The Role of Binders for Water-Based Anode Dispersions in Inkjet Printing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation and Background
1.2. Approach
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
2.2.1. Dispersions
2.2.2. Electrodes
2.2.3. Cells
2.3. Drop Monitoring
2.3.1. Drop Formation
2.3.2. Drop Deposition
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Processability
3.1.1. Stability
3.1.2. Printability
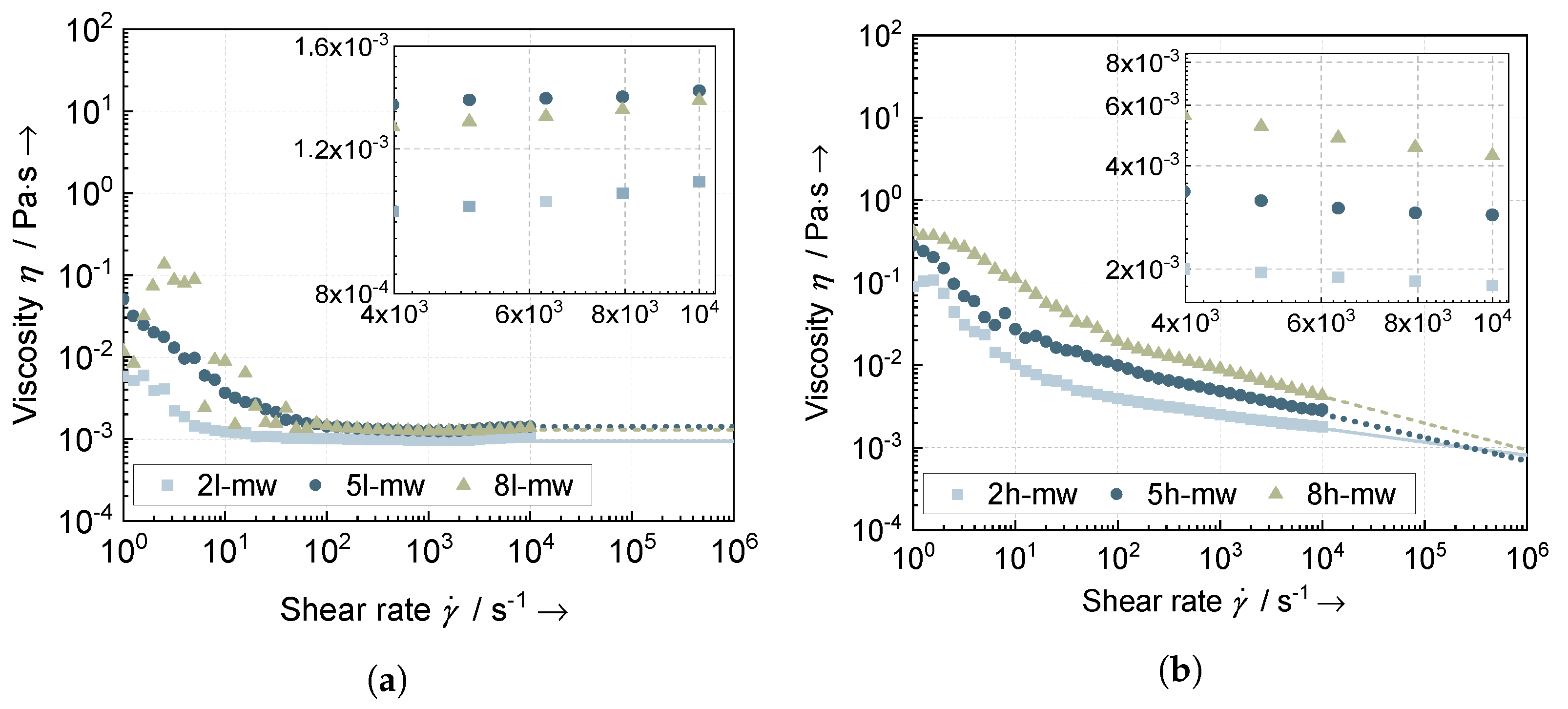
| Type | Binder Content | Consistency Index k | Index n | Flow Point | Adjusted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | in m% | - | - | - | - |
| l-mw | 2.0 | 5.68 × | −1.05 | 9.37 × | 0.927 |
| 5.0 | 45.63 × | −1.16 | 14.03 × | 0.989 | |
| 8.0 | 8.34 × | −2.13 | 12.90 × | 0.674 | |
| h-mw | 2.0 | 9.00 × | −0.19 | 1.77 × | 0.996 |
| 5.0 | 34.55 × | −0.28 | - | 0.976 | |
| 8.0 | 83.48 × | −0.33 | - | 0.998 |
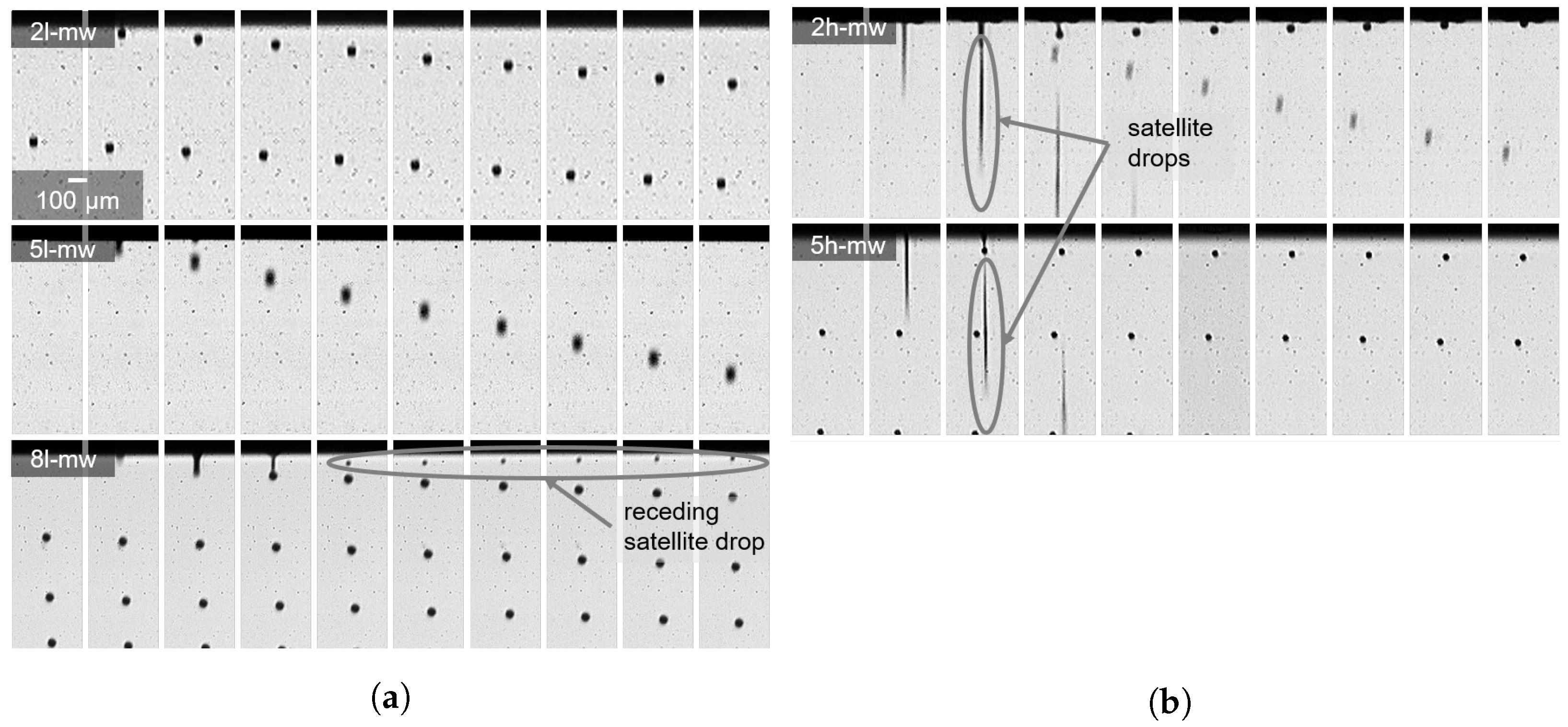
3.2. Drop Monitoring
3.2.1. Drop Formation
3.2.2. Drop Deposition
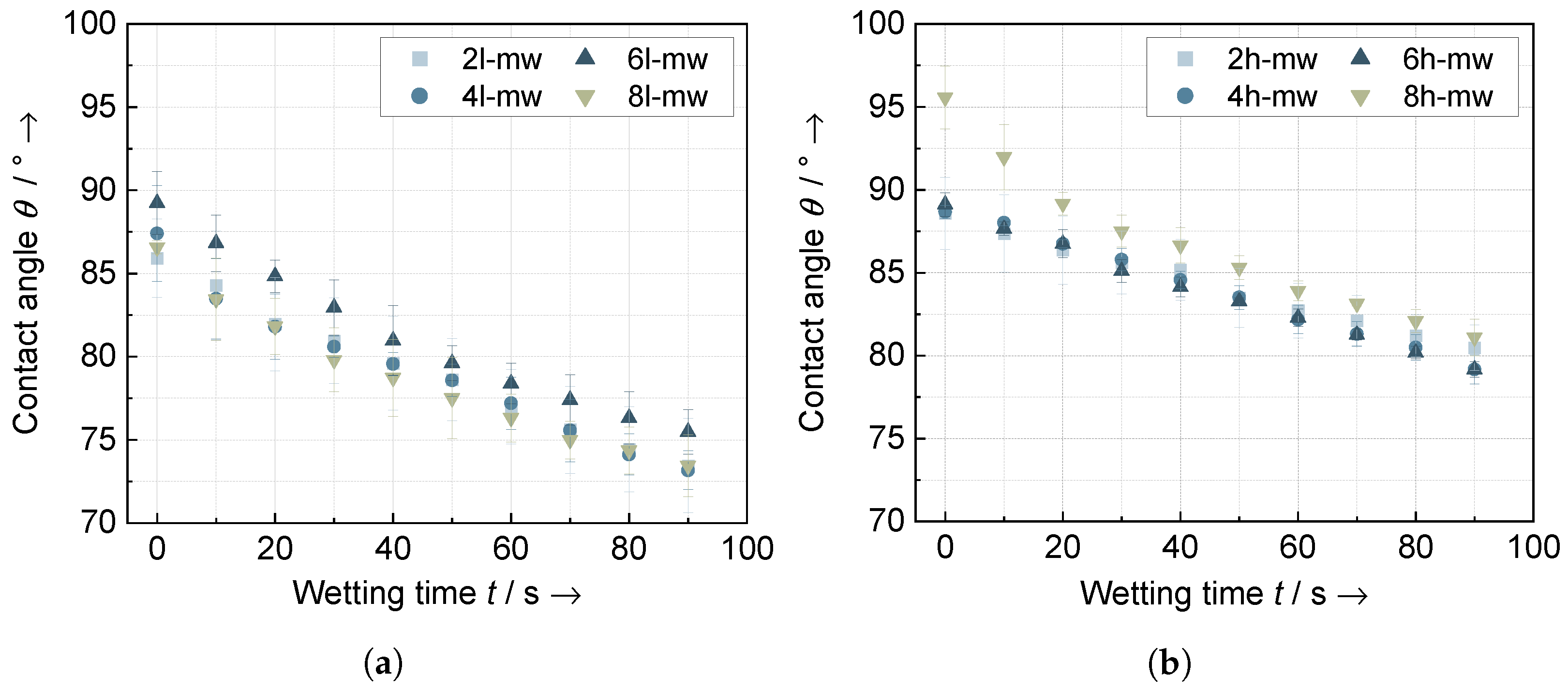
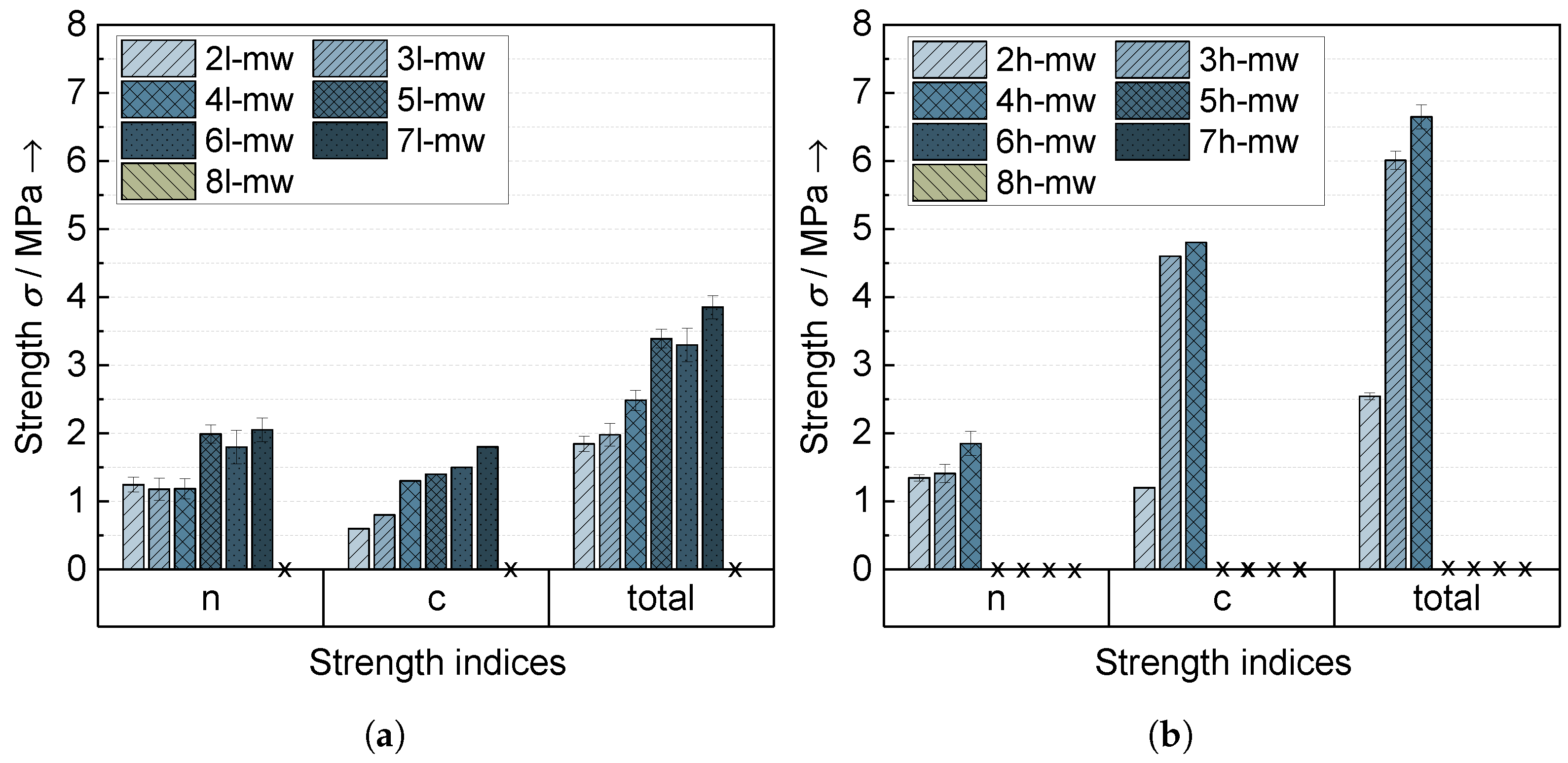
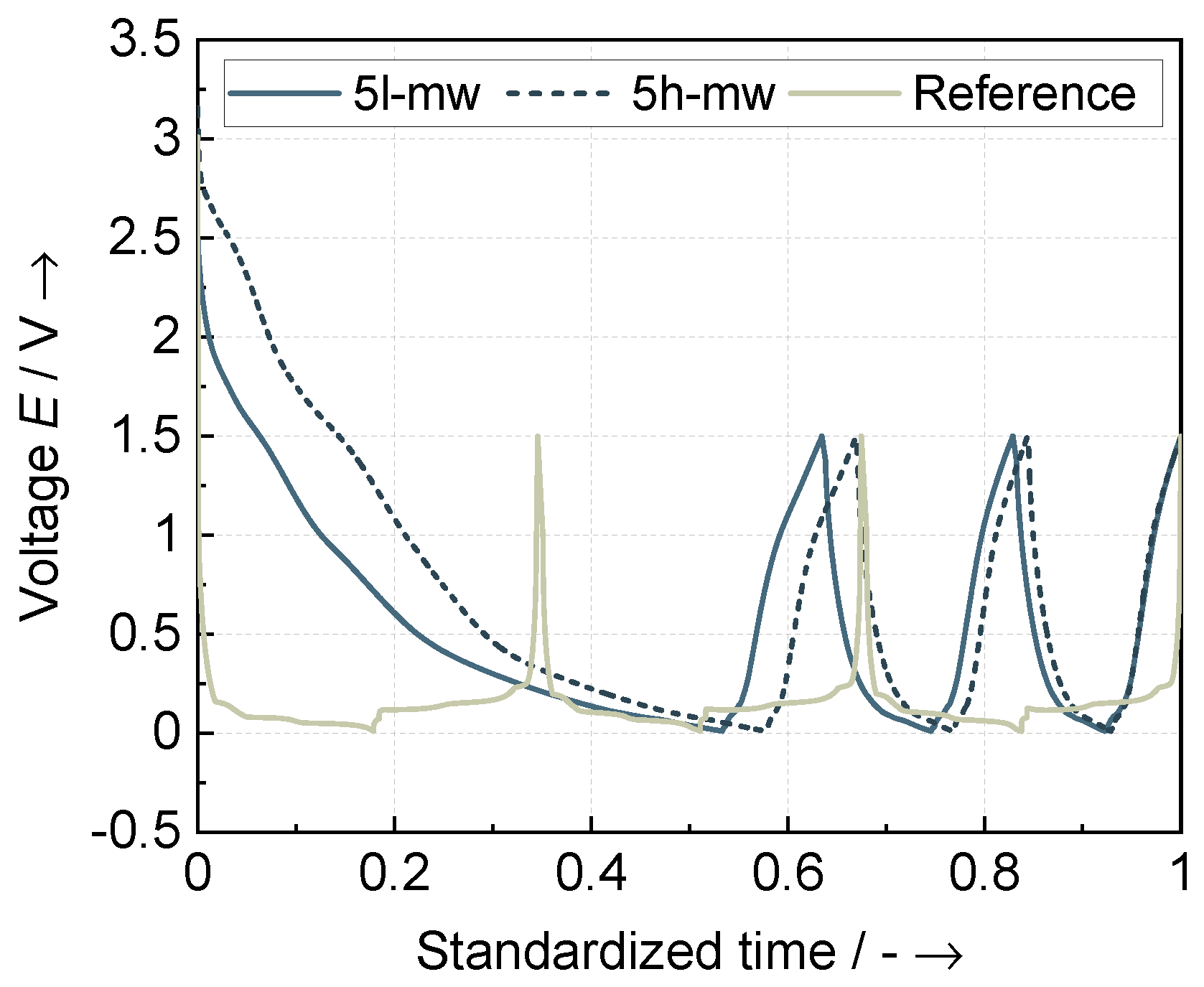
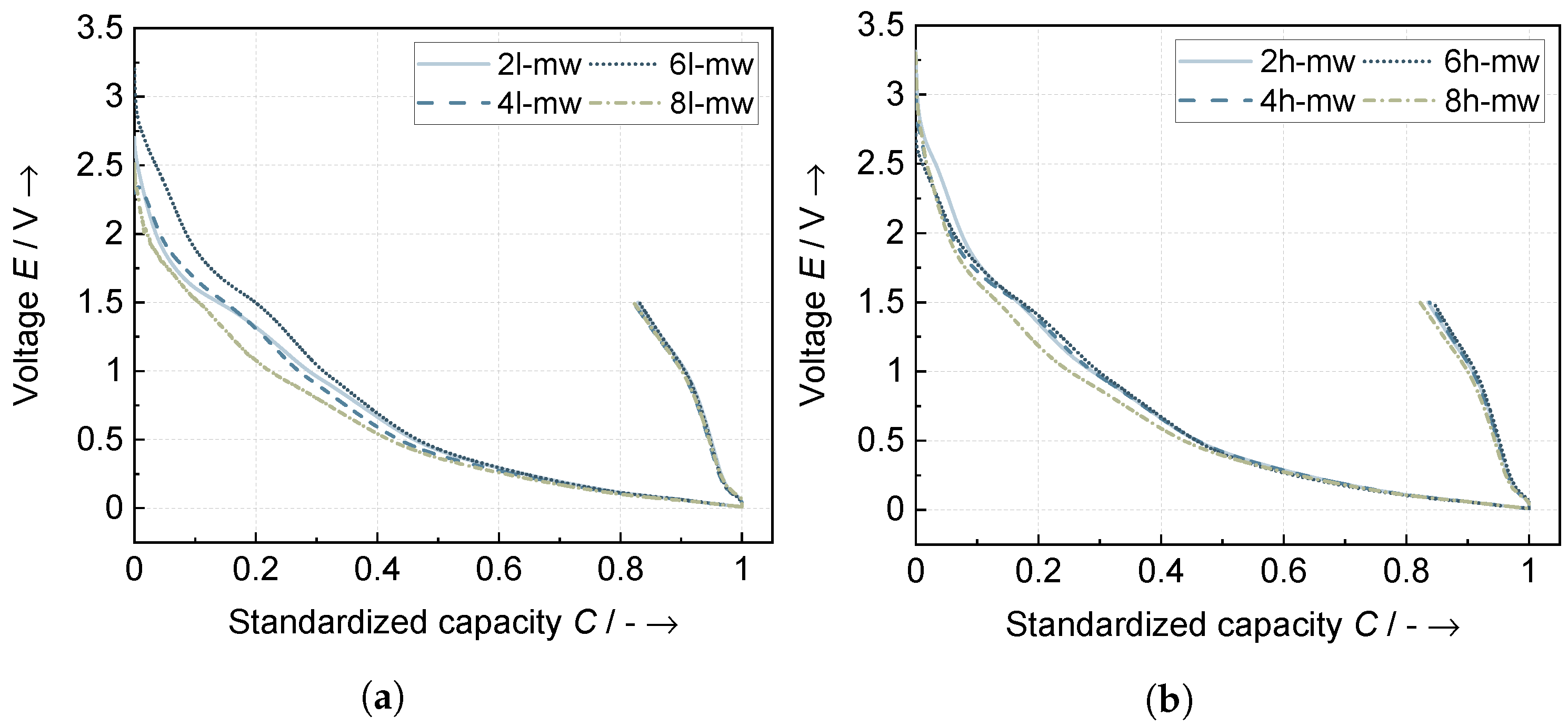
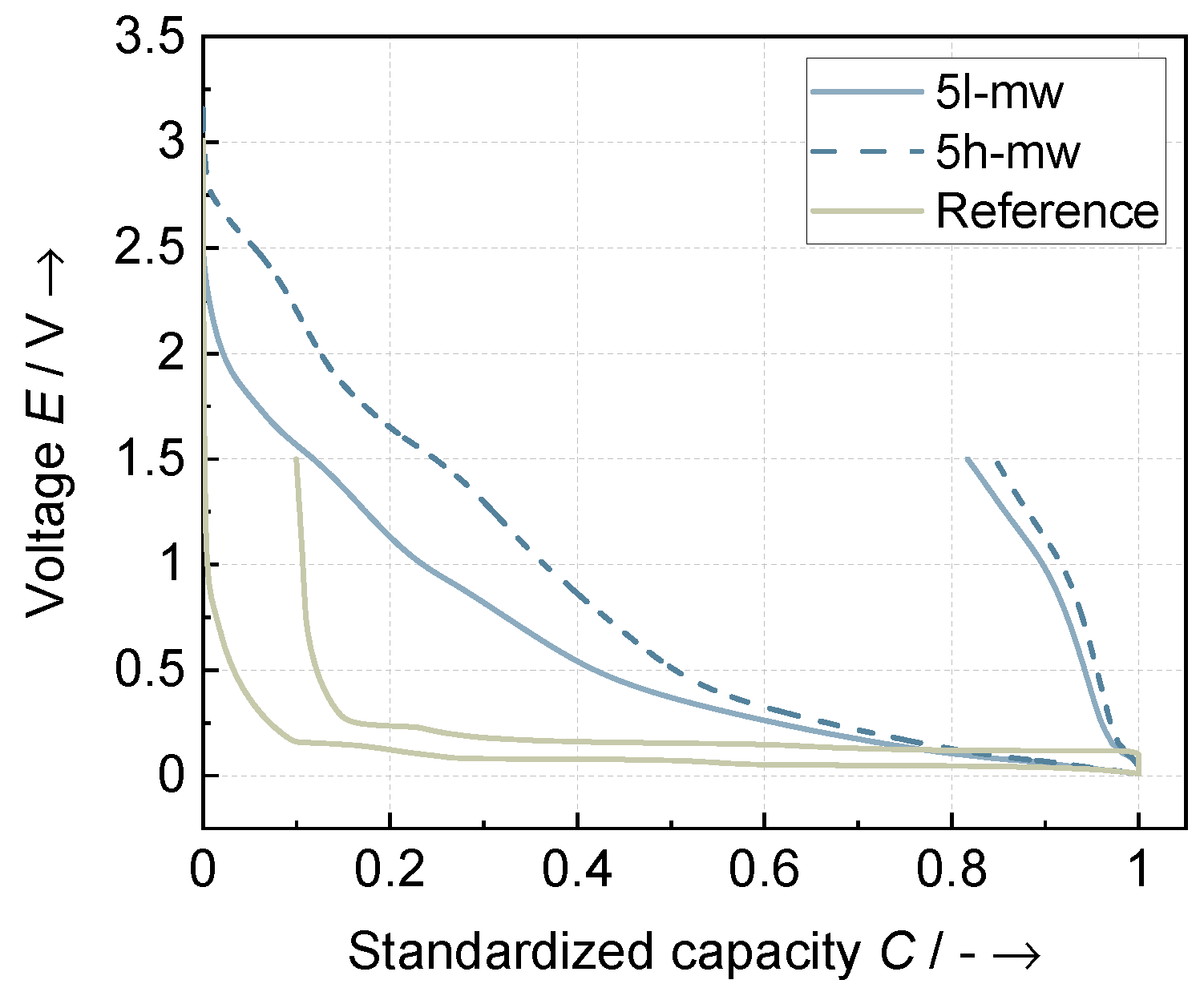
3.3. Electrode Characteristics
3.3.1. Adhesion and Cohesion Behavior
3.3.2. Electrochemical Characteristics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hawes, G.; Rehman, S.; Rangom, Y.; Pope, M. Advanced manufacturing approaches for electrochemical energy storage devices. Int. Mater. Rev. 2023, 68, 323–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Mei, H.; Zhou, S.; Dassios, K.; Cheng, L. 3D printed electrochemical energy storage devices. J. Mater. Chem. 2019, 7, 4230–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwade, A.; Haselrieder, W.; Leithoff, R.; Modlinger, A.; Dietrich, F.; Droeder, K. Current status and challenges for automotive battery production technologies. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wei, M.; Viswanathan, V.; Swart, B.; Shao, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhou, C. 3D printing technologies for electrochemical energy storage. Nano Energy 2017, 40, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, W.B.; Li, J. Electrode manufacturing for lithium-ion batteries—Analysis of current and next generation processing. J. Energy Storage 2019, 25, 100862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenze, G.; Bockholt, H.; Schilcher, C.; Froböse, L.; Jansen, D.; Krewer, U.; Kwade, A. Impacts of variations in manufacturing parameters on performance of lithium-ion-batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, A314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Liu, T.; Qian, F.; Chen, W.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Yao, B.; Song, Y.; Duoss, E.; Kuntz, J.; Spadaccini, C.; et al. 3D printed functional nanomaterials for electrochemical energy storage. Nano Today 2017, 15, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, C.; Ye, Y.; Huang, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Tang, Y. Overview on the applications of three-dimensional printing for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Appl. Energy 2020, 257, 114002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Costa, C.M. Printed Batteries: Materials, Technologies and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Beuth. ISO/ASTM 52900:2021; Additive Manufacturing—General Principles—Fundamentals and Vocabulary. Beuth: Berlin, Germany, 2022.
- Wijshoff, H. The dynamics of the piezo inkjet printhead operation. Phys. Rep. 2010, 491, 77–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, C.; Lehmann, M.; Kriegler, J.; Lindemann, J.-L.; Bachmann, A.; Zaeh, M. Qualifying water-based electrode dispersions for the inkjet printing process: A requirements analysis. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2022, 28, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derby, B.; Reis, N. Inkjet printing of highly particulate suspensions. MRS Bull. 2003, 28, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wu, A.; Sohn, H.; Nicoletti, C.; Iqbal, Z.; Federici, J. Fabrication of rechargeable lithium ion batteries using water-based inkjet printed cathodes. J. Manuf. Process 2015, 20, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clasen, C.; Philipps, P.; Palangetic, L.; Vermant, A. Dispensing of rheologically complex fluids: The map of misery. AIChE J. 2012, 58, 3242–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestriez, B. Functions of polymers in composite electrodes of lithium ion batteries. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2010, 13, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresser, D.; Buchholz, D.; Moretti, A.; Varzi, A.; Passerini, S. Alternative binders for sustainable electrochemical energy storage—The transition to aqueous electrode processing and bio-derived polymers. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 3096–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Lizundia, E.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Polymers for advanced lithium-ion batteries: State of the art and future needs on polymers for the different battery components. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2020, 79, 100846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.; White, R.E.; Doyle, M. Capacity fade mechanisms and side reactions in lithium-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 145, 3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahani, E.K.; Shenoy, V.B. Role of plastic deformation of binder on stress evolution during charging and discharging in lithium-ion battery negative electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, A1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcher, W.; Moreau, P.; Lestriez, B.; Jouanneau, S.; Le Cras, F.; Guyomard, D. Stability of LiFePO 4 in water and consequence on the Li battery behaviour. Ionics 2008, 14, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchdahl, R.; Thimm, J. The relationship between the rheological properties and working properties of printing inks. J. Appl. Phys. 1945, 16, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Sanchez-Romaguera, V.; Barbosa, S.; Travis, W.; de Wit, J.; Swan, P.; Yeates, S. Inkjet printing of polymer solutions and the role of chain entanglement. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 4902–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, H.J.; Harrison, G.M. The effect of added polymers on the formation of drops ejected from a nozzle. Phys. Fluids 2005, 17, 033104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, L. Colloidal processing of ceramics. Handb. Appl. Surf. Colloid Chem. 2001, 1, 201–217. [Google Scholar]
- Jianping, L.; Guiling, D. Technology development and basic theory study of fluid dispensing-A review. In Proceedings of the Sixth IEEE CPMT Conference on High Density Microsystem Design and Packaging and Component Failure Analysis (HDP’04), Shanghai, China, 3–4 July 2004; pp. 198–205. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, S.L.; Wang, J.Z.; Liu, H.K.; Dou, S.X. Rapid synthesis of Li4Ti5O12 microspheres as anode materials and its binder effect for lithium-ion battery. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 16220–16227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.R.; Oh, E.S. Effect of molecular weight and degree of substitution of a sodium-carboxymethyl cellulose binder on Li4Ti5O12 anodic performance. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 4404–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.S.; Oh, E.S.; Lee, S.M. Effect of polymeric binder type on the thermal stability and tolerance to roll-pressing of spherical natural graphite anodes for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 248, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lewis, R.; Dahn, J. Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose: A potential binder for Si negative electrodes for Li-ion batteries. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 2006, 10, A17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingappan, N.; Kong, L.; Pecht, M. The significance of aqueous binders in lithium-ion batteries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 147, 111227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.R.; Yang, M.H.; Wu, H.C.; Chiao, S.; Wu, N.L. Enhanced cycle life of Si anode for Li-ion batteries by using modified elastomeric binder. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 2004, 8, A100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Paik, U.; Hackley, V.A.; Choi, Y.M. Effect of carboxymethyl cellulose on aqueous processing of natural graphite negative electrodes and their electrochemical performance for lithium batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, A1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, C.G.; Lehmann, M.; Teixeira, C.M.; Maleksaeedi, S.; Zaeh, M.F. A priori evaluation of the printability of water-based anode dispersions in inkjet jetting. PIAM 2023, Submitted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, C.; Lehmann, M.; Lindemann, J.; Bachmann, A.; Zaeh, M. Improving the Dispersion Behavior of Organic Components in Water-Based Electrode Dispersions for Inkjet Printing Processes. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, C.; Lehmann, M.; Kulmer, D.; Zaeh, M. Modeling of the stability of water-based graphite dispersions using polyvinylpyrrolidone on the basis of the DLVO theory. Heliyon 2022, 8, 11988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuestenberg, T. Cellulose and Cellulose Derivatives in the Food Industry: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mark, H.F. Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology, Concise; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.; Paik, U.; Choi, Y.M. Aqueous processing of natural graphite particulates for lithium-ion battery anodes and their electrochemical performance. J. Power Sources 2005, 147, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, M.; Nakamura, H. Influence of molecular weight and concentration of carboxymethyl cellulose on rheological properties of concentrated anode slurries for lithium-ion batteries. JCIS Open 2022, 6, 100048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Yang, S.; Qin, Z.; Wen, B.; Zhang, C. The roles of wettability and surface tension in droplet formation during inkjet printing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, T. Rheology of Dispersions: Principles and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Herschel, W.; Bulkley, R. Konsistenzmessungen von Gummi-Benzollösungen. Kolloid Z. 1926, 39, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traube, J. Über die Capillaritätsconstanten organischer Stoffe in wässerigen Lösungen. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1891, 265, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haselrieder, W.; Westphal, B.; Bockholt, H.; Diener, A.; Höft, S.; Kwade, A. Measuring the coating adhesion strength of electrodes for lithium-ion batteries. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2015, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, M.; Kolb, C.G.; Klinger, F.; Zaeh, M.F. Preparation, characterization, and monitoring of an aqueous graphite ink for use in binder jetting. Mater. Des. 2021, 207, 109871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H. A Handbook of Elementary Rheology; University of Wales, Institute of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics: Wales, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Delannoy, P.; Riou, B.; Brousse, T.; Le Bideau, J. Ink-jet printed porous composite LiFePO4 electrode from aqueous suspension for microbatteries. J. Power Sources 2015, 287, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezger, T.G. The Rheology Handbook: For Users of Rotational and Oscillatory Rheometers; Vincentz Network: Hanover, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hoath, S. Fundamentals of Inkjet Printing: The Science of Inkjet and Droplets; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jeschull, F.; Brandell, D.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M.; Memm, M. Water-soluble binders for lithium-ion battery graphite electrodes: Slurry rheology, coating adhesion, and electrochemical performance. Energy Technol. 2017, 5, 2108–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, B.; Hermes, M.; Poon, W.C. Towards a unified description of the rheology of hard-particle suspensions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 088304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, R.; Seto, R.; Morris, J.F.; Denn, M.M. Shear thickening, frictionless and frictional rheologies in non-Brownian suspensions. J. Rheol. 2014, 58, 1693–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Kim, D.; Moon, J. Influence of fluid physical properties on ink-jet printability. Langmuir 2009, 25, 2629–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, N.F.; Harlen, O.G. Viscoelasticity in inkjet printing. Rheol. Acta 2010, 49, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, V.; Nirschl, H.; Nötzel, D. Challenges in lithium-ion-battery slurry preparation and potential of modifying electrode structures by different mixing processes. Energy Technol. 2015, 3, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, B.; Poduska, K. Roughness effects on contact angle measurements. Am. J. Phys. 2008, 76, 1074–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saulick, Y.; Lourenco, S.; Baudet, B. A semi-automated technique for repeatable and reproducible contact angle measurements in granular materials using the sessile drop method. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuckovac, M.; Latikka, M.; Liu, K.; Huhtamäki, T.; Ras, R. Uncertainties in contact angle goniometry. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 7089–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billot, N.; Beyer, M.; Koch, N.; Ihle, C.; Reinhart, G. Development of an adhesion model for graphite-based lithium-ion battery anodes. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 58, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, M.; Frank, C.W.; Mori, S.; Yamaguchi, S. Effect of poly (vinylidene fluoride) binder crystallinity and graphite structure on the mechanical strength of the composite anode in a lithium ion battery. Polymer 2003, 44, 4197–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, M.; Novák, P.; Monnier, A. Graphites for lithium-ion cells: The correlation of the first-cycle charge loss with the brunauer-emmett-teller surface area. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 145, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buiel, E.; Dahn, J. Li-insertion in hard carbon anode materials for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 1999, 45, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Component | Material | Supplier Specification | Content in m% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active material | Graphite | NG08BE0305, Nanografi, Turkey | 2 |
| Dispersant | PVP | Luvitec K17, BASF, Germany | 15 * |
| Binder 1 | CMC | l-mw: 419273, Merck, Germany | 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8 * |
| h-mw: Sunrose, Nippon Paper Industries, Japan | 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8 * | ||
| Binder 2 | SBR | SBR, Zeon Corporation, Japan | 5 * |
| Type | Degree of Substitution DS | Molecular Weight Mw in |
|---|---|---|
| l-mw | 0.70 | 9.0 × |
| h-mw | 0.94 | 1.8 × |
| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Aperture | f/2.8 |
| Exposure | 2.16 |
| Frame rate | 2000–20,000 fps |
| Binder Content | l-mw | h-mw |
|---|---|---|
| in m% | in % | in % |
| 2 | 0.01–7.94 | 0.01–2 |
| 3 | 0.01–7.95 | 0.01–0.102 |
| 4 | 0.01–0.198 | 0.01–0.796 |
| 5 | 0.01–0.795 | 0.01–10 |
| 6 | 0.01–1.26 | 0.01–12.6 |
| 7 | 0.01–2 | 0.01–1 |
| 8 | 0.01–2 | 0.01–100 |
| Sample | Sample | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2l-mw | 2h-mw | ||||
| 3l-mw | 3h-mw | ||||
| 4l-mw | 4h-mw | ||||
| 5l-mw | 5h-mw | ||||
| 6l-mw | 6h-mw | ||||
| 7l-mw | 7h-mw | ||||
| 8l-mw | 8h-mw |
| Characteristic | l-mw | h-mw |
|---|---|---|
| Processability | ||
| Drop formation | x | |
| Drop deposition | x | |
| Electrode characteristics | ||
| Adhesion behavior | x | |
| Cohesion behavior | x | |
| Electrochemical characteristics | x |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kolb, C.G.; Sommer, A.; Lehmann, M.; Teixeira, C.-M.; Panzer, H.; Maleksaeedi, S.; Zaeh, M.F. The Role of Binders for Water-Based Anode Dispersions in Inkjet Printing. Batteries 2023, 9, 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9110557
Kolb CG, Sommer A, Lehmann M, Teixeira C-M, Panzer H, Maleksaeedi S, Zaeh MF. The Role of Binders for Water-Based Anode Dispersions in Inkjet Printing. Batteries. 2023; 9(11):557. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9110557
Chicago/Turabian StyleKolb, Cara Greta, Alessandro Sommer, Maja Lehmann, Carys-May Teixeira, Hannes Panzer, Saeed Maleksaeedi, and Michael Friedrich Zaeh. 2023. "The Role of Binders for Water-Based Anode Dispersions in Inkjet Printing" Batteries 9, no. 11: 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9110557
APA StyleKolb, C. G., Sommer, A., Lehmann, M., Teixeira, C.-M., Panzer, H., Maleksaeedi, S., & Zaeh, M. F. (2023). The Role of Binders for Water-Based Anode Dispersions in Inkjet Printing. Batteries, 9(11), 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9110557







