H.M.; Balboul, B.A.; Awad, M.M. Environmental Policy to De-velop a Conceptual Design for the Water–Energy–Food Nexus: A Case Study in Wadi-Dara on the Red Sea Coast. Egypt. Water 2023, 15, 780. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y. Fatigue behaviours of asphalt mixture at different temperatures in four-point bending and indirect tensile fatigue tests. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 273, 121675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, M.; Ghanizadeh, A.R.; Omrani, H. Comparison of Fatigue Resistance of HMA and WMA Mixtures Modified by SBS. In Proceedings of the 2nd Conference of Transportation Research Group of India (2nd CTRG), Utter Pradesh, India, 12–15 December 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, K. The deterioration and performance improvement of long-term mechanical properties of warmmix asphalt mixtures under special environmental conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 135, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, H.A.; Mohammed, L.H.A.; Masood, L.G.G. Effect of rubber tire on behaviour of subgrade expansive Iraqi soils. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 870, 012066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hdabi, A.; Al Nageim, H. Performance of Half Warm Rolled Asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 162, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG E20-2011; Standard Test Methods of Asphalt and Asphalt Mixtures for Highway Engineering. China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Ma, X.; Li, Q.; Cui, Y.-C.; Ni, A.-Q. Performance of porous asphalt mixture with various additives. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2018, 19, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM, A. Standard Test Methods for Time of Setting of Hydraulic Cement by Vicat Needle; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Issa, I.S. Modification of Asphalt by Diols. J. Educ. Sci. 2008, 21, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society for Testing and Materials; Committee C-1 on Cement. Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50-mm] Cube Specimens); ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Fu, L.; Jiao, Y.; Tao, J.; Wang, X. Short-Term Aging Effect on Properties of Sustainable Pavement Asphalts Modified by Waste Rubber and Diatomite. Sustainability 2017, 9, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speight, J.G. Asphalt Materials Science and Technology; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 437–474. [Google Scholar]
- Mazumder, M.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.J. Performance properties of polymer modified asphalt binders containing wax additives. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2016, 9, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Chandra, S.; Bose, S. Strength characteristics of polymer modified mixes. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2006, 7, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, S.; Hajimohammadi, A.; Javadi, N.H.S.; Khalili, N. The use of plastic waste in asphalt: A critical review on asphalt mix design and Marshall properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 125185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelzaher, A.M. Experiential investigation on the effect of heavy fuel oil substitution by high sulfur petcoke on the physico-mechanical features and microstructure of white cement composites. Eng. Res. Express 2021, 3, 015028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, H.; Al-Kahlidi, M.M.A.; Abulridha, H.A.; Banoon, S.R.; Abdelzaher, M.A. Current Situation and Future Prospects for Plastic Waste in Maysan Governorate: Effects and Treatment During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Egypt. J. Chem. 2021, 64, 4449–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelzaher, M.A.; Shehata, N. Hydration and synergistic features of nanosilica-blended high alkaline white cement pastes composites. Appl. Nanosci. 2022, 12, 1731–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goli, A.; Rout, B.; Cyril, T.; Govindaraj, V. Evaluation of Mechanical Characteristics and Plastic Coating Efficiency in Plastic-Modified Asphalt Mixes. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2022, 16, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogundipe, O.M. The Use of Polyethylene Terephthalate Waste for Modifying Asphalt Concrete Using the Marshall Test. Slovak J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 27, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunanusont, N.; Sangpetngam, B.; Somwangthanaroj, A. Asphalt Incorporation with Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Copolymer and Natural Rubber (NR) Thermoplastic Vulcanizates (TPVs): Effects of TPV Gel Content on Physical and Rheo-logical Properties. Polymers 2021, 13, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelzaher, M.A.; Hamouda, A.S.; Ismail, I.M.; El-Sheikh, M.A. Nano titania reinforced limestone cement: Phys-ico-mechanical investgation. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Bach, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 786, pp. 248–257. [Google Scholar]
- Balboul, B.A.; Abdelzaher, M.; Hamouda, A.S.; Zaki, A.H. Nano titania combined with micro silica reinforced limestone cement: Physico-mechanical investigation. Egypt. J. Chem. 2019, 62, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelzaher, M.A. Sustainable development goals for industry, innovation, and infrastructure: Demolition waste incorporated with nanoplastic waste enhanced the physicomechanical properties of white cement paste composites. Appl. Nanosci. 2023, 13, 5521–5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkhouly, H.I.; Abdelzaher, M.A.; El-Kattan, I.M. Experimental and Modeling Investigation of Physicomechanical Properties and Firing Resistivity of Cement Pastes Incorporation of Micro-Date Seed Waste. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2022, 46, 2809–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).