Plant Regeneration via Somatic Embryogenesis and Indirect Organogenesis in Blue Honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Preparation of Tissue Culture
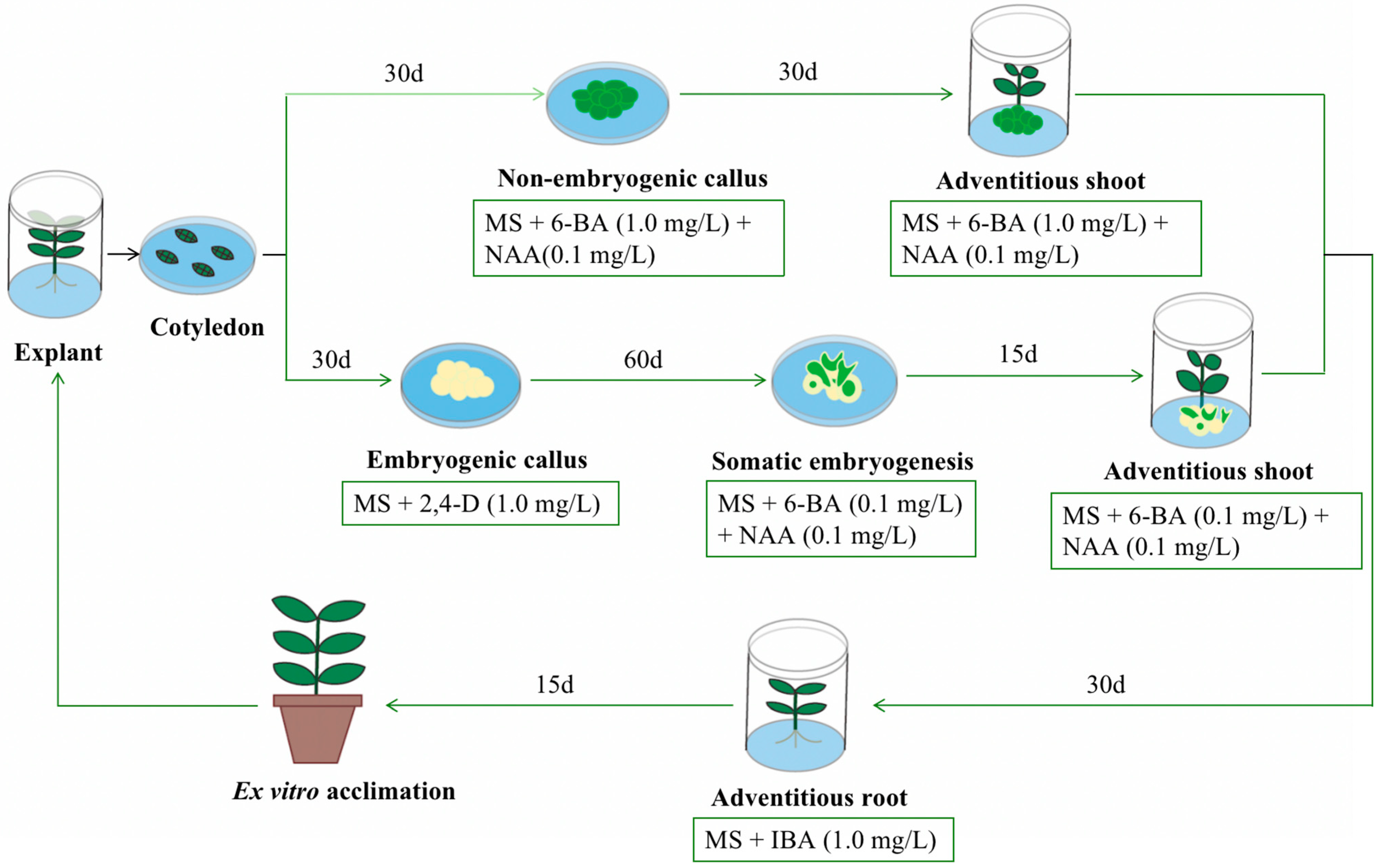
2.2. Callus Induction
2.3. Somatic Embryogenesis
2.4. Adventitious Shoot Induction
2.5. Adventitious Root Induction
2.6. Plant Regeneration and Transplantation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
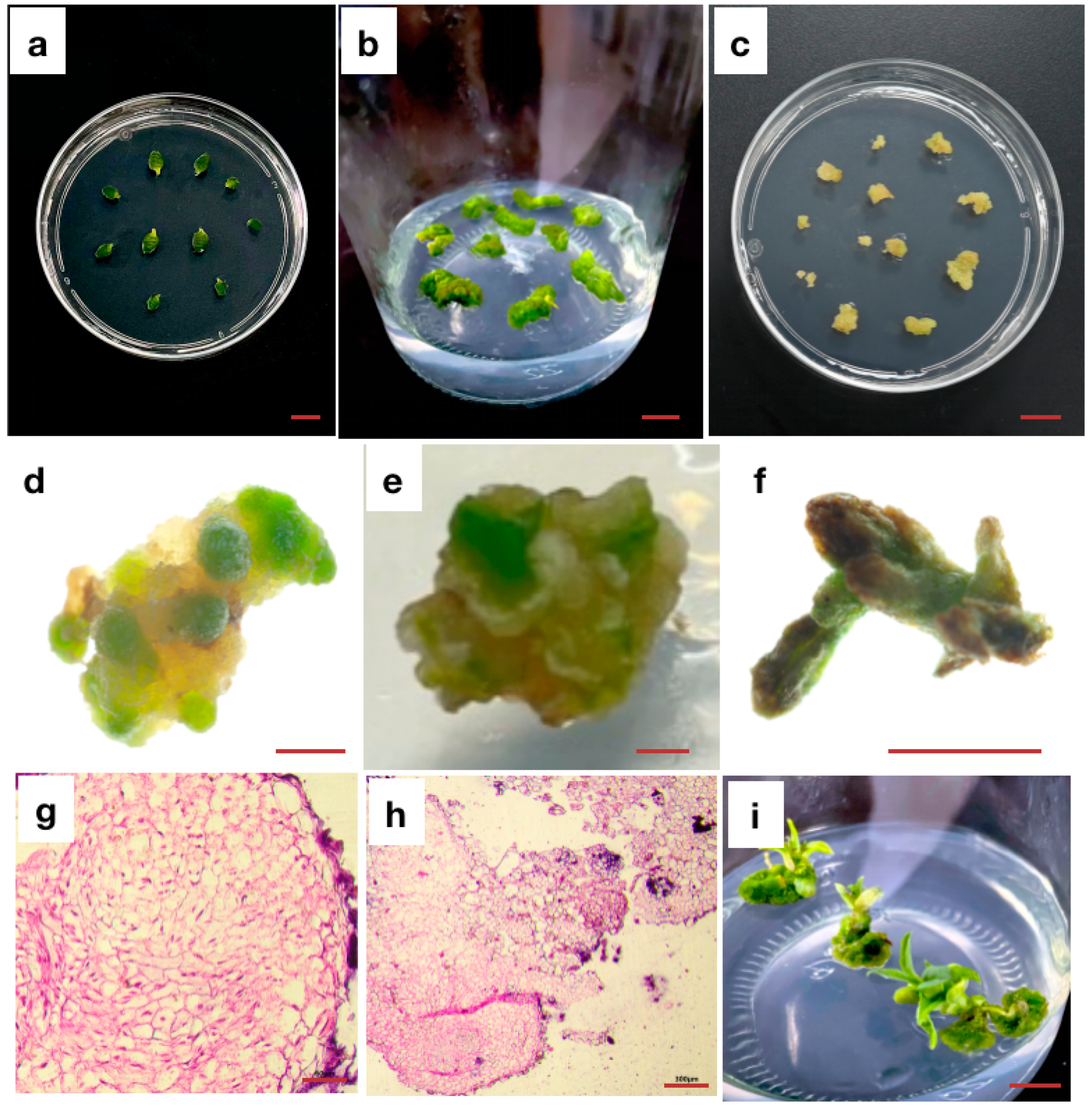
3.1. Effects of PGRs and Explant Types on Callus Induction
3.2. Effect of PGRs on Somatic Embryogenesis
3.3. Effects of PGRs and Genotypes on Adventitious Shoot Induction through Organogenesis
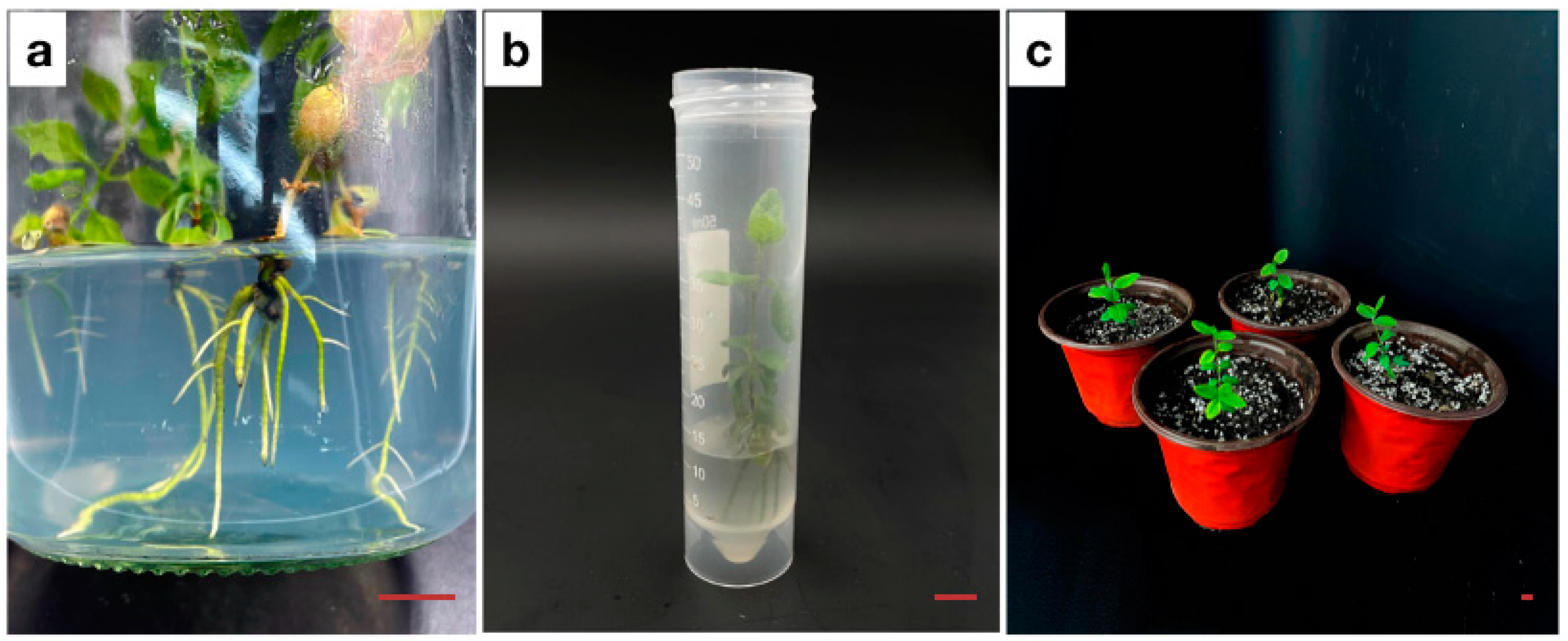
3.4. Adventitious Root Induction
3.5. Plant Regeneration and Conversion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bieniek, A.A.; Grygorieva, O.; Bielska, N. Biological Properties of Honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L.): A Review: The nutrition, health properties of honeysuckle. Agrobiodiversity Improv. Nutr. Health Life Qual. 2021, 5, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Karim, N.; Xie, L.; Xie, J.; Chen, W. Simulated gastrointestinal digestion and colonic fermentation of blue honeysuckle: Phenolic profile and protectivity on ethyl carbamate-induced oxidative damage. Process Biochem. 2022, 120, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaovanalikit, A.; Thompson, M.M.; Wrolstad, R.E. Characterization and Quantification of Anthocyanins and Polyphenolics in Blue Honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 848–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusznierewicz, B.; Piekarska, A.; Mrugalska, B.; Konieczka, P.; Namieśnik, J.; Bartoszek, A. Phenolic composition and antioxidant properties of Polish blue-berried honeysuckle genotypes by HPLC-DAD-MS, HPLC postcolumn derivatization with ABTS or FC, and TLC with DPPH visualization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowd, V.; Karim, N.; Shishir, M.R.I.; Xie, L.; Chen, W. Dietary polyphenols to combat the metabolic diseases via altering gut microbiota. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, T.; Shen, X.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, K.; Li, L.; Xia, Z.; Zheng, X.; et al. Therapeutic potential of plant iridoids in depression: A review. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 2167–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holubec, V.; Smekalova, T.; Leisova-Svobodova, L. Morphological and molecular evaluation of the Far East fruit genetic resources of Lonicera caerulea L.—Vegetation, ethnobotany, use and conservation. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2019, 66, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kithma, A.B.; Silva, H.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. Polyphenols composition and anti-diabetic properties in vitro of haskap (Lonicera caerulea L.) berries in relation to cultivar and harvesting date. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 88, 103402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisz, S.; Kieliszek, M. Influence of storage conditions on selected quality characteristics of blue honeysuckle berry juice. Agrochimica 2021, 66, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Sui, W.; Yang, G.; Yu, Z. Review of study on germplasm resources of blue honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L.). Acta Hortic. Sin. 2005, 32, 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Sun, X.; Fu, Q.; Zhan, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Yu, M.; Qin, D.; Zhang, L.; Huo, J. Complete chloroplast genome and phylogenetic analysis of Lonicera caerulea var. edulis (Caprifoliaceae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2023, 8, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casella, F.; Vurro, M.; Valerio, F.; Perrino, E.V.; Mezzapesa, G.N.; Boari, A. Phytotoxic Effects of Essential Oils from Six Lamiaceae Species. Agronomy 2023, 13, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-M.; Wu, Y.-F.; Li, Z.; Song, C.-B.; Wang, X.-P. Advancements in plant regeneration and genetic transformation of grapevine (Vitis spp.). J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 1407–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, M. Organogenesis in vitro. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 1999, 2, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, X. Regulation of somatic embryogenesis in higher plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2010, 29, 36–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaj, M.D. Direct somatic embryogenesis as a rapid and efficient system for in vitro regeneration of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2001, 64, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra-Jiménez, A.; Aronen, T.S.; Alegre, J.; Toribio, M. Cryopreservation of embryogenic tissues from mature holm oak trees. Cryobiology 2015, 70, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbanova, E. Simultaneous direct ex vitro rooting and adaptation of the blue honeysuckle micro-sprouts (Lonicera Caerulea L. var. Kamtschatica). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. Belarus. Agrar. Ser. 2020, 58, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malabadi, R.B.; Chalannavar, R.K.; Meti, N.T.; Mulgund, G.S.; Odhav, N.B. Detection of Glutathione S-Transferase gene (GST2, GST3) during induction of somatic embryogenesis in grape (Vitis vinifera L.). Res. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Grosser, J.W.; Ollitrault, P.; Olivares-Fuster, O. Somatic hybridization in citrus: An effective tool to facilitate variety improvement. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.—Plant 2000, 36, 434–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-M.; Lan, H.; Cao, H.-B.; Xu, Q.; Chen, C.-L.; Deng, X.-X.; Guo, W.-W. Recovery and characterization of homozygous lines from two sweet orange cultivars via anther culture. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2015, 123, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zheng, X.; Huang, Y.; Ye, J.; Chen, P.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, F.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, N.; et al. Genome sequencing and CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing of an early flowering Mini-Citrus (Fortunella hindsii). Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, G.; Singh, M.B.; Bhalla, P.L. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from commercial soybean cultivars. Plants 2020, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karhu, S.T. Axillary shoot proliferation of blue honeysuckle. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 1997, 48, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlák, J.; Paprštein, F. In vitro propagation of blue honeysuckle. Hortic. Sci. 2007, 34, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziedzic, E. Propagation of blue honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea var. kamtschatica Pojark.) in in vitro culture. J. Fruit Ornam. Plant Res. 2008, 16, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Al, F.; Clapa, D.; Cristea, V.; Plopa, C. In vitro propagation of Lonicera kamtschatica. Agric. -Sci. Pract. 2014, 1–2, 89–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinushkin, A.; Akimova, S.; Nikulina, E.; Tsirulnikova, N.; Kirkach, V.; Kalinitchenko, V.; Radzhabov, A.; Radkevich, E.; Marchenko, L.; Solovyov, A.; et al. Preliminary Study: Micropropagation Using Five Types of Chelated Iron and the Subsequent Acclimation of Blue Honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea var. kamtschatica Sevast.). Forests 2023, 14, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunková, J.; Szabóová, M.; Gajdošová, A. Protocols for adventitious regeneration of Amelanchier alnifolia var. cusickii and Lonicera kamtschatica ‘Jugana’. Plants 2021, 10, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolik, M.; Ochmian, I.; Bobrowska-Chwat, A.; Chwat, G.; Arus, L.; Banaszczak, P.; Bocianowski, J.; Milczarski, P.; Ostrowska, K. Fingerprinting, structure, and genetic relationships among selected accessions of blue honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L.) from European collections. Biotechnol. Rep. 2022, 34, e00721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.; Qin, D.; Huo, J. Two novel blue honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L.) cultivars: Lanjingling and Wulan. HortScience 2022, 57, 1145–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T. Study on Rapid Propagation Techniques of Tissue Culture of Blue Honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L.); Northeast Agricultural Universily: Harbin, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita, T.; Ohashi, T.; Shibata, F.; Araki, H.; Hoshino, Y. Plant regeneration with maintenance of the endosperm ploidy level by endosperm culture in Lonicera caerulea var. emphyllocalyx. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2009, 98, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plekhanova, M.N. Blue honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L.)—A new commercial berry crop for temperate climate: Genetic resources and breeding. Acta Hortic. 2000, 538, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, J.X.; Wen, S.C.; Hua, Z.Y.; Ming, L.X. Comparative study on different methods for Lonicera japonica Thunb. micropropagation and acclimatization. J. Med. Plants Res. 2012, 6, 4389–4393. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.W.; Cheol, O.S.; In, D.S.; Liu, J.R. High frequency somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in zygotic embryo cultures of Japanese honeysuckle. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2003, 72, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelina, K.-M.; Ochmian, I. Propagation of Blue Honeysuckles (Lonicera caerulea L.) in In Vitro Culture. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2014, 10, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaljević, I.; Tomaš, V.; Vuković, D.; Dugalić, K. Propagation of Three Blue Honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L.) Cultivars In Vitro Culture; Agricultural Institute Osijek: Osijek, Croatia; Croatian Agency for Agriculture and Food: Osije, Croatia, 2019; Volume 23, pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ochatt, S. Requirements for plant regeneration from protoplasts of the shrubby ornamental honeysuckle, Lonicera nitida cv. Maigrun. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 1991, 25, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Tan, M.; Mo, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, X.; Jiang, N. Application of the phosphomannose-isomerase/mannose selection system in the Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Lonicera hypoglauca Miq. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liang, Q.; Xia, X.; Yin, W. In vitro culture and plant regeneration from sprouting buds of Lonicera edulis Turcz. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2010, 32, 126–130. [Google Scholar]
| MS + PGR (mg/L) | Callus Induction Rate (%) | Morphological Feature | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotyledon | Euphylla | Tender Stem | Tender Root | ||
| 6-BA 0.5 + NAA 0.1 | 73.0 ± 5.2 c | 0 c | 56.7 ± 20.8 a | 60.3 ± 19.0 a | Green and compact |
| 6-BA 0.5 + NAA 0.2 | 88.4 ± 4.1 b | 37.3 ± 2.5 b | 73.3 ± 5.8 a | 63.0 ± 14.7 a | Green and compact |
| 6-BA 1.0 + NAA 0.1 | 98.9 ± 1.7 a | 65.7 ± 9.8 a | 73.0 ± 6.1 a | 83.7 ± 14.8 a | Green and compact |
| 6-BA 1.0 + NAA 0.2 | 86.4 ± 5.6 b | 46.7 ± 10.4 b | 68.3 ± 2.1 a | 69.7 ± 10.0 a | Green and compact |
| 2,4-D 0.5 | 95.6 ± 7.7 a | 5.7 ± 5.1 b | 85.0 ± 8.5 a | 71.3 ± 7.5 a | Yellow and friable |
| 2,4-D 1.0 | 97.6 ± 3.6 a | 60.0 ± 13.0 a | 85.3 ± 6.7 a | 75.7 ± 10.3 a | Yellow and friable |
| 2,4-D 2.0 | 86.7 ± 13.3 a | 17.7 ± 13.6 b | 85.3 ± 13.1 a | 86.7 ± 17.3 a | Yellow and friable |
| 2,4-D 3.0 | 93.8 ± 5.9 a | 4.7 ± 4.0 b | 71.6 ± 5.0 a | 69.0 ± 3.5 a | Yellow and friable |
| MS + PGR (mg/L) +AC (0.5 g/L) | Embryogenesis Induction Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| 6-BA 0.1 + NAA 0.1 | 28.3 ± 1.7 a |
| 6-BA 0.1 + NAA 0.2 | 13.3 ± 1.7 b |
| 6-BA 0.1 + NAA 0.3 | 11.1 ± 3.5 b |
| 6-BA 0.1 + NAA 0.4 | 9.4 ± 2.5 bc |
| 6-BA 0.1 + NAA 0.5 | 6.1 ± 1.0 c |
| 6-BA 0.2 + IBA 1.0 | 10.6 ± 5.9 bc |
| 6-BA 0.2 + IBA 2.0 | 21.1 ± 5.4 a |
| 6-BA 0.2 + IBA 3.0 | 11.1 ± 1.0 bc |
| 6-BA 0.5 + IBA 1.0 | 3.9 ± 2.5 c |
| 6-BA 0.5 + IBA 2.0 | 12.8 ± 3.5 b |
| 6-BA 0.5 + IBA 3.0 | 11.8 ± 6.3 bc |
| MS + PGR (mg/L) | Adventitious Shoot Induction Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| 6-BA 0.5 + NAA 0.1 | 10.6 ± 2.5 c |
| 6-BA 0.5 + NAA 0.2 | 13.3 ± 3.1 c |
| 6-BA 1.0 + NAA 0.1 | 51.6 ± 6.5 a |
| 6-BA 1.0 + NAA 0.2 | 35.6 ± 3.5 b |
| 6-BA 1.0 + IBA 0.1 | 16.7 ± 4.2 c |
| 6-BA 1.0 + IBA 0.2 | 42.8 ± 3.5 a |
| 6-BA 2.0 + IBA 0.1 | 31.7 ± 6.0 b |
| 6-BA 2.0 + IBA 0.2 | 36.1 ± 1.0 ab |
| Genotype | MS + PGRs (mg/L) | Adventitious Shoot Induction Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Berel | 6-BA 0.5 + NAA 0.1 | 12.8 ± 1.9 c |
| 6-BA 0.5 + NAA 0.2 | 13.9 ± 1.0 c | |
| 6-BA 1.0 + NAA 0.1 | 43.9 ± 2.5 a | |
| 6-BA 1.0 + NAA 0.2 | 32.8 ± 5.8 b | |
| Lanjingling | 6-BA 0.5 + NAA 0.1 | 14.4 ± 3.5 c |
| 6-BA 0.5 + NAA 0.2 | 16.7 ± 4.4 c | |
| 6-BA 1.0 + NAA 0.1 | 53.3 ± 2.9 a | |
| 6-BA 1.0 + NAA 0.2 | 27.2 ± 1.9 b | |
| Altai-4 | 6-BA 0.5 + NAA 0.1 | 18.3 ± 1.7 c |
| 6-BA 0.5 + NAA 0.2 | 28.3 ± 1.4 b | |
| 6-BA 1.0 + NAA 0.1 | 38.9 ± 2.5 a | |
| 6-BA 1.0 + NAA 0.2 | 15.6 ± 3.5 c |
| MS + PGR (mg/L) | Adventitious Root Induction Rate (%) | Root Length (cm) | Root Number per Plantlet |
|---|---|---|---|
| PGR-free | 67.0 ± 4.3 b | 2.4 ± 0.5 b | 7.0 ± 5.2 a |
| IBA 0.5 | 0 c | 0 c | 0 c |
| IBA 1.0 | 96.0 ± 3.3 a | 4.6 ± 1.8 a | 4.2 ± 2.4 b |
| IAA 0.5 | 74.0 ± 12.2 b | 1.8 ± 0.2 b | 8.8 ± 3.0 a |
| IAA 1.0 | 0 c | 0 c | 0 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Fu, Q.; Li, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, M.; Qin, D.; Huo, J.; Zhu, C. Plant Regeneration via Somatic Embryogenesis and Indirect Organogenesis in Blue Honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L.). Horticulturae 2023, 9, 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9090996
Liu Y, Zhan Y, Fu Q, Li S, Sun X, Wang Y, Yu M, Qin D, Huo J, Zhu C. Plant Regeneration via Somatic Embryogenesis and Indirect Organogenesis in Blue Honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L.). Horticulturae. 2023; 9(9):996. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9090996
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yu, Ying Zhan, Qiang Fu, Songlin Li, Xinyu Sun, Yaru Wang, Min Yu, Dong Qin, Junwei Huo, and Chenqiao Zhu. 2023. "Plant Regeneration via Somatic Embryogenesis and Indirect Organogenesis in Blue Honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L.)" Horticulturae 9, no. 9: 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9090996
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhan, Y., Fu, Q., Li, S., Sun, X., Wang, Y., Yu, M., Qin, D., Huo, J., & Zhu, C. (2023). Plant Regeneration via Somatic Embryogenesis and Indirect Organogenesis in Blue Honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L.). Horticulturae, 9(9), 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9090996





