Clean Grain Boundary Found in C14/Body-Center-Cubic Multi-Phase Metal Hydride Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy Results
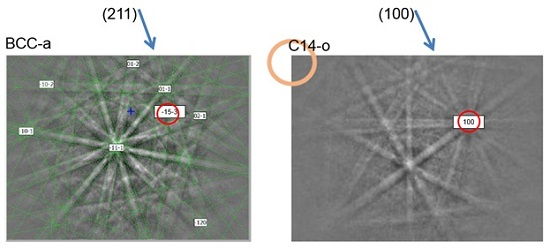
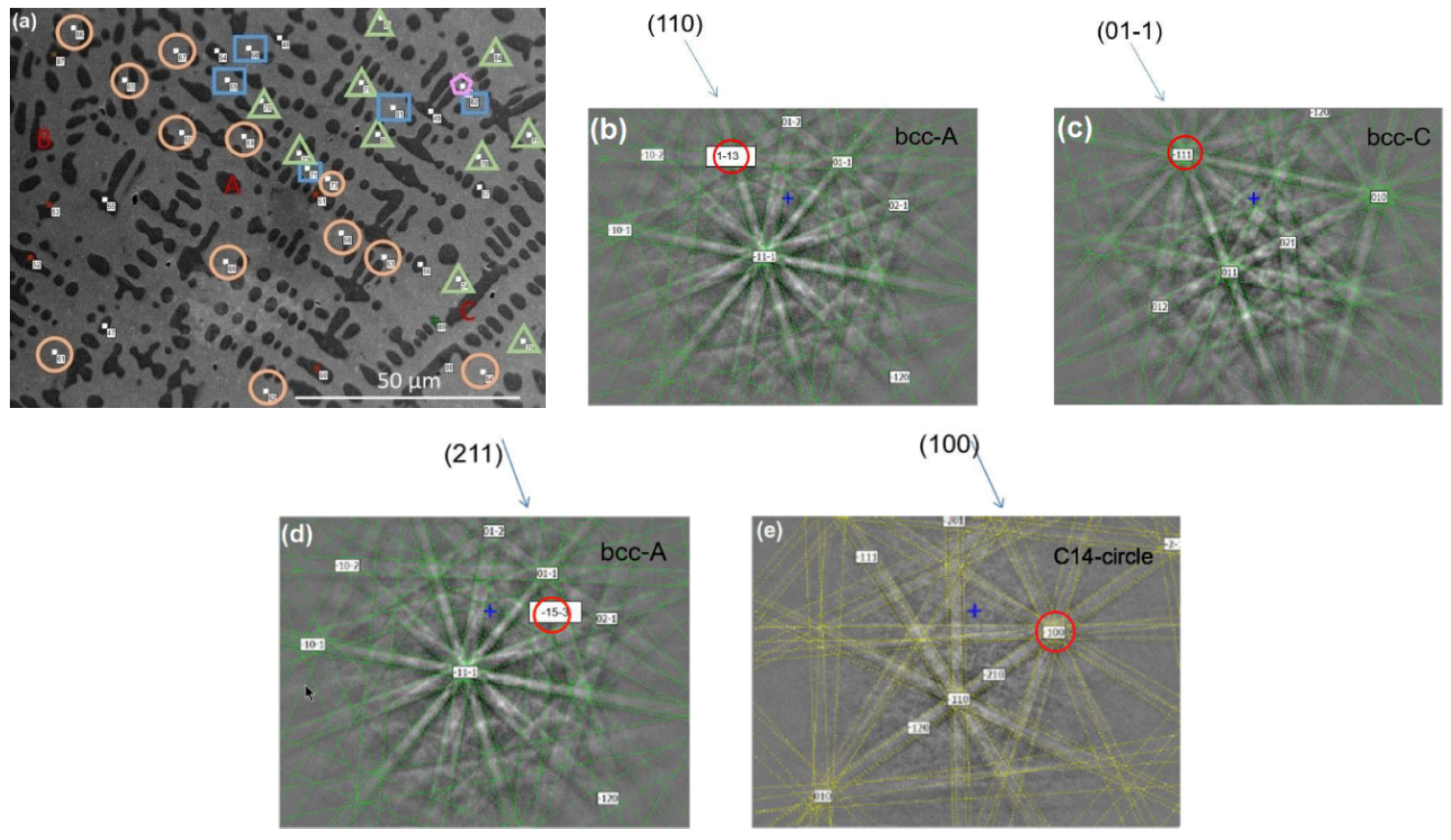
3.2. Electron Backscatter Diffraction Results
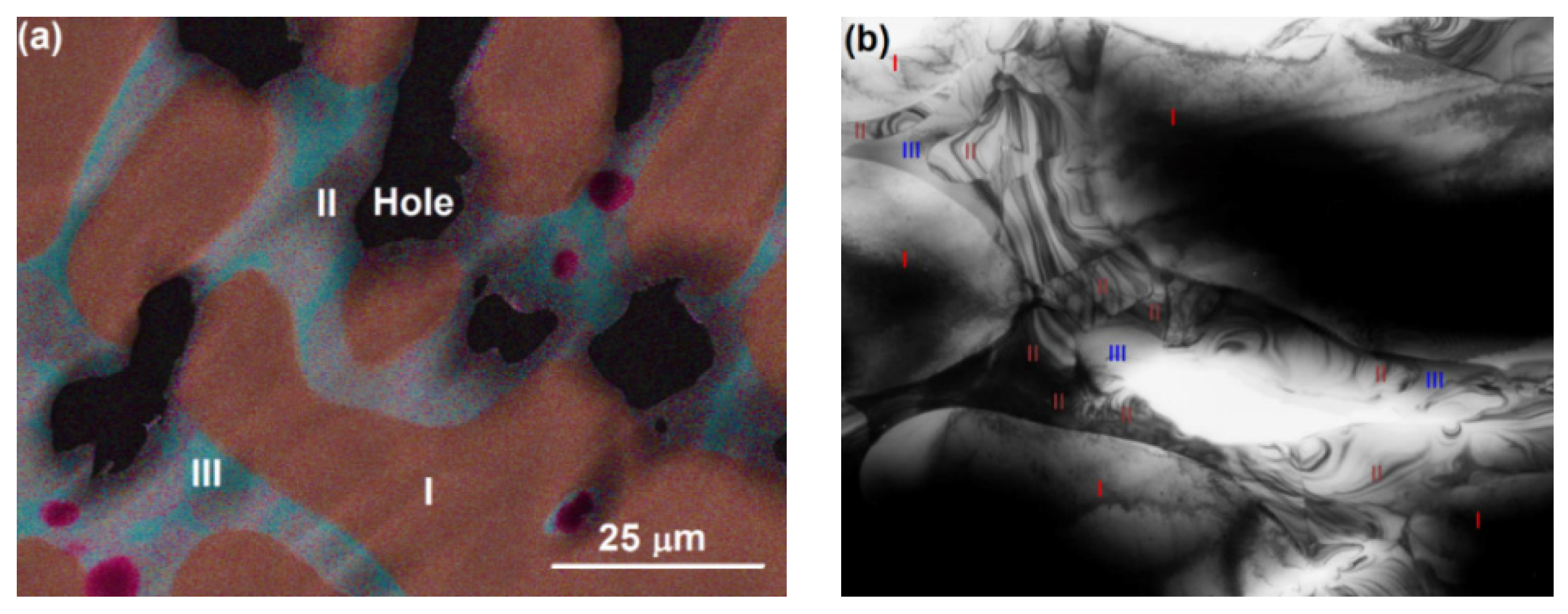
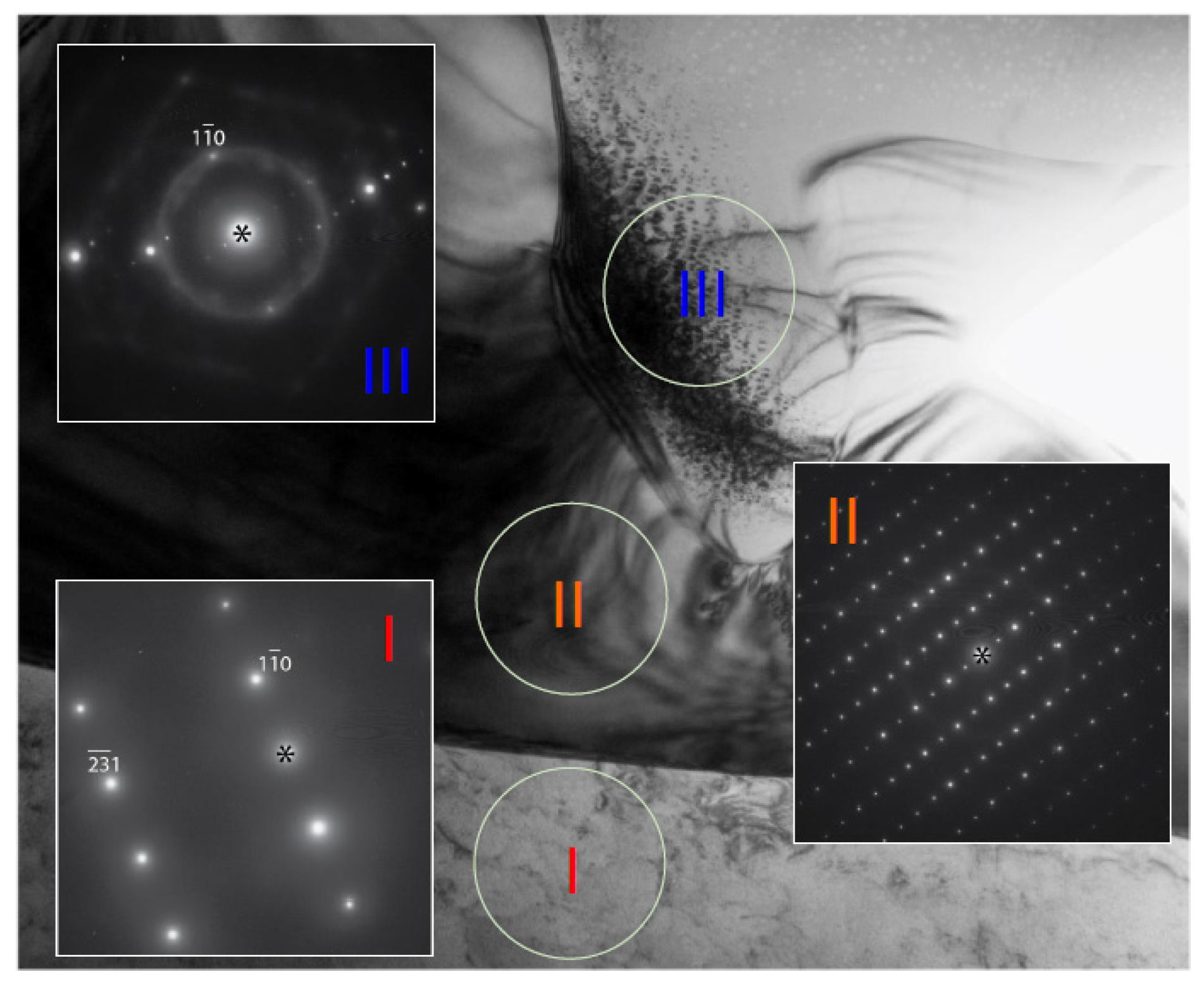
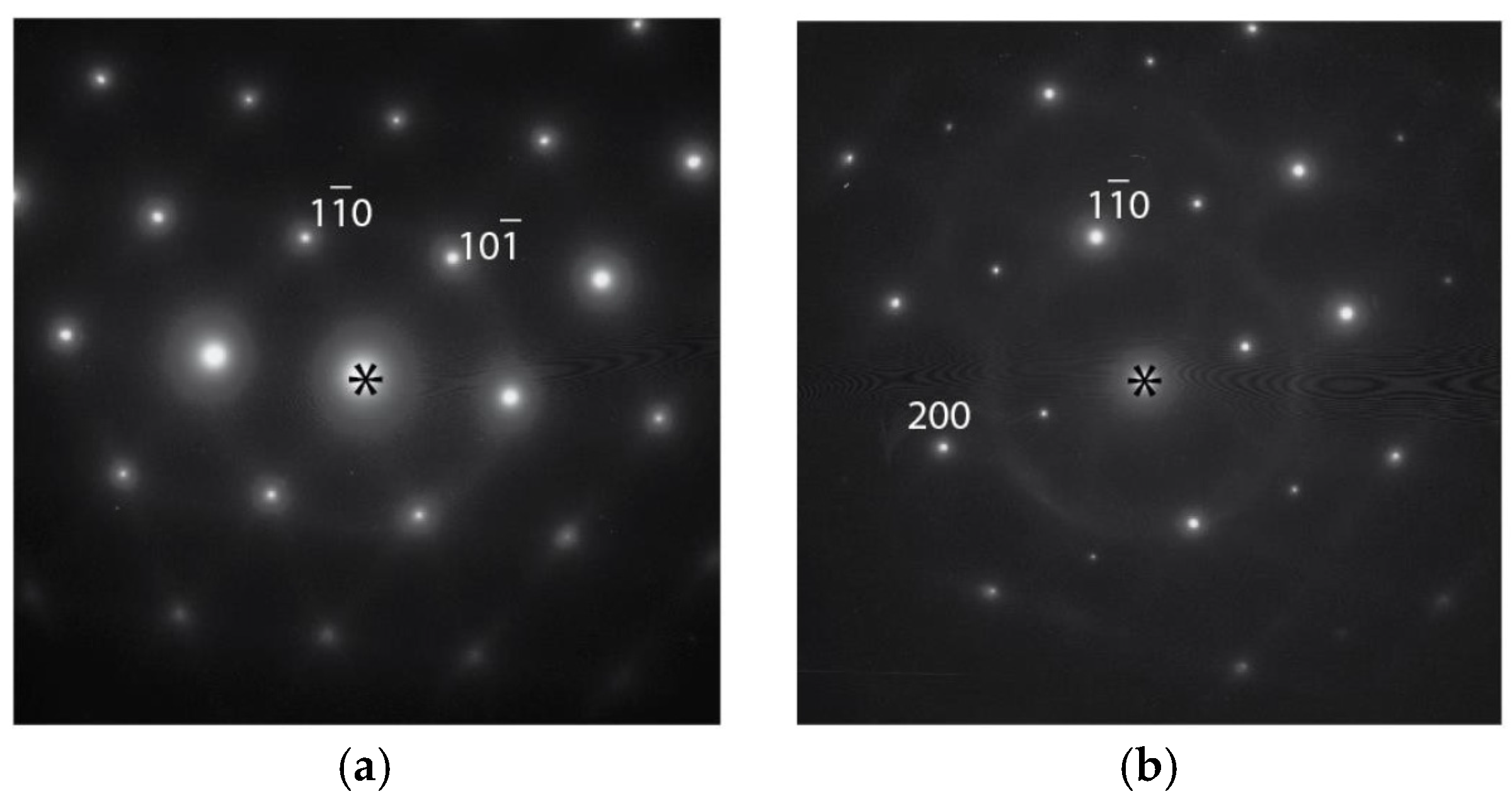
3.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy Results
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| bcc | Body-centered-cubic |
| EBSD | Electron backscattering diffraction |
| MH | Metal hydride |
| Ni/MH | Nickel/metal hydride |
| RANGE | Robust affordable next generation electric vehicles |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| ICP | Inductively coupled plasma |
| PCT | Pressure-concentration-temperature |
| BKD | Backscatter Kikuchi diffraction |
| OIM | Orientation imaging microscopy |
| EDS | Energy dispersive spectroscopy |
| OES | Optical emission spectrometer |
| BSE | Backscattering electron |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| SAED | Selected area electron diffraction |
| fcc | Face-centered cubic |
| D | Diffusion constant |
References
- Young, K.; Ng, K.Y.S.; Bendersky, L. A Technical Report of the Robust Affordable Next Generation Energy Storage System-BASF Program. Batteries 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Nei, J.; Wong, D.F.; Wang, L. Structural, hydrogen storage, and electrochemical properties of Laves phase-related body-centered-cubic solid solution metal hydride alloys. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 21489–21499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.; Arai, S.; Iwakura, C. Crystallographic and electrochemical characterization of TiV4−xNix alloys for nickel-metal hydride batteries. Electrochim. Acta 1996, 41, 937–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.B.; Wu, Z.; Xia, B.J.; Xu, N.X. A Ti-V-based bcc phase alloy for use as metal hydride electrode with high discharge capacity. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 121, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Li, R.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pan, H. Electrochemical hydrogenation and dehydrogenation mechanisms of the Ti-V base multiphase hydrogen storage electrode alloy. Acta Metal. Sin. 2004, 40, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, S.; Chu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, D.; Song, X.; Sun, L. Electrochemical kinetics and its temperature dependence behaviors of Ti0.17Zr0.08V0.35Cr0.10Ni0.30 alloy electrode. J. Alloy. Compd. 2009, 471, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, H.; Akiba, E. The relation between microstructure and hydrogen absorbing property in Laves phase-solid solution multiphase alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 1995, 231, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönnebro, E.; Noréus, D.; Sakai, T.; Tsukahara, M. Structural studies of a new Laves phase alloy (Hf,Ti)(Ni,V)2 and its very stable hydride. J. Alloy. Compd. 1995, 231, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukahara, M.; Takahashi, K.; Mishima, T.; Isomura, A.; Sakai, T. V-based solid solution alloys with Laves phase network: Hydrogen absorption properties and microstructure. J. Alloy. Compd. 1996, 236, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Nei, J.; Wang, L. Annealing effects on Laves phase-related body-centered-cubic solid solution metal hydride alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 654, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettinger, W.J.; Newbury, D.E.; Wang, K.; Bendersky, L.A.; Chiu, C.; Kattner, U.R.; Young, K.; Chao, B. Examination of multiphase (Zr, Ti)(V, Cr, Mn, Ni)2 Ni-MH electrode alloys: Part I. Dendritic solidification structure. Metall. Mater. Trans. 2010, 41A, 2033–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendersky, L.A.; Wang, K.; Boettinger, W.J.; Newbury, D.E.; Young, K.; Chao, B. Examination of multiphase (Zr, Ti)(V, Cr, Mn, Ni)2 Ni-MH electrode alloys: Part II. Solid-state transformation of the interdendric B2 phase. Metall. Mater. Trans. 2010, 41A, 1891–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Young, K. Microstructure investigation on metal hydride alloys by electron backscatter diffraction technique. Batteries 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visintin, A.; Peretti, H.A.; Fruiz, F.; Corso, H.L.; Triaca, W.E. Effect of additional catalytic phases imposed by sintering on the hydrogen absorption behavior of AB2 type Zr-based alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2007, 428, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.F.; Young, K.; Nei, J.; Wang, L.; Ng, K.Y.S. Effects of Nd-addition on the structural, hydrogen storage, and electrochemical properties of C14 metal hydride alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 647, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
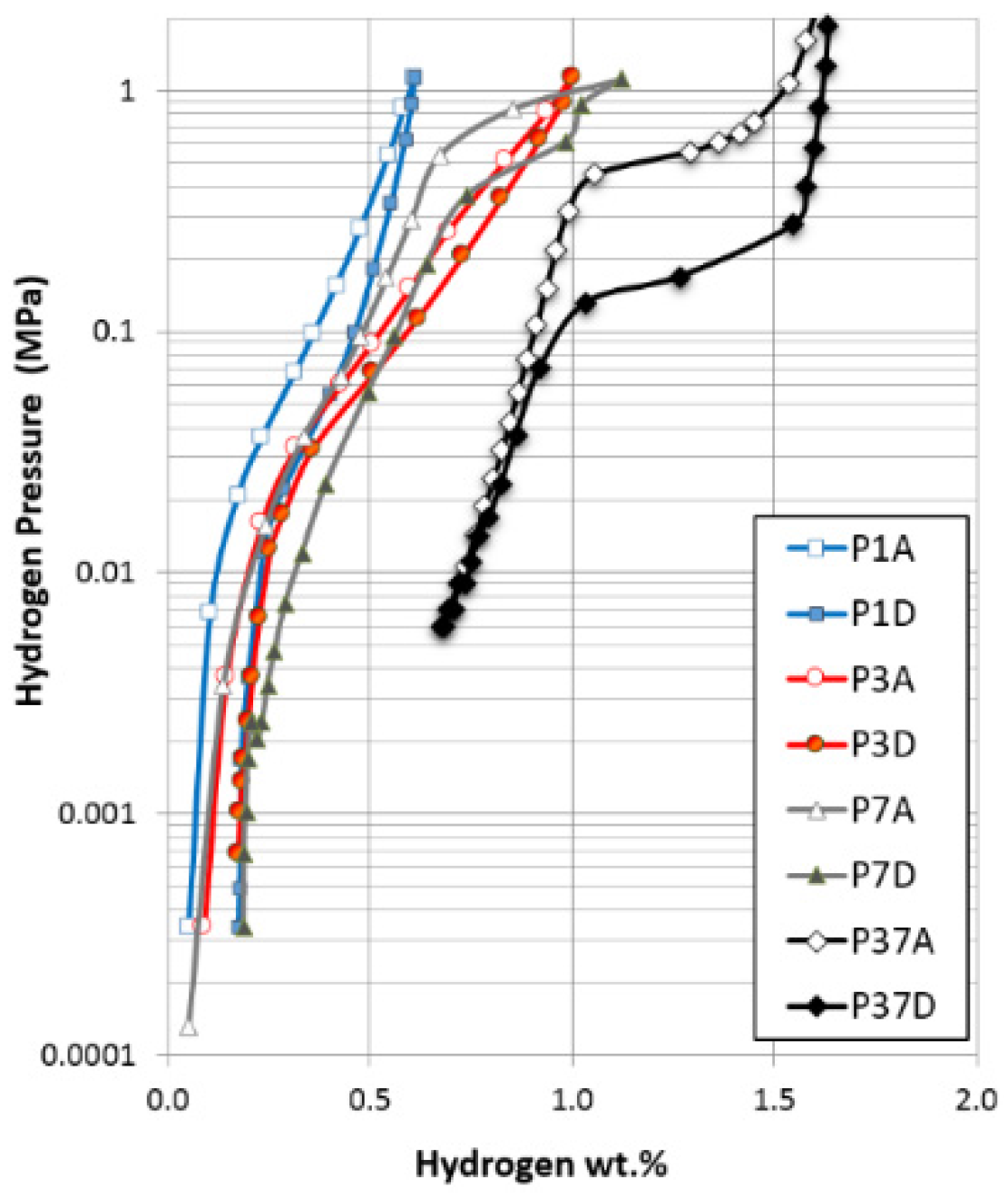
- Mosavati, N.; Young, K.; Meng, T.; Ng, K.Y.S. Electrochemical open-circuit voltage and pressure-concentration-temperature isotherm comparison for metal hydride alloys. Batteries 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Meng, T.; Wong, D.F. Studies on the synergetic effects in multi-phase metal hydride alloys. Batteries 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Wong, D.F.; Wang, L. Effect of Ti/Cr content on the microstructures and hydrogen storage properties of Laves phase-related body-centered-cubic solid solution metal hydride alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 622, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Huang, B.; Nei, J. Structure, hydrogen storage, and electrochemical properties of body-centered-cubic Ti40V30Cr15Mn13X2 alloys (X = B, Si, Mn, Ni, Zr, Nb, Mo, and La). Battereis 2005, 1, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Huang, B.; Nei, J. Effects of Cr, Zr, V, Mn, Fe, and Co to the hydride properties of Laves phase-related body-centered-cubic solid solution alloys. J. Power Sources 2015, 281, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Wong, D.F.; Nei, J. Effects of vanadium/nickel contents in Laves phase-related body-centered-cubic solid solution metal hydride alloys. Batteries 2005, 1, 34–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Xu, F. Effect of La partial substitution for Zr on the structural and electrochemical properties of Ti0.17Zr0.08−xLaxV0.35Cr0.1Ni0.3 (x = 0–0.04) electrode alloys. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 7246–7252. [Google Scholar]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Liu, Y.; Reichman, B.; Mays, W.; Fetcenko, M.A. Structural and electrochemical properties of TixZr7−xNi10. J. Alloy. Compd. 2009, 480, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Nei, J.; Ouchi, T.; Fetcenko, M.A. Phase abundances in AB2 metal hydride alloys and their correlations to various properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 509, 2277–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Huang, B.; Chao, B.; Fetcenko, M.A.; Bendersky, L.A.; Wang, K.; Chiu, C. The correlation of C14/C15 phase abundance and electrochemical properties in the AB2 alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2010, 506, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michal, G.M.; Singlair, R. The structure of TiNi martensite. Acta Crystallogr. 1981, B37, 1803–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Dolan, M.D.; Kellam, M.E.; Liang, D.; Zambelli, S. V-Ni-Ti multi-phase alloy membranes for hydrogen purification. J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 509, 9322–9328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Chao, B.; Nei, J. Microstructures of the activated Si-containing ab2 metal hydride alloy surface by transmission electron microscope. Batteries 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Huang, B.; Regmi, R.K.; Lawes, G.; Liu, Y. Comparisons of metallic clusters imbedded in the surface oxide of AB2, AB5, and A2B7 alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2010, 506, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.; Chang, S.; Young, K.; Nei, J. Hydrogen storage properties of ZrVxNi3.5−x (x = 0.0–0.9) metal hydride alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2013, 580, S171–S174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Young, M.; Chang, S.; Huang, B. Synergetic effects in electrochemical properties of ZrVxNi4.5−x (x = 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, and 0.5) metal hydride alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2013, 560, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Alloy | Ti | Zr | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 (design) | 14.7 | 13.8 | 20.0 | 6.0 | 12.6 | 1.2 | 2.6 | 28.5 | 0.6 |
| P1 (ICP) | 15.1 | 13.9 | 20.2 | 3.8 | 12.8 | 1.3 | 2.7 | 29.5 | 0.7 |
| P3 (design) | 14.3 | 8.9 | 30.1 | 9.0 | 10.2 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 23.1 | 0.5 |
| P3 (ICP) | 14.7 | 8.8 | 31.0 | 7.5 | 9.8 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 23.7 | 0.5 |
| P7 (design) | 13.7 | 3.1 | 42.0 | 12.6 | 7.4 | 2.6 | 1.5 | 16.8 | 0.3 |
| P7 (ICP) | 14.2 | 3.0 | 41.3 | 12.1 | 7.0 | 2.7 | 1.6 | 17.6 | 0.5 |
| P37 (design) | 14.5 | 1.7 | 46.6 | 11.9 | 6.5 | - | 1.5 | 16.9 | 0.4 |
| Phase | Structure | Ti | Zr | V | Cr | Mn | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P3 Phase I | bcc | 4 | <1 | 58 | 16 | 11 | 4 |
| P3 Phase II | C14 | 19 | 12 | 19 | 4 | 10 | 31 |
| P7 Phase I | bcc | 6 | <1 | 60 | 19 | 8 | 6 |
| P7 Phase II | C14 | 22 | 8 | 20 | 5 | 6 | 32 |
| P7 Phase III | B2 | 37 | 3 | 8 | <1 | 3 | 43 |
| Area | Ti | Zr | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Al | B/A | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 5.8 | 0.0 | 59.4 | 18.3 | 7.4 | 2.8 | 1.1 | 5.0 | 0.5 | 16 | bcc |
| II | 23.1 | 8.3 | 20.0 | 4.3 | 7.3 | 3.6 | 2.8 | 30.0 | 0.9 | 2.2 | C14 |
| III | 35.5 | 3.3 | 9.0 | 1.2 | 3.2 | 1.8 | 2.8 | 42.3 | 0.7 | 1.1 | B2 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, H.-T.; Young, K.-H.; Meng, T.; Bendersky, L.A. Clean Grain Boundary Found in C14/Body-Center-Cubic Multi-Phase Metal Hydride Alloys. Batteries 2016, 2, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries2030022
Shen H-T, Young K-H, Meng T, Bendersky LA. Clean Grain Boundary Found in C14/Body-Center-Cubic Multi-Phase Metal Hydride Alloys. Batteries. 2016; 2(3):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries2030022
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Hao-Ting, Kwo-Hsiung Young, Tiejun Meng, and Leonid A. Bendersky. 2016. "Clean Grain Boundary Found in C14/Body-Center-Cubic Multi-Phase Metal Hydride Alloys" Batteries 2, no. 3: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries2030022
APA StyleShen, H.-T., Young, K.-H., Meng, T., & Bendersky, L. A. (2016). Clean Grain Boundary Found in C14/Body-Center-Cubic Multi-Phase Metal Hydride Alloys. Batteries, 2(3), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries2030022