Magnetic Polymers for Magnetophoretic Separation in Microfluidic Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The PDMS Composite Approach
2.1. High Concentrated PDMS Composites
2.2. High Concentrated PDMS Composites with Anisotropic Magnetic Properties
2.3. Low Concentrated PDMS Composites with Anisotropic Magnetic Properties
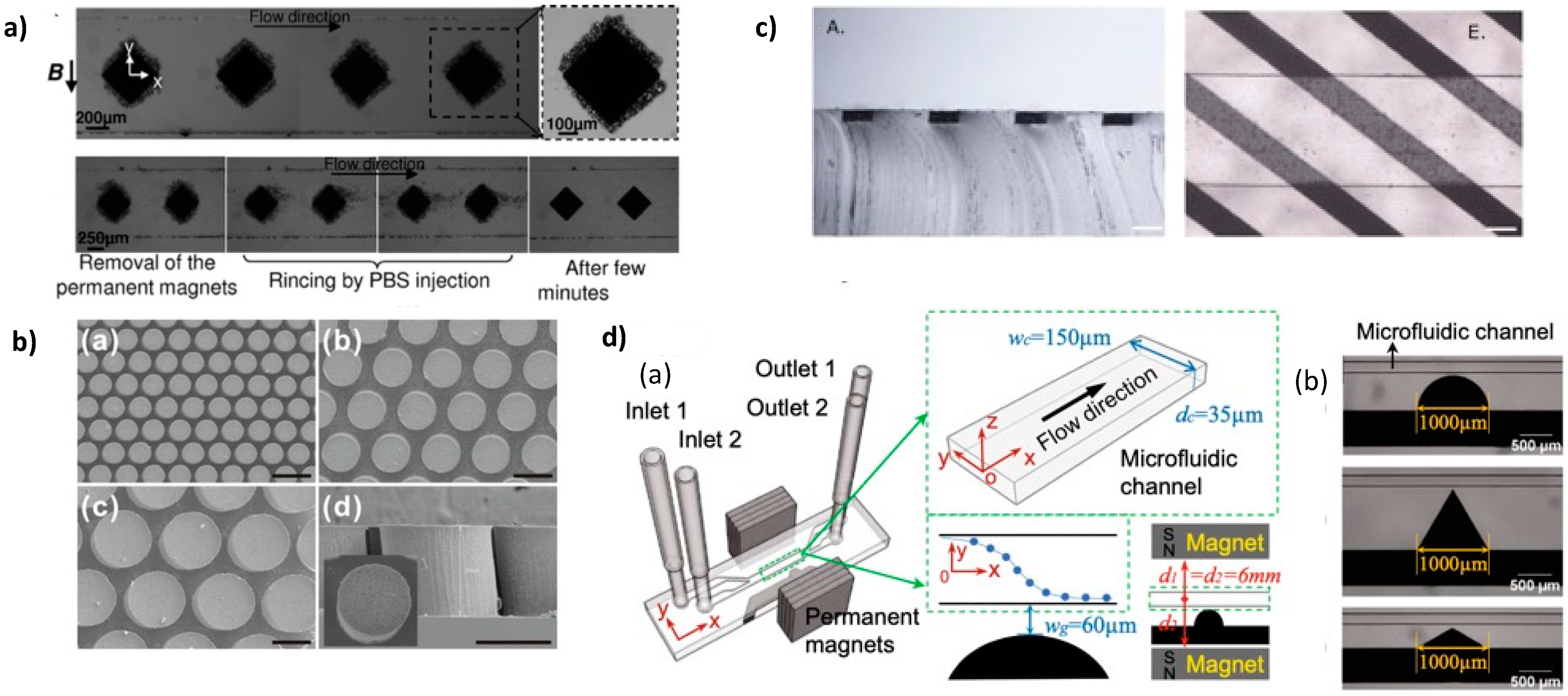
2.3.1. Preparation under Uniform Field
2.3.2. Preparation under Magnetic Field Gradient
3. Magnetic Fluids
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munaz, A.; Shiddiky, M.J.A.; Nguyen, N.T. Recent advances and current challenges in magnetophoresis based micro magnetofluidics. Biomicrofluidics 2018, 12, 031501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; He, Y. Magnetically driven microfluidics for isolation of circulating tumor cells. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 4207–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deman, A.-L.; Le Roy, D. Magnetophoresis in Bio-Devices. In Engineering of Micro/Nano Biosystems; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 309–361. [Google Scholar]
- Pamme, N. Magnetism and microfluidics. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Fan, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liu, C.; Han, X.; Li, L. Recent advances in manipulation of micro- and nano-objects with magnetic fields at small scales. Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7, 638–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, P.Y.; Jiang, P.S.; Lee, E.F.; Fan, S.K.; Lu, Y.W. Genomic DNA extraction from whole blood using a digital microfluidic (DMF) platform with magnetic beads. Microsyst. Technol. 2015, 23, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, T.M.; Cardoso, F.A.; Martins, S.A.M.; Martins, V.C.; Cardoso, S.; Gaspar, J.F.; Monteiro, G.; Freitas, P.P. Implementing a strategy for on-chip detection of cell-free DNA fragments using GMR sensors: A translational application in cancer diagnostics using ALU elements. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbarino, F.; Minero, G.A.S.; Rizzi, G.; Fock, J.; Hansen, M.F. Integration of rolling circle amplification and optomagnetic detection on a polymer chip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejhed, R.S.; Tian, B.; Eriksson, K.; Brucas, R.; Oscarsson, S.; Strömberg, M.; Svedlindh, P.; Gunnarsson, K. Magnetophoretic Transport Line System for Rapid On-Chip Attomole Protein Detection. Langmuir 2015, 31, 10296–10302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zirath, H.; Schnetz, G.; Glatz, A.; Spittler, A.; Redl, H.; Peham, J.R. Bedside Immune Monitoring: An Automated Immunoassay Platform for Quantification of Blood Biomarkers in Patient Serum within 20 Minutes. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 4817–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Huo, W.; Zhang, L.; Lian, J.; Tao, W.; Song, C.; Tang, J.; Shi, S.; Gao, Y. Multiplex measurement of twelve tumor markers using a GMR multi-biomarker immunoassay biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 123, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gijs, M.A.M.; Lacharme, F.; Lehmann, U. Microfluidic applications of magnetic particles for biological analysis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1518–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fachin, F.; Spuhler, P.; Martel-Foley, J.M.; Edd, J.F.; Barber, T.A.; Walsh, J.; Karabacak, M.; Pai, V.; Yu, M.; Smith, K.; et al. Monolithic Chip for High-throughput Blood Cell Depletion to Sort Rare Circulating Tumor Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cheng, R.; Lim, S.H.; Miller, J.R.; Zhang, W.; Tang, W.; Xie, J.; Mao, L. Biocompatible and label-free separation of cancer cells from cell culture lines from white blood cells in ferrofluids. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 2243–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Kim, J.; Jeon, C.W.; Han, K.H. A disposable microfluidic device with a reusable magnetophoretic functional substrate for isolation of circulating tumor cells. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 4113–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCloskey, K.E.; Chalmers, J.J.; Zborowski, M. Magnetic Cell Separation: Characterization of Magnetophoretic Mobility. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 6868–6874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plouffe, B.D.; Murthy, S.K.; Lewis, L.H. Fundamentals and application of magnetic particles in cell isolation and enrichment: A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2015, 78, 16601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, X. Recent advances in continuous-flow particle manipulations using magnetic fluids. Micromachines 2019, 10, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leong, S.S.; Ahmad, Z.; Low, S.C.; Camacho, J.; Faraudo, J.; Lim, J.K. Unified View of Magnetic Nanoparticle Separation under Magnetophoresis. Langmuir 2020, 36, 8033–8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzhir, P.; Magnet, C.; Ezzaier, H.; Zubarev, A.; Bossis, G. Magnetic filtration of phase separating ferrofluids: From basic concepts to microfluidic device. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 431, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dempsey, N.M.; Le Roy, D.; Marelli-Mathevon, H.; Shaw, G.; Dias, A.; Kramer, R.B.G.; Viet Cuong, L.; Kustov, M.; Zanini, L.F.; Villard, C.; et al. Micro-magnetic imprinting of high field gradient magnetic flux sources. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 262401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roy, D.; Shaw, G.; Haettel, R.; Hasselbach, K.; Dumas-Bouchiat, F.; Givord, D.; Dempsey, N.M. Fabrication and characterization of polymer membranes with integrated arrays of high performance micro-magnets. Mater. Today Commun. 2016, 6, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Goudu, S.R.; Torati, S.R.; Lim, B.; Kim, K.; Kim, C. An on-chip micromagnet frictionometer based on magnetically driven colloids for nano-bio interfaces. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 3485–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Torres, K.Y.; McLamore, E.S.; Arnold, D.P. A high-throughput microfluidic magnetic separation (μFMS) platform for water quality monitoring. Micromachines 2020, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.; Wen, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.L.; Pang, D.W. Control of magnetic field distribution by using nickel powder@PDMS pillars in microchannels. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 17660–17666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, S.; Sun, X.; Feng, Z.; Lei, C.; Zhou, Y. An innovative micro magnetic separator based on 3D micro-copper-coil exciting soft magnetic tips and FeNi wires for bio-target sorting. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2019, 23, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Xia, H.F.; Xu, C.M.; Feng, J.; Ren, J.G.; Miao, F.; Wu, M.; Wu, L.L.; Pang, D.W.; Chen, G.; et al. Magnetic Chip Based Extracorporeal Circulation: A New Tool for Circulating Tumor Cell In Vivo Detection. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 15260–15266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, T.; Prentiss, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Fabrication of magnetic microfiltration systems using soft lithography. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 461–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, G.; Kuzhir, P.; Izmaylov, Y.; Alves Marins, J.; Ezzaier, H.; Robert, L.; Doutre, F.; Noblin, X.; Lomenech, C.; Bossis, G.; et al. Microfluidic separation of magnetic nanoparticles on an ordered array of magnetized micropillars. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 93, 62604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaiswal, D.; Rad, A.T.; Nieh, M.P.; Claffey, K.P.; Hoshino, K. Micromagnetic Cancer Cell Immobilization and Release for Real-Time Single Cell Analysis. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 427, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Chen, P.; Wu, C.H.; Hoshino, K.; Sokolov, K.; Lane, N.; Liu, H.; Huebschman, M.; Frenkel, E.; Zhang, J.X.J. Screening and Molecular Analysis of Single Circulating Tumor Cells Using Micromagnet Array. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, O.; Toru, S.; Dumas-Bouchiat, F.; Dempsey, N.M.; Haddour, N.; Zanini, L.F.; Buret, F.; Reyne, G.; Frénéa-Robin, M. Microfluidic immunomagnetic cell separation using integrated permanent micromagnets. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 054115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ponomareva, S.; Dias, A.; Royer, B.; Marelli, H.; Motte, J.F.; Givord, D.; Dumas-Bouchiat, F.; Dempsey, N.M.; Marchi, F. A quantitative study of magnetic interactions between a micro-magnet array and individual magnetic micro-particles by scanning particle force microscopy. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2019, 29, 015010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.L.; Tang, M.; Hong, S.L.; Yu, X.; Pang, D.W.; Zhang, Z.L. Combination of dynamic magnetophoretic separation and stationary magnetic trap for highly sensitive and selective detection of Salmonella typhimurium in complex matrix. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malic, L.; Zhang, X.; Brassard, D.; Clime, L.; Daoud, J.; Luebbert, C.; Barrere, V.; Boutin, A.; Bidawid, S.; Farber, J.; et al. Polymer-based microfluidic chip for rapid and efficient immunomagnetic capture and release of Listeria monocytogenes. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 3994–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, B.L. A Review of Magnetic Composite Polymers Applied to Microfluidic Devices. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, B3173–B3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunas, J.; Mulyanti, B.; Hamidah, I.; Said, M.M.; Pawinanto, R.E.; Wan Ali, W.A.F.; Subandi, A.; Hamzah, A.A.; Latif, R.; Majlis, B.Y. Polymer-Based MEMS electromagnetic actuator for biomedical application: A review. Polymers 2020, 12, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thévenot, J.; Oliveira, H.; Sandre, O.; Lecommandoux, S. Magnetic responsive polymer composite materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7099–7116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Sheng, P.; Wen, W. Design and fabrication of microfluidic mixer from carbonyl iron-PDMS composite membrane. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2011, 10, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahara, T.; Suzuki, J.; Hosokawa, Y.; Shimokawa, F.; Kotera, H.; Suzuki, T. Fabrication of Magnetically Driven Microvalve Arrays Using a Photosensitive Composite. Magnetochemistry 2018, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Currie, C.E.; Gray, B.L. Bidirectional Magnetic Polymer Membrane Actuators Integrated into Thermoplastic Microfluidics. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 33rd International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 January 2020; pp. 1056–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Gholizadeh, A.; Javanmard, M. Magnetically Actuated Microfluidic Transistors: Miniaturized Micro-Valves Using Magnetorheological Fluids Integrated with Elastomeric Membranes. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2016, 25, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paknahad, A.A.; Tahmasebipour, M. An electromagnetic micro-actuator with PDMS-Fe3O4 nanocomposite magnetic membrane. Microelectron. Eng. 2019, 216, 111031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, M.M.; Yunas, J.; Bais, B.; Hamzah, A.A.; Majlis, B.Y. The design, fabrication, and testing of an electromagnetic micropump with a matrix-patterned magnetic polymer composite actuator membrane. Micromachines 2017, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakahara, T.; Ueda, Y.; Miyagawa, H.; Kotera, H.; Suzuki, T. Self-aligned fabrication process for active membrane in magnetically driven micropump using photosensitive composite. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2020, 30, 025006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Surendran, A.N.; Mejulu, M.; Lin, Y. Rapid microfluidic mixer based on ferrofluid and integrated microscale ndfeb-pdms magnet. Micromachines 2020, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, S.Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, S.; Yuan, D.; Zhao, Q.; Yan, S.; Deng, L.; Yun, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; et al. Versatile Microfluidic Platforms Enabled by Novel Magnetorheological Elastomer Microactuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahbar, M.; Shannon, L.; Gray, B.L. Microfluidic active mixers employing ultra-high aspect-ratio rare-earth magnetic nano-composite polymer artificial cilia. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2014, 24, 025003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cui, Z.; Wang, Y.; Den Toonder, J.M.J. Metachronal actuation of microscopic magnetic artificial cilia generates strong microfluidic pumping. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 3569–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Onck, P.R.; Den Toonder, J.M.J. Controlled Multidirectional Particle Transportation by Magnetic Artificial Cilia. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 10313–10323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.W.; Lee, Y.P. Magnetic microparticle-polydimethylsiloxane composite for reversible microchannel bonding. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2016, 17, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashouri, M.; Shafii, M.B.; Moosavi, A. Theoretical and experimental studies of a magnetically actuated valveless micropump. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2017, 27, 015016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.C.; Alfadhel, A.; Forouzandeh, F.; Borkholder, D.A. Biocompatible magnetic nanocomposite microcapsules as microfluidic one-way diffusion blocking valves with ultra-low opening pressure. Mater. Des. 2018, 150, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Evans, B.A.; Chang, C.H. Magnetically Actuated Dynamic Iridescence Inspired by the Neon Tetra. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 4657–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Zhang, X.A.; Evans, B.A.; Chang, C.H. Active Periodic Magnetic Nanostructures with High Aspect Ratio and Ultrahigh Pillar Density. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 11135–11143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, B.; Vavassori, P.; Sooryakumar, R.; Kim, C. Nano/micro-scale magnetophoretic devices for biomedical applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 033002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnaimat, F.; Karam, S.; Mathew, B.; Mathew, B. Magnetophoresis and Microfluidics: A Great Union. IEEE Nanotechnol. Mag. 2020, 14, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faivre, M.; Gelszinnis, R.; Terrier, N.; Ferrigno, R.; Deman, A. Magnetophoretic manipulation in microsystem using carbonyl iron-polydimethylsiloxane microstructures. Biomicrofluidics 2014, 8, 054103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ezzaier, H.; Marins, J.A.; Claudet, C.; Hemery, G.; Sandre, O.; Kuzhir, P. Kinetics of aggregation and magnetic separation of multicore iron oxide nanoparticles: Effect of the grafted layer thickness. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bae, Y.M.; Jeong, B.; Kim, J.I.; Kang, D.G.; Shin, K.Y.; Yoo, D.W. Array of 3D permanent micromagnet for immunomagnetic separation. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2019, 29, 085007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Pelt, S.; Frijns, A.; Den Toonder, J. Microfluidic magnetic bead conveyor belt. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 3826–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Royet, D.; Hériveaux, Y.; Marchalot, J.; Scorretti, R.; Dias, A.; Dempsey, N.M.; Bonfim, M.; Simonet, P.; Frénéa-Robin, M. Using injection molding and reversible bonding for easy fabrication of magnetic cell trapping and sorting devices. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 427, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Surendran, A.N. Study on micromagnets induced local wavy mixing in a microfluidic channel. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 117, 132408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, M.; Tanizaki, K.; Shibata, T. Batch Assembly of SU-8 Movable Components in Channel Under Mild Conditions for Dynamic Microsystems: Application to Biohybrid Systems. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2019, 28, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, M.; Gontran, E.; Hajjj, I.; Malaquin, L.; Viovy, J.-L.; Descroix, S.; Ferraro, D.; Hajji, I.; Serra, M.; Gotran, E.; et al. Development of a droplet microfluidics device based on integrated soft magnets and fluidic capacitor for passive extraction and redispersion of functionalized magnetic particles. In Advanced Materials Technologies; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Wang, C. Microfluidic separation of magnetic particles with soft magnetic microstructures. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2016, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Yang, Q.; Bai, F.; Werner, J.A.; Shi, H.; Ma, Y.; Wang, C. Fabrication and integration of microscale permanent magnets for particle separation in microfluidics. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2016, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deman, A.L.; Mekkaoui, S.; Dhungana, D.; Chateaux, J.F.; Tamion, A.; Degouttes, J. Dupuis, V.; Le Roy, D. Anisotropic composite polymer for high magnetic force in microfluidic systems. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2017, 21, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, J.; Issadore, D.; Ullal, A.; Lee, K.; Weissleder, R.; Lee, H. Rare cell isolation and profiling on a hybrid magnetic/size-sorting chip. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekkaoui, S.; Descamps, L.; Audry, M.; Deman, A.; Le Roy, D. Nanonewton Magnetophoretic Microtrap Array for Microsystems. Langmuir 2020, 36, 14546–14553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descamps, L.; Mekkaoui, S.; Audry, M.-C.; Deman, A.-L.; Le Roy, D. Optimized process for the fabrication of PDMS membranes integrating permanent micro-magnet arrays. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 15215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descamps, L.; Mekkaoui, S.; Laurenceau, E.; Audry, M.C.; Garcia, J.; Payen, L.; Le Roy, D.; Deman, A.L. Array of micro-magnets for CTC sorting in lab-on-a-chip devices. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference Miniaturized Systems for Chemistry and Life Sciences MicroTAS 2019, Basel, Switzerland, 27–31 October 2019; pp. 624–625. [Google Scholar]
- Myklatun, A.; Cappetta, M.; Winklhofer, M.; Ntziachristos, V.; Westmeyer, G.G. Microfluidic sorting of intrinsically magnetic cells under visual control. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abonnenc, M.; Gassner, A.L.; Morandini, J.; Josserand, J.; Girault, H.H. Magnetic track array for efficient bead capture in microchannels. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, C.; Hassanisaber, H.; Yu, R.; Ma, S.; Verbridge, S.S.; Lu, C. Paramagnetic Structures within a Microfluidic Channel for Enhanced Immunomagnetic Isolation and Surface Patterning of Cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mishra, A.; Dubash, T.D.; Edd, J.F.; Jewett, M.K.; Garre, S.G.; Karabacak, N.M.; Rabe, D.C.; Mutlu, B.R.; Walsh, J.R.; Kapur, R.; et al. Ultrahigh-throughput magnetic sorting of large blood volumes for epitope-agnostic isolation of circulating tumor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 16839–16847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Chen, X.; Du, J.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. Label-free separation of nanoscale particles by an ultrahigh gradient magnetic field in a microfluidic device. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, A.-E.; Saias, L.; Psychari, E.; Minc, N.; Simon, D.; Bidard, F.-C.; Mathiot, C.; Pierga, J.-Y.; Fraisier, V.; Salamero, J.; et al. Microfluidic sorting and multimodal typing of cancer cells in self-assembled magnetic arrays. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14524–14529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, X.; Peng, S.; Liu, L.; Wen, W.; Sheng, P. Characterizing and patterning of PDMS-based conducting composites. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2682–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deman, A.L.; Brun, M.; Quatresous, M.; Chateaux, J.F.; Frenea-Robin, M.; Haddour, N.; Semet, V.; Ferrigno, R. Characterization of C-PDMS electrodes for electrokinetic applications in microfluidic systems. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21, 095013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roy, D.; Dhungana, D.; Ourry, L.; Faivre, M.; Ferrigno, R.; Tamion, A.; Dupuis, V.; Salles, V.; Deman, A.L. Anisotropic ferromagnetic polymer: A first step for their implementation in microfluidic systems. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 056604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Lawrence, E.M.; Wu, A.; Ivey, M.L.; Flores, G.A.; Javier, K.; Bibette, J.; Richard, J. Field-induced structures in ferrofluid emulsions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 74, 2828–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.E.; Venturini, E.; Odinek, J.; Anderson, R.A. Anisotropic magnetism in field-structured composites. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Phys. Plasmas Fluids Relat. Interdiscip. Top. 2000, 61, 2818–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertoni, G.; Torre, B.; Falqui, A.; Fragouli, D.; Athanassiou, A.; Cingolani, R. Nanochains formation of superparamagnetic nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 7249–7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; He, L.; Yin, Y. Magnetic field guided colloidal assembly. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Puri, I.K. Changing the magnetic properties of microstructure by directing the self-assembly of superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Faraday Discuss. 2015, 181, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrossilis, D.; Röper, J.C.; Le Roy, D.; Driquez, B.; Michel, A.; Ménager, C.; Shaw, G.; Le Denmat, S.; Ranno, L.; Dumas-Bouchiat, F.; et al. Mechanotransductive cascade of Myo-II-dependent mesoderm and endoderm invaginations in embryo gastrulation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidan, C.M.; Fratzl, M.; Coullomb, A.; Moreau, P.; Lombard, A.H.; Wang, I.; Balland, M.; Boudou, T.; Dempsey, N.M.; Devillers, T.; et al. Magneto-active substrates for local mechanical stimulation of living cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ourry, L.; Le Roy, D.; Mekkaoui, S.; Douillard, T.; Deman, A.L.; Salles, V. Magnetic filaments for anisotropic composite polymers. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekkaoui, S. Développement de Polymères Composites Auto-Organisés Pour la Mise en Œuvre de Fonctions Magnétiques en Microsystèmes Fluidiques. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, Lyon, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dumas-Bouchiat, F.; Zanini, L.F.; Kustov, M.; Dempsey, N.M.; Grechishkin, R.; Hasselbach, K.; Orlianges, J.C.; Champeaux, C.; Catherinot, A.; Givord, D. Thermomagnetically patterned micromagnets. Appl. Phys. Lett 2010, 96, 102511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, P.S.; Bibette, J.; Bancaud, A.; Viovy, J.-L. Self-Assembled Magnetic Matrices for DNA Separation Chips. Science 2002, 295, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minc, N.; Fütterer, C.; Dorfman, K.D.; Bancaud, A.; Gosse, C.; Goubault, C.; Viovy, J.L. Quantitative microfluidic separation of DNA in self-assembled magnetic matrixes. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 3770–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.W. Polymer microfluidics: Simple, low-cost fabrication process bridging academic lab research to commercialized production. Micromachines 2016, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gencturk, E.; Mutlu, S.; Ulgen, K.O. Advances in microfluidic devices made from thermoplastics used in cell biology and analyses. Biomicrofluidics 2017, 11, 051502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Yuk, H.; Zhao, R.; Chester, S.A.; Zhao, X. Printing ferromagnetic domains for untethered fast-transforming soft materials. Nature 2018, 558, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Host Material | Doping Agent | Application | Implementation | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nature | Particle Diameter | Concentration | ||||
| PDMS | Carbonyl iron | 7 µm (Sigma-Aldrich) | 50–83 wt % | Micro-bead sorting and cell trapping | Pillars inside the channel | [58] |
| PDMS | Nickel | 50 nm (DeKeDaoKing, Beijing, China) | N/A | Magnetic bead and cell trapping | Pillars inside the channel | [25] |
| PDMS | Carbonyl iron | 1–3 µm (HQ grade, BASF, Germany) | N/A | Nano-bead trapping | Pillar inside the channel | [59] |
| PDMS | Neody-mium oxide | 5 µm (Molycorp.) | N/A | Immuno-magnetic sorting of beads | Pillars inside the channel | [60] |
| PDMS | Carbonyl iron | N/A | N/A | Magnetic bead conveyor belt | Mushroom-shaped structures buried under the channel | [61] |
| PDMS | Carbonyl iron | N/A (Sigma-Aldrich) | 75 wt % | Cell trapping and sorting | Composites stripes under the channel | [62] |
| PDMS | NdFeB | 5 µm (MQFP-B, Magnequench) | 66 wt % | Cell trapping and sorting | Composites stripes under the channel | [62] |
| PDMS | NdFeB | N/A | N/A | Microfluidic mixer | Composites stripes under the channel | [63] |
| PDMS | Fe3O4 | 50–100 nm (637106, Sigma-Aldrich) | 38 wt % | Trapping of magnetically labeled Vorticella | Composite blocks in the channel walls | [64] |
| PDMS | Iron | 1–6 µm (GoodFellow) | 44, 60, 70 wt % | Extraction and redispersion of functionalized magnetic particles | Integrated magnetic structure in the channel wall | [65] |
| PDMS | Carbonyl iron | N/A (C3518, Sigma-Aldrich) | 50, 66.7 wt % | Magnetic particle separation | Microstructured composite next to the channel | [66] |
| PDMS | NdFeB | N/A (MQFP-B-20076, Magnequench) | 66.7 wt % | Magnetic particle separation, Microfluidic mixer | Microstructured composite next to the channel | [67] |
| PDMS | Carbonyl iron | 7 µm (Sigma-Aldrich) | 83 wt % | Micro-bead trapping and magnetic force measurement | Self-ordered composite block in the channel wall | [46] |
| PDMS | NdFeB | N/A (MQFP-B-20076, Magnequench) | N/A | Cell sorting | Self-ordered composite under the channel | [68] |
| PDMS | Carbonyl iron | 0.5–7 µm (Sigma-Aldrich) | 1–5 wt % | Micro-bead trapping | Columnar agglomerates under the channel | [69,70] |
| PDMS | NdFeB | 0.5–7 µm (MQFP-B, Magnequench) | 1 wt % | Micro-bead trapping | Columnar agglomerates under the channel | [71,72] |
| Light Hydrocarbon Oil | Magnetite | 10 nm (EMG900, Ferrotec) | N/A | Cell sorting | Microchannel parallel to the sorting channel | [73] |
| Carbon ink | Iron | 10 µm | 25 wt % | Bead trapping | Magnetic tracks perpendicular to the sorting channel | [74] |
| Water 1 | Cobalt ferrite | N/A (MJ300, Liquid Research) | N/A | Cell trapping | Integrated magnetic structures in the channel wall | [75] |
| 50% Ethanol 2 | Iron | 40 µm | N/A | Cell sorting | Channels on the side of the sorting channel | [76] |
| Water 2 | Fe3O4 | N/A | 0.2 m/v% | Particle sorting | Magnetic pole arrays close to the sorting channel | [77] |
| Water 1 | Cobalt ferrite | N/A (MJ300, Liquid Research) | ≈10 wt % | Cell trapping | Spot arrays at the bottom of the channel | [78] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Descamps, L.; Le Roy, D.; Tomba, C.; Deman, A.-l. Magnetic Polymers for Magnetophoretic Separation in Microfluidic Devices. Magnetochemistry 2021, 7, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7070100
Descamps L, Le Roy D, Tomba C, Deman A-l. Magnetic Polymers for Magnetophoretic Separation in Microfluidic Devices. Magnetochemistry. 2021; 7(7):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7070100
Chicago/Turabian StyleDescamps, Lucie, Damien Le Roy, Caterina Tomba, and Anne-laure Deman. 2021. "Magnetic Polymers for Magnetophoretic Separation in Microfluidic Devices" Magnetochemistry 7, no. 7: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7070100
APA StyleDescamps, L., Le Roy, D., Tomba, C., & Deman, A.-l. (2021). Magnetic Polymers for Magnetophoretic Separation in Microfluidic Devices. Magnetochemistry, 7(7), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7070100







