Abstract
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are currently one of the most important electrochemical energy storage devices, powering electronic mobile devices and electric vehicles alike. However, there is a remarkable difference between their rate of production and rate of recycling. At the end of their lifecycle, only a limited number of LIBs undergo any recycling treatment, with the majority go to landfills or being hoarded in households. Further losses of LIB components occur because the the state-of-the-art LIB recycling processes are limited to components with high economic value, e.g., Co, Cu, Fe, and Al. With the increasing popularity of concepts such as “circular economy” (CE), new LIB recycling systems have been proposed that target a wider spectrum of compounds, thus reducing the environmental impact associated with LIB production. This review work presents a discussion of the current practices and some of the most promising emerging technologies for recycling LIBs. While other authoritative reviews have focused on the description of recycling processes, the aim of the present was is to offer an analysis of recycling technologies from a CE perspective. Consequently, the discussion is based on the ability of each technology to recover every component in LIBs. The gathered data depicted a direct relationship between process complexity and the variety and usability of the recovered fractions. Indeed, only processes employing a combination of mechanical processing, and hydro- and pyrometallurgical steps seemed able to obtain materials suitable for LIB (re)manufacture. On the other hand, processes relying on pyrometallurgical steps are robust, but only capable of recovering metallic components.
1. Introduction: The Societal and Economic Importance of Lithium-Ion Batteries
A secondary lithium-ion battery (LIB) is a rechargeable electrochemical energy storage device. Since their development in the 1970s, and because of their unique characteristics of high energy capacity and long lifespan, LIBs have become important in the field of portable electronic goods [1,2]. Compared to other types of batteries (e.g., NiMH and Pb-acid), LIBs present lower environmental risks, longer life-span, compact design, better resistance to self-discharge, higher resistance to elevated temperatures, and higher voltage output (e.g., 3.7 V for a LIB vs. 1.2 V for a Pb-acid battery) [3,4]. These technical advantages make them attractive for urban or industrial mobility applications [2,5,6,7] (e.g., the Tesla S car is powered by 7104 LIB cells [8]). In addition, as electrical vehicles are being pushed forward due to government and societal awareness of climate change, LIBs have become a promising option for the reduction CO2 emissions. The importance of LIBs as power sources is reflected by their constant increase in production rate and their continuously growing share of the market. In 2011, nearly 4500 million LIB cells were produced, an estimated increase of 43% compared to 2008 [9]. In 2015, at least 5600 million LIB cells were sold worldwide [10], and the LIB market size is forecasted to increase by another 10.6% from 2016 to 2024, reaching a market value of USD $56 billion by 2024 [11]. In addition, the electric power supplied by LIBs has presented unprecedented growth, shifting from approximately 100,000 MWh in 2016 to approximately 125,000 MWh in 2017, for example [12]. Notably, the 2019 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to the developers of LIBs, attesting to the importance of these energy storage devices in our modern society.
Consequently, there has been a direct increase in the exploitation required of mineral deposits to provide the raw materials needed by the LIB market [12,13,14]. Natural mineral deposits, however, are reaching critical grades of valuable metals. This has resulted in an increased environmental footprint associated with metals extraction, in direct conflict with the pursuit of climate change alleviation via electrically powered goods, in particular EVs. Furthermore, it has been estimated that 95% of the LIBs produced globally remain untreated in households [15]. Another typical pathway for end-of-life (EoL) LIBs is their exportation to emerging economies, where they can be treated at low cost [16]. In Europe alone, the LIB market reported a total of 65,500 tons of LIB consumed between the years 2013–2014 [5], while only about 1900 tons were recycled in the same period. The low recycling rates for LIBs can be presently attributed to several factors, ranging from deficient legislation, inefficient collection systems, and the lack of feasible recycling technologies for the rapidly changing stream of LIB waste.
The gap between recycling and production currently represents an untapped source of valuable materials. Apart from representing a direct economic loss and an environmental hazard, this gap results in a growing need for virgin raw materials, with their associated environmental footprint [15,17,18]. For example, an EV battery with an energy density of approximately 78 kWh/kg produces an estimated 172–196 kg of CO2 eq per kWh from raw material extraction, cell manufacturing, and assembly [19,20]. Ellingsen et al. (2013) [21] also demonstrated that a significant environmental footprint is incurred during production of the cathode paste and current collector.
Recycling processes thus represent a viable option for the reintroduction of LIB compounds into the economic cycle, reducing the need for primary raw materials [22,23,24,25,26]. Recycling processes are a fundamental aspect of the circular economy (CE) as they enable internal material flows, reducing the consumption of resources associated with the production of primary raw materials [26,27,28,29]. Indeed, the circular economy (CE) is intended to mimic natural process, where no waste is generated. It is worth noting that the stages of the circular economy are highly interdependent. For instance, to accomplish the expected CO2 reduction from LIB-powered transportation, the energy for their production should ideally come from renewable sources [30]. Evidently, a CE also depends on environmental, political, and financial conditions, turning it into a living and complex organism.
Geissdoerfer [28] presented conceptual means to achieve CE by “long-lasting design, maintenance, repair, re-use, remanufacturing, refurbishing, and recycling” of consumer goods. Van Schalkwyk et al. (2017) [31] described the need to define the CE concept by including thermodynamic losses into the loop.
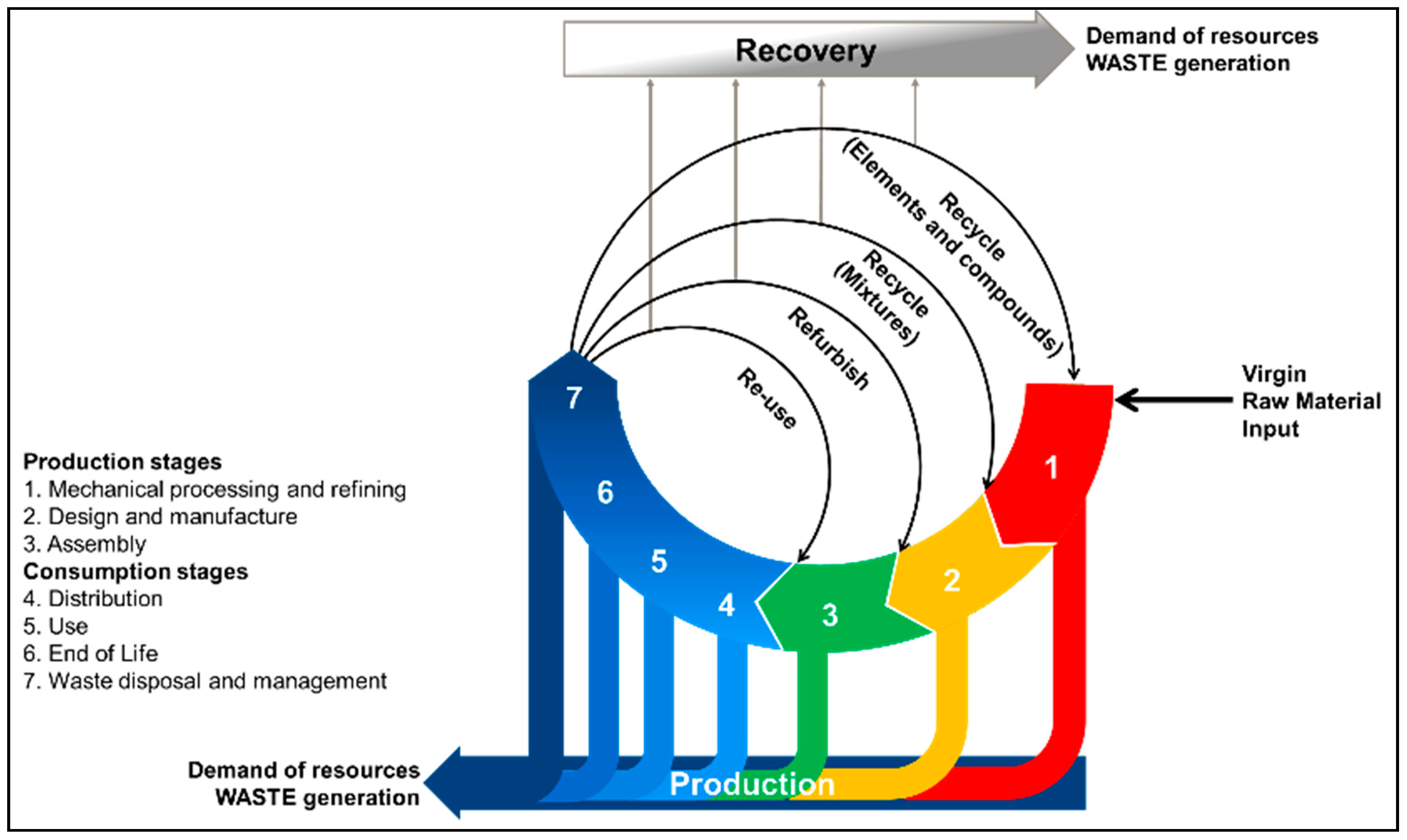
In a similar fashion, Figure 1 shows a recently proposed CE model that accounts for the losses of material inherent to the production and recovery of materials [32]. In the loops shown in Figure 1, the material moves from the input stage (1) towards the EoL of the product (6), where recovery systems (7) take action and reintroduce elements into the value generation chain. Unlike other models, Figure 1 shows different reintroduction points relative to the recovery process and their energy intensiveness. That is, the further the reinsertion point is from the waste disposal and management (7) point, the more resource-intensive the recovery process will be. It is well known that both economic and technological feasibility are bounded to the market trends, which decide whether LIBs will be processed down to level of elements and compounds [33]. Indirectly, these drivers also define the usability of the recovered materials. In other words, materials on the level of elements and compounds have a potentially broader field of application than those obtained through refurbishment. For example, elemental Li recovered from spent LIBs can be used for electrolyte production or as a construction additive [34]. In reality, industrial-scale LIB recycling processes present inefficiencies, resulting in inevitable material losses. It has also been suggested that state-of-the-art (SoA) technologies are lagging behind by approximately four years against the physical and chemical complexity of LIB compounds [15]. Indeed, only Al, Fe, and Co are currently targeted by LIB recycling processes, as their separation and refinement is technically simple and economically feasible, while other compounds such as graphite and Li are lost.
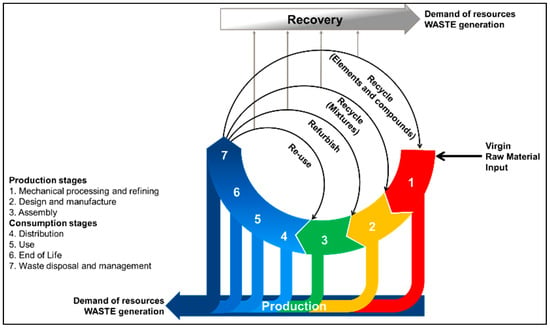
Figure 1.
Circular economy model from a material-centric perspective based on Martinez et al. (2019) [32].
This critical review offers an analysis of the SoA and emerging technologies for LIB recycling from a CE perspective, i.e., by considering the entire spectrum of recovered compounds and their quality. Thus, any emerging process claiming to be a “closed loop” is of special interest. It should be noted that, in this review, materials recovered for a purpose other than LIB production have been considered a downgrade, following the definition of an ideal CE loop.
Methodology and Scope
This review utilized as baseline the previous works of Xu et al. (2008), Espinosa et al. (2004), Bernardes et al. (2004), Farella et al. (2008), Ruffino et al. (2011), Ordoñes et al. (2016), Sayilgan et al. (2009), Vezzini (2014), and Zeng et al. (2014) [22,27,35,36,37,38,39,40,41] regarding battery recycling at industrial and laboratory scales. Other references were collected from scientific literature databases such as Scopus, Google Scholar, ResearchGate, ScienceDirect, and Google Patents. The search included original scientific articles, patents, edited books, online-available presentations, and, battery organizations’ webpages, employing keywords as “lithium-ion battery recycling” and “LIB recycling” with additional strings of “mechanical processing”, “separations”, company names, and owner patents. From all the data gathered regarding primary (disposable) and secondary (rechargeable) LIB recycling, the focus was narrowed down to processes targeting secondary LIBs, either as a single feed stream or as the major feed fraction. In addition, the processes were required to be in accordance with the European Council Directive 2006/66/EC and to recover a minimum of 50% by mass. The different processes thus identified and included in this review can be classified as follows:
- Established industrial processes with LIBs as the major or unique feed;
- Emerging technologies designed for LIB recycling;
- Processes which do not use LIBs as either a major or unique fraction of the feed, but accept them as secondary feed.
Due to the broad number of emerging technologies reported in the literature, those chosen include those in pilot plant stages, under permitting procedure, under commercialization, or that have produced several patents. The technologies chosen clearly support towards the CE philosophy by offering a broad range of recovered LIB material components. Hence, this review encompassed the following recycling technologies:
- Established: Umicore Valéas™ (Umicore, Bruxelles, Belgium), Retriev Technologies (Retriev), Recupyl Valibat (Recupyl), Akkuser, and Sumitomo–Sony (Sumitomo).
- Emerging: LithoRec, Accurec, Battery Resources, Steven Loop: OnTo Technology (OnTo), Aalto University Process.
- Other industrial processes accepting LIBs: BatRec, Inmetco, and Glencore.
The so-called “Aalto University Process” is a theoretical process partially based on the developments of Reference [42], applying laboratory-scale results to processing real LIB waste [43]. This process, analyzed by Reference [44], was classified into the “Emerging” category because it recovers all the LIB compounds.
Moreover, the recycling processes were analyzed using the following guidelines:
- What type of battery feed does the process accept?
- What are the main recoveries? What is their final quality?
- Which processes, i.e., hydro- or pyrometallurgy and/or mechanical processing, are used? What are their limitations?
- What other material inputs does the process require?
This review is divided into five main sections. Section 2 discusses the challenges of LIB recycling processes from a material and process perspective. Section 3 first describes the established processes (Section 3.1), followed by emerging technologies (Section 3.2). Section 4 provides a comparative analysis of all recycling processes from two different perspectives: based on the complexity of the process itself (Section 4.1), and based on the quality of recyclates (Section 4.2). Conclusions are presented in Section 5.
2. Challenges in LIB Recycling
Compound Challenges
In general terms, a LIB is formed of either a single or multiple electrochemical cells connected and enclosed in a metallic or plastic case. Table 1 presents the composition of a typical LIB based on Reference [17,22,45,46].

Table 1.
Lithium-Ion Battery (LiB) Constructive Components and Materials.
A cell, the basic construction unit of all LIBs, is formed of a transition metal compound as the cathode, graphite as the anode, Al and Cu as current collectors, Li salt as electrolyte, a polymeric separator, and a metallic cell casing [1,2,47]. The cathode, usually a lithiated transition metal oxide/phosphate (Table 1), defines the obtainable voltage of the LIB if there are no changes in the anode material [47]. The anode material, most commonly graphite, but also Li4Ti5O12 in some stationary applications, should enable the efficient flow of Li ions without excessive structural and volume changes, while being able to conduct electrons [47,48,49]. The polymeric separator is placed between the electrodes to prevent direct contact and short circuits. Nevertheless, the separator should have enough porosity to allow Li-ion migration [47]. The electrolyte consists of a Li salt dissolved in an organic solvent, its main purpose being to efficiently conduct the Li ions between electrodes [15,50,51]. PVDF binds the cell together and, thus, it should present high mechanical strength and good chemical and environmental endurance [52]. The electric current is carried through Al and Cu foils connected to the cathode and anode, respectively [15]. Finally, the cell components are enclosed in an Al, Fe, or plastic casing [47,48].
The five cathode chemistries displayed in Table 1 are currently dominant in the market. However, in the search of better performance, stability, and/or longer lifespan, an increasing number of cathode chemistries are being explored, potentially resulting in a higher degree of material complexity. For example, LiCoO2 provides a good specific capacity, but is expensive and presents safety risks at elevated temperatures [47,53]. The specific capacity, measured in mAh/g, describes how much electricity is delivered by a cell [2]. These drawbacks have been reportedly tackled by replacing the Co with Mn, either partially or totally, as LiMn2O4 offers a lower economic cost, higher stability at high temperatures, and better tolerance to overcharging [45,48]. Simultaneously, LiMn2O4 presents an irreversible loss of capacity during operation due to the dissolution of Mn ions into the electrolyte [45,54]. As LIB chemistries become more specialized, they include a larger amount of elements, increasing the cost of recycling [15,18,55,56,57]. The wide variety of mixed LIB chemistries reaching recycling streams is already generating further challenges in recycling processes [18]. In addition, consumer electronics powered by LIBs reach an EoL point at between 3 to 4 years, while EV or PHEV applications take 10 years or more, broadening the lag of recycling systems.
As the focus of the LIB recycling processes is driven by market value, Co and metallic fractions are currently their main target [58]. Currently, metallic components are commonly recovered as metallic alloys as a result of pyrometallurgical processes or, in the case of large casing materials, during mechanical dismantling. The remaining materials, e.g., Li compounds, electrolyte, plastics, and organic materials, are lost, except in China and South Korea, where Li is recovered as LiCO3 [59]. The latter is a useful material, since cathode compounds are manufactured from Li metal oxide/phosphate or Li carbonate/hydroxide [60]. While SoA processes successfully recover metallic fractions, emerging processes are focused on the recovery of cathode salts or their precursors. Co may be recovered in different chemical forms, either as a pure metal or as part of a chemical compound (e.g., cathode precursor salts).
3. Description of LIB Recycling Processes
The various stages in the recycling process can be broadly classified into pre-processing and mechanical, hydrometallurgical, and pyro-metallurgical methods. Pre-processing is here considered to be any process which does not alter the structure of the LIB cells, e.g., sorting by battery type from mixed waste. Mechanical processing involves the use of different techniques to liberate, classify, and concentrate materials without altering their chemistry. These techniques operate based on relative differences in the physical properties of materials, for instance density, shape, and size, and they generally occur before stages involving chemical reactions [61,62,63,64]. After mechanical processing, the material obtained is refined by hydrometallurgy, pyrometallurgy, or a mixture of both. Pyro-metallurgy refers to operations at elevated temperatures where redox reactions are activated to smelt and purify valuable metals [15,22,27]. Hydrometallurgy involves the leaching of valuable elements from a solid matrix and their subsequent precipitation through modification of the solvent-phase chemistry [65]. These techniques are highly resource-intensive, and they are thus strongly influenced by economic constraints [65].
3.1. Established LIB Recycling Processes
3.1.1. Retriev Technologies
Initially called “Toxco”, and developed for primary LIBs, this technology is nowadays also applied to secondary LIBs, and offers a capacity of 4500 tons/year. [66,67,68]. A schematic representation is presented in Figure 2.
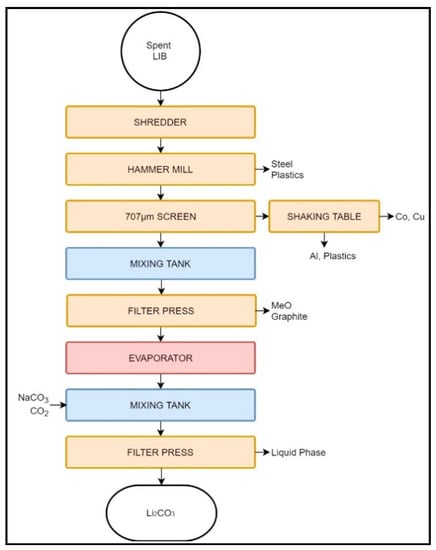
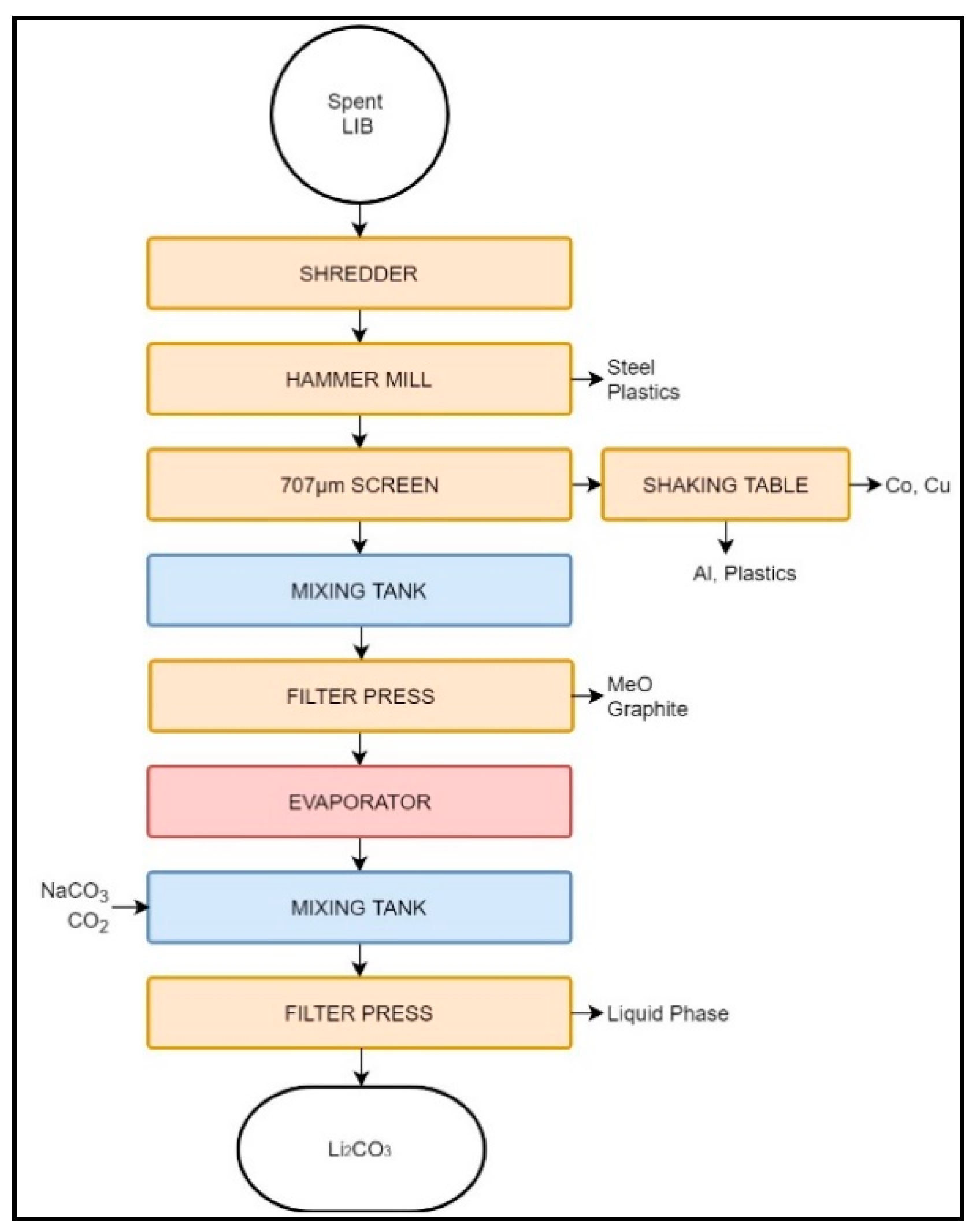
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the Retriev LIB recycling process.
The Toxco process begins by shredding LIBs submerged in a brine solution to deactivate the cells and prevent fire due to Li oxidation. Large LIB packs undergo preliminary manual disassembly, while small batteries and cells may be processed as-is [40,66,69]. Depending on the feed characteristics (i.e., between primary and secondary LIBs) the protective environment may change from brine to liquid N2 (cryogenic crushing), the latter being employed when the quantity of primary LIBs is high [40,66,69,70].
After shredding, the slurry is processed with a hammer mill, and the larger particles, containing mainly metallic components, are separated by screening. The resulting Cu–Co-rich overflow is treated with a shaking table to remove Al particles and plastics. The cathode-rich undersize particles are filtered to obtain a cake rich in C and metallic oxides (MeO). The filtered liquid is also rich in Li and may be reacted with Na2CO3 or CO2 to produce Li2CO3 [66,70]. The metallic oxide and Li2CO3 cakes are used in metal industry, and are thus considered downcycled [67,70].
Furthermore, the Retriev Technology company patented a method (Figure 3) to recover and regenerate cathode-grade material from spent LIBs [71]. However, this process is still undergoing commercialization and, at the time of writing this review, no evidence of its productivity was available [69].
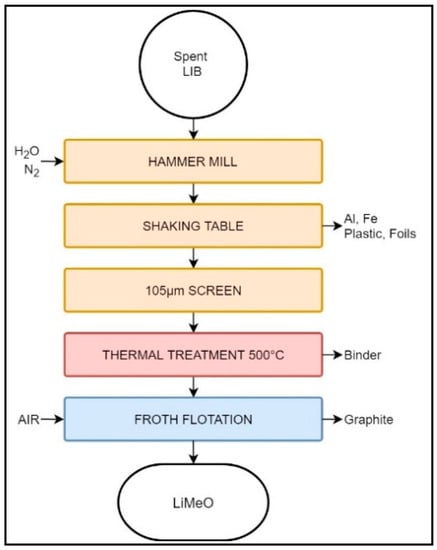
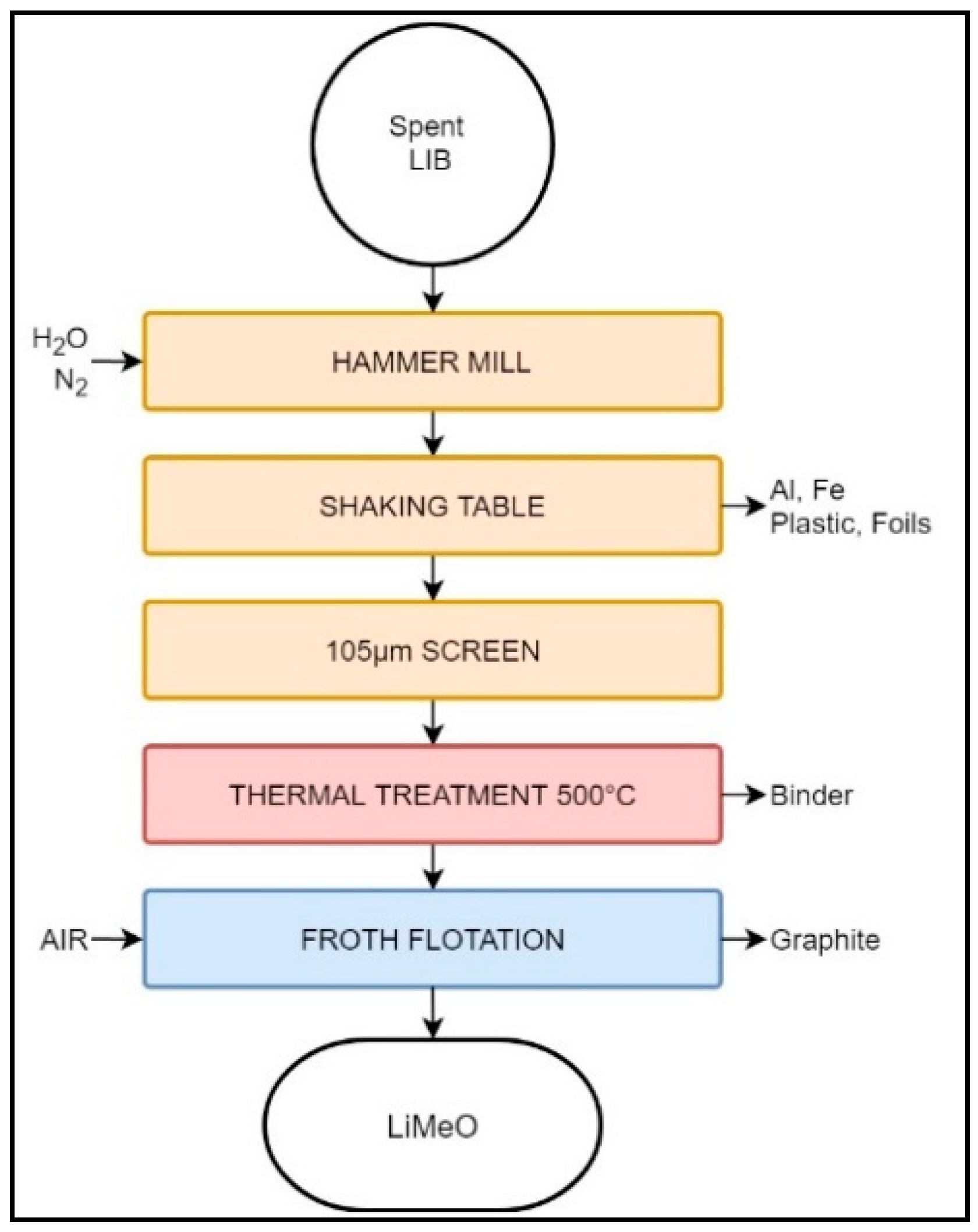
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of the Retriev LIB recycling process for cathode-grade material regeneration.
Similarly to the original Retriev process, this modified version starts by shredding the waste LIBs in an artificial atmosphere of N2 or spray water. Coarser particles of Al and Steel (Fe) are removed from the slurry using a shaking table. The remaining slurry, rich in electrode material, is split with a 105 µm sieve. The undersize fraction is heated at 500 °C for two hours, permitting the evaporation of water, pyrolysis of the binder, and structural modification of the carbon, while avoiding the ignition of the latter. The dry, binder-free material is subsequently mixed with distilled water and sent to a flotation process, where anode and cathode particles are separated via their differences of hydrophobicity. Anode powder reports to the froth phase, while cathode is recovered from the non-floated fraction [71].
3.1.2. Sumitomo–Sony
The Sony Process, with a capacity of 150 tons/year, was developed by a cooperation between Sony Electronics and Sumitomo Metal Mining Company [68,72]. Although the information regarding this process is scarce, this process was reportedly designed for the recycling of LIBs.
The Sony process starts with a calcination step to remove the electrolyte and other organic materials. The remaining fractions are subdued to a pyrometallurgical transformation, leading to the recovery of a metallic alloy consisting of Co, Ni, and Fe, while the Li is lost to the slag. Co is subsequently extracted from the metallic alloy by a leaching process. The main product of the Sumitomo–Sony process is CoO of sufficient quality that it can be used to manufacture LIBs [72]. Cu and Fe are by-products that are separated mechanically [72,73].
3.1.3. Recupyl Valibat
The Recupyl process, with a nominal capacity of 110 tons/year, was developed as a low-temperature LIB recycling technology, directly addressing the gas emissions resulting from pyrometallurgy in the above-mentioned processes. Figure 4 presents the Recupyl process.
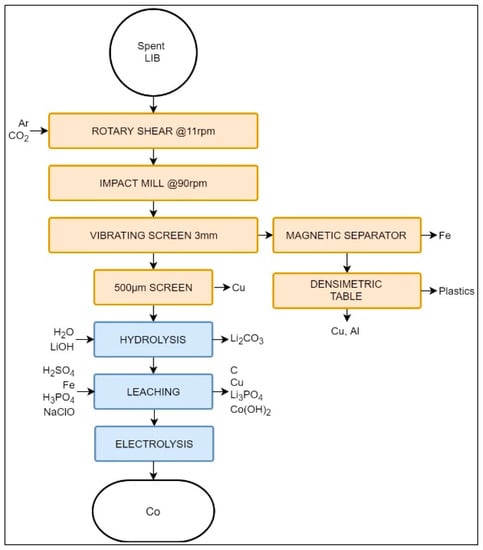
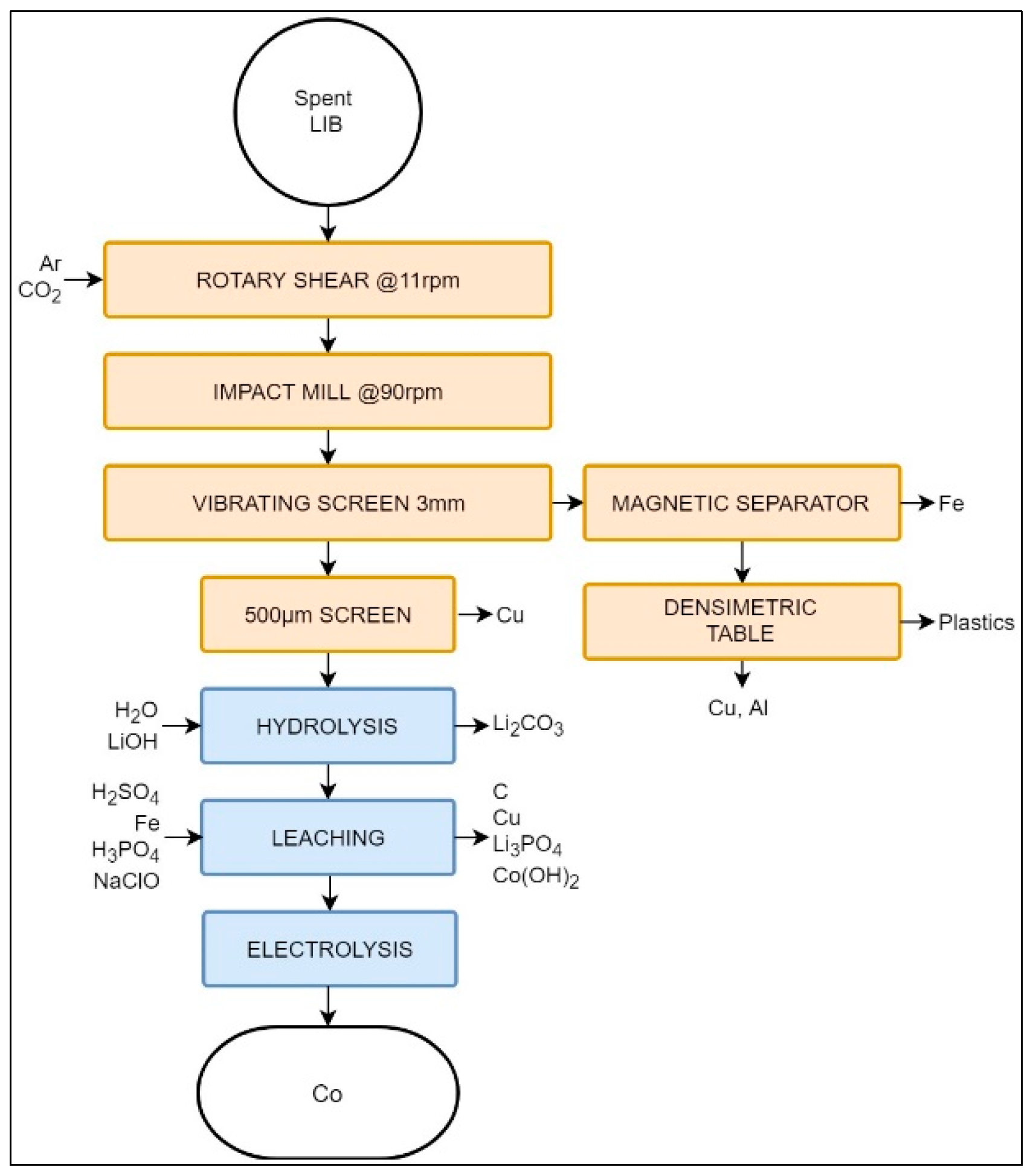
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of the Recupyl Valibat recycling process.
The feed in the Recupyl process may be either primary or secondary LIBs [74]. Batteries are then transferred to a two-step comminution. First, LIBs are treated in a low-speed rotary shear (11 rpm) in Ar or CO2 atmosphere to expose the internal compounds. The inert atmosphere ensures the safe processing of potentially charged batteries. When CO2 is used, it passivates the metallic Li of the primary LIBs, forming a surface of Li2CO3 and reducing fire risks. Secondary grinding is carried out in an impact mill at 90 rpm to reduce particles to a size lower than 3 mm. The target particle size is obtained with the help of a vibrating screen, thus creating over- and undersize fractions.
The oversize fraction is processed using a high-induction magnetic separator to remove ferrous metals. The non-magnetic fraction is then processed with a densimetric table. The relative difference in density creates a high-density fraction (containing Cu and Al) and a low-density fraction, formed by paper and plastics [74]. The 3 mm sieve undersize fraction is further classified using sieves with a 500 μm opening size. There, most of the remaining Cu particles are removed, the passing material containing only <0.3% of Cu [40,74]. Cu removal is a crucial step, since this metal is an impurity that will affect subsequent hydrometallurgical steps.
The electrode-rich fine fraction (i.e., <500 μm) is then mixed with water, and its pH is adjusted to 12. This step releases H2 due to hydrolysis. Li salts are then dissolved into the aqueous phase, leaving MeO and graphite suspended in the solution, to be separated by a filtration process. At this stage, it is possible to recover Li2CO3 or LiCoO2 from the liquid phase by the addition of gaseous CO2 or by solid/liquid separation [74].
The remaining solid fraction undergoes a series of leaching steps, first being treated by H2SO4 at 80 °C. C is filtered out from the solution and Cu is then cemented with steel, i.e., reduced to its elemental form. The possible remaining Li can be precipitated at this point as Li3PO4 by the addition of H3PO4. Finally, Co may be recovered as Co(OH)2 in the presence of NaClO, or as elemental Co by electrolysis [74].
3.1.4. Akkuser
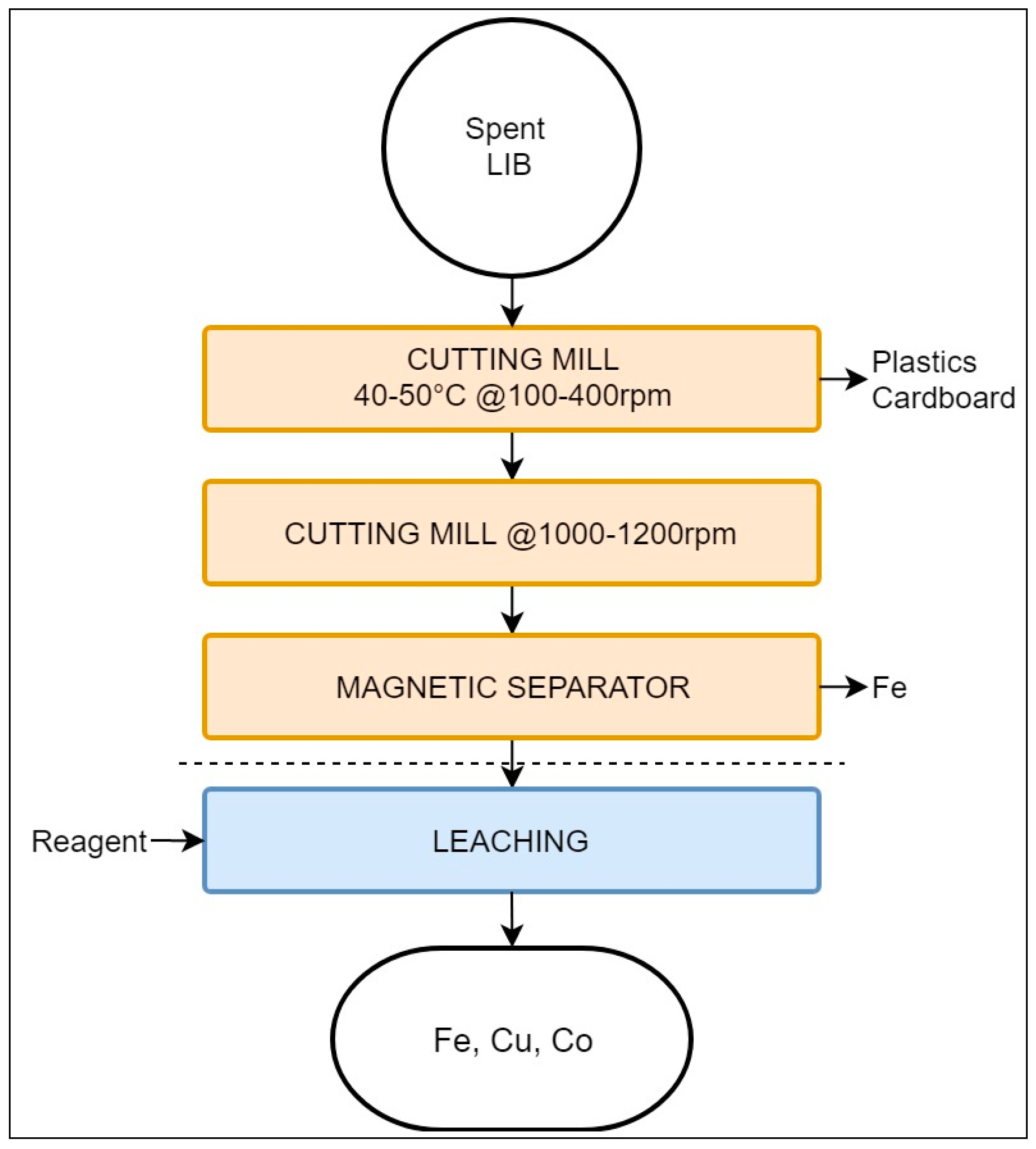
The Akkuser process employs low-temperature stages aimed at obtaining a metal-enriched fraction suitable for subsequent refining. This process involves only a mechanical pre-processing treatment and does not encompass hydro-or pyrometallurgical steps [40,75]. It is reported that Akkuser has a capacity of 4000 tons/year [68]. As this review is focused LIB recycling, the Akkuser process for this type of battery is presented, as depicted in Figure 5.
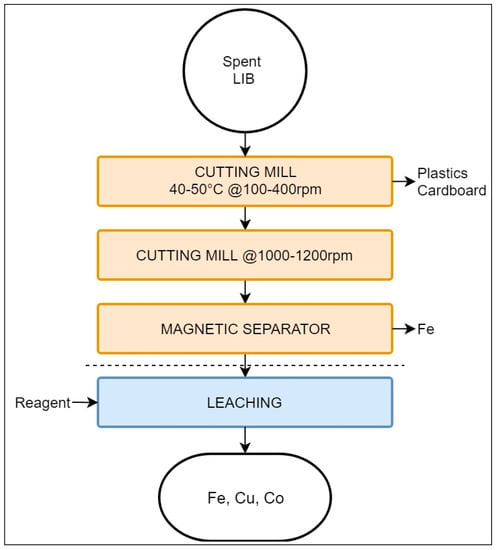
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the Akkuser recycling process.
This process accepts a mixed feed, as the batteries are pre-sorted by type [75]. After sorting, LIBs are processed by two continuous cutting mills. The first mill operates at a temperature range of 40 °C to 50 °C, at 100–400 rpm, reducing the battery size to the range of 1.25 to 2.5 cm. There is no mention in the literature of a protective atmosphere during size reduction; however, it may be inferred that fire risks are considered low. Naturally occurring gases, H2 and O2, are extracted and filtered using a cyclonic system. The filtration residues, most being plastic–metal particles, are then processed to recover Ni and Co by leaching. Upon reaching a pristine quality, the exhaust gases are then released into the atmosphere [75].
The shredded material is then transferred through an air-tight cooling tube into a secondary mill operating at 1000–1200 rpm. The secondary cutting mill reduces the material to a size <6mm. Volatile fine particles are captured with a secondary cyclonic air system, from which ferrous metals are recovered employing a magnetic separator. The resulting non-volatile fraction rich in Co and Cu is ready to be refined by either hydro- or pyrometallurgy [75].The final recovery composition is not detailed in the literature, but is likely a mixture of electrode materials and traces of Al [76].
3.1.5. Umicore Valéas™ (Bruxelles, Belgium)
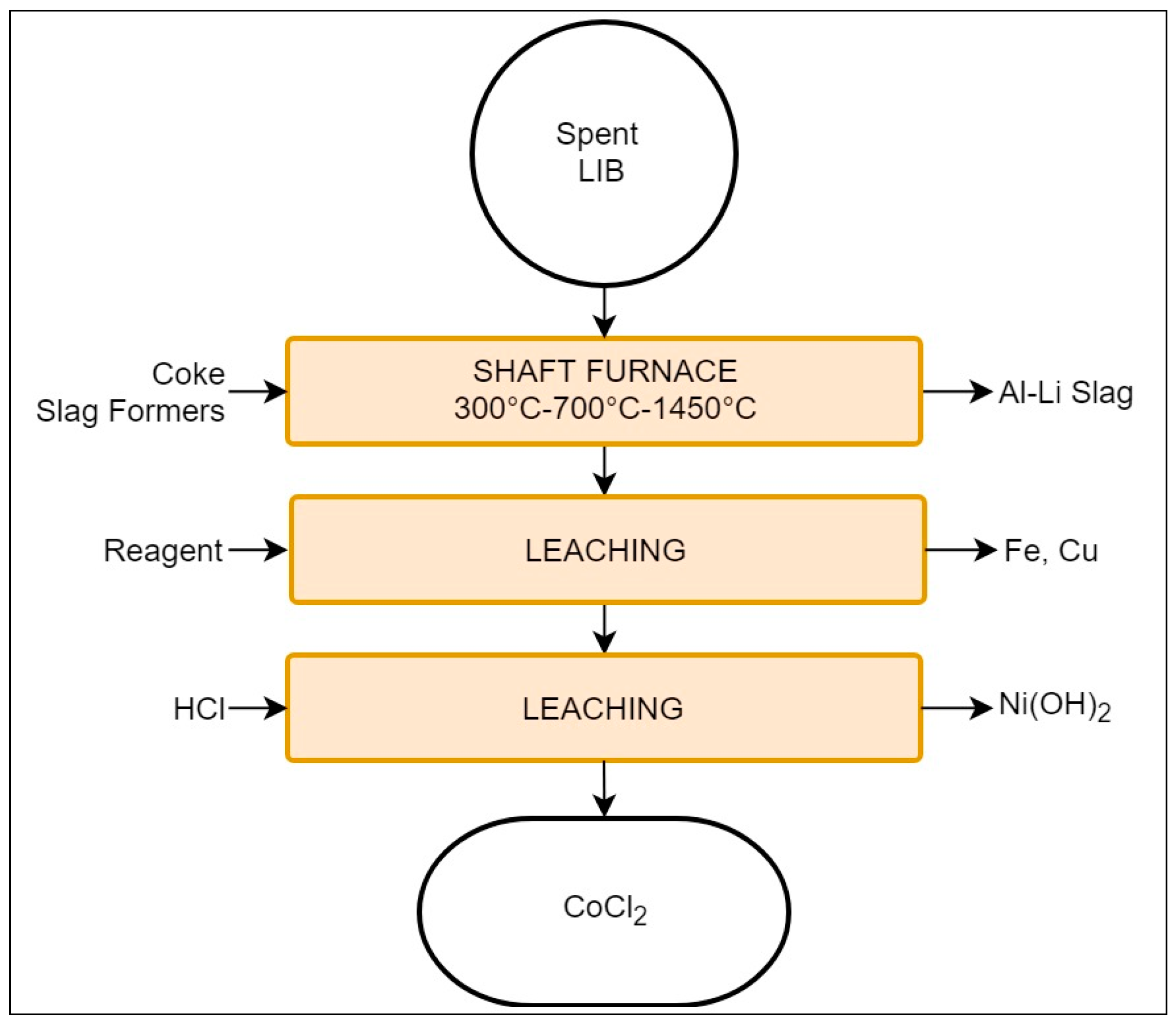
The Umicore process is focused on the recovery of Co and Ni, primarily from LIBs and NiMH batteries, and it presents the largest capacity of the discussed processes, with 7000 tons/year [68]. It involves a combination of pyro- and hydrometallurgical steps, as presented in Figure 6.
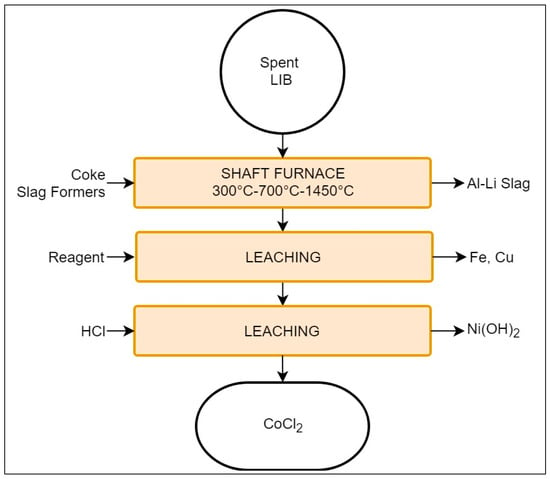
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of the Umicore Valéas recycling process.
The batteries undergo preliminary dismantling, removing unnecessary material (metallic or plastic casing) and exposing the cells. The process begins by introducing the cells into a shaft furnace which, in this case, may be divided into three different sections according to temperature: low = 300 °C; medium = 700 °C; and high = 1200–1450 °C [17,40]. Each section accomplishes pyrolysis of different materials and refinement of the recovery is as follows:
- Low temperature section: evaporation of electrolyte;
- Medium temperature: plastics pyrolysis;
- High temperature: smelting and reduction (1200–1450 °C).
Generally Na, Ca, or ZnO are introduced to capture halogens and volatile compounds. In cases where the feed contains alkaline batteries, their ZnO content is considered sufficient for such purposes [40,70]. The metallic product of the shaft contains Cu, Co, Ni, Li, and traces of Fe, while Al, Si, Ca, Fe, Mn, Li, and Rare earth elements (REEs) report to the slag [40,67]. The presence of Al and Fe in the slag is crucial, as they are considered impurities for the subsequent leaching stages [17,77]. The metallic alloy is then processed by hydrometallurgical means. Initially, Fe and Cu are enriched by an undisclosed leaching solution. The remaining fraction is treated with HCl, resulting in a solution of Ni(OH)2 and CoCl2, and the latter may be processed to obtain cathode grade LiCoO2 [67,70].
The Umicore process pays special attention to the exhaust gases. For example, the mid-section exhaust is recirculated into the low-temperature section, aiding with the electrolyte evaporation and reducing energy consumption. Additionally, the exhaust gases of the high temperature section are cooled down to avoid the formation of dioxins and furans, and are finally filtered [40,77].
3.1.6. Other Industrial Processes Accepting LIBs
Batrec
Batrec began battery recycling in the end of the 1980s, processing a mixture of alkaline and Zn–C batteries, focusing on the recovery of Zn and Hg [39,78]. The BatRec process presents a capacity of 200 tons/year and is a modification of the Japanese Sumitomo process [35]. LIBs are stored and shredded under a CO2 atmosphere to minimize possible reactions, then the batteries are neutralized by moist air [79]. The neutralized batteries are then crushed to expose the valuable components. However, details of the possible subsequent steps were not available in the literature [17,67,79,80].
Inmetco
In the Inmetco process, the batteries and other scrap (possible electric arc furnace fumes) are fed into a rotary hearth furnace along with reducing pellets. The molten material is then refined in an electric arc furnace. In this process, only Co, Ni, and Fe are recovered in the form of an alloy. Other metals are lost to the slag phase and organic materials are burned [17,27]. Inmetco operates with a capacity of 6000 tons/year.
Glencore
In similar manner, the Glencore process targets the recovery of Co, Ni, and Cu through pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical methods, and presents a capacity of 7000 tons/year. Any other components are consumed in the process, either as a source of energy or reducing agents or being lost to the slag phase [17,81]
3.2. Emerging LIB Recycling Processes
3.2.1. Accurec
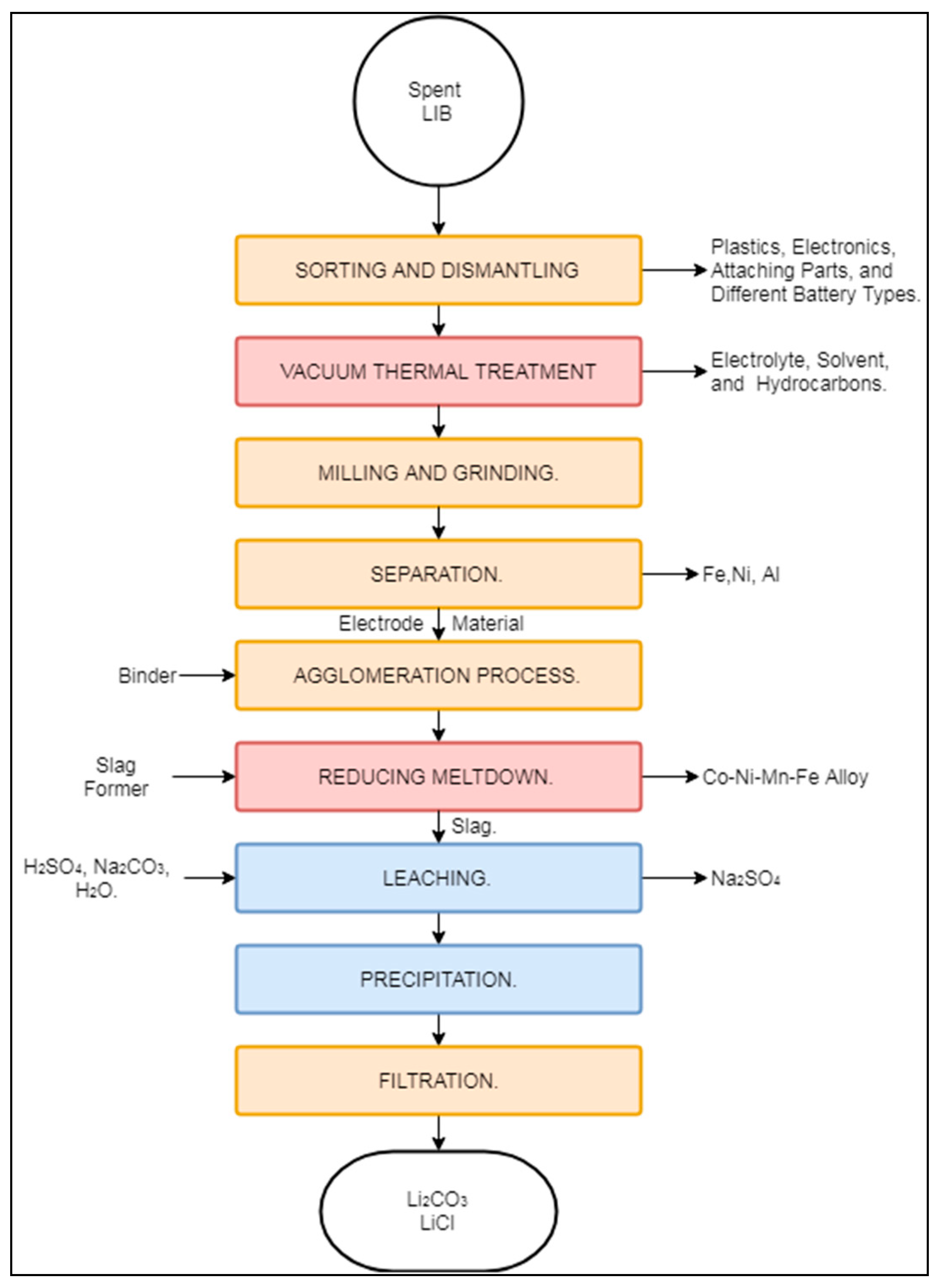
The process designed by the German company Accurec GmbH® (Krefeld, Germany) was initially designed to treat Ni–Cd batteries. Nevertheless, it has broadened its scope to process various types of batteries, including LIBs [27,29,40,82]. At the moment, LIB recycling by this process operates at a batch-industrial scale in Germany [82]. The Accurec process for LIBs, presented in Figure 7, is a combination of mechanical, pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical processes aimed at recovering a Li2CO3 cathode precursor and a Co–Ni–Mn alloy.
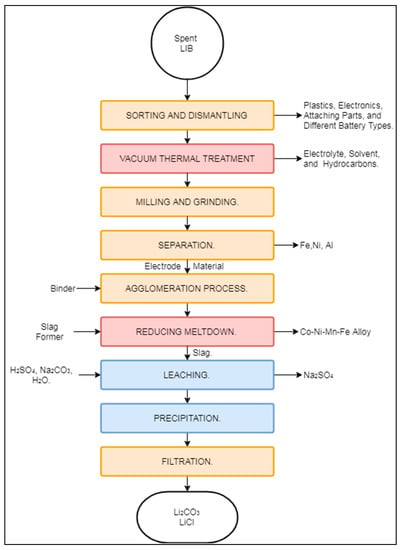
Figure 7.
Schematic representation of the Accurec process.
The process begins with the sorting, cleaning, and manual dismantling of spent LIBs from consumer goods and EVs [82]. The dismantled feed is transported to the company’s proprietary vacuum thermal treatment, where it is treated at 250 °C under a vacuum to remove electrolytes, solvents, and volatile hydrocarbons [82,83]. The produced fraction is then transported to milling and grinding operations to expose the enclosed constituents. Ground material undergoes a series of mechanical separation steps consisting of a vibrating screen, magnetic separator, and zig-zag classifier (“separation” box in Figure 7), although the exact order of these operations is not specified in the literature. The mechanical separation produces fractions of Fe–Ni, Al, and Al–Cu, from which base metals can be extracted. The remaining fraction is sent to agglomeration and a two-step pyrometallurgical process. The first pyrometallurgical step is carried out in a rotary kiln at 800 °C. The second pyrometallurgical operation is carried out in an electric arc furnace (EAF) (“reducing meltdown” box in Figure 2), where graphite is consumed to enhance the recovery of either Co or Mn, depending on the composition of the previously added slag. As the current market value of Co is higher than that of Mn, the purification of the former is favoured, while the latter is mostly lost in the slag phase [17]. According to Georgi-Maschler et al. (2012), the Co alloy recovered at this stage has commercial value. Similarly to Mn, Li is lost in the slag or volatilized as flue dust during EAF operation.
The concentration of Li in the flue dust and slag has been estimated to be 5 times higher than in the feed, thus offering the possibility of recovery by hydrometallurgical means in the form of the cathode precursor Li2CO3. In such cases, the slag is processed mechanically to obtain a particle size <100 μm, while the flue dust fraction is sent directly to hydrometallurgical treatment. Li is then leached using H2SO4, yielding Na2SO4 as a by-product. After extraction, Li is precipitated in the form of Li2CO3. The Accurec process claims to achieve a Li2CO3 recovery of 90%; it can then be used either as a cathode precursor or as a raw material for glass manufacturing [17].
3.2.2. Battery Resources “Closed Loop” Process
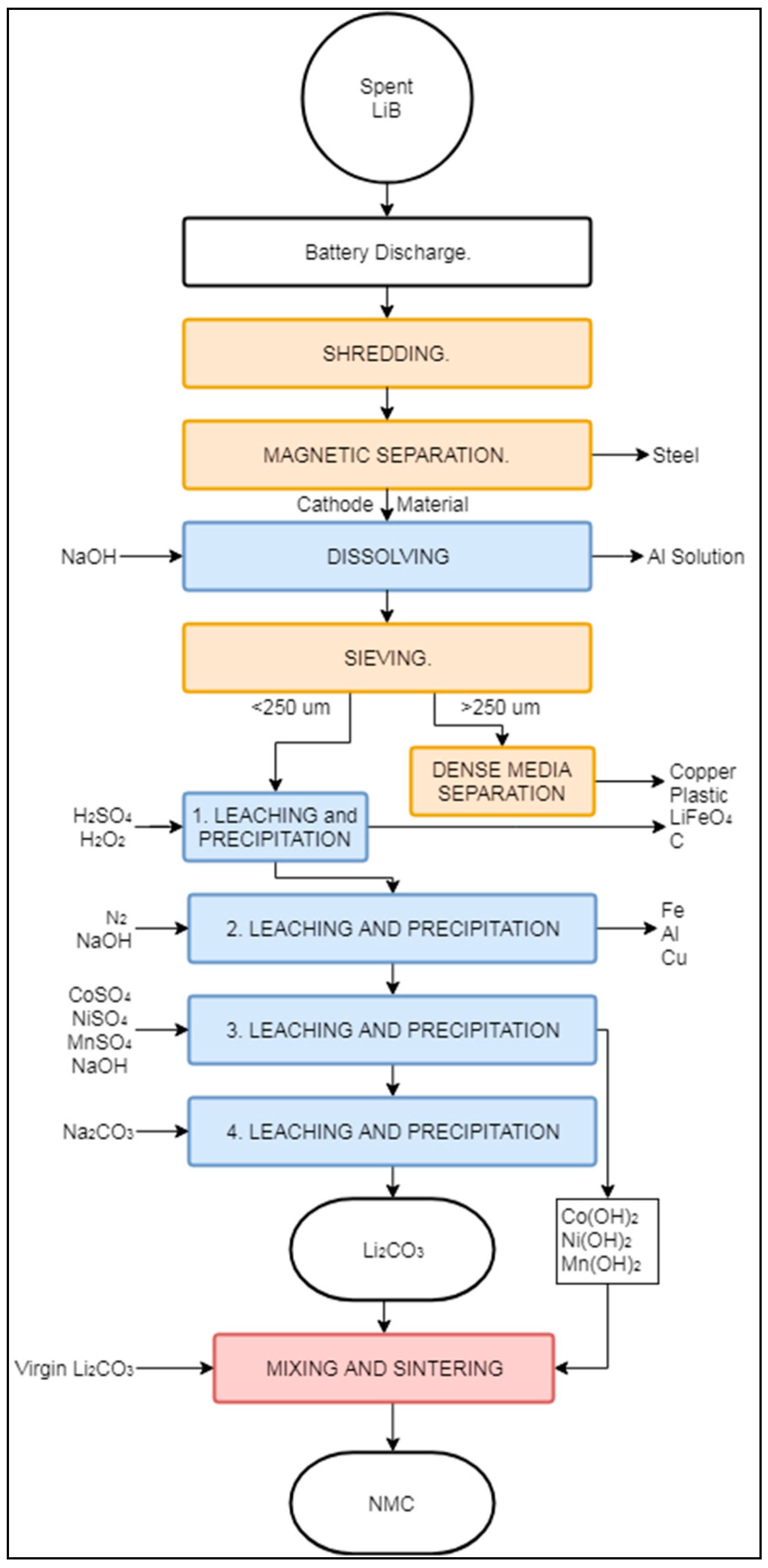
The Battery Resources process is considered a “closed loop” process by its developers, since it recovers battery components suitable for LIB production [84,85,86]. According to Heelan et.al. (2016) this process is currently in the commercialization phase, with a pilot plant operation ongoing since the summer of 2018 [87,88,89]. The Battery Resources process uses mostly mechanical and hydrometallurgical operations, with a single sintering step at the end for product refining. The Battery Resources process is designed to treat LIBs with LiNixMnyCozO2 cathode chemistry. Figure 8 presents a schematic representation of the process.
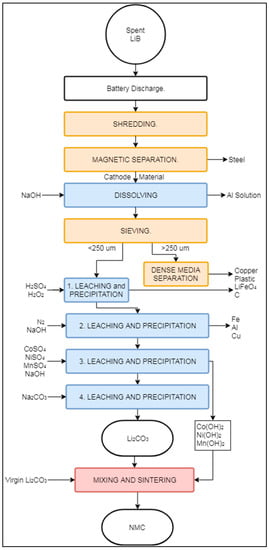
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of the Battery Resources recycling process.
Initially, spent LIBs undergo a discharging step to reduce the risk of spontaneous explosion during shredding. After discharging, the spent LIBs are shredded with a hammer mill to liberate the constituents and reduce the particle size to <6.3 mm. The shredded mixed material is treated by magnetic separation, producing a magnetic fraction with high content of steel and a cathode-containing non-magnetic fraction. The final destination of the magnetic fraction has not been mentioned in the literature [84,85], but refining could be carried out by a third party company. The non-magnetic fraction is mixed with NaOH in order to extract Al in the form of NaAlO2 (“dissolving” box in Figure 8). The resulting slurry is then filtered and dried at 60 °C, followed by sieving with an opening size of 250 μm. The coarser fraction is treated by dense media separation (DMS) to obtain a Cu-rich fraction. The fine fraction is sent to a four-step hydrometallurgical process. The first stage removes C, LiFePO4, and the remaining plastics in the presence of H2O2 and H2SO4 at a temperature between 65–70 °C. The remaining solution contains ionic forms of Co, Ni, Mn, Li, Al, and Cu. Adjusting the pH to 6.5 with the addition of NaOH promotes the precipitation of the remaining Al, Fe, and Cu (“2. Leaching and Precipitation” in Figure 8). At this stage, N2 gas is also added to prevent the oxidation of Mn2+ ions [86]. In the third leaching stage, different amounts of MnSO4, NiSO4, and CoSO4 are added (“3. Leaching and Precipitation” in Figure 8), to obtain a ratio of 1:1:1 of Co, Mn, and Ni in the solution. There were no details available in the literature about the origins of the Ni, Mn, and Co salts added [84]. Increasing the pH of the solution to 11 with additional NaOH promotes the precipitation of solid Co(OH)2, Mn(OH)2, and Ni(OH)2. During the final hydrometallurgical step (“4. Leaching and Precipitation” in Figure 8), Na2CO3 is added at a temperature of 40 °C to precipitate Li2CO3 from the remaining solution. The previously extracted Co(OH)2, Mn(OH)2, and Ni(OH)2 are mixed with the precipitated Li2CO3 and some additional virgin Li2CO3 to synthesize battery-grade cathode material through compression into pellets and sintering at 900 °C.
3.2.3. LithoRec
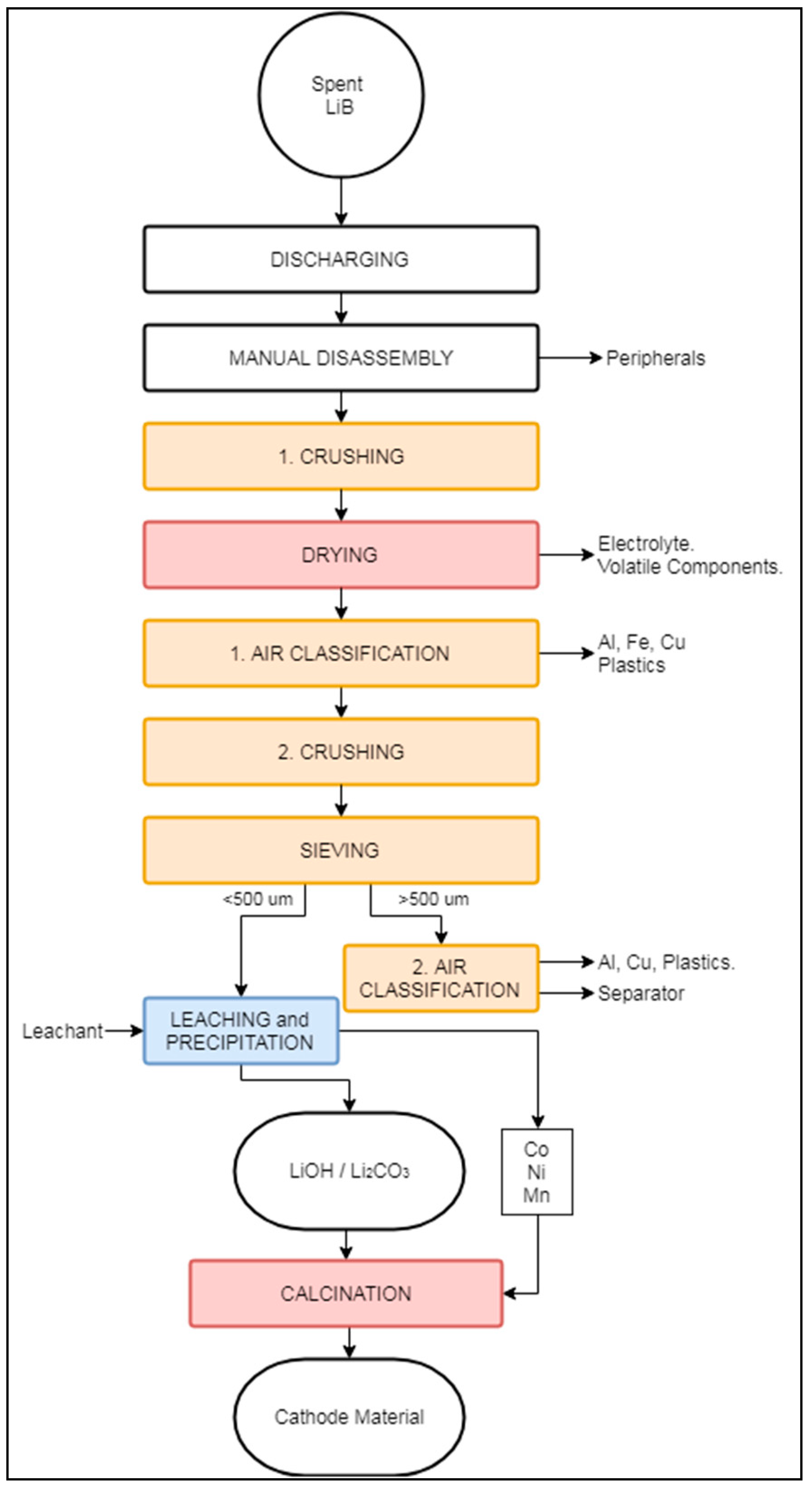
The LithoRec process, in general reference to the German projects LithoRec I and LithoRec II [90,91], aims to recover high-grade cathode material from traction LIB modules, mostly used in vehicles, e.g., forklifts, trucks, EVs, HEVs, and e-bikes [92]. It has been reported that this process offers a capacity of 2000 tons/year [68]. Currently, the company Duesenfeld in Germany bases its continuous operation on this process [93]. Compared to an average LIB (Table 1), those used for traction purposes contain 63% cell material, 5% electric components, 21% steel, and an additional 11% plastics [94]. Their comparatively larger plastic content, which aims to reduce the vibration during normal operation of the vehicle, requires a more complex process compared to the recycling of traditional LIBs. As the content of battery cell components in traction LIBs is low, it becomes highly important to achieve proper and efficient separation of casing materials. Hence, the LithoRec relies heavily on mechanical processing and hydrometallurgical operations rather than pyrometallurgy. A schematic flowsheet of the LithoRec process is displayed in Figure 9.
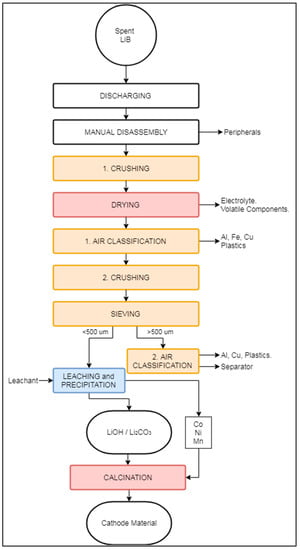
Figure 9.
Schematic representation of the LithoRec recycling process.
As the LIBs fed into the LithoRec process are larger than the LIBs used for traditional applications (e.g., mobile phones), the risk of sudden explosion is higher. Thus, the LithoRec process begins with the discharging of batteries [91]. After discharging, the LIB modules are manually disassembled to remove peripherals, i.e., protective case, wiring, plastics, and contaminants (“Peripherals” in Figure 9). The dismantled LIB modules are then crushed with a 20 mm rotary shear crusher between 100–140 °C under an N2 atmosphere, volatilizing solvents and evaporating the electrolyte. The crushed modules are subsequently sent for initial classification in a zig-zag sifter (“1. Air Classification” in Figure 9), where Al, Fe, Cu, and plastics are separated. The remaining fine solids (a.k.a., black mass) are mostly cathode and anode materials, and are further sent to a secondary crushing stage [91,92]. The crushed black mass is then sieved with a mesh opening size of 500 μm. The overflow is transferred to a second classification step (“2. Air Classification” in Figure 9), where it is split into fractions containing Al–Cu and plastics. The sieved underflow is directed to a leaching phase in the presence of an undisclosed extraction agent.
During leaching, graphite is initially removed from the solution, followed by Co, Ni, and Mn, which are precipitated in oxide form. The Li remaining in solution is then precipitated as LiOH, Li2CO3, by crystallization, or as a mixture of LiOH and Li2CO3 by electrochemical precipitation (“Leaching and Precipitation” in Figure 4). The Li-containing precipitates may include CoO, Ni, and MnO depending on which metals are carried in solution up to this point [95]. Finally, the Li precipitates are mixed with the extracted Co, Ni, and Mn oxides and sent to the “Calcination” process, producing a suitable precursor material for LIB production [96].
3.2.4. OnTo Technology
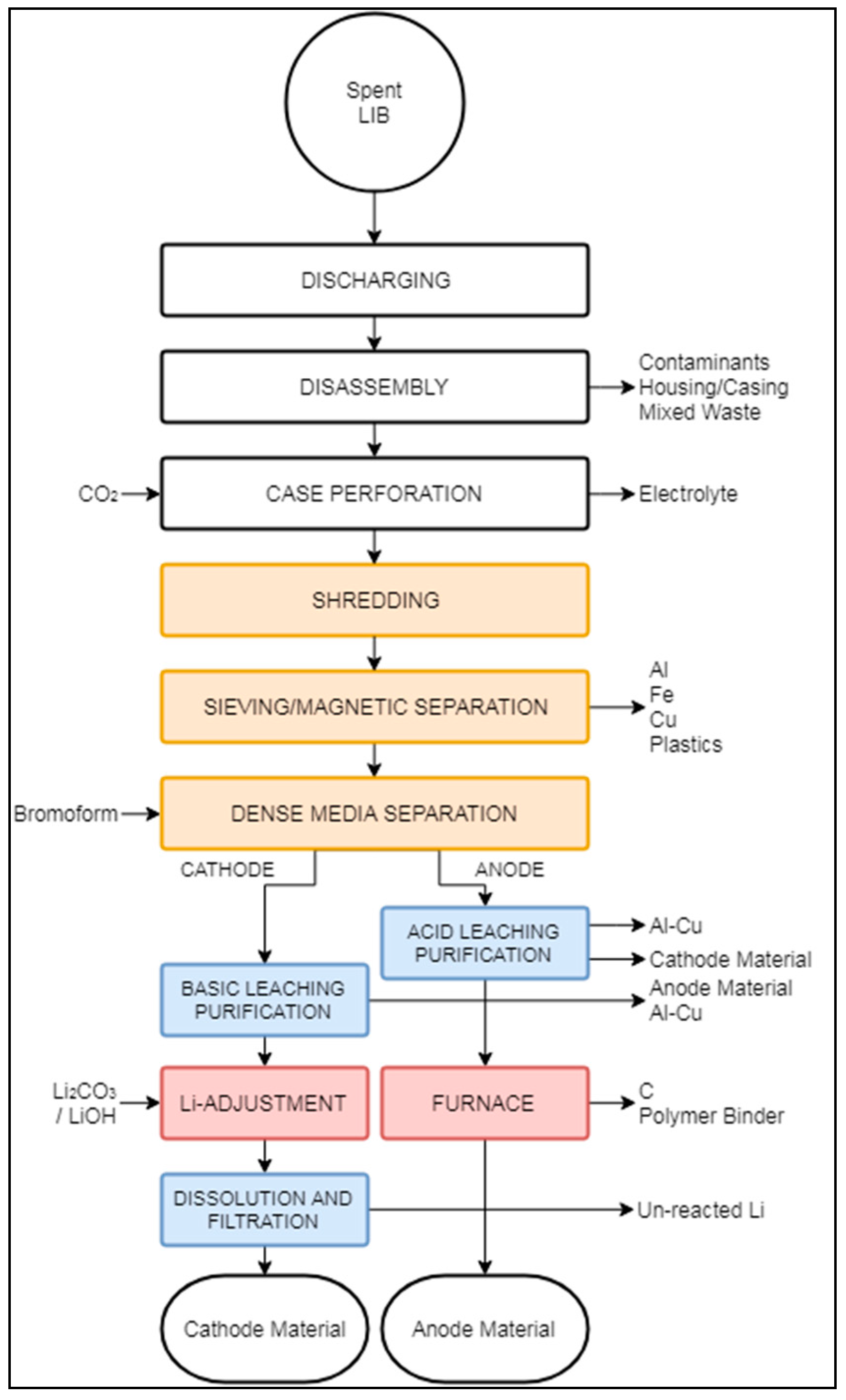
The OnTo Process (sometimes also referred to as EcoBat) aims to recover a wide range of LIB components, including anode, cathode, and metals, explicitly mentioning polymeric materials as the single loss [97,98,99]. At present, this process includes several patents and an operation at the laboratory scale [51,100,101,102,103,104]. Figure 10 presents a graphical representation as accurate as the publicly available information allowed.
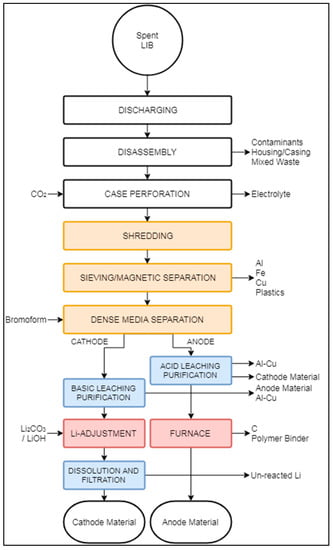
Figure 10.
Schematic representation of the OnTo recycling process.
Similarly to the Battery Resources and LithoRec processes, the OnTo process proposes an initial discharging to reduce the risk of explosion, followed by disassembling to remove large components in the feed. The clean, exposed cells undergo a perforation stage to expose the internal components [100]. After perforation, the cells are enclosed in a chamber with CO2 at supercritical condition (i.e., 74 bars and 31 °C). These conditions reportedly make possible the extraction and recovery of the solvent and electrolyte. The remaining cell, i.e., casing, anode, cathode, and separator, are then stabilized at atmospheric pressure and temperature. Shredding is then carried out, but is not performed under any particular environment, although an atmosphere free of moisture and oxygen has been suggested to avoid contamination of the material [51]. After shredding, Sloop (2010) presents the idea of sorting the elements into the following materials: (i) metal oxides, (ii) propylene, (iii) Li2CO3, (iv) Cu and Al, and (v) graphite. Hailey and Kepler (2015) [97] suggested the metals be separated based on particle size and magnetic properties, although they did not present the details of these proposed stages (“Sieve/Magnetic Separation” box in Figure 10).
The overflow fraction, rich in Al, Fe, Cu, and propylene, is extracted from the process, which can then be further treated to separate the metallic fractions. The underflow fraction, containing a mixture of electrode material, can be separated using dense media separation (DMS) to refurbish anode (graphitic carbon) and cathode (Li2CO3) materials. DMS is carried out in media of about 2.2 to 3.5 g/cm3 [97].
Cathode and anode streams are then directed to parallel hydrometallurgical purification processes. As the DMS process is not 100% efficient, anode particles need to be removed from the cathode fraction and vice versa. Anode purification occurs in two different environments to remove possible impurities: a low-pH treatment removes the remaining cathode particles, then a high-pH environment extracts Al and Cu particles. Cathode purification happens in a basic solution to extract anode particles. Further details about these stages were undisclosed, likely due to intellectual property concerns, but purification was reported to reach a purity of 99% for both anode and cathode materials [97].
Anode and cathode fractions are transferred to a pyrometallurgical stage, where the cathode material is regenerated in a high-energy environment with the addition of pristine Li2CO3 or LiOH. Anode regeneration occurs at a high temperature, where moisture, carbon, unreacted Li, and polymer impurities are eliminated. During pyrometallurgical treatment of the anode fraction, no additional input of chemical additives is required. After the regeneration stages, anode and cathode materials are reportedly suitable for LIB production.
3.2.5. Laboratory Process Suggested by Aalto University
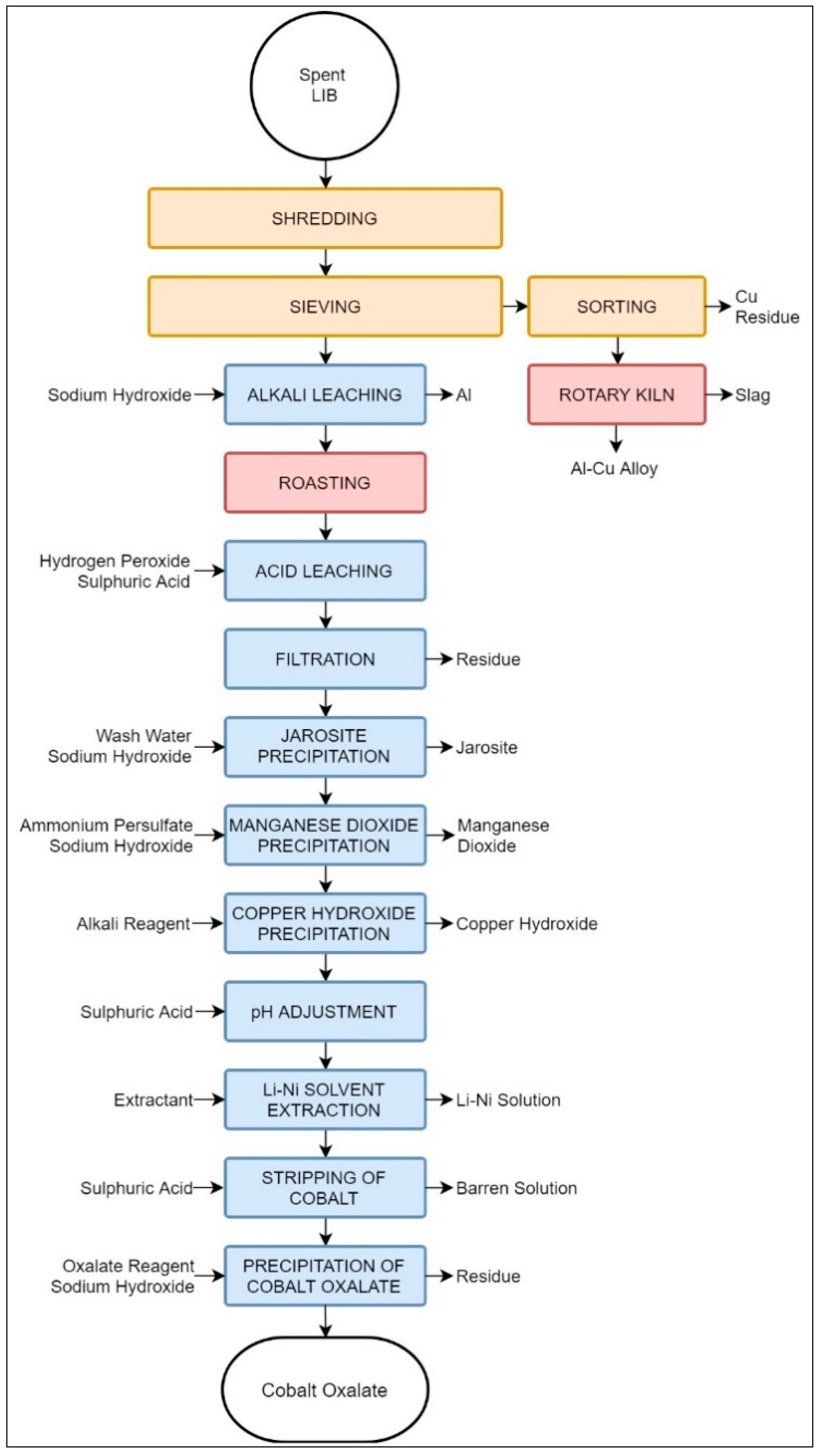
The process discussed by References [43,44] encompasses a mixture of mechanical pre-processing stages followed by a pyrometallurgical step and a thorough hydrometallurgical treatment to recover 99% of the LIB materials.
The process, shown in Figure 11, begins with crushing and sieving, resulting in two distinctive fractions: one formed mostly of the electric peripherals, current collectors, and foils, and a second one formed mostly of the electrode materials. As seen in Figure 10, the two fractions obtained mechanically are processed via two parallel paths: a hydrometallurgical and a pyrometallurgical process designed to treat the electrode material and metallic fraction, respectively. The hydrometallurgical treatment consists of a series of 11 steps specifically designed to obtain cobalt oxalate, CoC2O4, while recovering other elements found in the electrode material fraction, including Li, Ni, Fe, and Co. A pyrometallurgical treatment in a rotary kiln has been proposed to recover Al and Cu. Based on laboratory-scale experiments and process simulations, the Aalto University process has been claimed to recover the vast majority of elements contained in LIBs with a high efficiency [44]. That is, the hydrometallurgical stage recovers 99% of Al, 93% of Li, 89% of Co, 97% of Ni, 98% of Cu, 98% of Mn, and 99% of Fe. The pyrometallurgical path produces a molten phase with 74% of Al with 26% of Cu. It should be noted, however, that the hydrometallurgical products are not in their elemental forms, but rather in chemical compounds, which may require further treatment to be considered usable raw materials for the LIB industry.
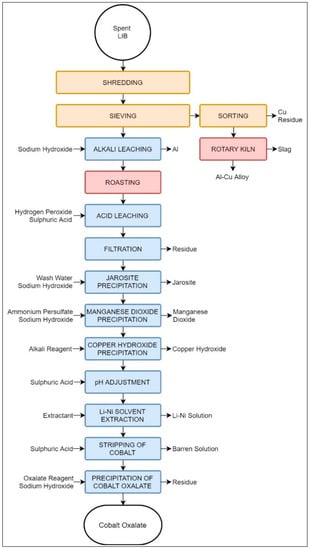
Figure 11.
Schematic representation of Aalto University’s suggested recycling process.
4. Discussion
4.1. Recycling Processes
In this section, a critical discussion on the suitability of the recycling processes and their viability to support a CE model is presented. Table 2 presents a summary of processing stages, final products and their target use, for all technologies discussed in Section 3.

Table 2.
Summary of LiB recycling processes.
As seen in Table 2, only two of the state-of-the-art recycling processes are specialized for treating LIB, i.e., Sumitomo–Sony and Akkuser. Of the emerging processes, only the OnTo Process is capable of treating primary and secondary LIBs simultaneously. The rest of the processes are specialized for one or the other. Nevertheless, while Umicore and Recupyl processes were not initially designed for the processing of LIB, the increasing presence of these types of battery in waste streams pushed for a redesign to accept LIBs as part of their feed. At the same time, the Umicore and Sumitomo–Sony processes claim that their products can be mixed with virgin materials and used as raw materials for batteries. In this manner, the requirement for pristine material is reduced without sacrificing quality requirements.
In the new process developed by Retriev Technologies (Figure 3), the material is ground to a smaller particle size (105 μm vs. 707 μm) compared to the original process (Figure 2). This change in particle size improves the separation of anode and cathode by froth flotation while removing carbon and binder, the presence of which deteriorates the performance of remanufactured cathode [104,105]. Nevertheless, employing a water-intensive technology such as froth flotation involves environmental risks, as it is well known that some hazardous battery components are water-soluble [51]. On the other hand, the wet-crushing system of the original Retriev Process, Figure 2, is at a disadvantage for carbon–binder separation [106]. This drawback is tackled by thermal treatment at 500 °C, where the binder is decomposed.
The Recupyl process is capable of recovering Co-containing cathode powder and LiFePO4 whenever it is present in the feed. In addition, processing of the electrolyte LiPF6 is possible, recovering PF6 and an ammonium salt during a hydrolysis phase (Figure 4) [80]
The high levels of recycling efficiency of the Akkuser process (i.e., >90%) and its low energy consumption (0.3 kWh/kgmaterial) set this process in a privileged position compared to the rest. It is, however, only possible to reach this cost/efficient value because this process is based only on mechanical processing steps, and aims to obtain a black mass for cathode precursor manufacturing by a third party [107,108]. Thus, the stages for refinement are not directly related to Akkuser, and have been left out of this process [75]. Moreover, the Akkuser process reports losses of plastics only during processing. The process was included in this review because it is a real industrial-scale operation [75,108].
There has been a general shift regarding the final aim for materials recovery from the SoA to emerging technologies. While the former focus on metals recovery (or alloys), the latter also aim to recover cathode or cathode precursor material. In addition, the goal of diminishing material losses is more explicitly pursued by the emerging processes. The extensive processing in emerging processes is directly related to the quality of the final recovery. In processes dominated by pyrometallurgy, the only expected product is a metallic alloy. More complex processes entailing hydro- and pyrometallurgy and mechanical processing are able obtain a wider variety of materials. Additionally, processes using pyrometallurgical operations report larger losses, e.g., Umicore Valéas™ and Sumitomo–Sony processes do not recover electrolyte, plastics, organic material, metals, and graphite. In the case of the Umicore Valéas™, the slag is not listed as a loss, but as a by-product, because this process explicitly pursues an afterlife for the slag phase as additive for the construction industry [34]. However, using a material in applications with low economic value can be considered a downgrading operation. Nevertheless, as seen in Table 2, methods presenting an initial pyrometallurgical step do not require a discharging step, as is the case for mechanical and hydrometallurgical processes. Discharge in a controlled environment is bound to the mechanical and hydrometallurgical stages, due to the risk of ignition [51,91]. For example, the Akkuser process requires environmental control carried out by a cyclone air system. In the Retriev process, the concentration of O2 in the environment needs to be adjusted, as it is highly reactive with the pure Li found in primary LIBs.
Other significant differences between SoA technologies and emerging processes is that the main products of the former are not specifically recovered for LIB manufacturing. In comparison, the emerging technologies aim to recover cathode and/or anode precursor materials to satisfy the specific needs of the LIB industry.
Consequently, the emerging technologies require a larger number of mechanical processing stages, in addition to a combination of hydro- and pyrometallurgical stages. Evidently, the higher complexity of the emerging technologies raises questions of their viability compared to simpler process recovering a limited variety of products. For instance, the Battery Resources process requires the consumption of various chemical reagents (e.g., MnSO4, NiSO4, and CoSO4) but obtains the most suitable product for use as a cathode material, at least out of the processes analyzed herein. This brings up the need for balance between the total number of stages, the overall process complexity, and the quality of the products [45]. It is well known that a more complex process, of any nature, is associated with a higher possibility of failure, and requires larger quantities of energy and chemical reagent input while not fully eliminating the generation of waste. For instance, the Aalto University process presents a high quality of products, but also demands a large number of reagents in the hydrometallurgical stages and high energy in the pyrometallurgical step, in addition to efficient mechanical pre-processing stages.
Comparing the different operations present in the processes, there is a clear advantage to the use of mechanical processing coupled hydrometallurgical operations from a CE perspective, i.e., an increase in the variety and usability of the recoveries [73]. This can especially be seen in the products of the Toxco and Recupyl processes, where the losses are diminished considerably in comparison to Umicore Valeas™ or Sumitomo–Sony. Even if the main recoveries of the Umicore Valeas™, Toxco, and Recupyl processes are intended to be used for cathode production, only the latter two recover Li2CO3 and LiCO2 in the same operation, which are considered cathode precursors. If a cathode precursor is defined as a material that do not require further processing to be used in cathode manufacture, the CoCl2 obtained in the Umicore Valeas™ process cannot considered a cathode precursor, as it requires further chemical treatment for cathode material synthesis [70,97]. Thus, it is possible to say that the Toxco and Recupyl are more in line with the idea of circular economy, in comparison to the rest of the processes.
As seen in Table 2, how close the recovered Li components are from being re-used as cathode material is directly related to the complexity of the process. For example, the Recupyl process recovers a cathode precursor, while Sumitomo–Sony produces CoO. Evidently, there are advantages and drawbacks for recycling processes based on either pyro- or hydrometallurgy. In general, pyrometallurgical processes are more energy intensive and lead to larger material losses, but the metallic components are easily upgraded to a commercially valuable state. On the other hand, processes based on hydrometallurgy can recover materials with chemical characteristics suitable for LIB manufacturing, thus “closing the loop” in a more efficient manner. However, hydrometallurgical processes are bound to mechanical processing operations in order to liberate the valuable elements confined in the LIBs. In addition, hydrometallurgical operations require vast amounts of reagents and strictly controlled chemical environments to perform dilution or precipitation of the target materials. In summary, the technologies presented in Table 2 suggest that processes with a higher degree of complexity are necessary to close the materials cycle for all components of LIBs.
From a CE perspective, the preferred processes should entail multiple layers of closed material loops using the fewest possible external inputs to obtain, for instance, cathode precursors. As described in previous sections, both emerging and state-of-the-art processes achieve to some extent the aims of CE for LIBs, bringing valuable materials back into the economic cycle. However, the recovery of materials is only one aspect of the CE. In a closed loop process, resource inputs should also be minimized. Emerging processes require the consumption of additional reagents to achieve the target recoveries. The internal loops in the Battery Resources and LithoRec processes support reduced consumption of external resources for the pyrometallurgical refining process for cathode precursors, e.g., Li2CO3. In addition, the OnTo process reports the possibility of recovering battery components suitable for LIB manufacturing [100,101,102].
Even though emerging processes appear to be closer to the ideal of circular economy, they are not without their drawbacks. For instance, they are mostly focused on one type of battery chemistry, reducing the flexibility of the feed compared to SoA technologies. Some of these technologies require chemical reagents considered hazardous, e.g., the bromoform used in the OnTo process to separate anode and cathode during dense media separation has been associated with kidney and liver injuries [109]. Evidently, there is still room for improvement. For example, the Accurec and LithoRec processes do not recover electrolyte, while the available information on the Battery Resources process does not mention electrolyte recovery whatsoever. The OnTo process is unique in this sense as it allegedly recovers the electrolyte components, i.e., solvent and Li salt [51,100,110]. It has been expressed that the OnTo process is able to recover about 80% of the LIB components, making it an attractive possibility for development at the industrial scale [99]. Interestingly, during a test conducted by Rothermel et al. [111] graphite recovered from the OnTo process outperformed new synthetic graphite in discharge capacity, although it presented a lower discharge capacity compared with non-synthetic graphite. This drawback was attributed to the environment used during the extraction of electrolyte with supercritical CO2, as it may have damaged the crystalline structure of the graphite [111]. As the emerging processes are still in early stages of development, additional risks may become evident during the scale-up phase [27,29,65,73].
4.2. Recovery of Materials
4.2.1. Cathode Active Material
The cathode active powder is the main target of most of emerging recycling processes because of its high economic value, particularly in formulations containing Co [58,70]. Indeed, Co-containing cathode chemistries (LiCoO2, LiNixMnyCozO2) have a relatively higher cost than other commercial cathode materials (LiMn2O4, LiNiO2, LiFePO4).
The recovery of cathodes is, however, a complicated process. As discussed in previous sections, it requires a vast number of preparation and enrichment stages before undergoing final hydrometallurgical refining. Proper purification of the EoL cathode material is crucial because of its high chemical sensibility, where minor contaminants may compromise the quality of the final product. For example, a concentration of Cu above 1.8% slows down the cathode capacity retention compared to pristine chemistries of LiNixMnyCozO2 [86,92], while Al in a concentration higher than 0.6% decreases the capacity from 6–14% within the first 500 cycles [96]. (A cycle is herein defined as the process of full charge and discharge of a battery.) Nevertheless, a concentration up to 0.3% of Al in the recycled cathode material does not result in a significant difference on the cell capacity compared to pristine material [84]. Moreover, the chemical sensibility of the hydrometallurgical steps is affected by the composition of the throughput. For example, during Ni precipitation processes Cu traces are co-precipitated, effectively resulting in Ni losses [85]. Nevertheless, the detrimental effect of impurities should be further researched in order to define tolerable concentrations. It is possible that the materials currently considered impurities could be turned into useful components at the right concentrations. This would make the recycling processes more flexible and, therefore, more suitable for industrial-scale operations. Table 3 presents a summary of the processes from a cathode recovery perspective.

Table 3.
Cathode material recovery summary of the recycling processes.
On the other hand, efforts to recycle LiFePO4 and LiMn2O4 cathode chemistries have been limited, mainly due to their relative lower commercial value [67,112]. However, these chemistries cover a larger share of the energy demand in the market, with LiFePO4 and LiMn2O4 representing 22% and 15%, respectively. In comparison, Co-containing chemistries represent only 10% of the market [9]. In addition, between the years 2008 to 2014, the market share for these cathode chemistries increased from 4 to 9% for LiFePO4 and 11 to 16% for LiMn2O4, while the share for LiCoO2 was reduced from 61% to 40% in the same period [15].
The emerging technologies Battery Resources, LithoRec, and OnTo are, however, capable of processing these upcoming chemistries. Although the Battery Resources process is mainly focused on Co-containing chemistries, it is claimed that it is able accept other chemistries. The Onto and LithoRec processes accept LiFePO4 and LiNixMnyCozO2 chemistries, respectively. The Battery Resources and LithoRec processes are of special interest from the circular economy perspective as they include an internal loop, where previously recovered materials (i.e., Li, Mn, Ni oxides, Li2CO3) are consumed in the final pyrometallurgical stages [84,105]. In both of these processes, the final product, i.e., cathode precursor of pristine quality, is obtained with marginal amounts of additional reagents. Such internal loops may require more complex process control strategies and additional energy for operation. On the other hand, the OnTo process is the only one to address direct use of the cathode material after re-lithiation [98]. The Aalto University process, on the other hand, does not obtain a cathode quality material, rather producing precursors containing Co and Li in solution.
Finally, an economic–energetic analysis conducted by Reference [113] revealed that the process of manufacturing of these cathode chemistries from either primary or secondary sources would surpass economic feasibility. Hence, until the economic panorama changes for LiFePO4 and LiMn2O4, these chemistries will remain secondary priorities for the recycling industry.
4.2.2. Lithium Recovery
Elemental Li is currently not a primary driver for LIB recycling, being mainly recovered as part of the cathode active materials. Other forms of Li (e.g., in electrolyte) are generally lost. Being present in at least two different compounds, the recovery of this element is complicated and not pursued by SoA recycling processes. In addition, Li is not considered to be a critical element by the EU [114,115,116], and the global reserves of this metal are deemed sufficient [117]. Li recovery is, thus, in a disadvantageous position compared to other LIB components. However, the losses of Li into waste contribute to unnecessary mining operations. Additionally, the importance of this metal may increase moving forward, and its recyclability may be justified by the increasing demand for LIBs [9,18,45,110,118].
As previously mentioned, Li recovery as part of the cathode is chemically demanding and requires carefully controlled environments. Thus, efficient Li recovery methods should be developed [84], or a replacement material found that is easier to recycle. Further complications come in the form of stability of the hydrometallurgical process feed, where Li precipitation is usually the final stage and therefore is highly dependent on the separation efficiency of previous stages. Table 4 summarizes the recycling processes from a lithium recovery standpoint, including recovery method, process efficiency, quality, and potential use of recovery.

Table 4.
Lithium recovery summary of the recycling processes.
As seen in Table 4, the efficiency of the processes varies from 76% to 95% of Li being recovered, reflecting processes with a potentially positive economic impact [17,85,91]. It has been proposed that Li recovery could lead to different possible uses after enrichment, ranging from ceramics and glass to cathode precursors, depending on its purity. Clearly, the quality of recovered Li salt from the emerging processes can be considered suitable for LIB industry and, thus, using them as glassware raw material would be a downgrade of the original material. Indeed, Accurec reports a 99% purity of Li recovery, while Battery Resources reports a “high purity” product. The Li2CO3 obtained in the Accurec and Battery Resources recoveries can also be used during Al production as an electrolyte additive [117]. However, the recovery process for Li compounds is a delicate process; for instance, as Li2CO3 cannot be precipitated from aqueous solutions, it is easily lost as a by-product [84]. In the Aalto University process, a high recovery of Li can be achieved (up to 93%), although in a highly diluted form. Since the recovery of Li–Ni in solution is, in fact, one of the last hydrometallurgical stages, there can be a high accumulation of liquid solvents. In addition, the extractant may not be highly efficient at separating Li from the cathode, thus requiring large quantities to effectively separate this compound into its elements.
Accurec, Battery Resources, and LithoRec mention active cathode powder manufacturing as the intended use for Li salts, although Accurec also mentions flask production as an alternative option. The OnTo technology recommends its Li compounds for battery production, among other unspecified uses. As the purity requirement for Li2CO3 to be reused in cathode production is 99.5% [119], it is likely that the only process able to achieve such quality will involve blending it with virgin materials. This strategy is already followed in some emerging processes. However, the purity requirements may rise up to 99.9% [119], in which case downgrading may be the most suitable afterlife for this element. In fact, Li could be used in the glass and ceramic industries, which represent a market share for Li2CO3 of similar size (32%) to batteries (35%) [117]. Other possible uses for Li salts could be as an electrolyte additive during Al production and metal casting [117].
4.2.3. Metals Recovery
The recovery of metals is the major driver for the SoA LIB recycling processes, and remains essential in the emerging processes. In emerging technologies, the extraction of metals entails collateral benefits, as Cu, Al, and Fe act as impurities in the hydrometallurgical cathode recovery process. Table 5 summarizes the recycling processes from a metal enrichment perspective.

Table 5.
Metal recovery summary of the recycling processes.
Those processes relying on pyrometallurgy as main recycling step present losses of metals in addition to the electrode components. However, the metallic fractions (mostly present in the form of foils) may be recovered by mechanical processing steps during pre-treatment [120]. This shows again that recycling processes employing a more thorough pre-processing may indeed recover the majority of the LIB components.
As see in Table 5, most of the processes recover Fe and Cu through mechanical processing operations, e.g., Retriev Technologies employing shaking tables, or the recovery of Fe in the Battery Resources process using magnetic separation. Those processes overlooking pre-concentration report further losses, i.e., Al is lost as slag in the Umicore and Sumitomo–Sony processes. Retriev employs shaking tables for metal separation, which is a reasonable choice as the intended application of products is in metals manufacturing, and materials of superior quality are not required. The two-step comminution process used by Recupyl and Akkuser seems to be associated with safe and controlled processing of the active cells. Even though the comminution parameters in the Akkuser process were not discussed in relation to separation efficiency, it is notable that a cutting mill was specifically chosen out of all available comminution options. Thus, there is some indication that cutting stress is associated with good separation results. In the Recupyl process, particular attention is paid to comminution due to the presence of primary Li cells. In the LithoRec, a two-step comminution under mild cutting stress was chosen for improved separation efficiency.
In the LithoRec and OnTo processes, metallic components such as Cu can be separated by sieving, as they report to specific particle size fractions after shredding [50,111]. However, shredding also delivers fine particles of which recovery may only be possible through leaching during the electrode purification stage, as in the OnTo process. The Accurec process uses an air separator followed by magnetic separation to promote the separation of Fe from the Al and Cu phases. Originally, LithoRec claimed to be able to separate steel without magnetic separation, although this step was added to the process in a follow-up project [50,111]. Detailed information about the exact methods OnTo implements for casing and foil separation was unavailable, but different types of density-based methods are mentioned as suggestions. The Aalto University process, on the other hand, relies on sieving followed by a rotary kiln to recover Al and Cu in alloy form.
As can be seen, casing and foil materials can be recovered by physical means, although they may require further processing to become raw materials suitable for LIB manufacturing. In addition, precipitation may be necessary during the hydrometallurgical steps for cathode recovery in order to further remove finer metallic fractions.
4.2.4. Graphite Recovery
Even though graphite is presently not of major interest for the battery recycling industry [92], promoting its reinsertion into the economic cycle is a valid concern from the CE perspective, as it will decrease the exploitation of mineral deposits and their associated environmental impact. Table 6 present a summary of the recycling processes based on their corresponding graphite recovery abilities.

Table 6.
Graphite recovery summary in emerging processes.
As shown in Table 6, details related to graphite recovery are scarce. It is also necessary to emphasize that, in most cases, the real recovery of graphite remains uncertain. Indeed, graphite is extracted from the feed but the subsequent phases are not typically discussed. In processes that use pyrometallurgical methods, like the Umicore, Sony, Accurec, and Aalto University processes, graphite is used as energy source and reducing agent. Retriev technologies recover graphite in an elemental form in a MeO filter cake. The Akkuser process seems to recover graphite as part of the black mass containing cathode material. In Recupyl and LithoRec, graphite is removed from the solution at the beginning of the leaching step. However, it is mentioned that utilizing such recovered graphite is not feasible at the moment [92], even though it has been proven technically possible to produce battery-grade graphite via subcritical CO2 cleaning combined with thermal treatment [112]. Battery Resources and OnTo state that they recover graphite, but the details of the exact method have not been provided. Nevertheless, the electrolyte recovery step with supercritical CO2 is capable of removing reactive functional groups from the graphite surface [51,111]. Monadi et al. [121] stated that to separate graphite by hydrometallurgical methods, the anode has to be treated separately from the cathode, pointing out the need for pre-separation of graphite.
As seen, OnTo is the only process in Table 6 that explicitly recovers graphite for LIB anode manufacturing using CO2 in supercritical conditions followed by thermal treatment [51]. The anode recovered from the OnTo process has the same physical characteristics (i.e., grain size and morphology) as pristine graphite [97]. However, the OnTo process is particularly complicated, since it requires pH control for the different components embedded in the cathode and anode. The Accurec process explicitly mentions the use of graphite as a reduction agent during the pyrometallurgical process. The Battery Resources and LithoRec processes are able to extract graphite as a by-product during their leaching processes, but they do not mention any particular use for the anode after extraction [92].
Compared to the cathode and metallic components, graphite production constitutes a small share of the total energy consumption of the cell materials during their life cycle [105]. Even though there is proof of the potential use of recycled graphite, further economic studies may be needed to demonstrate their feasibility [111].
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
This review offers a critical analysis of emerging and SoA recycling processes for LIBs, focusing on their potential to contribute to CE. It discussed emerging processes that are more in line with the concept of CE, as they recover a larger variety of components and aim to reduce the waste streams or repurpose the generated by-products. The OnTo process is of particular interest, as it recovers cathode and anode material from spent LIBs to a point where they can be reused directly for LIB manufacturing. Similar processes, like Battery Resources, LithoRec, and Accurec, obtain similar products in line with the CE concept. However, their processes still have flaws, i.e., losses in the form of non-recovered anode material. In addition, the Aalto University process presents a recovery of the vast majority of the LIB compounds; however, the recovered forms still require further processing to be considered usable raw materials. Contrastingly, the SoA technologies result in significant material losses, e.g., electrolyte, graphite, Cu, Ni, Li, etc.
Furthermore, the importance of developing processes that rely on fewer external inputs and lower waste generation was addressed. For instance, the LithoRec process reports a single battery type in the feed, leachant and multiple reagents as part of its regular operation, and output streams of cathode material, metallic fraction, electrolyte, and volatile material, which may be used again for LIB production. In comparison, the OnTo process requires multiple inputs (i.e., bromoform, CO2, and Li compounds) to recover suitable anode and cathode mixed materials, while also producing mixed waste containing electrolyte, C, and organic material. Thus, an ideal recycling process with a true attachment to the CE concept obtains materials in the same chemical form as those found in the products with a minimum input of external resources and negligible waste streams. From this perspective, the OnTo process may be the technology with a closest attachment to the goals of CE, from the alternatives studied in this review. In other emerging technologies, the recycling products require further chemical transformations before their use in the manufacturing of LIBs is possible. Although these processes still aim to fulfil the ideals of CE, additional processing is inevitably associated with the consumption of additional resources and generation of waste.
Further research on the subject of processing diluted mixtures and the correlation between feed and product quality is therefore advisable. Different authors have approached this challenge by proposing and discussing the use of process simulators, e.g., HSC Sim® (Outotec, Pori, Finland), Aspen Plus® (Hyprotech, Calgary, AB, Canada), Chemcad® (Chemstations, Smithfield, NC, USA), etc., to evaluate the costs of these complex physical and chemical transformations [122,123,124,125]. This type of metallurgical process analysis surpasses the capacity of traditional and expensive in situ testing through the calculation of thermodynamic and engineering parameters such as:
- Energy cost calculations,
- Plant efficiency.
Moreover, References [32,44] used process simulation to obtain a systemic assessment based on statistical entropy and material flow analysis. Such approaches describe recycling processes based on the material concentrating efficiency of a system, where the material losses (dilutions) have a measurable impact on the final entropic value. This use of process simulation tools, sometimes referred to as the “digitalization of circular economy”, is a necessity in systems with intricate materials such as LIBs, in order to objectively evaluate their impact on the circular economy.
Furthermore, the diversity of cathode chemistries presents an additional challenge, since they may require diverse conditions for an efficient recycling process. Thus, treating them simultaneously may increase the required resources (e.g., energy and time consumed by a sorting mechanism) or may have a negative impact on the quality of recovered components (e.g., incompatibilities among cathode chemistries or processing conditions). Current developments in battery chemistry may also introduce additional elements in the future. As countermeasure for these drawbacks, it is worth exploring the concentration limits for impurities in secondary raw materials. On the other hand, consensus between battery manufacturers as to the use of a standardized LIB labeling system (e.g., based on the cathode chemistry) might allow automatic sorting operations. In this way, resources would be better used to obtain a suitable feed for efficient processing. This review thus intended also to offer a starting point for serious discussion on the need to design batteries while taking into consideration the technical challenges currently present in recycling processes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S.-G., A.S.-A.; methodology, J.V., A.S.-A.; formal analysis, J.V., O.V.-M.; investigation, J.V., O.V.-M.; data curation, J.V.; writing—original draft preparation, O.V.-M.; writing—review and editing, O.V.-M., R.S.-G., J.V., A.S.-A.; visualization, O.V.M.; supervision, M.R., R.S.-G., A.S.-A.
Funding
This research was funded by the METYK-project (grant number 3254/31/2015), funded by Finnish innovation agency (TEKES), as well as the “Closing the loop for high-added value materials (CloseLoop)” project (grant number 303454) supported by the Academy of Finland.
Acknowledgments
O.V.M. thanks the National Council of Science and Technology (CONACYT) of Mexico for a Doctoral studies scholarship.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tarascon, J.M.; Armand, M. Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 2001, 414, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linden, D.; Reddy, B.T. (Eds.) Linden’s Handbook of Batteries, 4th ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Aditya, J.P.; Ferdowsi, M. Comparison of NiMH and Li-ion batteries in automotive applications. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Harbin, China, 3–5 September 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hameer, S.; Van Niekerk, J.L. A review of large-scale electrical energy storage. Int. J. Energy Res. 2015, 39, 1179–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EBRA. 2012: Noticeable Growth of the Quantity of Batteries Recycled; European Battery Recycling Association: Brussels, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- EUR-Lex. Directive 2006/66/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 6 September 2006 on batteries and accumulators and waste batteries and accumulators and repealing Directive 91/157/EEC. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 266, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Report on Critical Raw Materials for the EU; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Roper, L.D. Tesla Model S; Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University: USA, 2019. Available online: http://www.roperld.com/science/TeslaModelS.htm (accessed on 13 June 2019).
- Bernhart, W. The Lithium-Ion Battery Value Chain—Status, Trends and Implications. In Lithium-Ion Batteries; Elsevier: Rome, Italy, 2014; pp. 553–565. [Google Scholar]
- Pillot, C. The Rechargeable Battery Market and Main Trends 2014–2025. In Proceedings of the Advanced Automotive Battery Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 21 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, F. Electric Vehicle Battery Market Analysis: Lithium-Ion. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Modern Approaches in Engineering Science, Tbilisi, Georgia, 21 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pillot, C. The Rechargeable Battery Market 2017–2025. Avicenne Energy 2018, 6, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- HDR. Human Development Reports; United Nations Development Programme: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Earle, S.; Panchuk, K. Physical Geology, 2nd ed.; BC Campus: Victoria, BC, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Heelan, J.; Gratz, E.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Q.; Chen, M.; Apelian, D. Current and Prospective Li-Ion Battery Recycling and Recovery Processes. JOM 2016, 68, 2632–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledung, G. State-of-the-Art in Reuse and Recycling of Lithium-ion Batteries-A Research Review by Hans Eric Melin, Circular Energy Storage; The Swedish Energy Agency: Eskilstuna, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Georgi-Maschler, T.; Friedrich, B.; Weyhe, R.; Heegn, H.; Rutz, M. Development of a recycling process for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2012, 207, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gaustad, G.; Babbitt, C.W.; Richa, K. Economies of scale for future lithium-ion battery recycling infrastructure. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 83, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdas, F.; Titscher, P.; Bognar, N.; Schmuch, R.; Winter, M.; Kwade, A.; Herrmann, C. Exploring the Effect of Increased Energy Density on the Environmental Impacts of Traction Batteries: A Comparison of Energy Optimized Lithium-Ion and Lithium-Sulfur Batteries for Mobility Applications. Energies 2018, 11, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Wallington, T.J.; Arsenault, R.; Bae, C.; Ahn, S.; Lee, J. Cradle-to-Gate Emissions from a Commercial Electric Vehicle Li-Ion Battery: A Comparative Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7715–7722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingsen, L.A.W.; Majeau-Bettez, G.; Singh, B.; Srivastava, A.K.; Valøen, L.O.; Strømman, A.H.; Majeau-Bettez, G. Life Cycle Assessment of a Lithium-Ion Battery Vehicle Pack. J. Ind. Ecol. 2013, 18, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Thomas, H.; Francis, R.W.; Lum, K.R.; Wang, J.; Liang, B. A review of processes and technologies for the recycling of lithium-ion secondary batteries. J. Power Sources 2008, 177, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillot, C. Future Trends in the Rechargeable Battery Market; Avicenne Energy: Montreux, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kivi, J. Battery Recycling, Metal Recovery and Waste Processing State of the Art; Metallialan Ympäristö ja Kiertotalous: Espoo, Finland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.P.; Sun, S.Y.; Song, X.F.; Yu, J.G. Recovery of cathode materials and Al from spent lithium-ion batteries by ultrasonic cleaning. Waste Manag. 2015, 46, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa, A.J.; Matos, J.F.; Bernardes, A.M.; Müller, I.L. Beneficiation of cobalt, copper and aluminum from wasted lithium-ion batteries by mechanical processing. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 145, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, D.C.R.; Bernardes, A.M.; Tenório, J.A.S. An overview on the current processes for the recycling of batteries. J. Power Sources 2004, 135, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissdoerfer, M.; Savaget, P.; Bocken, N.M.; Hultink, E.J. The Circular Economy—A new sustainability paradigm? J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, M.A.; Worrell, E. Handbook of Recycling; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, T.R.; Singh, B.; Strømman, A.H.; Majeau-Bettez, G.; Majeau-Bettez, G. Comparative Environmental Life Cycle Assessment of Conventional and Electric Vehicles. J. Ind. Ecol. 2012, 17, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schalkwyk, R.F.; Reuter, M.; Gutzmer, J.; Stelter, M. Challenges of digitalizing the circular economy: Assessment of the state-of-the-art of metallurgical carrier metal platform for lead and its associated technology elements. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 186, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, O.V.; Boogaart, K.V.D.; Lundström, M.; Santasalo-Aarnio, A.; Reuter, M.; Serna-Guerrero, R. Statistical entropy analysis as tool for circular economy: Proof of concept by optimizing a lithium-ion battery waste sieving system. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 1568–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melin, H.E. The Lithium-Ion Battery End-of-Life Market—A Baseline Study; World Economic Forum: Cologny, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Pistoia, G. (Ed.) Lithium-Ion Batteries Advances and Applications, 1st ed.; Elsevier BV: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardes, A.; Espinosa, D.; Tenório, J.; Bernardes, A.; Espinosa, D.C.R. Recycling of batteries: A review of current processes and technologies. J. Power Sources 2004, 130, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferella, F.; De Michelis, I.; Vegliò, F. Process for the recycling of alkaline and zinc–carbon spent batteries. J. Power Sources 2008, 183, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffino, B.; Zanetti, M.; Marini, P. A mechanical pre-treatment process for the valorization of useful fractions from spent batteries. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez, J.; Gago, E.; Girard, A. Processes and technologies for the recycling and recovery of spent lithium-ion batteries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayilgan, E.; Kukrer, T.; Civelekoglu, G.; Ferella, F.; Akcil, A.; Veglio, F.; Kitis, M. A review of technologies for the recovery of metals from spent alkaline and zinc–carbon batteries. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 97, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzini, A. Manufacturers, Materials and Recycling Technologies. In Lithium-Ion Batteries; Elsevier BV: Rome, Italy, 2014; pp. 529–551. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.; Li, J.; Singh, N. Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Battery: A Critical Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 1129–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, Y. Process for the recovery of cobalt oxalate from spent lithium-ion batteries. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 108, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porvali, A.; Aaltonen, M.; Ojanen, S.; Velazquez-Martinez, O.; Eronen, E.; Liu, F.; Wilson, B.P.; Serna-Guerrero, R.; Lundström, M. Mechanical and hydrometallurgical processes in HCl media for the recycling of valuable metals from Li-ion battery waste. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 142, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, V.; Porvali, A.; Boogaart, V.D.; Aarnio, S.; Lundström, M.; Reuter, M.; Guerrero, S.; Velázquez-Martinez, O.; Boogaart, K.G.V.D.; Santasalo-Aarnio, A.; et al. On the Use of Statistical Entropy Analysis as Assessment Parameter for the Comparison of Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling Processes. Batteries 2019, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, Y. Lithium ion secondary batteries; past 10 years and the future. J. Power Sources 2001, 100, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, N.; Wu, F.; Lee, J.T.; Yushin, G. Li-ion battery materials: Present and future. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahn, J.; Ehrlich, G.M. Lithium-Ion Batteries. In Linden’s Handbook of Batteries, 4th ed.; Reddy, T.B., Ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1–79. [Google Scholar]
- Scrosati, B.; Garche, J. Lithium batteries: Status, prospects and future. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 2419–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomgren, G.E. The Development and Future of Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, A5019–A5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grützke, M.; Mönnighoff, X.; Horsthemke, F.; Kraft, V.; Nowak, S.; Winter, M. Extraction of lithium-ion battery electrolytes with liquid and supercritical carbon dioxide and additional solvents. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 43209–43217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloop, S.E. System and Method for Removing and Electrolyte from Energy Storage and/or Conversion Device Using a Supercritical Fluid. U.S. Patent 7,858,216 B2, 28 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nanografi. PVDF Binder for Li-ion Battery Electrodes. 2018. Available online: https://nanografi.com/blog/pvdf-binder-for-liion-battery-electrodes/ (accessed on 18 June 2019).
- Christmann, P.; Gloaguen, E.; Labbé, J.F.; Melleton, J.; Piantone, P. Global Lithium Resources and Sustainability Issues. In Lithium Process Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Broussely, M.; Biensan, P.; Bonhomme, F.; Blanchard, P.; Herreyre, S.; Nechev, K.; Staniewicz, R. Main aging mechanisms in Li ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2005, 146, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beukering, P.; Kuik, O.; Oosterhuis, F. The Economics of Recycling. In Handbook of Recycling; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 479–489. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, G.; Xu, Z. Environmentally-friendly oxygen-free roasting/wet magnetic separation technology for in situ recycling cobalt, lithium carbonate and graphite from spent LiCoO 2/graphite lithium batteries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 302, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan, D.A.; Masias, A. Batteries for electric and hybrid vehicles. In Linden’s Handbook of Batteries, 4th ed.; Reddy, T.B., Ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 3–48. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2018; Unites States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2018.
- Pagliaro, M.; Meneguzzo, F. Lithium battery reusing and recycling: A circular economy insight. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.B.; James, C.; Gaines, L.; Gallagher, K.; Dai, Q.; Kelly, J.C. Material and Energy Flows in the Production of Cathode and Anode Materials for Lithium Ion Batteries; Argonne National Laboratory: Chicago, IL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wills, B.A.; Finch, J.A.; Wills, B.A.; Finch, J.A. Introduction. In Wills’ Mineral Processing Technology; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kaya, M. Recovery of Metals from Electronic Waste by Physical and Chemical Recycling Processes. Int. J. Chem. Mol. Nucl. Mater. Metall. Eng. 2016, 10, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, W.; Tomas, J. Chapter 24 Liberation of Valuables Embedded in Particle Compounds and Solid Waste. In Handbook of Powder Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 12, pp. 989–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, J.H.; Farmer, T.J.; Herrero-Davila, L.; Sherwood, J. ChemInform Abstract: Circular Economy Design Considerations for Research and Process Development in the Chemical Sciences. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 3914–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, B.A.; Napier-Munn, T. Mineral Processing Technology An Introduction to the Practical Aspects of Ore Treatment and Mineral Recovery, 7th ed.; Elsevier Science & Technology Books: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin, W.; Adams, T.S. Li Reclamation Process. U.S. Patent 5,888,463, 30 March 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Comission for Environmental Cooperation. Environmentally Sound Management of End-of-Life Batteries from Electric-Drive Vehicles in North America; Comission for Environmental Cooperation: Montreal, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, W.; Wang, Z.; Cao, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.H. A Critical Review and Analysis on the Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1504–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retriev Technologies. Lithium-Ion, 2019. Available online: https://www.retrievtech.com/lithiumion (accessed on 19 June 2019).
- Gaines, L.L.; Dunn, J.B. Lithium-Ion Battery Environmental Impacts. In Lithium-Ion Batteries; Elsevier BV: Rome, Italy, 2014; pp. 483–508. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, W.N.; Swoffer, S. Process for Recovering and Regenerating Lithium Cathode Material from Lithium-Ion Batteries. U.S. Patent 8,882,007 B1, 11 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cardarelli, F.; Dube, J. Method for Rrecycling Spent Llithium Metal Polymer Rechargeable Batteries and Related Materials. U.S. Patent 7,192,564 B2, 20 March 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Thyabat, S.; Nakamura, T.; Shibata, E.; Iizuka, A. Adaptation of minerals processing operations for lithium-ion (LiBs) and nickel metal hydride (NiMH) batteries recycling: Critical review. Miner. Eng. 2013, 45, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedjar, F.; Foudraz, J.C. Method for the Mixed Recycling of Lithium-Based Anode Batteries and Cells. U.S. Patent 7,820,317 B2, 26 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pudas, J.; Erkkila, A.; Viljamaa, J. Battery Recycling Method. U.S. Patent 8,979,006 B2, 17 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; He, Y.; Wang, F.; Ge, L.; Zhu, X.; Li, H. Chemical and process mineralogical characterizations of spent lithium-ion batteries: An approach by multi-analytical techniques. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheret, D.; Santen, S. Battery Recycling. U.S. Patent 7,916,9206 B2, 30 January 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Batrec, “Batrec”. Available online: http://www.batrec.ch/en/ (accessed on 20 June 2019).
- Zenger, T.; Krebs, A.; van Deutekom, H.J.H. Method of and Apparatus for Dismantling and Storage of Objects Comprising Alkali Metals, Such as Alkali Metal Containing Batteries. U.S. Patent 7,833,646 B2, 16 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Vadenbo, C.O. Prospective Environmental Assessment of Lithium Recovery in Battery Recycling; Institute of Environmental Decisions: Zurich, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rombach, E.; Friedrich, B. Recycling of Rare Metals. In Handbook of Recycling; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 125–150. [Google Scholar]
- Accurec Recycling GmbH, “Accurec,” 2019. Available online: https://accurec.de/lithium (accessed on 30 October 2019).
- Meshram, P.; Pandey, B.; Mankhand, T. Extraction of lithium from primary and secondary sources by pre-treatment, leaching and separation: A comprehensive review. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 150, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratz, E.; Sa, Q.; Apelian, D.; Wang, Y. A closed loop process for recycling spent lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 262, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Gratz, E.; Apelian, D.; Wang, Y. A novel method to recycle mixed cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, Q.; Gratz, E.; He, M.; Lu, W.; Apelian, D.; Wang, Y. Synthesis of high performance LiNi1/3Mn1/3Co1/3O2 from lithium ion battery recovery stream. J. Power Sources 2015, 282, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, A. A Battery of Success, 2016. Available online: https://www.wpi.edu/news/battery-successes (accessed on 23 August 2019).
- National Science Foundation. SBIR Phase II: A Closed Loop Process for the Recycle of End-of-Life Li-Ion Batteries. 2017. Available online: https://www.nsf.gov/awardsearch/showAward?AWD_ID=1738027&HistoricalAw (accessed on 23 August 2019).
- Battery Resources, “Battery Resources News”. 2019. Available online: https://www.batteryresourcers.com/news (accessed on 23 August 2019).
- Weyhe, R.; Pan, Q. High Energy Lithium Suplhur Cells and Batteries; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2016; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann, J.; Hanisch, C.; Loellhoeffel, T.; Schälicke, G.; Kwade, A. Ecologically Friendly Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries—The LithoRec-Process. ECS Trans. 2016, 73, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekmann, J.; Hanisch, C.; Frob, L.; Sch, G.; Loellhoeffel, T.; Kwade, A. Ecological Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries from Electric Vehicles with Focus on Mechanical Processes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, 6184–6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duesenfeld. 2019. Available online: https://www.duesenfeld.com/recycling_en.html (accessed on 23 August 2019).
- Träger, T.; Friedrich, B.; Weyhe, R. Recovery Concept of Value Metals from Automotive Lithium-Ion Batteries. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2015, 87, 1550–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanisch, C.; Diekmann, J.; Stieger, A.; Haselrieder, W.; Kwade, A. Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries. In Handbook of Clean Energy Systems; Yan, J., Cabeza, L.F., Sioshansi, R., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Krüger, S.; Hanisch, C.; Kwade, A.; Winter, M.; Nowak, S. Effect of impurities caused by a recycling process on the electrochemical performance of Li[Ni0.33Co0.33Mn0.33]O2. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 726, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailey, P.; Kepler, K. Direct Recycling Technology for Plug-In electric Vehicle Lithium-Ion Battery Packs; Farasis Energy Inc.: Hayward, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sloop, S.E. Battery Materials Recycling; OnTo Technology LLC: Bend, OR, USA, 2015; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Gaines, L.; Sullivan, J.; Burnham, A.; Belharouak, I. Life-Cycle Analysis of Production and Recycling of Lithium Ion Batteries. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2011, 2252, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloop, S.E.; Parker, R. System and Method for Processing an End-of-Life or Reduced Performance Energy Storage and/or Conversion Device Using a Supercritical Fluid. U.S. Patent 8,067,107 B2, 29 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sloop, S.E. Reintroduction of Lithium into Recycled Battery Materials. U.S. Patent 8,846,225 B2, 30 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sloop, S.E. Reintroduction of Lithium into Recycled Battery Materials. U.S. Patent 9,287,552 B2, 15 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sloop, S.E. Recycling Positive-Electrode Material of a Lithium-Ion Battery. U.S. Patent 2016/004,3450 A1, 11 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sloop, S.E.; Bend, M.A. Recycling and Reconditioning of Battery Electrode Materials. U.S. Patent 9,484,606 B1, 1 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, J.B.; Gaines, L.; Sullivan, J.; Wang, M.Q. Impact of Recycling on Cradle-to-Gate Energy Consumption and Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Automotive Lithium-Ion Batteries. Environ. Sci. Techol. 2012, 46, 12704–12710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; He, Y.; Ge, L.; Fu, R.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y. Characteristics of wet and dry crushing methods in the recycling process of spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2013, 240, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekberg, C.; Petranikova, M. (Eds.) Lithium Process Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pudas, J. Best Battery Recycling, Dry Technology; Akkuser: Nivala, Finland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Agency for Toxic Substances & Disease Registry. ATSDR, 2015. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/phs/phs.asp?id=711&tid=128 (accessed on 15 August 2019).
- Dunn, J.; Gaines, L.; Barnes, M.; Wang, M.; Sullivan, J. Material and Energy Flows in the Materials Production, Assembly, and End-of-Life Stages of the Automotive Lithium-Ion Battery Life Cycle; Argonne National Laboratory: Chicago, IL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rothermel, S.; Evertz, M.; Kasnatscheew, J.; Qi, X.; Grützke, M.; Winter, M.; Nowak, S.; Kasnascheetw, J. Graphite Recycling from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 3473–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyden, A.; Soo, V.K.; Doolan, M. The Environmental Impacts of Recycling Portable Lithium-Ion Batteries. Procedia CIRP 2016, 48, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.B.; Gaines, L.; Kelly, J.C.; James, C.; Gallagher, K.G. The significance of Li-ion batteries in electric vehicle life-cycle energy and emissions and recycling’s role in its reduction. J. Ind. Ecol. 2015, 19, 518–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Comission. Report on Non-Critical Raw Material Profiles; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Glöser, S.; Espinoza, L.T.; Gandenberger, C.; Faulstich, M. Raw material criticality in the context of classical risk assessment. Resour. Policy 2015, 44, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.; Messagie, M.; Rangaraju, S.; Sanfelix, J.; Rivas, M.H.; Van Mierlo, J. Key issues of lithium-ion batteries—From resource depletion to environmental performance indicators. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 108, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.; Rentsch, L.; Höck, M.; Bertau, M. Lithium market research—Global supply, future demand and price development. Energy Storage Mater. 2017, 6, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, M.A.; Hudson, C.; van Schaik, A.; Heiskanen, K.; Meskers, C.; Hagelüken, C. Metal Recycling: Opportunities, Limits, Infrastructure, A Report of the Working Group on the Global Metal Flows to the Inter- national Resource Panel; United Nations Environmental Programme: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, T.; Luong, V.T. Lithium Production Processes. In Lithium Process Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 81–124. [Google Scholar]
- Hanisch, C.; Haselrieder, W.; Kwade, A. Recovery of Active Materials from Spent Lithium-Ion Electrodes and Electrode Production Rejects. In Glocalized Solutions for Sustainability in Manufacturing; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Moradi, B.; Botte, G.G. Recycling of graphite anodes for the next generation of lithium ion batteries. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2016, 46, 123–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llamas, A.A.; Delgado, A.V.; Capilla, A.V.; Cuadra, C.T.; Hultgren, M.; Peltomäki, M.; Roine, A.; Stelter, M.; Reuter, M. Simulation-based exergy, thermo-economic and environmental footprint analysis of primary copper production. Miner. Eng. 2019, 131, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaux, B.; Hannula, J.; Rudolph, M.; Reuter, M.; Boogaart, K.V.D.; Möckel, R.; Kobylin, P.; Hultgren, M.; Peltomäki, M.; Roine, A.; et al. Water-saving strategies in the mining industry—The potential of mineral processing simulators as a tool for their implementation. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 234, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose-Luis, P.; Abadias, A.; Valero, A.; Valero, A.; Reuter, M. The energy needed to concentrate minerals from common rocks: The case of copper ore. Energy 2019, 181, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, M.A.; Van Schaik, A.; Gutzmer, J.; Bartie, N.; Abadías-Llamas, A. Challenges of the Circular Economy: A Material, Metallurgical, and Product Design Perspective. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2019, 49, 253–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).