Design of Fe7S8@Lip Composite for the pH-Selective and Magnetically Targeted Programmed Release of H2S
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Preparation of Fe7S8@Lip Nanomedicine
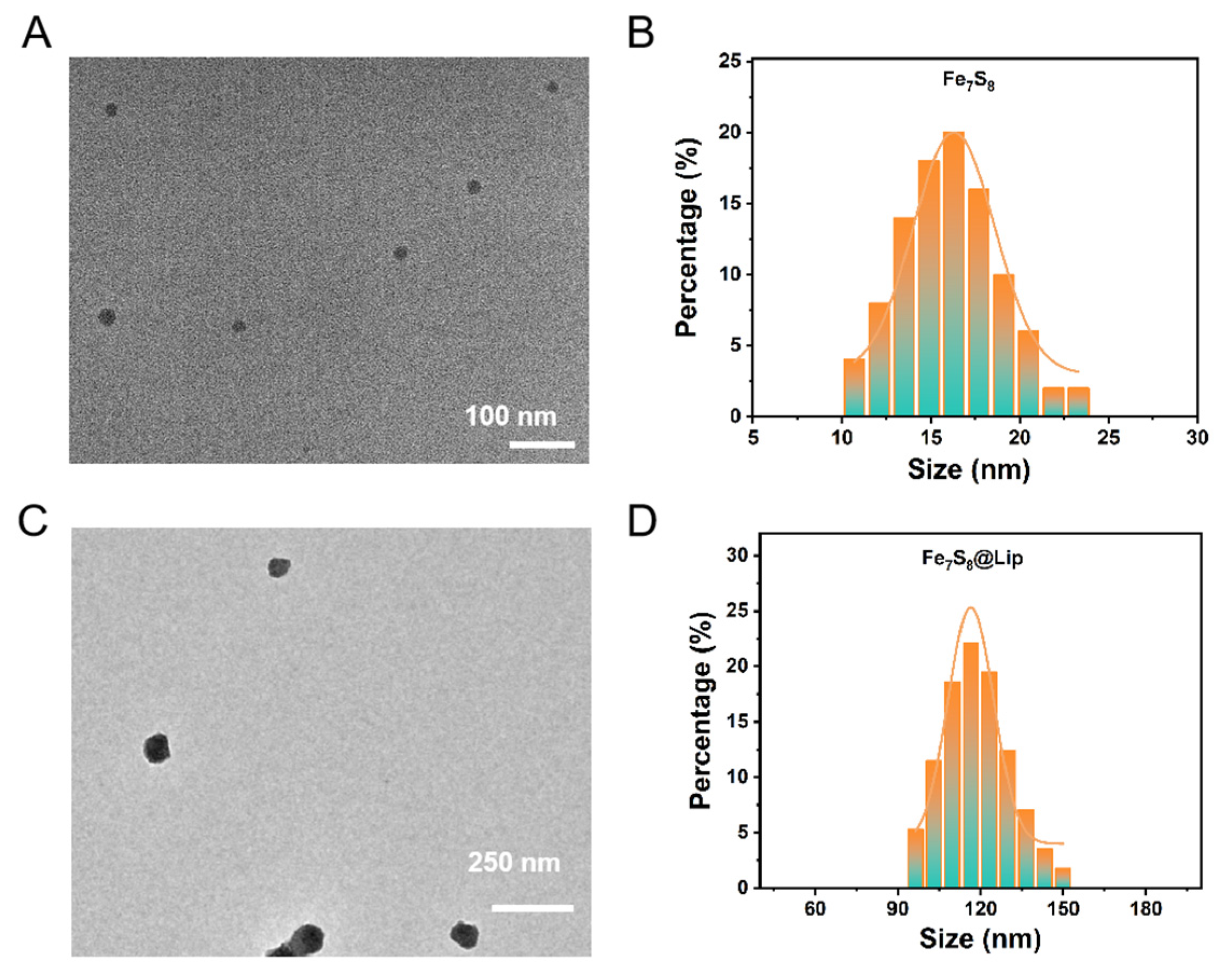
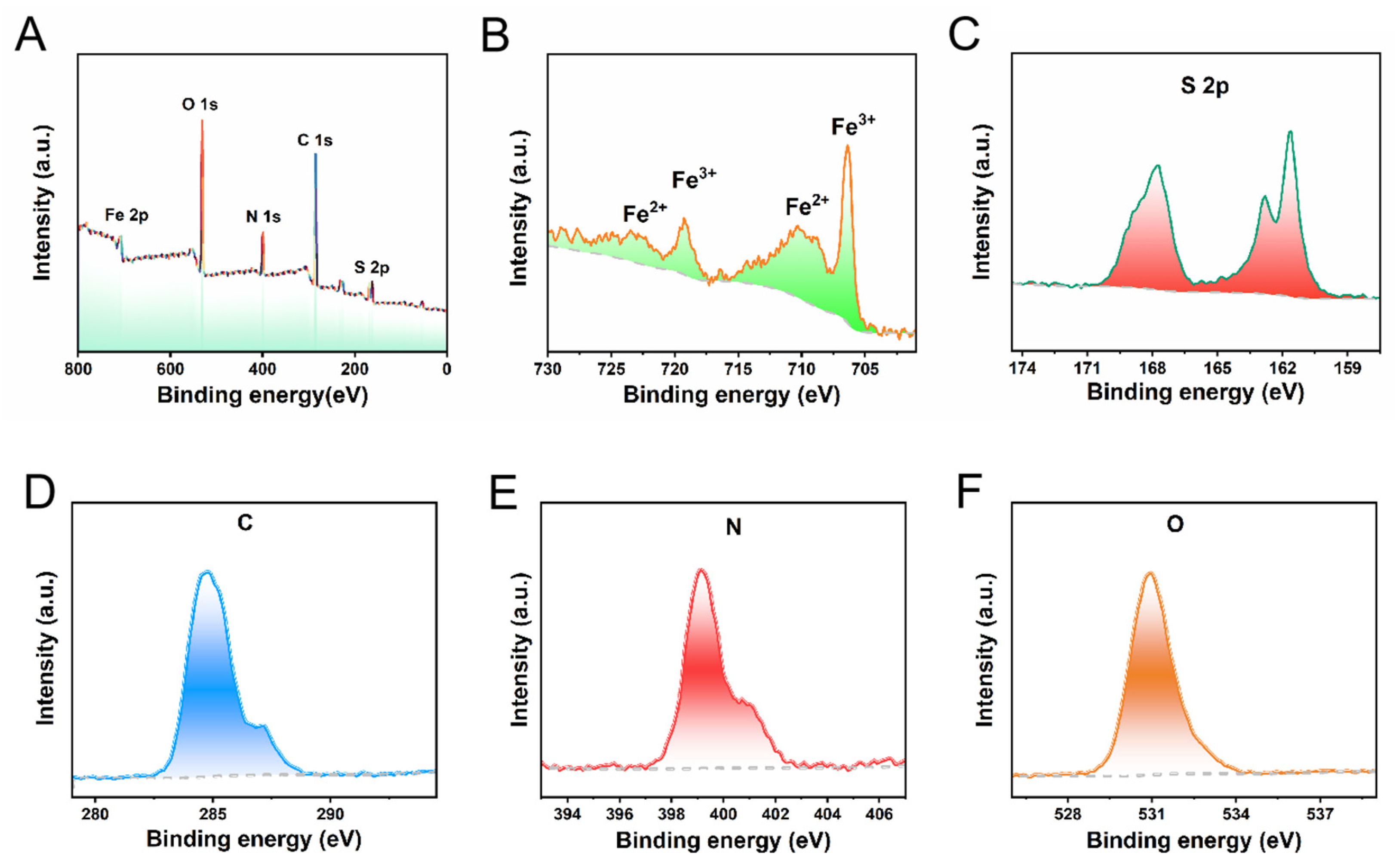
2.2. Structural Characterization of Fe7S8@Lip Nanomedicine
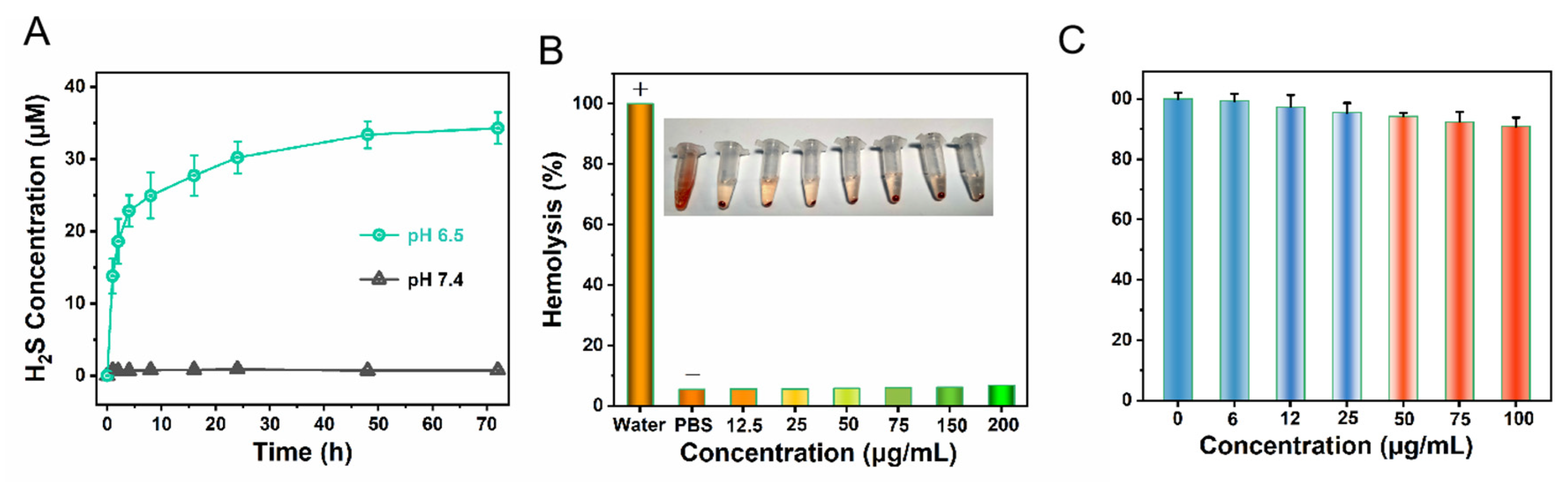
2.3. Evaluation of the Performance of Releasing H2S
2.4. CCK-8 Assay
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaik, R.; Kishore, R.; Kumar, A.; Shekhar, C.; Kumar, M. Metal oxide nanofibers based chemiresistive H2S gas sensors. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 471, 214752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.N.; Guo, W.Y.; Xu, C.W.; Wang, Q.; Mao, C.; Wan, M.M. Physiological functions and donor design of hydrogen sulffde and its application in central nervous system diseases. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H. Signaling by hydrogen sulffde (H2S) and polysulffdes (H2Sn) in the central nervous system. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 126, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.H.; Wu, Y.L.; Chen, J.J.; Zhong, J.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S.Z. A Turn-On Optoacoustic Probe for Imaging Metformin-Induced Upregulation of Hepatic Hydrogen Sulfide and Subsequent Liver Injury. Theranostics 2019, 9, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabil, O.; Banerjee, R. Enzymology of H2S Biogenesis, Decay and Signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Wu, L.; Jiang, B.; Yang, W.; Qi, J.; Cao, K. H2S as a Physiologic Vasorelaxant: Hypertension in Mice with Deletion of Cystathionine γ-Lyase. Science 2008, 322, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, K.; Kimura, H. The Possible Role of Hydrogen Sulfide as an Endogenous Neuromodulator. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiliński, B.; Wiliński, J.; Somogyi, E.; Piotrowska, J.; Opoka, W. Metformin Raises Hydrogen Sulfide Tissue Concentrations in Various Mouse Organs. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.N.; Wang, Q. Advances of H2S in Regulating Neurodegenerative Diseases by Preserving Mitochondria Function. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjana, M.; Kulkarni, R.M.; Sunil, D. Small Molecule Optical Probes for Detection of H2S in Water Samples: A Review. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 14672–14691. [Google Scholar]
- Bulemo, P.M.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, N.H.; Kim, I.D. Mesoporous SnO2 Nanotubes via Electrospinning–Etching Route: Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of H2S Molecule. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 26304–26313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xie, L.S.; Li, B.; Yin, C.; Wang, G.H.; Sang, W.; Li, W.X.; Tian, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.J.; et al. Engineering a Hydrogen-Sulfide-Based Nanomodulator to Normalize Hyperactive Photothermal Immunogenicity for Combination Cancer Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2008481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.J. Precision gas therapy using intelligent nanomedicine. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 2226–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Chang, J.H.; He, F.; Gai, S.L.; Yang, P.P. Hydrogen sulffde: An emerging precision strategy for gas therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2101984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Z.; Li, B.; Qin, J.; Peng, Z.; He, G.; Brett, D.J.; Wang, R.; Lu, X. Fe7S8 nanoparticles for arterial inflammation therapy: Integration of magnetic hyperthermia and photothermal treatment. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 18, 100457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.B.; Wang, X.B.; Liu, X.F.; Ling, C.C.; Shen, W.J.; Zhang, L.Z. Visible light promoted Fe3S4 Fenton oxidation of atrazine. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 277, 119229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabet, Y.; Elsabahy, M.; Eissa, N.G. Methods for preparation of niosomes: A focus on thin-film hydration method. Methods 2022, 199, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Wei, H.; Li, J.; Liu, N.; Deng, Z.; Huang, J. Design of Fe7S8@Lip Composite for the pH-Selective and Magnetically Targeted Programmed Release of H2S. Magnetochemistry 2025, 11, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11030022
Wang S, Wei H, Li J, Liu N, Deng Z, Huang J. Design of Fe7S8@Lip Composite for the pH-Selective and Magnetically Targeted Programmed Release of H2S. Magnetochemistry. 2025; 11(3):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11030022
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shenghua, Hanlin Wei, Jialian Li, Ning Liu, Zhiming Deng, and Junqing Huang. 2025. "Design of Fe7S8@Lip Composite for the pH-Selective and Magnetically Targeted Programmed Release of H2S" Magnetochemistry 11, no. 3: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11030022
APA StyleWang, S., Wei, H., Li, J., Liu, N., Deng, Z., & Huang, J. (2025). Design of Fe7S8@Lip Composite for the pH-Selective and Magnetically Targeted Programmed Release of H2S. Magnetochemistry, 11(3), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11030022





