Highlights
What are the main findings?
- A minimum population of 165,200 inhabitants is needed to enable a co-digestion.
- Energy rate of USD 0.139 with a 10-year payback can supply energy to 185,500 inhabitants.
- NPV of USD 23,336.94 with an IRR of 14.71% and LCOE of 0.103 USD/kWh.
What is the implication of the main finding?
- It is necessary to obtain technical data for the Brazilian reality.
- There is a need to encourage the creation of consortia for the wide use of biogas in Brazilian municipalities.
- Economy of financial resources for industries and public institutions, as well as the reduction of environmental impacts.
Abstract
The elevated presence of organic material in Brazilian urban solid waste, along with mismanagement of its disposal, can aggravate environmental problems from greenhouse gas emissions to water and soil pollution. In parallel, the paper and cellulose industries consume considerable resources and produce important solid wastes, including lime mud. These urban and industrial realities present common ground, from which a little-studied alternative arises in using biogas electrical energy from the co-digestion of the organic portion of urban solid waste using lime mud. This intersection can reduce the environmental impacts associated with inadequate management and disposal of solid waste, providing industry financial economy resources and contributing to Brazilian energy grid diversification. The current study used economic–financial indicators to evaluate the proposal’s economic feasibility. The obtained results presented a minimum population of 165,200 inhabitants, generating 39,295.77 m3/year of methane, in order to enable a co-digestion proposal. The sensitivity analysis indicated that a population of 185,500 inhabitants would provide a 10-year payback, an energy rate of USD 0.139, and 44,124.49 m3/year of methane to supply the population with power. The net present value was USD 23,336.94, with an internal return rate of 14.71% and a levelized energy cost of 0.103 USD/kWh.
Keywords:
urban solid waste; organic fraction; lime mud; co-digestion; biogas; energy; economic feasibility 1. Introduction
Solid waste (SW) is inherent to life and human activity. Its generation accompanies urbanization processes, population growth, and quality of life improvement, among other factors. Estimates place the global generation of SW at 2.01 billion tons per year, and the the sector is responsible for approximately 5% of all Greenhouse Gas Emissions (GGE), causing atmospheric pollution and contributing to global warming.
With the perspective of continued population growth, urbanization, quality of life changes, and consumption standards, it is estimated that waste generation will grow by 69.15% by 2050, including increases in Urban Solid Waste (USW) [1]. Brazil follows this growth trend for SW. In total, more than 79 million tons of USW are generated per year, which can lead to more complex and costly management, in addition to presenting risks to the environment and public health [2].
The National Policy on Solid Waste (PNRS—Política Nacional de Resíduos Sólidos in Portuguese), Federal Law n. 12.305/2010, which deals with solid waste management, establishes norms and objectives that aim to minimize the impacts of inadequate waste disposal. Thus, the objectives of this law include zero generation, reduction, reutilization, recycling, and treatment of SW, as well as final disposal in an environmentally suitable manner [3]. Additionally, according to Law no. 14.026 from 2020, which updated the Legal Framework for Basic Sanitation, all municipalities throughout the country must have environmentally adequate final disposal defined by 2024 [4].
Another environmentally sustainable practice is the recycling of solid waste, which is one of the most efficient ways of using energy, as it recovers raw materials used in the production processes, where energy consumption is usually high. According to [5], one of the most commonly used MSW treatment technologies in several parts of the world is incineration, which, in addition to reducing the volume of MSW by up to 90%, destroys organic contaminants. This allows for the recovery of metals, in addition to requiring small areas for implantation. Anaerobic Digestion (AD) is another option for generating energy from the biogases produced by the methanization of MSW. The combined use of anaerobic digestion and incineration was used by [6]. Ashes resulting from incineration can be used to manufacture cementitious materials, as described in [7]. Currently, the primary form of solid waste disposal in Brazil is through Sanitary Landfills (SL). Under these circumstances, 59.9% of USW is disposed in SL, while 23.0% is disposed in controlled landfills, and 17.5% is disposed in irregular trash dumping sites. These latter two options are not considered environmentally friendly, as they may generate impacts that affect environmental, social, and economic facets of society [8].
These impacts arise from the uncontrolled USW degradation processes, especially considering the organic fraction of urban solid waste (OFUSW), which accounts for 45.3% of all generated waste [9]. This waste derives from residential domiciles, domestic activities, and urban cleaning, including street sweeping and cleaning of public thoroughfares [10]. When improperly managed, this waste material can have diverse impacts during its degradation, especially with regard to atmospheric pollutants, given that methanogenic bacteria release biogases during decomposition of organic material (OM).
Ref. [11] stated that Brazil has great potential for biogas production due to its extensive agro-industrial production and the country’s population of more than 210 million inhabitants. Even so, less than 2% of this potential is used, e.g., biogas is still largely underexplored from chemical, economical, and political perspectives.
Biogas is typically composed of 50% to 70% methane (CH4), 30% to 45% carbon gas (CO2), 80 to 100 ppmV of ammonia (NH3), and 1000 to 3000 ppmV of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and hydrocarbons (<100 ppmV) [12]. Among these gases, CH4 and CO2 present the greatest risks as potential pollutants; when released into the atmosphere without proper treatment, they are directly responsible for exacerbating the greenhouse effect. The environmental impact of CH4 is 21 times greater than CO2 [13].
However, when correctly managed, biogas can be transformed from a pollutant into a renewable energy source due to its relatively elevated lower calorific value (LCV) of up to 35 MJ/Nm3 [14]. Thus, the incentives associated with leveraging biogas have become increasingly studied since they can lead to reductions in GGE [15], aiding in Brazil’s compliance with commitments with various international agreements including the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (1998), The Paris Accord (2015), Glasgow Climate Pact (2021), and the Global Methane Pledge (2021). To meet these objectives, Brazil instituted Decree 11.303 in 2022 [16], which incentivizes sustainable biogas and biomethane use.
Another incentive surrounding this energy usage is the need for diversification of the Brazilian energy grid due to environmental trends and water crises [17], which have resulted in reductions in electrical energy supply despite facing ever-increasing demand projected at 3.8% per year [18].
Currently, industry (32.1%) and transport (31.2%) consume almost two-thirds of the country’s power supply [19], which is due to Brazil’s significant industrial footprint, which is also a source of SW. Many of these industries, in turn, do not take advantage of the energy available in their waste materials and thus do not generate clean or renewable energy. Although industries such as paper or cellulose utilize a high percentage of byproducts as energy sources, anywhere from 60% to 70% of consumption comes from self-production [20], indicating that there is still room for improvement.
The Brazilian paper and cellulose industry stands out as the second largest global exporter, producing approximately 21.1 million tons of cellulose annually [21]. This significant generation also requires proper management of waste and rational use of resources and raw materials. Among the byproducts generated by this industry is lime mud (LM), an alkaline byproduct with diverse applications outside the industry. Its application as a covering medium in sanitary landfills has already been attested to [22], and it is able to provide economic resources of up to BRL 30 million per year [23] for the cellulose industry while reducing environmental impacts in surrounding neighborhoods [23,24,25].
In addition to these applications, another use of LM was studied by [26,27]. In these cases, the authors evaluated the use of the industrial byproduct as a co-substrate in anaerobic digestion processes (AD) of leftover food (present in OFUSW), which occurs in both biodigesters and SL. The results demonstrated an improvement in AD and an increase in the generation of CH4. In the first study, the authors obtained a concentration of 272.8 mL/gVS, while in the second study, the authors reached a concentration of CH4 between 120.2 and 251.0 mL/gVS.
Anaerobic co-digestion (ANCO) has produced consistent results when applied to different SW and OFUSW, as shown in [28]. When dealing with the waste generated by the pork industry, the authors analyzed the influence of the addition of iron flakes to aid in ANCO, which improved the removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD). This happens because the OFUSW contains low Nitrogen (N) levels, maintaining an ideal relation between Carbon (C) and N (C/N-30/1). Furthermore, the organic material contains a relatively high fraction of heavy metals; when there are high organic quantities, swift acidification may take place, as well as the reduction in pH and production of volatile fatty acids in long sequences, which can stress and inhibit the methanological activities performed by the group of microorganisms during the AD process [29].
Ref. [30] carried out a review study on co-digestion using sewage sludge as a substrate. The study generally showed an increase in energy generation and a decrease in GHG emissions, in addition to being an economically viable option.
According to [29], the main co-substrates employed in ANCO research with USW found in the literature are related to: sewer sludge (48%); food residuals (33%); animal waste (9%); agro-industrial (5%); and algae (5%). Furthermore, the authors concluded that the biogas generated from ANCO from OFUSW with other residuals with complementary characteristics is a feasible and viable option to improve methane production.
Ref. [6] carried out a study on the economic viability and energy generation of MSW, comparing landfill disposal, anaerobic digestion, incineration, and a combination of AD and incineration. Incineration proved to be the most effective in terms of energy generation. As for economic viability, the sanitary landfill expressed more positive values, although it was the least environmentally viable technique.
Ref. [31] evaluated ANCO from sewer sludge, USW, and plant pruning clippings to improve the synergy, stability, and optimization of the biogas production process. Their results increased CH4 production from 3.4% to 19.1%. Ref. [32] analyzed the potential for biomethane and hydrogen generated from the co-digestion of USW and winery byproducts and achieved an increased ANCO production rate compared to DA, resulting in 37.9 GgCH4 in 2018, This is significant considering that the potential for CH4 in 2018 from DA of OFUSW was 2.8 GgCH4 per year−1.
Ref. [33] investigated the co-fermentation activity between residual activated sludge and food waste for the production of carboxylic acids. The authors concluded that the co-fermentation yield was higher (96 mgCOD/gVS) than the mono fermentation yield (72 mgCOD/Gvs).
Ref. [34] studied the optimization of methane fermentation to utilize food waste products. The authors observed a significant relationship between substrate composition and biogas productivity.
The performance of methane production and the metabolic process of combined fermentation of coal and corn stover was investigated by [35]. The authors concluded that methane production from the combined fermentation of coal with higher coal content and corn straw showed a better synergistic effect due to the degradation products of cellulose and hemicellulose in corn straw and the dissolved organic matter in the liquid phase.
Several studies have investigated the economic viability of biogas usage using Net Present Value (NPV) and Levelized Cost of Electricity, demonstrating the potential involvement of monodigestion with OFUSW (MOCO) and/or ANCO with other residuals. Refs. [6,36,37] evaluated the economic viability of generating electricity from sanitary landfills and anaerobic reactors in the state of Minas Gerais. This study demonstrated that the state would benefit from the electrical energy generated: 15,400 MWh/year with an installed power capacity of 3200 kW generated by the OFUSW. The authors concluded that it is possible to produce electric energy using biogas derived from the decomposition of OFUSW in sanitary landfills or through anaerobic digestion, and that the economic feasibility of this process depends on the electrical energy rates.
Considering that most SW is destined for sanitary landfills and that there is potential energy to be captured, a study from [38] contributed to evaluating the feasibility of energy derived from OFUSW. Ref. [38] estimated the potential electrical energy that could be supplied by SL biogas in Brazil and concluded that the available energy can vary from 337 MW to 601 MW until 2030. Furthermore, the authors estimated that the minimum population required to enable this type of undertaking is 200,000 inhabitants; 221 of the 5570 municipalities in Brazil fit this characteristic [39]. The power increases even more when considering anaerobic biodigesters, as demonstrated by a study from the Energy Research Enterprise (EPE—Empresa de Pesquisa Energética in Portuguese), which reached the value of 868 MW, compared to a total of 134 GW available throughout the country.
In another study, Ref. [37] evaluated the energy potential and economic viability of generating electricity from USW in SL for two important Brazilian states. The energy results demonstrated a power availability of 139.5 MW for the state of São Paulo and 14 MW for Minas Gerais. The economic feasibility was confirmed, and the scenario for energy compensation obtained the best results in both states.
There is a scarcity of studies in the literature that assess the economic feasibility of biogas energy derived from ANCO using OFUSW and LM. In light of this, the present study addresses the need for greater knowledge regarding economic viability studies on ANCO using these two solid wastes for energy usage. Assuming, according to studies citing LM as a co-substrate, that co-digestion with this industrial waste increases methane production per digested OFUSW, the objective of this study is to assess if this investment is economically viable. Therefore, the study can contribute to the development of an alternative that may increase biogas generation in anaerobic environments, enabling the generation of electricity from a renewable energy source for use, especially at a local level. This can stimulate the diversification of the Brazilian electrical grid, reduce emissions, and avoid environmental impacts.
2. Results and Discussion
Energy Produced and Economic Viability
The calculations for the results were based on the most significant result from [26] for CH4. Compared to [27], the study of [26] presented more suitable conditions to make the project feasible, achieving a population 7.7 times smaller. In [26], for every 50 g of OFUSW, 5 g of LM was added to the co-digestion to obtain a proportion of 0.1 LM/OFUSW. This proportion enabled the estimation of the quantities necessary for co-digestion in tons/year for both materials. The average daily volume of CH4 generated for each 50 g of OFUSW was 0.00006923 m3/day, resulting from a volume of 2700 mL of CH4 produced in 39 days of experimentation. Thus, the proportion of CH4 volume generated daily and OFUSW added to the co-digestion resulted in approximately 0.001 m3 of CH4 per kilogram of OFUSW.
The established proportions also enabled the determination of the minimum population of 165,200 inhabitants needed to reach a positive NPV. Table 1 summarizes the necessary quantities of USW, OFUSW, and LM, along with presenting the estimated CH4 volume, power, and energy available per year associated with this population.

Table 1.
Materials results, CH4, power, and energy for the minimum population needed for economic feasibility (NPV > 0).
Thus, for a population of 165,200 inhabitants, a USW production capacity of 62,649.62 t/year was obtained. Considering that in Brazil, the organic fraction of this waste accounts for 45% of the total USW generated [9], the capacity of FORSU produced by this population was 28,380.28 t/year. Therefore, the proportion of LM used was 2838.03 t/year. A CH4 production capacity equal to 39,295.77 m³/year was obtained for this proportion. Some studies have demonstrated a strong relationship between substrate composition and the biogas productivity produced, depending on organic load and temperature parameters. The study by [33] evaluated the biogas production from co-fermentation between waste-activated sludge (WAS) and food waste (FW). The authors obtained a higher yield in biogas production when there was a higher concentration of FW; therefore, the higher the percentage of organic load, the higher the fermentation yield. For the scenario with a percentage of 50% WAS and 50% FW, the yield was 489 mgCOD/gVS. When the percentage of FW in the mixture was decreased to a ratio of 70% WAS and 30% FW, the fermentation yield decreased to 419 mgCOD/gVS, and in a mixture with a percentage of 90% WAS and 10% FW, the yield decreased to 175 mgCOD/gVS. In addition, the authors found that the impact of buffer capacity with co-fermentation was higher (96 mgCOD/gVS) compared to the monofermentation (72 mgCOD/gVS).
Temperature is also a deterministic factor in fermentation activities. According to [34], a higher biogas yield was obtained under mesophilic temperature conditions (37 °C) than under thermophilic temperature conditions (55 °C). For mesophilic conditions, the authors obtained a biogas yield of 740.4 ± 19 cm³gODM−1, containing 68.6 ± 1.8% CH4. Under thermophilic conditions, the biogas yield decreased from 2.1 to 2.8 times (108.8 ± 12.6 cm³gODM−1 to 274.7 ± 15.9 cm³gODM−1). Thus, the percentage of CH4 under thermophilic conditions was 59.5 ± 2.1%. Furthermore, the authors found that for an organic load greater than 6 gODM.dm-3.d-1, metabolic activity was inhibited, and thus biogas production decreased. Based on the studies presented, it can be seen that co-digestion improves CH4 yield, and the choice of the ratio 90% USW to 10% LM ensures a better yield and higher energy potential.
From an energy perspective, the power that would be generated relative to the populations was estimated from the volume of CH4 calculated to be produced. It should be noted that the energy generated resulted in 76.79 MWh/year for the minimum population, which was classified as the microgeneration distribution. It is worth mentioning that the study in [37] obtained a result of 450 kW for a population of 150,000 inhabitants under conditions similar to those considered in this article, indicating considerably more significant than those presented here.
Regarding the economic analysis, the graph in Figure 1 summarizes the revenue generated, the costs of O&M, and the cash flow throughout the 20-year project. In year 0, it was possible to identify the I0 as USD 52,586.93, with no revenue and operation, as per the previously outlined presumptions. In the following years, the estimated revenue was USD 8892.21, O&M costs were USD 2629.35, and cash flow was USD 6262.86 per year. Every eight years, as observed in years 8 and 17, the O&M costs included the change of the motor generator, adding USD 6245.02 to this category.
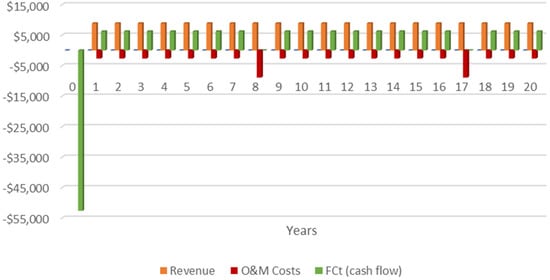
Figure 1.
Revenue, O&M costs, and cash flow for the minimum population needed to guarantee economic feasibility (NPV > 0).
The first positive NPV was USD 6.63 (Figure 1 and Figure 2) and was used to determine the minimum population. The payback period was approximately 20 years, which was the time stipulated for the project. Thus, the IRR reached 9%, enabling the recovery of the investment and reaching the MARR. It should be noted that a population of 200,000 inhabitants could be considered to make the project attractive (IRR > MARR). With this population, the NPV would be USD 8750.87, the IRR would accumulate 11.15%, and the payback period would be in approximately 14.04 years.
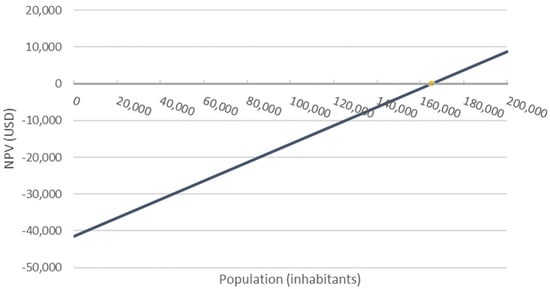
Figure 2.
NPV graph compared to population size.
The results of the calculations for the net present value of the unit cost for electricity throughout the project, known as LCOE, started at 195.67 USD/kWh and reached 0.1093 USD/kWh (Figure 3) for the minimum population. When compared to the rate of 0.1158 USD/kWh used to calculate the energetic compensation for the Distributed Generation (DG) system, this result demonstrated that the costs to generate 1 kWh were less than the compensation rate. If the population were considered to have 200,000 inhabitants, the LCOE would be 0.0989 USD/kWh.
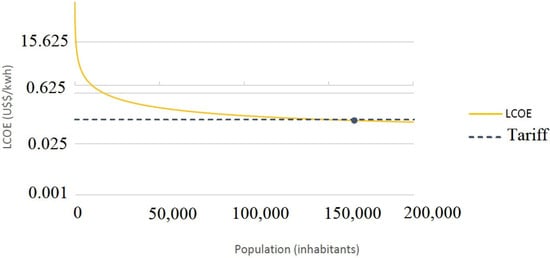
Figure 3.
LCOE graph compared to population on a logarithmic scale.
Thus, it should be noted that Brazil has 180 municipalities with populations greater than the minimum for economic feasibility [39]. Therefore, considering only population as a factor, there is potential for this paper’s proposal in all of these cities. Furthermore, the results are advantageous for populations with fewer than 200,000 inhabitants to enable sanitary landfill energy usage projects, as calculated by [38,40]. They foresaw that the minimum necessary population to become financially attractive would be 339,000 inhabitants.
Even if it is not feasible in cities with smaller populations, it is essential to assess this potential for public policies to be made to make the process viable. As 94% of municipalities in Brazil have less than 100,000 inhabitants, a partnership between neighboring cities can be established. According to [41], increasing the flow of waste to be treated can increase the energy produced and reduce MSW management and generation costs in these cities. Public consortia can ensure greater efficiency in applying public resources that allow the adoption of joint solutions for treating urban solid waste [42].
However, the minimum population does not guarantee the attractiveness of the project as an investment. Furthermore, the population criterion is just one of the influencing factors for the economic analysis. To evaluate conditions in which the proposal is financially attractive and to contemplate the uncertainties associated with the variations in the price of energy, a sensitivity analysis was carried out [43].
Table 2 and Table 3 present the results of rate variations between 80% and 120%, varied at intervals of 10%. Payback times of 15 and 10 years were considered. When payback was set to 10 years, it can be noted that the demands for the project to be feasible increased. The population is one of the variables that suffers most from a reduction in energy rates, along with the materials necessary for CH4 co-digestion.

Table 2.
Sensitivity analysis for 15-year payback, between 80% and 120% of the energy rate, varied at 10% intervals.

Table 3.
Sensitivity analysis for 10-year payback, between 80% and 120% of the energy rate, varied at 10% intervals.
For both payback timelines, the I0 values nearly doubled from one extreme to the other as the energy rate was reduced. The same can be said for NPV and available energy. The IRR was the parameter least affected, and the attractiveness remained the same in all cases, which demonstrates the feasibility of the proposal.
The rate reduction, which directly affects the project’s revenue, provoked an increase in costs, including I0, O&M, and cash flow. This behavior occurs because the unitary cost of the equipment remained constant, and it was necessary to spend more on equipment and greater power to achieve the established payback.
Regarding the minimum population for feasibility, it is worth highlighting that for the 15-year payback, a non-varying rate makes the project not only feasible, but also attractive, with 190,150 inhabitants, an NPV of BRL 33,765.07 (USD 6275.85), an IRR of 10.59%, and an LCOE 12.95% below the current market rates. In this payback period, the best result in terms of population would be with a 20% increase in the energy rates, reaching a population of 134,600 inhabitants despite the LCOE being 11.51% greater than the currently practiced rate. In terms of NPV, decreasing the rate by 20% would make the project more viable and more attractive, demanding a significantly larger population.
Considering a 10-year payback, there are more difficulties in maintaining the population below 200,000 inhabitants, which only occurs when the rate is increased to the extreme of 20% (0.139 USD/kWh). It should be noted that in this case, the difference between the rate and LCOE was 25.89% lower compared to the 15-year payback period. The LCOE for 10-year payback scenarios has lower electrical generation costs in relation to its rates. Based on the results in Table 3, the best option in terms of NPV, IRR, and LCOE is the 20% rate increase scenario. Furthermore, comparing the two 20% increases in the two tables, the 10-year payback would be more attractive and would bring about better conditions for implementation.
There are some general and important considerations to take from the results of the economic analysis. Changing out the motor generator every 8 years, which was a supposition of the project, increases the cost of the endeavor; however, the periodic maintenance associated with the removal of the other gases could prevent more costly repairs and reduce the costs involved. It is also worth mentioning that the energy rate did not incorporate any costs, fees, or taxes, which would reduce the project revenue in a real application. The daily production of CH4 was calculated from the proportion between the volume of CH4 generated and the total consumed mass of OFUSW. This calculation method does not guarantee great precision, and the use of total solids (TS) would be necessary to improve accuracy [44]. Furthermore, this same proportion was derived from an average CH4 production figure in a batch experiment (63.23 mL/d), which does not necessarily represent regular production and high methane yields, whichares expected and desirable for a continuous flow biodigester [29]. According to [30], the volume of CH4 obtained, 1.38 m3 of CH4 per ton of OFUSW, would be low: less than 60 m3 per ton of substrate. Furthermore, the authors reinforced that the characteristics of the waste material varied according to the country, region, culture, time of year, and socioeconomic conditions. Thus, it should be noted that the analyses were based on results conducted in a laboratory experiment from [26] in conditions which were not identical to those in Brazil. Although it is important for the technique’s development and indication for use, as in [45], it is still a long way from the realities in which large-scale and commercial biodigesters exist and operate.
In light of these considerations, and despite the relatively low production of CH4 and electrical energy, this study demonstrated that the conditions exist to leverage co-digestion of OFUSW with LM. There is a need for further study on this alternative in Brazil through experiments that examine specific technical questions in the country, thus examining its applicability on a local level, taking into account the economy on a more tangible scale.
3. Methodology
The methodology of this study presupposes the existence of a biodigestion plant with anaerobic digestors for the co-digestion of OFUSW using LM, originating from municipalities as well as paper and cellulose industries, respectively. The assumed fermentation process consists of several phases, including hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis, methanogenesis, and sulfetogenesis [46]. During each stage, OM undergoes a natural simplification of its compounds whereby complex molecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids are broken down into simpler molecules such as CH4, CO2, and H2S [47].
Hydrolysis can be a limiting phase of anaerobic digestion. In this phase, hydrolytic bacteria break down carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids by releasing exoenzymes. This step results in the production of amino acids, sugars, and long-chain fatty acids, which are simpler and water-soluble materials [48]. Acidogenesis, on the other hand, is the sequential and subsequent step to hydrolysis. The compounds generated through hydrolysis are processed by acidogenic fermentative bacteria, which release organic acids such as short-chain volatile fatty acids (propionates and butyrates), alcohols, lactic acid, mineral compounds, and microbial biomass [48]. This phase is dominated by strictly anaerobic bacteria [49]. The next step is acetogenesis, which involves the transformation of volatile fatty acids and other compounds into acetate, H2 (g), and CO2 (g) [48]. Acetogenic bacteria, the microorganisms responsible for the breakdown of OM, establish symbiotic relationships with methanogenic archaea [50].
In methanogenesis, 60% to 70% of methane is produced by acetoclastic methanogenic archaea, which use acetate as a source of carbon and energy [51]. The rest of the methane is generated by hydrogenotrophic archaea, which consume hydrogen as an energy source in the presence of CO2 [48]. Finally, sulfetogenesis occurs conditionally in the presence of an OM or a medium containing large amounts of sulfate (SO42−) [52]. During this phase, sulfates, sulfites, and sulfur compounds are simplified into H2S. When there is an imbalance in the fermentation process, sulfate-reducing bacteria can compete with methanogens, reducing methane production and H2S generation [48,53].
Based on the studies on which this work was based, the conditions for co-digestion would involve moist digestion (total solids ≤ 15%) in a continuous flow and complete mixture, with fluid heating to maintain the temperature of the mesophilic layer (37 ± 1 °C) [26]. For conversion of the biogas chemical energy, the biodigesters would be integrated into an internal combustion Otto cycle motor coupled to an electric generator (Figure 4). The energy usage would be assumed to be within a distributed generation (DG) system, with an energy compensation rate model adopted in Brazil in the private market [54].

Figure 4.
General framework for a biodigestion plant for producing electricity.
Taking these factors into consideration, the energy and economic aspects of co-digestion were investigated. The economic feasibility analysis estimated the available energy and supplied financial indicators for the project.
Energy and Economic Evaluation
The calculations for the generation of electrical energy were initially conducted in order to obtain the minimum population required to economically enable the co-digestion between OFUSW and LM. In order to do this, the generation estimates were calculated in Microsoft Excel spreadsheets, considering an initial population of 50 people and increasing at the same interval. Based on the USW per capita generation in Brazil (1.039 kg/person/day) and the proposition of OFUSW (45.3%) [9], the calculations were conducted to determine the generation for the population in consideration.
The ratio between LM and OFUSW and the average volume of CH4 generated by the OFUSW were determined in experiments detailed in [26]. Therefore, the annual methane flow for each population was determined. It was assumed that the food residuals studied by the authors were equivalent to the OFUSW. This allowed for the computation of the power to be generated, which was calculated using Equation (1) as adapted from [55]:
where:
P: power available each year (kW);
QCH4: methane flow each year (m3 CH4/year);
PCH4: calorific power of methane (equal to 35.53 × 106 J/m3 CH4);
Ec: efficiency of the biogas collection (%);
E: efficiency of the turbine/motor (%);
31,536,000: seconds in a year (s/year);
1/1000: conversion of J/s to kW;
Ec was assumed to be 75%, accounting leakage losses and dilution of biogas in the effluent of 25% [56]. For E, a standard combustion motor efficiency of 33% was adopted [57,58]. Finally, the energy to be generated was calculated as from the product of power, a capacity factor (CF) of 0.8, and the number of hours in the year (8760 h) [59].
The economic feasibility analysis calculated the parameters of NPV, IRR, LCOE, and discounted payback, and conducted sensitivity analysis. In order to verify the feasibility of the project, the net present value (NPV) was calculated, which considers revenue, costs, and investments converted to the present moment through the interest rate. An investment is considered viable when the NPV is positive. Equation (2) presents one form of expressing the calculation.
where:
NPV: net present value (USD);
r: discounted rate (%) (minimum attractive rate of return, MARR);
FCt: cashflow from t = 1 to t = n;
t: investment time (years);
Io: initial investment (USD).
The period considered for the project (t) was 20 years as it assumed sulfate treatment and water removal without encumbering the undertaking [37]. The calculations were carried out on a timeline adopted for each populational increase of 50 individuals. The motor generator was replaced every eight years [60]. Regarding the cash flow (FCt) involving revenue and operational and maintenance costs (O&M), the calculations were detailed as follows, along with I0. The rate r, or MARR, represents the minimum interest rate that would justify the choice of the investment endeavor over another investment. In this case, r was adopted as the equivalent of the Brazilian Selic rate goal for 2024, projected by the Central Bank of Brazil (BACEN) at 9.0% [61].
Initially, the energy production revenue was calculated in order to obtain the cash flow. The average rate of USD 0.116/kWh for Brazilian states was used [62] in order to compensate for the use of energy in the regulated, contracted environment, considering the hypothesis of energy being fed back into the distribution grid. The O&M costs for the equipment were set at 5% of the initial investment [63] (I0) (Equation (3)), which involves the purchase of equipment and project-related items [64]. The suppliers, models, and origin of the equipment were based on [55], which used representative technical data of exclusively Brazilian equipment available in the national market. The investment was directed towards the purchase of a motor generator, compressors, gasometers, and transport tubulation for the biogas, expressed in terms of costs or linear meters and not in terms of units:
where:
I0: initial investment (USD);
CG: unitary gasometer cost (USD/m3);
BMP: daily methane production potential (m3/day);
D: number of days of accumulated gas;
CC: unitary compressor cost (USD/m3/h);
CP: biogas tubing cost (USD/m);
L: length of biogas tubing (m);
CM: cost of internal combustion motor (USD).
Table 4 summarizes the equipment and their unitary costs in dollars (USD) [55]. The costs were adjusted for inflation using theIGP-M index [65] and considering the conversion of BRL 5.38 for each USD 1.00 [66]. The tubing required for the collection and transportation of the biogas was estimated at 200 linear meters, and the number of days of accumulated gas was 3 [67]. The final costs for the remaining equipment were determined based on the power and BMP. With the O&M and I0 costs established, the cash flow was obtained, and subsequently, the NPV was determined for each year based on each population.

Table 4.
Summary of the required equipment and their respective relative costs, updated in [65].
Next, the project’s attractiveness parameter was calculated: the internal rate of return (IRR) of the endeavor. Despite the NPV indicating project viability for specific conditions, the IRR adds to the level of attractiveness of the undertaking for an economic feasibility analysis. The project is attractive and viable when the IRR > MARR and is not attractive when the IRR < MARR. If IRR = MARR, it does not present economic benefits or disadvantages and is indifferent as an investment [68]. The calculation of IRR is performed using the equation for NPV (Equation (4)), substituting r for IRR and making NPV equal to 0. Furthermore, the period of time for the initial return on investment, payback, was calculated based on the discounted cash flow.
The Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) is calculated using the ratio between the sum of the total costs of the project (I0 and O&M) and the sum of energy generated each year. The LCOE was obtained (Equation (5)) for a 20-year period. With this information, it was possible to analyze the cost behaviors for the generation of 1 kWh (USD/kWh) and compare them to the rate used to ascertain the revenue. This also indicates the minimum cost of revenue per kWh needed to sustain O&M, I0, interest, and the return on investment [69]:
where:
CT: total costs of the project;
EP: total energy produced over the time of the endeavor.
In order to conduct the sum of annual costs (CAt) and obtain the CT, Equation (6) was used. The costs in year 0 were different from the others only in the substitution of O&M for I0:
where:
CAt: costs in year t;
r: interest rate (%);
t: year of the investment.
Finally, in order to determin the total energy generated, the energy for each year (EAt) was calculated using Equation (7), assuming that no electrical energy generation would occur in year 0:
where:
EA: energy generated in year t;
r: interest rate (%);
t: year of the investment.
Considering that the calculations above were elaborated to determine the minimum population for economic feasibility (NPV > 0), a sensitivity analysis was conducted not only to determine the attractiveness of the project (IRR > MARR), but also to account for uncertainties, which are inherent to any investment endeavor. This analysis involves the variation of an independent variable in the calculations to evaluate the impact on the results [43]. Thus, for the sensitivity analysis, payback periods of 10 and 15 years were prepared, with the energy rate varied between 80% and 120% of the initial value of 0.116 USD/kWh (100%), in 10% intervals.
4. Conclusions
The economic evaluation made it possible to determine the minimum feasibility conditions and its main results. A minimum population of 165,200 inhabitants resulted in a CH4 yield of 39,295.77 m³/year and an available energy of 76.79 MWh/year, which was below the threshold of 200,000 inhabitants. The study resulted in a positive NPV of USD 6.63 with a payback period of 20 years. The IRR was 9% and the LCOE started at 195.67 USD/kWh and reached 0.1093 USD/kWh. Thus, the results found in the literature demonstrate an advantage for the use of LM in co-digestion with OFUSW, which could be applied in more than 180 Brazilian municipalities. However, Brazil has 5000 municipalities with a population of fewer than 165,200 inhabitants. Therefore, politics public can be created, such as the formation of consortium groups among these municipalities to treat waste in an environmentally appropriate way and produce more sustainable energy. Other public policies, such as the reduction or exemption of taxes and fees on the sale of renewable energy, can contribute to making the enterprise more economically viable while encouraging the use of cleaner energy and low carbon emission in the country.
Moreover, to make the project attractive and viable, the sensitivity analysis demonstrated that the energy rate of BRL 0.748 (USD 0.139) for a 10-year payback provides a balance between the minimum population of 185,000 inhabitants and the other indicators such as NPV, IRR, and LCOE. Reducing the energy rates would impose considerable demands on the feasibility and attractiveness of the project. However, regardless of the circumstances, the economic feasibility for OFUSW with LM was established through this analysis.
It is worth highlighting that the considerations, approximations, and technical/methodological choices made throughout this study are relevant to the results and should be considered to the adequately understand of the study’s overall application. According to some studies, the characteristics of waste materials vary according to the country, region, culture, time of year, and socioeconomic conditions related to the population that generates them. In light of this, the studies used in this paper focused on countries other than Brazil, thus highlighting the need for a greater technical understanding of this alternative with data that more closely represent the country in question. Furthermore, it is worth noting that the project’s economic feasibility can improve with the incorporation of costs, fees, and taxes in the energy rates, along with periodic maintenance of the motor generator and removal of other biogases. Finally, the difference in scale observed in the generation of CH4 and, in turn, the available energy and power, reinforces the need for further studies on co-digestion.
In Brazil, there are many difficulties to be faced, including the adequate generation of USW, the diversification of the electrical energy matrix with renewable energy, and deriving value from waste products. However, studies such as this should serve as an incentive for overcoming these challenges. In general, through the economic evaluation conducted and considering the possible practical consequences of the results obtained, it is understood that co-digestion of OFUSW with LM stands out as a feasible alternative to other environmentally sound disposal methods for these materials. Furthermore, there is the potential for savings of financial resources for industries and public institutions, as well as the reduction of environmental impacts. The proposal is also aligned with the global trend towards circular economies as it reintroduces materials into the value chain that were previously discarded without added value. Thus, it can be concluded that the results obtained present economic feasibility that lays the groundwork for further study into the proposal and rational, sustainable, and economically feasible use of biogas from OFUSW with LM.
Considering that the potential of biogas generation from the co-digestion of OFUSW and LM offers efficiency in the reduction of environmental impacts, both in terms of MSW management and energy, it is suggested that future studies should deepen the economic analysis through a stochastic analysis, as this was a limitation of the current study. A life cycle analysis is also recommended to demonstrate the environmental viability of energy derived from OFUSW and LM.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.M.B., M.L.G.R. and G.L.T.F.; methodology, U.R.d.S.C., R.M.B., M.L.G.R. and G.L.T.F.; software, U.R.d.S.C.; formal analysis, U.R.d.S.C., A.M.d.C.C., M.A.d.B.M., R.M.B., M.L.G.R. and I.F.S.S.; investigation, U.R.d.S.C. and I.F.S.S.; resources, U.R.d.S.C.; writing—original draft, U.R.d.S.C., A.M.d.C.C., M.A.d.B.M., G.L.T.F. and I.F.S.S.; supervision, R.M.B. and M.L.G.R.; project administration, R.M.B.; funding acquisition, R.M.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Federal University of Itajubá (Universidade Federal de Itajubá, UNIFEI; in Portuguese) by granting the Master of Science scholarship to Ulisses Raad Coelho by its Institutional Scholarship Program. This research was funded also by the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, CNPq; in Portuguese) by granting the journals’s Article Processing Charge (APC) and the Productivity in Research scholarship to Regina Mambeli Barros (P1D Process Number 303036/2021-4), to Geraldo Lúcio Tiago Filho. This research was funded by the Minas Gerais State Agency for Research and Development (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais, FAPEMIG, in Portuguese) by granting financial support “Improvement of biogas energy potential from anaerobic (co)digestion of solid organic waste as an incentive to renewable energy sources: substrate pre-treatment and co(digestion) aiming at Hydrogen use” (Process N.: APQ-00568-21). Finally, this research was funded by FAPEMIG by granting the Master of Science scholarship (finance code I) to Adriele Maria de Cássia Crispim by FAPEMIG n°. APQ-03243-21 and by project RED-00090-21, “Theoretical-experimental evaluation of the production and use of green hydrogen in Minas Gerais”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available at: https://repositorio.unifei.edu.br/xmlui/handle/123456789/3244 (accessed on 10 May 2023).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Federal University of Itajubá (Universidade Federal de Itajubá, (UNIFEI) in Portuguese) for granting the Master of Science scholarship to Ulisses Raad Coelho through its Institutional Scholarship Program. The authors would like to thank the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, (CNPq) in Portuguese) for granting the journals’s Article Processing Charge (APC) and the Productivity in Research scholarship to Regina Mambeli Barros (P1D Process Number 303036/2021-4), and to Geraldo Lúcio Tiago Filho. We would like to thank the Minas Gerais State Agency for Research and Development (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais, (FAPEMIG) in Portuguese) for granting financial support for “Improvement of biogas energy potential from anaerobic (co)digestion of solid organic waste as an incentive to renewable energy sources: substrate pre-treatment and co(digestion) aiming at Hydrogen use” (Process N.: APQ-00568-21). We are thankful to FAPEMIG for granting the Master of Science scholarship (finance code I) to Adriele Maria de Cássia Crispim through FAPEMIG nº. APQ-03243-21. The authors would like to thank (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior, Capes; in Portuguese) for Master scholarship (finance code 1) to Adriele Maria de Cassia Crispim.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kaza, S.; Yao, L.; Bhada-Tata, P.; Van Woerden, F. What a Waste 2.0—A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; ISBN 9781464813290. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, R.d.Q.; Tavares, A.N.; Santos, G.V.; Bajay, S.V. Oportunidades Enterradas—Geração Elétrica a Partir Do Biogás de Resíduos Sólidos Urbanos; EDUFES, Ed.; Universidade do Espirito Santo: Vitoria, Brazil, 2019; ISBN 9788577724260. [Google Scholar]
- BRASIL LEI N° 12.305, de 2 de AGOSTO de 2010. Institui a Política Nacional de Resíduos Sólidos; Altera a Lei No 9.605, de 12 de Fevereiro de 1998; e Dá Outras Providências. 2010. Available online: https://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_ato2007-2010/2010/lei/l12305.htm (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- BRASIL LEI N° 14.026, de 15 de JULHO de 2020. Atualiza o Marco Legal Do Saneamento Básico e Altera a Lei N° 9.984, de 17 de Julho de 2000, Para Atribuir à Agência Nacional de Águas e Saneamento Básico (ANA) Competência Para Editar Normas de Referência Sobre o Se 2020. Available online: https://www.planalto.gov.br/ (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Neehaul, N.; Jeetah, P.; Deenapanray, P. Energy Recovery from Municipal Solid Waste in Mauritius: Opportunities and Challenges. Environ. Dev. 2020, 33, 100489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, I.F.S.; Gonçalves, A.T.T.; Borges, P.B.; Barros, R.M.; da Silva Lima, R. Combined Use of Biogas from Sanitary Landfill and Wastewater Treatment Plants for Distributed Energy Generation in Brazil. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barros Martins, M.A.; Crispim, A.; Ferreira, M.L.; Santos, I.F.; de Lourdes Noronha Motta Melo, M.; Barros, R.M.; Filho, G.L.T. Evaluating the Energy Consumption and Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Managing Municipal, Construction, and Demolition Solid Waste. Clean. Waste Syst. 2023, 4, 100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SNS (Secretaria Nacional de Saneamento). Panorama do Saneamento Básico no Brasil 2021; Ministério do Desenvolvimento Regional: Brasília, Brazil, 2021. Available online: https://legislacao.presidencia.gov.br (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- ABRELPE (Associação Brasileira de Limpeza Pública e Resíduos Especiais). Panorama dos Resíduos no Brasil 2020; ABRELPE: São Paulo, Brazil, 2020; p. 51. [Google Scholar]
- Mussatto, S.I.; Ballesteros, L.F.; Martins, S.; José, A.T. Chapt. 6: Use of Agro-Industrial Wastes in Solid-State Fermentation Processes. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2012, 10, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes Ferraz Junior, A.D.; Etchebehere, C.; Perecin, D.; Teixeira, S.; Woods, J. Advancing Anaerobic Digestion of Sugarcane Vinasse: Current Development, Struggles and Future Trends on Production and End-Uses of Biogas in Brazil. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 157, 112045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonzio, G. Upgrading of Biogas to Bio-Methane with Chemical Absorption Process: Simulation and Environmental Impact. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 131, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borba, P.F.d.S.; Martins, E.M.; Correa, S.M.; Ritter, E. Greenhouse Gases Emissions from a Landfill in Rio de Janeiro. Eng. Sanit. Ambient. 2018, 23, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avellar, L.H.N. A Valorização Dos Subprodutos Agroindustriais Visando a Co-Geração e a Redução da Poluição Ambiental. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Estadual Paulista “Júlio de Mesquita Filho”, São Paulo, Brazil, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, I.F.S.; Braz Vieira, N.D.; de Nóbrega, L.G.B.; Barros, R.M.; Tiago Filho, G.L. Assessment of Potential Biogas Production from Multiple Organic Wastes in Brazil: Impact on Energy Generation, Use, and Emissions Abatement. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 131, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BRASIL DECRETO No 11.003, de 21 de MARÇO de 2022—Institui a Estratégia Federal de Incentivo Ao Uso Sustentável de Biogás e Biometano. 2022; pp. 1–3. Available online: https://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_ato2019-2022/2022/decreto/d11003.htm (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- EPE (Empresa de Pesquisa Energética). Plano Nacional de Energia 2050—Demanda de Energia. Plano Nac. Energ. 2020, 1–232. Available online: https://www.epe.gov.br/pt/publicacoes-dados-abertos/publicacoes/Plano-Nacional-de-Energia-2050 (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- EPE (Empresa de Pesquisa Energética). 1a Revisão Quadrimestral das Projeções da Demanda de Energia Elétrica do Sistema Interligado Nacional 2019–2023; Estudos da Demanda; EPE: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2019; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
- EPE BEN. 2021 Relatório Síntese; Empresa de Pesquisa Energética: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2021; pp. 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Kravetz, C. Estudo Do Desempenho Energético das Caldeiras da Indústria de Polpa Celulósica Kraft. Master’s Dissertation, Universidade de São Paulo Escola Superior de Agricultura “Luiz de Queiroz”, Piracicaba, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- IBA (Industria Brasileira de Árvores). Relatório 2019; IBA: Brasília, Brazil, 2019; pp. 1–80. [Google Scholar]
- Farage, R.M.P.; Silva, C.M.; Passos Rezende, A.A.; Lelis Leal de Souza, J.J.; Teixeira de Matos, A.; Vinha Zanuncio, A.J. Intermediate Covering of Municipal Solid Waste Landfills with Alkaline Grits, Dregs and Lime Mud by-Products of Kraft Pulp Production. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 117985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farage, R.M.P. Aplicação Dos Sub-Produtos Alcalinos da Indústria De Polpa Celulósica Kraft Em Aterros Sanitários E Na Remediação De Drenagem Ácida. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal de Viçosa (UFV), Viçosa, Brazil, 2018; 83p . [Google Scholar]
- Alves, M.C.; Souza, Z.M. de Recuperação de Área Degradada Por Construção de Hidroelétrica Com Adubação Verde e Corretivo. Rev. Bras. Ciência Solo 2008, 32, 2505–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.R.P.; Chaves, A.D.C.G.; Crispim, D.L.; Marcos, J.; Trigueiro, A.; Maracaja, P.B.; Almeida, I.P.; Bulhões, A.A.; Silva, F.T. Proposta de Recuperação de Uma Área de Empréstimo Degradada Pela Atividade de Olaria No Município de Pombal-PB. Intesa 2015, 9, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, P.; Wang, Y. Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste Stabilized by Lime Mud from Papermaking Process. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 170, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Effects of Alkalinity Sources on the Stability of Anaerobic Digestion from Food Waste. Waste Manag. Res. 2015, 33, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro e Silva, H.L.; Silva, A.M.L.; Barros, R.M.; dos Santos, I.F.S.; de Freitas, J.V.R. Addition of Iron Ore Tailings to Increase the Efficiency of Anaerobic Digestion of Pig Manure: A Technical and Economic Analysis. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 148, 106013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, S.; Dubey, B.K. A Critical Review on Operating Parameters and Strategies to Improve the Biogas Yield from Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste. Renew. Energy 2019, 143, 779–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, V.K.; Fdez-Güelfo, L.A.; Zhou, Y.; Álvarez-Gallego, C.J.; Garcia, L.I.R.; Ng, W.J. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste (OFMSW): Progress and Challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 93, 380–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, K.; Ma, J.; Ifran, M.; Li, A. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Sewage Sludge, Food Waste and Yard Waste: Synergistic Enhancement on Process Stability and Biogas Production. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadaleti, W.C.; Martins, R.; Lourenço, V.; Przybyla, G.; Bariccatti, R.; Souza, S.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F.; Sunny, N. A Pioneering Study of Biomethane and Hydrogen Production from the Wine Industry in Brazil: Pollutant Emissions, Electricity Generation and Urban Bus Fleet Supply. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 19180–19201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Antich, C.; Perez-Esteban, N.; Astals, S.; Peces, M.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Dosta, J. Assessing the Potential of Waste Activated Sludge and Food Waste Co-Fermentation for Carboxylic Acids Production. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierowicz, J.; Dzienis, L.; Dębowski, M.; Zieliński, M. Optimisation of Methane Fermentation as a Valorisation Method for Food Waste Products. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 144, 105913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Z.; Shen, Y.; Lv, J.; Xu, X.; Yu, H. The Metabolic Process of Methane Production by Combined Fermentation of Coal and Corn Straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, R.C.; Barros, R.M.; dos Santos, I.F.S.; Tiago Filho, G.L.; Silva, D.; Galdino, S.P. Municipal Solid Waste Management and Economic Feasibility for Electricity Generation from Landfill Gas and Anaerobic Reactors in a Brazilian State. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, N.d.S.; Barros, R.M.; Santos, I.F.S.; Tiago Filho, G.L.; Silva, S.P.G. Electric Energy Generation from Biogas Derived from Municipal Solid Waste Using Two Systems: Landfills and Anaerobic Digesters in the States of São Paulo and Minas Gerais, Brazil. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 48, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mambeli Barros, R.; Tiago Filho, G.L.; da Silva, T.R. The Electric Energy Potential of Landfill Biogas in Brazil. Energy Policy 2014, 65, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBGE (Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística). Estimativas de População; IBGE: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2020.
- Chernicharo, C.A.D.L. Reatores Anaeróbios, 2nd ed.; Departamento de Engenharia Sanitária e Ambiental, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pastor-Poquet, V.; Papirio, S.; Steyer, J.P.; Trably, E.; Escudié, R.; Esposito, G. High-Solids Anaerobic Digestion Model for Homogenized Reactors. Water Res. 2018, 142, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.L.; Ortiz, R.; Steele, T.W.J.; Stuckey, D.C. Toxicants Inhibiting Anaerobic Digestion: A Review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.M.T.; Feiden, A.; Tavares, S.G. Fatores Que Influenciam o Processo de Digestão Anaeróbia Na Produção de Biogás. Nativa 2017, 5, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekunle, K.F.; Okolie, J.A. A Review of Biochemical Process of Anaerobic Digestion. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, E.F. Tratamento Anaeróbio de Efluentes Oriundos da Bovinocultura de Leite Em Biodigestor Tubular. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Estadual do Oeste do Paraná, Centro de Ciências Exatas e Tecnológicas, Cascavel, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- PROBIOGAS. O Estado da Arte da Tecnologia de Metanização Seca; Ministério das Cidades: Brasília, Brazil, 2015; ISBN 2013206534.
- Barros, R.M. Tratado Sobre Resíduos Sólidos: Gestão, Uso e Sustentabilidade; Editora Interciência, Ed.; Editora Interciência: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ANEEL (Agência Nacional de Energia Elétrica). Resolução Normativa N° 786, de 17 de o de 2017. Altera a Resolução Normativa N° 482, de 17 de Abril de 2012. Available online: https://www2.aneel.gov.br (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- CETESB (The Environmental Company of Sao Paulo). Biogas: Generation and Energy Use v. 1.0/CETESB 2006. Available online: https://cetesb.sp.gov.br (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Ribeiro, E.; Barros, R.M.; Tiago Filho, G.L.; Santos, I.F.S.; Sampaio, L.C.; Santos, T.V.; Silva, F.d.G.B.; Silva, A.P.M.; Freitas, J.V.R. Feasibility of Biogas and Energy Generation from Poultry Manure in Brazil. Waste Manag. Res. 2018, 36, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, H.R.; Reinhart, D.R.; Mackie, K.R. Determination of First-Order Landfill Gas Modeling Parameters and Uncertainties. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agamuthu, P. Landfilling in Developing Countries. Waste Manag. Res. 2013, 31, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, I.F.; Barros, R.M.; Filho, G.L.T. Biogas Production from Solid Waste Landfill. Encycl. Renew. Sustain. Mater. 2020, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leme, M.M.V.; Rocha, M.H.; Lora, E.E.S.; Venturini, O.J.; Lopes, B.M.; Ferreira, C.H. Techno-Economic Analysis and Environmental Impact Assessment of Energy Recovery from Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) in Brazil. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 87, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacen (Banco Central do Brasil). Boletim Focus. Available online: https://www.bcb.gov.br/publicacoes/focus (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- ANEEL (Agência Nacional de Energia Elétrica). Relatório—Ranking de Tarifas; Agência Nacional de Energia Elétrica: Brasília, Brazil, 2022.
- Lopes, M.M. Aproveitamento Energético Em Aterros Sanitários: Análise da Viabilidade Técnica e Econômica Para o Uso de Biogás e Instalação de Painéis Fotovoltaicos. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal de Itajubá, Itajubá, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, I.F.; Barros, R.M.; Lúcio, G. Uma Avaliação Energética, Econômica e Ambiental das Opções de Aproveitamento Energético Do Biogás de Um Aterro Sanitário No Brasil. Rev. Eletrônica em Gestão, Educ. Tecnol. Ambient. 2015, 19, 1344–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Bacen (Banco Central do Brasil). Correção Inflacionária; Bacen: Brasilia, Brazil, 2021.
- Bacen (Banco Central do Brasil). Cotação Moeda; Bacen: Brasilia, Brazil, 2021.
- Pinto, J.A. Estudo da Codigestão Anaeróbia de Dejetos Bovinos e Suínos: Análise da Viabilidade Técnica e Econômica. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal de Itajubá (UNIFEI), Itajuba, Brazil, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, S.R.M.P. A Análise de Investimentos Em Novas Tecnologias: A Importância da Utilização de Diferentes Métodos de Avaliação. Master’s Thesis, Universidade do Minho, Braga, Portugal, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi, R.K. Microgeração Fotovoltaica No Brasil: Condições Atuais E Perspectivas Futuras. Master’s Dissertation, Instituto de Energia e Ambiente, São Paulo, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Berhorst, N.L.; Grauer, A.F.; Neuffer, D.; Schmitz, A.P. Análise da Viabilidade Econômica da Geração de Energia a Partir de Resíduos da Produção Suinícola. Rev. Parana. Desenvolv. 2021, 41, 81–101. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, T.R.; Barros, R.M.; Tiago Filho, G.L.; dos Santos, I.F.S. Methodology for the Determination of Optimum Power of a Thermal Power Plant (TPP) by Biogas from Sanitary Landfill. Waste Manag. 2017, 65, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, R.E.; Santos, I.F.S.d.; Barros, R.M.; Bernal, A.P.; Tiago Filho, G.L.; Silva, F.d.G.B. da Generating Electrical Energy through Urban Solid Waste in Brazil: An Economic and Energy Comparative Analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Azevedo, C.R.; De Melo, M.C. Consórcios Públicos Para Gestão de Resíduos Sólidos Urbanos; Consórcios Públicos de Resíduos: Fortaleza, Brazil, 2020; p. 45.
- Siddique, M.N.I.; Wahid, Z.A. Achievements and Perspectives of Anaerobic Co-Digestion: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pin, B.V.d.R.; Barros, R.M.; Silva Lora, E.E.; Almazan del Olmo, O.; Silva dos Santos, I.F.; Ribeiro, E.M.; Victor de Freitas Rocha, J. Energetic Use of Biogas from the Anaerobic Digestion of Coffee Wastewater in Southern Minas Gerais, Brazil. Renew. Energy 2020, 146, 2084–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).