Case Study on Homogeneous–Heterogeneous Chemical Reactions in a Magneto Hydrodynamics Darcy–Forchheimer Model with Bioconvection in Inclined Channels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Formulation of the Model
- The flow is considered steady and incompressible.
- The influence of thermal energy and viscous dissipation is incorporated into the analysis.
- The flow is affected by non-parallel stretchable channels, which induce variable flow characteristics due to the channel geometry.
- The effects of the magnetic field and the non-Newtonian behavior are also considered, along with heat and mass transfer phenomena.
- The coupled system of equations is solved using suitable mathematical techniques, such as the similarity transformation, to obtain the flow and temperature profiles.
- We use polar coordinates to formulate the mode.
3. Engineering Quantities
4. Mathematical Technique and Validations
5. Results and Discussion
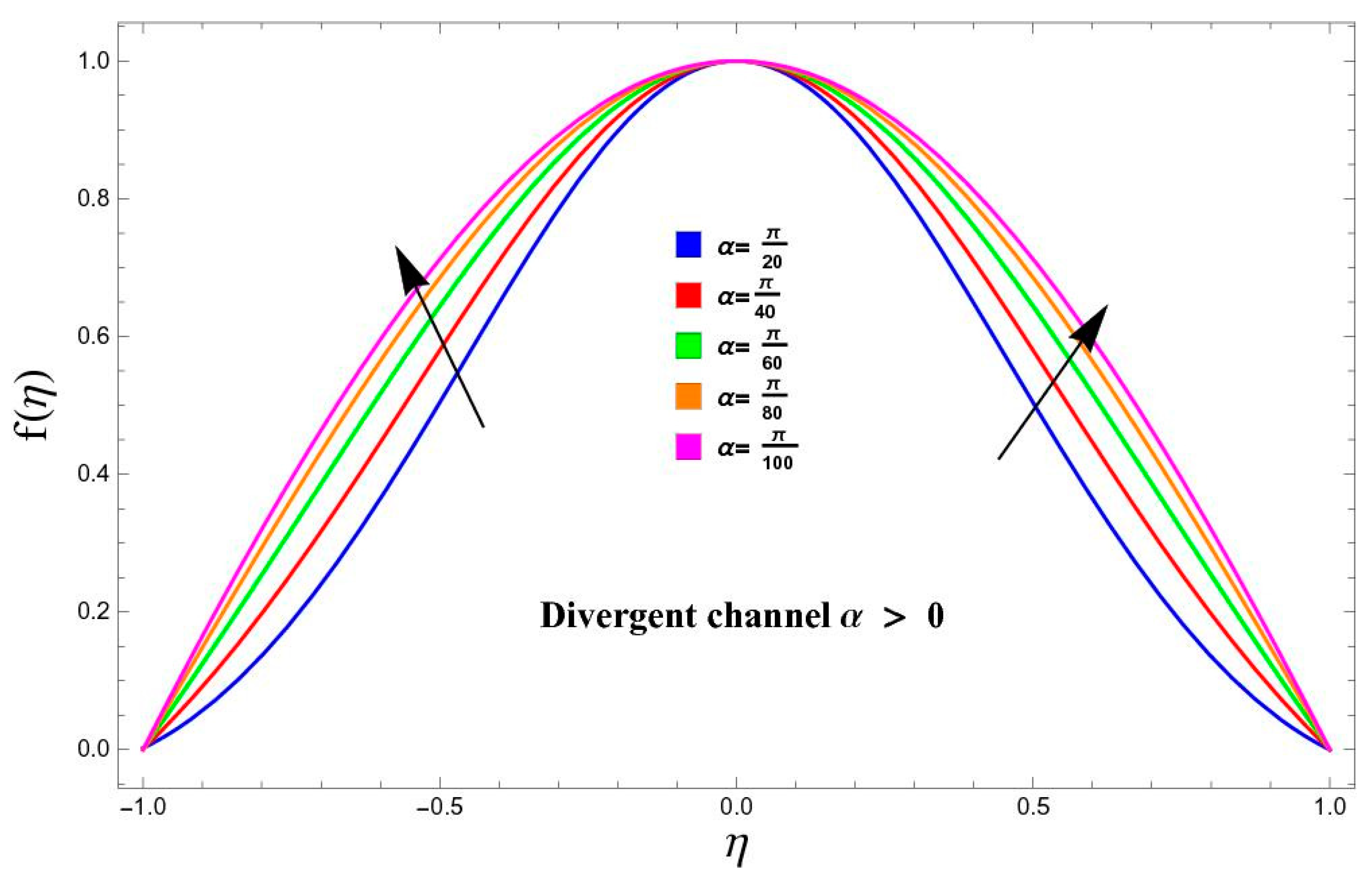
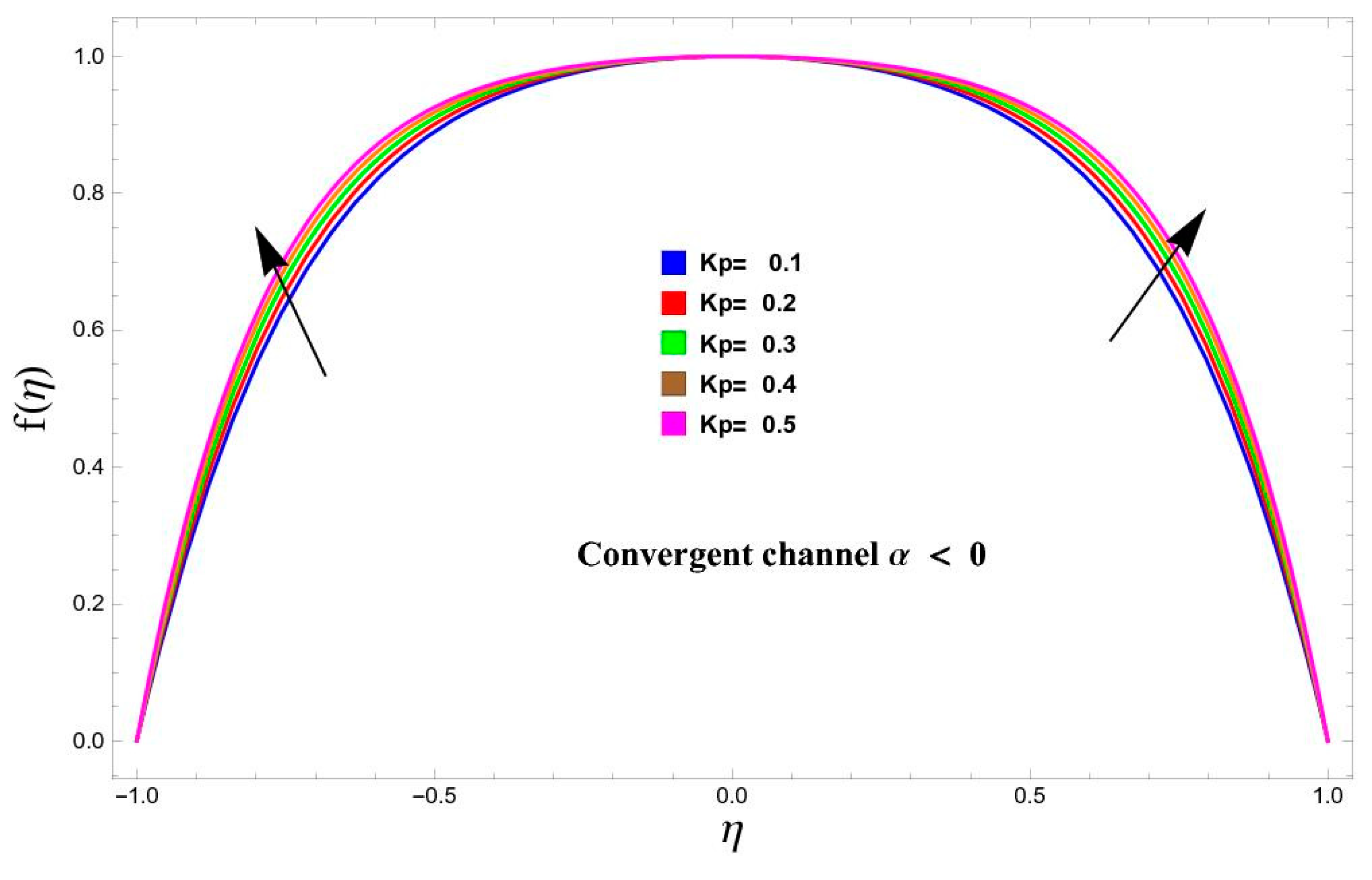
5.1. Variation in Velocity
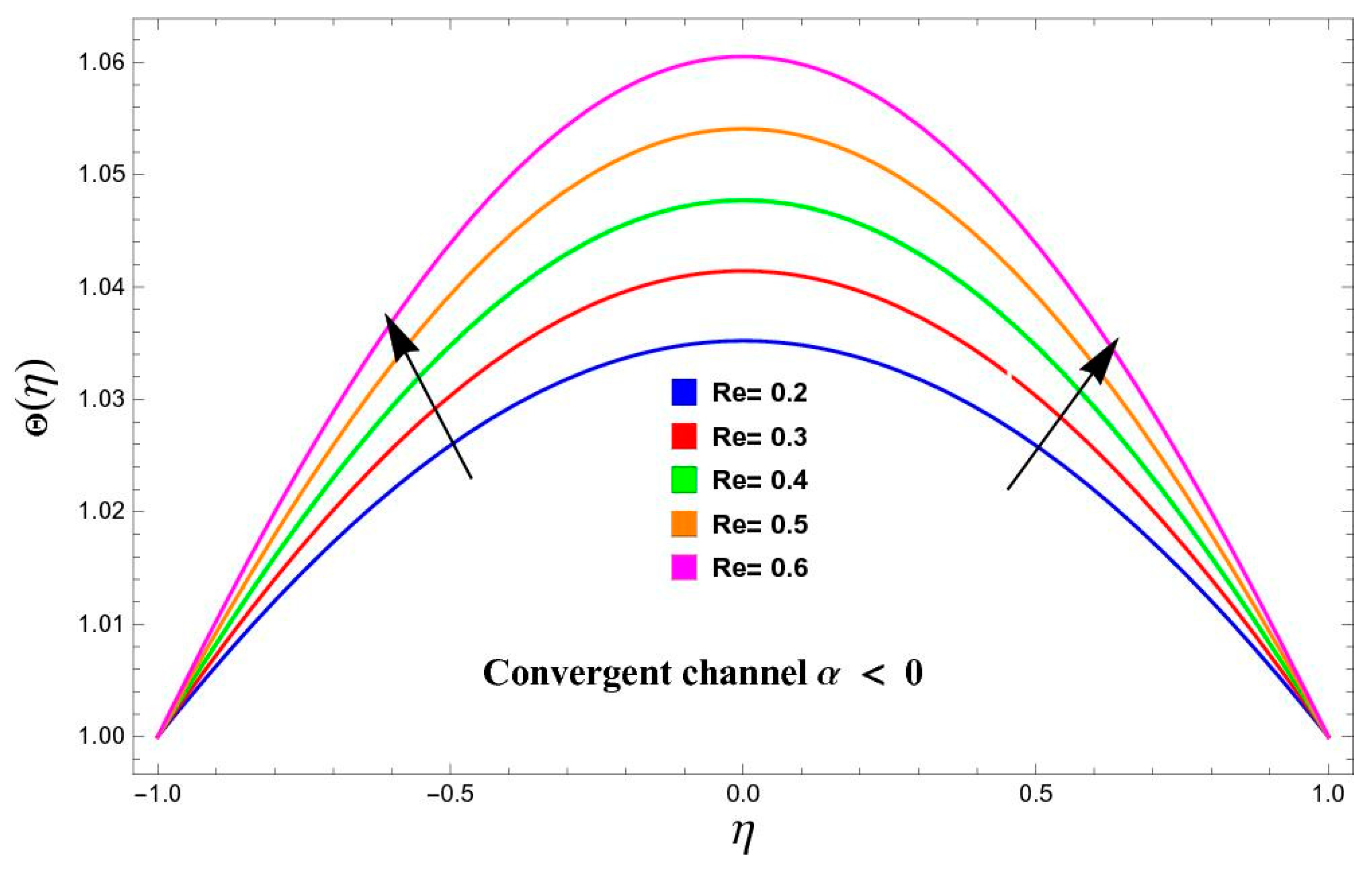
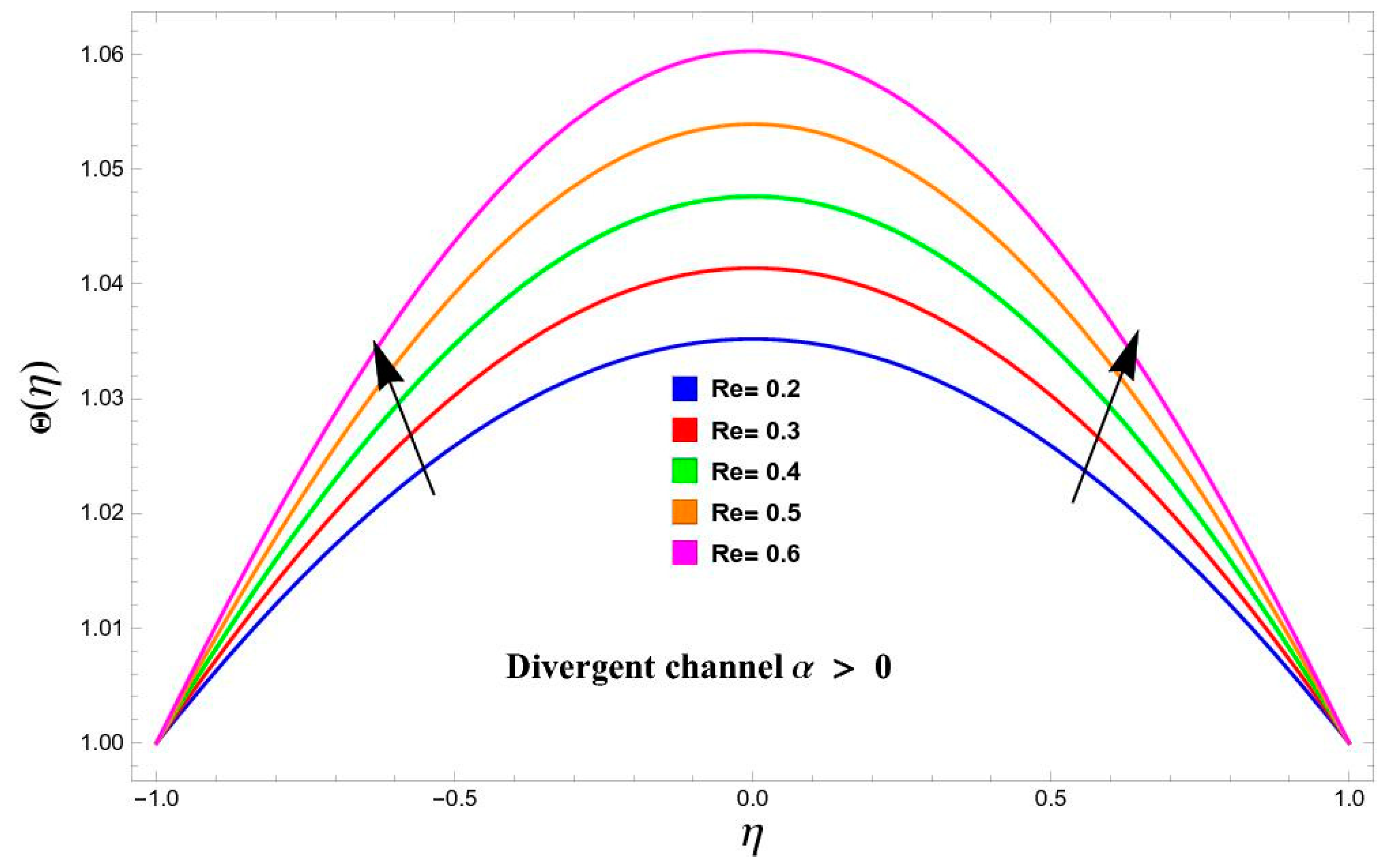
5.2. Variation in Temperature
5.3. Concentration Profile
5.4. Variation in Homogenous Reactions
6. Final Remarks
- Solutions obtained with the help of the NDSolve method used in Mathematica tool give good results.
- The alpha against velocity profile exhibits opposite behavior; that is, velocity decreases in the convergent channel while increasing in the divergent channel.
- The behavior of velocity against porosity is the same in both cases of the convergent/divergent channels.
- The influence of temperature versus various parameters such as and increases in both cases of convergent and divergent walls.
- The concentration rises for both convergent/divergent channels due to higher Reynolds number values.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chu, Y.-M.; Aziz, S.; Khan, M.I.; Khan, S.U.; Nazeer, M.; Ahmad, I.; Tlili, I. Nonlinear radiative bioconvection flow of Maxwell nanofluid configured by bidirectional oscillatory moving surface with heat generation phenomenon. Phys. Scr. 2020, 95, 105007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, M.; Chung, J.D.; Ullah, N. Radiative magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid flow due to gyrotactic microorganisms with chemical reaction and non-linear thermal radiation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017, 130, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairi, R.R.; Shaw, S.; Roy, S.; Raut, S. Thermosolutal marangoni impact on bioconvection in suspension of gyrotactic microorganisms over an inclined stretching sheet. J. Heat Transf. 2021, 143, 031201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhlamini, M.; Mondal, H.; Sibanda, P.; Mosta, S.S.; Shaw, S. A mathematical model for bioconvection flow with activation energy for chemical reaction and microbial activity. Pramana 2022, 96, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Majeed, A.; Ijaz, N.; Barghout, K.; Ali, M.R.; Muhammad, T. Melting thermal transportation in bioconvection Casson nanofluid flow over a nonlinear surface with motile microorganism: Application in bioprocessing thermal engineering. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 49, 103285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, A.; Mebarek-Oudina, F.; Sindhu, T.N.; Abidi, A. A study of dual stratification on stagnation point Walters’ B nanofluid flow via radiative Riga plate: A statistical approach. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2021, 136, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.; Hussien, M.A.; Elsiddieg, A.M.; Lone, S.A.; Hassan, A.M. Exploration of generalized two-phase free convection magnetohydrodynamic flow of dusty tetra-hybrid Casson nanofluid between parallel microplates. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2023, 12, 20230102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, A.; Hammouch, Z.; Sindhu, T.N. Bioconvective MHD flow of tangent hyperbolic nanofluid with newtonian heating. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017, 133, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, M.A.; Merkin, J.H. A simple isothermal model for homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions in boundary-layer flow. I Equal diffusivities. Fluid Dyn. Res. 1995, 16, 311–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, M.A.; Merkin, J.H. Homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions in boundary-layer flow: Effects of loss of reactant. Math. Comput. Model. 1996, 24, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkin, J.H. A model for isothermal homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions in boundary-layer flow. Math. Comput. Model. 1996, 24, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.; Abbas, Z. Homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions in stagnation point flow of Casson fluid due to a stretching/shrinking sheet with uniform suction and slip effects. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2017, 8, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar Giri, S.; Das, K.; Kundu, P.K. Homogeneous–heterogeneous reaction mechanism on MHD carbon nanotube flow over a stretching cylinder with prescribed heat flux using differential transform method. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2020, 7, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, S.; Khan, I.; Ismail, Z.; Salleh, M.Z.; Al-Mdallal, Q.M. Heat transfer enhancement in free convection flow of CNTs Maxwell nanofluids with four different types of molecular liquids. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiq, A.; Çolak, A.B.; Sindhu, T.N. Modeling of Soret and Dufour’s convective heat transfer in nanofluid flow through a moving needle with artificial neural network. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 2807–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, G.B. The two-dimensional steady motion of a viscous fluid. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1915, 29, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, G. Spiralformige bewegungen zaher flussigkeiten. Jahresbericht Deutschen Mathematiker-Vereinigung 1917, 25, 34–60. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.S.V.; Ben Ahmed, S.; Madhu, J.; Verma, A.; Gowda, R.J.P. Unsteady flow of a ternary nanofluid over a slow-rotating disk subject to uniform suction and backpropagated neural network. Numer. Heat Transf. Part B Fundam. 2023, 85, 1705–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, Z.; Saif, R.S.; Ali, N. Investigation of boundary stresses on MHD flow in a convergent/divergent channel: An analytical and numerical study. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 4479–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Farooq, M. Double-diffusive Hamel–Jeffrey flow of nanofluid in a convergent/divergent permeable medium under zero mass flux. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1102. [Google Scholar]
- Adnan; Ashraf, W. Joule heating and heat generation/absorption effects on the heat transfer mechanism in ternary nanofluid containing different shape factors in stretchable converging/diverging Channel. Waves Random Complex Media 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilpa, B.; Srilatha, P.; Khan, U.; Naveen Kumar, R.; Ben Ahmed, S.; Kumar, R. Numerical study of thermal and solutal advancements in ZnO–SAE50 nanolubricant flow past a convergent/divergent channel with the effects of thermophoretic particle deposition. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 6647–6658. [Google Scholar]
- Zada, L.; Ullah, I.; Nawaz, R.; Jamshed, W.; Saddam, E.N.; Idris, S.A.; Ahmad, H.; Amjad, A. Computational treatment and thermic case study of entropy resulting from nanofluid flow of convergent/divergent channel by applying the Lorentz force. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 54, 104034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnahdi, A.S.; Nasir, S.; Gul, T. Ternary Casson hybrid nanofluids in convergent/divergent channel for the application of medication. Therm. Sci. 2023, 27, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Ullah, I.; Ali, A.; Shah, K.; Abdeljawad, T. Investigation of cross-diffusion effect on radiative Jeffery-Hamel flow in convergent/divergent stretchable channel with Lorentz force and Joule heating. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 86, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Ali, A.; Ullah, I.; Alam, M.M.; Khan, Z.A. Activation energy and non-Darcy effects on magnetized Jeffery-Hamel (JH) flow in convergent/divergent channels. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 189, 115749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Khan, D.; Mahariq, I.; Elkotb, M.A.; Elnaqeeb, T. Viscous dissipation effects on time-dependent MHD Casson nanofluid over stretching surface: A hybrid nanofluid study. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 408, 125370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Ullah, S.; Kouki, M.; Khan, H.; Khan, Z.A. Analysis of activation and dissipation energies in Jeffery-Hamel flow (JHF) through non-parallel stretchable channels. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouki, M.; Ullah, I.; Ullah, S.; Alam, M.M.; Khan, H.; Abdou, M.M.M. Exploring the impact of thermal energy and exothermic-endothermic reactions on differential type fluid flow in a convergent/divergent channel. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 55, 104163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinde, O.; Mabood, F.; Khan, W.; Tshehla, M. MHD flow of a variable viscosity nanofluid over a radially stretching convective surface with radiative heat. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 219, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.E.; Mohamed, R.; Ali, A.; Chamkha, A.; Soliman, M. MHD Casson nanofluid flow over a stretching surface embedded in a porous medium: Effects of thermal radiation and slip conditions. Lat. Am. Appl. Res 2021, 51, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.S.; Toghraie, D.; Mehmandoust, B. Effect of MHD on the flow and heat transfer characteristics of nanofluid in a grooved channel with internal heat generation. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2018, 29, 1403–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shorbagy, M.; Eslami, F.; Ibrahim, M.; Barnoon, P.; Xia, W.-F.; Toghraie, D. Numerical investigation of mixed convection of nanofluid flow in a trapezoidal channel with different aspect ratios in the presence of porous medium. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 25, 100977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Nassab, S.G. Combined influences of radiation and inclined magnetic field on natural convection in a cavity with complex geometry. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 134, 106030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabani, I.; Mebarek-Oudina, F.; Ismail, A.A.I. MHD flow of a hybrid nano-fluid in a triangular enclosure with zigzags and an elliptic obstacle. Micromachines 2022, 13, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.; Kumam, P.; Suttiarporn, P.; Srisurat, T. Fourier’s and Fick’s laws analysis of couple stress MHD sodium alginate based Casson tetra hybrid nanofluid along with porous medium and two parallel plates. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 47, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, H.; Tripathi, D.; Mebarek-Oudina, F.; Rajashekhar, C.; Mehmet Baskonus, H.; Prasad, K.V.; Shivaleela. Scrutiny of MHD impact on Carreau Yasuda (CY) fluid flow over a heated wall of the uniform micro-channel. Chin. J. Phys. 2024, 87, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.; Kumam, P.; Watthayu, W. Multi-generalized slip and ramped wall temperature effect on MHD Casson fluid: Second law analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 13597–13609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeelani, M.B.; Abbas, A. Al2O3-Cu\Ethylene glycol-based magnetohydrodynamic non-Newtonian Maxwell hybrid nanofluid flow with suction effects in a porous space: Energy saving by solar radiation. Symmetry 2023, 15, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchi, S.; Gaddala, P.R.; Gurram, S. Impact of Activation Energy, Diffusion Thermo, Thermal Diffusion and Hall Current on MHD Casson Fluid Flow with Inclined Plates. CFD Lett. 2024, 16, 90–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.; Ullah, S.; Kumam, P.; Watthayu, W.; Ullah, Z.; Galal, A.M. A generalized dusty Brinkman type fluid of MHD free convection two phase flow between parallel plates. Phys. Lett. A 2022, 450, 128368. [Google Scholar]
- Aman, S.; Al-Mdallal, Q.; Khan, I. Heat transfer and second order slip effect on MHD flow of fractional Maxwell fluid in a porous medium. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2020, 32, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, A.; Andaç Batur, Ç.; Tabassum Naz, S. A Hybrid Approach of Buongiorno’s Law and Darcy–Forchheimer Theory Using Artificial Neural Networks: Modeling Convective Transport in Al2O3-EO Mono-Nanofluid Around a Riga Wedge in Porous Medium. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2025, 97, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullah, S.; Emam, W.; Ali, Z.; Khan, D.; Pamucar, D.; Khan, Z.A. Case Study on Homogeneous–Heterogeneous Chemical Reactions in a Magneto Hydrodynamics Darcy–Forchheimer Model with Bioconvection in Inclined Channels. Magnetochemistry 2025, 11, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11050037
Ullah S, Emam W, Ali Z, Khan D, Pamucar D, Khan ZA. Case Study on Homogeneous–Heterogeneous Chemical Reactions in a Magneto Hydrodynamics Darcy–Forchheimer Model with Bioconvection in Inclined Channels. Magnetochemistry. 2025; 11(5):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11050037
Chicago/Turabian StyleUllah, Subhan, Walid Emam, Zeeshan Ali, Dolat Khan, Dragan Pamucar, and Zareen A. Khan. 2025. "Case Study on Homogeneous–Heterogeneous Chemical Reactions in a Magneto Hydrodynamics Darcy–Forchheimer Model with Bioconvection in Inclined Channels" Magnetochemistry 11, no. 5: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11050037
APA StyleUllah, S., Emam, W., Ali, Z., Khan, D., Pamucar, D., & Khan, Z. A. (2025). Case Study on Homogeneous–Heterogeneous Chemical Reactions in a Magneto Hydrodynamics Darcy–Forchheimer Model with Bioconvection in Inclined Channels. Magnetochemistry, 11(5), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11050037




