Abstract
The recycling of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) is becoming increasingly important due to the depletion of natural resources and potential pollution from the spent batteries. In this work, different types of acids (2 M citric (C6H8O7), 1 M oxalic (C2H2O4), 2 M sulfuric (H2SO4), 4 M hydrochloric (HCl), and 1 M nitric (HNO3) acid)) and reducing agents (hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), glucose (C6H12O6) and ascorbic acid (C6H8O6)) were selected for investigating the recovery of valuable metals from waste LIBs. The crushed and sieved material contained on average 23% (w/w) cobalt, 3% (w/w) lithium, and 1–5% (w/w) nickel, copper, manganese, aluminum, and iron. Results indicated that mineral acids (4 M HCl and 2 M H2SO4 with 1% (v/v) H2O2) produced generally higher yields compared with organic acids, with a nearly complete dissolution of lithium, cobalt, and nickel at 25 °C with a slurry density of 5% (w/v). Further leaching experiments carried out with H2SO4 media and different reducing agents with a slurry density of 10% (w/v) show that nearly all of the cobalt and lithium can be leached out in sulfuric acid (2 M) when using C6H8O6 as a reducing agent (10% g/gscraps) at 80 °C.
1. Introduction
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are currently widely used in consumer electronics, and their demand in electric and hybrid vehicles and renewable energy-related energy storage applications is expected to grow in the near future [1]. In spite of the widespread use of LIBs, according to the recent United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) recycling report [2], less than 1% of lithium from various applications was recycled globally in 2011. LIBs contain a variety of metals, and the chemical compositions vary by manufacturer and by application. LIBs consist of positive and negative electrodes, an electrolyte, a separator, and battery casing. The most common positive and negative electrode materials in LIBs for consumer electronics are lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2, LCO) and graphite, respectively [3]. Nevertheless, there are numerous other commercialized positive electrode materials that include lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (LiNi0.33Mn0.33Co0.33O2, NMC), lithium nickel cobalt aluminum oxide (LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2, NCA), spinel (Li2Mn2O4, LMO), and lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4, LFP) [4]. As a consequence, spent battery waste offers a rich source of both critical (Co) and economically valuable (Li, Ni, Cu) materials, the concentrations of which are comparable with current ore bodies e.g., Co ~20% w/w cf. 0.1–0.4% (sedimentary ores, Mt. Isa, Australia) [5]; Li 2.9–3.7% w/w cf. 0.4–4% (Hectorite, Jaderite and Pegmatite minerals, Sonora, Mexico, Jadar, Serbia and North Carolina, USA) [6].
The leaching of spent LIBs has been investigated in both mineral acids, such as sulfuric (H2SO4), hydrochloric (HCl), and nitric acids (HNO3) [7,8,9,10]; and in organic acids, e.g., citric (C6H8O7) and oxalic acids (C2H2O4) [11,12,13,14]. In addition, the effect of different reducing agents in leaching, for instance, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) [15], sodium thiosulfate (Na2S2O3) [16], sodium bisulfite (NaHSO3) [17], and some carbohydrates, including d-glucose [18] and ascorbic acid [19], which are added to accelerate the leaching process of metal ions, has been explored. The decomposition i.e., dissolution of LiCoO2 is a reduction reaction in nature, as opposed to, e.g., metallic copper dissolution, and thus requires the addition of a reduction agent. Previous research shows that the leaching efficiencies of lithium and cobalt can reach or even exceed 99% with the addition of reductants such as hydrogen peroxide, d-glucose, and ascorbic acid to the leaching solution [20].
Many of the aforementioned research papers have focused on the leaching of manually separated cathodic materials. From the point of view of large-scale LIBs recycling, manual dismantling of the batteries can be labourous and uneconomical. In addition, the pretreatment methods and leaching parameters in previous research papers differ, which makes direct comparison of the leaching lixiviants and conditions challenging. In this study, the experiments were conducted on crushed spent LIBs sourced from an industrial process, and similar leaching parameters were used throughout for all lixiviants. This allows a more straightforward comparison of the different leaching conditions and thus the challenges related to the leaching of LiB wastes—in particular the inconsistences of the metal content of the waste stream—to be assessed more easily in terms of leaching process scale-up.
This study presents the results of leaching tests performed on commercially crushed and sieved spent LIBs. The leaching tests were performed with five different acids, with and without the addition of a reducing agent (H2O2). In addition, the effects of three different reducing agents on the LIB leaching efficiency in H2SO4 are presented.
2. Experimental
2.1. Material
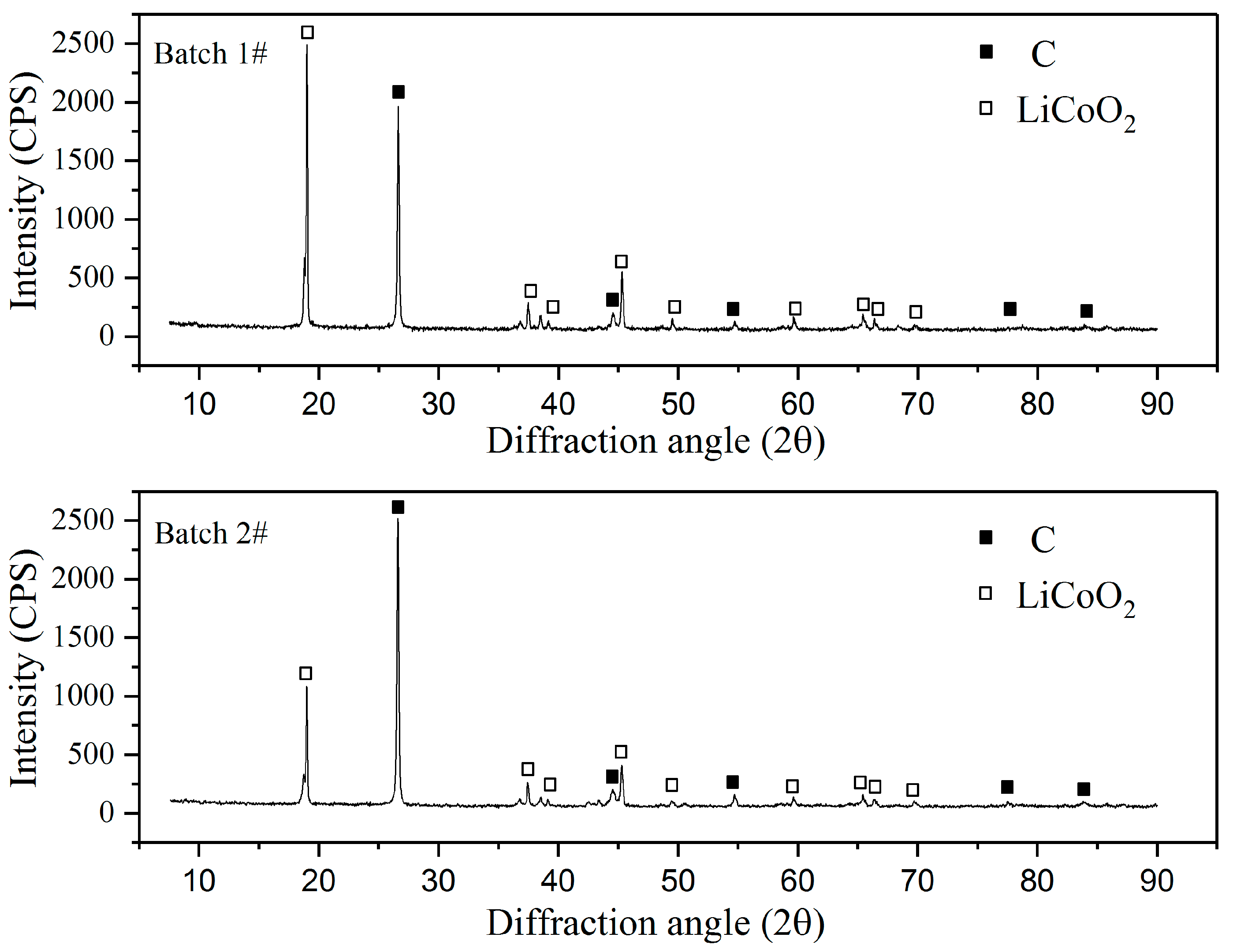
In the leaching experiments, waste LIBs—commercially collected from numerous sources—were used. LIBs were first industrially crushed without previously separating anode and cathode materials. This upstream material was then mechanically and magnetically processed in a similar manner to that previously patented [21], in order to obtain a sieved underflow fraction of ≤1 mm. In order to assess the metal content in the solids, the material was subjected to total leaching in aqua regia, after which lithium, cobalt, copper, nickel, manganese, and iron were analyzed with atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) (Varian AA240), and aluminum was analyzed with inductively coupled plasma spectrometry (ICP-OES) (Perkin Elmer 7100 DV). In the tests, raw material Batches 1 and 2 were used for leaching and the reducing agent tests, respectively. The compositions of the main metals in the LIBs (Batches 1 and 2) are presented in Table 1. The scraps of both Batches 1 and 2 were subjected to XRD analysis (PANalytical X’Pert Pro Powder, Almelo, The Netherlands), with a CuKα radiation source at a scan rate of 2°/min (acceleration potential 45 kV, current 40 mA). Results were analyzed with HighScore Plus 4.1 (PANalytical) software to identify the species (see Figure 1). In the analysis, profile fit was used in order to achieve the best results.

Table 1.
Chemical compositions of the commercially crushed and sieved (approximately ≤1 mm) lithium-ion battery (LIB) underflow Batches 1 and 2 used as raw material. Units are in % (w/w).
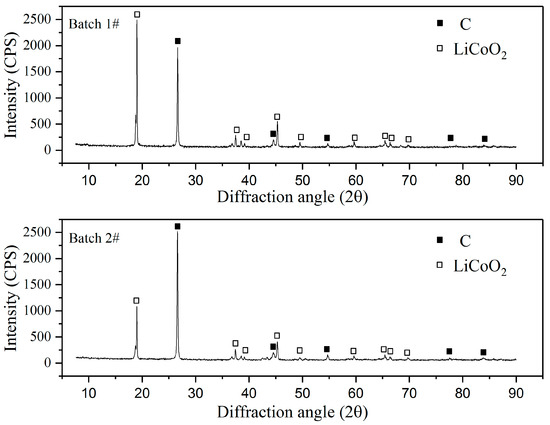
Figure 1.
The XRD patterns of the LIB underflow Batches 1 and 2.
Table 1 shows the heterogeneous nature of the raw material, as the concentrations of the main metals analyzed in solid samples are shown to vary in the parallel samples of the same batch (Batch 1), as well as between Batches 1 and 2. Based on the XRD pattern (Figure 1) of LCO, carbon or graphite (C) and NMC are likely species present in the material. Other possible species in the material are NCA-resembling Li0.99Ni0.71Co0.15Al0.15O2, which has a similar XRD pattern as NMC, and cobalt oxide (Co3O4) [22], the presence of which could not be verified due to overlapping peaks. As can be seen from Figure 1, the XRD pattern of Batch 2 is similar, but not the same as that measured for Batch 1, which demonstrates the inhomogeneity in metal content between different batches of crushed and processed LiB waste.
2 M citric (C6H8O7), 1 M oxalic (C2H2O4), 2 M sulfuric (H2SO4), 4 M hydrochloric (HCl), and 1 M nitric (HNO3) acids were investigated as leaching media. The organic acid solutions were prepared by mixing C6H8O7 (99.8%, VWR Chemicals) and C2H2O4 H2O (99%, Merck Millipore) into distilled water. Similarly, the mineral acids (H2SO4 (95–97%, Merck Millipore), HCl (32%, Merck Millipore) and HNO3 (65%, Merck Millipore)) were diluted into target concentrations by using distilled water. The reducing agents used in this study were all of analytical grade. All of the leaching tests were conducted with and without 1% (v/v) of H2O2 dosage.
2.2. Methods
A stirring plate (IKA RT10) was used to conduct the long-term leaching tests (24 h). The stirring speed was 100 rpm, slurry volume 150 mL, slurry density 5% (w/v), and T = 25 °C. In the reductive leaching tests series with different reducing agents (hydrogen peroxide 0–5% (v/v), d-glucose 0–16% (g/gscraps), ascorbic acid 0–12% (g/gscraps)), experiments were performed in closed Erlenmeyer flasks (250 mL) in a water-shaking bath (Stuart SBS40). In each experiment, the shaking speed was 150 rpm, [H2SO4] = 2 M, slurry density was 10% (w/v), T = 70 °C (H2O2) or 80 °C (C6H12O6, C6H8O6), and leaching time was 5 h. After leaching, the solids were filtrated, which yielded residues and filtrates for analysis. The redox potential was measured using a platinum electrode and a silver chloride reference electrode (Inlab® Redox, Mettler Toledo, GmbH, Switzerland).
The yields in the leaching tests were calculated based on the solution samples, and some of the leaching residues were also analyzed in order to verify the results. The highest chemical analysis of Batch 1 (Table 1) was used to represent the chemical composition of the raw material. However, due to the heterogenous nature of the industrially-crushed LIBs waste raw material, this resulted in long-term H2SO4 and HCl leaching yields slightly higher than 100%. Similarly, also in the reducing agent leaching tests, some of yields exceeded 100%.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Long-Term Leaching Tests with Different Acids
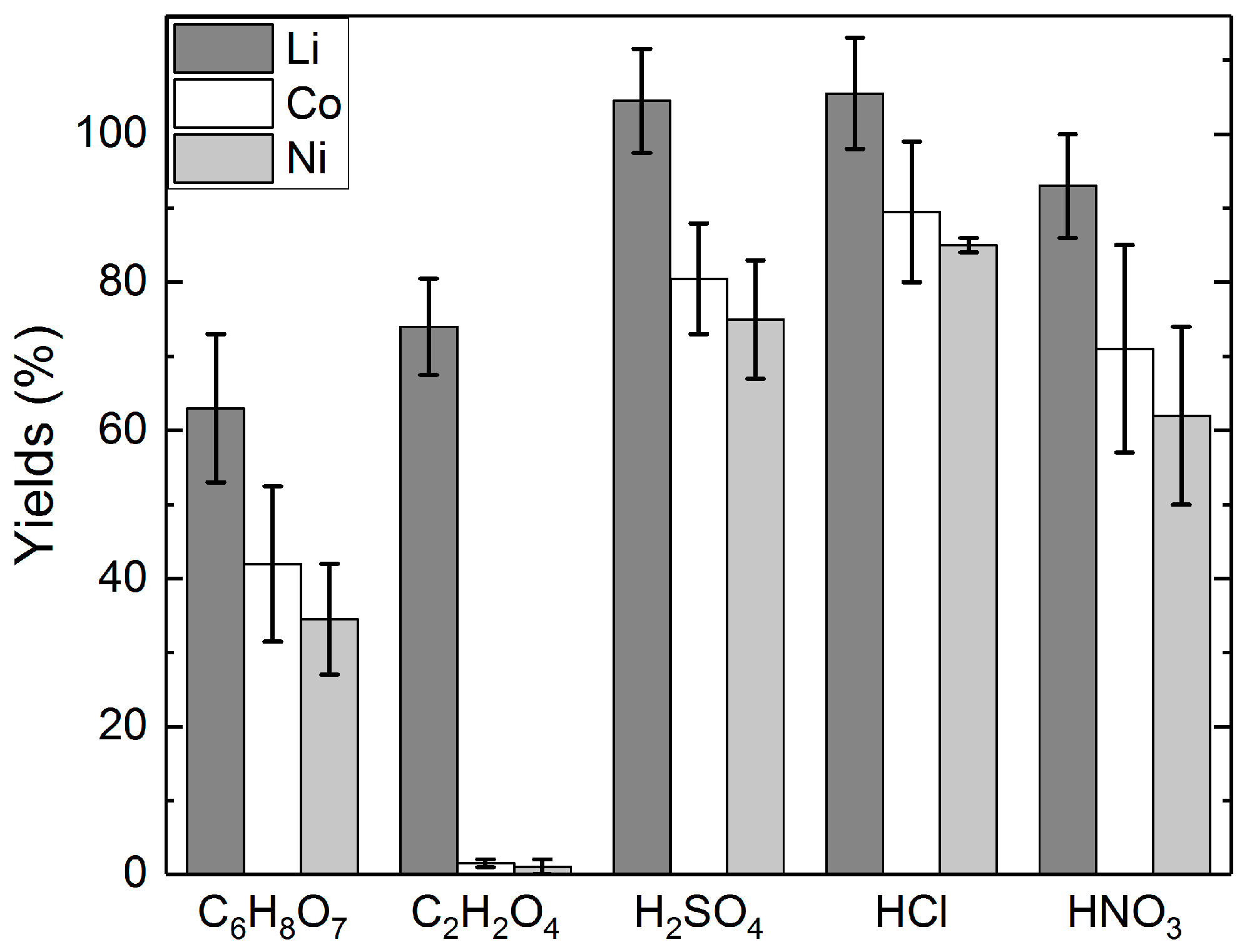
The metal yields to the different acids is presented without (Figure 2) and with H2O2 addition (Figure 3). From Figure 2, it can be seen that the yields of Li to the mineral acids were over 90% in each acid solution investigated. In C2H2O4 leaching, the yield of lithium was approximately 74%, whereas in C6H8O7 leaching, the yield of Li was on average 63%. Figure 2 also shows that the yields of cobalt were generally 20–30 percent points (pp) lower than the yields of lithium. C2H2O4 showed higher selectivity between Li and Co, as only 2% of cobalt was dissolved. Yields of nickel were shown to generally follow the yields of cobalt.
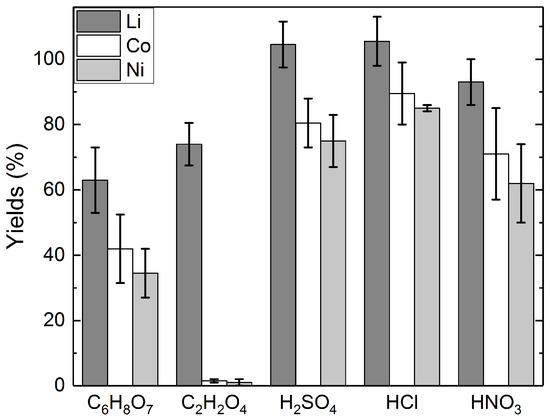
Figure 2.
Yields of lithium, cobalt, and nickel in different acid solutions: acid concentrations = 2 M C6H8O7; 1 M C2H2O4; 2 M H2SO4; 4 M HCl; 1 M HNO3, slurry density = 5% (w/v), T = 25 °C, t = 24 h.
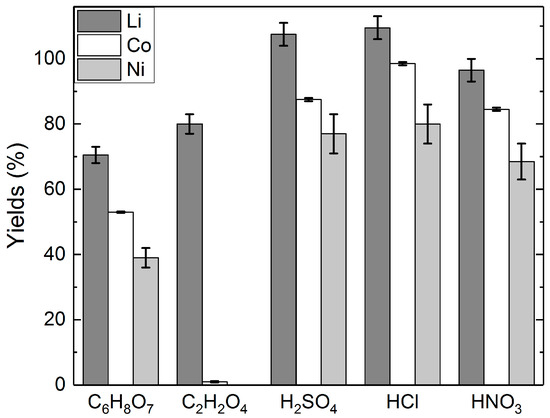
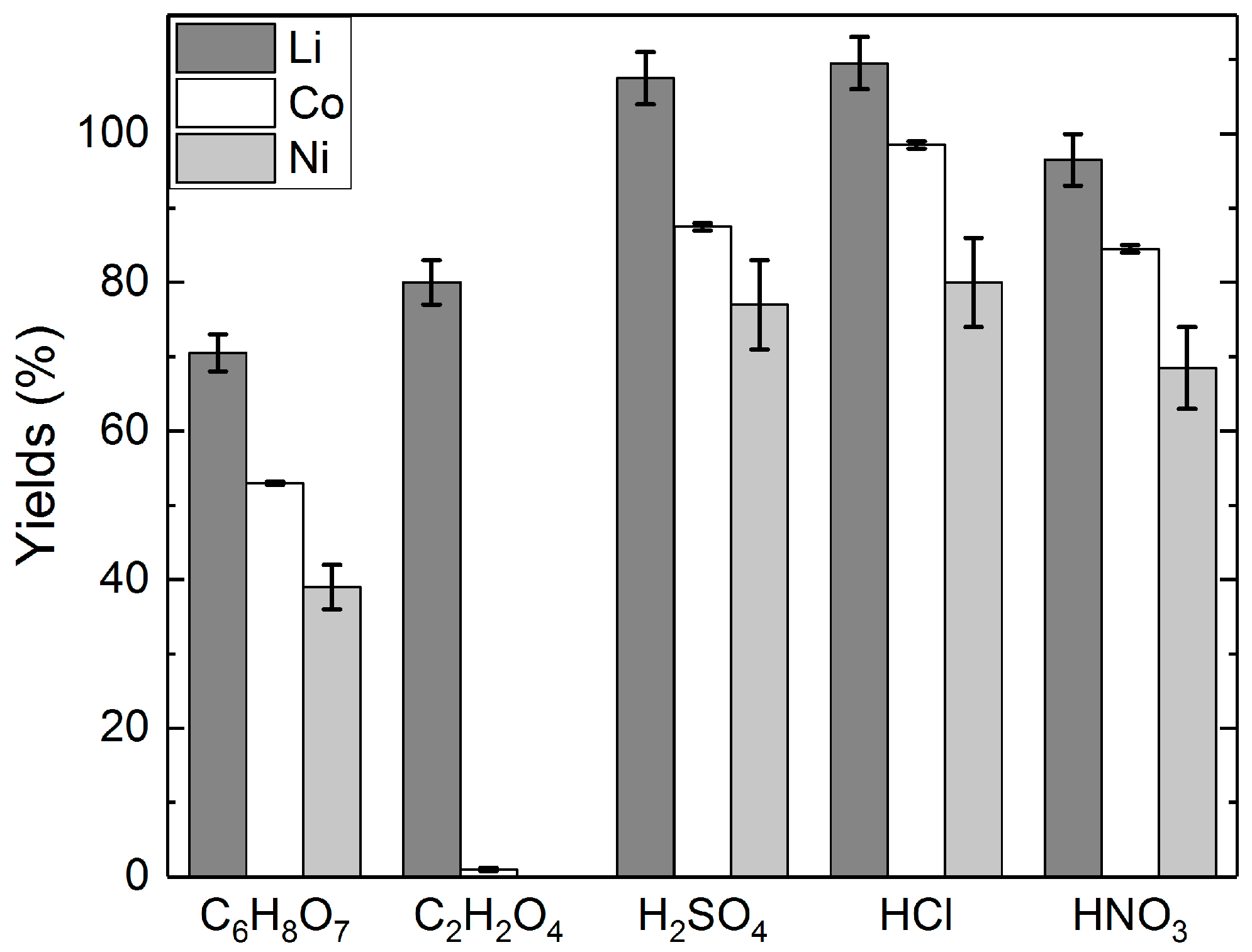
Figure 3.
Yields of lithium, cobalt, and nickel in different acid solutions: acid concentrations = 2 M C6H8O7; 1 M C2H2O4; 2 M H2SO4; 4 M HCl; 1 M HNO3, H2O2 concentration = 1% (v/v), slurry density = 5% (w/v), T = 25 °C, t = 24 h.
Figure 3 shows the effect of H2O2 addition on the yields of lithium, cobalt, and nickel. The addition of H2O2 increased the yields of lithium in each investigated solution. The effect was shown to be similar for cobalt and nickel, with the exception of the C2H2O4 leaching, where only insignificant quantities of cobalt and nickel were leached into the solution in any of the experiments. The leaching residues from H2SO4 and HCl leaching were also analyzed, and based on the analyses, the yield of Li was 88% to H2SO4, and 91% to HCl in the leaching tests without H2O2 addition. Similarly, with H2O2 addition, the yield of Li was 92% to H2SO4, and 98% to HCl. The results of the leaching tests with different acids indicate that H2SO4 and HCl seem to be the most effective leaching media for lithium leaching, with or without the addition of H2O2. Nevertheless, the experiments with C2H2O4 highlight its selectivity for lithium, which offers the possibility for a two-step leaching process that first separates Li from Co and Ni.
3.2. Leaching in Sulfuric Acid with Different Reducing Agents
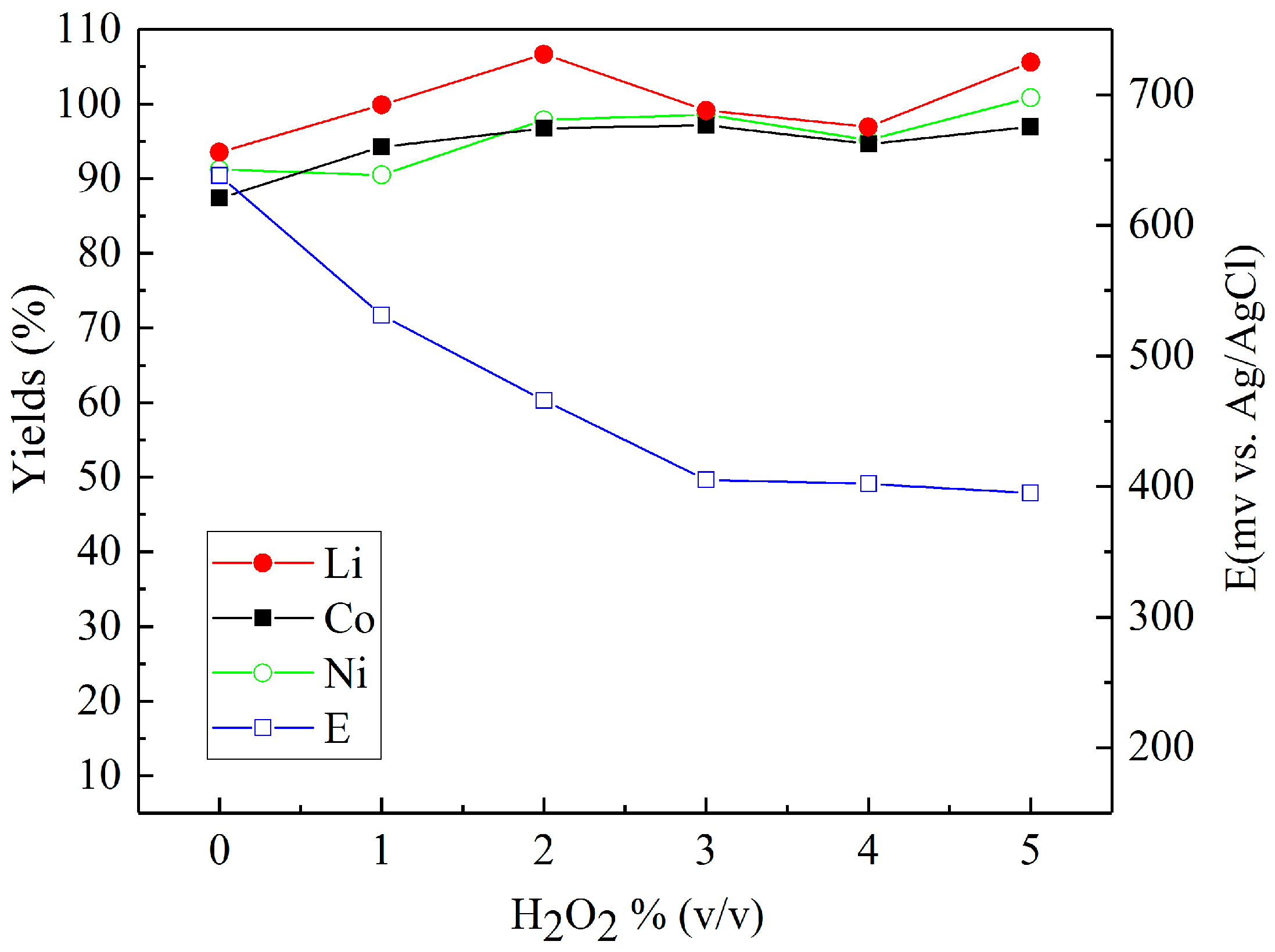
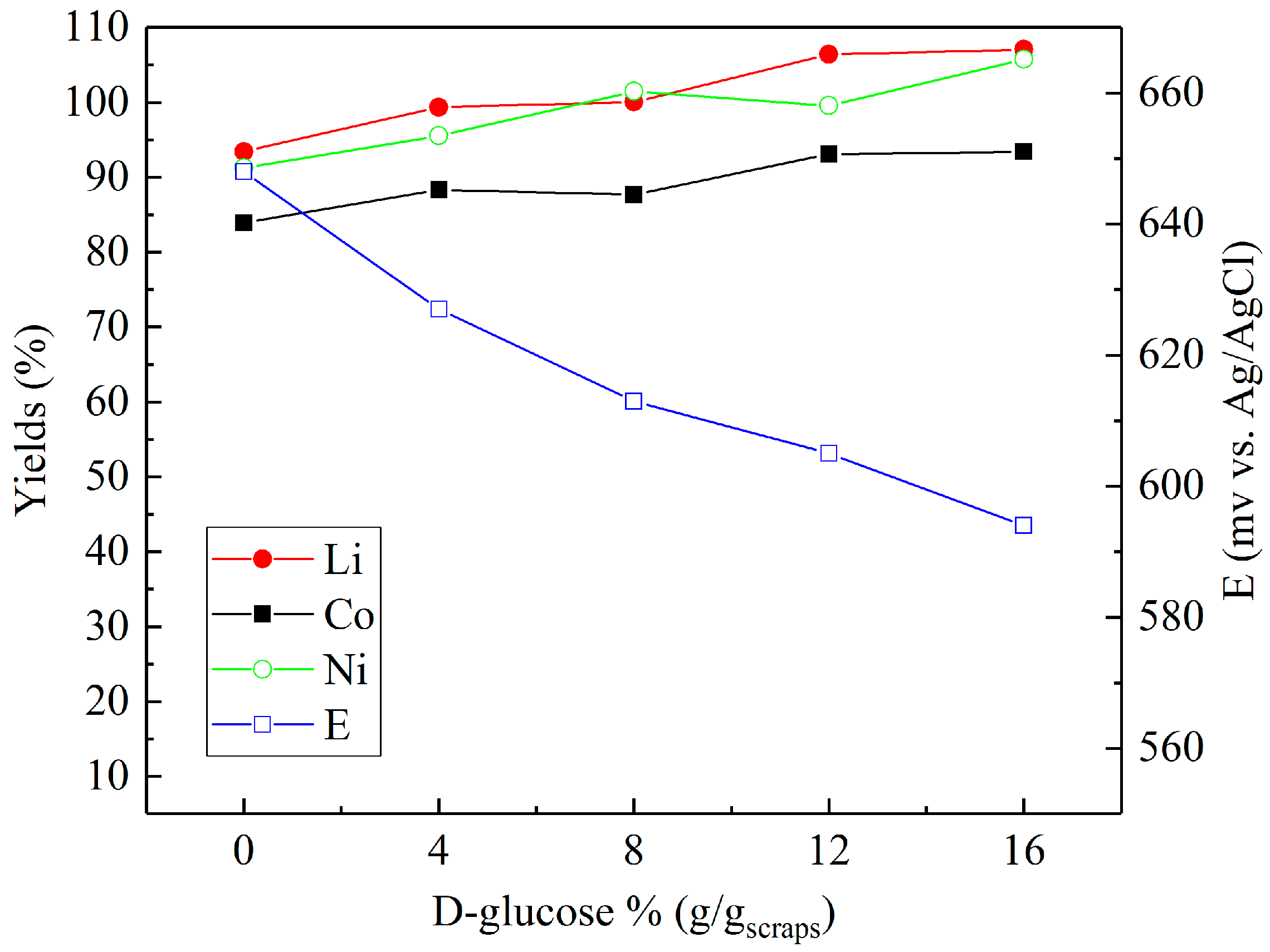
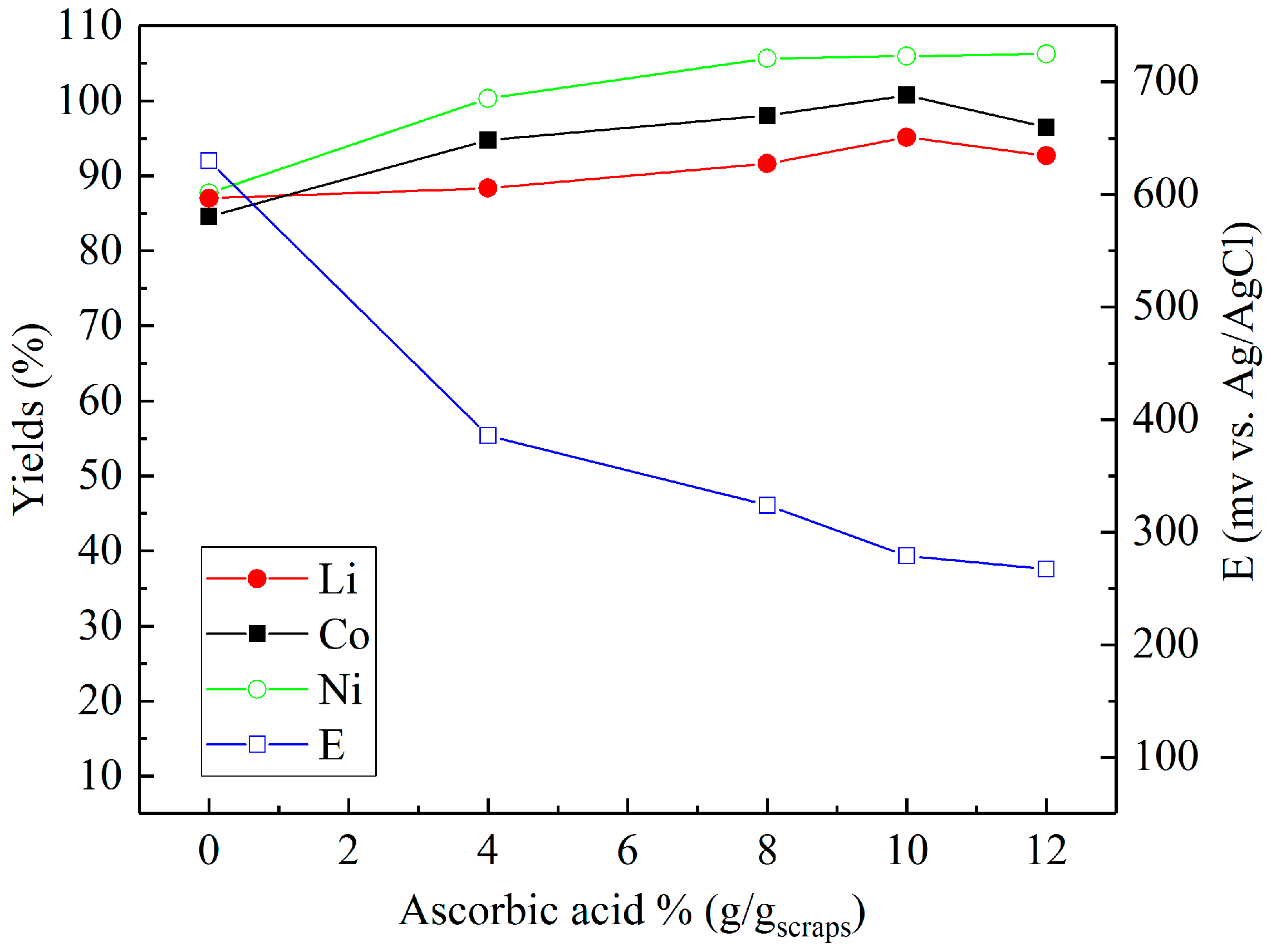
Sulfuric acid (2 M) was chosen to investigate the effect of reducing agents in more detail. Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 present the metal yields achieved. Figure 4 shows that the maximum yields (106.7% for lithium, 96.7% for cobalt, and 97.9% for nickel) were achieved with 2% (v/v) H2O2 dosage. Using d-glucose as a reducing agent (Figure 5), the respective maximum leaching efficiencies of lithium, cobalt, and nickel were 106.4%, 93.1%, and 99.6% with a consumption of 12% (g/gscraps) d-glucose. Compared with H2O2 and d-glucose, ascorbic acid (Figure 6) shows greater reducing ability, reducing the system ORP (oxidation/reduction potential) from 630 mV (0%) to nearly 300 mV (above 6%). With 10% (g/gscraps) ascorbic dosage, the leaching efficiencies of lithium, cobalt, and nickel were up to 95.1%, 100.7%, and 105.9%, respectively. The contents of these metals in the corresponding leaching residue were as low as 0.03% (Li), 0.11% (Co), and 0.17% (Ni).
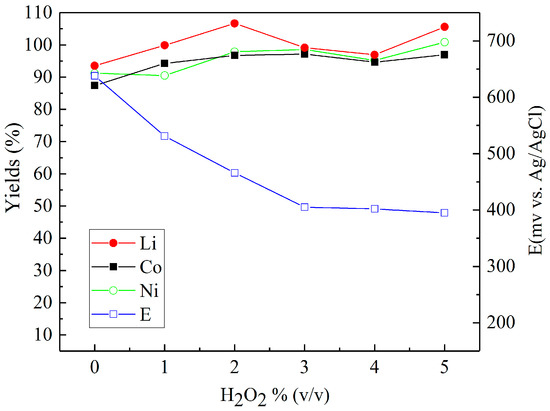
Figure 4.
Influence of H2O2 dosage on the leaching efficiencies of lithium, cobalt, and nickel: H2SO4 concentration: 2 M, H2O2 concentrations: 0–5% (v/v), slurry density = 10% (w/v), T = 70 °C, t = 5 h.
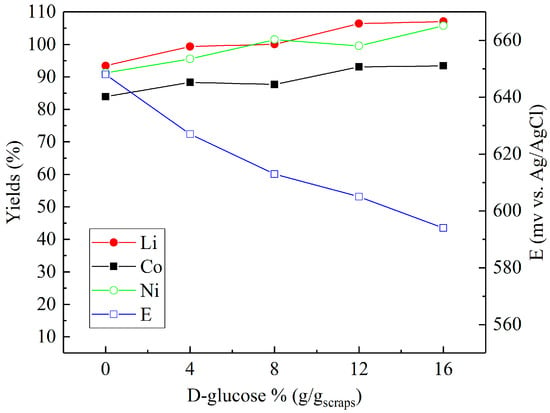
Figure 5.
Influence of d-glucose dosage on the leaching efficiencies of lithium, cobalt, and nickel: H2SO4 concentration = 2 M, d-glucose concentrations = 0–16% (g/gscraps), slurry density = 10% (w/v), T = 80 °C, t = 5 h.
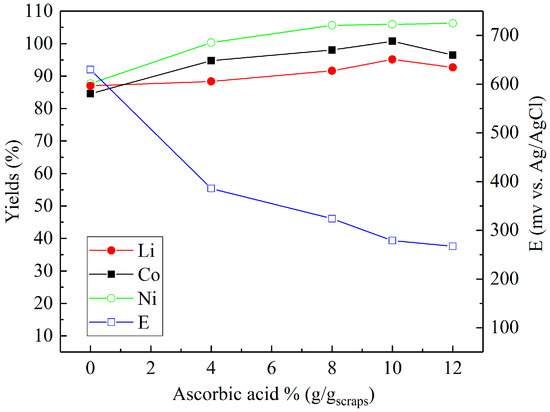
Figure 6.
Influence of ascorbic acid dosage on the leaching efficiencies of lithium, cobalt, and nickel: H2SO4 concentration = 2 M, ascorbic acid concentrations = 0–12% (g/gscraps), slurry density = 10% (w/v), T = 80 °C, t = 5 h.
As can be seen from Figure 4, the concentration of hydrogen peroxide in the leach solution is an initial increase in the recovery of Li, Co, and Ni up to approximately 2% (v/v). The presence of H2O2 in the leach solution is able to facilitate the reduction of the cobalt in lithium cobalt oxide from Co (III) to Co (II), and thus, in turn, it also aids the dissolution of Li from within the same compound [19], as shown in Equation (1):
2LiCoO2 + 3H2SO4 + 3H2O2 → 2CoSO4 + Li2SO4 + 6H2O + 2O2
Such a result is similar to previous observations detailed in the literature [23,24], which have demonstrated that the presence of H2O2 in the leach solution only has a positive effect on metal recoveries up to a concentration of 2 vol %. Concentrations >2% (v/v) have a limited impact on the level of metal recovery due to the instability of H2O2, which tends to undergo enhanced levels of decomposition at higher concentrations, especially when subject to the elevated temperature used in these experiments [25]. This decomposition behavior of the peroxide is further evidenced by the stabilization of the recorded ORP at around 400 mV (vs. Ag/AgCl), which suggests that further additions of H2O2 have no influence on the reductive nature of the leach solution.
The results shown in Figure 5 demonstrate that increased d-glucose concentration results in enhanced efficiencies for all of the metals between 10–15%. d-glucose’s reductive nature is due to the wide range of possible intermediates generated during the oxidative transition to formic acid, and previously outlined by Pagnanelli et al. [18]. From the results, it can be suggested that as with H2O2, the reduction of Co (III) to Co (II) is initially promoted by glucose oxidation, and that Li is seen to follow exactly the same trend as a result of the degradation of the lithium cobalt oxide (Equation (2)):
24LiCoO2 + 36H2SO4 + C6H12O6 → 24CoSO4 + 12Li2SO4 + 42H2O + 6CO2
Interestingly, the recovery of Ni measured under these experimental conditions also follows a similar trend to that seen for Li and Co. This is in contrast to the results of Granata et al. [26], who found a slight reduction in Ni leaching efficiency with increased levels of glucose concentration. However, the conditions—leach time = 3 h, 2:1 ratio H2SO4 to solids, 100% stoichiometric excess of glucose, and temperature of 30 °C—were markedly different to the ones detailed here.
In the case of leaching with ascorbic acid (C6H8O6), as displayed in Figure 6, previous research by Li et al. [27] has shown that the LiCoO2 within battery waste is dissolved by ascorbic acid and forms the soluble compound C6H6O6Li2. Concurrently, the cobalt is reduced from Co3+ to the soluble Co2+ species, C6H6O6Co, as the ascorbic acid is oxidized to dehydroascorbic acid (C6H6O6) [28,29]. A similar reaction is known to also occur with Ni [28], hence, the observed progressive increases in metal (Ni, Co, Li) recovery with increased concentrations of ascorbic acid. In addition, the measured drop in system ORP is the result of the negative reduction potentials related to the dissociation of ascorbate species in aqueous solutions, which are enhanced with higher concentrations of ascorbic acid in solution [30].
4. Conclusions
The mineral acids, especially 2 M H2SO4 and 4 M HCl, were shown to be the most effective for lithium leaching from the industrially-crushed LIB batch investigated, with and without the addition of a reducing agent (H2O2), with H2O2 having a positive effect on metals extraction. It was also shown that C2H2O4 was the most selective leaching media between Li and Ni/Co, as the latter divalent metals are known to precipitate as oxalates.
The efficiency of reduction agents in LIBs sulfuric acid (2 M) leaching was investigated, and it was shown to be ascorbic acid C6H8O6, d-glucose, and H2O2, in descending order, with the parameter range studied (C6H8O6 = 0–12% g/gscraps, d-glucose = 0–16% g/gscraps and H2O2 = 0–5% (v/v)). The highest metal extraction into the sulfuric acid was achieved using 10% (g/gscraps) C6H8O6 as a reducing agent. The heterogenous nature of the industrially-crushed LIBs had resulted metal yields of 100.7% to cobalt, 95.1% to Li, and 105.9% to Ni at maximum, based on solution analysis. Therefore, leach residue was also analyzed, and showed that the remaining contents of cobalt, lithium, and nickel in the leaching residue were as low as 0.11%, 0.03%, and 0.17%, respectively.
Acknowledgments
The authors of this research paper are grateful to the METYK project, which is funded by the Finnish innovation agency, as well as to the China Scholarship Council (CSC) for the funding of the research. The research was also supported by the Strategic Research Council at the Academy of Finland, project Closeloop (grant number 303454), project NoWASTE (grant number 297962), and RawMatTERS Finland Infrastructure (RAMI), which is funded by the Academy of Finland. Special thanks also goes to Petteri Halli for his shared expertise.
Author Contributions
Miamari Aaltonen conceived and designed the experiments. Miamari Aaltonen and Chao Peng performed the experiments. Miamari Aaltonen and Chao Peng analyzed the data with significant contribution of Mari Lundström. Miamari Aaltonen wrote the paper and significant contribution to writing was made by Benjamin P. Wilson and Mari Lundström. Mari Lundström is the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Christmann, P.; Gloaguen, E.; Labbé, J.F.; Melleton, J.; Piantone, P. Global Lithium Resources and Sustainability Issues. In Lithium Process Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Graedel, T.E.; Allwood, J.; Birat, J.P.; Buchert, M.; Hagelüken, C.; Reck, B.K.; Sibley, S.F.; Sonnemann, G. UNEP 2011 Recycling Rates of Metals–A Status Report, A Report of the Working Group on the Global Metal Flows to the International Resource Panel; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2011; p. 44. ISBN 978-92-807-3161-3. [Google Scholar]
- Swiatowska, J.; Barboux, P. Lithium Battery Technologies: From the Electrodes to the Batteries. In Lithium Process Chemistry, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 125–166. ISBN 9780128016862. [Google Scholar]
- Nitta, N.; Wu, F.; Lee, J.T.; Yushin, G. Li-ion battery materials: Present and future. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannis, S.; Minks, A. Cobalt; British Geological Survey: Nottingham, UK, 2009; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Walters, A.; Idoine, N.; Gunn, G.; Shaw, R.A.; Rayner, D. Lithium; British Geological Survey: Nottingham, UK, 2016; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Yokoyama, T.; Itabashi, O.; Suzuki, T.M.; Inoue, K. Hydrometallurgical process for recovery of metal values from spent lithium-ion secondary batteries. Hydrometallurgy 1998, 47, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joulié, M.; Lacournet, R.; Billy, E. Hydrometallurgical process for the recovery of high value metals from spent lithium nickel cobalt aluminum oxide based lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 247, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Senanayake, G.; Sohn, J.; Shin, S.M. Recovery of cobalt sulfate from spent lithium ion batteries by reductive leaching and solvent extraction with Cyanex 272. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 100, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Rhee, K.I. Preparation of LiCoO2 from spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2002, 109, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ge, J.; Wu, F.; Chen, R.; Chen, S.; Wu, B. Recovery of cobalt and lithium from spent lithium ion batteries using organic citric acid as leachant. J. Hazard Mater. 2010, 176, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, T. Hydrometallurgical process for the recovery of metal values from spent lithium-ion batteries in citric acid media. Waste Manag. Res. 2014, 32, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Qiu, K. Organic oxalate as leachant and precipitant for the recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Li, J.; Shen, B. Novel approach to recover cobalt and lithium from spent lithium-ion battery using oxalic acid. J. Hazard Mater. 2015, 295, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Sun, R.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z.; Kang, M. Recovery of cobalt from spent lithium ion batteries using sulphuric acid leaching followed by solid–liquid separation and solvent extraction. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 85303–85311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, M.; Chen, H.; Luo, T.; Xu, Z. Leaching study of spent Li-ion batteries. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 16, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, P.; Pandey, B.D.; Mankhand, T.R.; Deveci, H. Comparison of different reductants in leaching of spent lithium ion batteries. JOM 2016, 68, 2613–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnanelli, F.; Moscardini, E.; Granata, G.; Cerbelli, S.; Agosta, L.; Fieramosca, A.; Toro, L. Acid reducing leaching of cathodic powder from spent lithium ion batteries: Glucose oxidative pathways and particle area evolution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 3201–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayaka, G.P.; Manjanna, J.; Pai, K.V.; Vadavi, R.; Keny, S.J.; Tripathi, V.S. Recovery of valuable metal ions from the spent lithium-ion battery using aqueous mixture of mild organic acids as alternative to mineral acids. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 151, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckberg, C.; Petranikova, M. Lithium Battery Recycling. In Lithium Process Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 245–248. [Google Scholar]
- Pudas, J.; Erkkila, A.; Viljamaa, J. Battery Recycling Method. WIPO Patent WO2011113860A1, 22 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, M.B.J.G.; Garcia, E.M. Electrochemical recycling of cobalt from cathodes of spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2007, 171, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; He, W.; Li, G.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J. Recovery of Co and Li from spent lithium-ion batteries by combination method of acid leaching and chemical precipitation. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 2274–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ge, J.; Chen, R.; Wu, F.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X. Environmental friendly leaching reagent for cobalt and lithium recovery from spent lithium-ion batteries. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 2615–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeki, S.; Lee, J.; Zhang, Q.; Saito, F. Co-grinding LiCoO2 with PVC and water leaching of metal chlorides formed in ground product. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2004, 74, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, G.; Moscardini, E.; Pagnanelli, F.; Trabucco, F.; Toro, L. Product recovery from Li-ion battery wastes coming from an industrial pre-treatment plant: Lab scale tests and process simulations. J. Power Sources 2012, 206, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lu, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, X.X.; Chen, R.J.; Wu, F.; Amine, K. Ascorbic-acid-assisted recovery of cobalt and lithium from spent Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2012, 218, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creutz, C. The Complexities of Ascorbate as a Reducing Agent. Inorg. Chem. 1981, 20, 4449–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.B. Reactions of L-Ascorbic Acid with Transition Metal Complexes. Polyhedron 1992, 11, 285–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniyar, S.A.; Jargar, J.G.; Das, S.N.; Dhundasi, S.A.; Das, K.K. Alteration of chemical behavior of L-ascorbic acid in combination with nickel sulfate at different pH solutions in vitro. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).