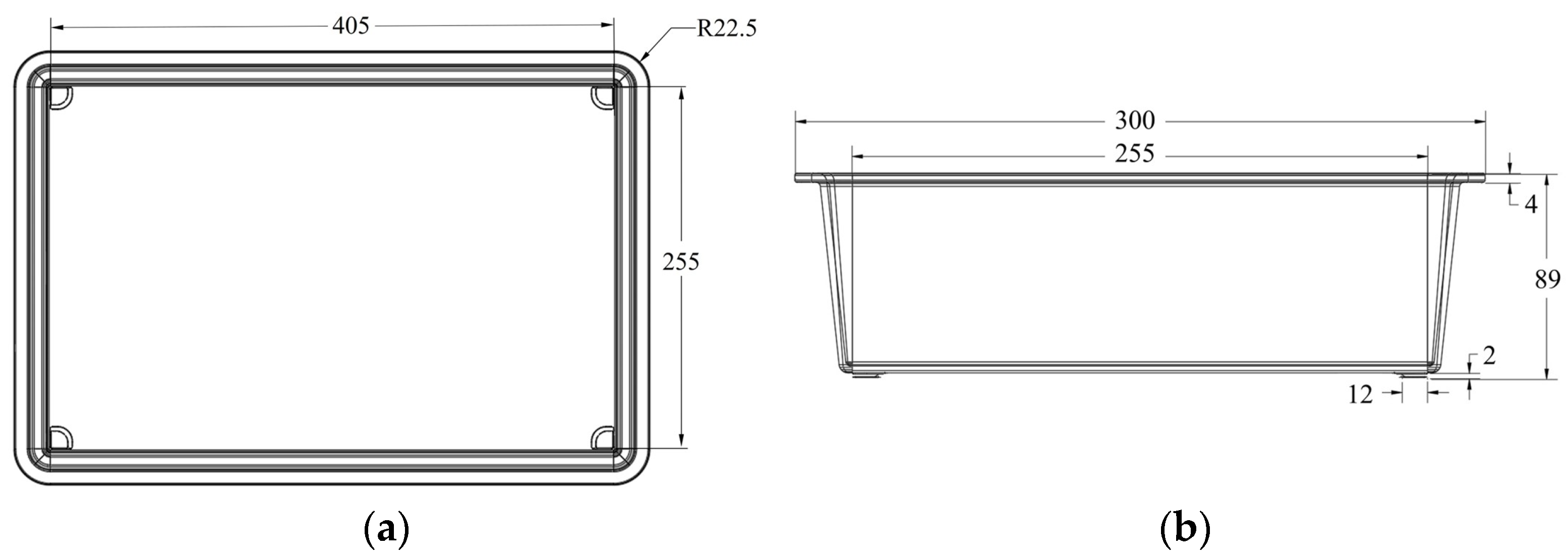
Figure 1.
Geometry and dimensions (in mm) of the housing: (a) x-y plane; (b) y-z plane.
Figure 1.
Geometry and dimensions (in mm) of the housing: (a) x-y plane; (b) y-z plane.
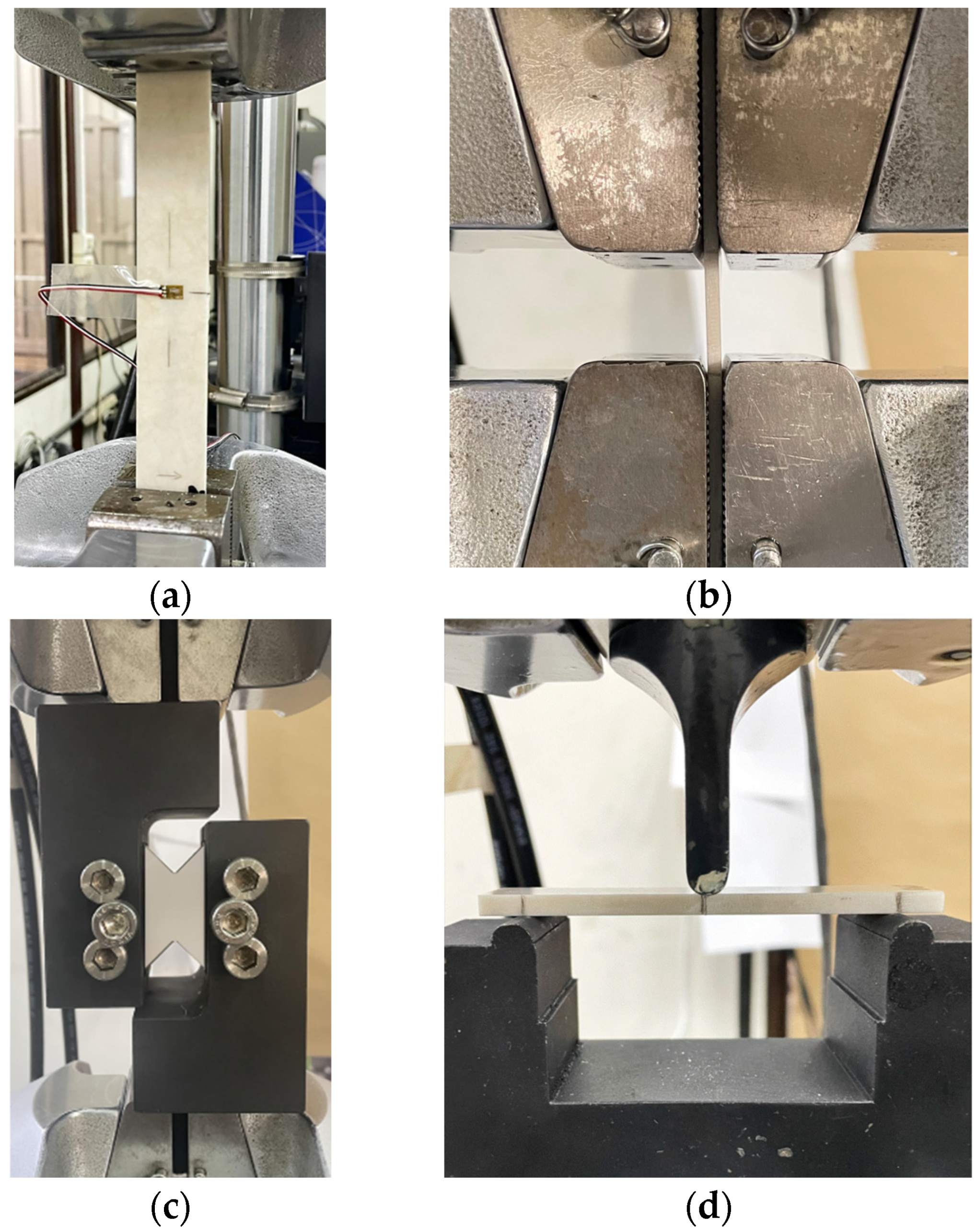
Figure 2.
Testing configuration and mounted specimens of (a) tension test, (b) compression test, (c) shear test, and (d) three-point bending test.
Figure 2.
Testing configuration and mounted specimens of (a) tension test, (b) compression test, (c) shear test, and (d) three-point bending test.
Figure 3.
Force-displacement curves of the SMC specimens subjected to (a) tension, (b) compression, (c) shear, (d) three-point bending.
Figure 3.
Force-displacement curves of the SMC specimens subjected to (a) tension, (b) compression, (c) shear, (d) three-point bending.
Figure 4.
Failure modes of the SMC specimens subjected to (a) tension, (b) compression, (c) shear, (d) three-point bending.
Figure 4.
Failure modes of the SMC specimens subjected to (a) tension, (b) compression, (c) shear, (d) three-point bending.
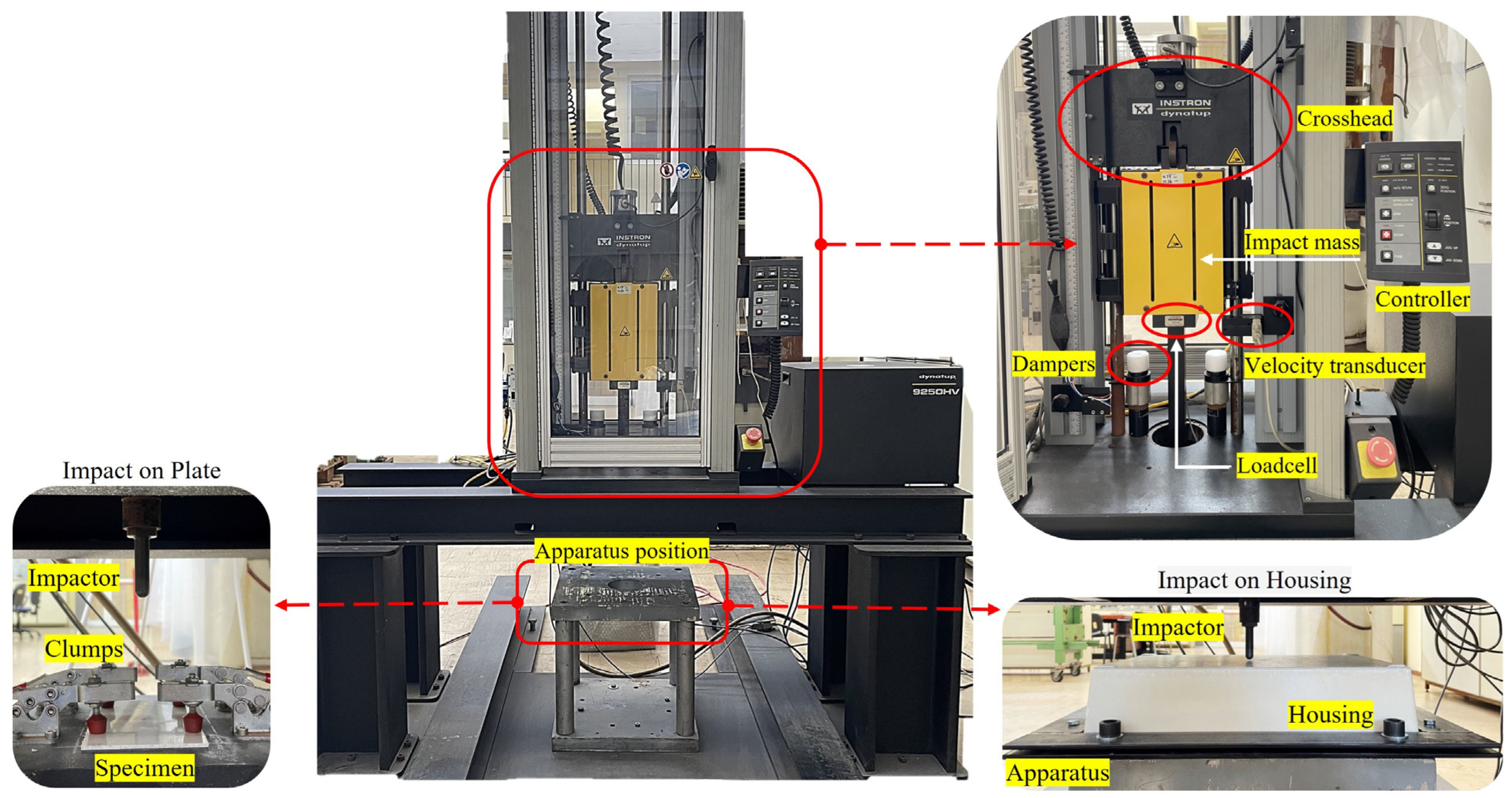
Figure 5.
Instron drop tower testing setup.
Figure 5.
Instron drop tower testing setup.
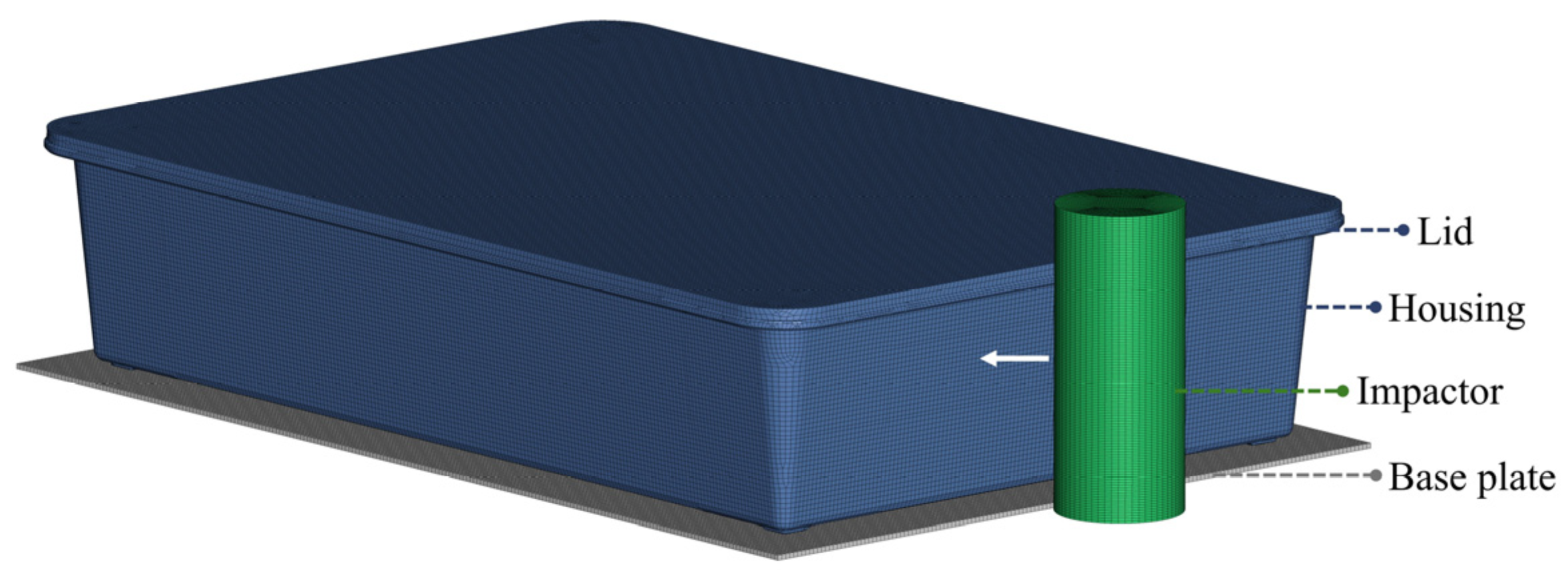
Figure 6.
Configuration of the drop tower model for the plate.
Figure 6.
Configuration of the drop tower model for the plate.
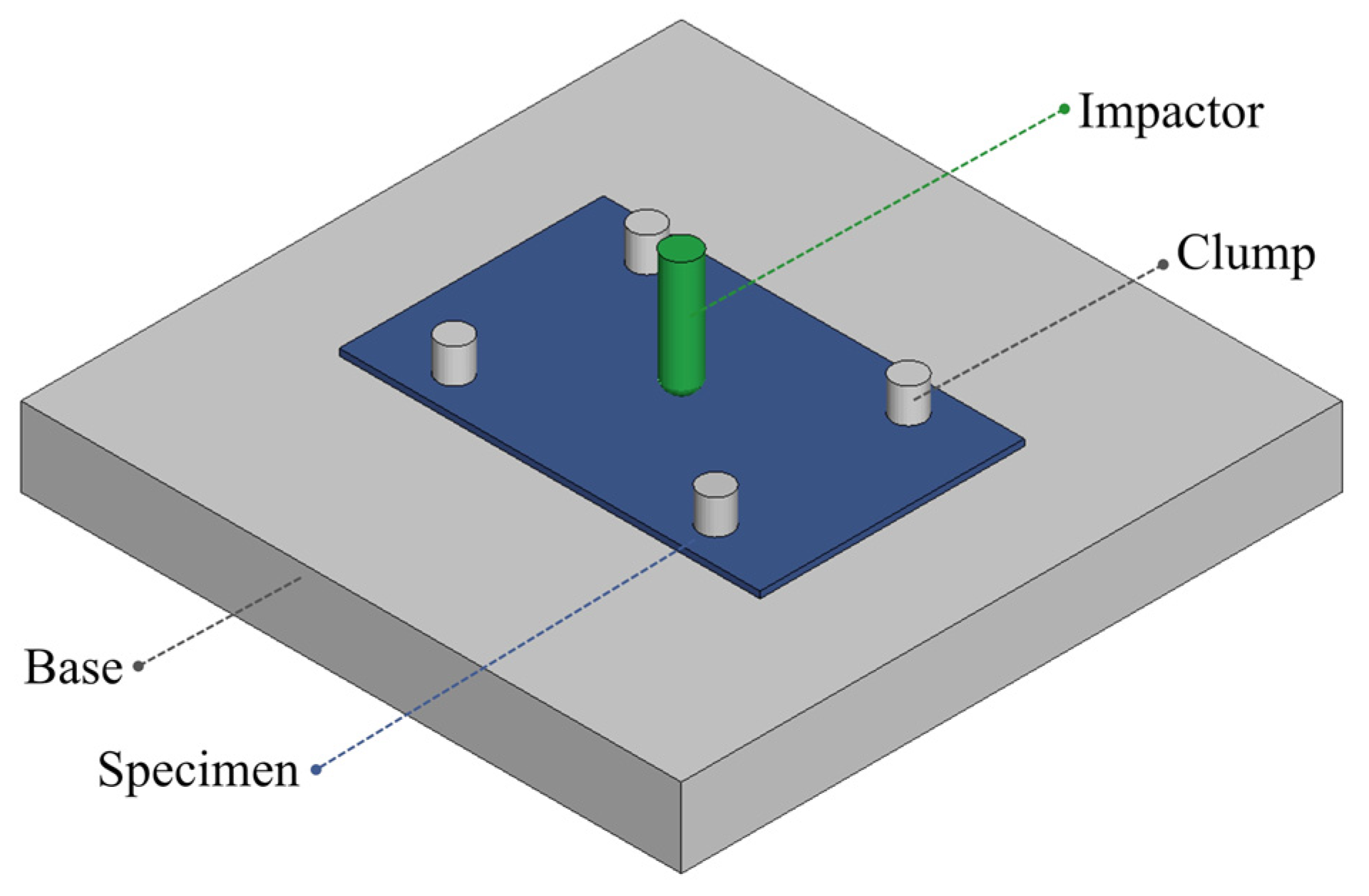
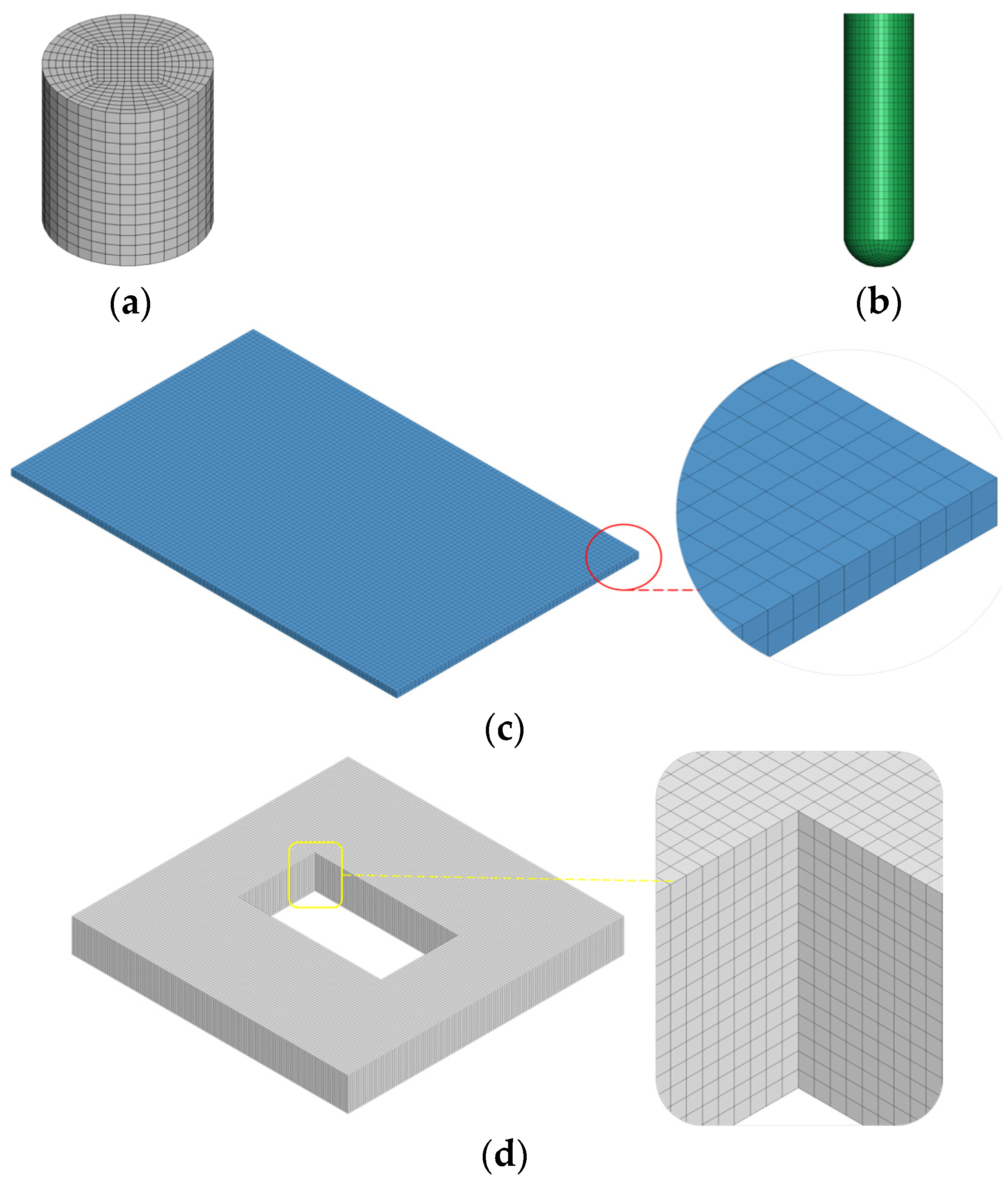
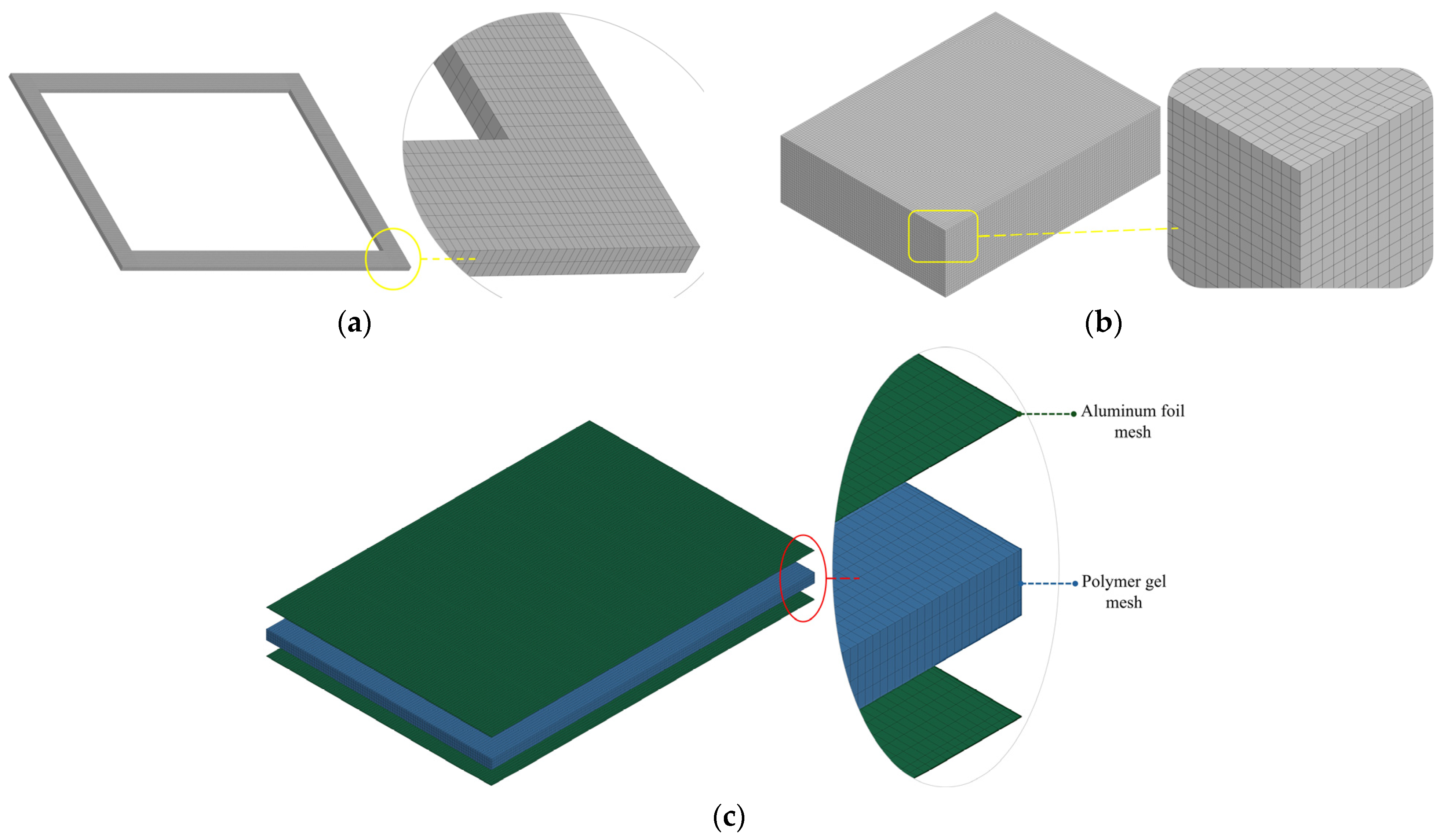
Figure 7.
FE mesh of the drop tower model components for the plate: (a) clump, (b) impactor, (c) plate, and (d) base.
Figure 7.
FE mesh of the drop tower model components for the plate: (a) clump, (b) impactor, (c) plate, and (d) base.
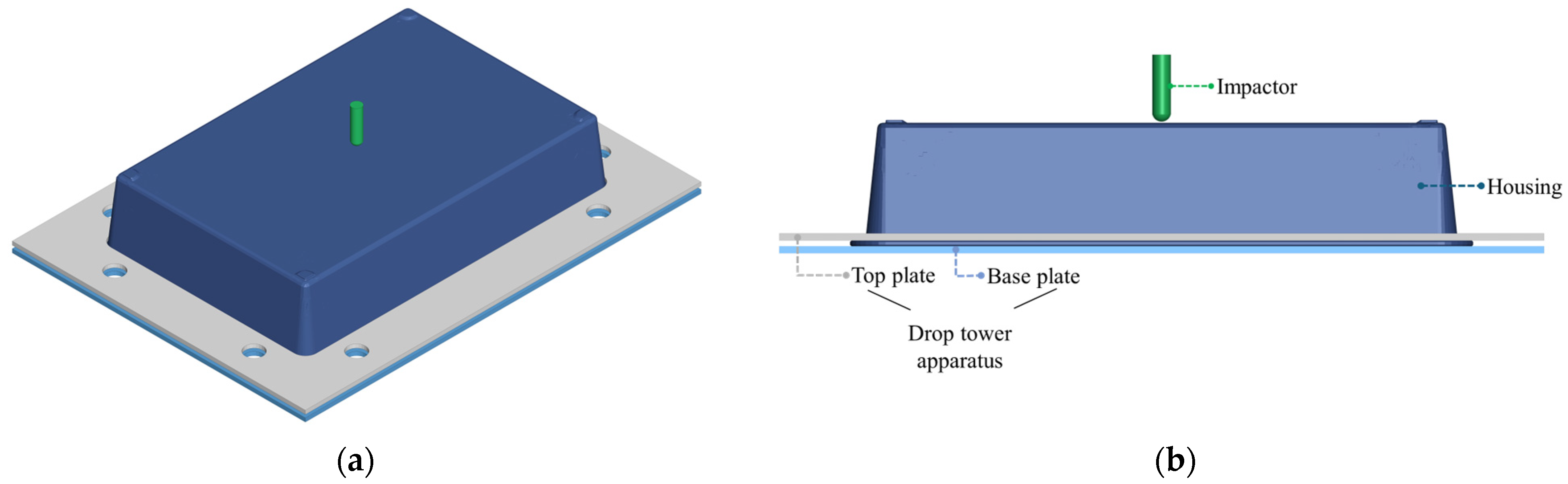
Figure 8.
Configuration of the drop tower model for the housing: (a) isometric view and (b) side view.
Figure 8.
Configuration of the drop tower model for the housing: (a) isometric view and (b) side view.
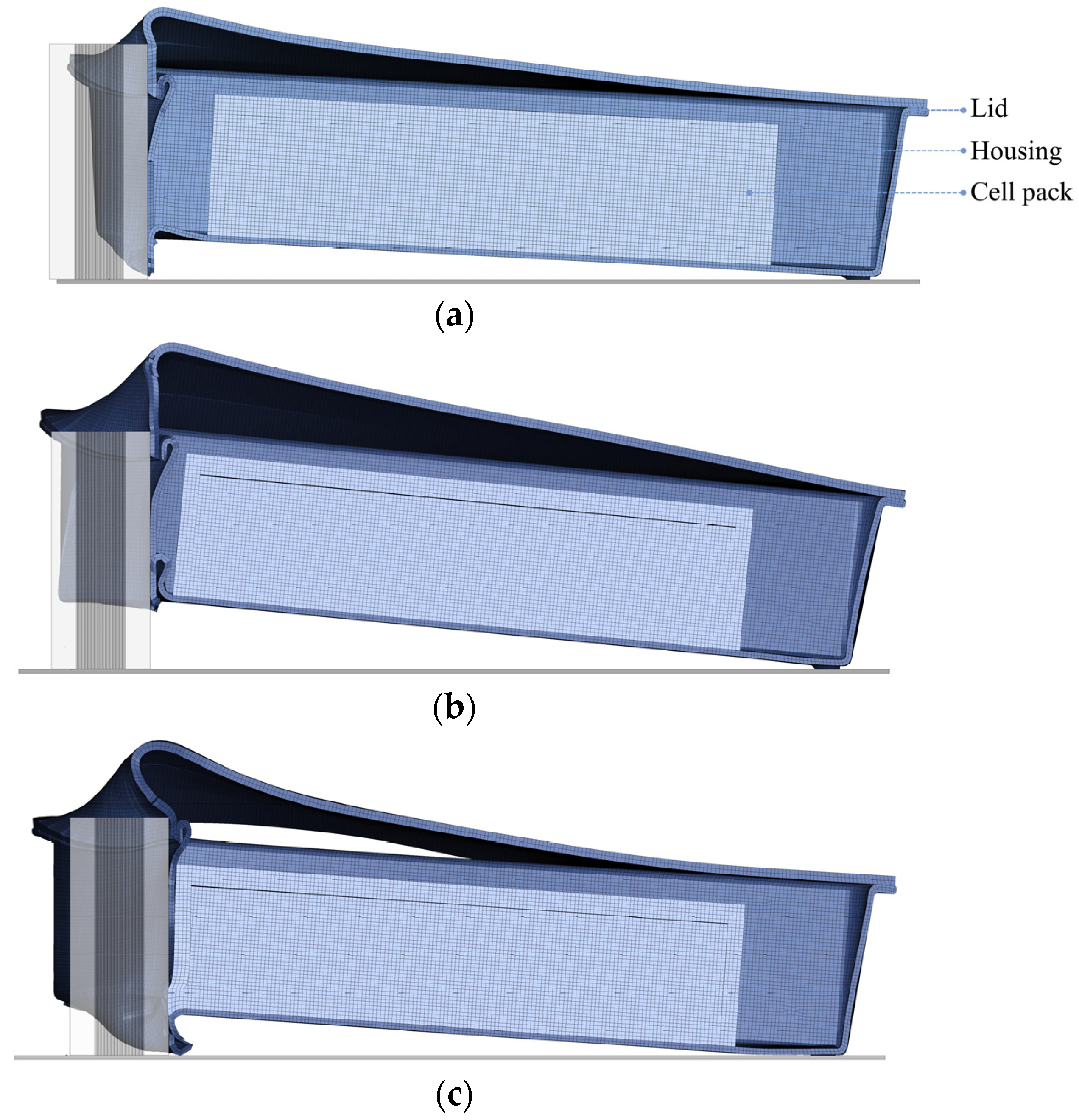
Figure 9.
FE mesh of (a) the apparatus of the drop tower model for the housing, and (b) the housing.
Figure 9.
FE mesh of (a) the apparatus of the drop tower model for the housing, and (b) the housing.
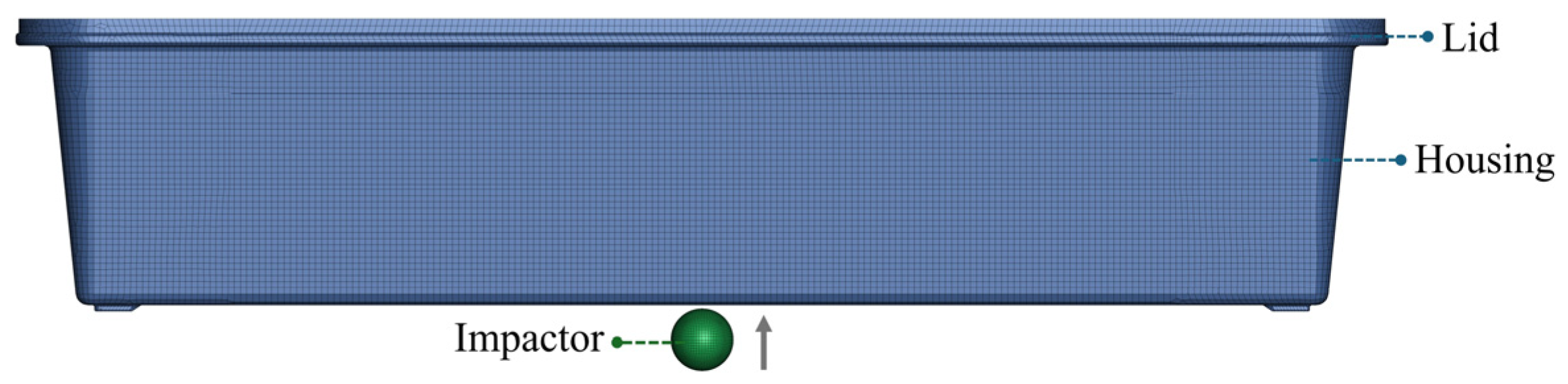
Figure 10.
FE mesh of the housing and the impactor of the ground impact model.
Figure 10.
FE mesh of the housing and the impactor of the ground impact model.
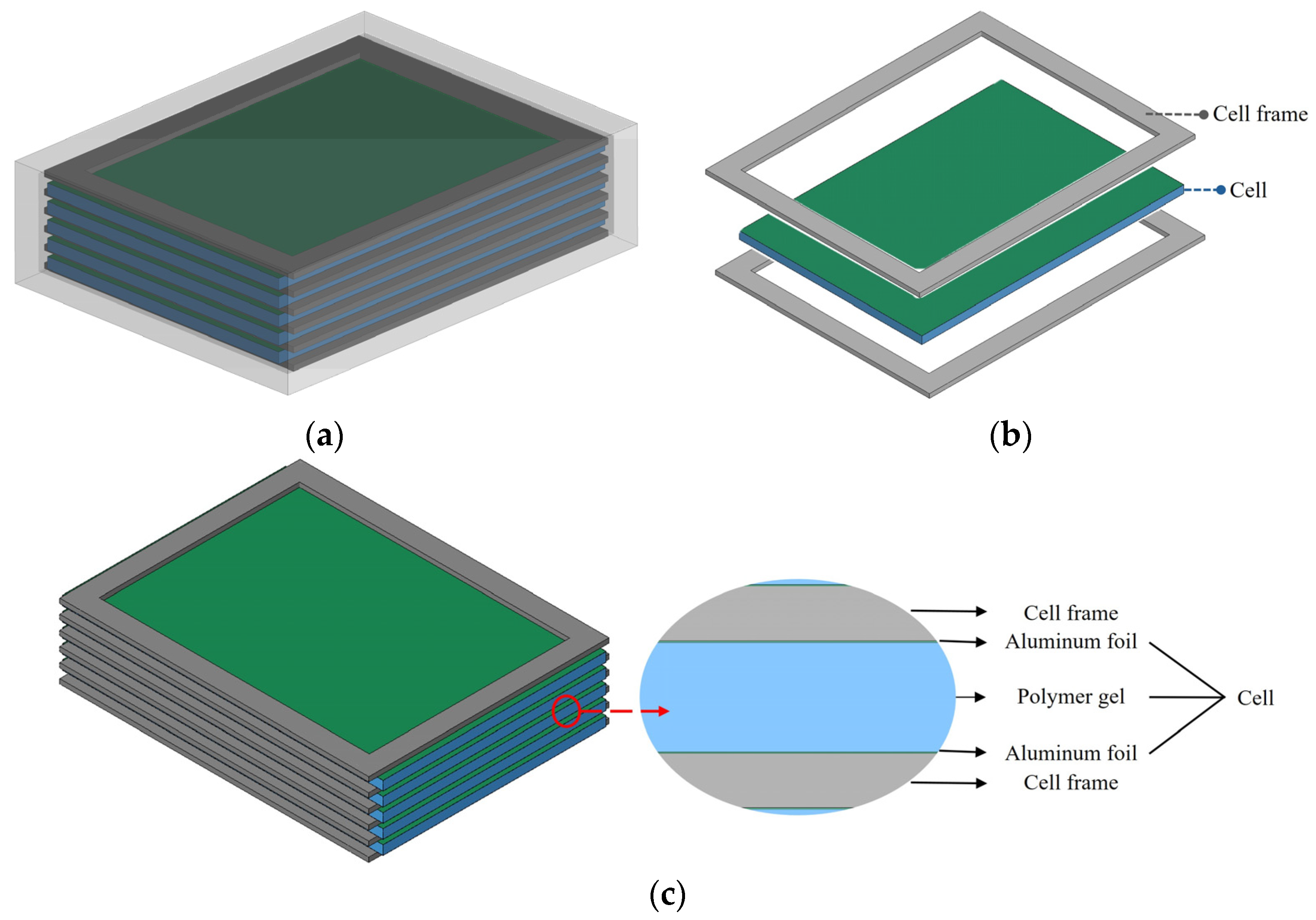
Figure 11.
Geometry of (a) the cell pack, (b) the cell frames, and (c) the cells.
Figure 11.
Geometry of (a) the cell pack, (b) the cell frames, and (c) the cells.
Figure 12.
FE mesh of (a) the cell frame, (b) the cell pack, and (c) the cell.
Figure 12.
FE mesh of (a) the cell frame, (b) the cell pack, and (c) the cell.
Figure 13.
FE mesh of the housing and the impactor of the pole impact/crash model.
Figure 13.
FE mesh of the housing and the impactor of the pole impact/crash model.
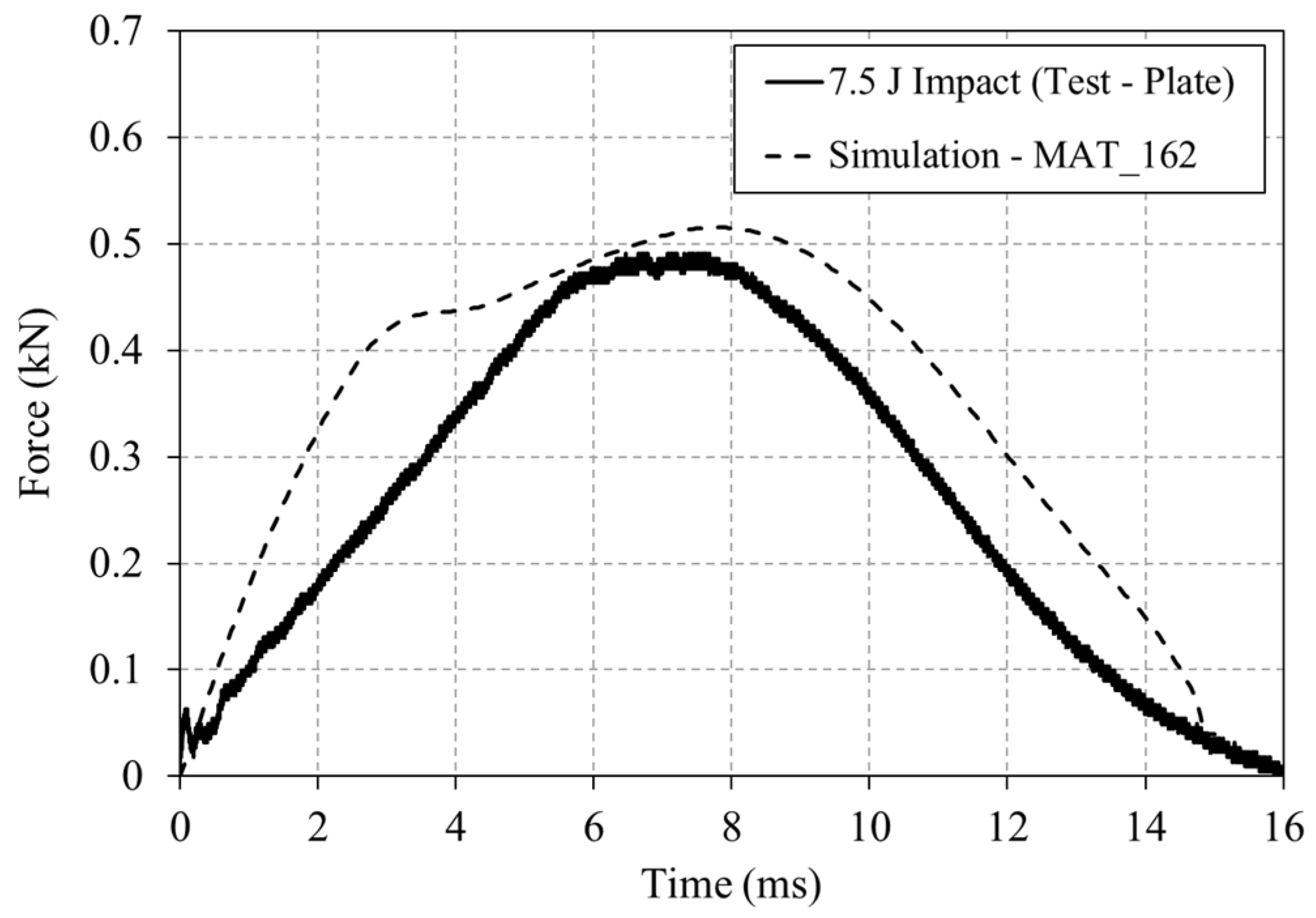
Figure 14.
Experimental and numerical force–time curves for the 7.5 J impact of the drop tower impact on the plate.
Figure 14.
Experimental and numerical force–time curves for the 7.5 J impact of the drop tower impact on the plate.
Figure 15.
Experimental versus numerical results of the SMC plate subjected to 7.5 J impact. (a) Front face, (b) back face, (c) side profile comparison.
Figure 15.
Experimental versus numerical results of the SMC plate subjected to 7.5 J impact. (a) Front face, (b) back face, (c) side profile comparison.
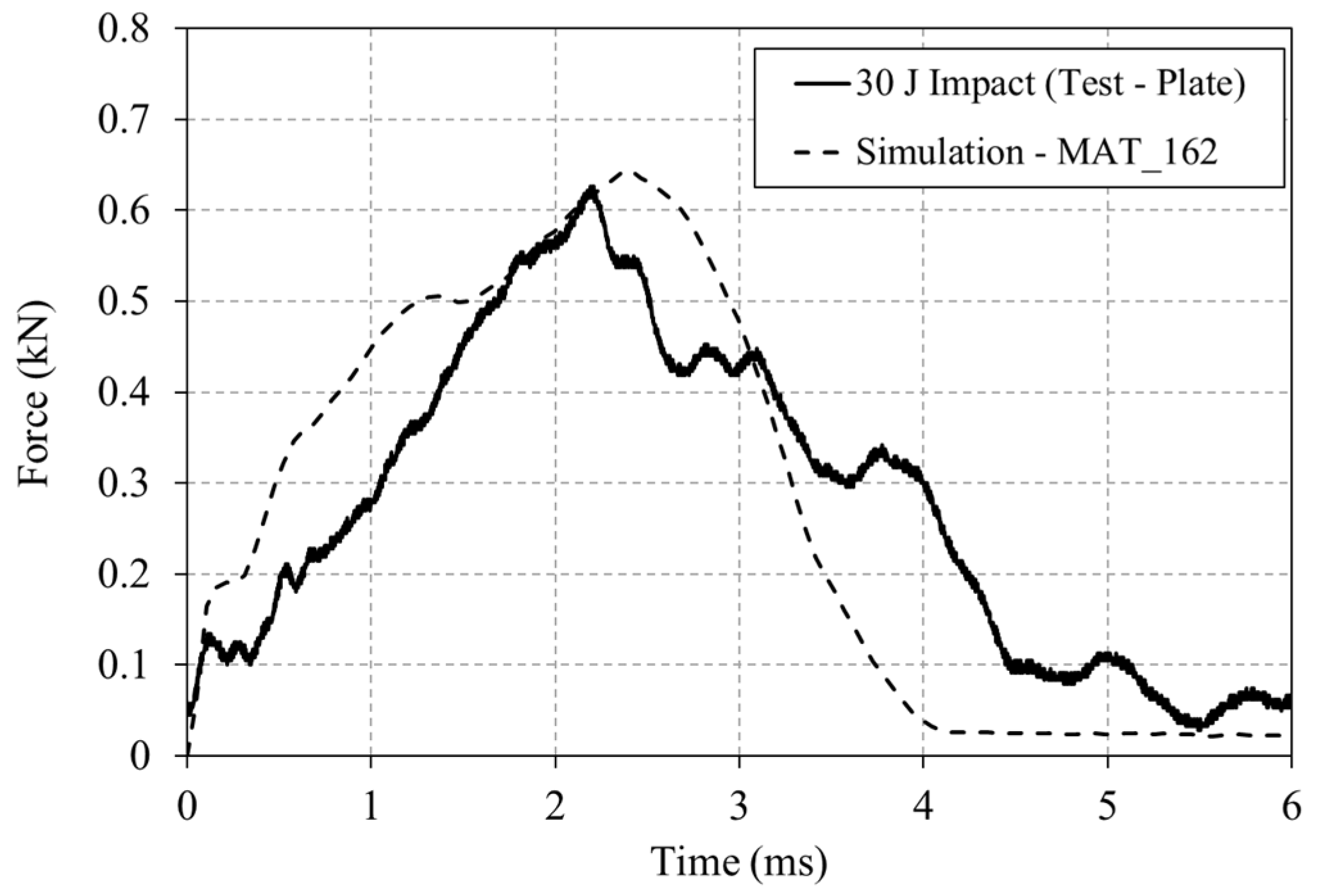
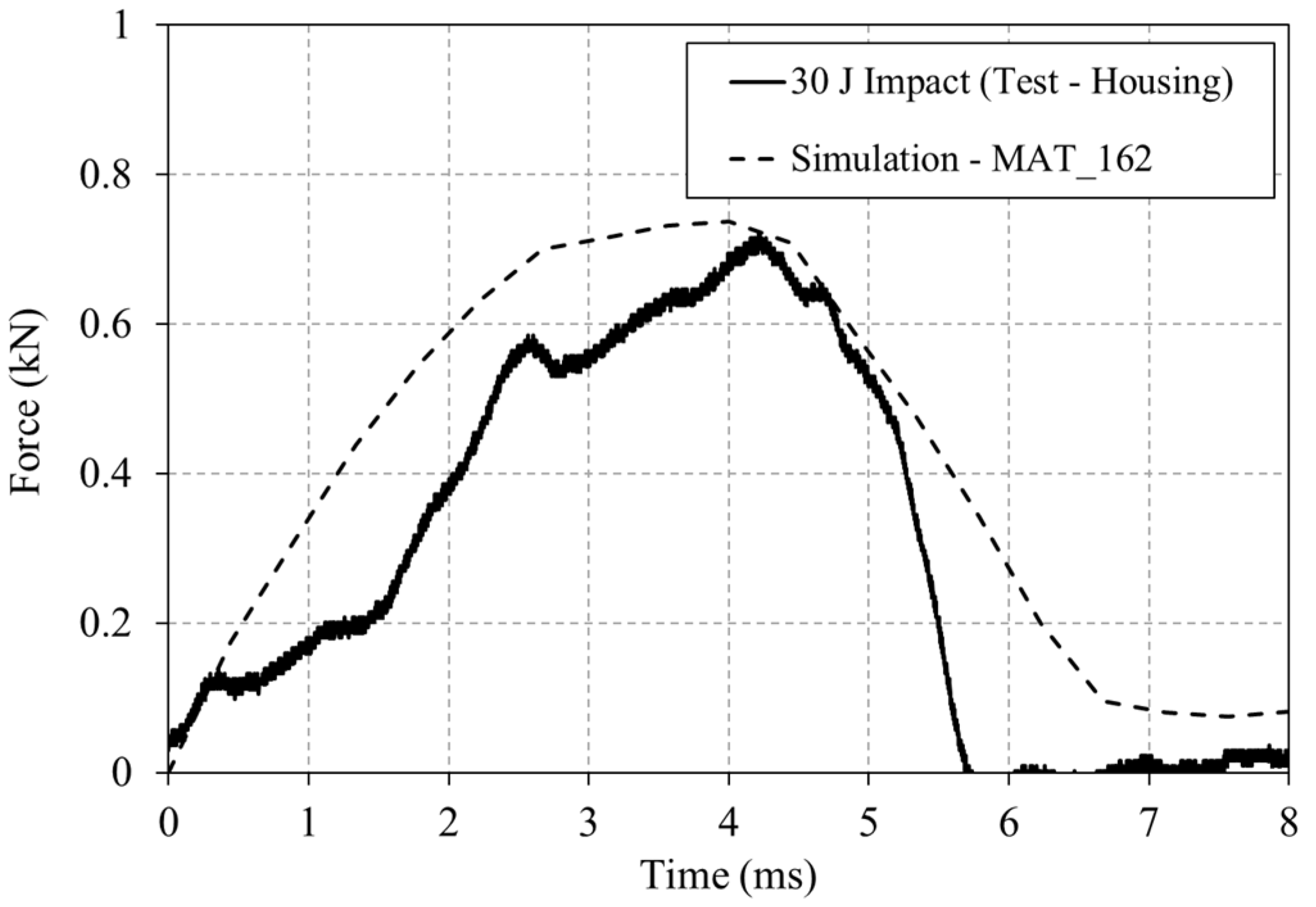
Figure 16.
Experimental and numerical force–time curves for the 30 J impact of the drop tower impact on the plate.
Figure 16.
Experimental and numerical force–time curves for the 30 J impact of the drop tower impact on the plate.
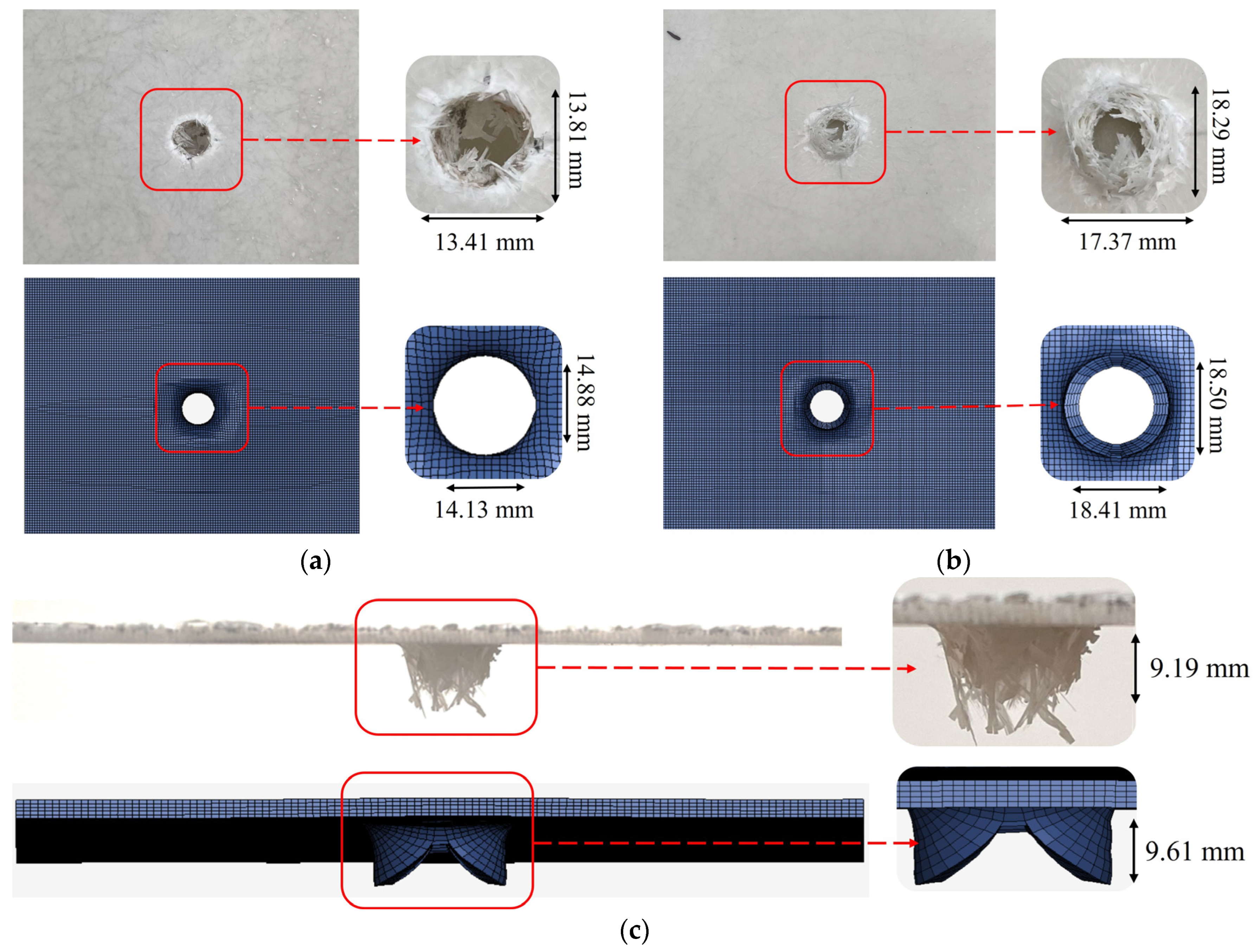
Figure 17.
Experimental versus numerical results of the SMC plate subjected to 30 J impact. (a) Front face, (b) back face, (c) side profile comparison.
Figure 17.
Experimental versus numerical results of the SMC plate subjected to 30 J impact. (a) Front face, (b) back face, (c) side profile comparison.
Figure 18.
Experimental and numerical force–time curves for the 7.5 J impact of the drop tower impact on the housing.
Figure 18.
Experimental and numerical force–time curves for the 7.5 J impact of the drop tower impact on the housing.
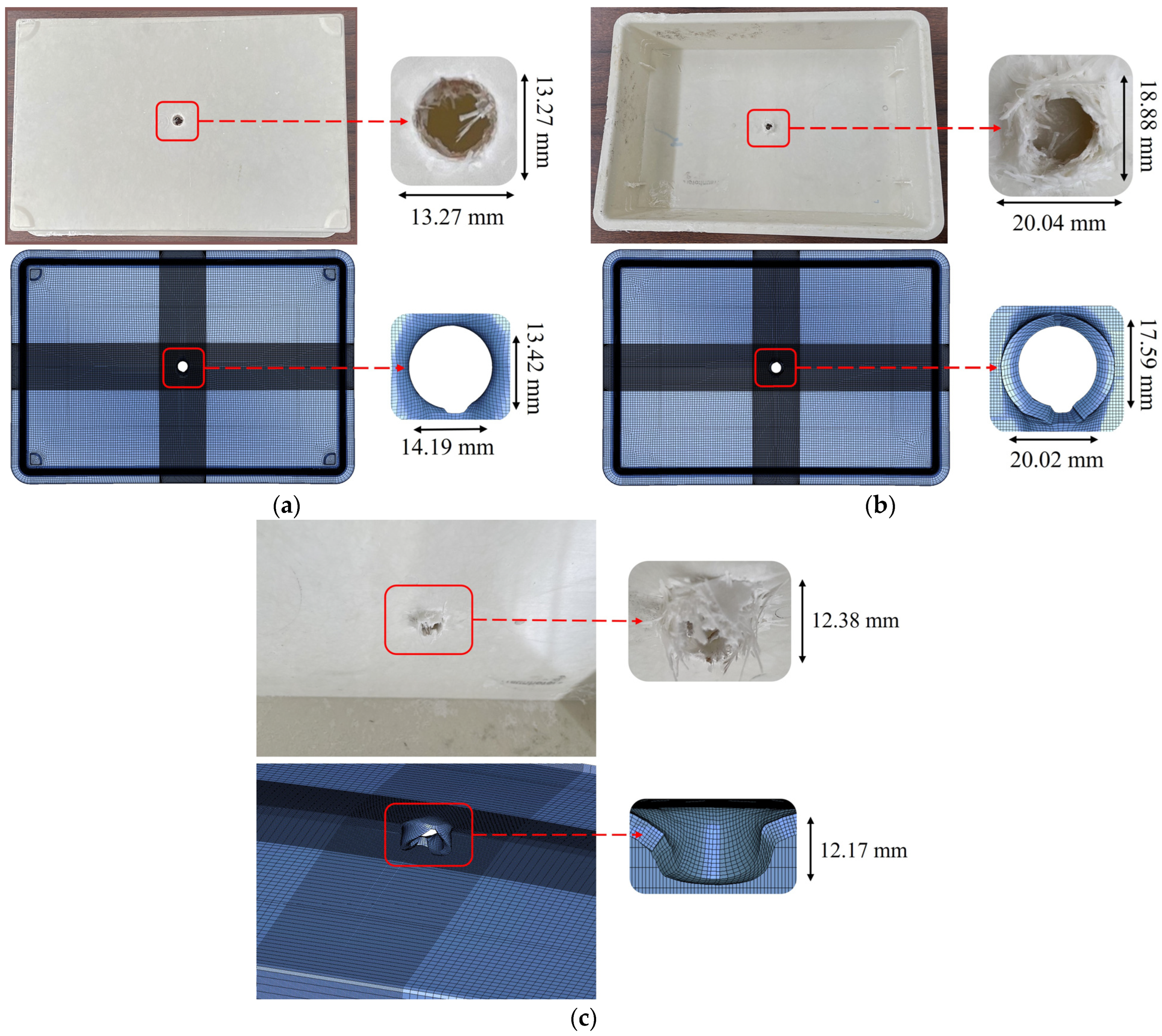
Figure 19.
Experimental versus numerical results of SMC housing subjected to 30 J impact. (a) Front face, (b) back face, (c) side profile comparison.
Figure 19.
Experimental versus numerical results of SMC housing subjected to 30 J impact. (a) Front face, (b) back face, (c) side profile comparison.
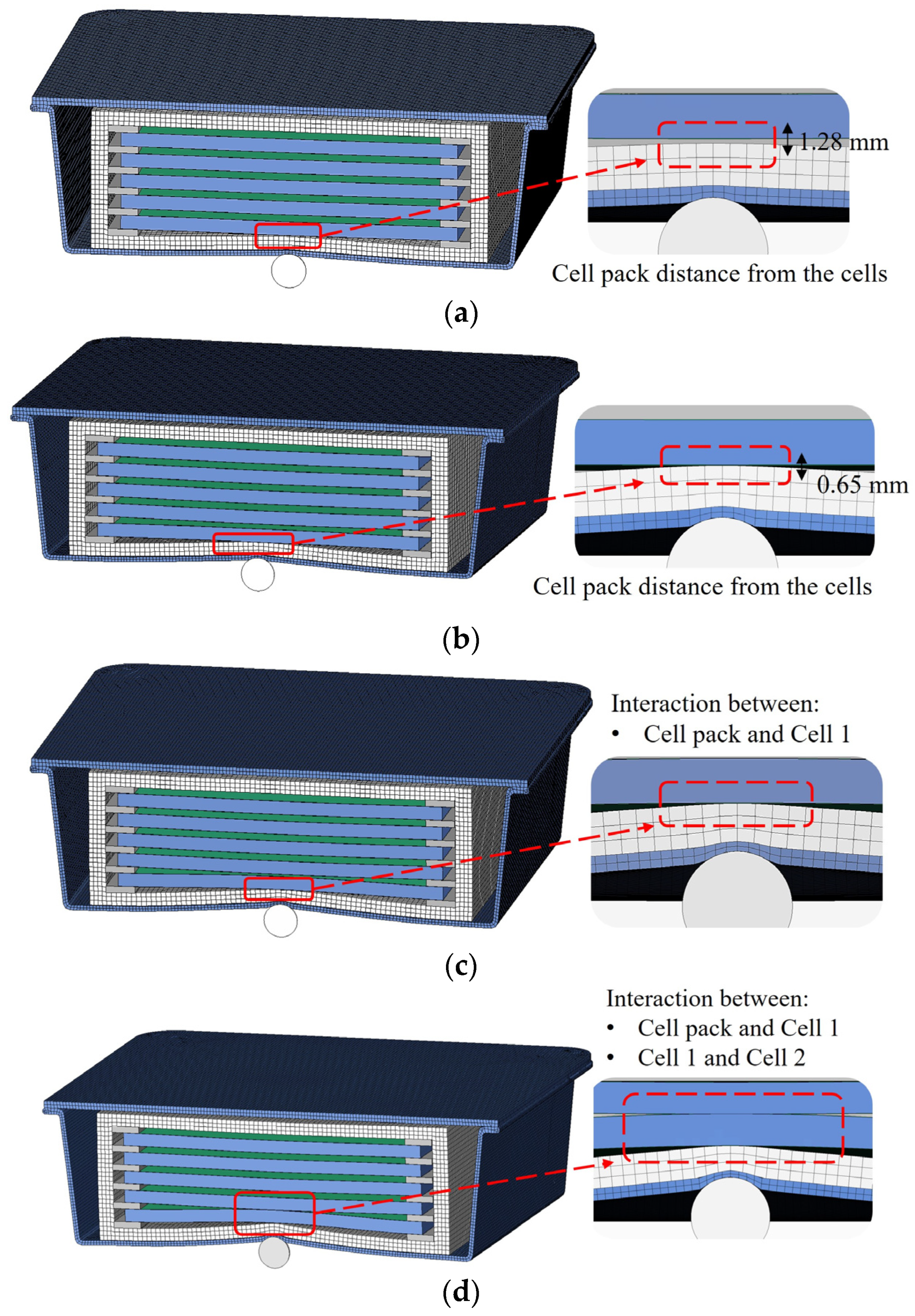
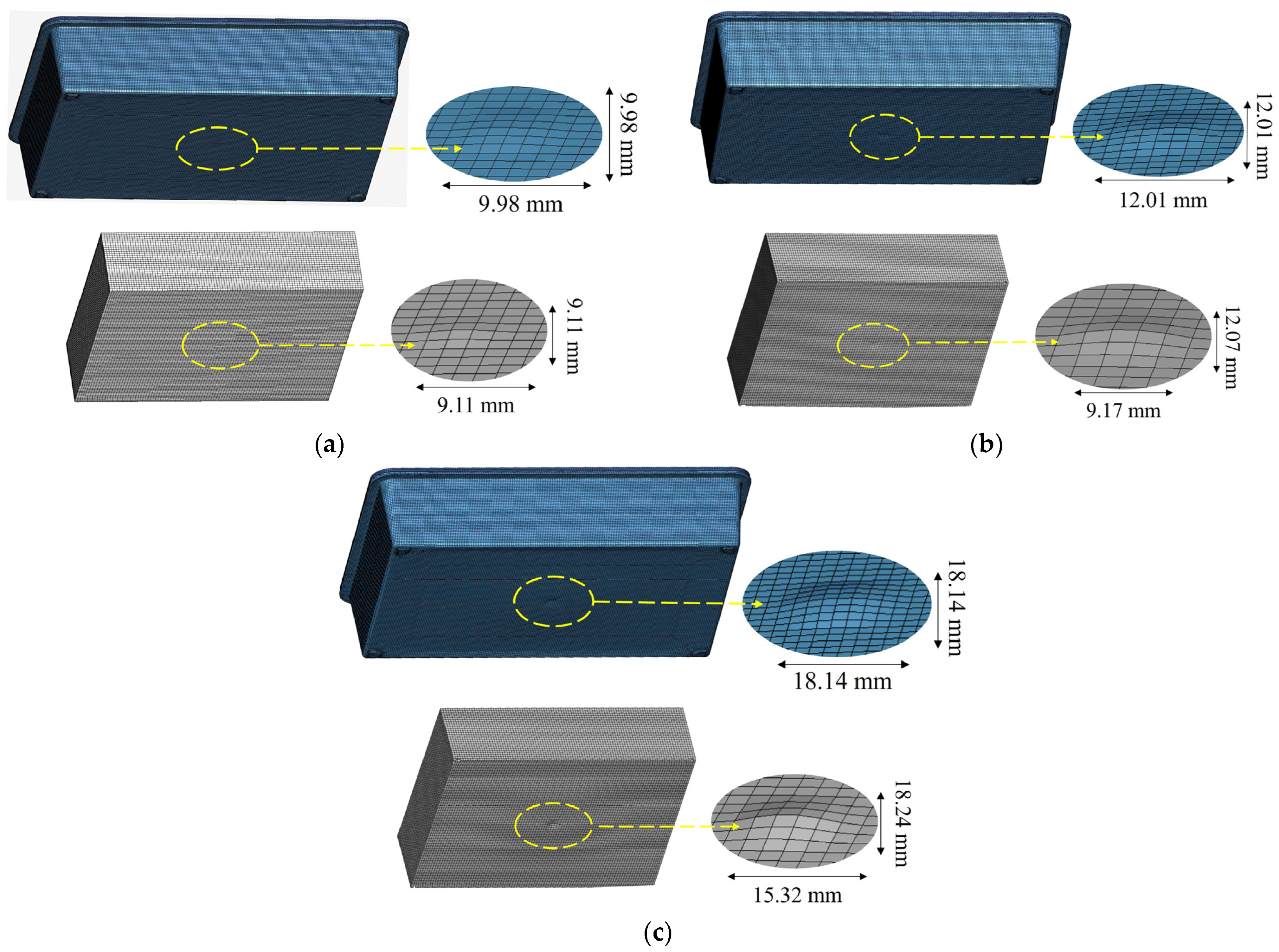
Figure 20.
Interaction of the housing and the cells/cell pack at the maximum displacement of the impactor for the impact cases of (a) 10 m/s, (b) 15 m/s, (c) 20 m/s, and (d) 25 m/s.
Figure 20.
Interaction of the housing and the cells/cell pack at the maximum displacement of the impactor for the impact cases of (a) 10 m/s, (b) 15 m/s, (c) 20 m/s, and (d) 25 m/s.
Figure 21.
Permanent deformation in the x and y directions for the housing and the cell pack after being subjected to ground impact of (a) 15 m/s, (b) 20 m/s, (c) 25 m/s.
Figure 21.
Permanent deformation in the x and y directions for the housing and the cell pack after being subjected to ground impact of (a) 15 m/s, (b) 20 m/s, (c) 25 m/s.
Figure 22.
Maximum displacement of the housing and cell pack after the event of (a) 10 m/s, (b) 12.5 m/s and (c) 15 m/s pole impact.
Figure 22.
Maximum displacement of the housing and cell pack after the event of (a) 10 m/s, (b) 12.5 m/s and (c) 15 m/s pole impact.
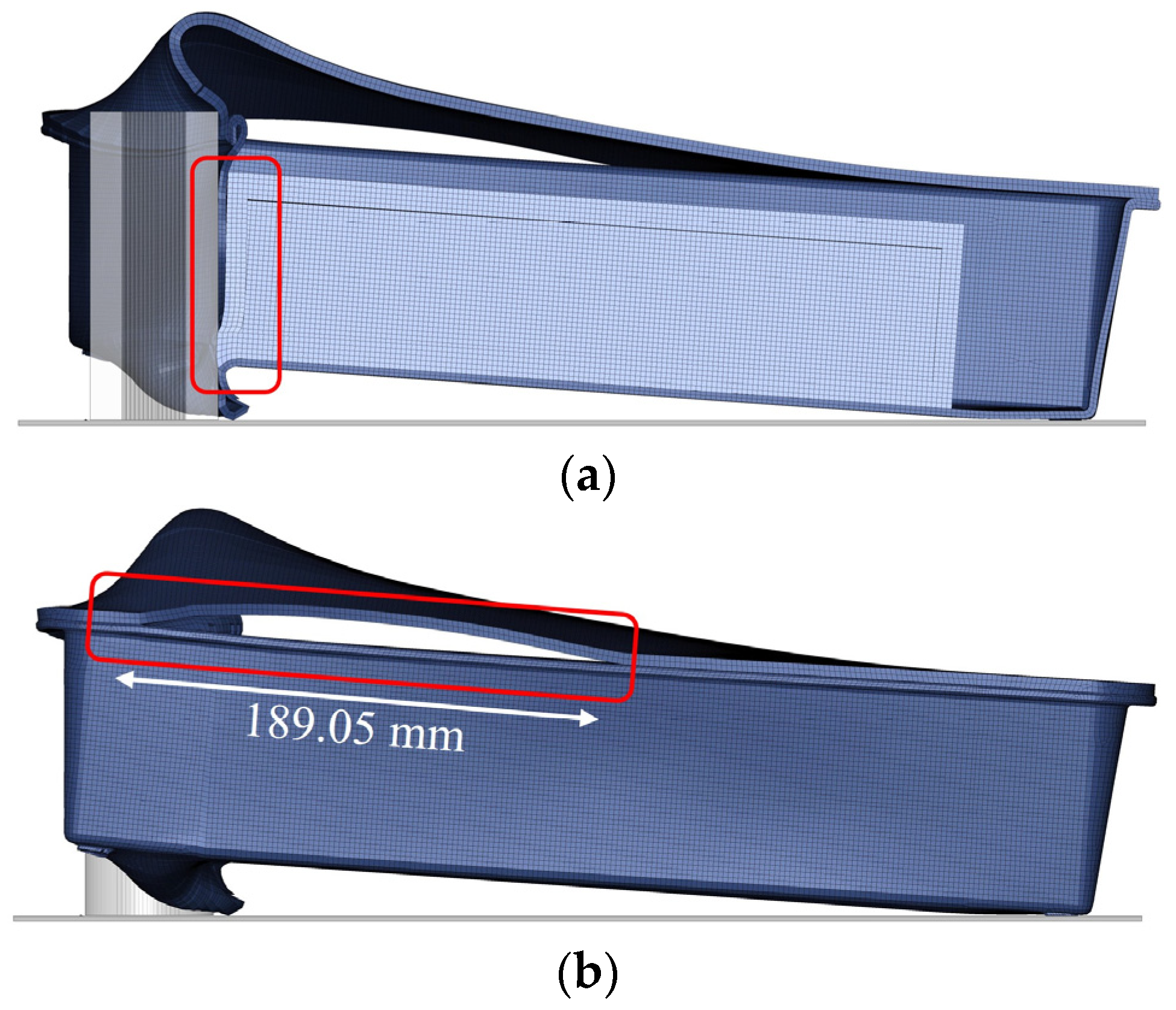
Figure 23.
Interaction of the housing and the cell pack/lid at the maximum displacement of the impactor after the event of the 15 m/s pole impact: (a) left view (intersection), (b) right view.
Figure 23.
Interaction of the housing and the cell pack/lid at the maximum displacement of the impactor after the event of the 15 m/s pole impact: (a) left view (intersection), (b) right view.
Table 1.
Mechanical testing parameters.
Table 1.
Mechanical testing parameters.
| Test | Standard | Specimen Dimensions | Speed of Testing |
|---|
| Tension | ASTM D3039 | 250 × 25 × 2.5 mm3 | 1 mm/min |
| Compression | ASTM D3410 | 140 × 25 × 2.5 mm3 | 1 mm/min |
| Three-point bending | ASTM D790 | 95 × 18 × 4.5 mm3 | 2.2 mm/min |
| Shear | ASTM D7078 | 76 × 56 × 4.5 mm3 | 2 mm/min |
Table 2.
Mechanical properties of the SMC composite derived from standardized testing.
Table 2.
Mechanical properties of the SMC composite derived from standardized testing.
| Property | Value |
|---|
| Modulus of Elasticity | 12.26 GPa |
| Tensile strength | 94.99 MPa |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.15 (-) |
| Compressive modulus | 13.61 GPa |
| Compressive strength | 133.83 MPa |
| Flexural modulus | 12.91 GPa |
| Flexural strength | 190.31 MPa |
| Shear modulus | 5.8 GPa |
| Shear strength | 76.92 MPa |
Table 3.
Steel input parameters for MAT_20.
Table 3.
Steel input parameters for MAT_20.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|
| Density, RO | 7580 kg/m3 |
| Young’s modulus, E | 200 GPa |
| Poisson’s ratio, PR | 0.33 (-) |
Table 4.
SMC input parameters for MAT_162.
Table 4.
SMC input parameters for MAT_162.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|
| Density, RO | 1878 kg/m3 |
| Young’s modulus—longitudinal direction, Ea | 12.2 GPa |
| Young’s modulus—transverse direction, Eb | 12.2 GPa |
| Young’s modulus—through-thickness direction, Ec | 5 GPa |
| Poisson’s ratio, vba | 0.15 (-) |
| Poisson’s ratio, vca, vcb | 0.18 (-) |
| Shear modulus, Gab | 5.8 GPa |
| Shear modulus, Gbc, Gca | 3.5 GPa |
| Longitudinal tensile strength, SaT | 95 MPa |
| Transverse tensile strength, SbT | 95 MPa |
| Through-thickness tensile strength, ScT | 75 MPa |
| Longitudinal compressive strength, SaC | 133 MPa |
| Transverse compressive strength, SbC | 133 MPa |
| Matrix mode shear strength, Sab, Sbc, Sca | 76 MPa |
| Strength properties strain rate coefficient, CERATE1 | 0.024 |
| Longitudinal moduli strain rate coefficient, CERATE2 | 0.03 |
| Shear moduli strain rate coefficient, CERATE3 | 0.03 |
| Transverse moduli strain rate coefficient, CERATE4 | 0.03 |
Table 5.
Delamination damage model input data for Tiebreak contact.
Table 5.
Delamination damage model input data for Tiebreak contact.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|
| Normal failure stress (peak traction), NFLS | 40 MPa |
| Shear failure stress (peak traction), SFLS | 60 MPa |
| Exponent of the mixed mode criterion (Power law), PARAM | 2 |
| Normal energy release rate, ERATEN | 1.7 MPa·mm |
| Shear energy release rate, ERATES | 0.789 MPa·mm |
| Tangential stiffness to normal stiffness, CT2CN | 1 |
| Normal stiffness, CN | 106 MPa/mm |
Table 6.
Ground impact parameters.
Table 6.
Ground impact parameters.
| | Impactor’s Initial Velocity | Total Energy |
|---|
| i. | 10 m/s | 15 J |
| ii. | 15 m/s | 33.75 J |
| iii. | 20 m/s | 60 J |
| iv. | 25 m/s | 93.75 J |
Table 7.
Material input data for ABS properties.
Table 7.
Material input data for ABS properties.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|
| | MAT_12 |
| Density, RO | 1040 kg/m3 |
| Shear modulus, G | 0.85 GPa |
| Yield stress, SIGY | 41.5 MPa |
| Bulk modulus, BULK | 3.94 GPa |
| | MAT_ADD_EROSION |
| Equivalent stress at failure, SIGVM | 55 MPa |
Table 8.
Material parameters of the cell components implemented in MAT_01.
Table 8.
Material parameters of the cell components implemented in MAT_01.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|
| | Aluminum foil | Polymer gel |
| Density, RO | 2700 kg/m3 | 900 kg/m3 |
| Young’s modulus, E | 69 GPa | 1.5 GPa |
| Poisson’s ratio, PR | 0.33 (-) | 0.45 (-) |
Table 9.
Pole impact model parameters.
Table 9.
Pole impact model parameters.
| | Impactor’s Initial Velocity | Total Energy |
|---|
| i. | 10 m/s | 350 J |
| ii. | 12.5 m/s | 547 J |
| iii. | 15 m/s | 787 J |
Table 10.
Permanent deformation of the housing and the cell pack in the z direction after ground impact of 10, 15, 20, 25 m/s.
Table 10.
Permanent deformation of the housing and the cell pack in the z direction after ground impact of 10, 15, 20, 25 m/s.
| Impact Velocity | Permanent Deformation |
|---|
| | | Housing | Cell Pack |
| i. | 10 m/s | 0.07 mm | 0.01 mm |
| ii. | 15 m/s | 0.57 mm | 0.72 mm |
| iii. | 20 m/s | 1.01 mm | 1.25 mm |
| iv. | 25 m/s | 1.07 mm | 1.32 mm |