Balancing the Performance and Environmental Concerns of Used Motor Oil as Rejuvenator in Asphalt Mixes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Material Properties
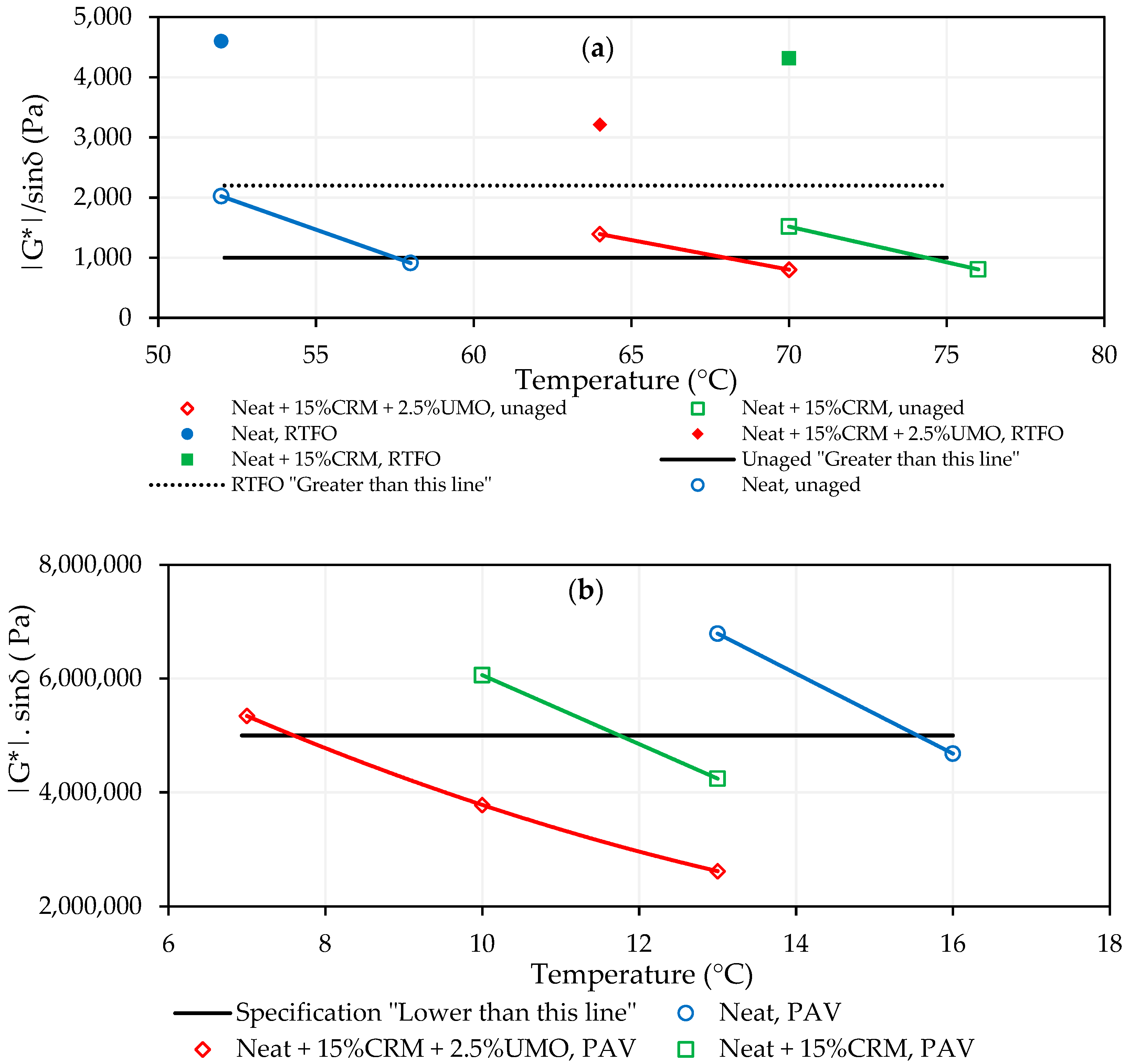
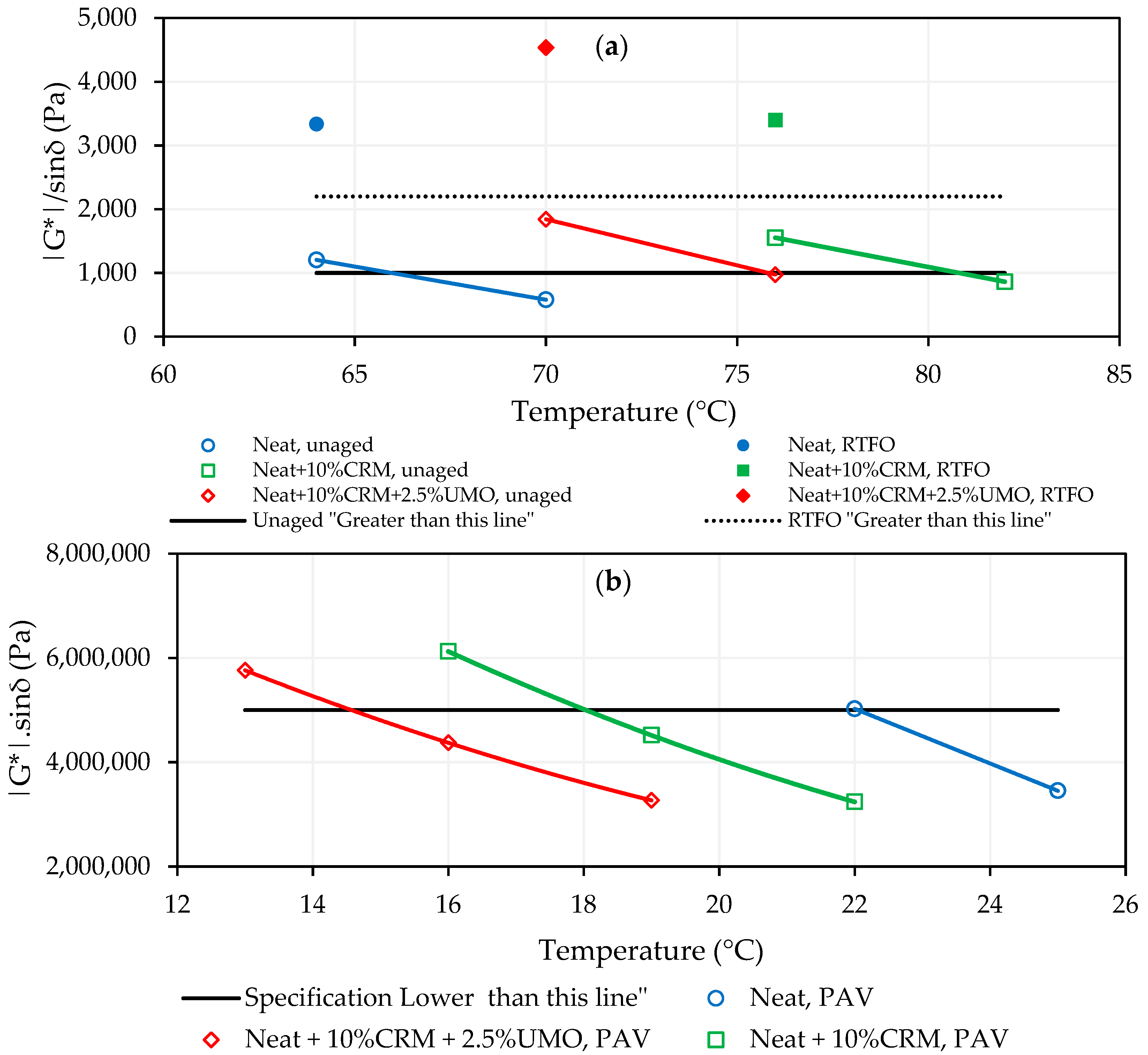
2.1.1. Neat and Modified Asphalt Binders’ PG Determination
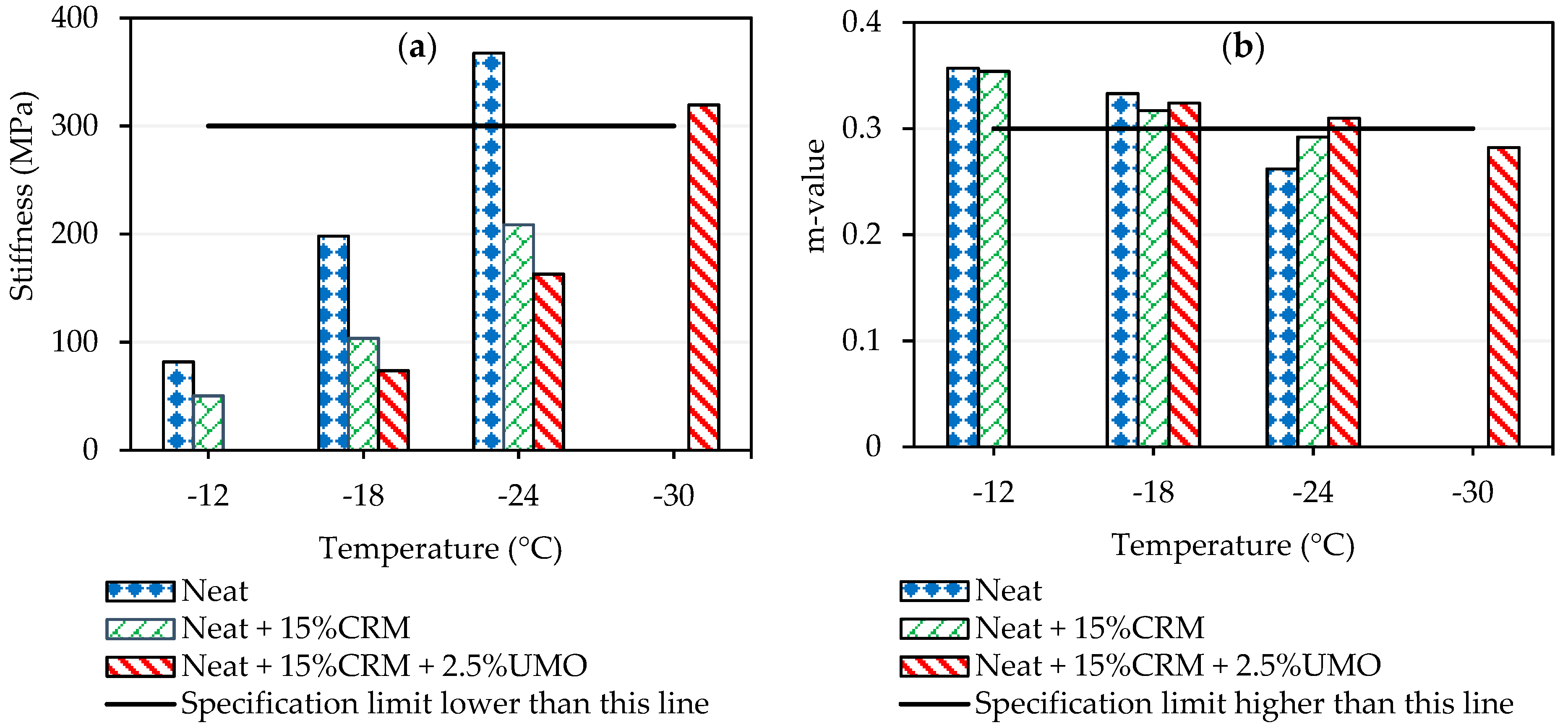
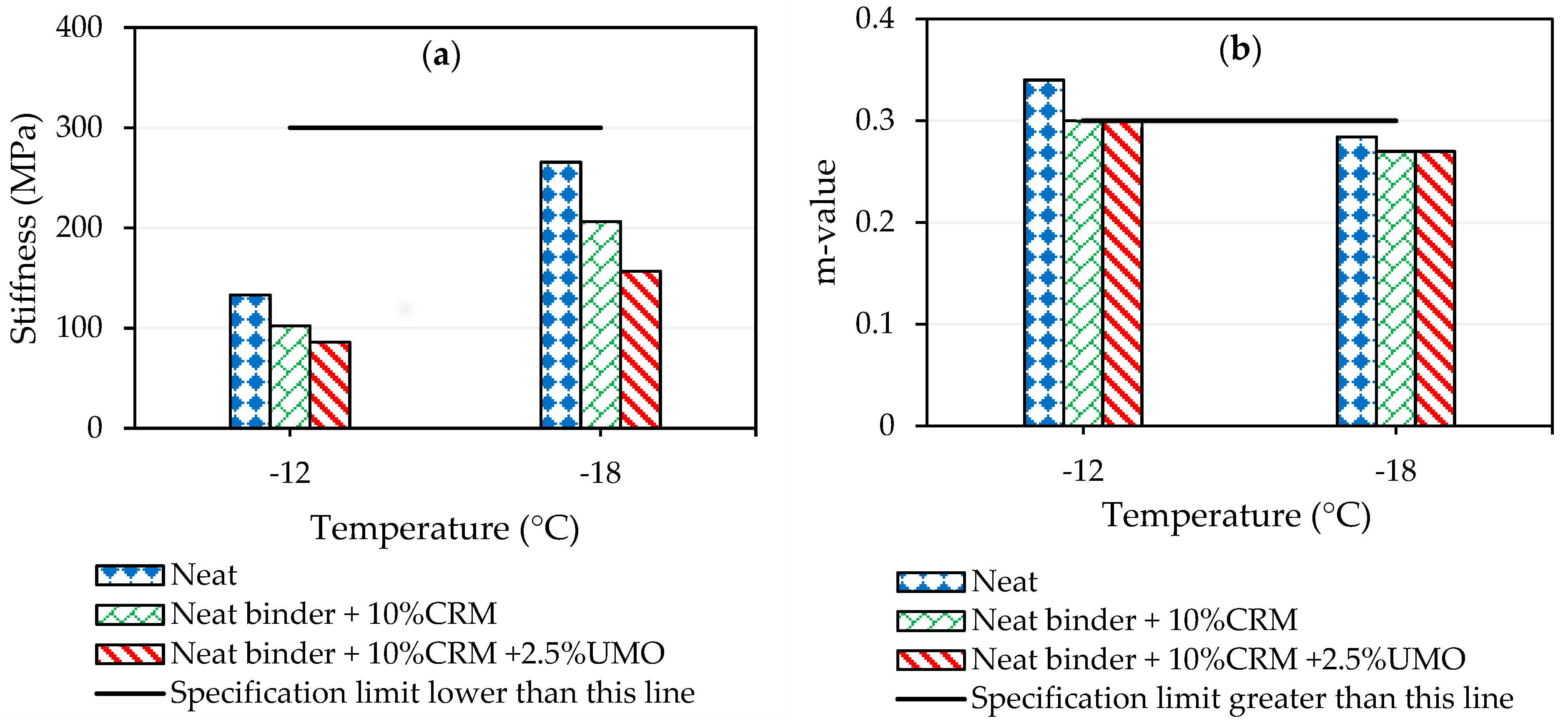
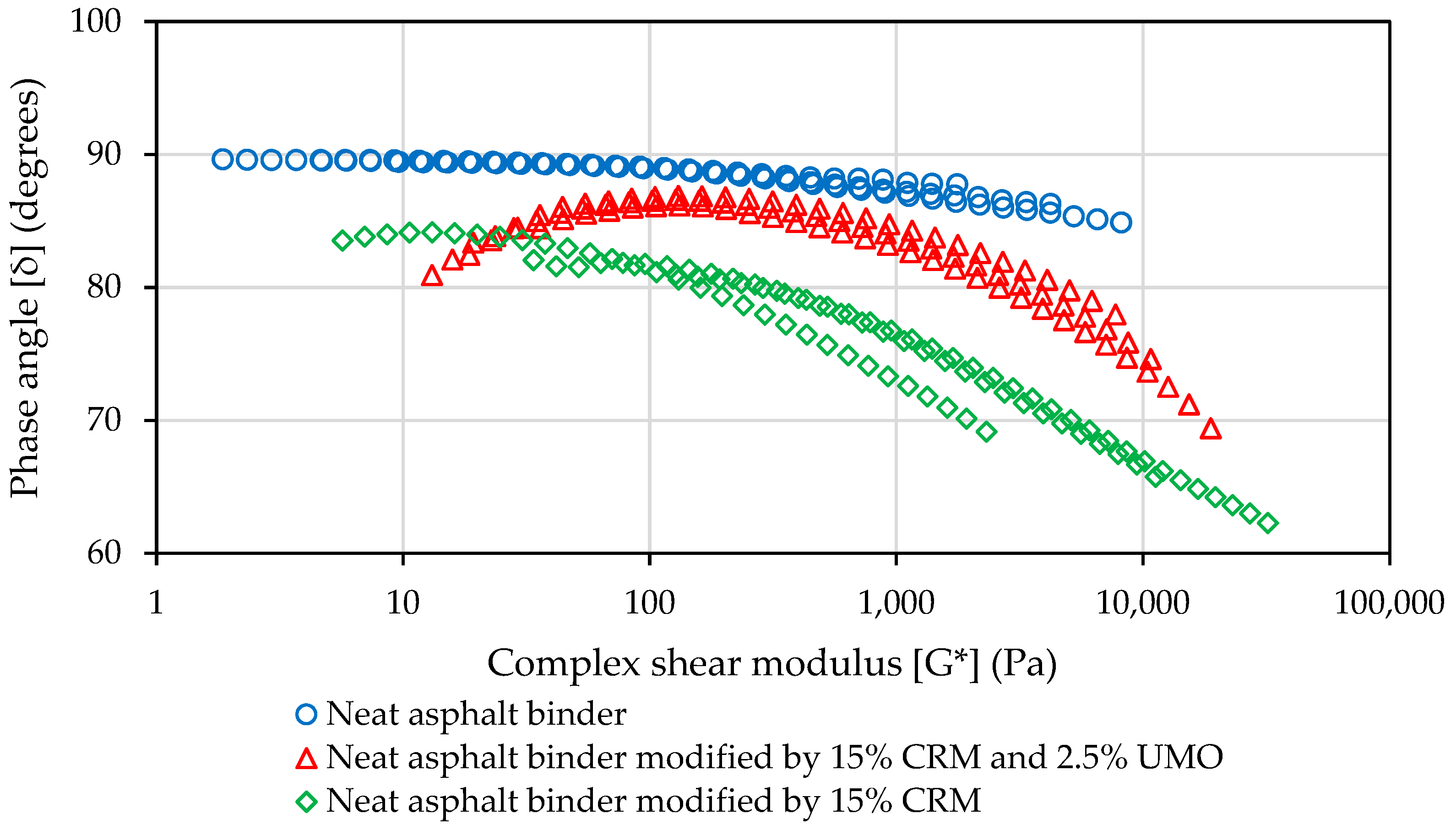
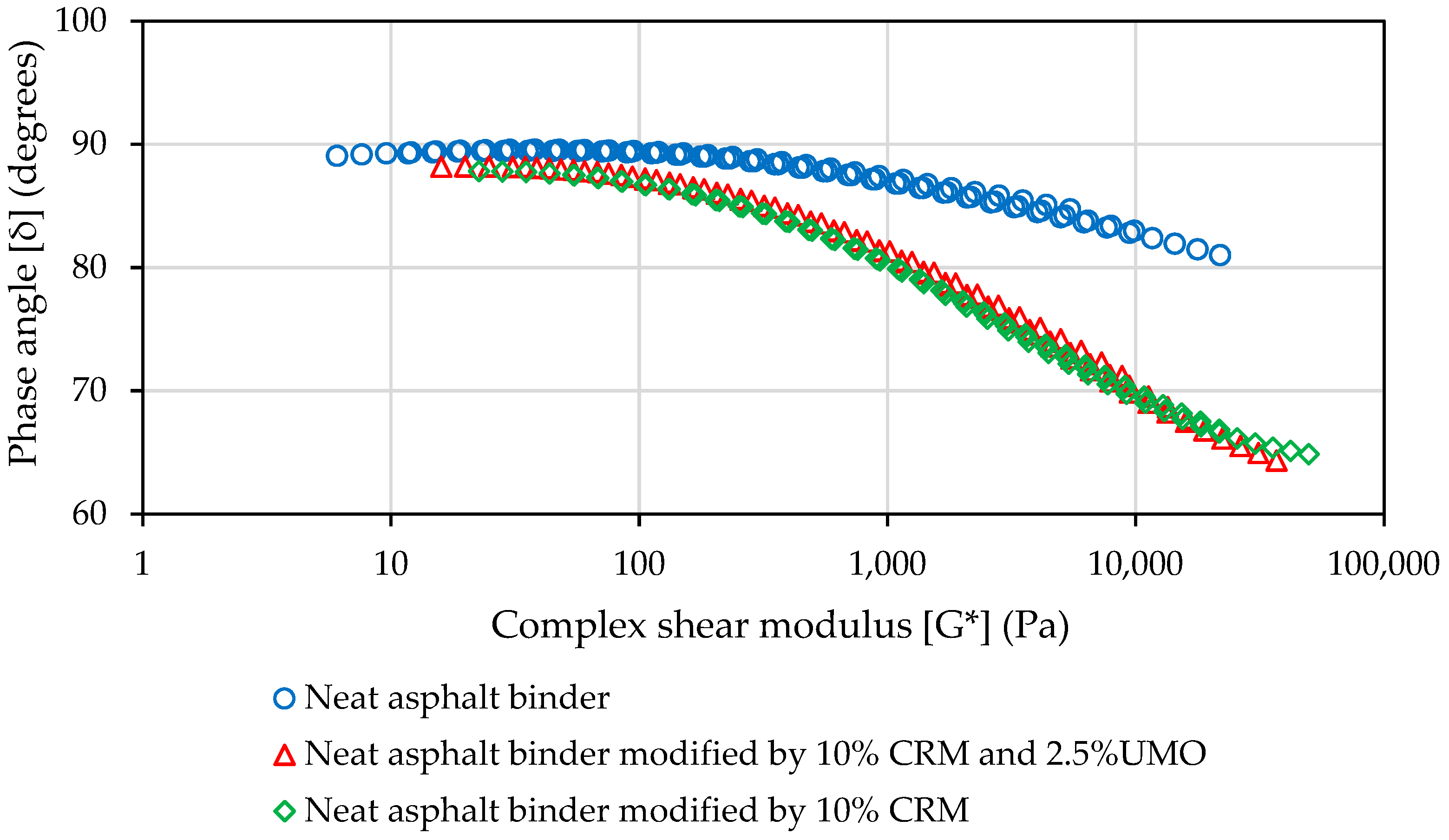
2.1.2. Evaluation of Neat and Modified Asphalt Binders’ Rheological Properties at High, Intermediate and Low Temperatures
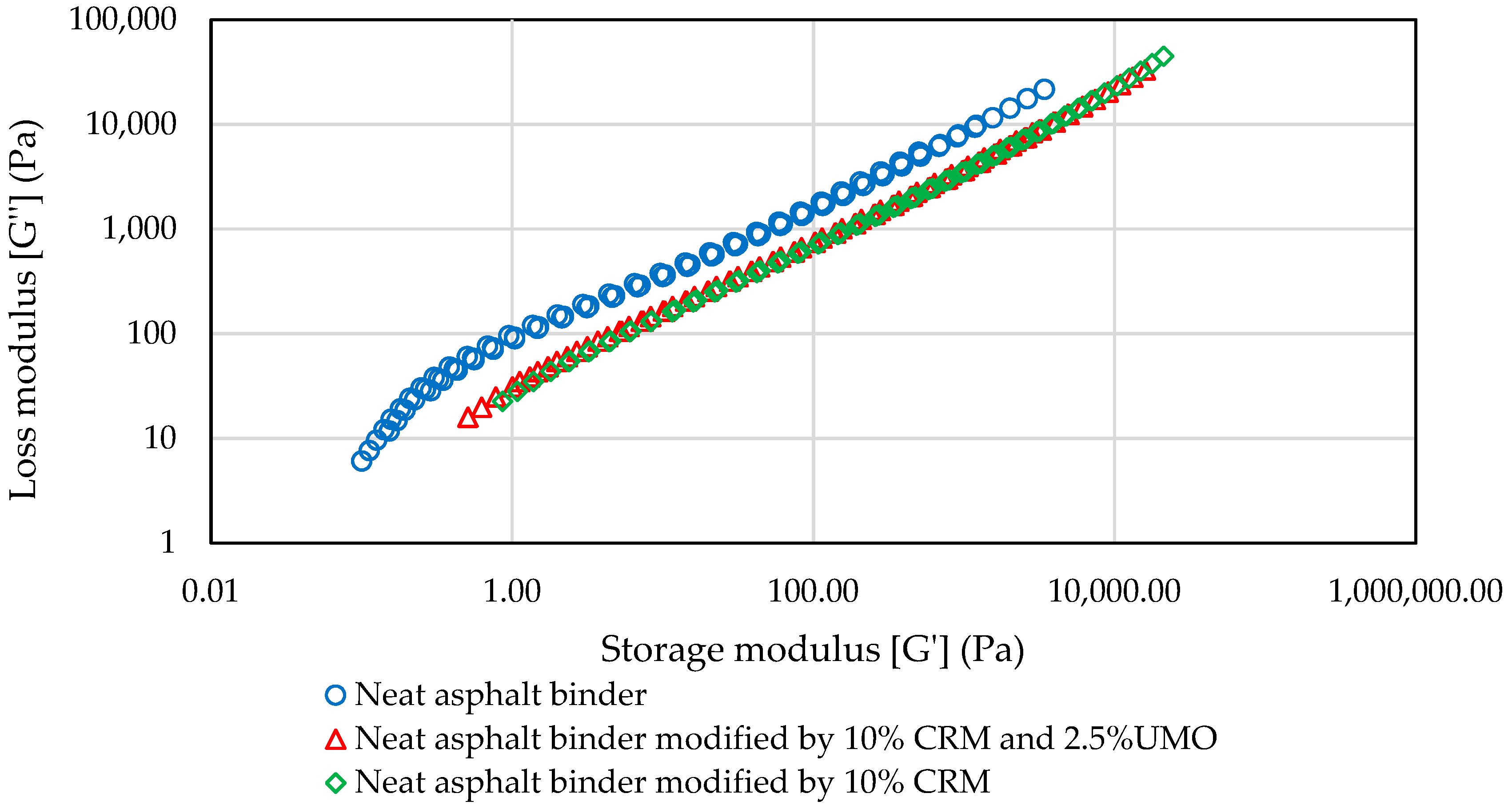
2.1.3. Frequency Sweep Test
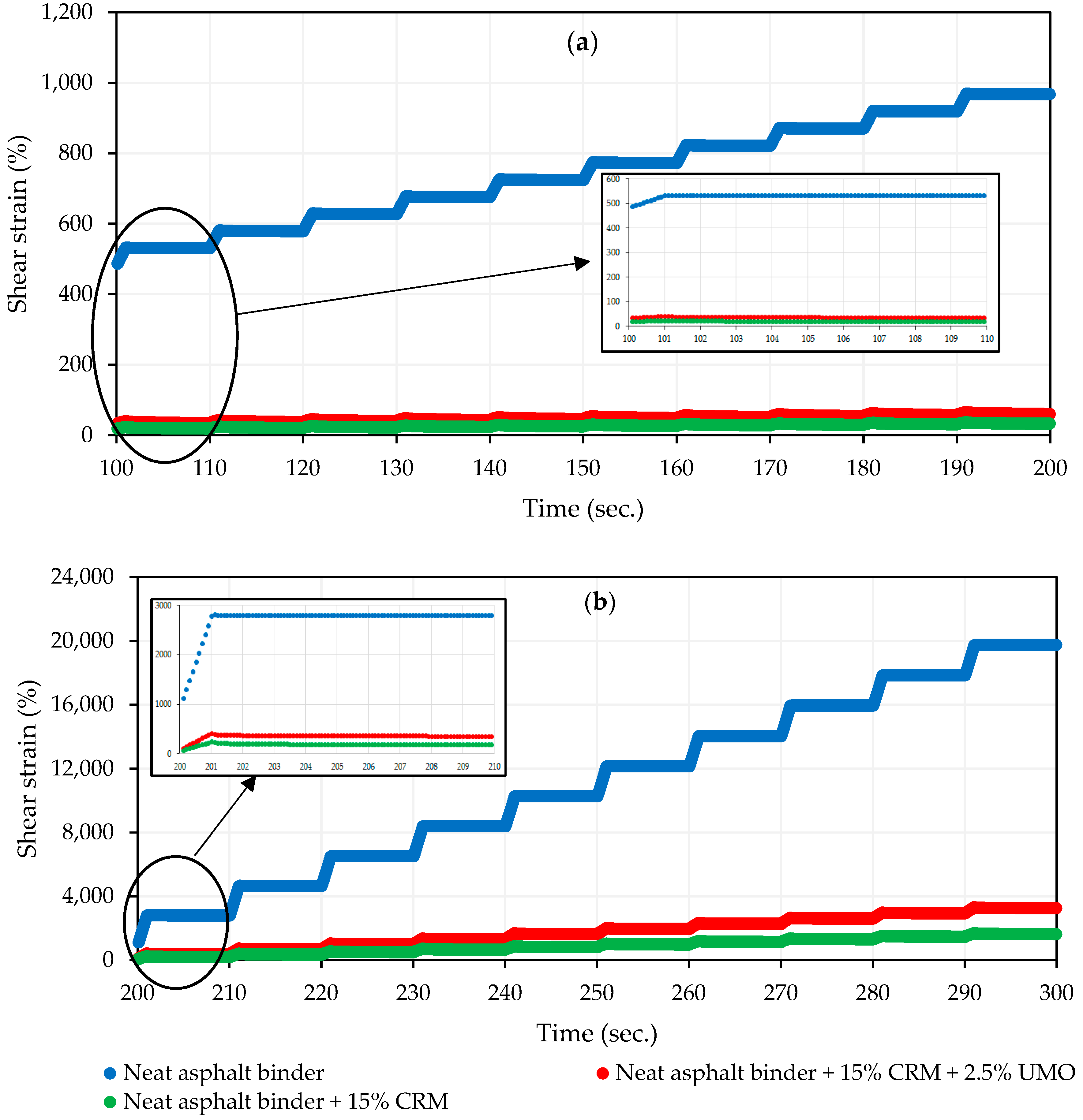
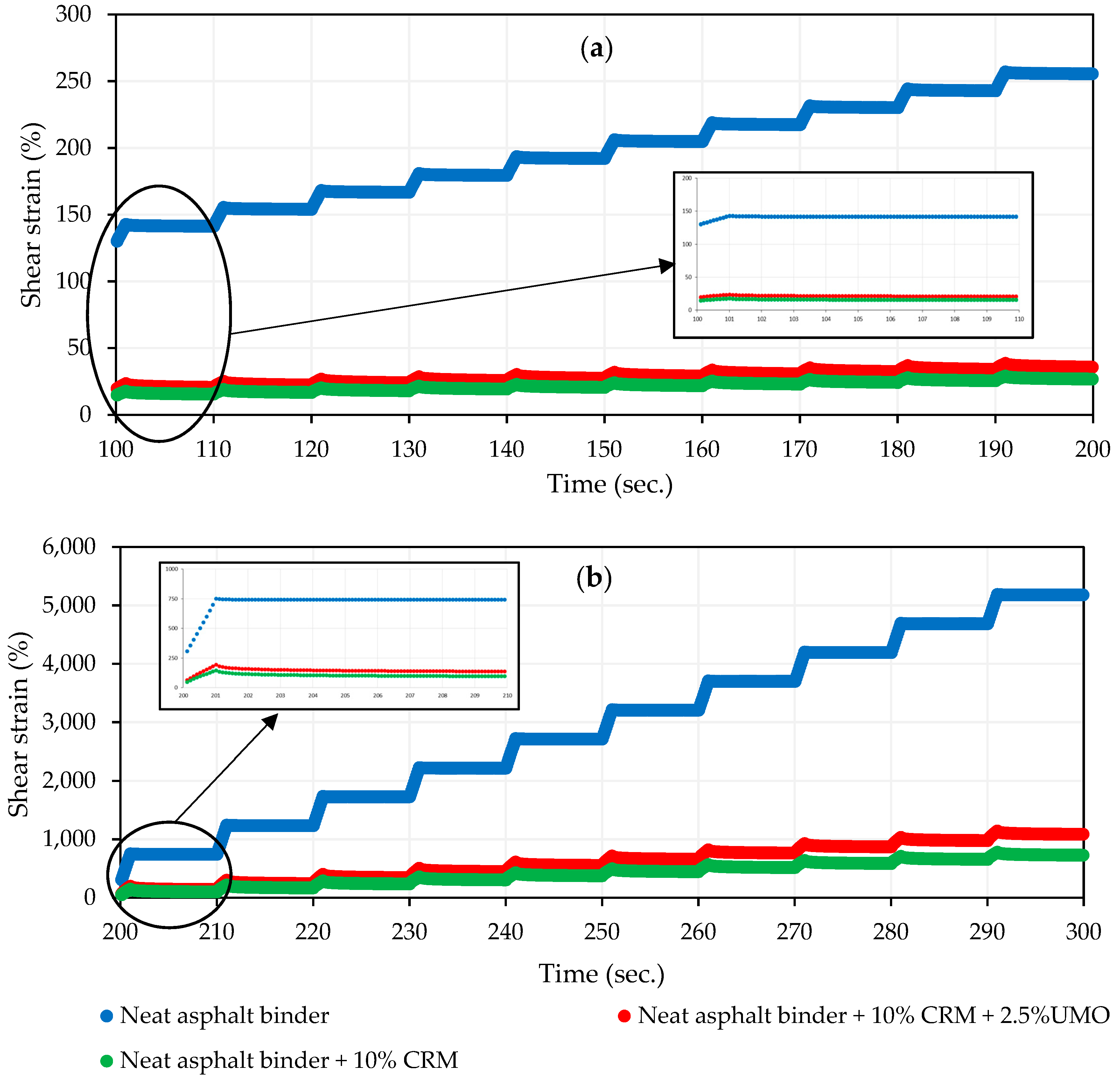
2.1.4. Multiple Stress Creep Recovery (MSCR) Test
- εr (0.1, N) = ;
- ε1: the adjusted strain value at the end of the creep portion (after 1 sec.) of each cycle;
- ε1 = εc − ε0;
- ε0: initial strain value at the beginning of the creep portion of each cycle;
- εc: strain value at the end of the creep portion (after 1 sec.) of each cycle;
- If εr (0.1, N) < 0 then record εr (0.1, N) as zero;
- ε10: the adjusted strain value at the end of the recovery portion (after 10 sec.) of each cycle;
- ε10 = εr − ε0; and
- εr: strain value at the end of the recovery portion (after 10 sec.) of each cycle.
- εr (3.2, N) = ;
- ε1 and ε10 are the same laws for 0.1 KPa but they are calculated at 3.2 KPa shear stress; and
- If εr (3.2, N) < 0 then record εr (3.2, N) as zero.
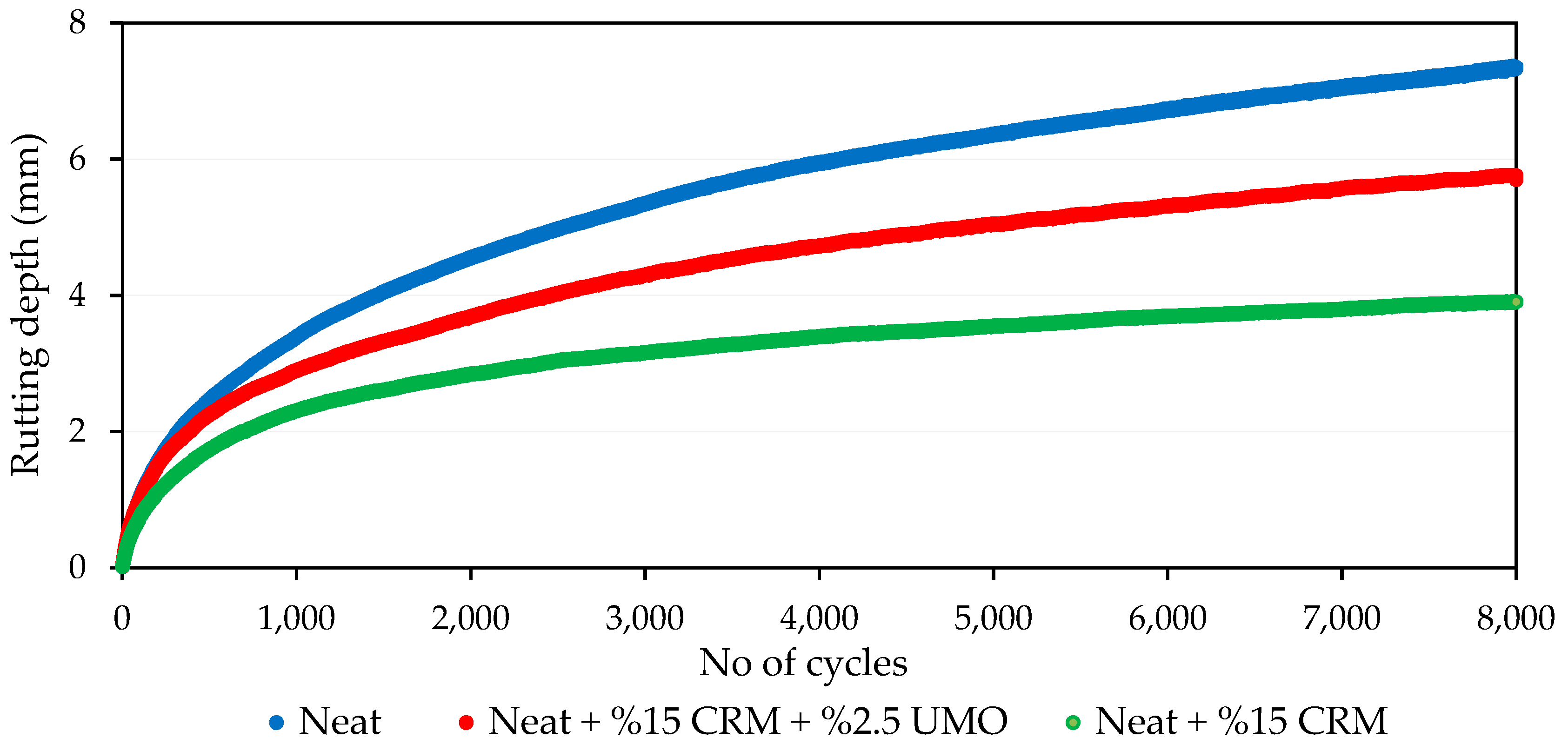
2.1.5. HMA Rutting Evaluation Using APA
2.2. Environmental Results
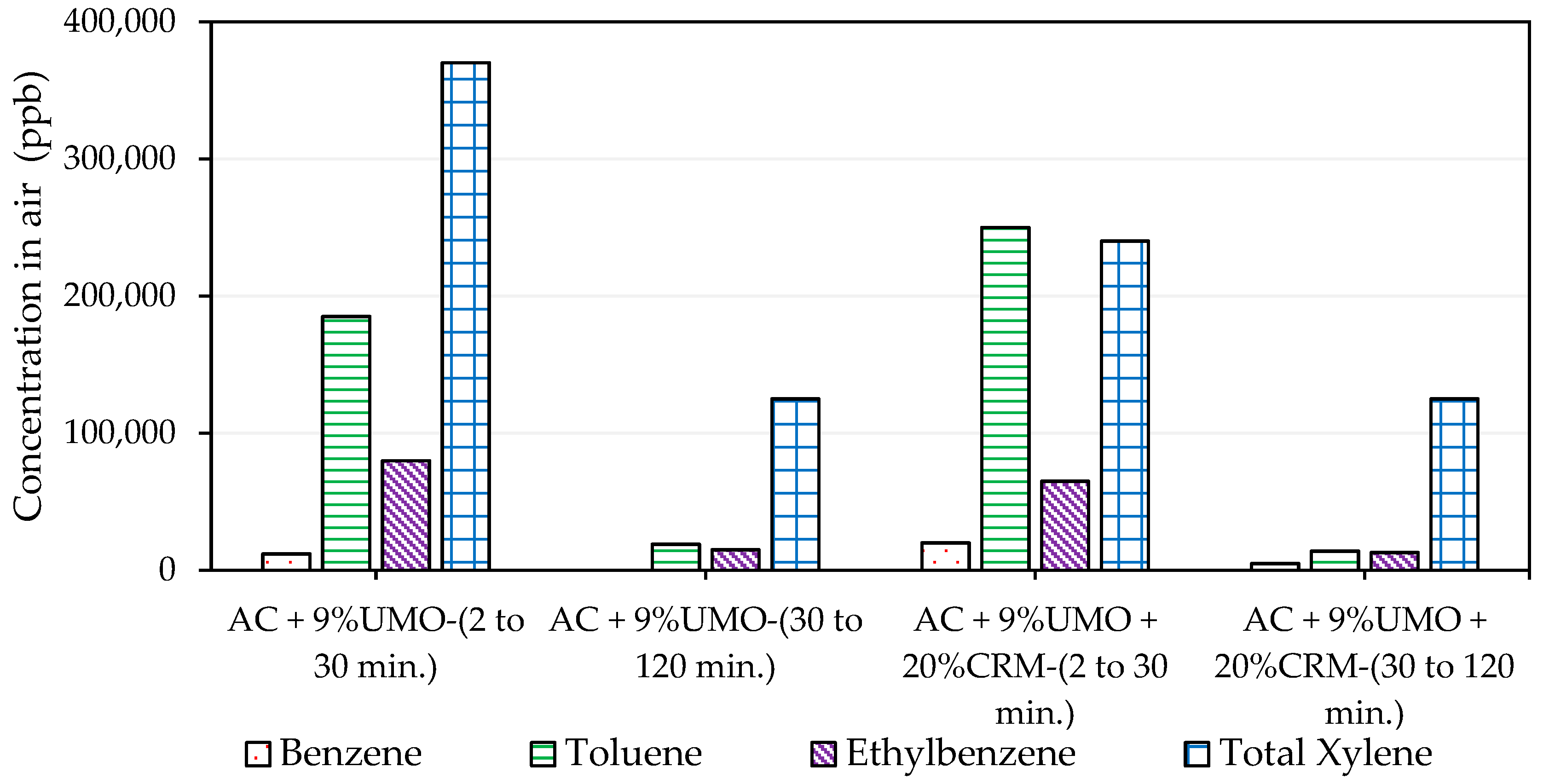
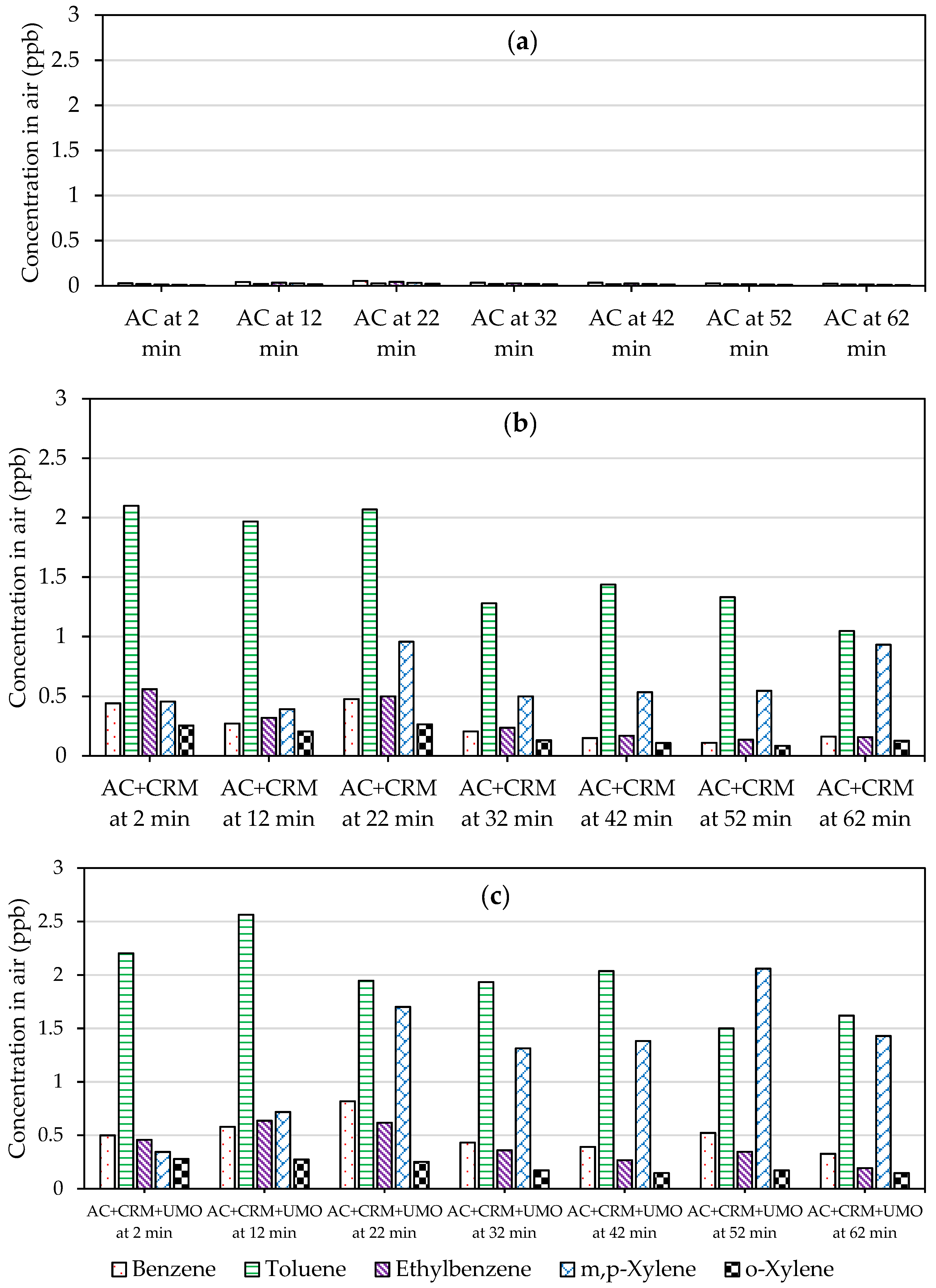
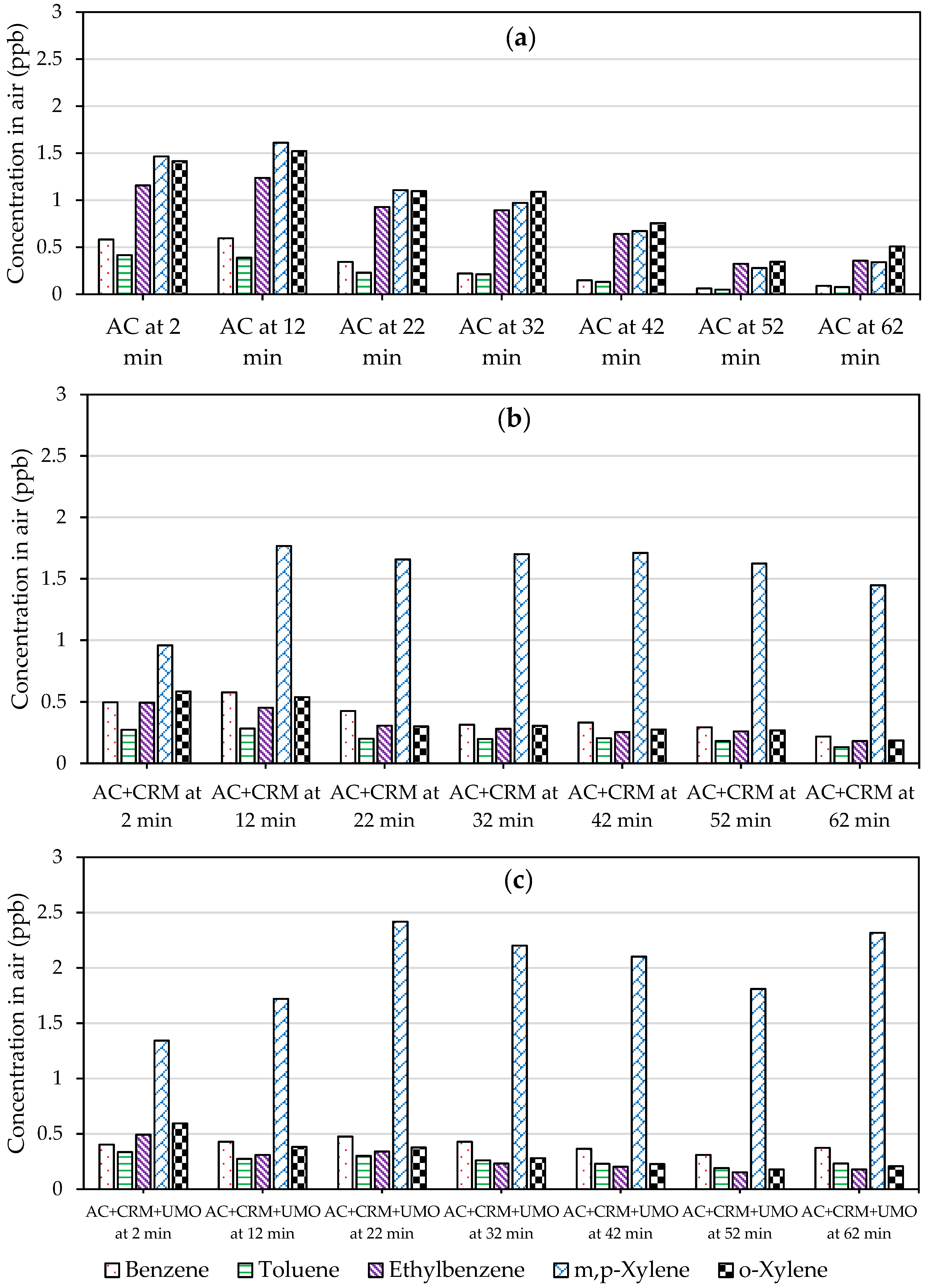
2.2.1. Portable Gas Chromatography Results
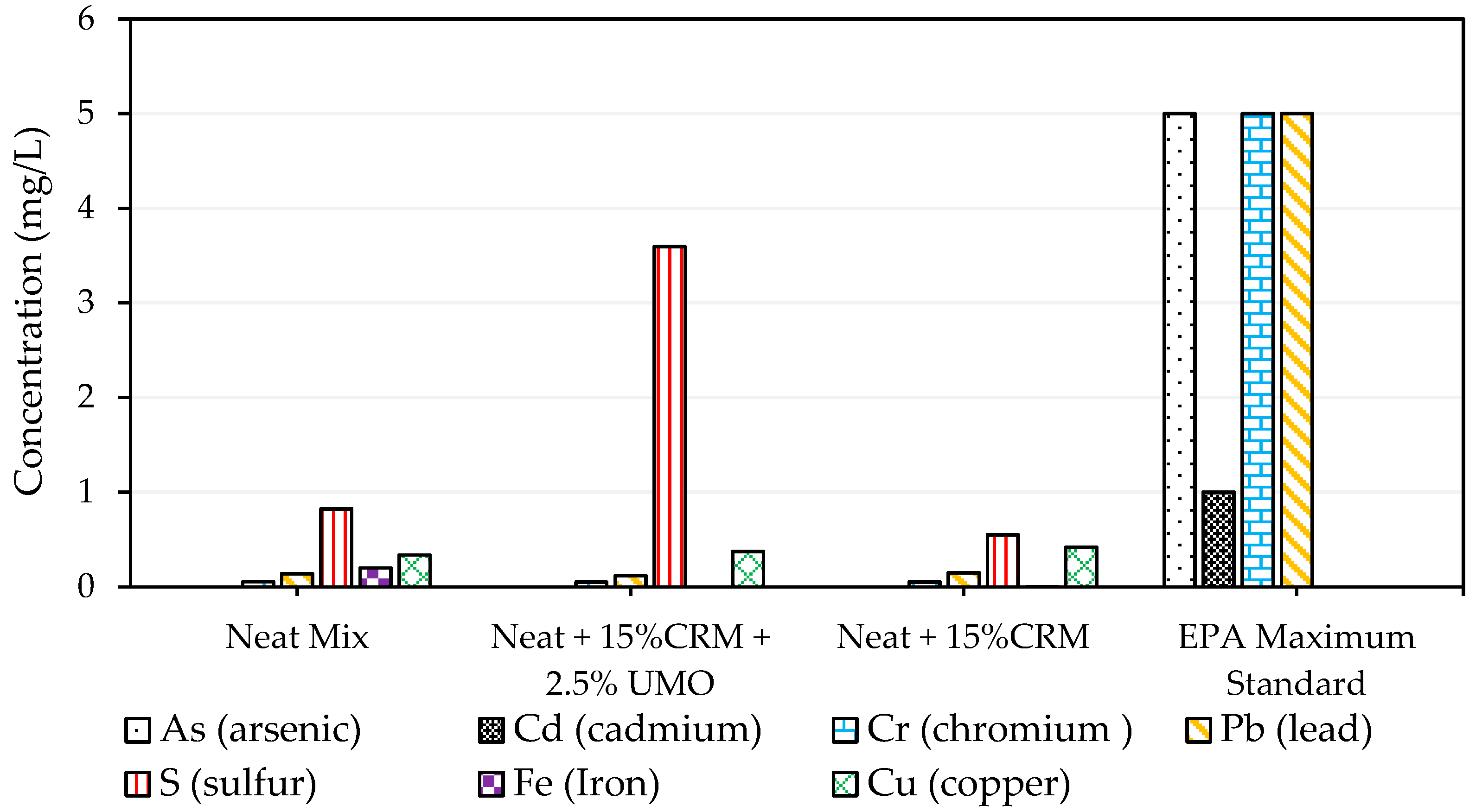
2.2.2. TCLP Test Results
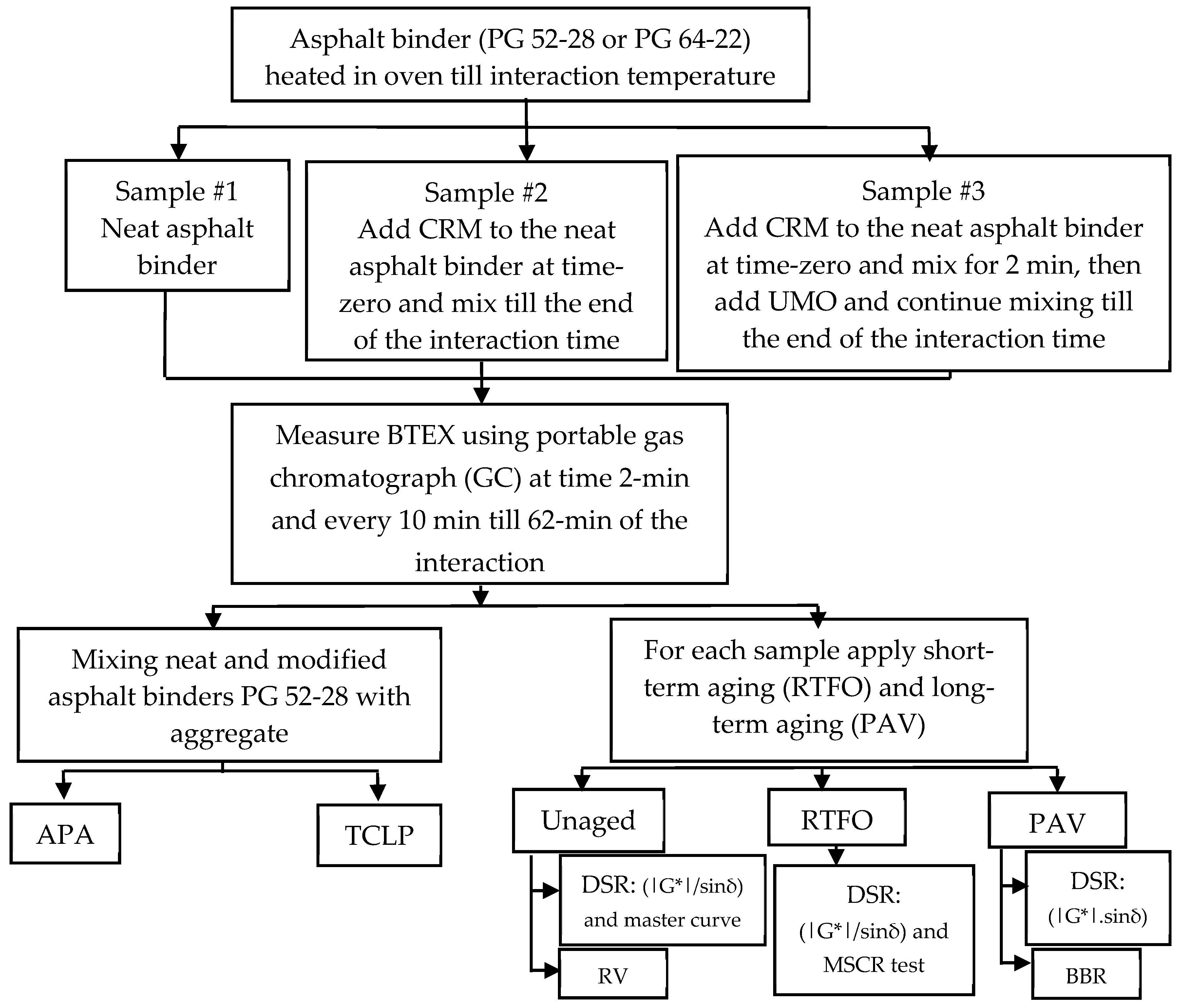
3. Materials and Experimental Procedures
3.1. Raw Materials
3.2. CRMA-UMO Interactions
3.3. Experimental Design
3.3.1. Dynamic Shear Rheometer
3.3.2. Viscosity of Asphalt Binder
3.3.3. Short-Term Aging (RTFO)
3.3.4. Long-Term Aging (PAV)
3.3.5. Bending Beam Rheometer
3.3.6. Performance of Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) at High Temperature Degrees
3.3.7. Gas Chromatography
3.3.8. Measuring Toxicity Leaching Characteristics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdelrahman, M.; Ragab, M.; Bergerson, D. Effect of Used Motor Oil on the Macro and Micromechanical Properties of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt. Int. J. Waste Res. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, M.; Abdelrahman, M. Investigation of the Physical and Molecular Properties of Asphalt Binders Processed with Used Motor Oils. J. Mater. 2015, 2015, 632534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.; Costa, L.; Silva, H.; Oliveira, J. Effect of Incorporating Different Waste Materials in Bitumen. Ciênc. Tecnol. Mater. 2017, 29, e204–e209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrington, P.R.; Dravitzki, V.K.; Wood, C.W.B.; Patrick, J.E. Waste Oil Distillation Bottoms as Bitumen Extenders. Road Transport Res. 1993, 2, 56–68. [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva, A.; Ho, S.; Zanzotto, L. Asphalt Modification with Used Lubricating Oil. Can. J. Civil Eng. 2008, 35, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Huang, B.; Bowers, B.F.; Zhao, S. Infrared Spectra and Rheological Properties of Asphalt Cement Containing Waste Engine Oil Residues. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 50, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.S.; Wu, T.L.; Chang, C.W.; Chou, B.Y. Effect of Recycling Agents on Aged Asphalt Binders and Reclaimed Asphalt Concrete. Mater. Struct. 2011, 44, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhan, M.N.; Suja, F.; Ismail, A.; Rahmat, R.A.O.K. The Effects of Used Cylinder Oil on Asphalt Mixes. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2009, 28, 398–411. [Google Scholar]
- DeDene, C.D. Investigation of Using Waste Engine Oil Blended with Reclaimed Asphalt Materials to Improve Pavement Recyclability. Master’s Thesis, Michigan Technological University, Houghton, Michigan, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Paliukaite, M.; Assuras, M.; Hesp, S.A.M. Effect of Recycled Engine Oil Bottoms on the Ductile Failure Properties of Straight and Polymer-Modified Asphalt Cements. Constr. Build Mater. 2016, 126, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.A.; Lenz, I.R.; Than, C.T.; Glover, C.J. Investigation of the Effects of Recycled Engine Oil Bottoms on Asphalt Field Performance Following an Oxidation Modeling Approach. Petrol. Sci. Tech. 2016, 34, 1768–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.; Peralta, J.; Oliverira, J.R.M.; Williams, R.C.; Silva, H.M.R.D. Improving Asphalt Mixture Performance by Partially Replacing Bitumen with Waste Motor Oil and Elastomer Modifiers. Appl. Sci. J. 2017, 7, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Huang, B.; Moore, J.A.; Zhao, S. Influence of Waste Engine Oil on Asphalt Mixtures Containing Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement. J. Mater. Civil Eng. 2015, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Duhalt, R. Environmental Impact of Used Motor Oil. Sci. Total Environ. 1989, 79, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregerson, D.; Abdelrahman, M.; Ragab, M. Environmental study of thr release of BTEX from asphalt modified with used motor oil and crumb rubber modifier. Int. J. Waste Res. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasetto, M.; Baliello, A.; Giacomello, G.; Pasquini, E. Rheological Characterization of Warm-Modified Asphalt Mastics Containing Electric Arc Furnace Steel Slags. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 9535940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airey, G.D. Rheological Characteristics of Polymer Modified and Aged Binder. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ashish, P.K.; Singh, D.; Bohm, S. Investigation on influence of nanoclay addition on rheological performance of asphalt binder. Road Mater. Pavement 2016, 18, 1007–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akisetty, C.K.; Gandhi, T.; Lee, S.-J.; Amirkhaniana, S.N. Analysis of rheological properties of rubberized binders containing warm asphalt additives. Can. J. Civil Eng. 2010, 37, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Shi, Q.; Chung, K.H.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, N.; Zhao, S.; Xu, C. Molecular Characterization of Sulfur Compounds in Venezuela Crude Oil and Its SARA Fractions by Electrospray Ionization Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 5089–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best Practices in Scrap Tires & Rubber Recycling: Ambient Versus Cryogenic Grinding, [Online]. Available online: www.asphaltrubber.org/ari/General.../Ambient_vs_Cryogenic_Grinding.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2018).

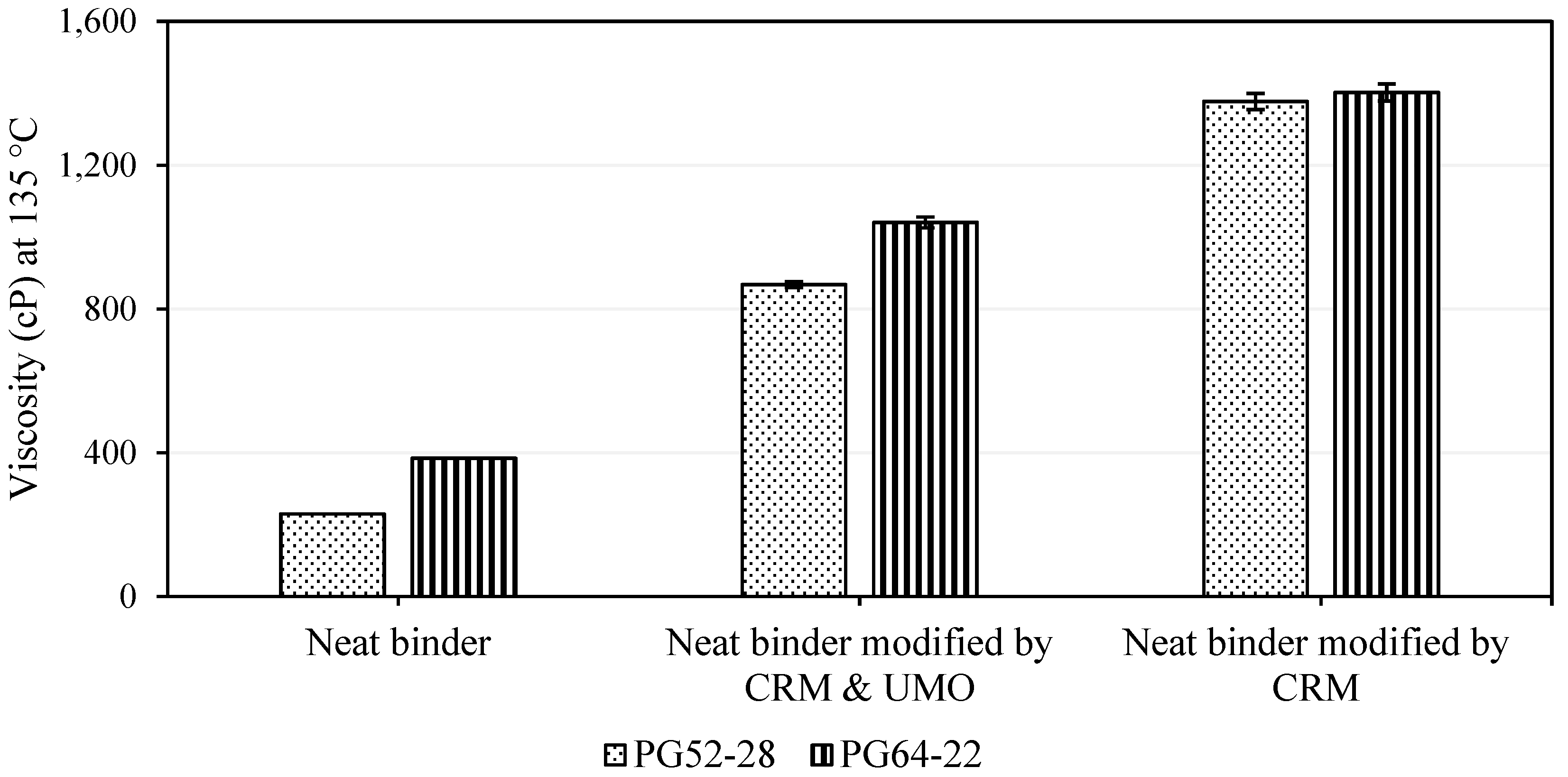
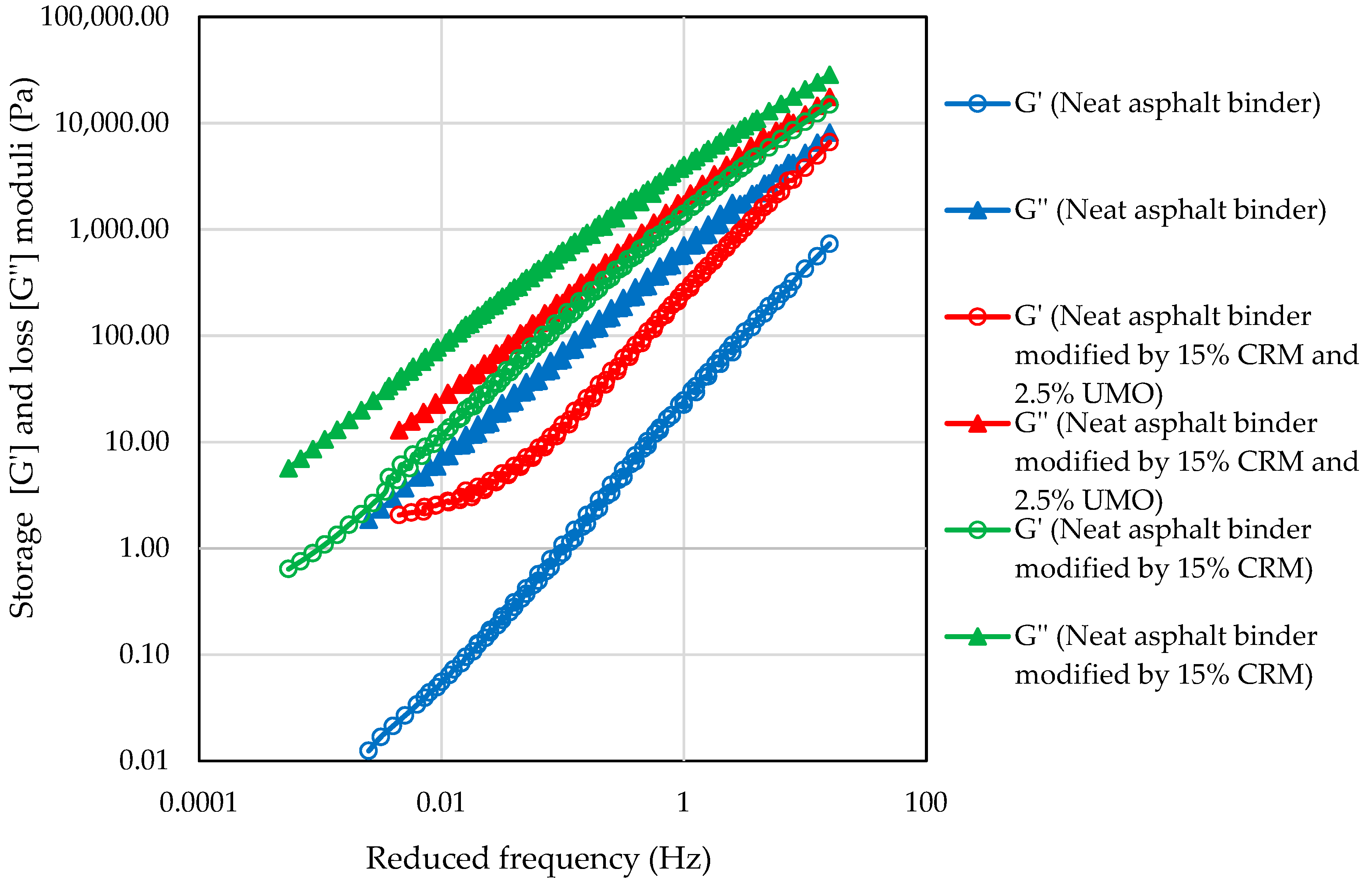
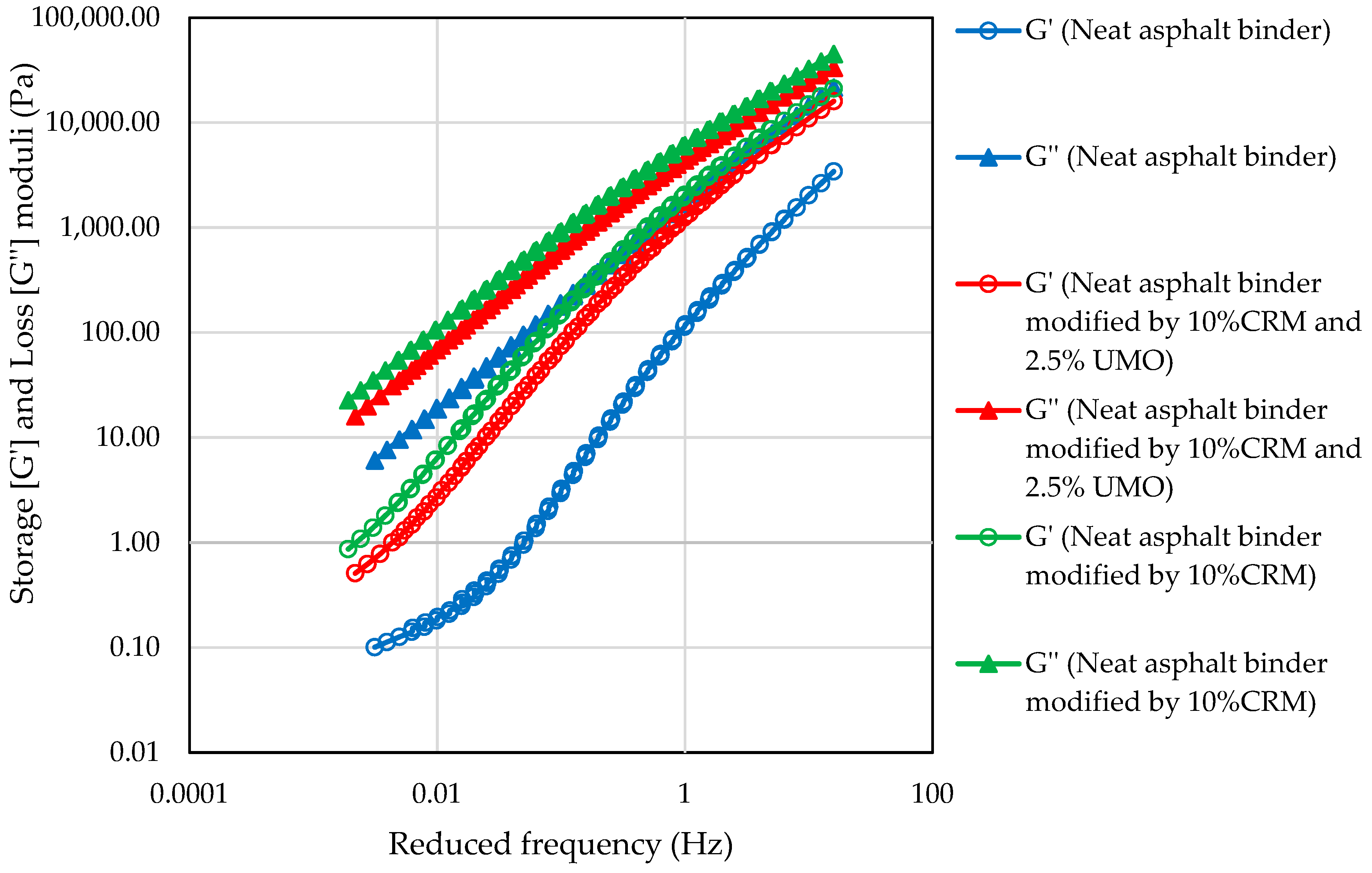
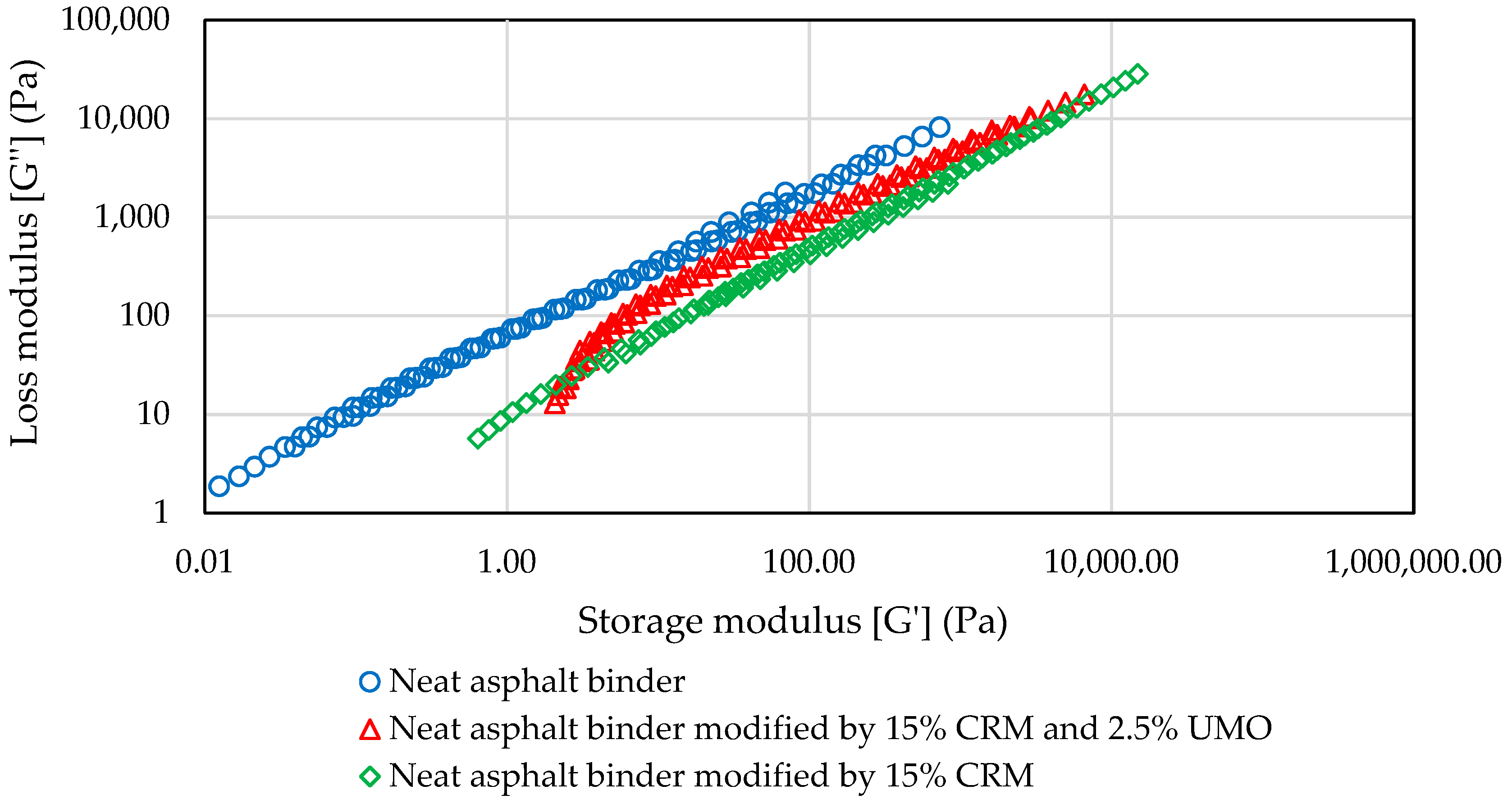

| Asphalt Binder | CRM % | UMO % | Interaction Temperature (°C) | Interaction Speed (Hz) | Testing | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Shear Rheometer [G* & δ] | Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry [BTEX] | |||||
| PG 64-22 | 20 | 9 | 190 | 30 | √ | √ |
| 20 | 0 | √ | ||||
| 0 | 9 | √ | √ | |||
| PG High Temperature Results Using DSR (Unaged and RTFO-aged Samples) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Name | PG 52-28 | PG 64-22 | ||||
| Temperature (°C) | |G*|/sinδ (Pa) | Temperature (°C) | |G*|/sinδ (Pa) | |||
| Neat asphalt binder, unaged | 52 58 | 2023 912 | 64 70 | 1205 580 | ||
| Neat asphalt binder, RTFO aged | 52 58 | 4601 2017 | 64 70 | 3336 1540 | ||
| Asphalt binder modified by CRM, unaged | 70 76 | 1518 806 | 76 82 | 1554 863 | ||
| Asphalt binder modified by CRM, RTFO aged | 70 76 | 3215 1891 | 76 82 | 3401 1839 | ||
| Asphalt binder modified by CRM and UMO, unaged | 64 70 | 1393 802 | 70 76 | 1843 975 | ||
| Asphalt binder modified by CRM and UMO, RTFO aged | 64 70 | 4317 2540 | 70 76 | 4538 2420 | ||
| PG Low Temperature Results Using BBR (PAV-aged Samples) | ||||||
| Sample Name | PG 52-28 | PG 64-22 | ||||
| Temperature (°C) | Stiffness (MPa) | m-Value | Temperature (°C) | Stiffness (MPa) | m-Value | |
| Neat asphalt binder | −12 −18 −24 | 81.71 198.11 367.53 | 0.357 0.333 0.262 | −12 −18 | 132.99 265.57 | 0.34 0.284 |
| Asphalt binder modified by CRM | −12 −18 −24 | 50.33 103.66 208.55 | 0.354 0.317 0.292 | −12 −18 | 102.3 206.22 | 0.30 0.27 |
| Asphalt binder modified by CRM and UMO | −18 −24 −30 | 73.55 163.05 319.59 | 0.324 0.309 0.282 | −12 −18 | 86.06 156.78 | 0.30 0.27 |
| PG High and Low Temperature Results | ||||||
| Sample Name | PG 52-28 | PG 64-22 | ||||
| PG | PG | |||||
| Neat asphalt binder | 52-28 | 64-22 | ||||
| Asphalt binder modified by CRM | 70-28 | 76-22 | ||||
| Asphalt binder modified by CRM and UMO | 64-34 | 70-22 | ||||
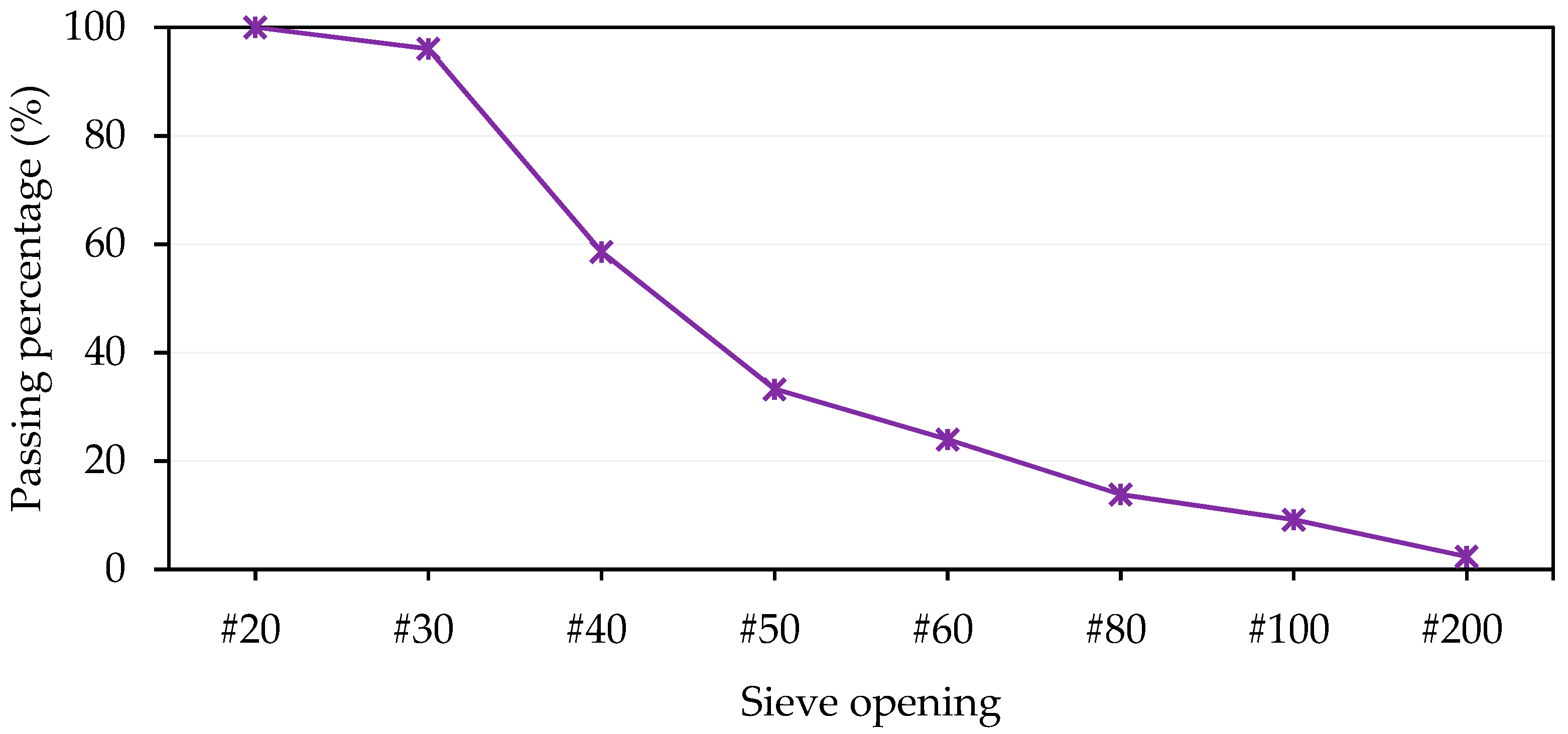
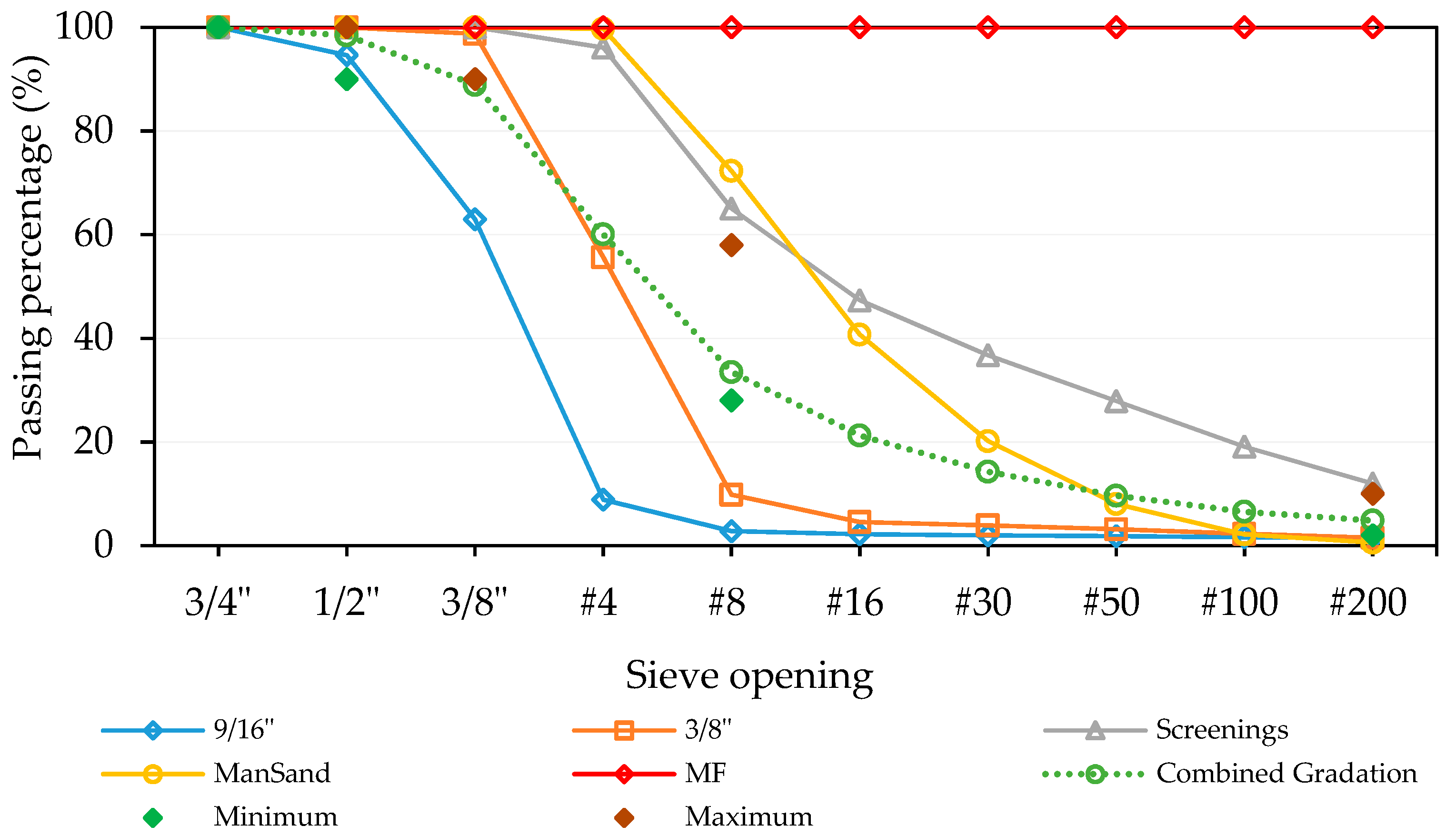
| Material | 9/16″ | 3/8″ | Screenings | ManSand * | MF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proportions (%wt) | 29 | 29 | 15 | 25 | 2 |
| Bulk Specific Gravity (Gsb) | 2.735 | 2.681 | 2.664 | 2.383 | |
| Apparent Specific Gravity (Gsa) | 2.810 | 2.801 | 2.813 | 2.658 | |
| Absorption (%) | 1.0 | 1.6 |
| Asphalt Binder | CRM % | UMO % | Interaction Temperature (°C) | Interaction Speed (Hz) | Interaction Time (min) | Modified Asphalt Binder Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PG 52-28 | 15 | 0 | 170 | 50 | 75 | Neat PG 52-28 + 15%CRM (170 °C—50 Hz—75 min) |
| 2.5 | Neat PG 52-28 + 15%CRM + 2.5% UMO (170 °C—50 Hz—75 min) | |||||
| PG 64-22 | 10 | 0 | 190 | 50 | 62 | Neat PG 64-22 + 10%CRM (190 °C—50 Hz—62 min) |
| 2.5 | Neat PG 64-22 + 10%CRM + 2.5% UMO (190 °C—50 Hz—62 min) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deef-Allah, E.; Abdelrahman, M.; Fitch, M.; Ragab, M.; Bose, M.; He, X. Balancing the Performance and Environmental Concerns of Used Motor Oil as Rejuvenator in Asphalt Mixes. Recycling 2019, 4, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4010011
Deef-Allah E, Abdelrahman M, Fitch M, Ragab M, Bose M, He X. Balancing the Performance and Environmental Concerns of Used Motor Oil as Rejuvenator in Asphalt Mixes. Recycling. 2019; 4(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeef-Allah, Eslam, Magdy Abdelrahman, Mark Fitch, Mohyeldin Ragab, Mousumi Bose, and Xiaolong He. 2019. "Balancing the Performance and Environmental Concerns of Used Motor Oil as Rejuvenator in Asphalt Mixes" Recycling 4, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4010011
APA StyleDeef-Allah, E., Abdelrahman, M., Fitch, M., Ragab, M., Bose, M., & He, X. (2019). Balancing the Performance and Environmental Concerns of Used Motor Oil as Rejuvenator in Asphalt Mixes. Recycling, 4(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4010011




