A Review on Synthesis of Mullite Ceramics from Industrial Wastes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Synthesis of Mullite Ceramics
2.1. Starting Materials
2.2. Sintering Temperature
2.3. Sintering Aids–Additives
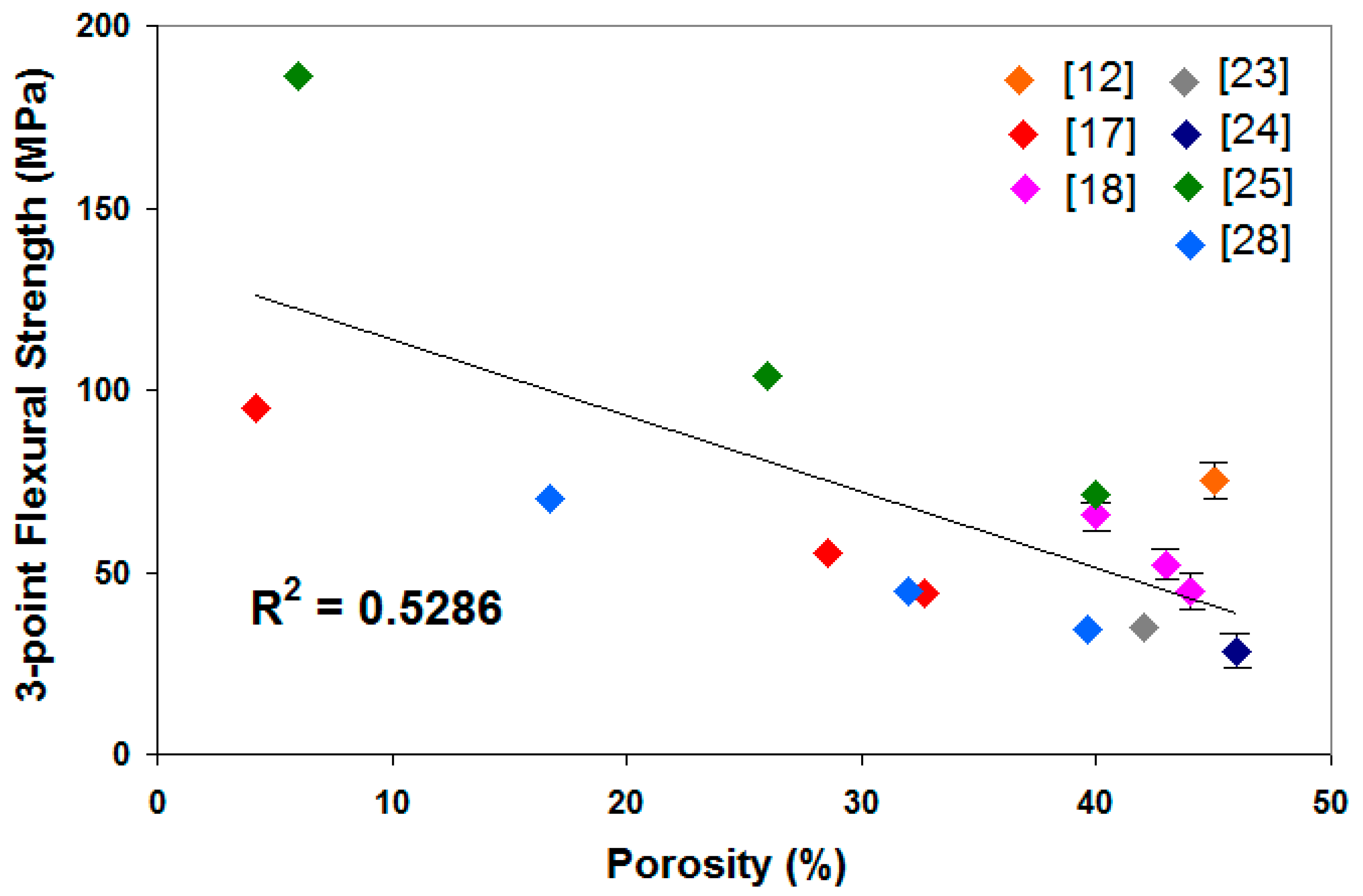
3. Mechanical Strength
4. Thermal Expansion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schneider, H.; Komarneni, S. Mullite; Wiley VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; p. 241. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, N.L.; Greig, J.W. The system: Al2O3∙SiO2. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1924, 7, 238–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.G.M.U.; Nakai, Z.; Minegishi, K. Synthesis of mullite powder and its characteristics. Int. J. High Technol. Ceram. 1986, 2, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.R.; Elsayed, H.; Bernardo, E. Highly porous mullite ceramics from engineered alkali activated suspensions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 101, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.J.; Labrincha, J.A. Properties of sintered mullite and cordierite pressed bodies manufactured using Al-rich anodising sludge. Ceram. Int. 2008, 34, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.J.; Tulyagavov, D.U.; Ferreira, J.M.; Labrincha, J.A. High-temperature mullite dissolution in ceramic bodies derived from Al-rich sludge. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 25, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, A.; Vilminot, S. Crystallisation kinetics of mullite glass-ceramics obtained from alumina—Silica wastes. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2013, 6, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocardo, J.C.E.; Torres, J.T. Development of mullite/zirconia composites from a mixture of aluminum dross and zircon. Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 921–924. [Google Scholar]
- Suriyanarayanan, N.; Kannannithin, K.V.; Bernardo, E. Mullite glass ceramic production from coal ash and alumina by high-temperature plasma. J. Non-Oxide Glasses 2009, 1, 247–260. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.S.; Park, H.C. Mullite ceramics derived from coal fly ash. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2001, 20, 1089–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.Y.; Ji, H.B.; Yoon, S.Y.; Kim, B.K.; Park, H.C. Porous mullite composite with controlled pore structure processed using a freeze casting of TBA-based coal fly ash slurries. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Du, H.; Guo, A.; Xu, H.; Yang, D. Preparation of self-reinforcement of porous mullite ceramics through in situ synthesis of mullite whisker in flyash body. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Diwu, J.; Feng, X.; Feng, X.; Liu, X.; Meng, G. Phase evolution and sintering characteristics of porous mullite ceramics produced from the flyash-Al(OH)3 coating powders. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 460, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H. Preparation of mullite whiskers from coal fly ash using sodium sulfate flux. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2011, 100, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.M.; Yang, T.Y.; Yoon, S.Y.; Stevens, R.; Park, H.C. Mullite whiskers derived from coal fly ash. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 455, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, T.F.; Salleh, M.A.M.; Kok, K.Y.; Matori, K.A. Mineralogy and thermal expansion study of mullite-based ceramics synthesized from coal fly ash and aluminum dross industrial wastes. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 884–890. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Ma, H.; Huang, W. Effect of V2O5 on the properties of mullite ceramics synthesized from high-aluminum fly ash and bauxite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 1535–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lin, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Miao, L.; Lang, Y.; Liu, X.; Meng, G. Reaction-sintered porous mineral-based mullite ceramic membrane supports made from recycled materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Dong, Y.; Hampshire, S.; Cerneaux, S.; Winnubst, L. Waste-to-resource preparation of a porous ceramic membrane support featuring elongated mullite whiskers with enhanced porosity and permeance. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Dong, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; You, S. Fabrication of mullite-whisker-structured porous. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 11163–11174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Dong, X.; Li, L.; Dong, Y.; Hampshire, S. Recycling of waste fly ash for production of porous mullite ceramic membrane supports with increased porosity. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 34, 3181–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yugeswaran, S.; Ananthapadmanabhan, P.V.; Kobayashi, A.; Lusvarghi, L. Transferred arc plasma processed mullite from coal ash and bauxite. Ceram. Int. 2011, 37, 3437–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Hampshire, S.; Zhou, J.; Ji, Z.; Wang, J.; Meng, G. Sintering and characterization of flyash-based mullite with MgO addition. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Hampshire, S.; Zhou, J.; Lin, B.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, X.; Meng, G. Recycling of fly ash for preparing porous mullite membrane supports with titania addition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 180, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Feng, X.; Feng, X.; Ding, Y.; Liu, X.; Meng, G. Preparation of low-cost mullite ceramics from natural bauxite and industrial waste fly ash. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 460, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.; Maitra, S.; Chandra, S.; Mitra, N.K. Alumina-Mullite Composites through Interaction of Bauxite and Fly Ash. Trans. Indian Ceram. Soc. 2008, 67, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusnierova, M.; Prascakova, M.; Matysek, D.; Cablík, V. Mullitization of black coal fly ashes. Acta Montan. Slovaca 2011, 16, 192–196. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, A.; Liu, J.; Xu, R.; Xu, H.; Wang, C. Preparation of mullite from desilication-flyash. Fuel 2010, 89, 3630–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Li, S.; Hou, X.; Li, H. Preparation of high performance mullite ceramics from high aluminum fly ash by an effective method. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 623, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, L.; Sousa, J.; Martins, I.M.; Vieira, M.T.; Oliveira, M.M. Ceramic products obtained from rock wastes. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 144, 843–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, L.P.D.F.; Mansur, H.S. Production and characterization of ceramic pieces obtained by slip casting using powder wastes. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 145, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.A.C.; Livramento, V.; Delmas, F. Novel mullite-based ceramics manufactured from inorganic wastes I. Densification behaviour. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 6, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, I.M.; Sousa, J.B.; Catarino, L.; Vieira, M.T.; Oliveira, M. The Formation of Mullite from Rock Wastes Containing Alumina and Silica. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publications: Zurich, Switzerland, 2002; Volume 230, pp. 380–383. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, I.M.; Vieira, S.; Livramento, V.; Sousa, J.; Delmas, F.; Oliveira, M.M.; Viera, M.T. Manufacture of Ceramic Products Using Inertized Aluminum Sludges. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publications: Zurich, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 456, pp. 822–826. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, M.T.; Catarino, L.; Oliveira, M.; Sousa, J.; Torralba, J.M.; Cambronero, L.E.G.; Gonzalez-Mesones, F.L.; Victoria, A. Optimization of the sintering process of raw material wastes. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1999, 93, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasileiro, M.I.; Rodrigues, A.W.B.; Menezes, R.R.; Neves, G.A.; Santana, L.N.L. The Kaolin Residue and Its Use for Production of Mullite Bodies. In Sustainable Development—Energy, Engineering and Technologies—Manufacturing and Environment; Ghenai, C., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 117–142. [Google Scholar]
- Choo, T.F.; Murshidi, J.A.; Saidin, N.U.; Paulus, W.; Abdullah, Y. Production of Mullite Ceramic Bodies from Kaolin Processing Waste and Aluminum Hydroxide. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publications: Zurich, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 888, pp. 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Sembiring, S.; Simanjuntak, W.; Manurung, P.; Asmi, D.; Low, I.M. Synthesis and characterisation of gel-derived mullite precursors from rice husk silica. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 7067–7072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, M.F.; Conconi, M.S.; Gauna, M.R.; Suárez, G.; Aglietti, E.F.; Rendtorff, N.M. Mullite (3Al2O3·2SiO2) ceramics obtained by reaction sintering of rice husk ash and alumina, phase evolution, sintering and microstructure. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2016, 4, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aripin, H.; Mitsudo, S.; Prima, E.S.; Sudiana, I.N.; Kikuchi, H.; Sano, S.; Sabchevski, S. Crystalline mullite formation from mixtures of alumina and a novel material—Silica xerogel converted from sago waste ash. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 6488–6497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, R.M.; EL-Rafei, A.M.; Zawrah, M.F. In situ formation of sintered cordierite–mullite nano–micro composites by utilizing of waste silica fume. Mater. Res. Bull. 2012, 47, 2662–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, M. Microstructure, Microchemistry, and Flexural Strength of Mullite Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1991, 74, 3017–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, C.; Amrani, I.E.; Albizane, A. Recent advances in silica-alumina refractory: A review. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2014, 2, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbison, W. Handbook of Refractory Practice; Harbison-walker refractories Co.: Mount Union, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Q. Diesel Engine System Design; Woodhead Publishing in Mechanical Engineering: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Shi, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. Phase transformation and properties of high-quality mullite ceramics synthesized using desert drift sands as raw materials. Mater. Lett. 2018, 221, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahnicka-Goremikina, L.; Svinka, R.; Svinka, V. Influence of ZrO2 and WO3 doping additives on the thermal properties of porous mullite ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 16873–16879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peretz, I.; Bradt, R.C. Linear thermal expansion coefficients of mullite-matrix aluminosilicate refractory bodies. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1983, 66, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Jang, B.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, K.S. Effect of Yb2SiO5 addition on the physical and mechanical properties of sintered mullite ceramic as an environmental barrier coating material. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 15203–15208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
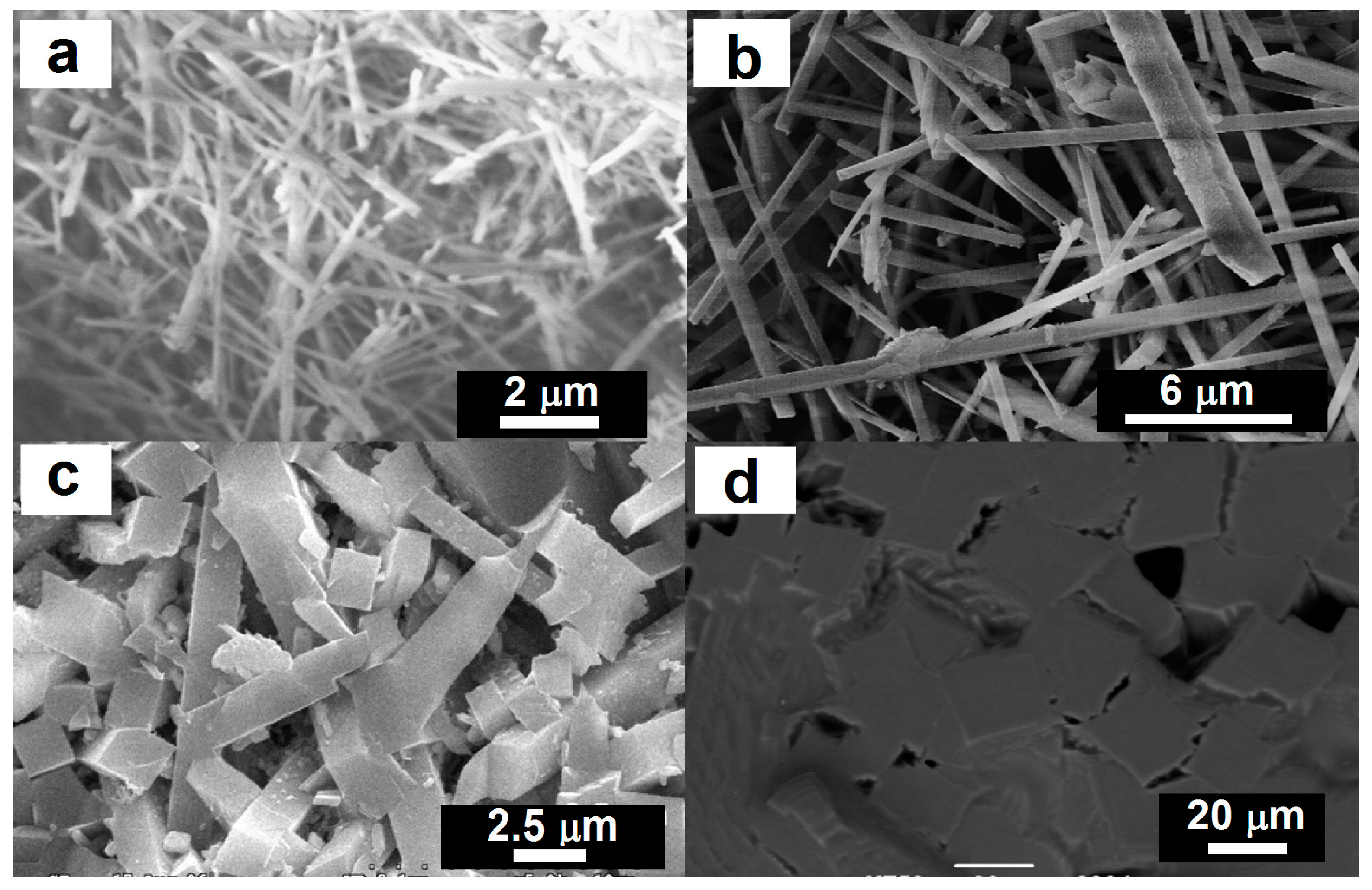
| Ref. | Ceramics Product | Industrial Wastes Type | Sintering Temperature (°C) | Processing Method | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [5] | mullite | aluminum sludge + ceramic raw materials | 1450–1650 | mixing, pressing | 2008 |
| [6] | mullite | aluminum sludge + ceramic raw materials | 1250–1650 | mixing, pressing | 2005 |
| [7] | Glass-ceramics | aluminum sludge + waste glasses | 1650 | mixing | 2013 |
| [8] | mullite/zirconia | aluminum dross + zircon | 1400–1500 | mixing, pressing | 2009 |
| [9] | mullite | coal fly ash + Al2O3 | Plasma heating | mixing | 2009 |
| [10] | mullite | coal fly ash + Al2O3 | 1200–1600 | mixing, pressing | 2001 |
| [11] | porous mullite | coal fly ash + Al2O3 | 1300–1500 | freeze casting | 2010 |
| [12] | porous mullite | coal fly ash + Al2O3/Al(OH)3 | 1400–1600 | mixing, molding | 2012 |
| [13] | porous mullite | coal fly ash + Al(OH)3 | 1000–1500 | mixing, pressing | 2008 |
| [14] | mullite whiskers | coal fly ash + Al2(SO4)3∙18H2O | 800–1200 | mixing, leaching | 2011 |
| [15] | mullite whiskers | coal fly ash + Ammonium aluminum sulfate hydrate | 1300 | mixing, leaching | 2007 |
| [16] | mullite | coal fly ash + aluminum dross | 1500 | mixing, pressing | 2019 |
| [17] | mullite | coal fly ash + bauxite | 1100–1500 | mixing, pressing | 2009 |
| [18] | porous mullite | coal fly ash + bauxite | 1200–1550 | mixing, pressing | 2009 |
| [19] | porous mullite | coal fly ash + bauxite | 1100–1500 | mixing, pressing | 2015 |
| [20] | porous mullite/corundum | coal fly ash + bauxite | 1100–1400 | mixing, pressing | 2015 |
| [21] | porous mullite | coal fly ash + bauxite | 1200–1500 | mixing, pressing | 2014 |
| [22] | mullite | coal fly ash + bauxite | Plasma heating | mixing | 2011 |
| [23] | mullite | coal fly ash + bauxite | 1300–1550 | mixing, pressing | 2011 |
| [24] | porous mullite | coal fly ash + bauxite | 1300–1500 | mixing, pressing | 2010 |
| [25] | mullite | coal fly ash + bauxite | 1000–1600 | mixing, pressing | 2008 |
| [26] | mullite/alumina | coal fly ash + bauxite | 1000–1200 | mixing, pressing | 2008 |
| [27] | Glass ceramics | coal fly ash | 1050–1500 | mixing | 2011 |
| [28] | mullite | coal fly ash | 1300–1600 | mixing, molding | 2010 |
| [29] | mullite | coal fly ash | 1200–1600 | leaching, molding | 2015 |
| [30] | Glass ceramics | slate waste | 1150–1170 | pressing | 2003 |
| [31] | mullite | slate waste | 1100 | slip casting | 2004 |
| [32] | mullite | slate waste + Al2O3 | 1250–1475 | mixing, pressing | 2008 |
| [33] | mullite | slate waste + Al2O3 | 1150–1250 | mixing, pressing | 2002 |
| [34] | mullite | slate waste + aluminum sludge | 1170–1300 | mixing, pressing | 2004 |
| [35] | mullite | schist waste | 1000–1200 | pressing | 1999 |
| [36] | mullite | kaolin waste + Al2O3 | 1400–1600 | mixing, pressing | 2012 |
| [37] | mullite | kaolin waste + Al(OH)3 | 1300–1600 | mixing, pressing | 2017 |
| [38] | mullite | rice husk silica + Al(NO3)3∙9H2O | 1150–1350 | sol-gel | 2014 |
| [39] | mullite | rice husk silica + Al2O3 | 1100–1600 | mixing, pressing | 2016 |
| [40] | mullite | sago waste + Al2O3 | 1400–1700 | Sol-gel, mixing, pressing | 2015 |
| [41] | mullite/cordierite | waste silica + ball clay + Al2O3 | 1350–1450 | mixing, pressing | 2012 |
| Ref. | Ceramics Product | Industrial Wastes Type | Additives | Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [7] | Glass ceramics | Aluminum sludge + waste glasses | CaF2, H3BO3 | reduced sintering temperature |
| [10] | mullite | coal fly ash + Al2O3 | 3Y-PSZ | increased densification |
| [11] | porous mullite | Coal fly ash + Al2O3 | Y2O3-doped ZrO2 (3YZ) | increased densification |
| [12] | porous mullite | Coal fly ash + Al2O3/Al(OH)3 | AlF3 | assisted anisotropic mullite growth |
| [14] | mullite whiskers | Coal fly ash + aluminum sulfate anhydrous | Na2SO4 | reduced sintering temperature, assisted anisotropic mullite growth |
| [15] | mullite whiskers | Coal fly ash + Ammonium aluminum sulfate hydrate | NaH2PO4·2H2O | assisted anisotropic mullite growth |
| [17] | mullite | Coal fly ash + bauxite | V2O5 | increased densification |
| [19] | porous mullite | Coal fly ash + bauxite | AlF3, MoO3 | reduced sintering temperature |
| [20] | porous mullite | Coal fly ash + bauxite | AlF3, MoO3 | reduced sintering temperature |
| [21] | porous mullite | Coal fly ash + bauxite | AlF3, V2O5 | assisted anisotropic mullite growth |
| [23] | mullite | Coal fly ash + bauxite | MgO | assisted anisotropic mullite growth |
| [24] | porous mullite | Coal fly ash + bauxite | TiO2 | reduced sintering temperature |
| Ref. | Ceramics Product | Sintering Temp. (°C) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Flexural Strength(MPa)/Type | Fracture Strength (MPa) | Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [10] | mullite | 1500 | - | 169/4-point | 395 | - |
| [17] | mullite | 1500 | - | 108/3-point | - | 1.42 |
| [25] | Mullite | 1400 | - | 71/3-point | - | 40 |
| 1500 | - | 104/3-point | - | 26 | ||
| 1600 | - | 186/3-point | - | 6 | ||
| [28] | Mullite | 1300 | - | 34/3-point | - | 39.6 |
| 1400 | - | 45/3-point | - | 32.7 | ||
| 1500 | - | 70/3-point | - | 16.7 | ||
| [29] | Mullite | 1400 | 80 | - | - | 27 |
| 1500 | 104 | - | - | 13 | ||
| 1600 | 169 | - | - | 1 | ||
| [33] | mullite | 1250 | - | 43/3-point | - | - |
| [11] | mullite | 1500 | 23.2 | - | - | 66.9 |
| [12] | mullite | 1600 | - | 75/3-point | - | 45 |
| [18] | Mullite | 1450 | - | 45/3-point | - | 44 |
| 1500 | - | 52/3-point | 43 | |||
| 1550 | - | 66/3-point | - | 40 | ||
| [23] | mullite | 1500 | - | 35/3-point | - | 42 |
| [24] | mullite | 1450 | - | 28/3-point | - | 46 |
| [5] | mullite-containing glass ceramics | 1650 | - | 59/3-point | - | - |
| [30] | mullite-containing glass ceramics | 1170 | - | 92/3-point | - | - |
| [35] | mullite-containing glass ceramics | 1100 | - | 45/3-point | - | - |
| 1170 | - | 95/3-point | - | - | ||
| 1200 | - | 80/3-point | - | - | ||
| [19] | mullite/corundum composite | 1200 | - | 80/Biaxial | - | 48 |
| 1300 | - | 105/Biaxial | - | 46 | ||
| 1400 | - | 145/Biaxial | - | 42 | ||
| 1500 | - | 158/Biaxial | - | 30 | ||
| [20] | mullite/corundum composite | 1200 | - | 61/3-point | - | - |
| 1300 | - | 68/3-point | - | - | ||
| [21] | mullite/corundum composite | 1200 | - | 48/Biaxial | - | 33 |
| 1300 | - | 65/Biaxial | - | 38 | ||
| 1400 | - | 70/Biaxial | - | 40 | ||
| 1500 | - | 115/Biaxial | - | 23 | ||
| [34] | mullite/corundum composite | 1250 | - | 67/3-point | - | - |
| 1270 | - | 113/3-point | - | - | ||
| 1300 | - | 126/3-point | - | - | ||
| [41] | mullite/cordierite composite | 1400 | 180 | - | - | 30 |
| Ref. | Raw Materials | Type of Raw Materials | Ceramics Product | CTE (× 10−6 °C−1)/Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [5] | aluminum sludge + ceramic raw materials | Industrial wastes | mullite | 5.6/20–800 °C |
| [16] | coal fly ash + Al dross | Industrial wastes | mullite | 5.8/30–1000 °C |
| [18] | coal fly ash + bauxite | Industrial wastes | porous mullite | 6.1/26–1000 °C |
| [23] | coal fly ash + bauxite | Industrial wastes | mullite | 5.9/26–1550 °C |
| [46] | drift sand + alumina | minerals | mullite | 5.5/30–900 °C |
| [47] | alumina + silica + kaolin | minerals | porous mullite | 5.6/200–900 °C |
| [48] | ball clay + alumina + kaolin | minerals | Mullite/alumina | 5.0–5.7/400–1200 °C |
| [49] | commercial mullite (Duramul 325F) | Laboratory grade chemicals | Porous mullite | 5.5/30–1200 °C |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choo, T.F.; Mohd Salleh, M.A.; Kok, K.Y.; Matori, K.A. A Review on Synthesis of Mullite Ceramics from Industrial Wastes. Recycling 2019, 4, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4030039
Choo TF, Mohd Salleh MA, Kok KY, Matori KA. A Review on Synthesis of Mullite Ceramics from Industrial Wastes. Recycling. 2019; 4(3):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4030039
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoo, Thye Foo, Mohamad Amran Mohd Salleh, Kuan Ying Kok, and Khamirul Amin Matori. 2019. "A Review on Synthesis of Mullite Ceramics from Industrial Wastes" Recycling 4, no. 3: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4030039
APA StyleChoo, T. F., Mohd Salleh, M. A., Kok, K. Y., & Matori, K. A. (2019). A Review on Synthesis of Mullite Ceramics from Industrial Wastes. Recycling, 4(3), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4030039





