Ball Milled Gd Flakes Subjected to Heat Treatments: Structure, Magnetic and Magnetocaloric Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franco, V.; Blázquez, J.S.; Ipus, J.J.; Law, J.Y.; Moreno-Ramírez, L.M.; Conde, A. Magnetocaloric effect: From materials research to refrigeration devices. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 93, 112–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chzhan, V.B.; Kurganskaya, A.A.; Tereshina, I.S.; Karpenkov, A.Y.; Ovchenkova, I.A.; Tereshina-Chitrova, E.A.; Andreev, A.V.; Gorbunov, D.I.; Lushnikov, S.A.; Verbetsky, V.N. Influence of interstitial and substitutional atoms on magnetocaloric effects in RNi compounds. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 264, 124455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yan, M. Recent progress in the development of RE2TMTM’O6 double perovskite oxides for cryogenic magnetic refrigeration. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 136, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, L. Electronic structure, magnetic properties and magnetocaloric performance in rare earths (RE) based RE2BaZnO5 (RE = Gd, Dy, Ho, and Er) compounds. Acta Mater. 2022, 236, 118114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, L.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Yan, M. Excellent magnetocaloric performance in the carbide compounds RE2Cr2C3 (RE = Er, Ho, and Dy) and their composites. Mater. Today Phys. 2022, 27, 100786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Yu, B.F.; Wang, C.F.; Zhang, B.; Yang, D.X.; Zhang, Y. Experimental investigation on refrigeration performance of a reciprocating active magnetic regenerator of room temperature magnetic refrigeration. Int. J. Refrig. 2006, 29, 1274–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blázquez, J.S.; Ipus, J.J.; Moreno-Ramírez, L.M.; Borrego, J.M.; Lozano-Pérez, S.; Franco, V.; Conde, C.F.; Conde, A. Analysis of the magnetocaloric effect in powder samples obtained by ball milling. Metall. Mater. Trans. E 2015, 2, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrobak, A.; Bajorek, A.; Chełkowska, G.; Haneczok, G.; Kwiecień, M. Magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effect of Gd(Ni1−xFex)3 crystalline compound and powder. Phys. Status Solidi A 2009, 206, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Rey, R.; Vieites-Prado, A.; Argibay, B.; Campos, F.; Bañobre-López, M.; Sobrino, T.; Rivas, J.; Castillo, J. Magnetocaloric effect for inducing hypothermia as new therapeutic strategy for stroke: A physical approach. J. Appl. Biomed. 2017, 15, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.L.; Belo, J.H.; Turcaud, J.; Oliveira, G.N.P.; Araújo, J.P.; Berenov, A.; Cohen, L.F.; Lopes, A.M.L.; Pereira, A.M. Influence of short time milling in R5(Si,Ge)4, R = Gd and Tb, magnetocaloric materials. Mater. Des. 2015, 85, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svalov, A.V.; Arkhipov, A.V.; Andreev, S.V.; Neznakhin, D.S.; Larrañaga, A.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V. Modified field dependence of the magnetocaloric effect in Gd powder obtained by ball milling. Mater. Lett. 2021, 284, 128921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurlyandskaya, G.V.; Safronov, A.P.; Bhagat, S.M.; Lofland, S.E.; Beketov, I.V.; Marcano Prieto, L. Tailoring functional properties of Ni nanoparticles-acrylic copolymer composites with different concentrations of magnetic filler. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 123917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedoi, V.S.; Ivanov, Y.F. Particles and crystallites under electrical explosion of wires. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 145710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blázquez, J.S.; Ipus, J.J.; Moreno-Ramírez, L.M.; Álvarez-Gómez, J.M.; Sánchez-Jiménez, D.; Lozano-Pérez, S.; Franco, V.; Conde, A. Ball milling as a way to produce magnetic and magnetocaloric materials: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 11834–11850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirian, R.; Souca, G.; Popa, F.; Gutoiu, S.; Pop, V.; Isnard, O.; Tetean, R. Interphase exchange coupling and magnetocaloric effect in Co3Gd4/Co7Gd12 magnetic nanocomposites, obtained by mechanical milling. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 559, 169505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starostenko, S.N.; Petrov, D.A.; Rozanov, K.N.; Shiryaev, A.O.; Lomaeva, S.F. Effect of temperature on microwave permeability of an air-stable composite filled with gadolinium powder. Sensors 2022, 22, 3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doblas, D.; Moreno-Ramírez, L.M.; Franco, V.; Conde, A.; Svalov, A.V.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V. Nanostructuring as a procedure to control the field dependence of the magnetocaloric effect. Mater. Des. 2017, 114, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Ramírez, L.M.; Law, J.Y.; Pramana, S.S.; Giri, A.K.; Franco, V. Analysis of the magnetic field dependence of the isothermal entropy change of inverse magnetocaloric materials. Results Phys. 2021, 22, 103933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhanov, G.S.; Kolchugina, N.B.; Tereshina, E.A.; Tereshina, I.S.; Politova, G.A.; Chzhan, V.B.; Badurski, D.; Chistyakov, O.D.; Paukov, M.; Drulis, H.; et al. Magnetocaloric properties of distilled gadolinium: Effects of structural inhomogeneity and hydrogen impurity. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 242402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschall, T.; Kuz’min, M.D.; Skokov, K.P.; Skourski, Y.; Fries, M.; Gutfleisch, O.; Ghorbani Zavareh, M.; Schlagel, D.L.; Mudryk, Y.; Pecharsky, V.; et al. Magnetocaloric effect of gadolinium in high magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 99, 134429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuz’min, M.D. Shape of temperature dependence of spontaneous magnetization of ferromagnets: Quantitative analysis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 107204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuz’min, M.D.; Skokov, K.P.; Diop, L.V.B.; Radulov, I.A.; Gutfleisch, O. Exchange stiffness of ferromagnets. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2020, 135, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskaev, S.V.; Buchelnikov, V.D.; Pellenen, A.P.; Kuz’min, M.D.; Skokov, K.P.; Karpenkov, D.Y.; Bataev, D.S.; Gutfleisch, O. Influence of thermal treatment on magnetocaloric properties of Gd cold rolled ribbons. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 17A933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svalov, A.; Andreev, S.; Arkhipov, A.; Kudyukov, E.; Neznakhin, D.; Larrañaga, A.; Kurlyandskaya, G. Magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of Gd melt-spun ribbons. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1389, 012100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hémon, S.; Cowley, R.A.; Ward, R.C.C.; Wells, M.R.; Douysset, L.; Ronnow, H. Magnetic structure of Gd, GdH2 and NdH2 single crystal films. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2000, 12, 5011–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, P.; Fruchart, D.; Givord, D. Magnetic properties of epitaxial gadolinium hydride films. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 330, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.K. On a generalised approach to first and second order magnetic transitions. Phys. Lett. 1964, 12, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzer, G.; Fähnle, M.; Egami, T.; Kronmüller, H. Micromagnetic theory of phase transitions in inhomogeneous ferromagnets III. Non-local Landau-Ginzburg theory. Phys. Stat. Sol. B 1980, 101, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, H.S.; Swain, D.; Adiga, S.; Hariharan, N.; Narayana, C.; Elzabeth, S. Griffiths phase-like behavior and spin-phonon coupling in double perovskite Tb2NiMnO6. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 123919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döbrich, F.; Kohlbrecher, J.; Sharp, M.; Eckerlebe, H.; Birringer, R.; Michels, A. Neutron scattering study of the magnetic microstructure of nanocrystalline gadolinium. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 85, 094411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
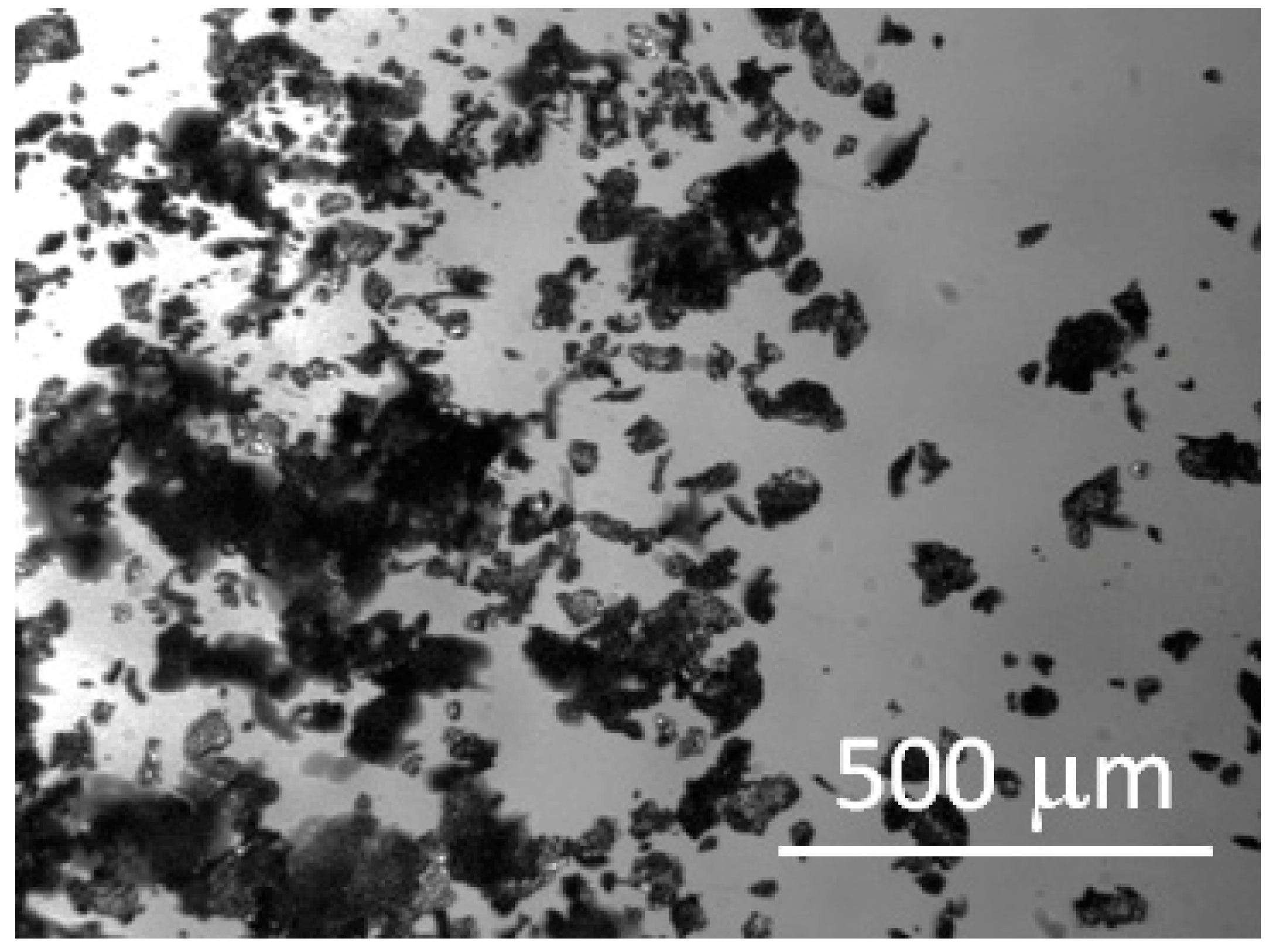
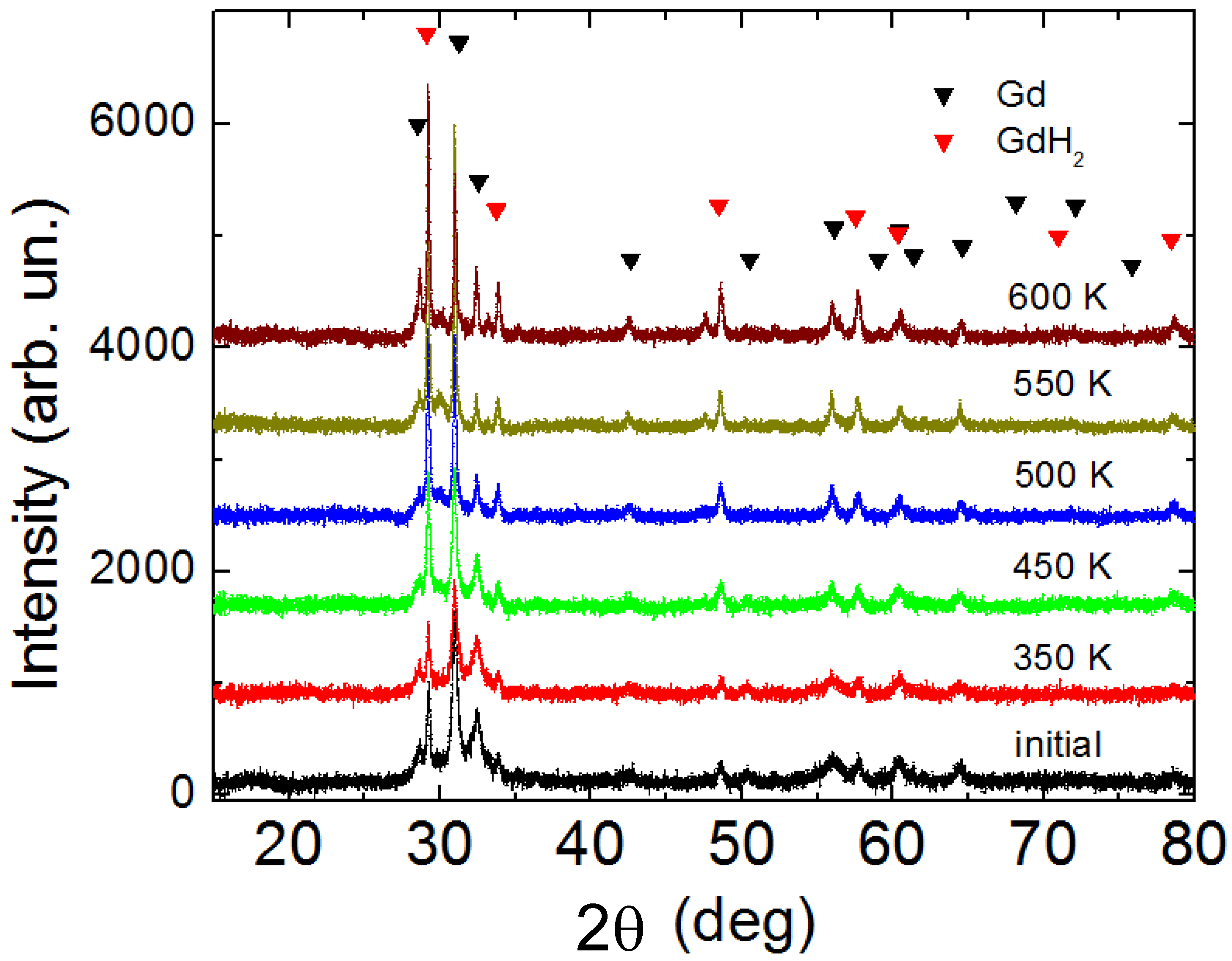
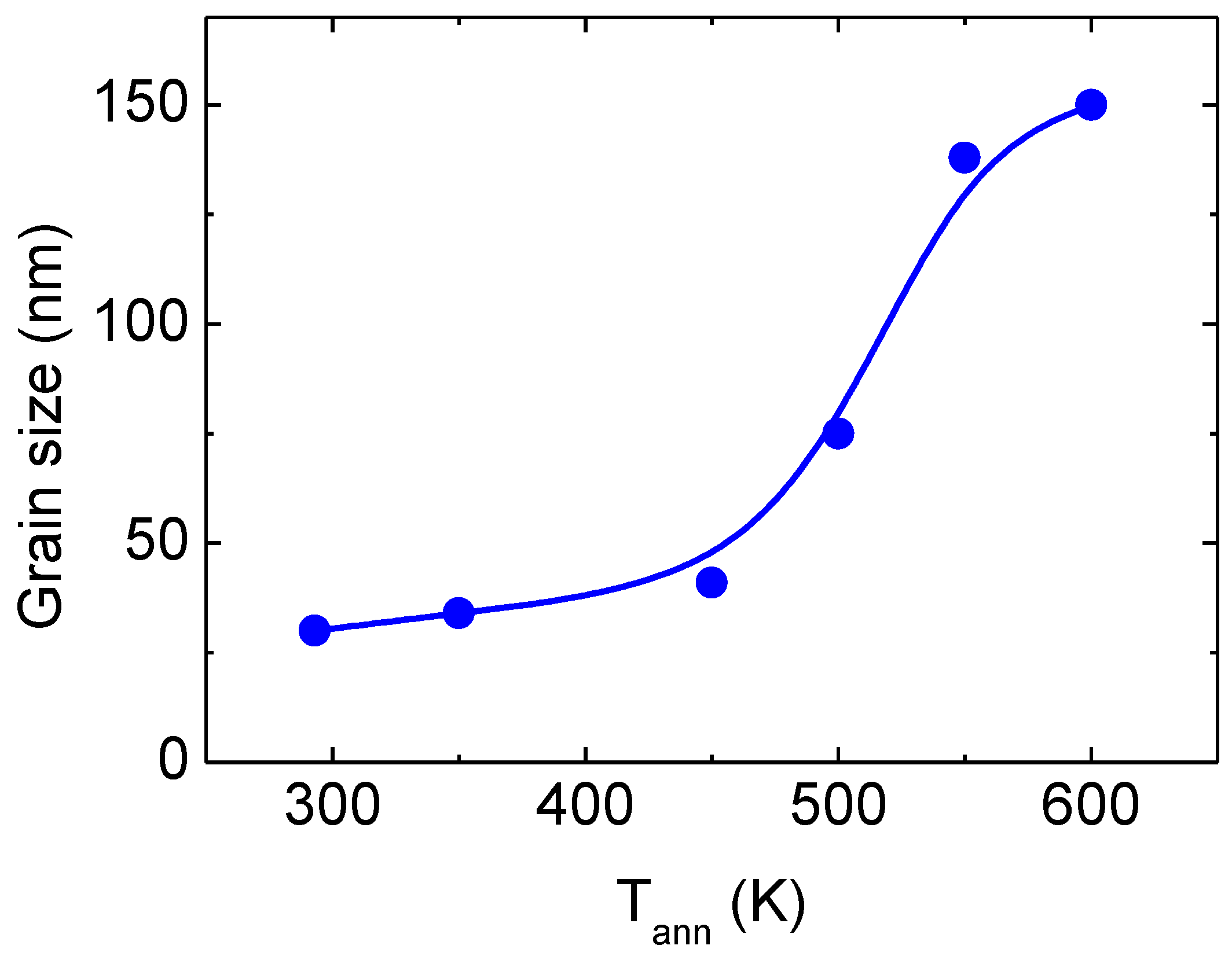
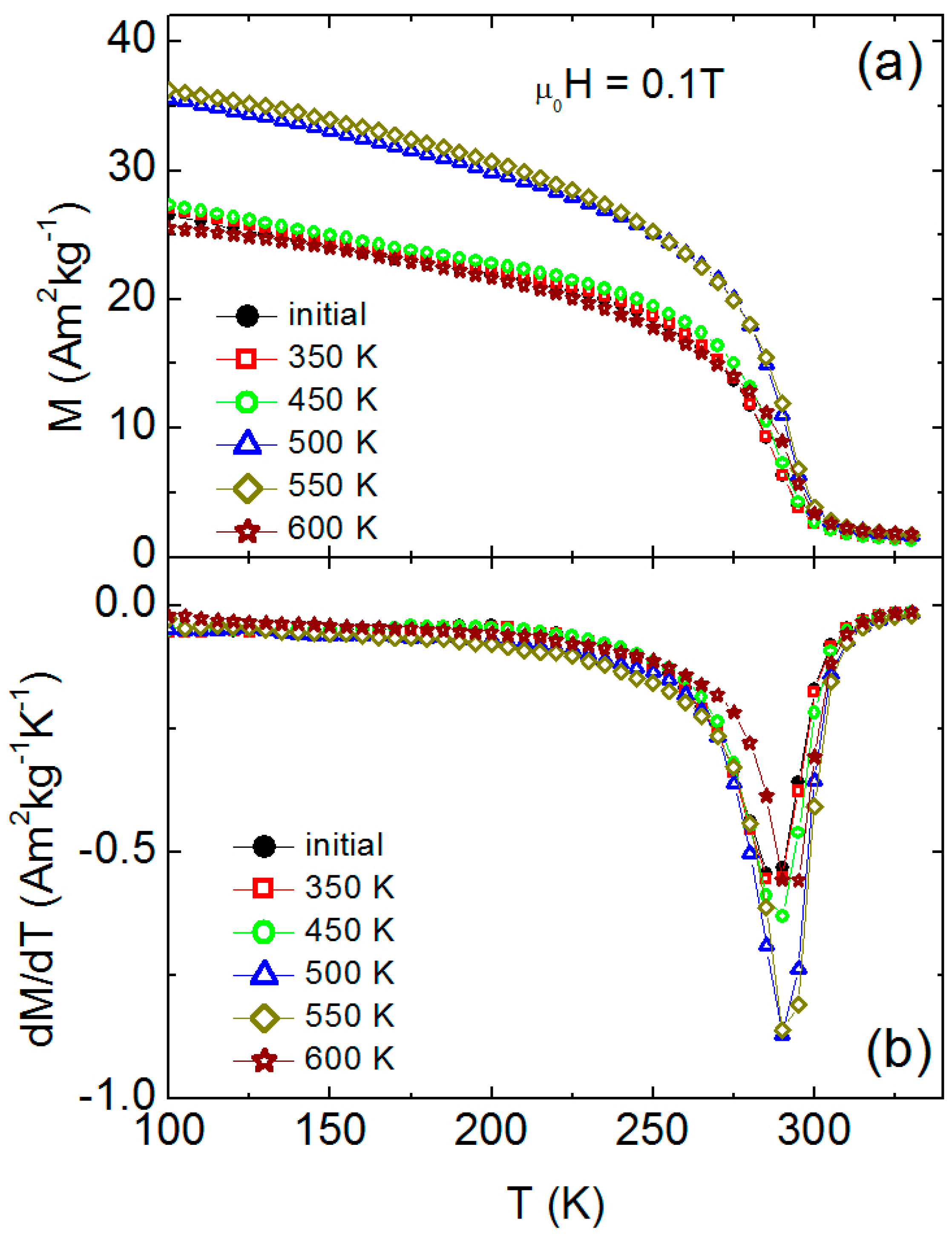

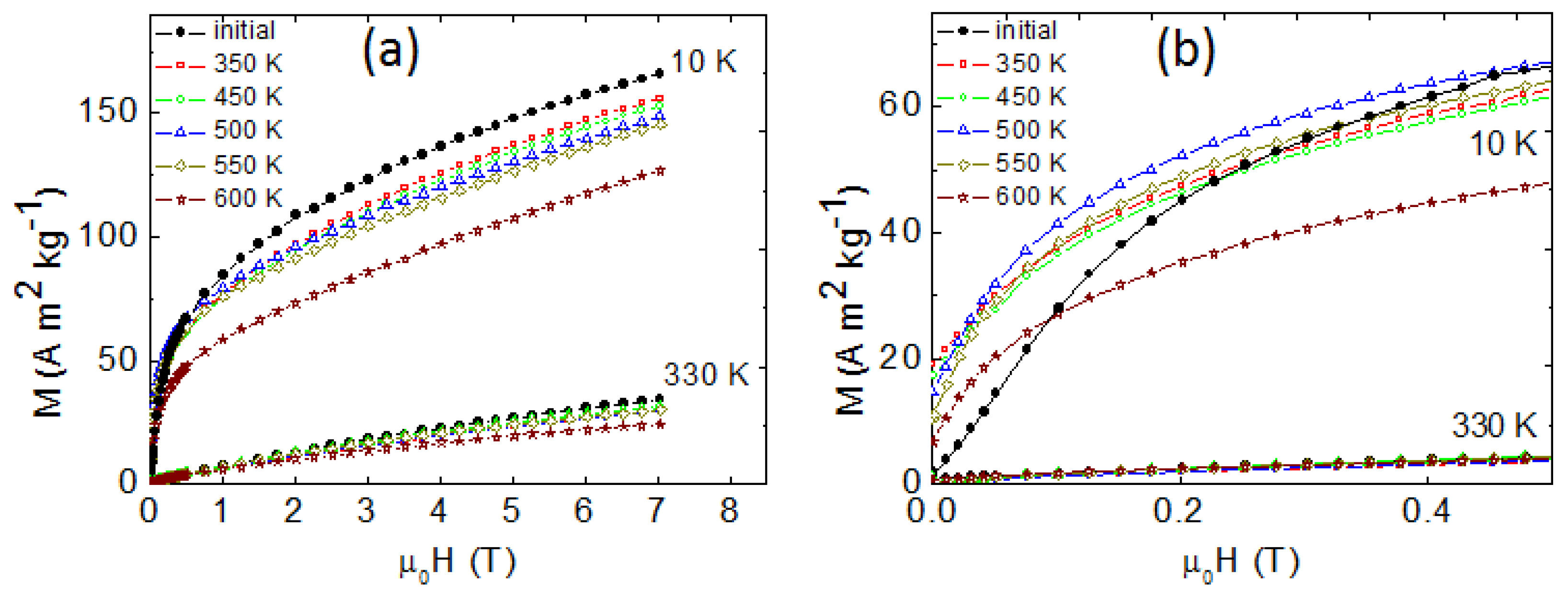
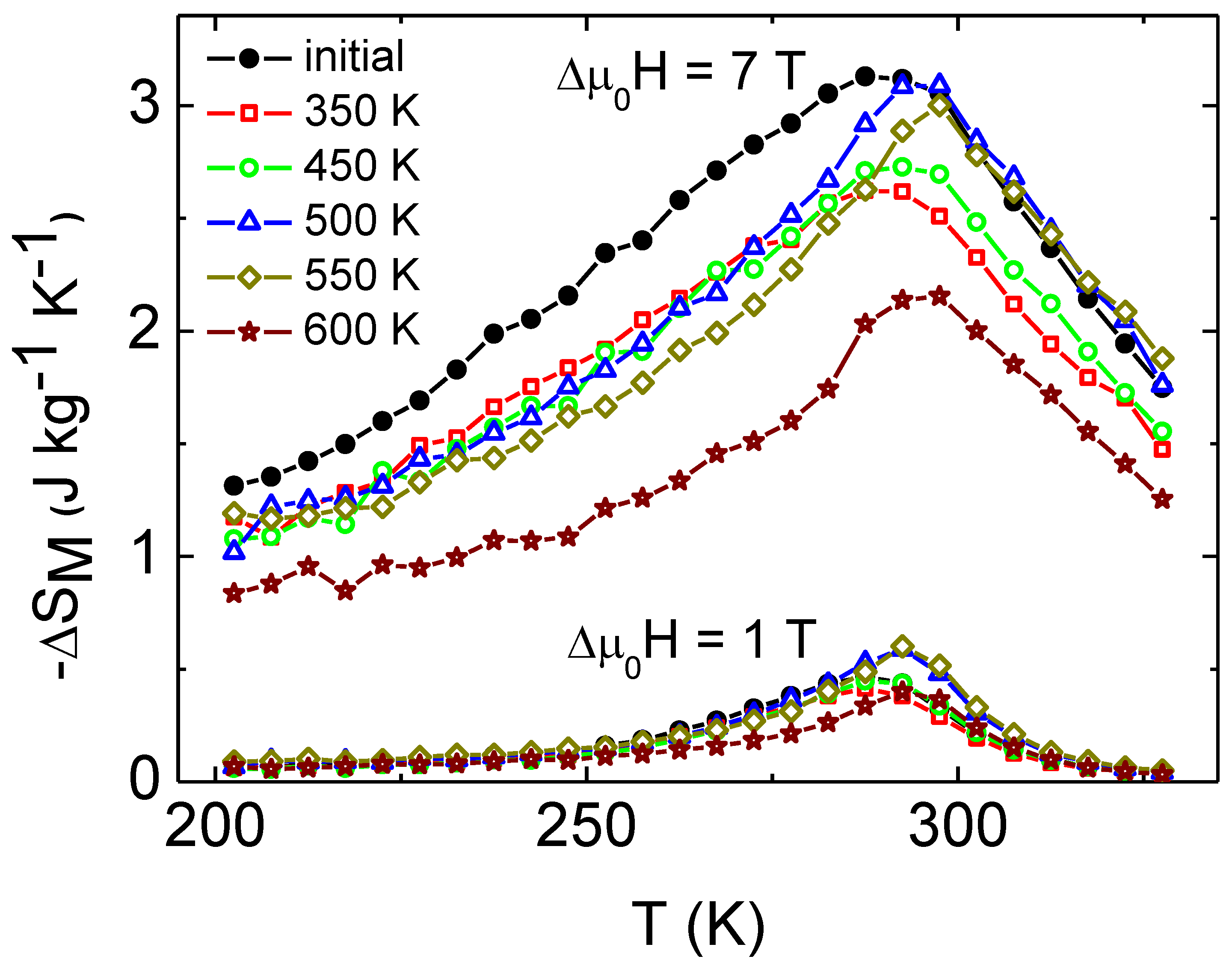
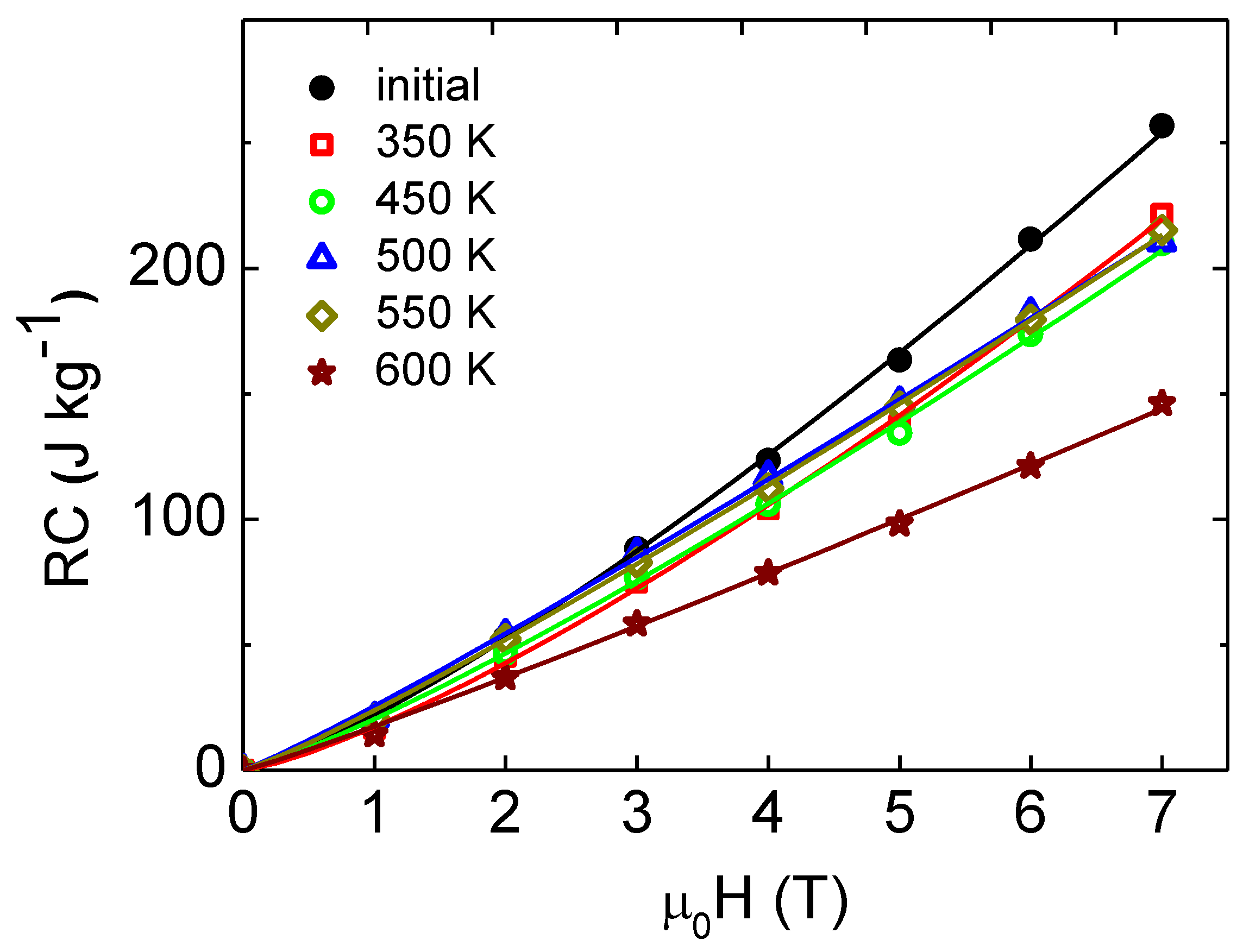
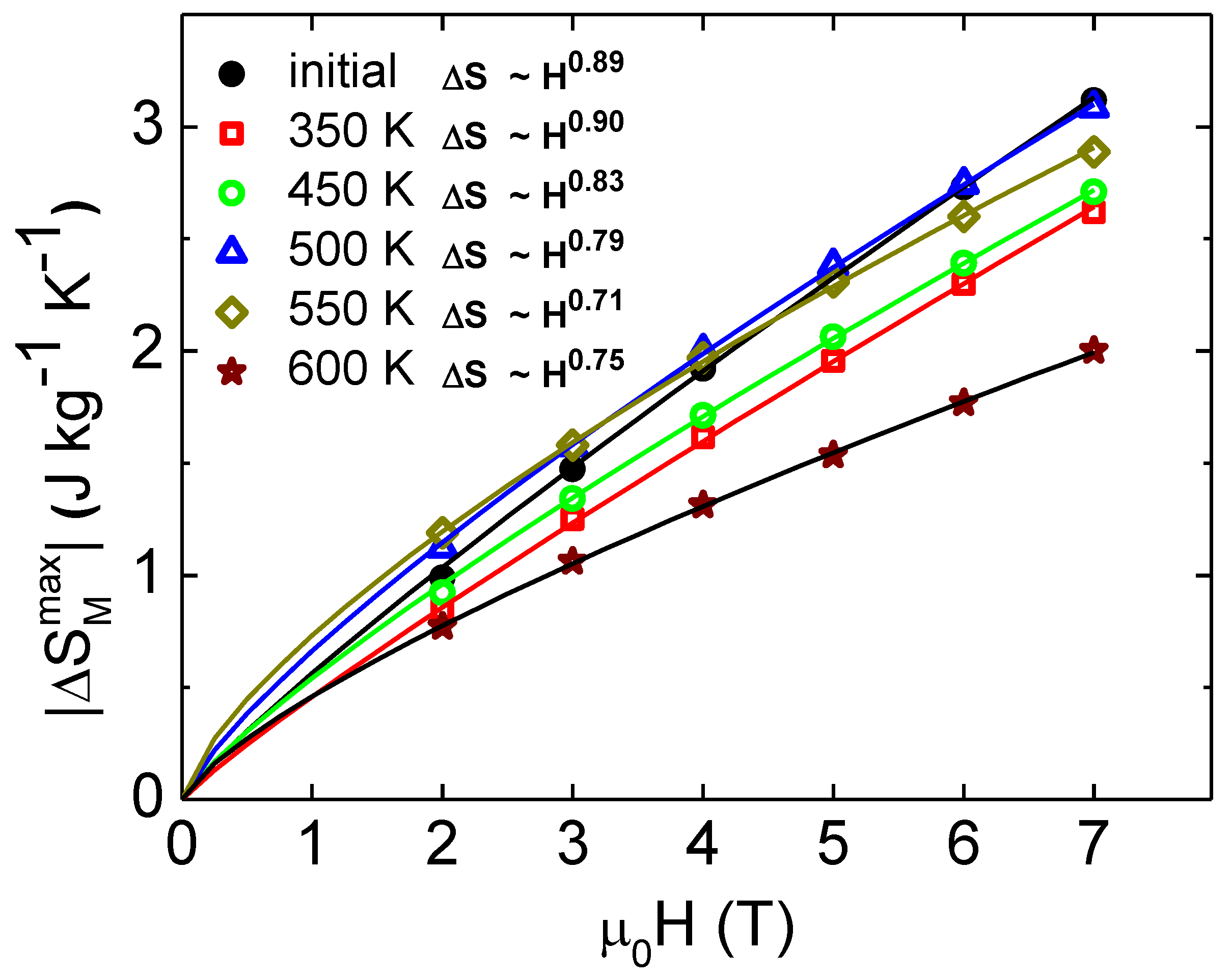
| Sample | Exponent n | ΔSMmax (Jkg−1K−1) |
|---|---|---|
| initial | 0.89 | 0.5 |
| 350 K | 0.90 | 0.4 |
| 450 K | 0.83 | 0.5 |
| 500 K | 0.79 | 0.6 |
| 550 K | 0.71 | 0.6 |
| 600 K | 0.75 | 0.4 |
| Gd bulk | 0.78 [14] | 2.8 [1] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Svalov, A.V.; Neznakhin, D.S.; Arkhipov, A.V.; Andreev, S.V.; Selezneva, N.V.; Larrañaga, A.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V. Ball Milled Gd Flakes Subjected to Heat Treatments: Structure, Magnetic and Magnetocaloric Properties. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8110138
Svalov AV, Neznakhin DS, Arkhipov AV, Andreev SV, Selezneva NV, Larrañaga A, Kurlyandskaya GV. Ball Milled Gd Flakes Subjected to Heat Treatments: Structure, Magnetic and Magnetocaloric Properties. Magnetochemistry. 2022; 8(11):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8110138
Chicago/Turabian StyleSvalov, Andrey V., Dmitriy S. Neznakhin, Andrey V. Arkhipov, Sergey V. Andreev, Nadezhda V. Selezneva, Aitor Larrañaga, and Galina V. Kurlyandskaya. 2022. "Ball Milled Gd Flakes Subjected to Heat Treatments: Structure, Magnetic and Magnetocaloric Properties" Magnetochemistry 8, no. 11: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8110138
APA StyleSvalov, A. V., Neznakhin, D. S., Arkhipov, A. V., Andreev, S. V., Selezneva, N. V., Larrañaga, A., & Kurlyandskaya, G. V. (2022). Ball Milled Gd Flakes Subjected to Heat Treatments: Structure, Magnetic and Magnetocaloric Properties. Magnetochemistry, 8(11), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8110138







