Abstract
Purpose: In the current study, we aimed to look into the macroscopic and microscopic dose enhancement effect of metallic nanoparticles in interstitial brachytherapy of gastric adenocarcinoma by Iodine-125 source using a nano-lattice model in MCNPX (2.7) and MCNP6.1 codes. Materials and methods: Based on a nano-lattice simulation model containing a radiation source and a tumor tissue with cellular compartments loaded with 7 mg/g spherical nanoparticles, the microscopic and macroscopic levels of energy deposition by the secondary electrons was estimated. Results: The results show that the values of macroscopic DEF are higher than microscopic DEF values and the macroscopic DEF values decrease by increasing the distance from the surface of brachytherapy source. Accordingly, it could be noted that gold nanoparticles have the highest radiosensitization effect among the other nanoparticles and the related DEF value is close to the resultant DEF values for bismuth nanoparticles. Moreover, the results revealed a remarkable discrepancy between the DEF and secondary electron spectra calculated by MCNPX (2.7) and MCNP6.1 codes, which could be justified by the difference in energy cut-off and electron transport algorithms of two codes. Conclusions: According to the both MCNPX (2.7) and MCNP6.1 outputs, it could be concluded that the presence of metallic nanoparticles in the tumor tissue of gastric adenocarcinoma increases the physical effectiveness of brachytherapy by I-125 source. This study aims to provide recommendations for future preclinical studies. Actually, the results presented herein give a physical view of radiosensitization potential of different metallic nanoparticles and could be considered in design of analytical and experimental radiosensitization studies in tumor regions using various radiotherapy modalities in the presence of heavy nanomaterials.
1. Introduction
To further widen the therapeutic window, new advances in nanotechnology are investigated to enhance therapeutic outcome of cancer therapy [1,2]. Owing to the recent developments of nanotechnology, it is increasingly possible to selectively accumulate metallic nanomaterials in the tumor cells to enhance the contrast between tumor and normal tissues, leading to increased radiosensitizing properties when compared to radiotherapy alone. Numerous investigations have been conducted to assess the radiosensitization features of various metallic nanoparticles in more realistic environment including in vitro and in vivo conditions for a wide range of cancerous tissues and cells [3,4]. Nevertheless, the contribution of different influencing parameters and processes including, physical, chemical and biological process in radiosensitization of nanoparticles have not been fully understood. There are a several studies regarding the ability of MC simulations in predicting the radiosensitization potential of nanoparticles [5].
To deliver the prescribed radiation dose to the tumor with a nearby source, the high dose rate and rapid dose drop off after tumor is required for effective tumor treatment while sparing the normal tissue around it. Brachytherapy, which entails low-energy photons (≤500 keV), is one among the foremost effective approaches in radiotherapy for high Z material injection [6]. Bahreyni Toossi et al. [7] indicated the shielding effect of nanoparticles on the tissues after the nanoparticle-loaded tumor as the advantage of nanoparticles-aided brachytherapy. The physical mechanism for high Z nanoparticle-mediated radiosensitization relies on the release of low-energy electrons due to increased attenuation of low-energy photons by high-Z materials through the photoelectric effect. Generation of enormous short-range electrons, known as Auger cascades, show a significantly higher linear energy transfer (LET) can enhance both macroscopic and microscopic dose delivered to the target volume.
Gastric cancer is one among the foremost types of cancer worldwide. Appropriate implantation of I-125 brachytherapy seeds in stomach walls is safe and reliable [8]. Wang and colleagues [9] found that applying the I-125 implantation to the advanced gastric cancer could improve the clinical symptoms and the quality of life of the patients. Ma et al. [10] and Zhang et al. [11] showed that 4Gy irradiation by I-125 brachytherapy source, significantly induced cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis in gastric cancer cells.
Various levels of radiosensitization of nanoparticles have been investigated including the macroscopic and microscopic dose enhancement [12,13,14], where the words micro relate to nanometer to micrometer vicinities of nanoparticle and macro refer to millimeter to centimeter [15]. Monte Carlo (MC) simulation for nanodosimetry is different from macrodosimetry. In nanodosimetery the secondary electrons are tracked down to a very low energy range (~10 eV) within the cellular or DNA medium [16]. Moreover, some particle interactions, such as Auger process, which is not significant in macrodosimetry, has to be implemented properly in the nanometer level.
In the current study, we investigated the macroscopic and microscopic dose enhancement effects of gold, bismuth, gadolinium, hafnium and iridium nanoparticles in interstitial brachytherapy of gastric adenocarcinoma by Iodine-125 (I-125) source using a nano-lattice model in MCNPX (2.7) and MCNP6.1 codes. Although there are several studies regarding nanoparticle-aided radiotherapy, there is no study to address the physical dose enhancement in nano-lattice model in cellular level with differentiation in nucleus and cytoplasm of gastric adenocarcinoma cells and aforementioned nanoparticles. In this MC investigation, we focus on the growing amount of physical evidence which demonstrates metallic nanoparticles as radiosensitizers and show specific impact of Auger electrons in radiosensitization. Furthermore, the induced DEF value by metallic nanoparticles in nanoscale is calculated which can be used in the selection of optimum metallic nanoparticle as a radiosensitizer in future radiobiological and radiosensitization studies. This study also aimed to assess the spectra and fluence of the photo/Auger electrons within a nanoparticle-loaded tumor under x-ray irradiation by I-125 source which can be corresponded well with the nanoparticle dose enhancement factor. It is worth emphasizing that comparison of the results exported from MCNPX (2.7) and MCNP6.1 codes could be helpful to assess the ability of new single-event and condensed-history modalities in photon/electron track in nano-lattice model.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Monte Carlo Code
The MC simulation was performed using MCNPX (2.7.0) and MCN6.1.0 (database: ENDF/B-VI Release 8). In this work, the single-event algorithm was utilized for electron transport in the MCNP6.1 version using eprdata12 photon library (p. 12). The brachytherapy source of I-125 was simulated as radiation source. The dose delivered by secondary electrons was calculated in the tumor tissue of gastric adenocarcinoma and its cytoplasm and nucleus, using *F8: e tally. The *F8 tally directly scores the deposited energy (MeV) by each electron and tracks the secondary particle in the analogue manner since their absorption, escape, or other terminal event (such as energy decreasing below the cut-off). In this study, MC methods were used to determine the macroscopic dose enhancement factors. Furthermore, the microscopic dose enhancement factors were determined in cytoplasm and nucleus of the gastric adenocarcinoma cells. Each photon history was traced down to 1 keV, as a default cutoff energy set by the MCNPX code. While, for MCNP6.1 code each photon history was traced down to 10 eV, a default cutoff energy set.
Physically, the dose enhancement factor (DEF) is defined as the factor by which the water equivalent dose is increased due to the presence of nanoparticles: Equation (1):
In order to determine the secondary electron spectra within a tumor tissue loaded by metallic nanoparticles during brachytherapy with I-125, the MCNPX and MCNP6 codes were modified to output the energy of any electron generated from Compton scattering, photoelectric absorption and atomic relaxation for a proper binning depending on the electron energy and interaction type using F4 tally.
For a better estimation of the secondary electron spectra, a realistic energy spectrum of I-125 source measured outside a seed was used (Table 1). In this simulation study, we used I-125 seed source model which includes I-125 adsorbed on palladium-coated silvers spheres of 0.5 mm in diameter [6]. The capsule is titanium (density: 4.506 g/cm3) of 4.75 mm in length and 0.8 mm in diameter.

Table 1.
Physical characteristics and source model of I-125 brachytherapy source.
2.2. Geometry of the Simulation
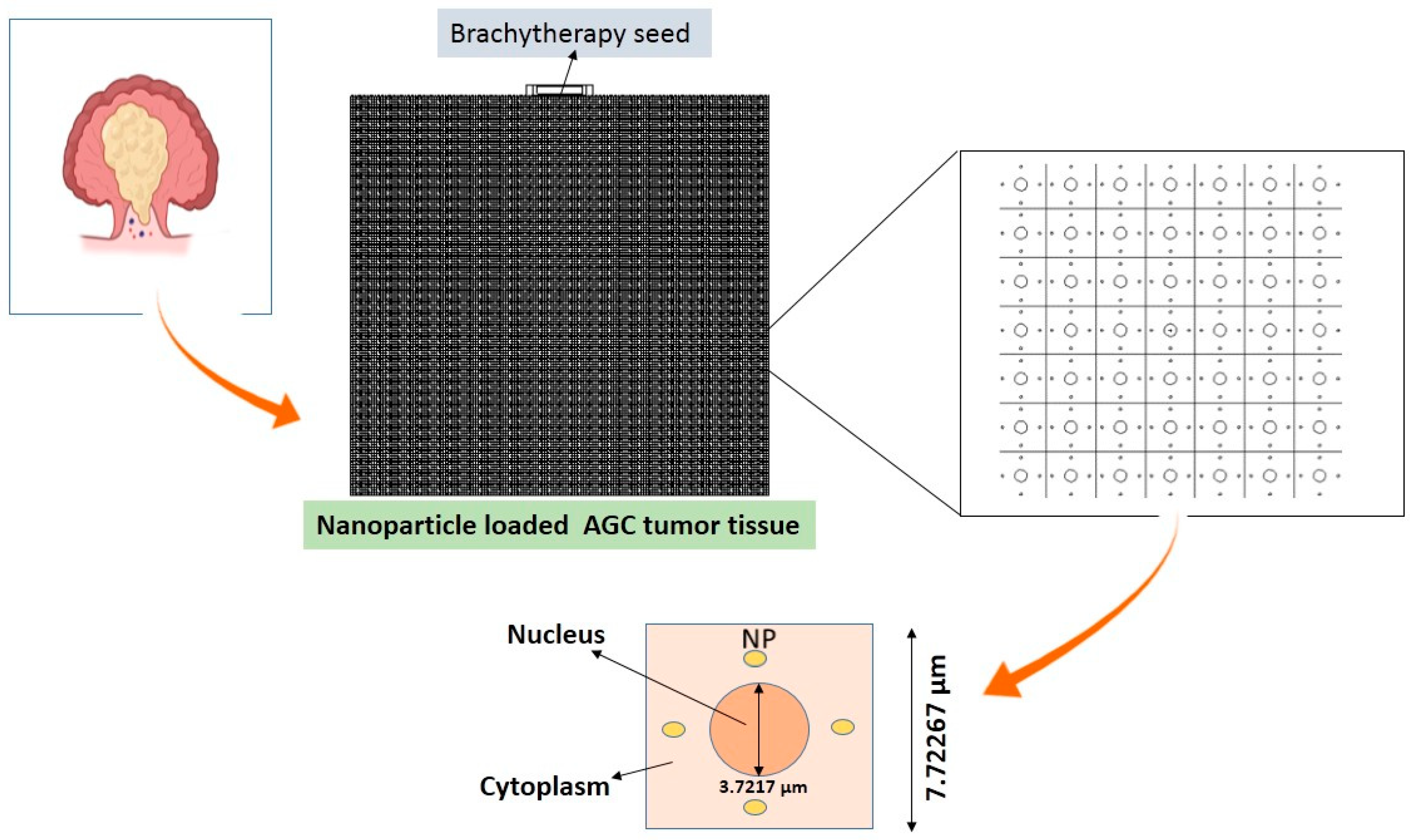
As it is illustrated in Figure 1, a cube-shaped tumor tissue of gastric adenocarcinoma was simulated with MC nanoparticle transport code system (MCNP) code. Gastric adenocarcinoma cells were defined as a cube with 7.72267 µm side with a spherical nucleus (diameter is 3.7217 µm) in the center. We used a simplified multi-cell configuration including tumor cells with cytoplasm loaded with spherical nanoparticles and a centrally located nucleus. Tumor tissue (cytoplasm of the cells) was loaded with 7 mg/g of gold, bismuth, gadolinium nanoparticles [17] with an attached brachytherapy source of I-125. Spherical nanoparticles with a radius of 25 nm were simulated in cytoplasm of each cell (Figure 1). Studied nanoparticles comprised of Bismuth (Bi, Z = 83, density = 9.78 g/cm3), Gold (Au, Z = 79, density = 19.32 g/cm3), Gadolinium (Gd, Z = 64, density = 7.89 g/cm3), Hafnium (Hf, Z = 72, density = 13.31 g/cm3) and Iridium (Ir, Z = 77, density = 22.56 g/cm3).

Figure 1.
The simulated nanoparticle-loaded gastric adenocarcinoma tumor tissue irradiated by brachytherapy seed of I-125.
Material composition of the tumor was taken as defined by the International Commission on Radiation Units and measurements (ICRU1989). In this simulation study, we used nano-lattice model as the more realistic model to simulate the nano-scale of nanoparticles. Based on a nano-lattice simulation model containing a radiation source and target loaded with nanoparticle in a bulk tumor or cellular medium, the energy deposited by the secondary electrons and the macroscopic and microscopic DEF can accurately be determined. Each nanoparticle-loaded tumor cell was considered to have a uniform distribution of nanoparticles. MCNPX code visual editor was used to ensure accurate geometry and monitor photon paths.
3. Results and Discussion
In this study, we assumed uniform distribution of nanoparticles within the cytoplasm of gastric adenocarcinoma tumor tissue using nano-lattice model (Figure 1). A uniform distribution of nanoparticles within tumor tissue requires a sustained release of the nanoparticles, or direct injection of nanoparticles into the tumor. Unlike untargeted nanoparticles, small targeted nanoparticles have the potential to penetrate the tumor interstitium and bind specifically to tumor cells, resulting in a more uniform and homogeneous distribution within the tumor tissue. Nanoparticles localization plays an important role in radiosensitization of cells specifically when the energy of photon source is below the K-edge of targeted nanoparticle [18]. Nanoparticles commonly connect with cells in their cytoplasm and/or cytoplasmic vesicles [19] and most nanoparticles do not penetrate the nucleus [20,21]. Zabihzadeh et al. [22] indicated that nano-lattice model underestimates DEF up to 4% and 3.6% for 30mgr/gr gold and gadolinium nanoparticles, respectively. Zhang et al. [23] reported that simple-mixture model of nanoparticle-loaded tumor overestimates DEF up to 16%, compared to the nano-lattice model.
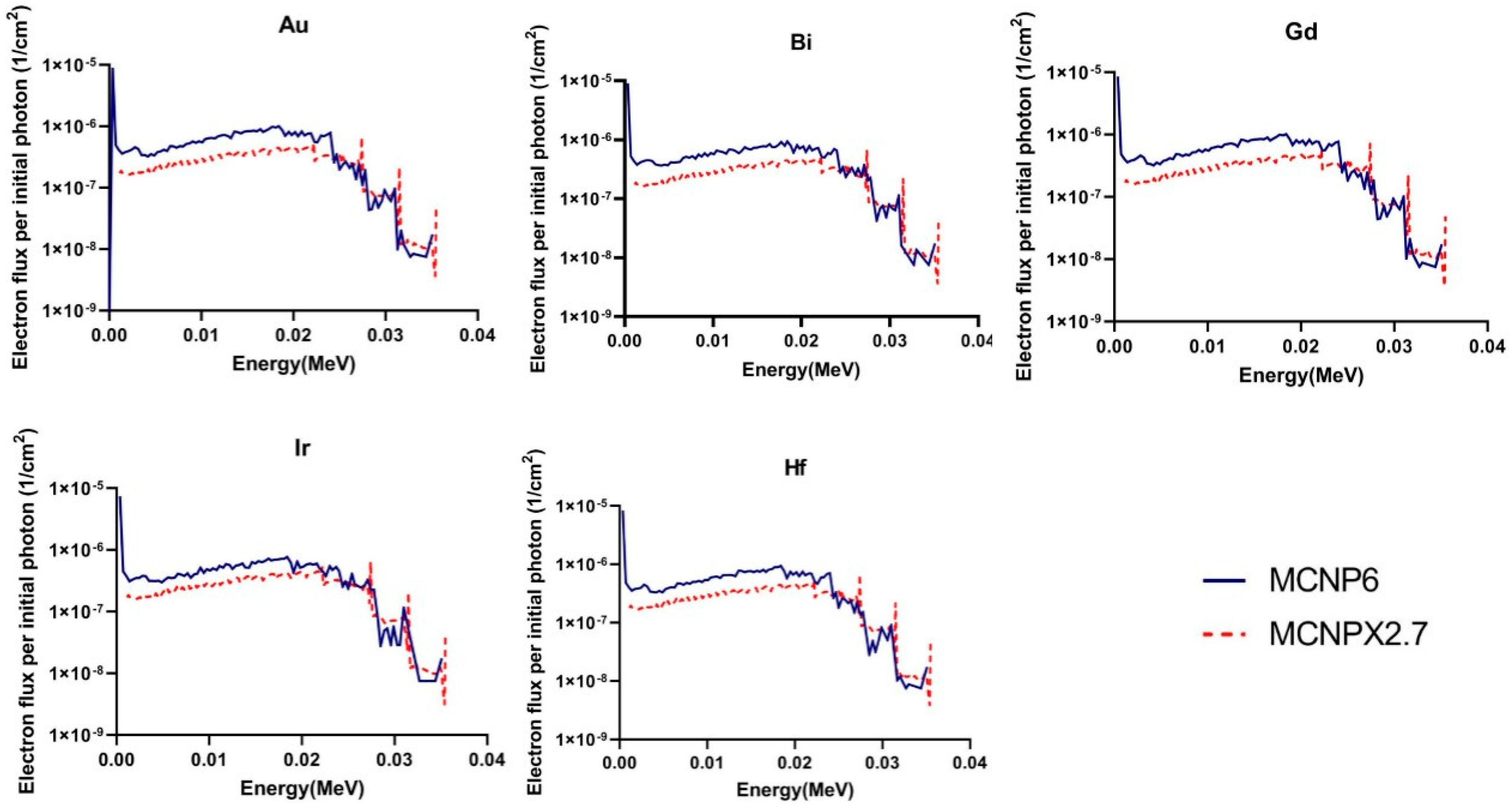
Figure 2 shows the calculated fluence and energy spectra of the generated Auger and photoelectrons within the nanoparticle-loaded tumor during I-125 brachytherapy seed irradiation, exported from MCNPX (2.7) and MCNP6.1 outputs. As it can be seen, there are good agreements between the two electron spectra for electrons higher than 25 keV for all nanoparticles. However, for electrons lower than 25 keV MCNP6.1 code estimates higher number of electrons for all nanomaterials (about 25%) than MCNPX (2.7). Moreover, considerable discrepancy exists between two spectra for electron lower than 1 keV which is completely attributed to the difference in the cut off energy of two codes. MCNPX fails in the energy range below 1 keV because the lowest available energy cutoff for MCNPX is 1 keV for photons and 10 keV for electrons. While for the MCNP6 code, cutoff energy could be set to 1 eV for photons and 10 eV for electrons meaning that the photon history could traced down to 10 eV. Unlike MCNPX codes, which only considers the transition of K-shell and average L-shells, MCNP6 addresses full detailed atomic relaxation cascade. The MCNP6 is able to model complete atomic-relaxation processes, with the emission of fluorescent X-rays and Auger and Coster–Kronig electrons. The discrepancy between secondary electron yields of two codes spectra in energy range of 1–25 keV could be discussed by the difference in electron transport algorithms employed in each code. The2 MCNP6 employs the new single event algorithm. The new single-event mode with the ENDF/B VI.8 database, dispense with the multiple-scattering theories, sub step-based approximations, un-correlated processes, and other aspects of the condensed-history approach, in favor of direct sampling of microscopic data distributions and consequently an accurate low-energy transport. Moreover, a new single event algorithm covers all scattering angles at all energies.
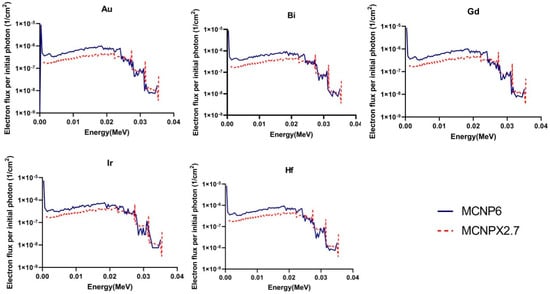
Figure 2.
Calculated fluence and energy spectra of the generated Auger and photo electrons within the nanoparticle-loaded tumor during I-125 brachytherapy seed irradiation, exported from MCNPX (2.7) and MCNP6.1 outputs.
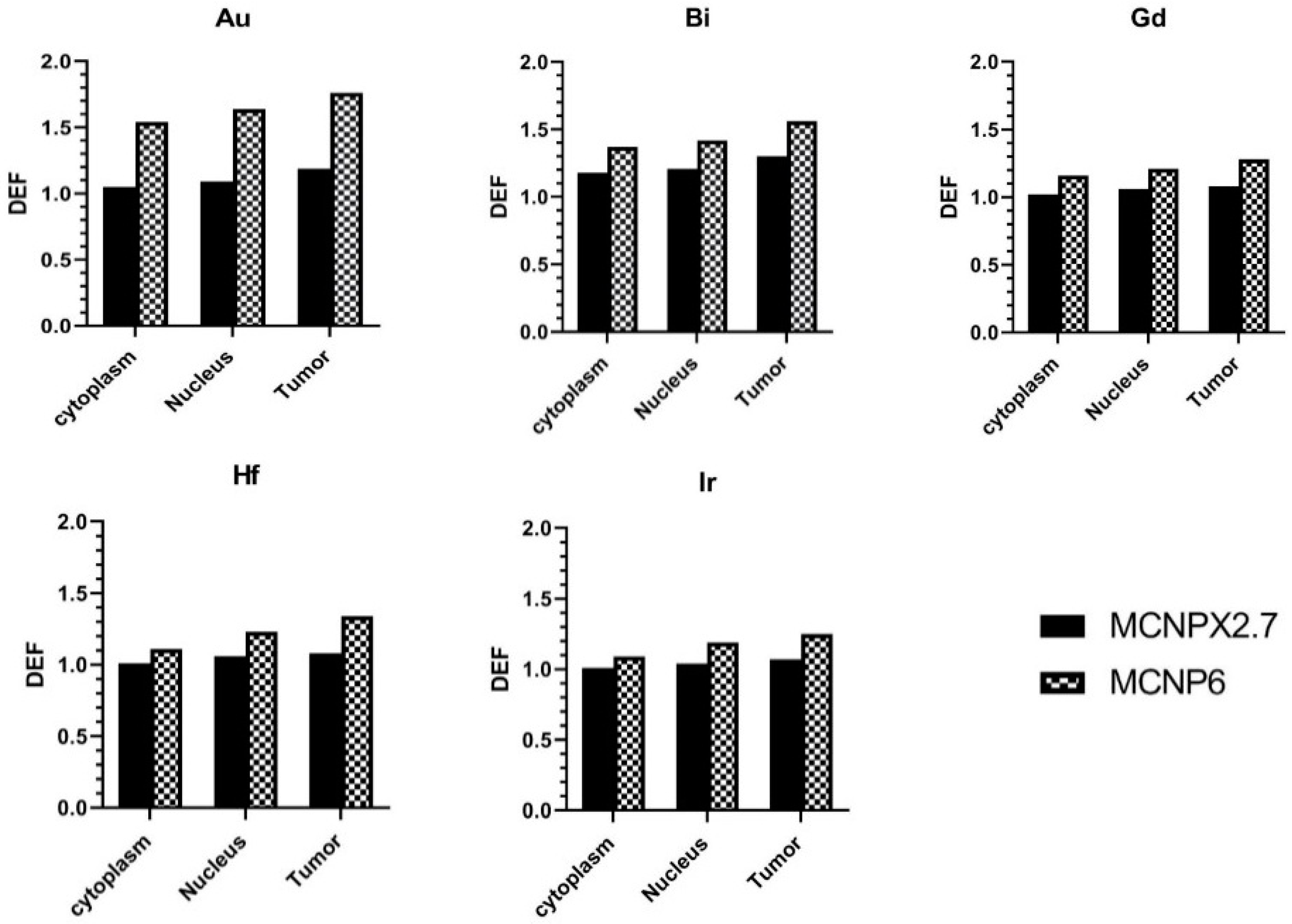
The DEF calculations in tumor tissue (macroscopic), and cytoplasm and nucleus of the cells (microscopic) are summarized in Figure 3, which shows an increased DEF (14–42%) in MCNP6.1 outputs comparing to the MCNPX (2.7). Moreover, it is clear that the DEF values are different for tumor tissue, and cytoplasm and nucleus of the tumor cells. In nanoscale dosimetry, the calculation of absorbed dose and DEF values can be affected by cutoff energy setting during the electron transport [15,24]. As mentioned before, unlike the MCNPX, MCNP6.1 is able to score the electrons with energy less than 1 keV and the discrepancy between the DEFs of two codes could be explained by the difference in exported electron spectra for the electrons lower than 25 keV shown in Figure 2. The MCNPX results are in good agreement with the results reported by Cho et al. [6]. Jones et al. [25] used EGSnrc to directly obtain the spectra of generated secondary electrons. Their results showed that presence of gold nanoparticles during brachytherapy using I-125 X rays could leads to microscopic dose enhancement. Analytical and MC methods have been used to calculate the production of secondary electrons in terms of the DEF. MC results from Seniwal et al. [26] study show that the use of different nanoparticles led to an increase in DEF up to 40%. The macroscopic dose enhancement of 40–70% was reported for I-125, Yb-169, and 50 kVp sources at presence of uniform gold nanoparticle concentration of 7 mg Au/g tumor [17].
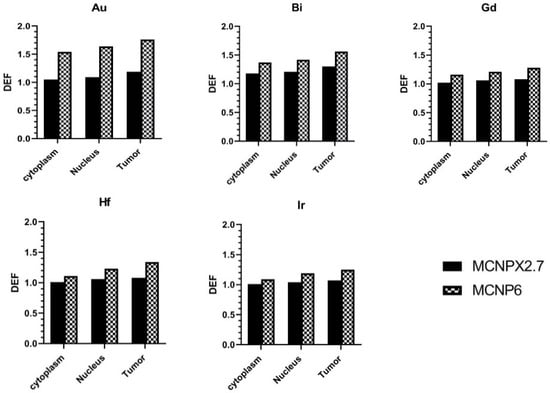
Figure 3.
The calculated dose enhancement factor (DEF) in tumor tissue, cytoplasm and nucleus of the cells loaded with different nanoparticles.
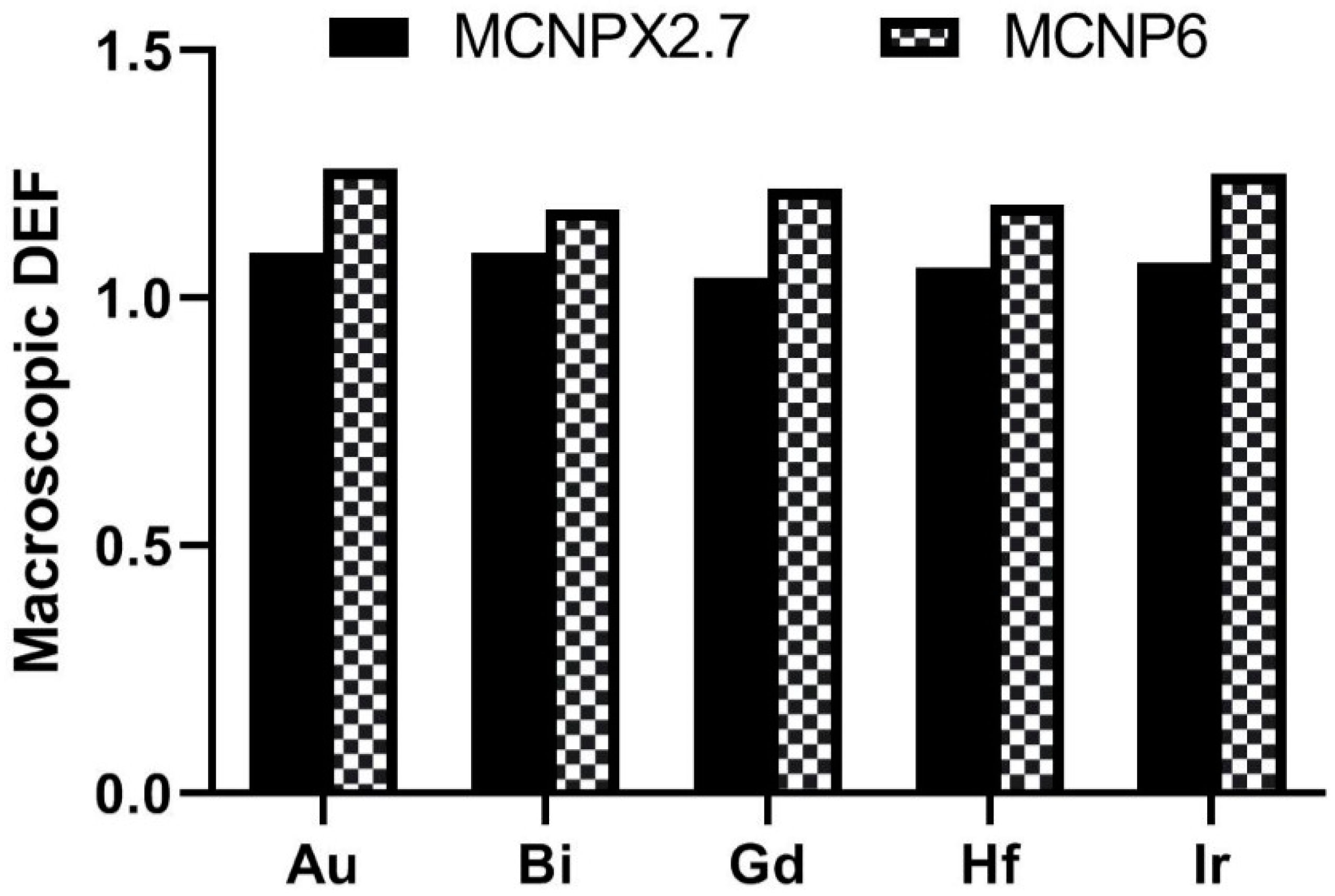
The comparison of macroscopic DEF of different nanoparticles is shown in Figure 4. In a good agreement with Seniwal et al. [26], our results showed that the gold nanoparticles have the highest radiosensitization effect among the other nanoparticles. Accordingly, it could be noted that bismuth provide a DEF close to the DEF of gold nanoparticles. From the MC results using a water phantom, Bahreyni Toossi et al. [7] found that gold nanoparticles showed higher dose enhancement than gadolinium nanoparticles as a radiosensitizer in nanoparticle-loaded tumor. Maggiorella et al. [27] reported hafnium oxide as an effective radiosensitizers of X-ray irradiation. Stewart et al. [19] reported the radioenhancement of 9L-gliosarcoma tumor cells loaded withBi2O3 nanoparticles for both kVp and MV energies. Ghasemi Jangjoo et al. [28] indicated that using the gold nanoparticles and low energy-high dose rate 103Pd source leads to an average DEF of 23% in brachytherapy of prostate cancer. The feasibility of gold nanoparticle-aided radiation therapy using low energy photons (approximately 100 keV) was studied by Roeske et al. [12] predicted a 65% radiation dose enhancement for the tumor loaded with gold nanoparticles than in the absence of gold nanoparticles. In another study, Benlakhdar et al. [29] showed that the presence of gold or platinum nanoparticles in the tumor significantly increases the absorbed dose in the tumor.
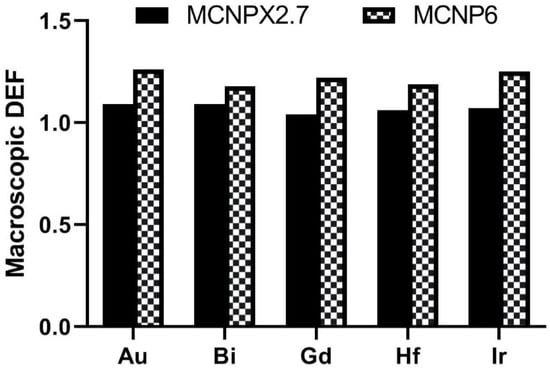
Figure 4.
The comparison of macroscopic dose enhancement factor (DEF) of different nanoparticles.
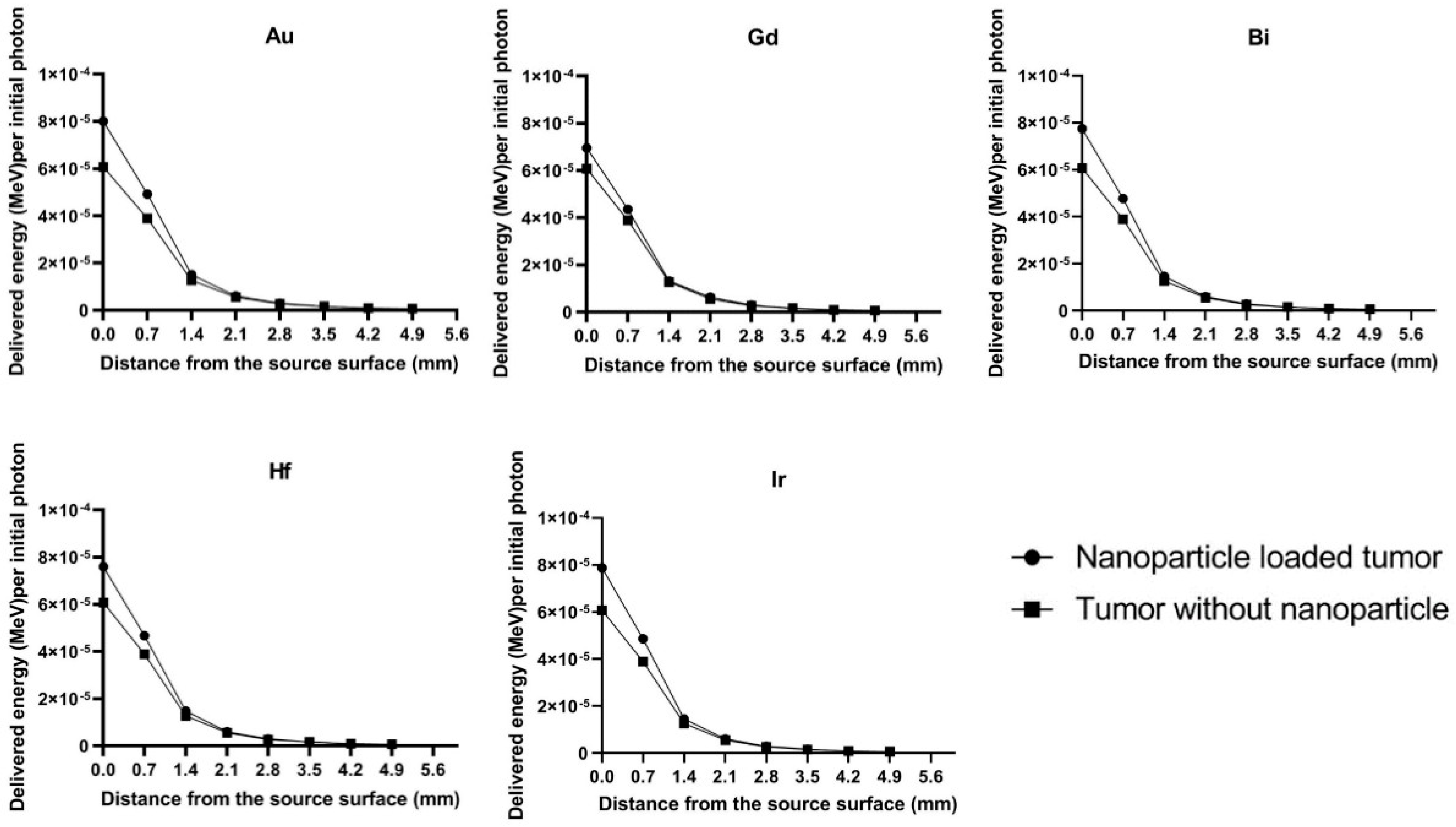
Figure 5 shows the delivered energy (MeV) to the nanoparticle loaded gastric adenocarcinoma tumor (7 mg/g) tissue and the gastric adenocarcinoma tumor without nanoparticle as a function of radial distance from the brachytherapy source (exported from MCNPX (2.7) output). It is clear that the delivered energy in nanoparticle-loaded tumor tissue is more than that of the tumor tissue without nanoparticles (up to 25%), to the distance of about 1.5 mm from the surface of the brachytherapy source. This issue is due to the increased probability of photoelectric interactions in presence of considered nanoparticles which can finally lead to the increment of secondary electron intensity respect to the lack of nanoparticles. Accordingly, it could be concluded that the DEF decreases as a function of distance from the source surface. It has been shown that the microscopic dose over the first 500 nm surrounding the gold nanoparticles was decreased up to 34%, while the microscopic dose was reduced by up to 14% [30]. Macroscopic studies involve physical phenomenon of energy deposition and analysis of the deterministic parameters, such as absorbed dose in tissue with dimensions of millimeter and above. These properties increase the potential of local dose delivery to the tumor as the dose intensity fall off with increasing radial distance. The secondary electrons energy distribution peaks near the radiation source, and within the order of 100 nm. A MC-based gold nanoparticle radiosensitization model was developed by Zygmanski et al. [15] showing that the intensity of photons incident on gold nanoparticles is reduced by only a factor of approximately 2/3 in 100 µm, while the most energetic electrons born in the gold, due to photoelectric interactions, can be stopped in about one tenth of that distance. Auger electrons have very low energies and mostly deposit their energy within 200 nm; their range in tissue is on the order of tens of nm with most energy being deposited within 200 nm [31]. On the other hand, the photoelectrons rang in soft tissue at these energies are about 2–100 μm, 20 or about 1/10 cell diameters. Jones et al. [25] showed the dose enhancement factor of 2 to 20 in the presence of gold nanoparticles at distances below 5 μm from gold nanoparticles, while at distance about 30 μm, it only reaches to 5%.

Figure 5.
The delivered energy (MeV) to the nanoparticle loaded gastric adenocarcinoma tumor (7 mg NP g−1 tumor) tissue and the gastric adenocarcinoma tumor without nanoparticle as a function of radial distance from the brachytherapy source (exported from MCNPX (2.7) output).
4. Conclusions
According to the both MCNPX (2.7) and MCNP6.1 outputs, it could be concluded that the presence of metallic nanoparticles in the tumor tissue of gastric adenocarcinoma increases the physical effectiveness of brachytherapy by I-125 source. The delivered energy in nanoparticle-loaded tumor tissue is 25% more than that of the tumor tissue without nanoparticle. Based on the results, it is obvious that the values of macroscopic DEF are higher than microscopic DEF values, and the macroscopic DEF values decrease as a function of distance from the brachytherapy source surface. It could be noted that the MCNP6.1 is able to present more detailed data about interaction of photon with the matter and score the fluence and energy of produced secondary electrons and absorbed dose higher than the MCNPX (2.7) code for the energy range below 25 keV. According to the results, 14–42% increase in DEF in MCNP6.1 outputs comparing to the MCNPX (2.7).
The results of this study could provide a physical view for the future radiosensitization investigations. It is suggested that both uniform and non-uniform distribution of nanoparticles considered in future studies.
Author Contributions
The core idea of this study came from E.M., A.M. They also directed the other authors and analyzed the collected papers. E.M. and A.M. performed the simulation and data analyses parts. E.M., A.M., M.S.H. and V.T. wrote the manuscript in collaboration with F.S. Final editing was performed by A.M. and H.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This investigation was supported by Drug applied Research Center of Tabriz University of Medical Science funds as a part of the Ph.D. thesis (66155/IR.TBZMED.VCR.REC.1399.438) in medical physics.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
This work was ethically approved by ethical committee of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences (IR.TBZMED.VCR.REC.1399.438).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Molecular Medicine Research Center and Medical Physics department of Tabriz University of Medical Science, for their kind support in terms of scientific and facilities.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mansouri, E.; Mesbahi, A.; Yazdani, P. Analysis of physical dose enhancement in nano-scale for nanoparticle-based radiation therapy: A Cluster and endothelial cell model. Nanomed. J. 2021, 8, 30–41. [Google Scholar]
- Yousefi, V.; Tarhriz, V.; Eyvazi, S.; Dilmaghani, A. Synthesis and application of magnetic@layered double hydroxide as an anti-inflammatory drugs nanocarrier. J. Nanobiotechnology 2020, 18, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, E.; Mesbahi, A.; Malekzadeh, R.; Mansouri, A. Shielding characteristics of nanocomposites for protection against X- and gamma rays in medical applications: Effect of particle size, photon energy and nano-particle concentration. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2020, 59, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parivar, Y.; Mansouri, E.; Eyvazi, S.; Yousefi, V.; Kahroba, H.; Hejazi, M.S.; Mesbahi, A.; Tarhriz, V.; Abolghasemi, M.M. Layered double hydroxide nanoparticles as an appealing nanoparticle in gene/plasmid and drug delivery system in C2C12 myoblast cells. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 436–442. [Google Scholar]
- Moradi, F.; Saraee, K.R.E.; Sani, S.A.; Bradley, D. Metallic nanoparticle radiosensitization: The role of Monte Carlo simulations towards progress. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2021, 180, 109294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, C.H.; Yoon, M. Monte Carlo simulation study on dose enhancement by gold nanoparticles in brachytherapy. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2010, 56, 1754. [Google Scholar]
- Bahreyni Toossi, M.T.; Ghorbani, M.; Mehrpouyan, M.; Akbari, F.; Sobhkhiz Sabet, L.; Soleimani Meigooni, A. A Monte Carlo study on tissue dose enhancement in brachytherapy: A comparison between gadolinium and gold nanoparticles. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2012, 35, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, R. Experimental study on radiation damage of (125) I seeds implanted in canine gastric wall tissue. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2020, 16, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sui, A.; Jia, Y.; Xu, B.; Wei, L.; Chen, J.; Shen, W. Treatment of unresectable advanced gastric cancer using lodine-125 brachytherapy. Chin. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 3, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.-H.; Yang, Y.; Zou, L.; Luo, K.-Y. 125I seed irradiation induces up-regulation of the genes associated with apoptosis and cell cycle arrest and inhibits growth of gastric cancer xenografts. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 31, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.F.; Jin, W.D.; Li, B.; Wang, M.C.; Li, X.G.; Mao, W.Y.; Luo, K.Y. Effect of brachytherapy on NF-κB and VEGF in gastric carcinoma xenografts. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roeske, J.C.; Nuñez, L.; Hoggarth, M.; Labay, E.; Weichselbaum, R.R. Characterization of the theorectical radiation dose enhancement from nanoparticles. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 6, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechtman, E.; Mashouf, S.; Chattopadhyay, N.; Keller, B.M.; Lai, P.; Cai, Z.; Reilly, R.M.; Pignol, J.P. A Monte Carlo-based model of gold nanoparticle radiosensitization accounting for increased radiobiological effectiveness. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, 3075–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.H. Estimation of tumour dose enhancement due to gold nanoparticles during typical radiation treatments: A preliminary Monte Carlo study. Phys. Med. Biol. 2005, 50, N163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zygmanski, P.; Sajo, E. Nanoscale radiation transport and clinical beam modeling for gold nanoparticle dose enhanced radiotherapy (GNPT) using X-rays. Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20150200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J. Recent progress in Monte Carlo simulation on gold nanoparticle radiosensitization. AIMS Biophys. 2018, 5, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Jones, B.L.; Krishnan, S. The dosimetric feasibility of gold nanoparticle-aided radiation therapy (GNRT) via brachytherapy using low-energy gamma-/x-ray sources. Phys. Med. Biol. 2009, 54, 4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, S.; Vaez-Zadeh, M.; Masoudi, S.F.; Rahmani, F.; Knaup, C.; Meigooni, A.S. Gold nanoparticle-based brachytherapy enhancement in choroidal melanoma using a full Monte Carlo model of the human eye. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2015, 16, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.; Konstantinov, K.; McKinnon, S.; Guatelli, S.; Lerch, M.; Rosenfeld, A.; Tehei, M.; Corde, S. First proof of bismuth oxide nanoparticles as efficient radiosensitisers on highly radioresistant cancer cells. Phys. Med. 2016, 32, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Coulter, J.A.; Hounsell, A.R.; Butterworth, K.T.; McMahon, S.J.; Hyland, W.B.; Muir, M.F.; Dickson, G.R.; Prise, K.M.; Currell, F.J.; et al. Cell-specific radiosensitization by gold nanoparticles at megavoltage radiation energies. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 79, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.; Zeng, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, J.; McQuarrie, S.; McEwan, A.; Roa, W.; Chen, J.; Xing, J.Z. Enhancement of Radiation Cytotoxicity in Breast-Cancer Cells by Localized Attachment of Gold Nanoparticles. Small 2008, 4, 1537–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabihzadeh, M.; Arefian, S. Tumor dose enhancement by nanoparticles during high dose rate 192Ir brachytherapy. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2015, 11, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xing, J.Z.; Chen, J.; Ko, L.; Amanie, J.; Gulavita, S.; Pervez, N.; Yee, D.; Moore, R.; Roa, W. Enhanced radiation sensitivity in prostate cancer by gold-nanoparticles. Clin. Investig. Med. 2008, 31, E160–E167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robatjazi, M.; Baghani, H.R.; Rostami, A.; Pashazadeh, A. Monte Carlo-based calculation of nano-scale dose enhancement factor and relative biological effectiveness in using different nanoparticles as a radiosensitizer. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2021, 97, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.L.; Krishnan, S.; Cho, S.H. Estimation of microscopic dose enhancement factor around gold nanoparticles by Monte Carlo calculations. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seniwal, B.; Mendes, B.M.; Malano, F.; Pérez, P.; Valente, M.; Fonseca, T.C. Monte Carlo assessment of low energy electron range in liquid water and dosimetry effects. Phys. Med. 2020, 80, 363–372. [Google Scholar]
- Maggiorella, L.; Barouch, G.; Devaux, C.; Pottier, A.; Deutsch, E.; Bourhis, J.; Borghi, E.; Levy, L. Nanoscale radiotherapy with hafnium oxide nanoparticles. Future Oncol. 2012, 8, 1167–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangjoo, A.G.; Ghiasi, H.; Mesbahi, A. A Monte Carlo study on the radio-sensitization effect of gold nanoparticles in brachytherapy of prostate by Pd seeds. Pol. J. Med. Phys. Eng. 2019, 25, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benlakhdar, F.; Dib, A.; Belbachir, A. Effect of nanomaterials on the absorbed dose during an X-ray exposure. Radioprotection 2016, 51, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koger, B.; Kirkby, C. Dosimetric effects of polyethylene glycol surface coatings on gold nanoparticle radiosensitization. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 8455–8469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, X.; Reynoso, F.J. Modeling Gold Nanoparticle Radiosensitization using a Clustering Algorithm to Quantify DNA Double-Strand Breaks with Mixed-Physics Monte Carlo Simulation. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 5314–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).