Abstract
Efficient extraction of Li from brine at a low cost is becoming a key technology to solve energy and environmental problems. Electrochemical extraction of Li has become a research hotspot due to its low energy consumption, high selectivity, and environmental friendliness. LiMn2O4, LiFePO4, and LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 are widely used as cathode materials for the electrochemical extraction of Li but they also have some drawbacks, such as a small adsorption capacity. In this paper, the principle of electrochemical Li extraction from brine is reviewed and the research progress and analysis of the above three working electrode materials is summarized. In addition, analysis of the extraction of other rare ions from the working electrode material and the effect of micro-organisms on the working electrode material is also presented. Next, the shortcomings of working electrode materials are expounded upon and the research direction of working electrode materials in electrochemical Li extraction technology are prospected. It is hoped that this paper can provide insights and guidance for the research and application of electrochemical Li extraction from brine.
1. Introduction
Lithium (Li) is the lightest metal element in the world, with active chemical properties, high electrical conductivity, and specific heat capacity [1]. It is widely used in batteries, ceramics, the nuclear industry, and other fields [2]. In recent years, with the development of electronic products and new energy vehicles, the market demand for lithium resources has been increasing [3]. In addition, global lithium resources are unevenly distributed, mainly in Chile, Argentina, Bolivia, China, and Australia [4]. Generally, Li exists mainly in the form of compounds in Li ore, brine, and seawater. In particular, the Li content of brine is much larger than that of Li ore, and ore lithium extraction has the disadvantages of being highly energy-intensive and polluting, with half of the global Li raw materials coming from brine extraction [5]. In addition to Li ions, brine also contains a large amount of alkali metal ions and alkaline earth metal ions (Li+, Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, and Ba2+) [6]. It is difficult to separate the lithium ions from the brine because the hydration radii and chemical properties of magnesium and lithium ions are very similar [7]. In addition, a large number of micro-organisms are present in the brine. The research shows that, in the Atacama Salt Lake in northern Chile, when the total salt concentration is 55.6%, there are still hundreds of micro-organisms, including the Archaea halovenus, Halobacterium, and haloccus, of which the most abundant is Scutellaria [8]. There are also a large number of halophilic micro-organisms in the Utah salt lake with a total salt concentration of more than 30%, in which the density of prokaryotes is greater than 2–3 × 107 cells/mL, mainly Salinibacter, Halobacillus halophilic archaea, unicellular green algae, and Dunaliella [9].
There are various methods for the extraction of brine, such as the extraction method, adsorption method, membrane separation technology, precipitation method, solar pond crystallization technology, etc. [10]. The extraction method requires a large amount of organic solvents [11]. The adsorbent in the adsorption method may cause the corrosion of equipment [12]. Membrane separation technology is expensive, and the membrane is prone to clogging [13]. The precipitation method is too time-consuming [14]. Solar pond crystallization technology has a long process cycle and is limited by geography [15]. However, the electrochemical extraction of Li has the advantages of green environmental protection [16], strong adaptability, process simplicity, and high efficiency [17], which have attracted extensive attention from researchers.
Based on the working principle of Li iron phosphate batteries, the electrochemical extraction process of Li utilizes potential-controlled electrode materials to extract Li from brine. The selection and preparation of electrode materials are one of the main factors affecting electrochemical Li extraction. Therefore, the research progress of working electrode materials in the electrochemical extraction of Li was reviewed in this paper. In addition, due to the strong corrosiveness of brine and the existence of micro-organisms, the influence of brine and micro-organisms on the working electrode material was further analyzed. Next, analysis of the shortcomings of the working electrode in the current electrochemical extraction process of Li is summarized and its follow-up research direction is prospected. It is hoped that this review will provide new ideas for the development and application of Li electrochemical extraction processes.
2. Principle of Electrochemical Extraction of Li from Brine
Typically, Li-ion battery cathode materials are employed in the electrochemical extraction process of Li [18]. The extraction of Li is achieved through the movement of Li ions between the electrode and the electrolyte during charge and discharge [19]. Li ions are reduced from the electrolyte and intercalated into the cathode material (working electrode material) during discharge; Li ions are desorbed from the cathode material into the electrolyte during charging. According to the principle of charge and discharge, the electrolyte is replaced with brine. Li ions in brine intercalate into the cathode material during discharge; Li ions enter a single recovery solution to achieve Li-ion extraction during charging. The principle of electrochemical extraction of Li from brine is shown in Figure 1. Based on the above principles, Pasta et al. [20] proposed the electrochemical ion pumping technology, using FePO4 as the working electrode, which does not need to regenerate the adsorption material through chemical substances, requires a short time, minimizes the enthalpy term related to chemical bond breaking and formation, and requires less energy. The reaction formulas are given in (1) and (2) [21].
FePO4 + LiCl + Ag → LiFeO4 + AgCl
LiFeO4 + AgCl → FeO4 + LiCl + Ag
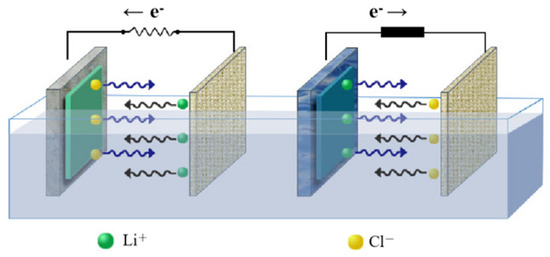
Figure 1.
The principle of electrochemical extraction of Li.
Currently, LiMn2O4, LiFePO4, and LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 are widely used as cathode materials for the electrochemical extraction of Li. The electrochemical extraction process of Li based on LiMn2O4/Li1-xMn2O4 has the advantages of low cost and high Li selectivity and is an effective method to alleviate the shortage of Li resources and the extraction process is shown in Figure 2 [22]. In particular, LiMn2O4 has been widely used in the extraction of Li resources due to its high selectivity for Li+. Due to the high selectivity of electrode materials, only lithium ions are allowed to be embedded in the corresponding lattice in the extraction process and acidic or strong oxidizing eluents are not used to elute the ion sieve in the process of lithium extraction, which realizes the environmental friendliness of lithium extraction and avoids the damage of eluents to the structure of the ion sieve. In addition, the properties of cathode materials are also one of the main factors limiting the electrochemical extraction of Li. Therefore, the optimization of electrode materials and performance improvement are of great significance for the application of the electrochemical extraction of lithium. Selectivity, exchange capacity, cycling stability, etc., are the directions of electrode material optimization. In particular, selectivity needs to be prioritized.
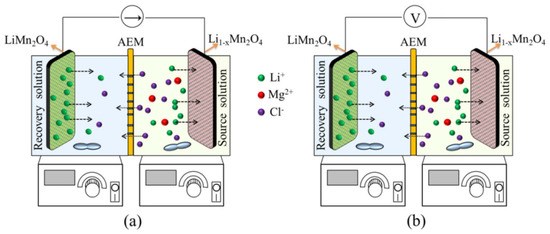
Figure 2.
Schematic of lithium extraction with the driving mode of (a) CC and (b) CV [22].
3. Research Progress of Working Electrode Materials in Electrochemical Extraction of Li from Brine
At present, Li manganate, Li iron phosphate, Li cobalt oxide, etc., are commonly used as working electrode materials for the electrochemical extraction of Li, which can improve the electrochemical insertion and removal of Li ions. The above electrode materials should be most considered in the practical application process for their selectivity, exchange capacity, and cyclic stability of lithium ions. Spinel-structured Li manganate, olivine-structured Li iron phosphate, and layer-structured LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 have been widely studied due to their desirable properties (Figure 3). Therefore, analysis of the structure, principle, and research progress of the above three working electrode materials is summarized here.
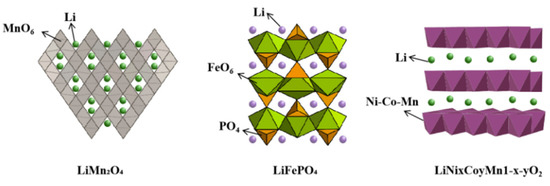
Figure 3.
Three kinds of working electrodes for electrochemical extraction of Li.
3.1. Spinel Structure
LiMn2O4 has higher electrical conductivity than LiFePO4, which might be due to the alternate arrangement of manganese and oxygen in MnO2. The structure formed a channel that is favorable for the (de)intercalation of Li ions. In particular, the spinel-type structure remained unchanged during the extraction or intercalation process and the λ-MnO2 formed after Li extraction was highly selective to Li [23]. However, LiMn2O4 exhibited poor cycling stability due to Mn leaching, which could be improved by improving its preparation method [24].
To overcome the above deficiencies, Shang et al. [25] prepared a multi-walled carbon nanotube (CNT) tandem LiMn2O4 (CNT-s-LMO) composite, which exhibited a favorable selectivity and extraction rate (84%) that was synergistic with the CNT-s-LMO hybrid capacitive deionization (HCDI). Furthermore, the capacity retention rate was 90% after 100 cycles [26]. In addition, spinel-type Li1-xNi0.5Mn1.5O4 (LNMO) had a higher capacity than LiMn2O4 (the adsorption capacity can reach 1.259 mmol/g) and the working electrode does not deteriorate after 50 cycles. It can be used as a Li-ion deintercalation material for the electrochemical extraction of Li [27]. It has been reported that the λ-MnO2/rGO-based CDI system exhibited favorable selectivity and high cycle stability for Li extraction from synthetic salt lake brine, which was attributed to its special intercalation structure. The structure has abundant active sites and a fast ion transport rate [28]. Similarly, the separation factors of Li+/Na+ and Li+/M2+ in simulated brine are 1040.57 and 358.96 for the prepared scalable 3D porous composite electroactive membrane (λ-MnO2/rGO/Ca-Alg), respectively. The excellent Li-ion extraction performance is due to the porous network structure and the potential-responsive ion pump effect in the ESIX process [29]. Xie et al. designed an electrochemical flow-through HCDI system with adequate trapping ability and stability for Li ions, and the lithium absorption capacity was as high as 18.1 mg/g, which was attributed to the trapping of Li ions in the λ-MnO2 electrode via a Faraday redox reaction. Additionally, the λ-MnO2 electrode exhibited excellent Li-ion selectivity when the brine contained a variety of cations, while avoiding the use of harmful acids or organic solvents [30]. Mu et al. [31] developed an electrode based on mesoporous λ-MnO2/LiMn2O4 modification with a large specific surface area of 183 m2/g, an extracted Li content of 75 mg/h per gram of LiMn2O4, and energy consumption of 23.4 Wh/mol; the electrode system provides an energy-efficient method for Li+ extraction from brine. To improve the cycling stability of the electrodes, LiMn2O4 electrodes coated with Al2O3-ZrO2 thin films were prepared. Due to the synergistic effect of Al2O3-ZrO2 during charge and discharge, the chemical stability and high active sites on the electrode surface significantly improved the cycle capacity. After 30 cycles, the extraction capacity of lithium increased from 29.21% to 57.67% [32]. The reaction formulas for extracting lithium using LiMn2O4 are given in (3) and (4).
2λ-MnO2 + Ag + LiCl = LiMn2O4 + AgCl
LiMn2O4 + AgCl = 2λ-MnO2 + Ag + LiCl4
Electrochemical extraction of Li needs to be carried out in corrosive brines, so cathode materials with high cycling stability are required. The three-dimensional nano-structured inorganic gel framework electrode prepared by introducing polypyrrole/Al2O3 on the surface of LiMn2O4. Lithium was extracted from simulated brine with an initial capacity of 1.85 mmol/g and after 100 cycles, it showed a capacity retention rate of 85%, indicating its high cycling stability [33]. Fang et al. fabricated LiMn2O4@C/N-4 (LMO@CN-4) membrane electrodes with a maximum capacity of 34.57 mg/g in 40 min through in situ polymerization and high-level annealing. This might be due to the carbon encapsulation as a conductive layer that enhances charge and ion transport and prevents the bulk collapse of the crystal and the dissolution of Mn as a buffer layer [34]. In addition, Li extraction from low-concentration brine, seawater, and wastewater with low-concentration Li content should be of concern.
3.2. Olivine Structure
LiFePO4 with an olivine structure is a crystal framework composed of many FeO6 octahedra and PO4 tetrahedrons, which realizes the insertion and extraction of Li+ during the oxidation and reduction of iron [35]. LiFePO4 has a higher theoretical capacity and lower Li intercalation potential than λ-MnO2 (Ramasubramanian et al., 2022). LiFePO4 electrode material (Ag is used as the counter electrode) exhibited high stability and Li-ion deintercalation capacity in an aqueous solution; the Li-Na ratio increased from 1:100 to 5:1, so it was selected as the working electrode for electrochemical extraction of Li [36]. The PO4 tetrahedron between LiO6 and FeO6 in the olivine structure limited the volume change in LiFePO4, which also limited the insertion and extraction of Li+ during charge and discharge. The olivine-structured LiFePO4 had better cycling stability due to its high lattice stability. The PPy/Al2O3/LMO of 3D nanocomposite inorganic gel framework structure prepared by the sol-gel method and polymerization method effectively improved the adsorption capacity and cycling stability of Li. This was attributed to the protection of the PPy/Al2O3 coating and the larger specific surface area [33]. In addition, LiFePO4 exhibited high efficiency and stability during selective Li extraction from seawater, which was mainly achieved by the difference in electrochemical potential in the intercalation or deintercalation reaction and the diffusion-activated barrier in the FePO4 framework, with molar selectivity as high as 1.8 × 104 [37]. Kim et al. [38] used FePO4 electrode to recover Li from simulated artificial seawater. Inspired by mussels, they coated the electrode surface with polydopamine coating, which increased the amount of Li recovered and improved the selectivity by about 20 times. The Li0.3FePO4 electrode exhibited favorable ion selectivity, cycling stability, and adsorption capacity, showing promising application potential [39]. The reaction formulas for extracting lithium using LiFePO4 are given in (5) and (6).
FePO4 + Li+ + e− → LiFePO4
LiFePO4 − e− → FePO4 + Li
3.3. Layered Structure
The layered structure of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 (NCM) had the advantages of high theoretical discharge capacity, high charge-discharge rate, effective cycle stability, low cost, and low environmental toxicity [40]. NCM is the most ideal working electrode material, which is widely used in the electrochemical extraction of lithium. The synthesis method is simple and the electrochemical performance is excellent. The initial specific capacity of NCM was 193 mAh/g. After 1000 cycles at 1 C, the specific capacity is still 155 mAh/g [41]. NCM adopts a diamond-shape α-NaFeO2 structure and continuous alternating [MO2]− (M = Ni, Co, Mn) and Li layers, in which only Ni2+ and CO3+ are active; Mn4+ is conducive to maintaining the stability of crystal structure. The research showed that the NCM material in the Li electrochemical extraction system exhibited favorable selectivity and adsorption capacity and could achieve efficient Li extraction under the condition of the coexistence of various impurity ions. Compared with traditional Li extraction, it had the advantages of low energy consumption, high Li+ yield, short duration, and green environmental protection [42]. In addition, compared with the organic solution, NCM exhibited a fast charge-discharge rate and adequate stability in aqueous solution. The diffusion coefficient of NCM in the aqueous solution is 1.39 × 10−10 and the charge and discharge are completed within a few seconds. After 1000 cycles, its capacity loss was only 9.1% [43]. Applied electrode material NCM to the actual brine can show high selectivity for lithium ions and can obtain Li chloride with a purity of up to 96.4% (i = ± 0.25 mA/cm) [42]. Zhao et al. developed a continuous-flow NMMO/AC hybrid supercapacitor (CF-NMMO/AC) using a depolymerized LNMMO cathode (NMMO) and an AC anode, exhibiting high capacity, high rate, and excellent cycling stability. The device consumed only 7.91 Wh/mol in simulated brine, and the extraction rate of Li+ was as high as 97.2% [44]. Although NCM has a fast Li-ion intercalation and deintercalation rate and favorable cycle stability, its preparation conditions are harsh and the cost is high. In addition, the corrosiveness of brine puts forward higher requirements on the chemical stability of electrode materials. Zhao et al. prepared a graphene gauze-modified LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 core-shell microsphere (rGO/NCM) with high capacity, effective cycling stability, and fast (de)intercalation rate, and the extraction rate of Li+ was up to 93% in simulated saline. This was attributed to the electron transfer pathway provided by graphene gauze instead of ion transfer between lattices, which effectively reduced the possibility of NCM lattice collapse [45]. In conclusion, NCM with excellent screening performance and a simple preparation process is the main research direction for future studies.
In view of the current shortcomings of the above three working electrode materials, new electrode materials with favorable selectivity, high adsorption capacity, and effective cycle stability could be developed by modification methods, such as electrode doping and coating. In addition, it is also a research direction to combine the excellent properties of the three. In particular, layered spinel hetero-structured Li-rich material (LSNCM) and nanocrystalline bismuth (NCBI) constituted a desalination battery with a Li recovery rate as high as 99%, which could be used for Li extraction from low-salinity brine [46]. The lithium extraction performance of the above three electrode materials is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Summary of lithium extraction performance of three electrode materials.
3.4. Working Electrode Material to Extract Other Rare Ions
Electrochemical working electrode materials can extract not only lithium ions from seawater or brine but also other high-value ions, such as rubidium ions, by the same mechanism [53]. Rubidium is widely present in brines, and its coexistence with alkali metals with similar properties makes extraction more complicated [54]. Xu et al. [55] prepared lithium/rubidium imprinted layered porous silica (Li/Rb-IHPS) for the selective recovery of lithium and rubidium from aqueous solutions, which showed high absorption capacities of 166 μg/g and 141 μg/g for both lithium and rubidium, respectively. Current studies on the extraction of other high-value ions using working electrode materials are scarce, so the exploration of other rare elements using existing electrochemical lithium extraction systems is essential.
3.5. The Effects of Micro-Organisms on Working Electrode Materials
There are many micro-organisms in brine, such as halophilic bacteria, and some of them can be used as anode catalysts. Salt-loving bacteria can be used as anode catalysts in microbial fuel cells to enhance the performance of microbial fuel cells, such as starch degradation [56]. In addition, using chromium wastewater as an anion and anaerobic micro-organisms as an anode biocatalyst, hexavalent chromium (Cr6+) can be reduced on an abiotic cathode by using an exogenous biofilm on the anode of a microbial fuel cell (MFC) [57]. It is found that Halophilic archaea safranine sodium can cause corrosion of steel materials and its impact on cathode materials is rarely reported [58]. The aerobic halophilic archaeon Natronorubrum tibetense can cause severe localized corrosion of Q235 carbon steel [59]. Therefore, the interactions between micro-organisms and working electrode materials should also be paid attention to. In addition, there are a large number of suspended solids and micro-organisms in the brine, which can block the electrode materials [60].
4. Conclusions and Prospects
The demand for Li and its compounds is increasing year by year with the rapid development of the new energy industry. The electrochemical extraction process of Li has attracted more and more attention due to its advantages of being green, having high efficiency, saving energy, and being safe. However, there are also a series of problems in the actual application process, such as low Li-ion migration rate, low Li-ion adsorption capacity, and poor cycle stability in the working electrode. Therefore, we should address the above problems from the following perspectives:
- (1)
- It is necessary to develop working electrode materials with excellent comprehensive properties. Improving the electrochemical performance of the working electrode is the key to realizing engineering applications, which can start from the aspects of porosity, particle size, and synthesis route. The high saline-alkali environment of brine should also be considered. Furthermore, protective coatings can be developed to enhance the corrosion resistance of electrode materials by exploring the relationship between lattice size change and corrosion.
- (2)
- The current research on working electrodes is heavily dependent on experimental conditions and lack of standardized methods. Therefore, it is necessary to establish a scientific evaluation system of electrode materials as soon as possible to obtain electrode materials with application prospects.
- (3)
- The influence of micro-organisms on extraction equipment and electrode materials deserves further study due to their abundant presence in brines. Micro-organisms affect the performance of cathode materials and affect the safety, stability, and extraction efficiency of extraction equipment by corroding metal materials (such as pipes), and their mechanism of action needs to be further explored. In addition, the working electrode is prone to be blocked by micro-organisms during long-term use, so the removal of micro-organisms in brine deserves attention.
- (4)
- Material genomics integrate high-throughput computing, high-throughput preparation, high-throughput detection, and database systems, which can greatly shorten the material development cycle. Facing the problems existing in the current working electrode for electrochemical lithium extraction, material genomics can be used to design and prepare electrode materials.
- (5)
- Parameters such as brine flow rate and electric field distribution also have an impact on the efficiency, ion concentration, and lifetime of electrochemical lithium extraction [61]. For example, a flow-by-flow configuration with a small amount of intercalation material is not suitable for large-scale lithium extraction from brine, while a cross-flow configuration is suitable for industrial scale-up at a moderate flow rate. In addition, the lithium extraction efficiency also depends on the total current applied to the reactor. Therefore, operational parameters must be traded off to find the optimal conditions (capacity and capture rate) for the electrochemical extraction of lithium.
- (6)
- In addition to the working electrode materials, the construction of an electrochemical lithium extraction system has an important impact on the cost, efficiency, and energy consumption of electrochemical lithium extraction. Therefore, the development of electrochemical lithium extraction can be promoted by improving the electrode system and one such improvement is the exploration of the counter electrode system. The function of a counter electrode is to form a closed circuit in the electrochemical lithium extraction system and maintain the electric neutrality of the electrochemical lithium extraction system. Common counter electrodes are Ag electrode, Pt electrode, titanium electrode, activated carbon electrode, polymer electrode, etc. Compared with traditional precious metals, the environmentally friendly material-activated carbon electrode yields significant cost benefits. Next, we should also integrate the working electrode material with the counter electrode system to enhance the performance of the electrochemical lithium extraction system.
- (7)
- The biggest challenge of current electrochemical lithium extraction is the amplification effect in the real industrial scale-up process for which the existing working electrode materials, devices, specific operating parameters (such as DC potential, feed flow rate, the cycles of the recovered solution, etc.), energy consumption, etc., should be optimized and integrated.
In general, the electrochemical extraction of Li from brine is still the trend of Li resource acquisition and electrode materials are the bottleneck restricting its industrial application. The performance of electrode materials are one of the main research directions for future studies. In addition, the impact of other aspects of brine on electrode materials should also be comprehensively considered to sustainably extract Li resources from brine.
Author Contributions
Y.W., H.Z. and G.D. conceived the manuscript. Y.W. and G.Z. wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Y.W., G.Z., G.D. and H.Z. revised each part of the manuscript in detail. All four authors participated in the revision of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Key Technologies and Demonstration Applications for Comprehensive Recovery and Utilization of Sulfate-type Salt Lake Tailings Resources (2021E02038).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The study did not report any data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Battistel, A.; Palagonia, M.S.; Brogioli, D.; La Mantia, F.; Trocoli, R. Electrochemical Methods for Lithium Recovery: A Comprehensive and Critical Review. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1905440. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Shang, X.; Nie, P.; Zhang, B.; Yang, J.; Liu, J. Lithium ion sieve modified three-dimensional graphene electrode for selective extraction of lithium by capacitive deionization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 612, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, E.J. Electrochemical methods for sustainable recovery of lithium from natural brines and battery recycling. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 15, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Cubillos, C.F.; Aguilar, P.; Grágeda, M.; Dorador, C. Microbial Communities From the World’s Largest Lithium Reserve, Salar de Atacama, Chile: Life at High LiCl Concentrations. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeoences 2018, 123, 3668–3681. [Google Scholar]
- Delmas, C.; Maccario, M.; Croguennec, L.; Le Cras, F.; Weill, F. Lithium deintercalation in LiFePO4 nanoparticles via a domino-cascade model. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabre, C.; Ourti, N.E.; Ballouard, C.; Mercadier, J.; Cauzid, J. Handheld LIBS analysis for in situ quantification of Li and detection of the trace elements (Be, Rb and Cs). J. Geochem. Explor. 2022, 236, 106979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.-W.; Wang, J.; Ji, Z.-Y.; Cui, J.-L.; Guo, Z.-Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Yuan, J.-S. Establishment of PPy-derived carbon encapsulated LiMn2O4 film electrode and its performance for efficient Li+ electrosorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 280, 119726. [Google Scholar]
- Flexer, V.; Fernando Baspineiro, C.; Ines Galli, C. Lithium recovery from brines: A vital raw material for green energies with a potential environmental impact in its mining and processing. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1188–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandoman, F.H.; Jaguemont, J.; Goutam, S.; Gopalakrishnan, R.; Firouz, Y.; Kalogiannis, T.; Omar, N.; Van Mierlo, J. Concept of reliability and safety assessment of lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles: Basics, progress, and challenges. Appl. Energy 2019, 251, 113343. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, G.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Zhou, G.; Sun, J.; Chen, L.; Chao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, W. Electrochemical lithium ions pump for lithium recovery from brine by using a surface stability Al2O3-ZrO2 coated LiMn2O4 electrode. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 69, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.-Y.; Ji, Z.-Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.-F.; Liang, J.-S. Electrochemical lithium extraction based on “rocking-chair” electrode system with high energy-efficient: The driving mode of constant current-constant voltage. Desalination 2022, 533, 115767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Y.; Ji, Z.Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.Y.; Yuan, J.S. Development of electrochemical lithium extraction based on a rocking chair system of LiMn2O4/Li1-xMn2O4: Self-driven plus external voltage driven. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 259, 118154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.A.; Lipu, M.S.H.; Hussain, A.; Mohamed, A. A review of lithium-ion battery state of charge estimation and management system in electric vehicle applications: Challenges and recommendations. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 834–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Xu, W.; Song, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Z. New Insights into the Application of Lithium-Ion Battery Materials: Selective Extraction of Lithium from Brines via a Rocking-Chair Lithium-Ion Battery System. Glob. Chall. 2018, 2, 1700079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Kaur, S.; Kostecki, R. Mining Lithium from Seawater. Joule 2020, 4, 1357–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Jiang, H.; Hu, X.; Liu, K. Dependence of concentration polarization on discharge profile in electrochemical lithium extraction. Desalination 2022, 527, 115567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Jia, X.; Wang, C.; Zheng, M.; Dong, Q. Electrochemical Performance of the LiNi_(1/3)Co_(1/3)Mn_(1/3)O_2 in Aqueous Electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 16, 151. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Choi, S.; Shin, J.; Choi, J.W. An Electrochemical Cell for Selective Lithium Capture from Seawater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9415–9422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Su, X.; Kim, C. Electrochemical lithium recovery system through the simultaneous lithium enrichment via sustainable redox reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 420, 127715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawagon, C.P.; Nisola, G.M.; Cuevas, R.; Torrejos, R.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.P.; Chung, W.J. Li1−xNi0.5Mn1.5O4/Ag for electrochemical lithium recovery from brine and its optimized performance via response surface methodology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawagon, C.P.; Nisola, G.M.; Cuevas, R.A.I.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.P.; Chung, W.J. Li1−xNi0.33Co1/3Mn1/3O2/Ag for electrochemical Lithium recovery from brine. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Mo, Y.; Qing, W.; Shao, S.; Tang, C.Y.; Li, J. Membrane-based technologies for lithium recovery from water lithium resources: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 591, 117317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Lin, D.; Hsu, P.C.; Chu, S. Lithium Extraction from Seawater through Pulsed Electrochemical Intercalation. Joule 2020, 4, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Xu, W.; Xiong, J.; He, L.; Zhao, Z. Electrochemical system with LiMn2O4 porous electrode for lithium recovery and its kinetics. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 270, 118809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhao, Z.; Ghahreman, A. Novel approaches for lithium extraction from salt-lake brines: A review. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 187, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, M.; Kong, Q.H.; McGrory, J.; Fowler, M. Simulation of lithium ion battery replacement in a battery pack for application in electric vehicles. J. Power Sources 2017, 349, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, P.; Pandey, B.D.; Mankhand, T.R. Extraction of lithium from primary and secondary sources by pre-treatment, leaching and separation: A comprehensive review. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 150, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y. Electrochemical lithium recovery from brine with high Mg2+/Li+ ratio using mesoporous λ-MnO2/LiMn2O4 modified 3D graphite felt electrodes. Desalination 2021, 511, 115112. [Google Scholar]
- Oren, A. The microbiology of red brines. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 113, 57–110. [Google Scholar]
- Pasta, M.; Battistel, A.; Mantia, F.L. Batteries for lithium recovery from brines. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 9487–9491. [Google Scholar]
- Pasta, M.; Wessells, C.D.; Cui, Y.; Mantia, F.L. A Desalination Battery. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Zhao, Q. A Nano-Heterogeneous Membrane for Efficient Separation of Lithium from High Magnesium/Lithium Ratio Brine. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009430. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, H.; Zhang, D.; Lou, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, D.; Du, C.; Li, X. Laboratory investigation of microbiologically influenced corrosion of Q235 carbon steel by halophilic archaea Natronorubrum tibetense. Corros. Sci. 2018, 145, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Liu, J.; Hu, B.; Nie, P.; Yang, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhan, F.; Qiu, J. CNT-Strung LiMn2O4 for Lithium Extraction with High Selectivity and Stability. Small Methods 2022, 6, 2200508. [Google Scholar]
- Sophia, A.C.; Saikant, S. Reduction of chromium(VI) with energy recovery using microbial fuel cell technology. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 11, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, X. Highly Efficient Lithium Extraction from Brine with a High Sodium Content by Adsorption-Coupled Electrochemical Technology. Acs Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 11022–11031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Liu, Y.; Tang, P.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, T.; Bai, Y.; Tiraferri, A.; Liu, B. Lithium extraction from shale gas flowback and produced water using H1.33Mn1.67O4 adsorbent. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 185, 106476. [Google Scholar]
- Trócoli, R.; Battistel, A.; Mantia, F.L. Selectivity of a Lithium-Recovery Process Based on LiFePO4. Chem. A Eur. J. 2014, 20, 9888–9891. [Google Scholar]
- Trócoli, R.; Erinmwingbovo, C.; La Mantia, F. Optimized Lithium Recovery from Brines by using an Electrochemical Ion-Pumping Process Based on λ-MnO2 and Nickel Hexacyanoferrate. ChemElectroChem 2017, 4, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, A.; Arora, S.; Gupta, S.; Chhabra, M. Halophilic starch degrading bacteria isolated from Sambhar Lake, India, as potential anode catalyst in microbial fuel cell: A promising process for saline water treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 256, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Gong, J.; Hu, X. Fabricating a Flow-Through Hybrid Capacitive Deionization Cell for Selective Recovery of Lithium Ions. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2021, 4, 13036–13043. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, P.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Ma, B. Rubidium extraction from mineral and brine resources: A review. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 203, 105644. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; He, L.; Zhao, Z. Lithium extraction from high-sodium raw brine with Li0.3FePO4 electrode. Desalination 2022, 535, 115822. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, D.; He, L. Direct lithium extraction from raw brine by chemical redox method with LiFePO4/FePO4 materials. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 290, 120789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, Z.; Kahn, N.U.; Haq Khan, Z.U.; Tang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wan, P.; Chen, Y.; Fan, M. A Self-Supported—MnO2 Film Electrode used for Electrochemical Lithium Recovery from Brines. ChemPlusChem 2018, 83, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; He, L.; Zhao, Z. Lithium extraction from high Mg/Li brine via electrochemical intercalation/de-intercalation system using LiMn2O4 materials. Desalination 2021, 503, 114935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, D.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Pan, J.; Zhang, T.; Xu, J.; Qiu, F.; Yan, Y.; et al. A facile strategy toward ion-imprinted hierarchical mesoporous material via dual-template method for simultaneous selective extraction of lithium and rubidium. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 264–274. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Huang, M.; Huang, J.; Fang, Z. Preparation and Rate Capability of Carbon Coated LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 as Cathode Material in Lithium Ion Batteries. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 12408–12415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, F.; Ding, H.; He, P.; Zhou, H. Lithium Metal Extraction from Seawater. Joule 2018, 2, 1648–1651. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Zheng, M.; Wu, Q.; Nie, Z.; Bu, L. Extracting lithium from Tibetan Dangxiong Tso Salt Lake of carbonate type by using geothermal salinity-gradient solar pond. Sol. Energy 2015, 115, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Rui, H.; Shi, D.; Peng, X.; Ji, L.; Song, X. Lithium recovery from effluent of spent lithium battery recycling process using solvent extraction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.; Xu, R.; Wang, L.; Tang, H. Lithium extraction from water lithium resources through green electrochemical-battery approaches: A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Feng, M.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sha, Z. Lithium extraction from brine in an ionic selective desalination battery. Desalination 2020, 481, 114360. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Jiao, Y.; Xue, P.; Feng, M.; Sha, Z. Efficiently lithium extraction from brine by using three-dimensional (3D) nanostructured hybrid inorganic-gel framework electrode. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 4827–4837. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Li, G.; Feng, M.; Wang, Y. Semi-continuous electrochemical extraction of lithium from brine using CF-NMMO/AC asymmetric hybrid capacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 331, 135285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Sha, Z. Review on the electrochemical extraction of lithium from seawater/brine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 850, 113389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhu, L. Lithium extraction from brine by an asymmetric hybrid capacitor composed of heterostructured lithium-rich cathode and nano-bismuth anode. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 274, 119078. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, E.; Xu, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gu, T.; Yang, K.; Wang, F. Laboratory investigation of microbiologically influenced corrosion of 2205 duplex stainless steel by marine Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm using electrochemical noise. Corros. Sci. 2018, 143, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, G.; Guo, Z.; Feng, C. Self-Assembled LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 Nanosheet Cathode with High Electrochemical Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 39560–39568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Du, X.; Wang, Q.; Gao, F.; Jin, T.; Hao, X.; Ma, P.; Li, J.; Guan, G. A scalable three-dimensional porous λ-MnO2/rGO/Ca-alginate composite electroactive film with potential-responsive ion-pumping effect for selective recovery of lithium ions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 259, 118111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubi, G.; Dufo-Lopez, R.; Carvalho, M.; Pasaoglu, G. The lithium-ion battery: State of the art and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 89, 292–308. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).