Sustainable Recovery of Critical Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Deep Eutectic Solvents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instrumentation and Analysis Methods
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Preparation for DES
2.3.2. Leaching Process
3. Results and Discussion
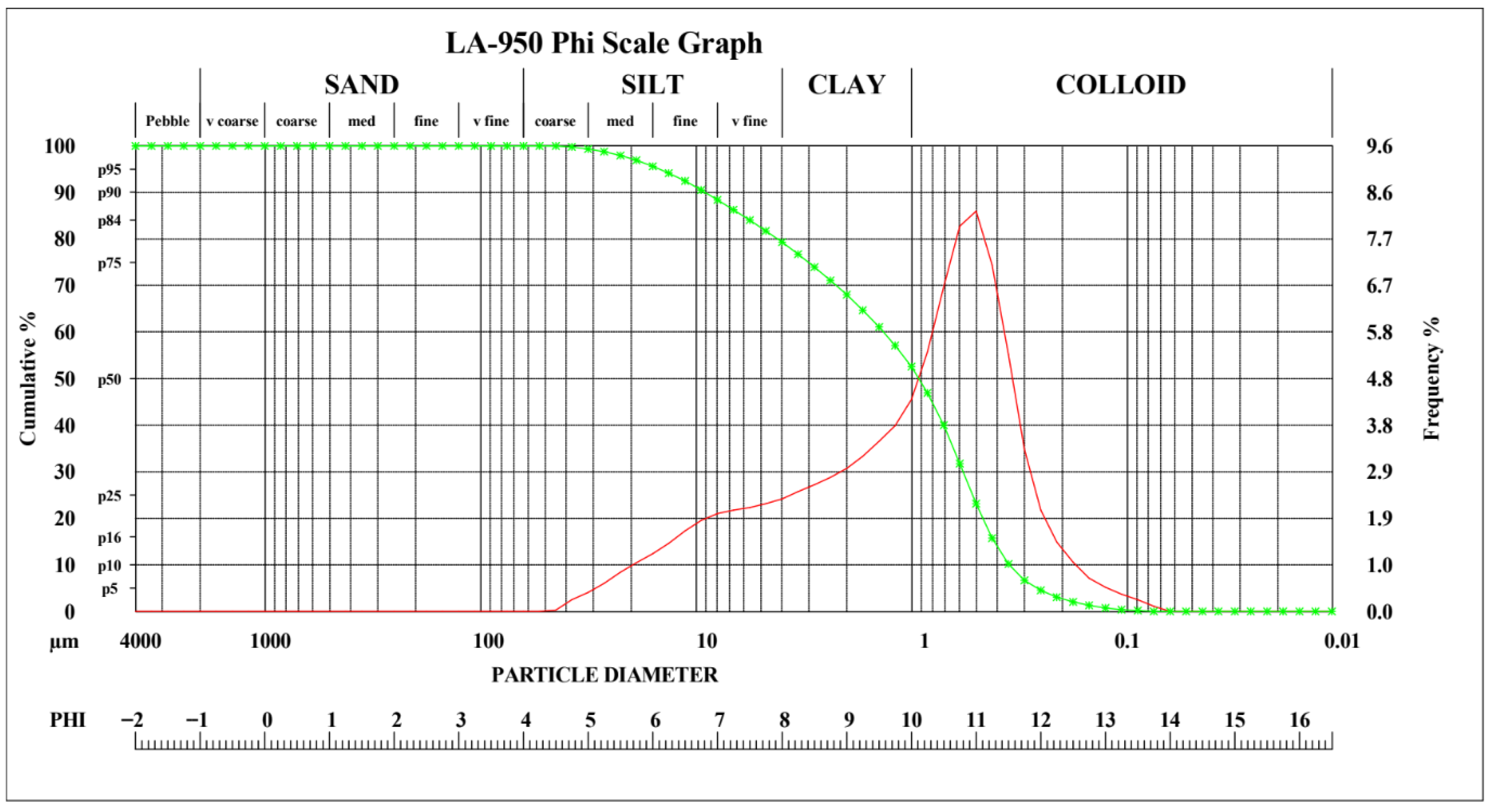
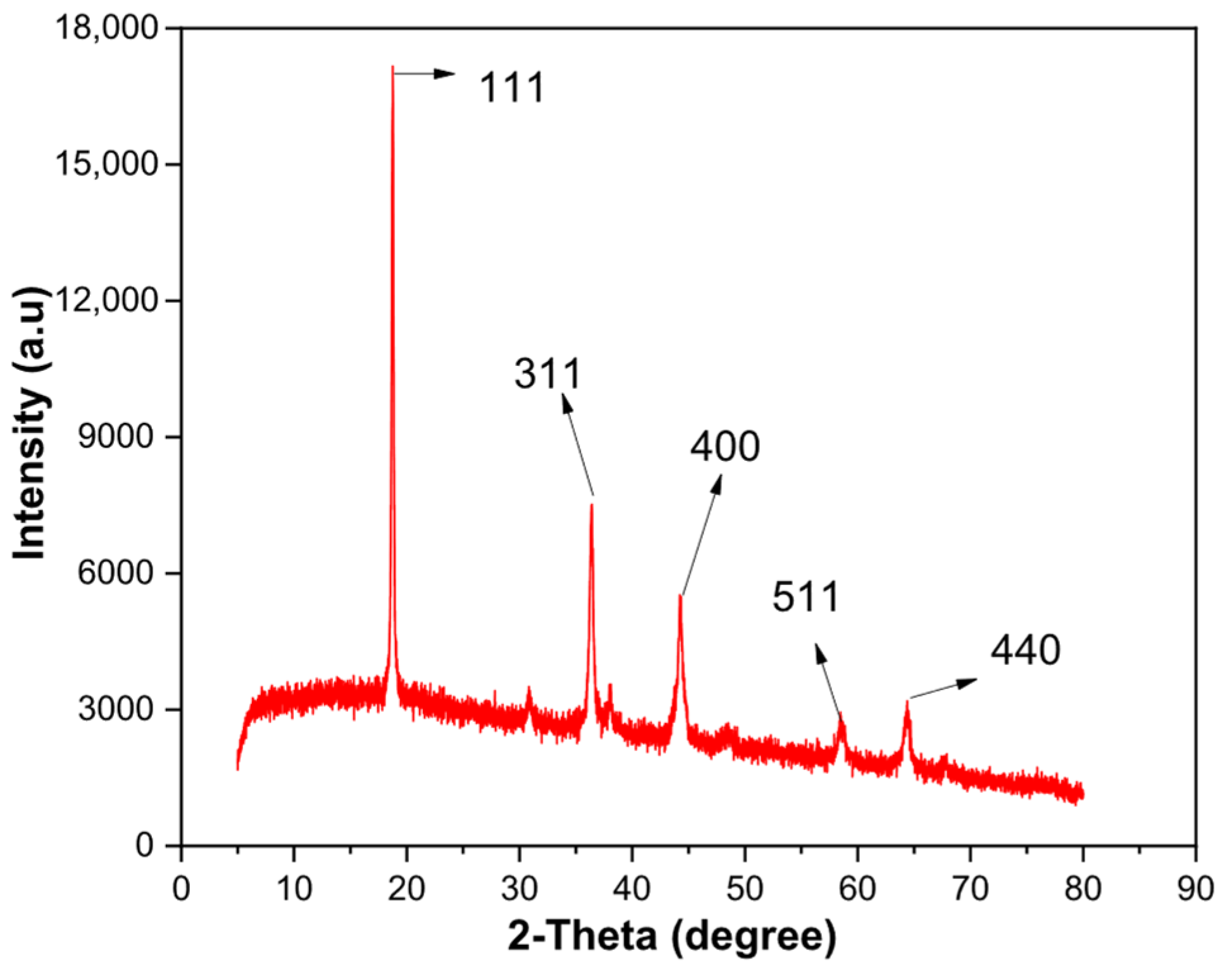
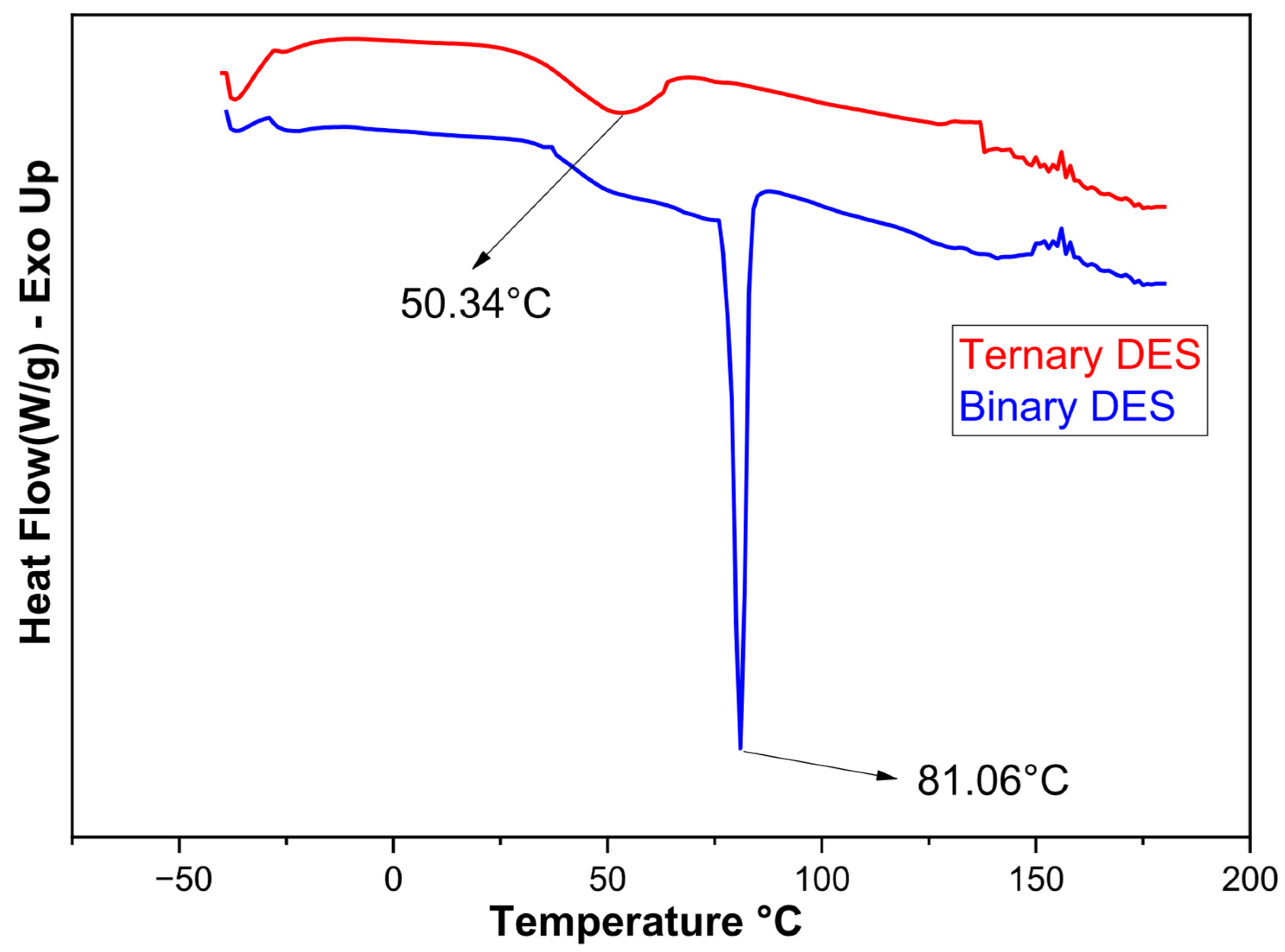
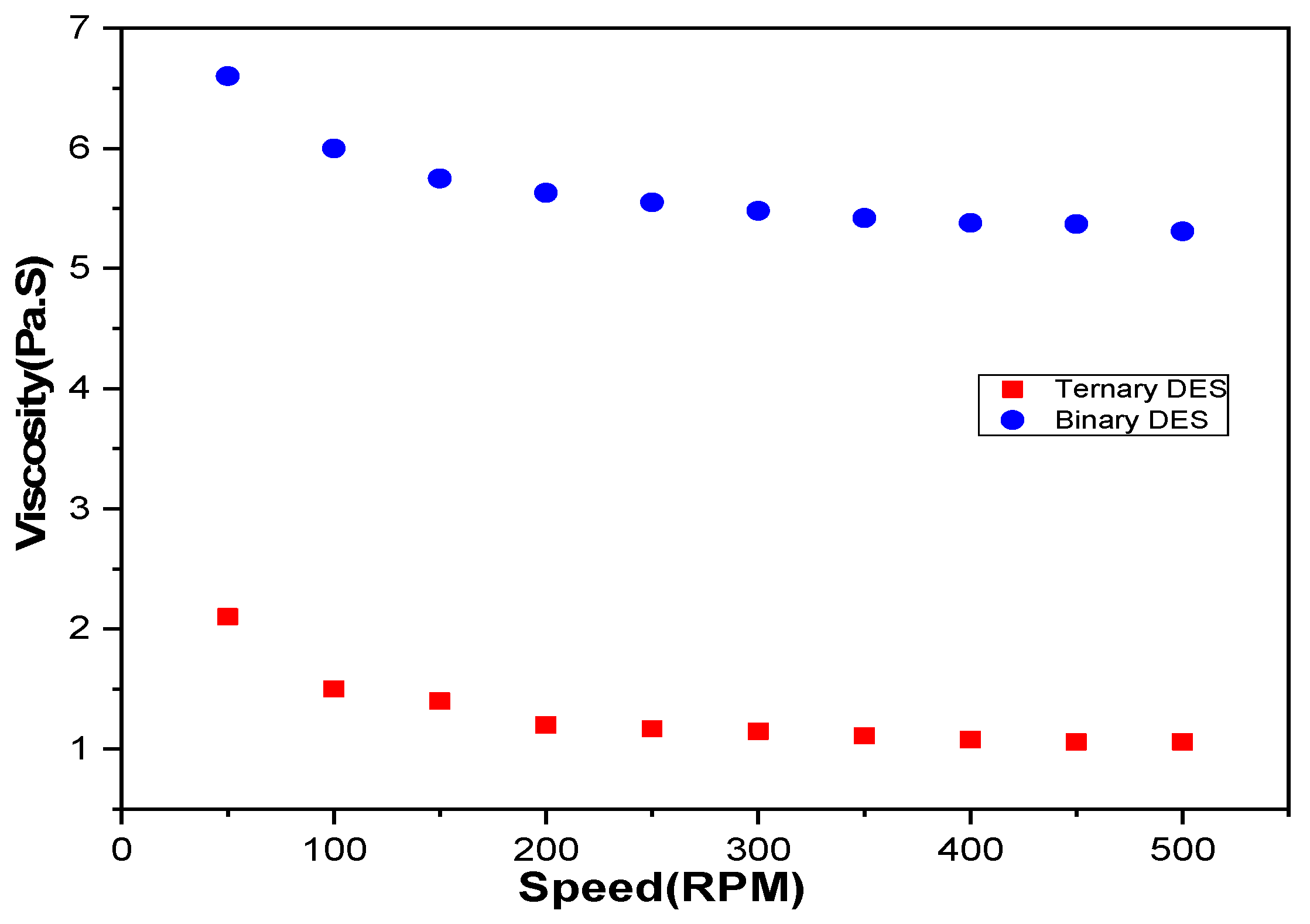
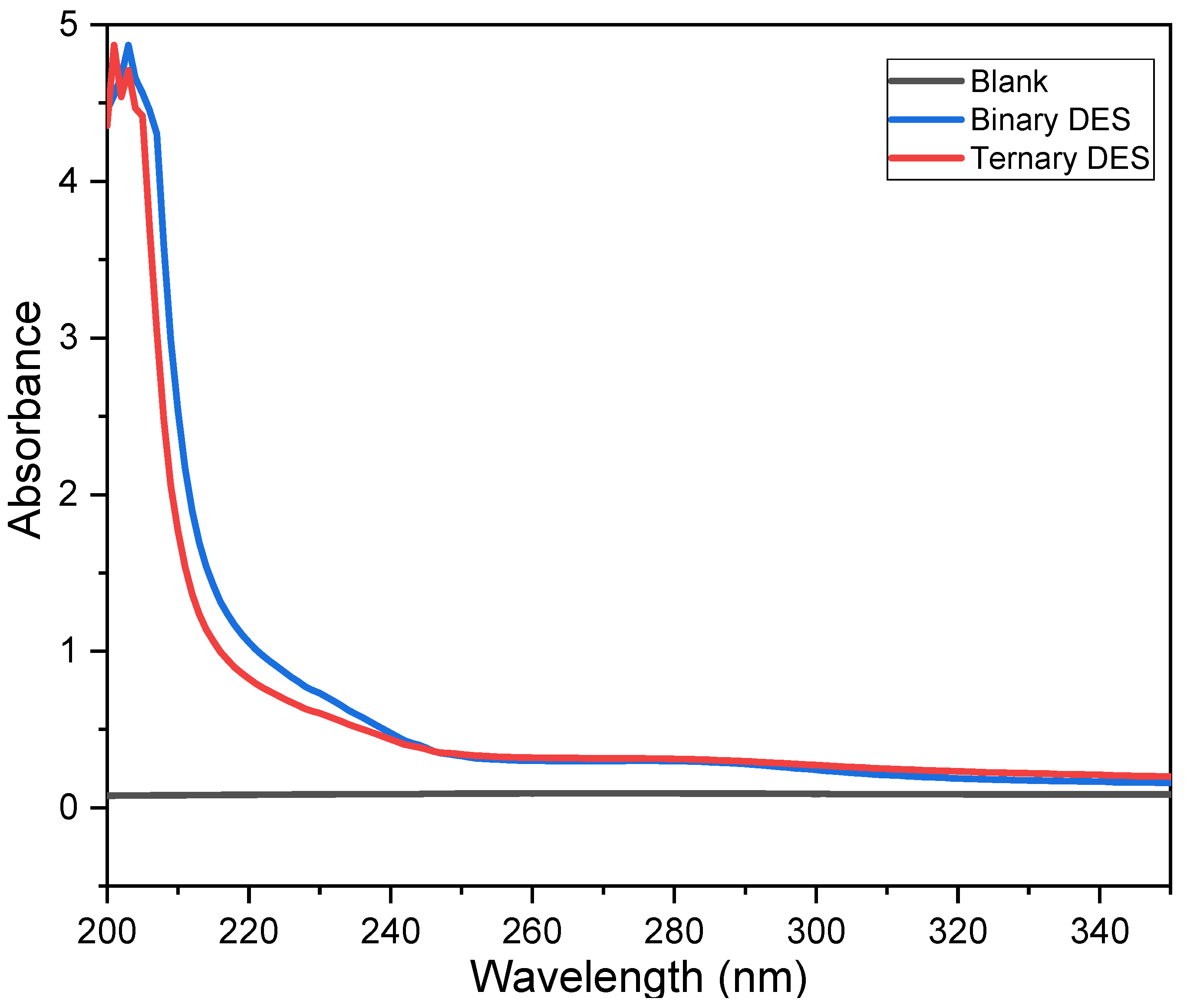
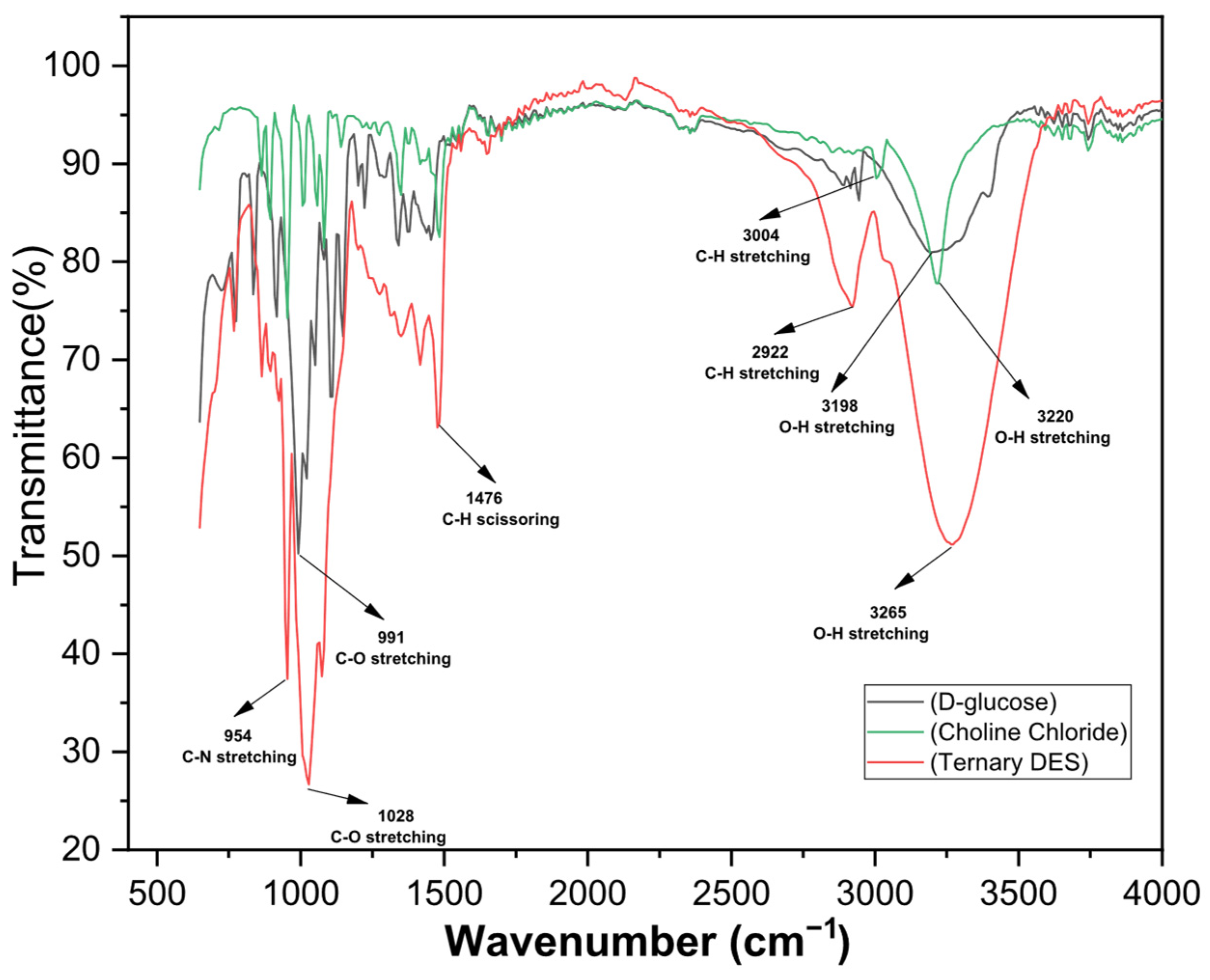
3.1. Characterizations of the Spent LIB Sample and DES
3.2. Leaching of Spent LIB Sample
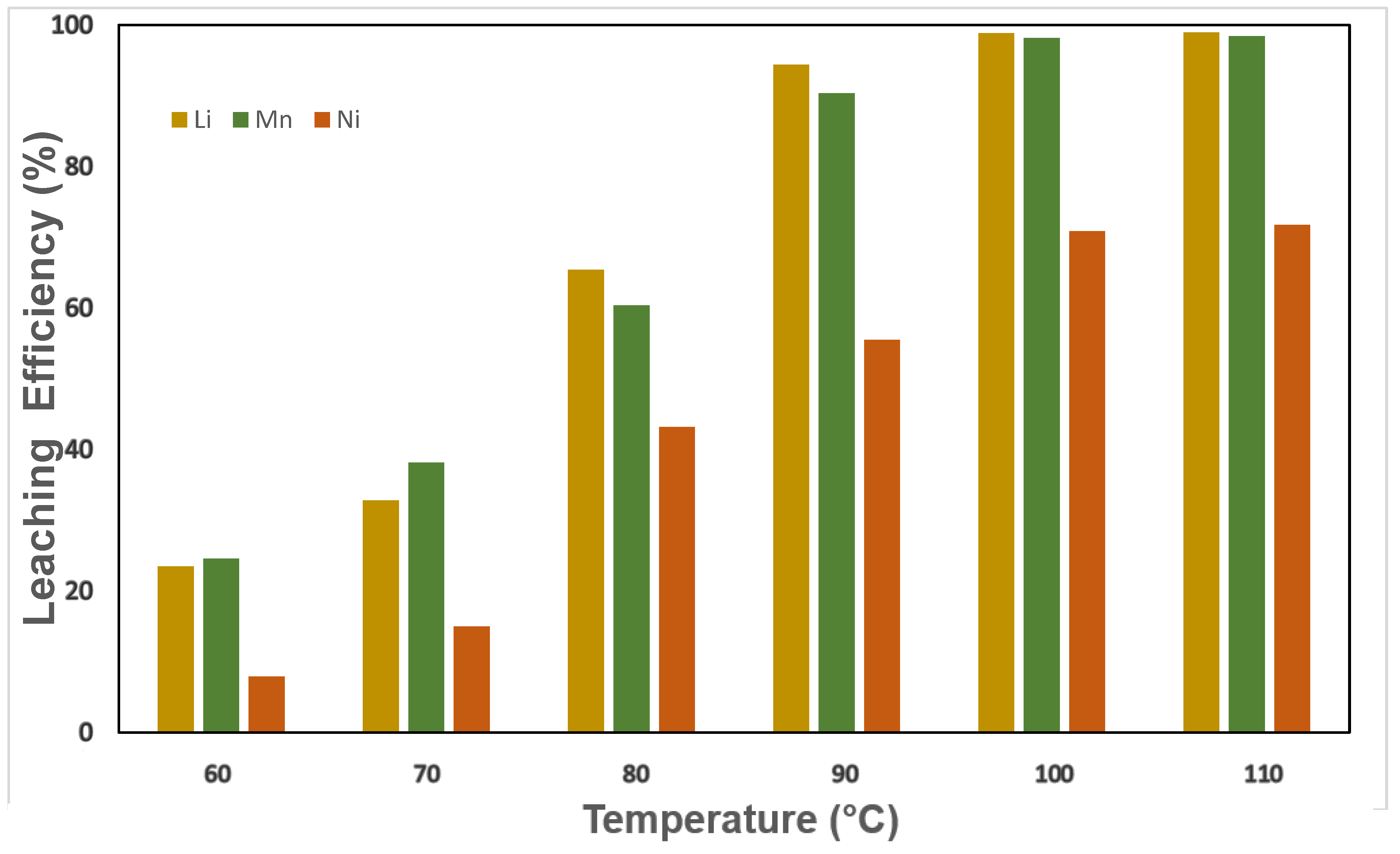
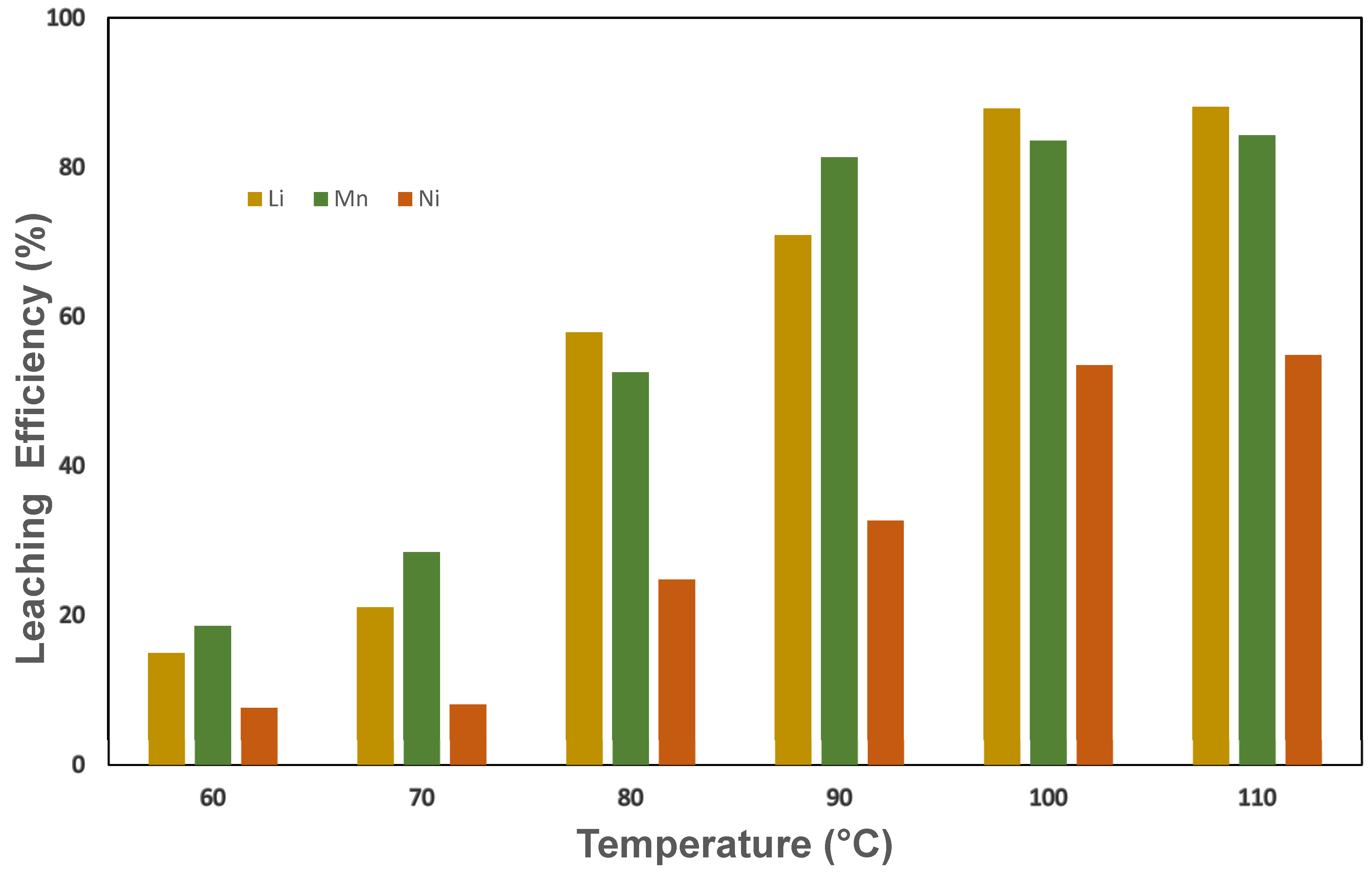
3.2.1. Effect of Temperature on Leaching Efficiency Using Binary and Ternary DES
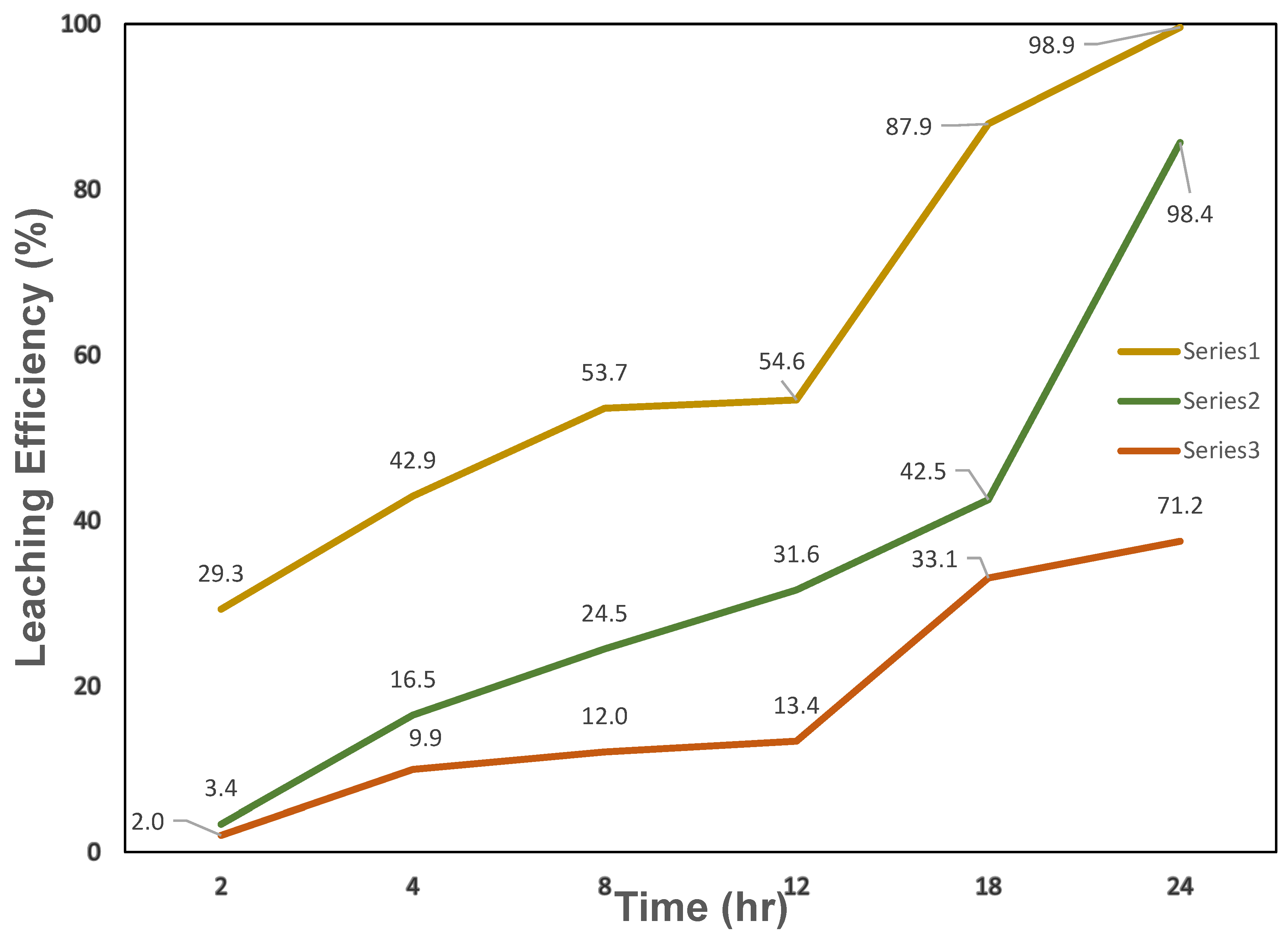
3.2.2. Effect of Leaching Time on Metal Extraction Efficiency Using Ternary DES
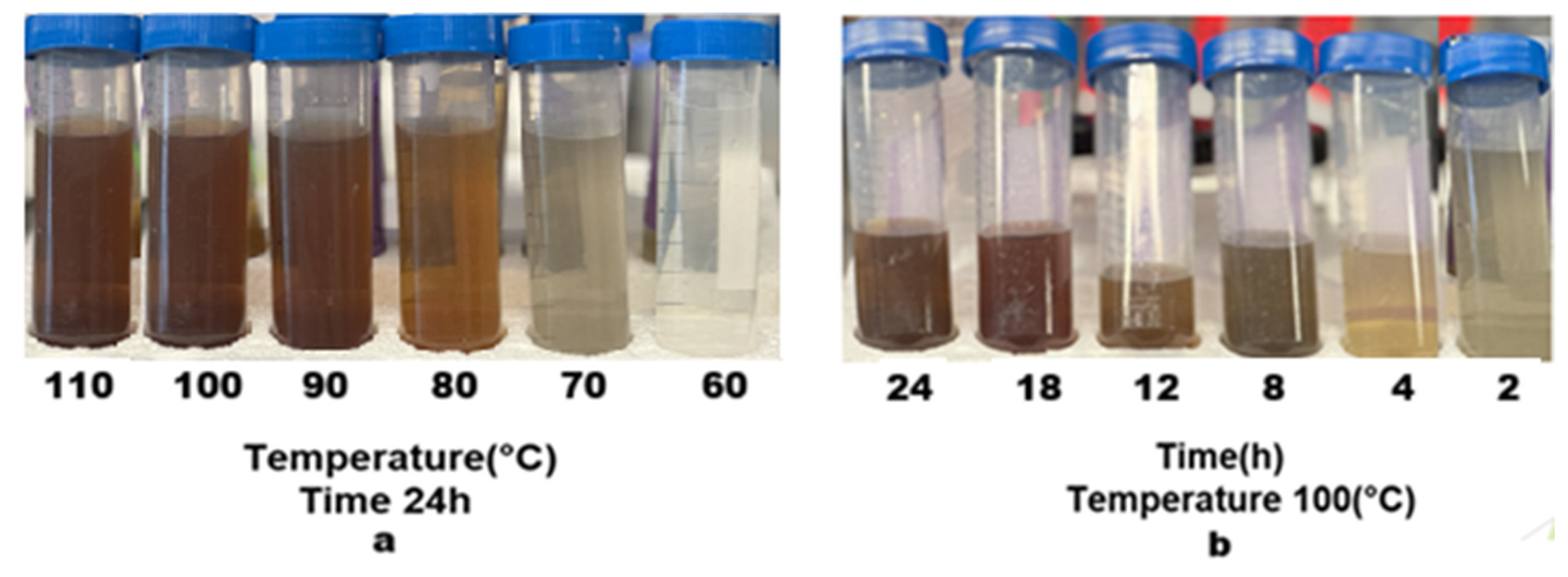
3.2.3. Visual Indicators of Leaching Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tran, M.K.; Rodrigues, M.-T.F.F.; Kato, K.; Babu, G.; Ajayan, P.M. Deep eutectic solvents for cathode recycling of Li-ion batteries. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garole, D.J.; Hossain, R.; Garole, V.J.; Sahajwalla, V.; Nerkar, J.; Dubal, D.P. Recycle, Recover and Repurpose Strategy of Spent Li-ion Batteries and Catalysts: Current Status and Future Opportunities. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 3079–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Luo, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xu, C.; Guo, J.; Cheali, P.; Xia, X. Progress, challenges, and prospects of spent lithium-ion batteries recycling: A review. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 89, 144–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yang, H.; Chen, K.; Yang, L.; Huang, M.; Wang, Z.; Lv, H.; Xu, C.; Chen, L.; Luo, X. Non–closed–loop recycling strategies for spent lithium–ion batteries: Current status and future prospects. Energy Storage Mater. 2024, 67, 103288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milian, Y.E.; Jamett, N.; Cruz, C.; Herrera-León, S.; Chacana-Olivares, J. A comprehensive review of emerging technologies for recycling spent lithium-ion batteries. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 910, 168543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, F.D.; Cutaia, L.; Vaccari, M. End-of-life automotive lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) in Brazil: Prediction of flows and revenues by 2030. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 169, 105522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liang, H.; Zhong, X.; Cao, H.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z. Recovery of metals from sulfate leach solutions of spent ternary lithium-ion batteries by precipitation with phosphate and solvent extraction with P507. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 210, 105861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuza, B.; Tian, Q.; Guo, X.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Yu, D. Pyrometallurgical options for recycling spent lithium-ion batteries: A comprehensive review. J. Power Sources 2021, 491, 229622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Chen, R.; Gu, J.-N.; Li, J.; Xue, Y.; Shi, F.; Huang, B.; Guo, M.; Jia, J.; Li, K.; et al. Sustainable recycling of spent ternary lithium-ion batteries via an environmentally friendly process: Selective recovery of lithium and non-hazardous upcycling of residue. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.; Al-Greer, M.; Burn, A.S.; Short, M.; Cui, X. High-Volume Battery Recycling: Technical Review of Challenges and Future Directions. Batteries 2025, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, G.; Ebin, B.; St. Foreman, M.R.J.; Steenari, B.-M.; Petranikova, M. Chemical Transformations in Li-Ion Battery Electrode Materials by Carbothermic Reduction. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 13668–13679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethurajan, M.; Gaydardzhiev, S. Bioprocessing of spent lithium-ion batteries for critical metals recovery—A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 165, 105225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Niu, B.; Song, Q.; Zhan, L.; Xu, Z. Novel targetedly extracting lithium: An environmental-friendly controlled chlorinating technology and mechanism of spent lithium-ion batteries recovery. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 123947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Kong, Y.; Jiang, P.; Zhang, G.; Cong, J.; Shi, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Y. Development and challenges of deep eutectic solvents for cathode recycling of end-of-life lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 463, 142278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarascon, J.-M.; Armand, M. Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 2001, 414, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, J.B.; Park, K.-S. The Li-Ion Rechargeable Battery: A Perspective. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, E.; Kordloo, M.; Khodadadmahmoudi, G.; Rezaei, A.; Ganjali, M.; Azimi, G. Solvometallurgical recycling of spent LiNixCoyMnzO2 (NCM) cathode material using ternary choline chloride-ethylene glycol-p-toluenesulfonic acid deep eutectic solvent. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 222, 106184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Ali, S.; Saeed, K.; Usman, M.; Khan, I. Advanced cathode materials and efficient electrolytes for rechargeable batteries: Practical challenges and future perspectives. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 10159–10173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Rohani, S.; Teng, L.; Gao, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, W. Thermochemically driven layer structure collapse via sulfate roasting toward the selective extraction of lithium and cobalt from spent LiCoO2 batteries. J. Power Sources 2023, 572, 233094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rensmo, A.; Savvidou, E.K.; Cousins, I.T.; Hu, X.; Schellenberger, S.; Benskin, J.P. Lithium-ion battery recycling: A source of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) to the environment? Environ. Sci. Process. Lmpacts 2023, 25, 1015–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaines, L. Lithium-ion battery recycling processes: Research towards a sustainable course. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2018, 17, e00068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Jin, X.; Zhang, X.; Duan, X.; Zhang, P.; Teng, L.; Liu, Q.; Liu, W. Combined pyro-hydrometallurgical technology for recovering valuable metal elements from spent lithium-ion batteries: A review of recent developments. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 6561–6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yildizbasi, A.; Wang, Y.; Sarkis, J. Safety Concerns for the Management of End-of-Life Lithium-Ion Batteries. Glob. Chall. 2022, 6, 202200049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelio, A.; Zanoletti, A.; Bontempi, E. Recent progress in pyrometallurgy for the recovery of spent lithium-ion batteries: A review of state-of-the-art developments. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2024, 46, 100881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, L.; Vrucak, D.; Woeste, R.; Lucas, H.; Rombach, E.; Friedrich, B.; Letmathe, P. Pyrometallurgical recycling of different lithium-ion battery cell systems: Economic and technical analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 416, 137834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalini, E.A.; Karimi, G.; Zandevakili, S.; Goodarzi, M. A Review on Environmental, Economic and Hydrometallurgical Processes of Recycling Spent Lithium-ion Batteries. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2020, 42, 451–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yu, J.; Hu, J.; Xu, J.; Yu, A.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Luo, X.; Deng, C.; Luo, F.; et al. Ultra-low viscosity betaine hydrochloride-formic acid deep eutectic solvent for leaching critical metals from spent NCM lithium-ion batteries. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, L.; Junior, A.B.; Espinosa, D. Sulfuric acid leaching of metals from waste Li-ion batteries without using reducing agent. Miner. Eng. 2022, 183, 107597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouquette, L.M.; Petranikova, M.; Vieceli, N. Complete and selective recovery of lithium from EV lithium-ion batteries: Modeling and optimization using oxalic acid as a leaching agent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 320, 124143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Liu, B.; Bao, S.; Ding, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, X.; Lin, C.; Chen, B. Recovery of Li, Ni, Co and Mn from spent lithium-ion batteries assisted by organic acids: Process optimization and leaching mechanism. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2024, 31, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Cheng, H.-M.; Zhou, G. Fundamentals, status and challenges of direct recycling technologies for lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 8194–8244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, K.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Valix, M.; Tsang, D.C. Challenges in Recycling Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: Spotlight on Polyvinylidene Fluoride Removal. Glob. Chall. 2023, 7, 2200237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep Eutectic Solvents formed between choline chloride and carboxylic acids: Versatile alternatives to ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, N.; Binnemans, K.; Riaño, S. Solvometallurgical recovery of cobalt from lithium-ion battery cathode materials using deep-eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 4210–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Liu, H.; Yong, W.F.; She, Q.; Esteban, J. Status and advances of deep eutectic solvents for metal separation and recovery. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 1895–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; McKenzie, K.J.; Obi, S.U. Solubility of metal oxides in deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2006, 51, 1280–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, B.; Wang, F.; Xu, B.; Liang, D.; Wang, L. A Review of Processes and Technologies for the Recycling of Spent Lithium-ion Batteries. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 782, 022025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Shen, J.; Duan, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Xing, Z.; Liu, R. The Le Chatelier’s principle enables closed loop regenerating ternary cathode materials for spent lithium-ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2024, 67, 103250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, P.; Teng, L.; Rohani, S.; He, M.; Meng, F.; Liu, Q.; Liu, W. Acid-free extraction of valuable metal elements from spent lithium-ion batteries using waste copperas. Waste Manag. 2023, 165, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Xu, Z. A novel method for screening deep eutectic solvent to recycle the cathode of Li-ion batteries. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 4473–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Bian, X.; Han, W.; Cao, D.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, K.; Wang, S. The application of deep eutectic solvents in lithium-ion battery recycling: A comprehensive review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 188, 106690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.; Rantala, V.; Mehdipour, P.; Kauppinen, T.; Tuomikoski, S.; Heponiemi, A.; Runtti, H.; Tynjälä, P.; Dos Reis, G.S.; Lassi, U. A comprehensive review of the reclamation of resources from spent lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavi, P.G.; Altimari, P.; Branchi, M.; Zanoni, R.; Simonetti, G.; Navarra, M.A.; Pagnanelli, F. Selective recovery of cobalt from mixed lithium-ion battery wastes using deep eutectic solvent. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Tang, S.; Zhang, M.; Guo, M. Strategies for overcoming challenges in using deep eutectic solvents for the selective extraction of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorella, G.; Mansur, M.B. A study of the separation of cobalt from spent Li-ion battery residues. J. Power Sources 2007, 170, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnajady, B.; Seyf, J.Y.; Karimi, S.; Moradi, M.; Sohrabi, M. Molecular dynamic (MD) simulation and density function theory (DFT) calculation relevant to green leaching of metals from spent lithium-ion battery cathode materials using glucose-based deep eutectic solvent (DES). Hydrometallurgy 2024, 223, 106223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmohammadzadeh, R.; Rashchi, F.; Vahidi, E. Recovery of lithium and cobalt from spent lithium-ion batteries using organic acids: Process optimization and kinetic aspects. Waste Manag. 2017, 64, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyf, J.Y.; Zarei, F. Density, Viscosity, and Refractive Index of a Choline Chloride + d -(-)-Fructose Deep Eutectic Solvent + Water Mixture at Different Temperatures: An Experimental Study and Thermodynamic Modeling. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2022, 67, 3007–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriele, F.; Chiarini, M.; Germani, R.; Tiecco, M.; Spreti, N. Effect of water addition on choline chloride/glycol deep eutectic solvents: Characterization of their structural and physicochemical properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 291, 11301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravena, P.; Cea-Klapp, E.; Gajardo-Parra, N.F.; Held, C.; Garrido, J.M.; Canales, R.I. Effect of water and hydrogen bond acceptor on the density and viscosity of glycol-based eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 389, 122856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivelä, H.; Salomäki, M.; Vainikka, P.; Mäkilä, E.; Poletti, F.; Ruggeri, S.; Terzi, F.; Lukkari, J. Effect of Water on a Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, L.; Elbourne, A.; Greaves, T.L.; Bryant, G.; Bryant, S.J. Physico-chemical characterisation of glycerol- and ethylene glycol-based deep eutectic solvents. Mol. Liq. 2024, 394, 123777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, S.; Benito, C.; Alcalde, R.; Atilhan, M.; Aparicio, S. Insights on the water effect on deep eutectic solvents properties and structuring: The archetypical case of choline chloride + ethylene glycol. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 344, 117717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Yu, Z.; Alhadid, A.; Minceva, M. Modeling the Viscosity of ChCl-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Mixtures with Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 1623–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, T.; Hussain, S.; Zhu, M. Deep eutectic solvents as an emerging green platform for the synthesis of functional materials. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 3627–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, C.; Ju, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yang, M. Efficient and Selective Dissolution of Li from Lithium-Ion Battery LiFePO4 Cathode by Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents. Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 5391–5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lyu, Y.; Zeng, R.; Zhang, S.; Davey, K.; Mao, J.; Guo, Z. Green recycling of spent Li-ion battery cathodes via deep-eutectic solvents. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 17, 867–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padwal, C.; Pham, H.D.; Jadhav, S.; Do, T.T.; Nerkar, J.; Hoang, L.T.M.; Nanjundan, A.K.; Mundree, S.G.; Dubal, D.P. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Green Approach for Cathode Recycling of Li-Ion Batteries. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2022, 3, 2100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaibuna, M.; Theresa, L.V.; Sreekumar, K. Neoteric deep eutectic solvents: History, recent developments, and catalytic applications. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 2695–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yuan, X.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Xie, W. Recent advances in pretreating technology for recycling valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; Fan, M.; Gu, C.; He, W.; Meng, Q.; Wan, L.; Guo, Y. Selective extraction of transition metals from spent LiNixCoγMn1−x−γO2 cathode via regulation of coordination environment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202202558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Element | Lithium (Li) | Manganese (Mn) | Nickel (Ni) | Cobalt (Co) | Aluminum (Al) | Copper (Cu) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight Percentage (%) | 2.5 | 33.78 | 8.74 | 7.90 | 0.17 | 0.017 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goudarzi, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, G.; Hu, J.; Zaghib, K.; Deng, S.; Dar, A.A.; Wang, X.; Haghighat, F.; Mulligan, C.N.; et al. Sustainable Recovery of Critical Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Batteries 2025, 11, 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11090340
Goudarzi J, Chen Z, Zhang G, Hu J, Zaghib K, Deng S, Dar AA, Wang X, Haghighat F, Mulligan CN, et al. Sustainable Recovery of Critical Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Batteries. 2025; 11(9):340. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11090340
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoudarzi, Jafar, Zhi Chen, Gaixia Zhang, Jinguang Hu, Karim Zaghib, Sixu Deng, Afzal Ahmed Dar, Xiaolei Wang, Fariborz Haghighat, Catherine N. Mulligan, and et al. 2025. "Sustainable Recovery of Critical Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Deep Eutectic Solvents" Batteries 11, no. 9: 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11090340
APA StyleGoudarzi, J., Chen, Z., Zhang, G., Hu, J., Zaghib, K., Deng, S., Dar, A. A., Wang, X., Haghighat, F., Mulligan, C. N., An, C., & Avalos Ramirez, A. (2025). Sustainable Recovery of Critical Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Batteries, 11(9), 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11090340














