Postmortem Analysis of 18650 Graphite/LFP Cells in a Long-Term Aging Study for Second-Life Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Graphite/LFP Cell Aging Experiment
2.2. Pristine Cell Characterization
2.3. Aged Electrodes Characterization
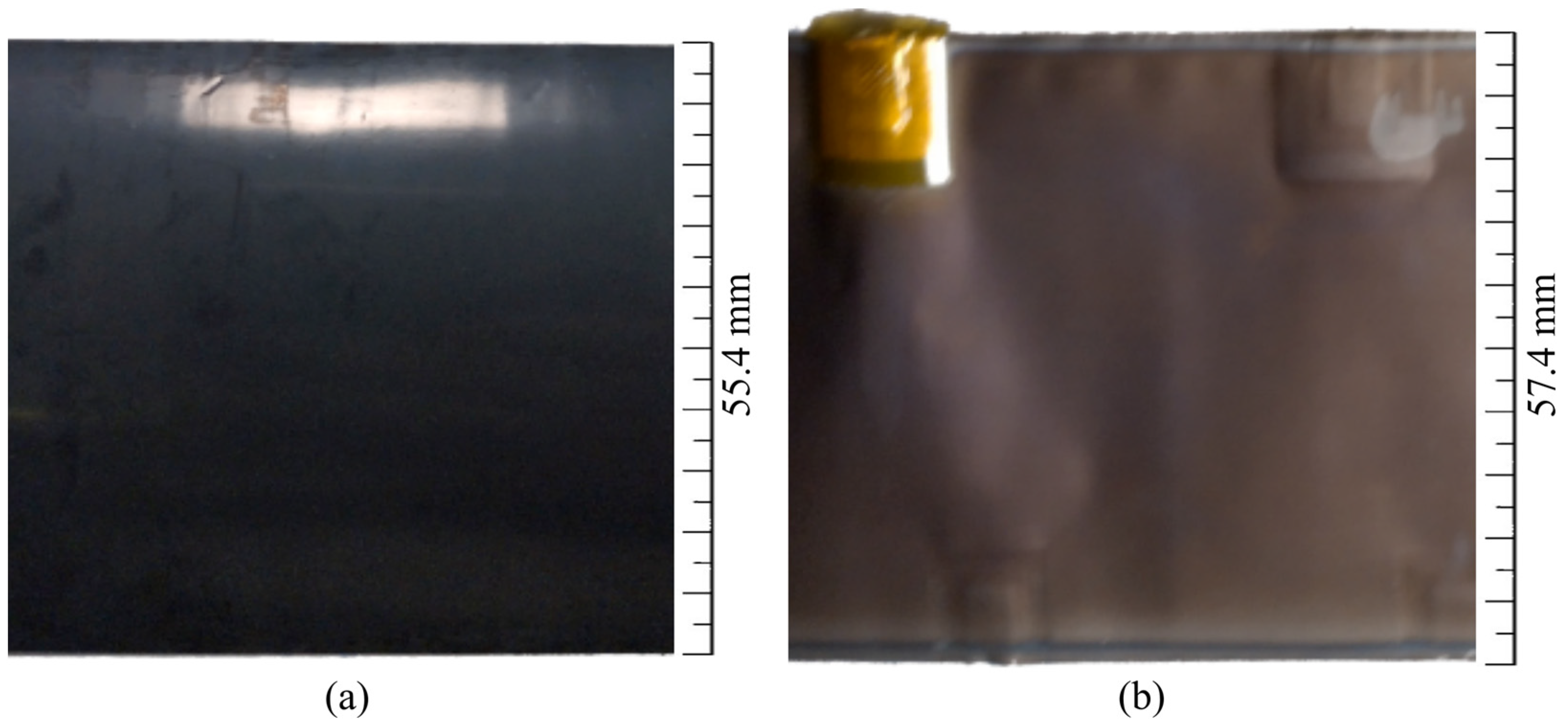
2.3.1. Macroscopic Analysis
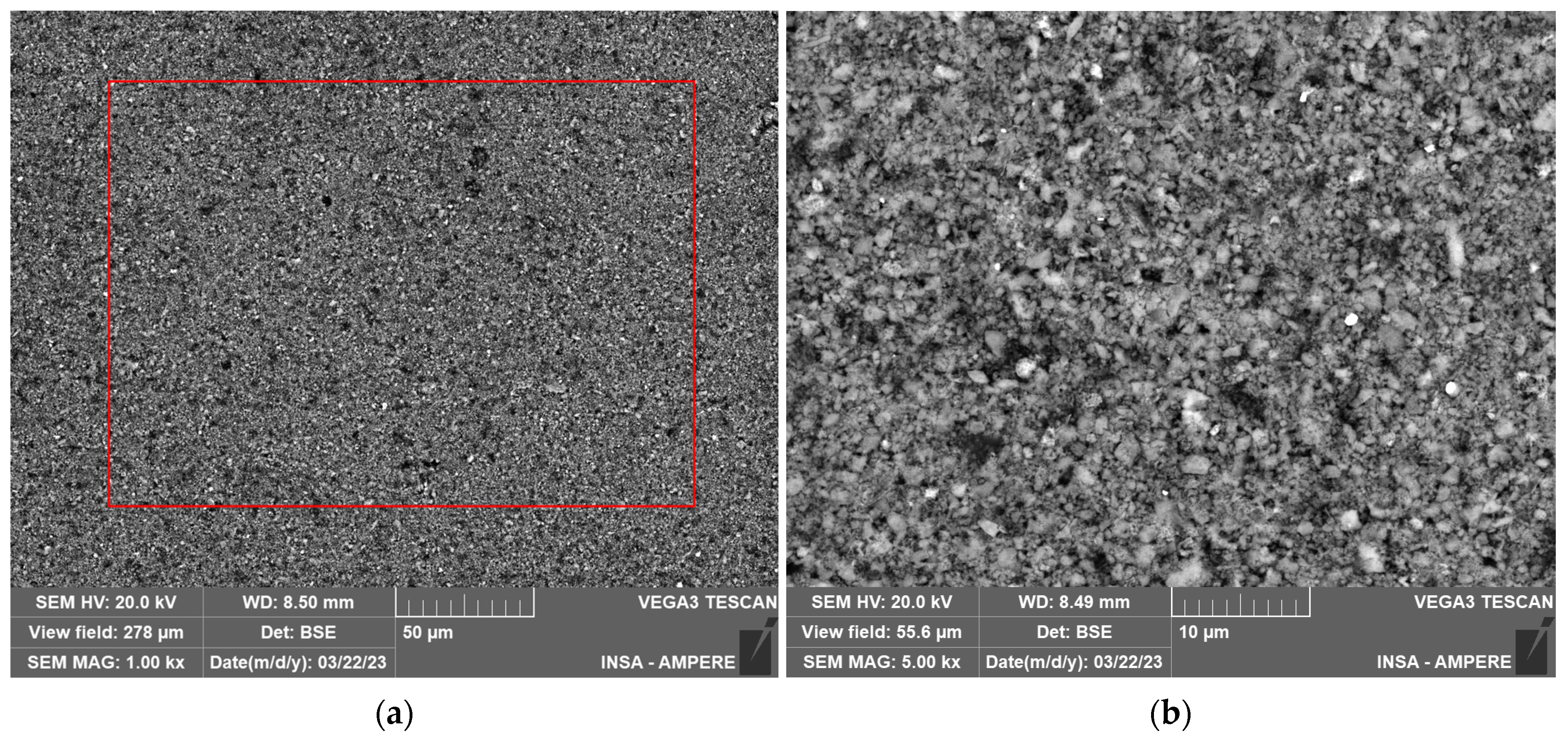
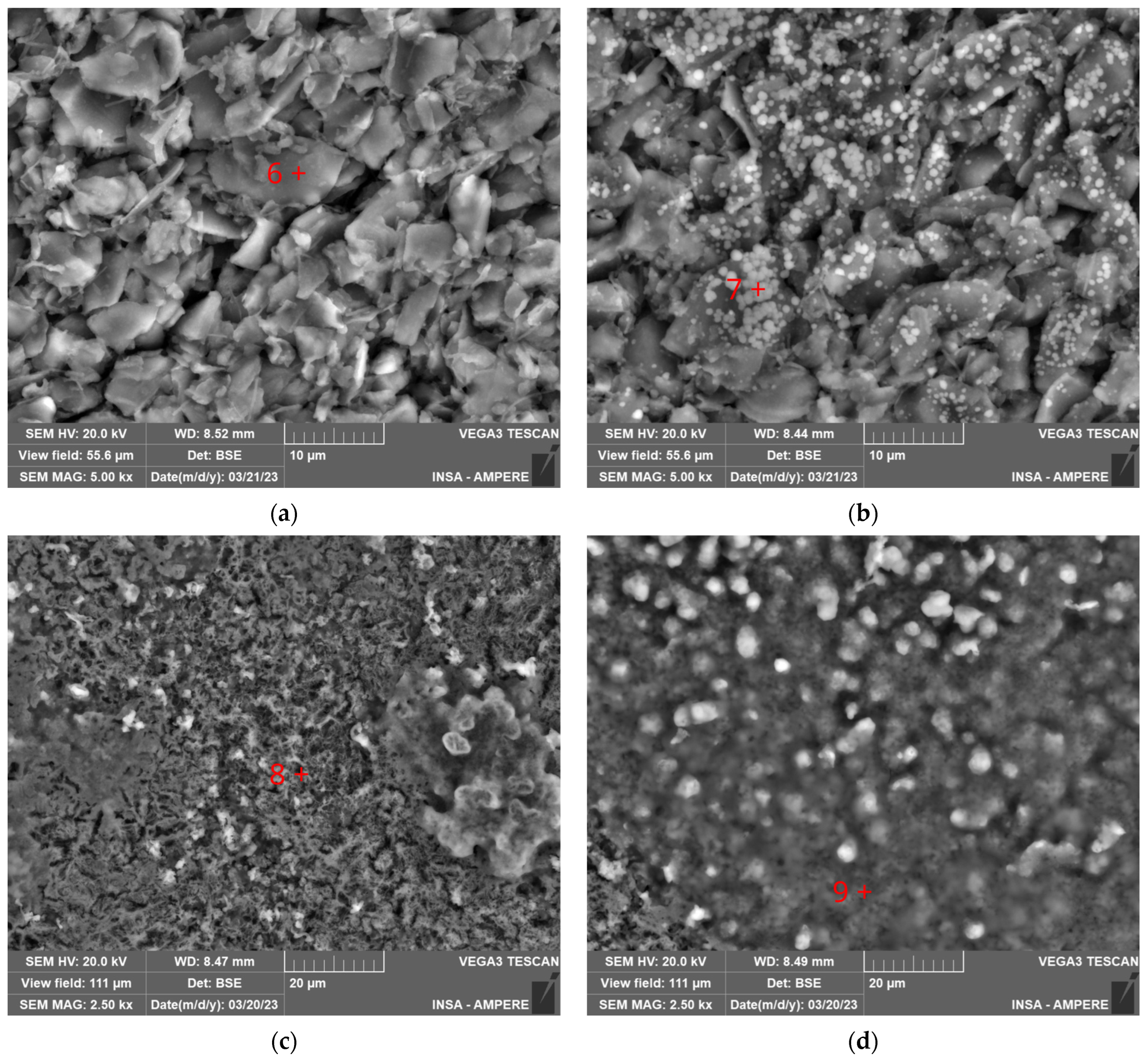
2.3.2. SEM and EDXS Analysis
2.3.3. Electrochemical Analysis in Coin Cells
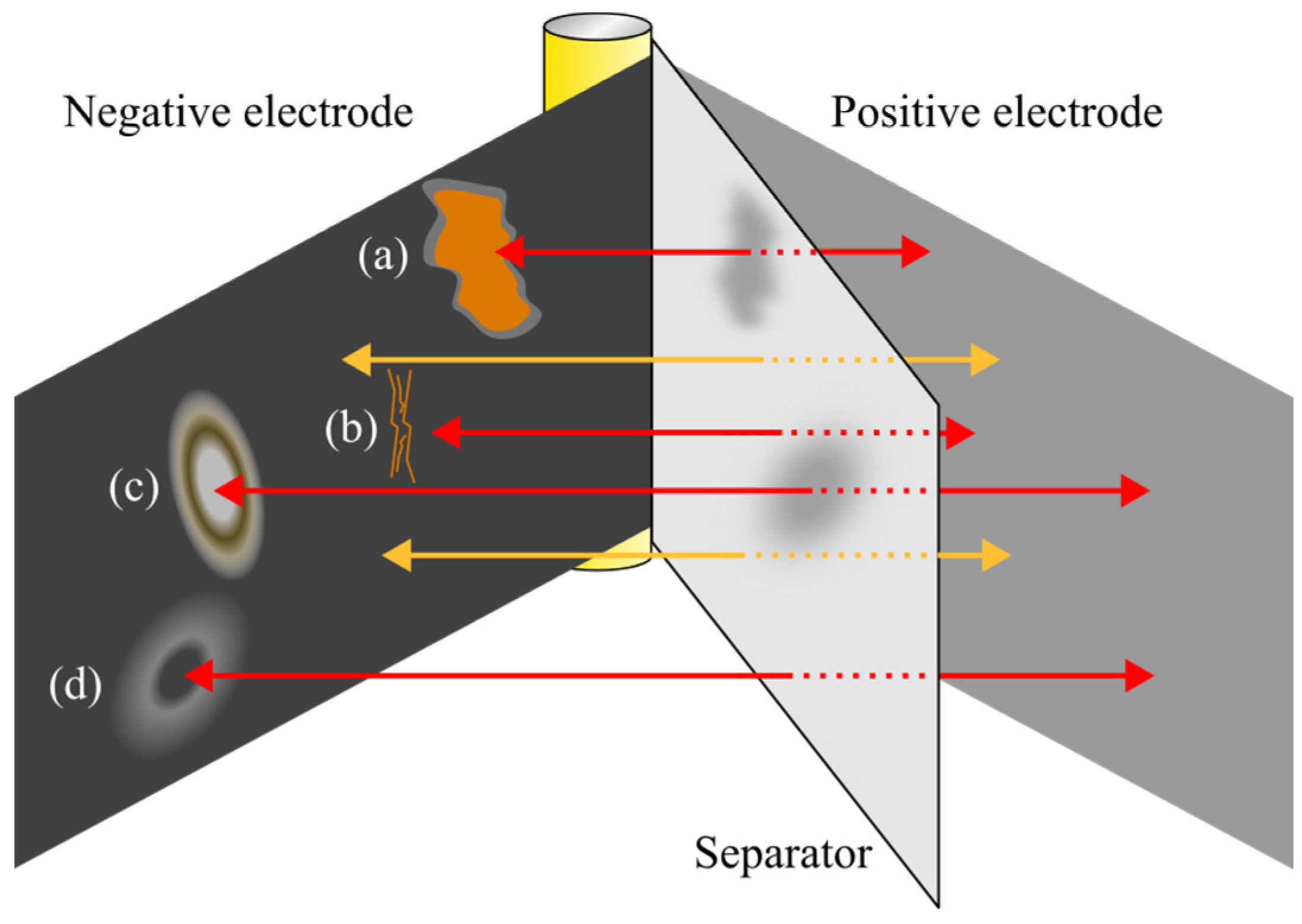
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinez-Laserna, E.; Sarasketa-Zabala, E.; Villarreal Sarria, I.; Stroe, D.-I.; Swierczynski, M.; Warnecke, A.; Timmermans, J.-M.; Goutam, S.; Omar, N.; Rodriguez, P. Technical Viability of Battery Second Life: A Study From the Ageing Perspective. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 2703–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinard, H.; Redondo-Iglesias, E.; Pelissier, S.; Venet, P. Fast Electrical Characterizations of High-Energy Second Life Lithium-Ion Batteries for Embedded and Stationary Applications. Batteries 2019, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klett, M.; Eriksson, R.; Groot, J.; Svens, P.; Ciosek Högström, K.; Lindström, R.W.; Berg, H.; Gustafson, T.; Lindbergh, G.; Edström, K. Non-Uniform Aging of Cycled Commercial LiFePO4//Graphite Cylindrical Cells Revealed by Post-Mortem Analysis. J. Power Sources 2014, 257, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumhöfer, T.; Brühl, M.; Rothgang, S.; Sauer, D.U. Production Caused Variation in Capacity Aging Trend and Correlation to Initial Cell Performance. J. Power Sources 2014, 247, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, M.; Nieto, N.; Käbitz, S.; Schmalstieg, J.; Blanke, H.; Warnecke, A.; Sauer, D.U. Calendar and Cycle Life Study of Li(NiMnCo)O2-Based 18650 Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 248, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.J.; Harris, D.J.; Li, C. Failure Statistics for Commercial Lithium Ion Batteries: A Study of 24 Pouch Cells. J. Power Sources 2017, 342, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, R.; Briat, O.; Gyan, P.; Vinassa, J.-M. Fast Charging for Electric Vehicles Applications: Numerical Optimization of a Multi-Stage Charging Protocol for Lithium-Ion Battery and Impact on Cycle Life. J. Energy Storage 2021, 40, 102756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, R.; Briat, O.; Gyan, P.; Vinassa, J.-M. Comparison of the Impact of Fast Charging on the Cycle Life of Three Lithium-Ion Cells under Several Parameters of Charge Protocol and Temperatures. Appl. Energy 2021, 283, 116344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, P.M.; Bills, A.; Brosa Planella, F.; Dechent, P.; Dos Reis, G.; Dubarry, M.; Gasper, P.; Gilchrist, R.; Greenbank, S.; Howey, D.; et al. Review—“Knees” in Lithium-Ion Battery Aging Trajectories. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 060517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Fernández, C.; Yu, T.F.; Widanage, W.D.; Marco, J. Critical Review of Non-Invasive Diagnosis Techniques for Quantification of Degradation Modes in Lithium-Ion Batteries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 109, 138–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, W.; Venet, P.; Bultel, Y.; Sari, A.; Riviere, E. Aging in First and Second Life of a G/LFP 18650 Cell: Diagnosis and Evolution of the State of Health of the Cell and the Negative Electrode under Cycling. Batteries 2024. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Birkl, C.R.; Roberts, M.R.; McTurk, E.; Bruce, P.G.; Howey, D.A. Degradation Diagnostics for Lithium Ion Cells. J. Power Sources 2017, 341, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, T.; Iturrondobeitia, A.; Kasper, M.; Ghanbari, N.; Aguesse, F.; Bekaert, E.; Daniel, L.; Genies, S.; Gordon, I.J.; Löble, M.W.; et al. Review—Post-Mortem Analysis of Aged Lithium-Ion Batteries: Disassembly Methodology and Physico-Chemical Analysis Techniques. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, A2149–A2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, T.; Wilka, M.; Kasper, M.; Fleischhammer, M.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M. Temperature Dependent Ageing Mechanisms in Lithium-Ion Batteries—A Post-Mortem Study. J. Power Sources 2014, 262, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.C.; Kassam, A.; Sinha, N.N.; Downie, L.E.; Solnickova, L.; Way, B.M.; Dahn, J.R. Predicting and Extending the Lifetime of Li-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, A1451–A1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiaszny, B.; Ziegler, J.C.; Krauß, E.E.; Schmidt, J.P.; Ivers-Tiffée, E. Electrochemical Characterization and Post-Mortem Analysis of Aged LiMn2O4–Li(Ni0.5Mn0.3Co0.2)O2/Graphite Lithium Ion Batteries. Part I: Cycle Aging. J. Power Sources 2014, 251, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, T.; Gorse, S.; Samtleben, T.; Schneider, G.; Knoblauch, V.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M. A Mechanical Aging Mechanism in Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, A1742–A1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Addendum 15: Global Technical Regulation No. 15, Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure. ECE/TRANS/180/Add.15; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–234. [Google Scholar]
- Dubarry, M.; Truchot, C.; Liaw, B.Y. Synthesize Battery Degradation Modes via a Diagnostic and Prognostic Model. J. Power Sources 2012, 219, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shellikeri, A.; Watson, V.; Adams, D.; Kalu, E.E.; Read, J.A.; Jow, T.R.; Zheng, J.S.; Zheng, J.P. Investigation of Pre-Lithiation in Graphite and Hard-Carbon Anodes Using Different Lithium Source Structures. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, A3914–A3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ender, M.; Joos, J.; Weber, A.; Ivers-Tiffée, E. Anode Microstructures from High-Energy and High-Power Lithium-Ion Cylindrical Cells Obtained by X-Ray Nano-Tomography. J. Power Sources 2014, 269, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, A.M.; Edström, K. Chemical Composition and Morphology of the Elevated Temperature SEI on Graphite. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, A1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Yang, G.; Rajput, N.N.; Self, J.; Park, S.-W.; Nanda, J.; Persson, K.A. The Influence of FEC on the Solvation Structure and Reduction Reaction of LiPF6/EC Electrolytes and Its Implication for Solid Electrolyte Interphase Formation. Nano Energy 2019, 64, 103881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parimalam, B.S.; MacIntosh, A.D.; Kadam, R.; Lucht, B.L. Decomposition Reactions of Anode Solid Electrolyte Interphase (SEI) Components with LiPF6. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 22733–22738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K. Predicting the Voltage Dependence of Interfacial Electrochemical Processes at Lithium-Intercalated Graphite Edge Planes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 1637–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henschel, J.; Horsthemke, F.; Stenzel, Y.P.; Evertz, M.; Girod, S.; Lürenbaum, C.; Kösters, K.; Wiemers-Meyer, S.; Winter, M.; Nowak, S. Lithium Ion Battery Electrolyte Degradation of Field-Tested Electric Vehicle Battery Cells—A Comprehensive Analytical Study. J. Power Sources 2020, 447, 227370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spotte-Smith, E.W.C.; Petrocelli, T.B.; Patel, H.D.; Blau, S.M.; Persson, K.A. Elementary Decomposition Mechanisms of Lithium Hexafluorophosphate in Battery Electrolytes and Interphases. ACS Energy Lett. 2023, 8, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurbach, D. Review of Selected Electrode–Solution Interactions Which Determine the Performance of Li and Li Ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 2000, 89, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.; Dong, P.; Ge, H.; Fu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. Capacity Plunge of Lithium-Ion Batteries Induced by Electrolyte Drying-out: Experimental and Modeling Study. J. Energy Storage 2021, 42, 103013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweidler, S.; De Biasi, L.; Schiele, A.; Hartmann, P.; Brezesinski, T.; Janek, J. Volume Changes of Graphite Anodes Revisited: A Combined Operando X-Ray Diffraction and In Situ Pressure Analysis Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 8829–8835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
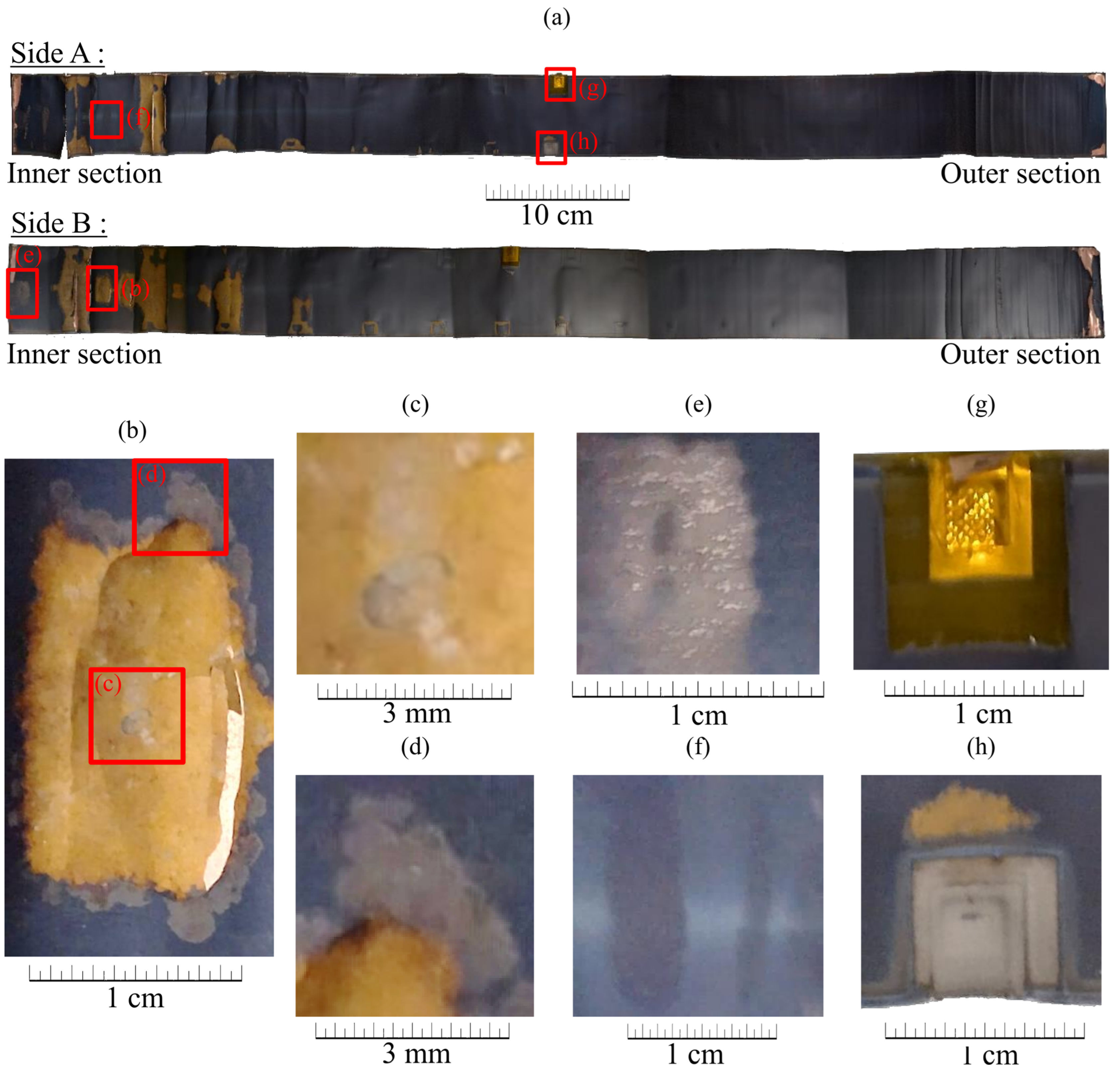






| Grey Areas in LFP Electrode: Position 1 from Figure 3a 1 | White Defect in LFP Electrode: Position 2 from Figure 3a 1 | Dark Grey Areas in LFP Electrode: Position 3 from Figure 3a 1 | Graphite Particle in Graphite Electrode: Position 4 from Figure 3b 1 | Defect in Graphite Electrode: Position 5 from Figure 3b 1 | EDXS Mapping on Graphite Electrode: Zone from Figure 3b 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 15.09 ± 4.93 | 18.66 ± 5.82 | 15.9 ± 5.04 | 86.79 ± 19.14 | 78.38 ± 17.48 | 78.60 ± 17.20 |
| Fe | 30.43 ± 1.69 | 29.0 ± 1.62 | 26.1 ± 1.46 | / | / | / |
| F | 1.18 ± 0.62 | 7.37 ± 2.46 | 4.83 ± 1.66 | 1.57 ± 0.68 | 10.04 ± 2.78 | 6.64 ± 1.90 |
| N | / | / | / | 10.04 ± 4.00 | 5.65 ± 2.50 | 8.33 ± 3.10 |
| O | 36.5 ± 9.03 | 53.71 ± 12.84 | 31.80 ± 7.94 | / | 3.26 ± 1.32 | 4.08 ± 1.46 |
| Cu | / | / | / | 1.13 ± 0.14 | 1.74 ± 0.18 | 1.45 ± 0.14 |
| P | 15.66 ± 1.27 | 13.26 ± 1.09 | 14.36 ± 1.18 | 0.48 ± 0.10 | 0.93 ± 0.14 | 0.90 ± 0.12 |
| EDXS Mapping on Aged LFP from Figure 5a 1 | Non-Damaged Graphite from Position 6 in Figure 6a 1 | Graphite Grain Covered with LiPF6 from Position 7 in Figure 6b 1 | Heterogeneous Bulky Deposit on Top Graphite from Position 8 in Figure 6c 1 | Bulky Deposit on Top Graphite from Position 9 in Figure 6d 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 12.40 ± 2.84 | 77.59 ± 17.34 | 28.45 ± 7.44 | 43.96 ± 10.86 | 18.9 ± 5.18 |
| Fe | 30.06 ± 1.67 | / | / | / | / |
| F | 3.76 ± 0.91 | 1.75 ± 0.74 | 62.06 ± 14.08 | * | * |
| N | / | 11.58 ± 4.44 | / | * | * |
| O | 37.21 ± 7.79 | 7.11 ± 2.50 | 7.80 ± 15.86 | 51.50 ± 12.88 | 77.11 ± 17.52 |
| Cu | / | 1.98 ± 0.18 | 1.69 ± 0.86 | 4.54 ± 0.36 | 3.99 ± 0.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wheeler, W.; Bultel, Y.; Venet, P.; Sari, A.; Riviere, E. Postmortem Analysis of 18650 Graphite/LFP Cells in a Long-Term Aging Study for Second-Life Applications. Batteries 2024, 10, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10040119
Wheeler W, Bultel Y, Venet P, Sari A, Riviere E. Postmortem Analysis of 18650 Graphite/LFP Cells in a Long-Term Aging Study for Second-Life Applications. Batteries. 2024; 10(4):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10040119
Chicago/Turabian StyleWheeler, William, Yann Bultel, Pascal Venet, Ali Sari, and Elie Riviere. 2024. "Postmortem Analysis of 18650 Graphite/LFP Cells in a Long-Term Aging Study for Second-Life Applications" Batteries 10, no. 4: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10040119
APA StyleWheeler, W., Bultel, Y., Venet, P., Sari, A., & Riviere, E. (2024). Postmortem Analysis of 18650 Graphite/LFP Cells in a Long-Term Aging Study for Second-Life Applications. Batteries, 10(4), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10040119








