Abstract
The construction industry increasingly seeks sustainable solutions to reduce environmental impact and energy consumption. This study explores the innovative use of industrial sludge generated from the wastewater treatment of detergent manufacturing as a partial substitute for Portland cement in mortar production. The sludge, characterized by high SiO2 (46.58%) and CaO (28.66%) content, was incorporated at substitution rates of 0% to 30%. Mortars were prepared and tested according to NF EN 196-1 standards for mechanical strength, and thermophysical properties were assessed using the Hot Disk TPS 1500 system. The results demonstrate that up to 20% sludge replacement maintains acceptable mechanical performance (compressive strength: 12.63 MPa at 28 days vs. 13.91 MPa for the control; flexural strength: 3.93 MPa vs. 4.65 MPa) while significantly enhancing thermal insulation. Thermal conductivity decreased from 1.054 W/m·K (0% sludge) to 0.797 W/m·K (20% sludge), and thermal diffusivity dropped from 0.6096 mm2/s to 0.504 mm2/s. XRD analysis revealed the formation of new phases, such as gismondine, indicating beneficial pozzolanic activity. These findings highlight the dual benefit of valorizing detergent sludge and improving building energy efficiency, offering an eco-efficient alternative to traditional mortars aligned with circular economy and low-carbon construction goals.
1. Introduction
The management of industrial waste, particularly sludge generated from wastewater treatment processes, presents a persistent environmental and economic challenge. In the detergent manufacturing sector, the sludge is especially problematic due to its complex chemical composition and heavy metal content—including chromium, arsenic, nickel, zinc, iron, and cadmium [1]. These metals originate from additives and raw materials used in detergent formulations and, if not properly managed, can pose long-term risks to ecosystems and human health [2,3]. Conventional disposal methods such as landfilling or incineration are not only costly and pollutive but also underutilize the latent potential of this waste.
Recent research has demonstrated that industrial and municipal sludges can be effectively used as supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) or aggregates in construction. Their chemical and mineralogical compositions—rich in SiO2, CaO, and Al2O3—closely resemble those of traditional cementitious binders and clays, allowing their integration into bricks, tiles, and mortars [4,5]. Lin and Chakraborty showed that sludge ash and industrial byproducts can partially replace raw materials in cement and mortar, improving mechanical performance while reducing carbon emissions [6,7,8]. However, the potential of sludge from detergent wastewater treatment—a unique type with high silica and calcium oxide content—remains largely unexplored.
An important advantage of using sludge in cementitious materials lies in its ability to stabilize toxic heavy metals during hydration. The formation of calcium silicate hydrate (C–S–H) and portlandite in cement can immobilize heavy metals by physical encapsulation or chemical bonding, thereby reducing their leachability [9,10,11]. This mechanism makes cement-based matrices a promising solution for the safe and sustainable valorization of metal-rich sludges.
Energy efficiency is a key pillar of sustainable construction, particularly in light of rising global energy demand and CO2 emissions. The building sector alone accounts for nearly one-third of total energy use and emissions [12,13]. In climates like Morocco’s—characterized by large temperature fluctuations—thermal performance of materials becomes critical for maintaining comfort without reliance on energy-intensive HVAC systems [14]. Thermophysical properties such as thermal conductivity (λ), diffusivity (α), capacity (ρcp), and effusivity (E) define a material’s ability to retain and transmit heat. Materials with low thermal conductivity and high thermal inertia contribute to better indoor temperature regulation and lower energy costs [15,16,17,18].
Beyond sludge valorization, ongoing research emphasizes the role of alternative SCMs—both natural and industrial—in reducing clinker content in cement [19]. Volcanic ash, calcined clay, and biomass-derived ashes are among the most promising options. Simultaneously, improvements in aggregate design, such as the optimization of grain size distribution and ITZ (interfacial transition zone) engineering, have shown to enhance mechanical strength and fracture toughness of concrete composites [20]. These advances point toward an integrative approach to sustainable material design.
Despite these developments, limited work has investigated the valorization of detergent industry sludge, which possesses distinct physicochemical and mineralogical properties. This study addresses this gap by evaluating the mechanical and thermal behavior of mortars in which cement is partially replaced (0–30%) with sludge derived from the treatment of detergent wastewater. The mortars were prepared according to NF EN 196-1 standards [21], and their mechanical strengths (flexural and compressive) and thermophysical properties (λ, α, ρcp, E) were assessed using a Hot Disk TPS 1500 system (Hot Disk AB, Gothenburg, Sweden) [14]. X-ray diffraction and ICP-OES analyses were also conducted to investigate mineral phase evolution and heavy metal stabilization. The objective is to determine whether detergent sludge can serve as a sustainable, safe, and thermally efficient cement substitute—contributing to waste valorization, CO2 reduction, and energy-efficient building design.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Used in Mortar Production
This study utilized three primary components: sludge obtained from detergent wastewater treatment, (CEM II cement (CPJ 45)), and natural coastal sand from Souiria, Morocco.
2.1.1. Detergent Sludge
The sludge was gray in color, with a powdery appearance after drying and grinding. It resulted from a percolation treatment process combining fly ash, bottom ash, and sand. Its chemical composition—rich in SiO2 (46.58%), CaO (28.66%), and Al2O3 (15.54%)—was determined by X-ray fluorescence and is shown in Table S5. The D50 and D90 of the ground sludge powder were 81.7 µm and 173.2 µm, respectively, measured using a laser particle size analyzer (Malvern Mastersizer 2000, Malvern Instruments Ltd., Malvern, UK) [2]. No screening was applied post-grinding, but the entire sludge was passed through a 315 µm sieve to ensure consistency. The sludge was first sun-dried for approximately 3–4 days, depending on ambient humidity (mean daily temperature ~30 °C), and then oven-dried at 105 °C for 24 h to remove residual moisture. Samples were left unsealed during drying, and the moisture content was not measured before grinding. Figure S1 shows the appearance of the sludge after drying.
2.1.2. Cement (CPJ 45)
A commercially available CEM II Portland cement conforming to NF EN 197-1 was used. It consists of 68% clinker [21], 27% limestone, and 5% gypsum. Tables S1 and S2 detail its physical and chemical properties. The cement is gray in color with a fine, uniform texture.
2.1.3. Sand
Sand was sourced from Souiria beach (Safi, Morocco), thoroughly washed with distilled water to remove salts and organic matter, oven-dried at 40 °C, and sieved. The particle size ranged from 0.063 mm to 2 mm, with a fineness modulus of 2.4 and good granulometric uniformity. The chemical composition (Table S3) reveals high silica content (>90% SiO2), making it suitable for mortar formulation [22].
2.1.4. Mechanism of Sludge Generation
The sludge was produced via infiltration/percolation using a 3-layer filter column comprising:
- Fly ash (30%);
- Bottom ash (30%);
- Coastal sand (40%).
Fly ash, composed mainly of spherical glassy particles rich in SiO2 and Al2O3, enhances pozzolanic reactivity and improves sludge binding capacity. Bottom ash, coarser and porous, improves filtration by retaining solids and adsorbing heavy metals. Coastal sand stabilizes the column and ensures permeability. The 30/30/40 ratio was determined based on a previous optimization study [2], balancing treatment efficiency and sludge stabilization. After percolation, the accumulated sludge was collected, dried, and ground as described above.
2.2. Mix Design for Mortar Preparation
Various mortars were prepared by partially replacing cement with wastewater sludge from the detergent manufacturing industry in proportions of 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, and 30%. The mixes are designated as M5, M10, M15, M20, M25, and M30, respectively, with the control mortar (without sludge) identified as M0. The preparation of the mortars followed the European standard NF EN 196-1 [23], which prescribes a standard mortar composition by mass: 450 g of cement, 1350 g of sand, and 225 g of water. The specific details of the cement-sludge mortar formulations are outlined in Table S4.
The mortar was prepared according to the NF EN 196-1 standard using a 5 L electric mixer [23]. The mixing process, lasting 4 min, proceeded as follows: water was added first, followed by cement, and the mixture was then stirred at low speed for 30 s. The sand was gradually added, the mixer was set to high speed for 60 s, and mixing was paused for 1 min and 30 s to scrape down the mortar adhering to the walls. Finally, mixing resumed at high speed for another 60 s.
2.3. X-Ray Diffraction and Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy
X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a powerful technique for identifying crystalline phases in solids and determining crystal structure dimensions [22,24]. In this research, an advanced X-ray diffractometer equipped with a copper (Cu) Kα anticathode was utilized as the X-ray source, producing radiation with a wavelength of λKα = 1.5406 Å. The instrument included a rotatable sample holder with an automatic changer to ensure precise sample positioning. An X′Celerator detector, combined with a secondary monochromator, enhanced the accuracy of the measurements. Diffractograms were interpreted using the ICDD PDF-2 database (International Center for Diffraction Data, Powder Diffraction File version) to identify the crystalline phases in the mortar samples. Furthermore, the sludge was analyzed for metal content (As, Co, Cr, Cu, Al, Ni, Pb, Zn, and Fe) using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES) [25].
2.4. Infrared Spectroscopy
Infrared spectra were acquired using a Nicolet iS10 Thermo Scientific spectrometer (Waltham, MA, USA)) equipped with an Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) accessory [24]. Each spectrum was generated by averaging 32 scans recorded at a high resolution of 4 cm−1. Solid samples were analyzed, with spectra representing the ratio of sample scans to a corresponding background spectrum recorded under identical conditions without the sample. This rigorous approach ensured reliable spectra, providing valuable insights into the molecular vibrations and composition of the studied materials.
2.5. Evaluation of Mechanical Properties
2.5.1. Preparation of Studied Samples
Before starting the mechanical study, the mortars are prepared in a parallelepiped form with dimensions of 4 × 4 × 16 cm3, as shown in Figure 1. The samples are then stored in a room with controlled temperature (20 °C) and humidity. These specimens are tested for flexural and compressive strength after 7 and 28 days [21].
Figure 1.
Mortar Specimens for Mechanical Study.
2.5.2. Methodology for Flexural and Compressive Strengths
The flexural and compressive strengths were measured using an MTS Criterion Electromechanical Press with three-point bending (TPB) tests. Each test was conducted in triplicate, and the average results were compared with a reference sample. The breaking load was obtained by applying a continuous force Ff to the upper surface of the specimen at a constant rate of 2 mm/min until fracture occurred, as depicted in Figure S2a. The breaking strength was then determined [21]. The flexural rupture strength Rf is determined using the formula:
where is the fracture force, is the support span, and represent the sample width and height, respectively (refer to Figure S2). Following the flexural tests, the resulting half-prisms were utilized to measure the compressive strength (see Figure S2b), calculated as:
where A is the cross-sectional area (4 × 4 cm2) [21]. A continuous force was applied to this transverse section at the same speed until fracture, providing the compressive strength value.
2.6. Studied Thermo-Physical Properties
2.6.1. Preparation of Samples
Seven samples were prepared using mortars in which cement was partially replaced by wastewater sludge from detergent manufacturing, in proportions of 0%, 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, and 30%. This setup aimed to study the thermophysical properties and select the optimal building proportions, as shown in Figure 2. These samples are parallelepipeds with dimensions of 3.5 × 7 × 11 cm3. For precise measurement of thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity in low-conductivity materials, the sample thickness typically ranges from 20 to 40 mm and should ideally not be smaller than the radius of the hot disk sensor [26]. All the samples were demolded after 24 h and then air-dried in the laboratory for 28 days. The results presented were obtained by calculating the average of the results from the different analyses.

Figure 2.
Mortar samples for thermal conductivity measurements.
2.6.2. Experimental Method
Most studies on construction materials focus on examining the absolute value of heat transfer (thermal conductivity) and the speed of this transfer (thermal diffusivity). Materials with low thermal conductivity serve as insulators and exhibit high thermal resistance [14]. When thermal conductivity varies with spatial coordinates (x, y, z) and temperature (T), which is time-dependent (t), the Fourier equation is represented as:
When the parameters do not depend on temperature, Equation (3) simplifies to:
The heat equation describing transient one-dimensional heat transfer in a homogeneous wall of thickness is therefore expressed as:
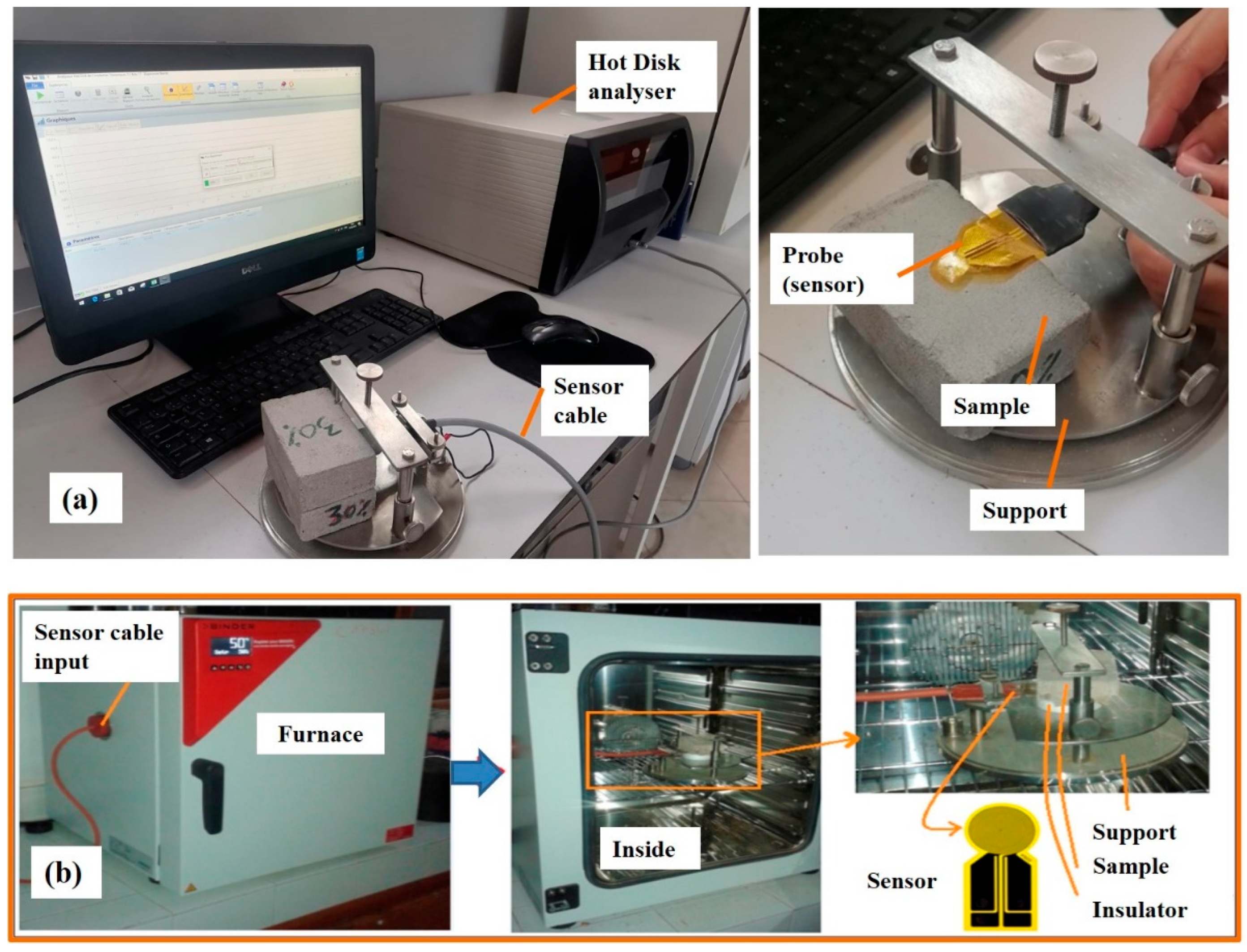
The thermal conductivity of building materials is typically measured using the stationary hot plate method. In this study, material characterization was performed with a Hot Disk TPS 1500 device (Figure 3), which is designed to simultaneously determine both thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity [26].
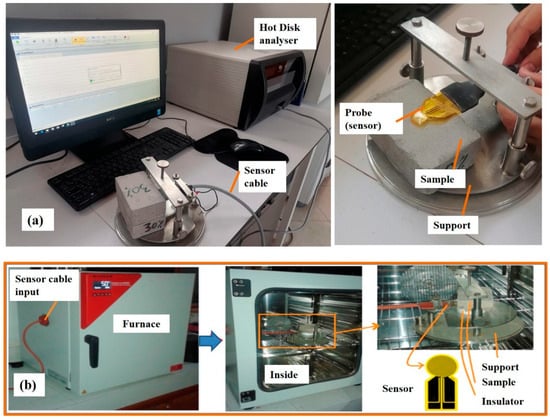
Figure 3.
Setup for measuring thermal properties: (a) at ambient temperature, (b) at varying temperatures.
The measurement principle is based on applying a uniform heat flow across a plane that divides two symmetrically placed samples. A probe situated between these samples delivers a constant electrical power (acting as the heat source) and monitors the temperature change in the samples (serving as the temperature sensor). The probe consists of a double nickel spiral, 10 μm thick, sandwiched between two layers of Kapton insulation. The increase in electrical resistance of the probe corresponds to the temperature rise, which can be represented over time as follows [14]:
R0 represents the resistance of the disk at the initial time t = 0, right before heating begins. The variable r denotes the temperature coefficient of resistivity, while indicates the constant temperature difference that quickly develops across the thin insulating layers on each side of the sensor. When thermal contact is perfect, = 0.
The opposite side of the sensor is in contact with an insulating material that has well-defined thermal properties (see Figure 3a). The sensor’s sensitive area is protected from environmental influences and only interacts with the sample and the insulating material, allowing it to measure the temperature difference immediately after power is applied.
(τ) denotes the temperature increase on the sensor surface facing the sample.
To assess thermal properties at different temperatures (30, 40, and 50 °C), a furnace connected to the Hot Disk device was used (see Figure 3b). Prior to each measurement, the sample was heated in the furnace for about 30 min to ensure temperature stabilization.
Once thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity, and density are determined, specific heat can be calculated directly using the following formula:
Thermal effusivity is an essential property for describing heat fluxes, particularly when heat moves through various materials. It reflects how quickly a material’s surface temperature increases. This property can be determined using the values for thermal conductivity and thermal capacity, as demonstrated in Equation (8).
with
- (W/m·K): Thermal conductivity;
- α (mm2/s): Thermal diffusivity = λ/(ρ·cp);
- (kg/m3): Density;
- (J/kg·K): Specific heat capacity;
- (MJ/m3·K): Volumetric heat capacity;
- E (J/m2·K·s½): Thermal effusivity.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Particle Size and Chemical Composition of Sludge
3.1.1. Particle Size Analysis of Sludge
The particle size analysis of sludge, shown in Figure S3, illustrates the particle size distribution and identifies the proportion of fine particles, which is essential for construction applications. The curve reveals three distinct zones: a low proportion of particles smaller than 0.2 mm, a significant concentration of particles between 0.2 mm and 0.4 mm, reaching 90% at 0.4 mm, and a final zone where particle size reaches 98% at 0.63 mm.
The analysis indicates a high proportion of fine particles in the sludge, making it particularly suitable for use in construction materials, especially as an additive in eco-friendly mortars. The fine particles in the sludge enhance mortar cohesion and density by filling voids between larger sand or gravel grains. This improves compaction, which can increase the mechanical strength of the final material. Moreover, incorporating sludge in mortars reduces the demand for cement, which is energy-intensive to produce and a source of CO2 emissions [27].
3.1.2. Chemical Composition of Sludge
Table S5 shows that the chemical composition of sludge includes a significant concentration of SiO2 (46.58%) and CaO (28.66%), indicating strong potential for pozzolanic applications, where these components can partially replace Portland cement by contributing to material solidification and stabilization. The high SiO2 content, which exceeds that of Portland cement, enhances the sludge’s ability to participate in cementitious reactions, improving the mechanical properties of mixtures. The presence of Al2O3 (15.54%) further supports this by contributing to the formation of alumino-silicate compounds, while Fe2O3 (3.55%) and MgO (2.24%) offer additional stabilizing properties. The low proportions of Na2O (0.63%) and K2O (0.34%) minimize the risk of alkali-silica reactions (ASR), which is advantageous for material durability. Overall, this sludge has a balanced composition favorable for ecological construction, as it can function effectively as an activator or binder in pozzolanic processes while maintaining stable chemical properties [28,29].
3.2. Evaluation of the Mechanical Properties of Sludge-Based Mortars
To evaluate the mechanical properties of the mortars, samples were prepared by substituting cement with sludge at varying levels, ranging from 0% to 30%. flexural and compression tests were conducted on these samples after maturation periods of 7 and 28 days. The primary objective was to identify the optimal substitution rate of cement with sludge by analyzing its impact on the mechanical performance of the mortars.
3.2.1. Flexural Strength
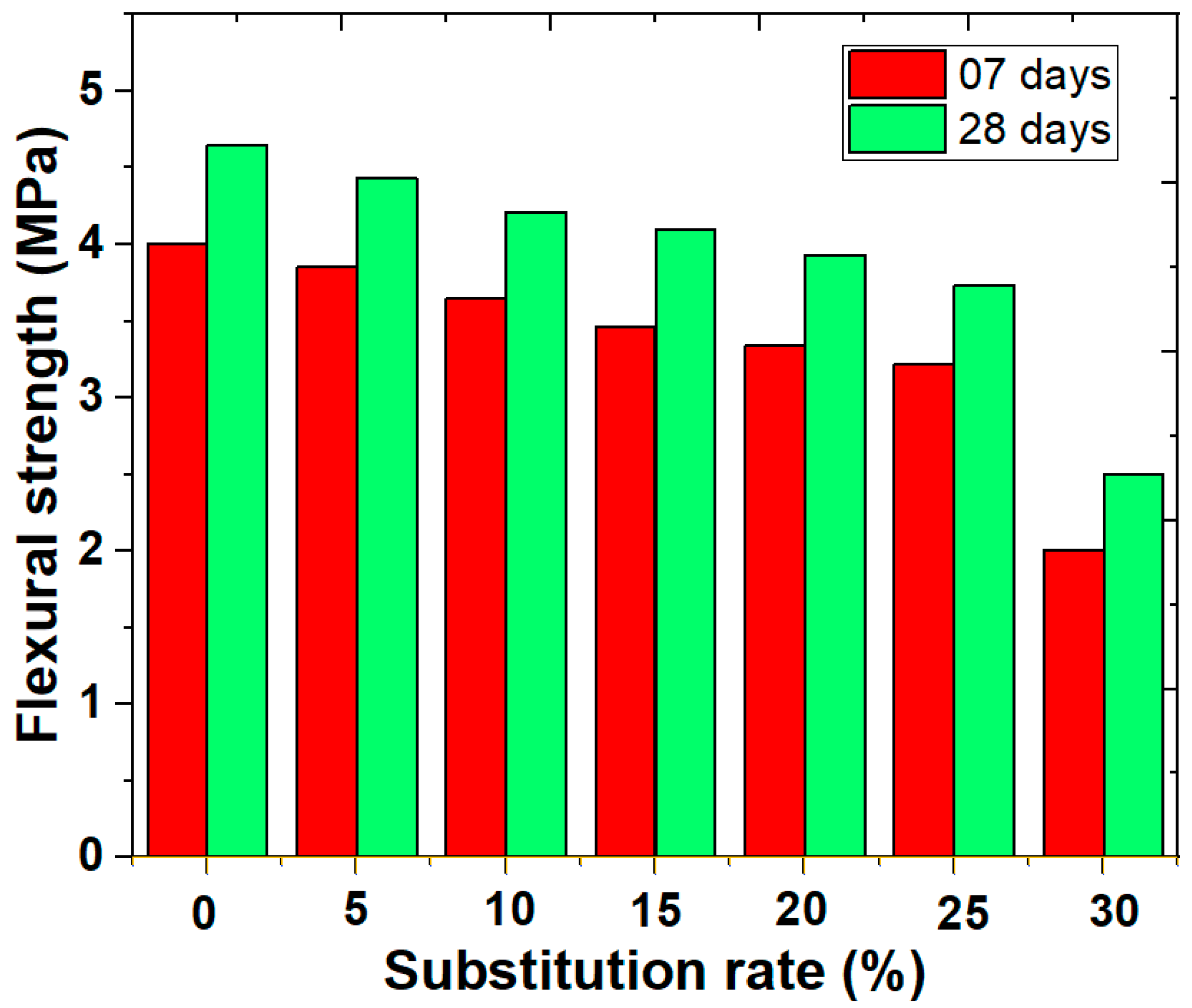
Flexural strength is a fundamental criterion in the design of construction materials, as it ensures the structural performance of elements subjected to bending stresses. The data in Figure 4 indicate that the flexural strength of mortars decreases significantly as the cement substitution rate by sewage sludge increases. For the mortar without sludge, the strength is 4.00 MPa after 7 days and 4.65 MPa after 28 days, serving as the reference. With a 5% sludge substitution, the strength slightly decreases to 3.85 MPa after 7 days and 4.43 MPa after 28 days, corresponding to a reduction rate of 3.75% and 4.73%, respectively. At 10% substitution, the strength falls to 3.65 MPa after 7 days and 4.21 MPa after 28 days, representing decreases of 8.75% after 7 days and 9.46% after 28 days. From 15% substitution, the drop becomes more noticeable, with strengths of 3.46 MPa (13.50% decrease) after 7 days and 4.10 MPa (11.83% decrease) after 28 days. At 20% sludge, the strength declines to 3.34 MPa after 7 days and 3.93 MPa after 28 days, corresponding to reduction rates of 16.50% and 15.48%, respectively. With 25% substitution, the strength is 3.22 MPa after 7 days and 3.73 MPa after 28 days, showing a decrease of 19.50% after 7 days and 19.78% after 28 days. Finally, at 30% substitution, the strength drastically decreases to 2.01 MPa after 7 days and 2.50 MPa after 28 days, a significant reduction of 49.75% after 7 days and 46.24% after 28 days.
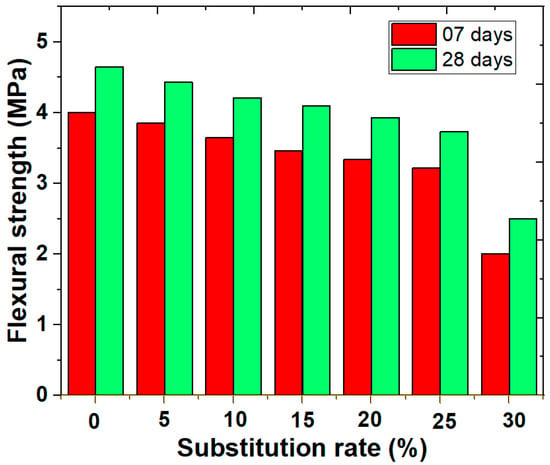
Figure 4.
Flexural strength of cement–sludge mortars after 7 and 28 days of curing.
Figure 4 presents the mean flexural strength values (±standard deviation) for mortars cured for 7 and 28 days. As sludge content increased, strength decreased gradually due to higher porosity and reduced cement hydration products.
- M0 (0% sludge): 4.65 ± 0.08 MPa;
- M20 (20% sludge): 3.93 ± 0.06 MPa (15.5% decrease);
- M30 (30% sludge): 2.50 ± 0.09 MPa (46.2% decrease).
Although 20% substitution reduces flexural strength, it remains above the minimum threshold of 3.5 MPa for non-load-bearing masonry units according to EN 998-2.
The reductions in strength are attributed to the increased porosity and heterogeneity of the mortar’s microstructure due to the incorporation of sludge, which weakens its cohesion [30,31]. To maintain optimal mechanical performance, it is recommended not to exceed a 20% substitution rate.
3.2.2. Compressive Strength
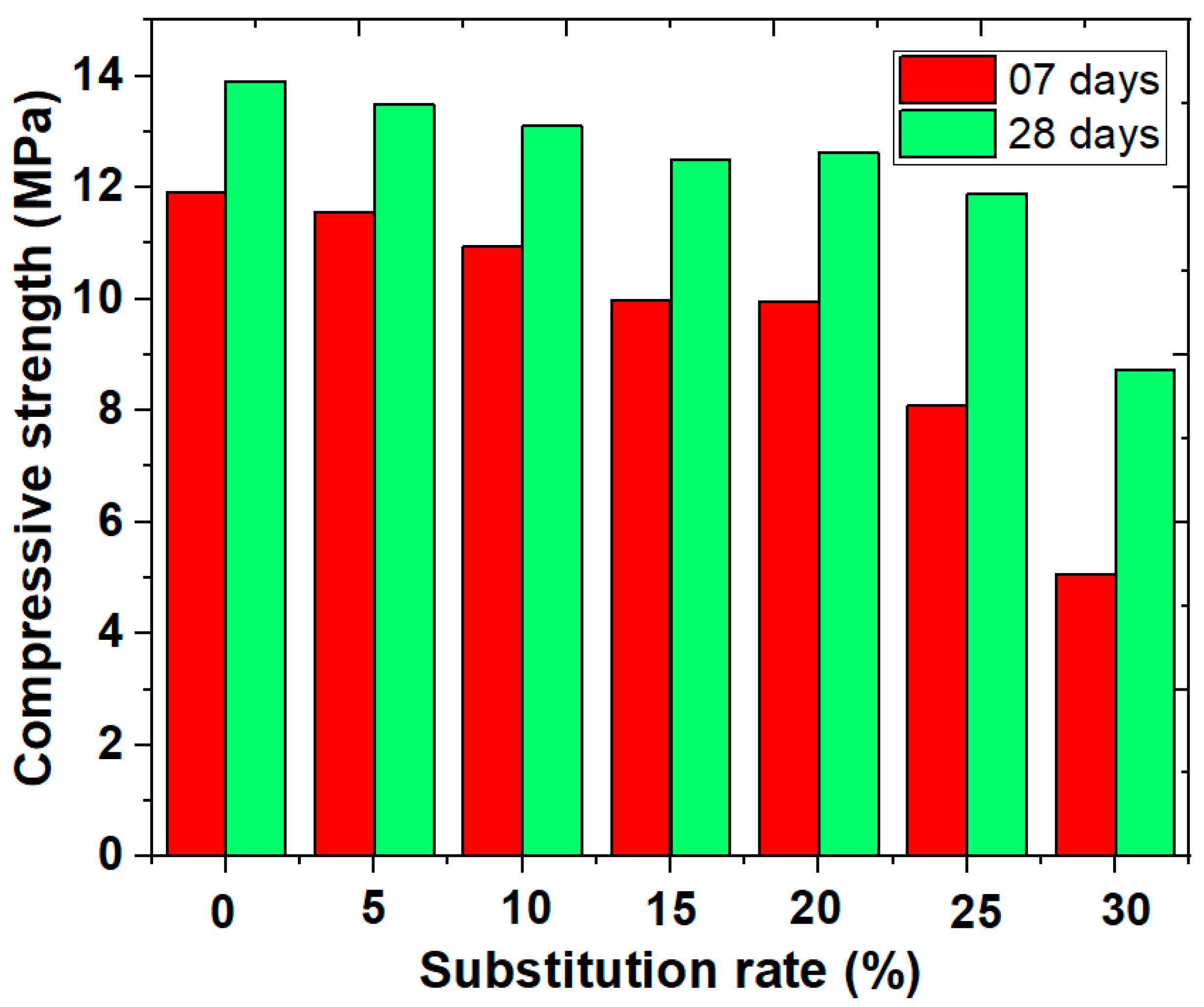
Compressive strength is a key indicator of construction material quality [32]. Figure 5 shows the effect of partially replacing cement with sludge from wastewater treatment in detergent manufacturing on the compressive strength of mortars after 7 and 28 days of curing. In all cases, compressive strength increases over time, with values at 28 days exceeding those at 7 days. This indicates that the addition of sludge does not hinder mortar solidification, regardless of the substitution percentage used [33].
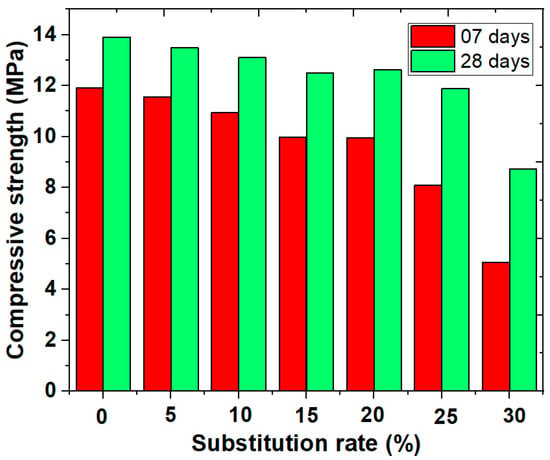
Figure 5.
Compressive strength of cement–sludge mortars after 7 and 28 days of curing.
The reference mortar, without sludge, has a compressive strength of 11.91 MPa at 7 days and 13.91 MPa at 28 days. As the cement substitution rate with sludge increases, compressive strength gradually decreases. For instance, after 7 days, a mortar with 5% sludge shows a slight reduction in strength to 11.55 MPa (a 3% decrease compared to the reference mortar), while with 30% sludge, the strength drops to 5.06 MPa, nearly a 57.5% reduction. This gradual decline in strength is also observed at 28 days, though the impact is slightly less pronounced over the long term. At 28 days, the mortar with 5% sludge reaches 13.48 MPa, nearly equivalent to the reference mortar with only a 3.1% reduction, while with 30% sludge, it falls to 8.73 MPa, representing a 37.2% decrease. At a 20% substitution rate, strength values are 9.95 MPa at 7 days (a 16.4% reduction) and 12.63 MPa at 28 days (a 9.2% reduction), which is considered the maximum substitution rate to maintain acceptable performance [34].
The results show a clear trend: as the proportion of sludge increases, compressive strength decreases. This reduction can be attributed to the decrease in reactive cement available for forming hydration products that contribute to the mortar’s strength. While the inclusion of sewage sludge in mortar mixes may offer ecological or economic benefits, it is crucial to limit its proportion to maintain adequate mechanical performance [34]. Specifically, substitution rates up to 20% result in strength reductions that remain within an acceptable range, allowing the mortar to develop sufficient strength after 7 and 28 days. Such rates could be suitable for non-structural applications or uses with less stringent strength requirements. In contrast, substitution rates above 20% lead to significant strength reductions, potentially compromising the mortar’s performance in applications requiring high mechanical robustness. For instance, a 25% sludge substitution yields a strength of 8.09 MPa at 7 days and 11.88 MPa at 28 days, representing respective reductions of 32% at 7 days and 14.6% at 28 days compared to the reference mortar.
The optimal sludge substitution rate for maintaining acceptable mechanical performance appears to be limited to around 20%. Beyond this threshold, the negative impacts on compressive strength become too pronounced for typical applications.
At 28 days, the reduction in strength is less pronounced than at 7 days, indicating that the negative effect of the sludge decreases over time. This gradual improvement reduces the strength gap between sludge-containing mortars and reference mortars. This trend can be attributed to the relatively slow pozzolanic reactivity of the sludge [4].
The reduction in strength is attributed to the excessive presence of waste, which slows down the hydration reaction and hinders the formation of portlandite and calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H), both essential for enhancing the mechanical strength of materials. This less intense hydration reaction may be due to the lower calcium oxide content in the sludge compared to that in cement [10]. To maintain optimal mortar performance, the sludge substitution rate should not exceed 20%.
The partial replacement of cement with 20% sludge shows a notable improvement in compressive strength at 28 days, likely due to a more pronounced pozzolanic reaction [11].
Compressive strength increased from 7 to 28 days across all mixtures (Figure 5), confirming ongoing hydration.
- M0: 13.91 ± 0.13 MPa at 28 days;
- M20: 12.63 ± 0.11 MPa (9.2% reduction);
- M30: 8.73 ± 0.14 MPa (37.2% reduction).
At 20% substitution, the mortar satisfies the standard EN 998-2 for structural masonry (≥10 MPa), making it technically viable. Higher substitution levels compromise compressive strength due to dilution of cementitious material and increased pore connectivity.
This improvement highlights the potential of sludge to positively influence the properties of mortar when used within optimal limits. These findings prompt further investigation into the crystallographic properties of mortars, particularly through X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, to evaluate the mineralogical changes occurring during the hydration process. This analysis is especially valuable for understanding the formation of beneficial hydration products like C-S-H, which are essential for enhancing the material’s strength and durability [30].
3.3. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis Results of Mortars
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns shown in Figure S4 for both hearth ash and fly ash clearly reveal diffraction lines corresponding to the crystalline structures of quartz (SiO2) and mullite (3Al2O3·2SiO2). These identifications are based on their precise match with standard Powder Diffraction File (PDF) data, specifically PDF No. #01-085-0794# for quartz and #00-006-0259# for mullite [2].
Additionally, Infrared (IR) analysis further confirms this identification by providing spectra for both types of ash. The IR spectra exhibit no significant differences between hearth ash and fly ash, displaying characteristic bands associated with O-Si-O and O-Al-O vibrations, consistent with literature reports [35] (Figure S5).
The combined evidence from XRD and IR analyses provides a robust understanding of the crystalline phases in the hearth ash and fly ash samples. The lack of variation in the IR spectra highlights the similarity in their chemical compositions, particularly regarding O-Si-O and O-Al-O functionalities. This integrated analytical approach reinforces the confidence in the identified crystalline structures, offering valuable insights into the mineralogical composition of the ash samples.
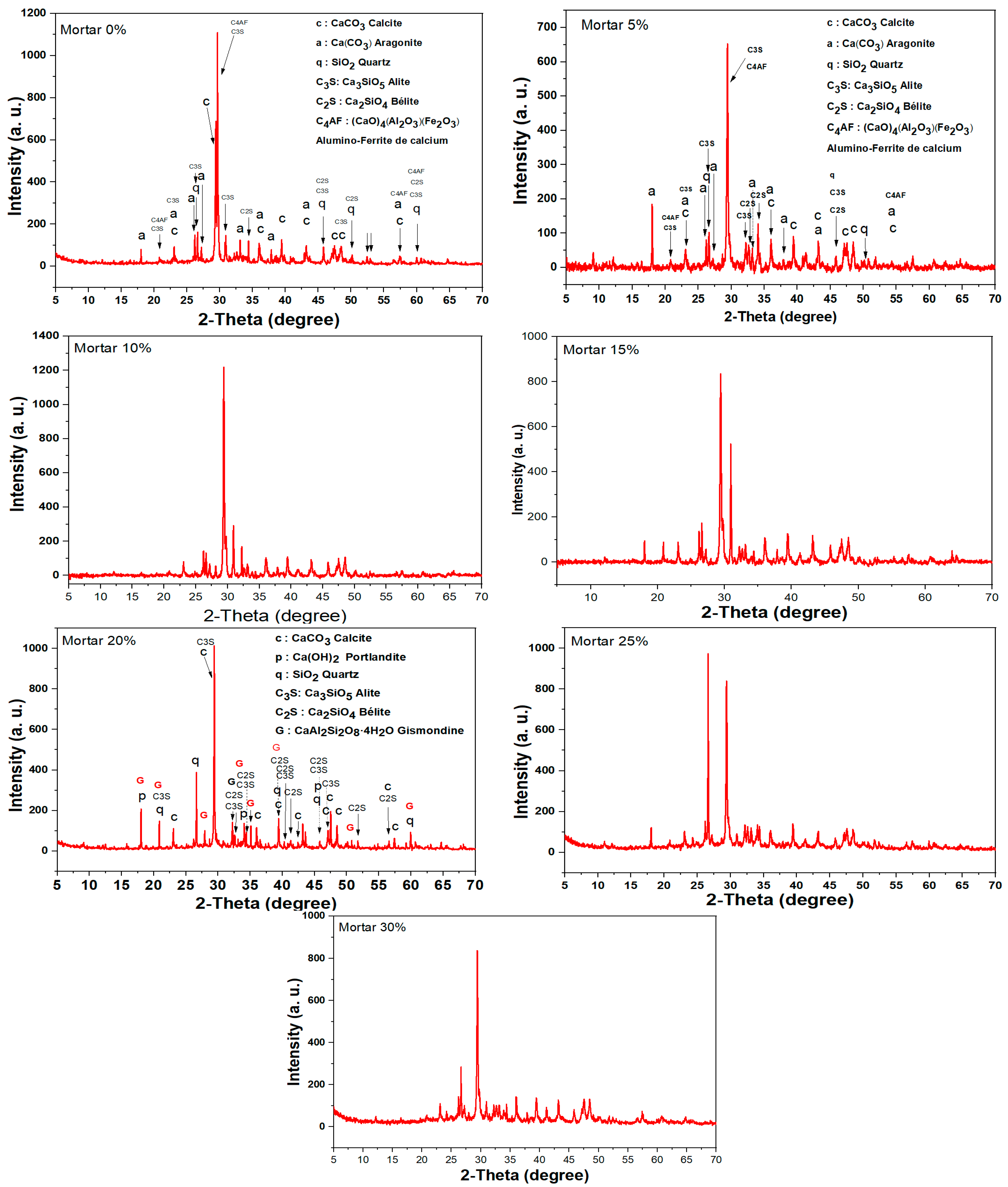
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) diagram of the mortar containing 0%, 5%, 10%, 15%, 25%, and 30% sludge, prepared using cement clinker and sand, is illustrated in Table S6 and Figure 6. The XRD pattern exhibits sharp peaks, providing 2θ angle values corresponding to various phases present in the cement clinker and sand. The identified phases closely align with the diffraction patterns of pure substances, including calcite (CaCO3), aragonite (CaCO3), quartz (SiO2), alite (C3S, tricalcium silicate), belite (C2S, dicalcium silicate), and calcium alumino-ferrite ((CaO)4(Al2O3)(Fe2O3)), which are the primary minerals found in clinker cement and sand [36].
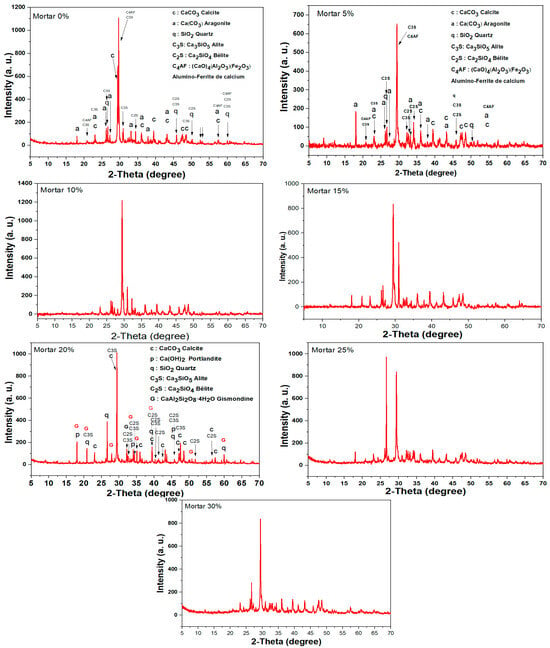
Figure 6.
XRD patterns of mortars 0%, 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, and 30%.
The diffraction peaks match the standard Powder Diffraction File (PDF) data for each identified phase, specifically for calcite, aragonite, quartz, alite (C3S), belite (C2S), and calcium alumino-ferrite. These phases represent the principal constituents of clinker cement, comprising tricalcium silicates, dicalcium silicate, tetracalcium ferro-aluminate, and quartz. Their presence in the mortar confirms a well-defined and expected mineralogical composition consistent with the raw materials used in its preparation. The XRD analysis proves instrumental in characterizing the crystalline phases of the mortar, offering valuable insights into its structural and compositional attributes [37].
Additionally, the XRD pattern of the mortar incorporating 20% sludge (residual solids derived from wastewater treatment using hearth ashes and fly ashes, both pozzolanic materials) reveals the emergence of a novel phase, gismondine (calcium aluminum silicate tetrahydrate). This new phase indicates a transformation in the mineralogical composition of the mortar due to the addition of sludge [38]. Figure 5 demonstrates that the inclusion of 20% sludge significantly enhances the mortar’s compressive strength. This improvement is attributed to the pozzolanic reaction within the mixture, leading to the conversion of tetracalcium alumino-ferrite into calcium aluminosilicate tetrahydrate, which substantially contributes to the observed increase in strength.
The use of pozzolanic additions, such as fly ash and sludge, not only introduces new mineral phases but also improves the mechanical performance of the mortar over the long term. This enhancement is particularly evident in increased resistance to compression and bending. The underlying mechanism involves the pozzolanic reaction between silica and portlandite (Ca(OH)2), which results in the formation of additional calcium aluminosilicate hydrates. These hydrates densify the mortar matrix, thereby improving its mechanical properties.
The XRD analysis and compressive strength assessment highlight the positive effects of incorporating sludge and fly ash into mortar. The findings underscore the significance of pozzolanic reactions in enhancing the material’s long-term mechanical performance and structural integrity.
3.4. Evaluation of the Thermophysical Properties of Sludge-Based Mortars
3.4.1. Analysis of Thermophysical Properties
The design of a building is based on two main factors: thermal comfort and energy efficiency [39]. While retaining heat is important for lowering energy consumption, it alone is not enough to achieve optimal thermal performance year-round. Equally important is the capacity to store heat within the building to reduce temperature fluctuations and maximize free solar gains [26].
Thermal inertia (or thermal mass) and thermal phase shift are key aspects of building design, as they significantly affect thermal comfort. Thermal inertia refers to a material’s ability to absorb and gradually release heat, mainly influenced by its thermal capacity. Thermal phase shift, on the other hand, refers to the time delay for heat flux to travel through a wall of a certain thickness, which is affected by the material’s thermal capacity and the type of insulation used [40].
When selecting the most appropriate construction materials, it is important to assess several thermophysical properties: thermal conductivity (λ), which measures how well a material conducts heat; thermal diffusivity (α), which indicates how quickly heat moves through the material; thermal effusivity (E), which describes a material’s ability to exchange heat with its surroundings; and thermal capacity, the product of specific heat capacity (cp) and density (ρ). These properties are essential for determining a material’s ability to provide optimal thermal comfort while enhancing energy efficiency [14].
3.4.2. Results of Thermophysical Properties
The study aimed to repurpose sludge generated from wastewater treatment in detergent manufacturing as a component of construction materials, with the objective of reducing thermal conductivity and enhancing thermal storage capacity at room temperature. Thermophysical property measurements for each sample were performed three times to calculate average values and assess measurement errors. Prior to the measurements, the samples were in their standard (dry) state and were conditioned for three days under controlled laboratory conditions: a temperature of 30 ± 2 °C and a pressure of 1 atm.
Thermophysical Characterization
Table 1 summarizes the thermophysical properties of the studied samples, measured under standard laboratory conditions. Uncertainty analyses for these measurements are also included in Table 1. These uncertainties were calculated using the following equations, resulting in highly satisfactory outcomes [14]:

Table 1.
Thermophysical properties of mortars incorporating wastewater sludge from the detergent industry at ambient temperature.
Table 1 summarizes the thermophysical properties of various mortars containing different percentages of wastewater sludge from the detergent manufacturing industry, measured at an ambient temperature of 30 °C. The properties measured include thermal conductivity (λ) in W/m·K, thermal diffusivity (α) in mm2/s, thermal capacity () in MJ/m3·K, and thermal effusivity (E) in J/m2·K·s1/2 for each mortar formulation, with sludge content ranging from 0% to 30% by weight of cement.
The study of the thermophysical properties of mortars reveals significant variations in thermal conductivity (λ) and thermal diffusivity (α) with increasing sludge content. According to the literature, an insulating material typically has a thermal conductivity below 0.1 W/m·K [14]. In this study, the thermal conductivity decreases from 1.054 W/m·K for mortar without sludge to 0.6699 W/m·K for mortar containing 30% sludge, which can be attributed to the presence of materials less conductive than pure cement. Similarly, the thermal diffusivity follows a comparable trend, decreasing from 0.6096 mm2/s to 0.4706 mm2/s as the sludge content increases. These findings indicate that the material retains heat for longer periods, enhancing thermal stability. The relative uncertainties for these measurements, expressed as Δλ/λ and Δα/α, range from 0.18% to 1.15% and 0.13% to 2.38%, respectively, highlighting the high precision of the results.
The analysis reveals that the thermal capacity of mortars generally decreases as sludge content increases, dropping from 1.729 MJ/m3·K for mortar without sludge to 1.424 MJ/m3·K for mortar containing 30% sludge. This reduction is attributed to the lower density and less thermally conductive nature of sludge particles compared to pure cement. Similarly, thermal effusivity exhibits a comparable trend, decreasing from 1349.9 J/K·m2·s1/2 to 976.7 J/K·m2·s1/2 over the same range of sludge percentages. These findings suggest that mortars incorporating wastewater sludge can experience significant variations in thermal performance, potentially affecting their suitability for applications requiring precise heat management. The relative uncertainties for these measurements, expressed as Δ(ρcp)/(ρcp) and ΔE/E, range from 0.98% to 2.92% for thermal capacity and from 0.7% to 1.935% for thermal effusivity, underscoring the high precision of the results.
The addition of sludge to mortar enhances its insulating properties by reducing its ability to transmit and propagate heat, making it more suitable for applications requiring effective thermal insulation [41]. These findings suggest that incorporating wastewater sludge into mortars can significantly improve their thermal insulation performance.
The variations in the thermal properties of mortars containing wastewater sludge are driven by several mechanisms. The incorporation of sludge, which is less dense and less thermally conductive than cement, reduces thermal conductivity by disrupting the heat transmission pathways. This also affects thermal diffusivity by hindering the uniform dispersion of heat within the mortar. Furthermore, the addition of sludge decreases the heat capacity of the mortar, reducing its ability to store heat. These changes collectively influence thermal effusivity, which integrates thermal conductivity and thermal capacity to define the material’s response to temperature variations. Consequently, the addition of sludge induces a complex transformation in the thermal properties of the mortar, making it possible to tailor its performance to meet specific thermal insulation and thermal inertia requirements in various applications [42].
Effect of Sludge Content on Thermal Conductivity
Figure S6 illustrates the thermal conductivity of mortars as a function of sludge percentage at ambient temperature. The data analysis clearly demonstrates the significant impact of sludge content on the thermal conductivity of mortars. As the percentage of wastewater sludge increases, thermal conductivity progressively decreases. For example, at 5% sludge, the average thermal conductivity is 0.9059 W/m·K, while at 30% sludge, it decreases to approximately 0.6699 W/m·K. This linear trend indicates that partially replacing cement with sludge, which is less dense and less thermally conductive, effectively reduces the mortar’s ability to transmit heat. Moreover, cement particles contribute to enhanced contact and bonding between clay grains, resulting in improved compaction and, an increase in the material’s thermal conductivity [43].
These results indicate that increasing the sludge content improves the thermal insulation properties of the mortar, which can be advantageous for applications requiring enhanced energy efficiency. However, it is also essential to consider other mechanical properties and the durability of the mortar when evaluating these formulations for practical use.
Variation in Thermal Conductivity with Temperature
Table 2 presents detailed results of thermal conductivity measurements for mortar samples containing varying proportions of wastewater treatment sludge from the detergent manufacturing industry, used as a partial replacement for cement. The samples were evaluated at three specific temperatures: 30 °C, 40 °C, and 50 °C. For each sludge content (5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, and 30%) and temperature, the average thermal conductivity values (λ Average) and relative variations (Δλ/λ %) are provided. These measurements are crucial for understanding the thermal performance of these mortars under realistic conditions, such as those encountered in building structures. The data from Table 2 are also represented in Figure S7. The influence of temperature on thermal conductivity was significant. The results indicate that the average thermal conductivity increases with temperature for all samples, though the rate of increase varies with sludge content. This finding aligns with the study on palm fiber concrete conducted by Tiskatine et al. [14].

Table 2.
Thermal conductivity of mortar samples at different temperatures.
At 30 °C, the average thermal conductivity decreases from 1.054 W/m·K for the mortar without sludge to 0.6699 W/m·K for the mortar containing 30% sludge, indicating a progressive reduction in the mortar’s ability to conduct heat as the sludge content increases. This trend continues at higher temperatures. At 40 °C, the thermal conductivity increases by 1.14% for the mortar with 5% sludge and by 0.53% for the mortar with 30% sludge. Similarly, at 50 °C, the increases are 0.37% and 0.53%, respectively. At 50 °C, the highest thermal conductivity is observed for the mortar without sludge (1.083 W/m·K), while the lowest is recorded for the mortar containing 30% sludge (0.6745 W/m·K). The results also show that, although thermal conductivity increases slightly with temperature for each formulation, the relative differences (Δλ/λ) remain small, indicating a stable thermal response despite temperature variations. These findings highlight that, while thermal conductivity increases with temperature, the use of wastewater sludge as a partial cement substitute significantly reduces the material’s thermal conductivity. This reinforces the potential utility of these mortars in applications where thermal insulation is a priority.
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrated the technical, thermal, and economic feasibility of using sludge derived from detergent industry wastewater treatment as a partial cement substitute in mortar formulations. The results indicate that a 20% substitution rate by mass of cement offers the best compromise between mechanical performance and thermal efficiency. At this level, the mortars achieved compressive strength above 12 MPa and a 25% reduction in thermal conductivity, making them suitable for specific non-load-bearing applications such as interior wall blocks, partition panels, and thermal insulation mortar layers. For applications where insulation is prioritized over strength—such as plasters or insulating underlayers—higher substitution levels (up to 30%) may be acceptable. A comparative cost analysis shows a reduction of approximately 12–15% in production costs compared to conventional mortars, while also eliminating sludge disposal costs, estimated between EUR 20 and EUR 40 per ton. These findings reinforce the value of this circular approach, especially in regions facing high cement costs or strict environmental regulations. The formation of gismondine at the 20% level indicates pozzolanic activity that enhances long-term durability. In the future, these eco-efficient mortars could be integrated into green building certification frameworks and low-carbon construction policies, promoting their adoption in the sustainable materials market.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/recycling10050192/s1, Figure S1. Wastewater sludge before and after drying and grinding; Figure S2. Flexural (a) and compressive strength tests (b); Figure S3. Particle size distribution of wastewater treatment sludge; Figure S4. X ray diffraction diagrams of hearth ashes and fly ashes; Figure S5. Infrared spectra of hearth ashes and fly ashes; Figure S6. Variation of thermal conductivity at ambient temperature as a function of sludge content; Figure S7. Thermal conductivity of mortar samples as a function of temperature; Table S1. Chemical composition of Portland cement (CPJ 45); Table S2. Physical characteristics of cement; Table S3. Chemical composition of sand souiria; Table S4. Formulation of Mortar Specimens Based on Sludge; Table S5. Chemical composition (in mass %) of the sludge; Table S6. Mineral phases identified in mortars with different percentages of sludge and standard PDF data.
Author Contributions
E.M.E.H. played a key role in sample collection and selection, data curation, analysis, methodology development, interpretation, writing, and initial project planning. A.M. and B.L. contributed to the design and refinement of tables and figures, while E.G.C. and S.L. participated in the revision process. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors confirm that no funding was received for this work.
Data Availability Statement
The data will be provided upon request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere appreciation to Rachid Safoui from the Department of Physics at the University Ibn Zohr—Agadir for his invaluable help in carrying out the thermophysical property measurements.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Parde, D.; Behera, M. Challenges of wastewater and wastewater management. In Sustainable Industrial Wastewater Treatment and Pollution Control; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 229–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hafidi, E.M.; Mortadi, A.; Graich, A.; Chahid, E.G.; Laasri, S.; Moznine, R.E.; Monkade, M. Monitoring treatment of industrial wastewater using conventional methods and impedance spectroscopy. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulke, A.B.; Ratanpal, S.; Sonker, S. Understanding heavy metal toxicity: Implications on human health, marine ecosystems and bioremediation strategies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 206, 116707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Z.; Long, G.; Zhou, J.L.; Ma, C. Valorization of sewage sludge in the fabrication of construction and building materials: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 154, 104606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherghel, A.; Teodosiu, C.; De Gisi, S. A review on wastewater sludge valorisation and its challenges in the context of circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 244–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.L.; Lin, C.Y. Hydration characteristics of waste sludge ash utilized as raw cement material. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1999–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.L.; Chiang, K.Y.; Lin, C.Y. Hydration characteristics of waste sludge ash that is reused in eco-cement clinkers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Jo, B.W.; Jo, J.H.; Baloch, Z. Effectiveness of sewage sludge ash combined with waste pozzolanic minerals in developing sustainable construction material: An alternative approach for waste management. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 153, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejdi, M.; Saillio, M.; Chaussadent, T.; Divet, L.; Tagnit-Hamou, A. Hydration mechanisms of sewage sludge ashes used as cement replacement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 135, 106115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Su, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Luo, X.; Zhou, M.; Luo, W.; et al. Mechanistic study of the effect of potassium ferrate and straw fiber on the enhancement of strength in cement-based solidified municipal sludge. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agra, T.M.; Lima, V.M.; Basto, P.E.; Neto, A.A.M. Characterizing and processing a kaolinite-rich water treatment sludge for use as high-reactivity pozzolan in cement manufacturing. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 236, 106870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Han, M.Y.; Liu, S.Y.; Chen, G.Q. Energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions by buildings: A multi-scale perspective. Build. Environ. 2019, 151, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, D.; Hu, S.; Guo, S. Modelling of energy consumption and carbon emission from the building construction sector in China, a process-based LCA approach. Energy Policy 2019, 134, 110949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiskatine, R.; Bougdour, N.; Oaddi, R.; Gourdo, L.; Rahib, Y.; Bouzit, S.; Bazgaou, A.; Bouirden, L.; Ihlal, A.; Aharoune, A. Thermo-physical analysis of low-cost ecological composites for building construction. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 20, 762–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, S.S.; Sharma, V.; Marwah, B.M. Review of energy efficient features in vernacular architecture for improving indoor thermal comfort conditions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 65, 459–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfano, F.R.D.A.; Olesen, B.W.; Palella, B.I.; Riccio, G. Thermal comfort: Design and assessment for energy saving. Energy Build. 2014, 81, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, G.; Buonomano, A.; Forzano, C.; Giuzio, G.F.; Palombo, A.; Russo, G. A new thermal comfort model based on physiological parameters for the smart design and control of energy-efficient HVAC systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 173, 113015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, D.S.; Sivasuriyan, A.; Patchamuthu, P.; Jayaseelan, R. Thermal performance of energy-efficient buildings for sustainable development. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 51130–51142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassiri, S.; Butt, A.A.; Zarei, A.; Roy, S.; Filani, I.; Pandit, G.A.; Mateos, A.; Haider, M.M.; Harvey, J.T. Opportunities for Supplementary Cementitious Materials from Natural Sources and Industrial Byproducts: Literature Insights and Supply Assessment. Buildings 2025, 15, 3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golewski, G.L. The Investigation of Shear Fracture Toughness and Structure of ITZ of Limestone Concrete with Different Aggregate Grain Size. Materials 2025, 18, 3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mghaiouini, R.; Abderrazzak, G.; Benzbiria, N.; Elaoud, A.; Garmim, T.; Belghiti, M.E.; Hozayn, M.; Monkade, M.; El Bouari, A. Elaboration and physico-mechanical characterization of a new eco-mortar composite based on magnetized water and fly ash. J. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 21, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hafidi, E.M.; Mortadi, A.; Lizoul, B.; Hairch, Y.; Mghaiouini, R.; Sabor, A.; Mnaouer, K.; Chahid, E.G.; Jebbari, S.; El Moznine, R.; et al. Assessment of sand and hearth ash filtration for wastewater treatment and novel monitoring via complex conductivity. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2025, 10, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaich, F.Z.; Maherzi, W.; Benzerzour, M.; Taleb, M.; Abriak, N.E.; Rais, Z.; Senouci, A. Mortar mixing using treated wastewater feasibility. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 352, 128983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizoul, B.; Mortadi, A.; El Hafidi, E.M.; Kounbach, S.; Elmelouky, A. Exploring the interactions of apatitic tricalcium phosphate with copper ions: Time-resolved structural transformations and electrical property insights. Solid State Ion. 2024, 410, 116552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laasri, S.; El Hafidi, E.M.; Mortadi, A.; Chahid, E.G. Solar-powered single-stage distillation and complex conductivity analysis for sustainable domestic wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 29321–29333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiskatine, R.; Bougdour, N.; Idoum, A.; Bazgaou, A.; Oaddi, R.; Ihlal, A.; Aharoune, A. Experimental investigation on rock thermal properties under the influence of temperature. Thermochim. Acta 2023, 720, 179424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcu, M.; Gencel, O.; Erdogmus, E.; Kizinievic, O.; Kizinievic, V.; Karimipour, A.; Velasco, P.M. Low cost and eco-friendly building materials derived from wastes: Combined effects of bottom ash and water treatment sludge. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 324, 126669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świerczek, L.; Cieślik, B.M.; Konieczka, P. The potential of raw sewage sludge in construction industry—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 200, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, R.; de la Villa, R.V.; Vegas, I.; Frías, M.; de Rojas, M.S. The pozzolanic properties of paper sludge waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaly, A.O.; Shalaby, B.N.; Rashwan, M.A. Performance of mortar and concrete incorporating granite sludge as cement replacement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 800–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Ning, Y.; Zhang, W. Experimental study on the effect of wastewater and waste slurry of mixing plant on mechanical properties and microstructure of concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 52, 104307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, S.; Gunal, H.; Ersahin, S. Assesment of clay bricks compressive strength using quantitative values of colour components. Constr. Build. Mater. 2006, 20, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingunza, M.D.P.D.; Camarini, G.; da Costa, F.M.S. Performance of mortars with the addition of septic tank sludge ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, X.; He, L.; Zhang, Y. Effect of sewage sludge ash on mechanical properties, drying shrinkage and high-temperature resistance of cement mortar. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kong, J.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Fang, Y.; Shi, J.; Ge, T.; Fang, T.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, R.; et al. Mechanisms and adsorption capacities of ball milled biomass fly ash/biochar composites for the adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.H.; Wang, B.; Shi, J.Y.; Rong, H.; Tao, H.Y.; Jamal, A.S.; Han, X.D. Recycling drinking water treatment sludge in construction and building materials: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krakowiak, K.J.; Wilson, W.; James, S.; Musso, S.; Ulm, F.J. Inference of the phase-to-mechanical property link via coupled X-ray spectrometry and indentation analysis: Application to cement-based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 67, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ren, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Pang, H.; Wang, X.; Lu, J. Thermally activated drinking water treatment sludge as a supplementary cementitious material: Properties, pozzolanic activity and hydration characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 365, 130027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Molina, A.; Tort-Ausina, I.; Cho, S.; Vivancos, J.L. Energy efficiency and thermal comfort in historic buildings: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 61, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, S.; Audenaert, A. Thermal inertia in buildings: A review of impacts across climate and building use. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2300–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Yan, S.; Liu, X.; Sun, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Dan, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, J. Development of solid waste-based self-insulating material with high strength and low thermal conductivity. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 5239–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, F.; Zhu, R.; Dai, G.; Wang, W.; Wang, W.; Guo, X.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Z. Mechanism analysis of pore structure and crystalline phase of thermal insulation bricks with high municipal sewage sludge content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 263, 120021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanou, I.; Bamogo, H.; Sory, N.; Gansoré, A.; Millogo, Y. Effect of the coconut fibers and cement on the physico-mechanical and thermal properties of adobe blocks. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).