Abstract
The AP2/ERF (APETALA2/Ethylene−Responsive element binding factor) family genes play crucial roles in plant growth and development, and responses to environmental factors; however, this family has not been characterized in Diospyros species. In Diospyros, the diploid Oily persimmon (D. oleifera, 2n = 2x = 30) has been released with complete genome assembly, which makes it possible for genome-wide gene family identification and exploration of molecular function in cultivated persimmon (D. kaki, 2n = 6x = 90). Here, we identified the AP2/ERF family in Oily persimmon for the first time and investigated its classification, main physicochemical properties, structural characteristic, chromosome distribution, gene replication and collinearity, cis-factor binding sites deduction, GO term annotation, and PPI interaction, as well as its expression profiles in different tissue and under the treatment of polyamines. A total of 157 AP2/ERF genes, including four subfamilies (AP2, RAV, Soloist, and ERF), were identified with distribution on all 15 chromosomes. DkAP2/ERF gene expression patterns were extensive and diverse. They were detected expression in every examined tissue, with the highest number of DkAP2/ERF genes expressed in the root. DkAP2/ERF gene expression analysis in adventitious root generation and elongation of polyamines showed their different responses to the action of polyamines, and more pairs of DkAP2/ERF genes with high correlation in gene expression were obtained. In addition, some DkAP2/ERF genes were detected remarkably correlated with genes related to polyamine synthesis and cell metabolism, including S-adenosyl-L-methionine Decarboxyla2 (SAMDC2), D-type cyclin1 (CYCD1), and D-type cyclin2 (CYCD2) genes,. indicating that DkAP2/ERF genes may play a synergistic role in adventitious root development This study was the first to analyze the AP2/ERF gene comprehensively in Diospyros on a genome−wide scale and will provide insights into the application of adventitious root formation in cultivated persimmon.
1. Introduction
Cultivated persimmon (D. kaki, 2n = 6x = 90) belongs to the Diospyros genus. It is a very economically important woody species in this genus. Cultivated persimmon can be divided into four types: pollination-constant astringent (PCA), pollination-constant non-astringent (PCNA), pollination-variant non-astringent (PVNA), and pollination-variant astringent (PVA) [1]. Different from traditional widely planted PCA varieties, PCNA persimmon does not require additional artificial deastringent treatment before being eaten, saving the cost of deastringency and avoiding the unpleasant feeling caused by incomplete astringency removal or astringency return of persimmon. Hence, it is widely popular among consumers. In recent years, PCNA persimmon is also favored by growers. Hence, seedling demand has been increased sharply.
Cultivated persimmon is mainly propagated by grafting. In China, excellent cultivars of PCNA persimmon were basically introduced from Japan. However, until 1994, it was not grown on a large scale because of a lack of rootstock varieties with good affinity. Fortunately, we discovered ‘Xiaoguotianshi’ (D. kaki, 2n = 6x = 90) in 2000. After more than 20 years of observation, we found that it is not only completely compatible with Japanese PCNA persimmon, but also has a wide range of wonderful adaptability. That is to say, for the current superior PCNA varieties, ‘Xiaoguotianshi’ is a very precious rootstock variety with good comprehensive characteristics. This discovery made the large-scale development of excellent PCNA persimmon varieties in China see the dawn. However, difficulty in rooting was found to be the biggest obstacle to the large-scale propagation of ‘Xiaoguotianshi’ by tissue culture. Therefore, it is of great significance to excavate candidate rooting genes related to adventitious roots and understand the rooting mechanism of cultivated persimmon for further building the optimum clonal propagation system of tissue culture and variety improvement.
AP2/ERF is a plant-specific ethylene response factor and is one of the largest transcription factor families. AP2/ERF has a wide range of biological functions, playing an important role in the whole growth and development process of plants, such as germination, growth, flowering, and fruiting, as well as various abiotic stress responses [2]. AP2/ERF is a multi-gene family, and family members share a highly conserved AP2/ERF DNA binding domain, which consists of 60–70 amino acids. According to the amount of AP2 domain contained in the gene and the similarity between the sequences, the AP2/ERF superfamily can be divided into four categories: ERF (ethylene response element binding), AP2, RAV (related to ABI3/VP1), and Soloist34. The AP2 subfamily contains one or more tandem repeated AP2 domains [3,4]; the ERF subfamilies have only a single AP2 domain [3,4,5]; the RAV subfamily contains one AP2 domain and one B3 [5,6]; the Soloist subfamily also possesses only one AP2 domain, but its binding DNA sequence is significantly different from that of other AP2/ERF members [4]. This gene family has been reported in a variety of plants, ranging from 127 [3] to 288 [7]. The proportions of the four subfamilies in the AP2/ERF family are usually different. ERF accounts for the largest proportion, followed by AP2, RAV, and Soloist, in which the last two subfamilies are significantly less than the first two subgroups.
AP2/ERF gene expression is tissue-specific and developmental-specific; moreover, different family members often have different functions. Even if they regulate the same life activity, they may have completely different ways to take. AP2/ERF genes can either activate or repress target gene expression [8,9].
Rooting is a complex process. Auxin, cytokinin, abscisic acid and other hormones, cell wall synthesis, and metabolism protein genes work together to form a complex network to regulate root development, in which polyamines and ethylene are also very important factors [10]. As an ethylene response factor, it has been demonstrated that AP2/ERF play roles in rooting processes by interacting with auxin, regulating the balance between auxin and cytokinin, or directly initiating ethylene synthesis and signal transduction in vivo [11]. For example, PUCHI and ERF13 regulate lateral roots (LRs) development by coordinating cell proliferation during LR development in Arabidopsis [12]. OsAP2/ERF-40 initiates root-specific developmental program by regulating auxin and OsERF3–OsWOX11–OsRR2 signaling pathways in the rice shoot tissues [13]. In Popla, PtAIL1 positively regulates adventitious rooting by promoting the formation of root primordia [14]. Polyamines (PAs), mainly including primarily spermidine (Spd), spermine (Spm), and putrescine (Put), act on root generation by influencing several processes such as cell division and cell development [15]. At present, abundant research on the expression characteristics of AP2/ERF gene during rooting are available, but few studies have been done on their activation and expression during the rooting process under the action of polyamines. In cultivated persimmon, due to the complexity of chromosome ploidy, the studies on gene family and function are still relatively backward. So far, there is not any systematic report on AP2/ERF family yet. The AP2/ERF family is so important to plants that it is of great significance to comprehensively identify and study its basic characteristics at the genome level and to analyze and utilize the molecular mechanism of important traits involved in them in the future. In view of this, by way of bioinformatics methods, we performed genome-wide discovery AP2/ERF genes in Oily persimmon genome, identified and analyzed the classfication, structure, and physical and chemical properties, subcellular localization, transmembrane structure, chromosome localization, possible cis-acting elements binding sites, collinearity, GO annotation function prediction, and PPI protein interaction analysis, as well as the expression characteristics in different tissues of persimmon. At the same time, the responses of AP2/ERF gene during root development of tissue culture of ‘Xiaoguotianshi’ under different concentrations of polyamines were preliminarily explored, in order to provide theoretical guidance and gene resources for the mechanism research of cultivated persimmon rooting mediated by AP2/ERF transcription factor.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of AP2/ERF Gene Family Members
The Oily persimmon genome was retrieved from the GigaScience database GigaDB [16]. Using the amino acid sequences of Arabidopsis AP2/ERF as reference, obtained from TAIR webserver (http://www.arabidopsis.org/ accessed on 8 August 2021), the AP2/ERF family in the Oily persimmon genome was identified by bidirectional BLAST method. The bidirectional BLAST method is described as follows: The Arabidopsis AP2/ERF gene family members were compared to the Oily persimmon genome to obtain Oily persimmon AP2/ERF identifiers, and the obtained identifiers were then compared to the Swiss-Port database to confirm as AP2/ERF family members. The conserved domain was Identified by Jalview2 [17] through multiple sequences alignment. At the same time, the AP2 domain of AP2/ERF gene was predicted by CDD tool of NCBI website. False positive sequences that did not contain the AP2 were eliminated. The physical and chemical properties, coding protein secondary structure, signal peptide, transmembrane domain structure, and subcellular localization analysis were performed by using online software ProParam (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/ accessed on 1 August 2022), SWISSMODEL (https://swiss-model.expasy.org/interactive accessed on 1 August 2022), SignalP-5.0 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/ accessed on 1 August 2022), TMHMM (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/ accessed on 1 August 2022), Plant-mPLoc (http://www.csbio.sjtu.edu.cn/bioinf/plant-multi/ accessed on 1 August 2022), respectively. TBtools software [18] was used to map the identified AP2/ERF genes to chromosomes.
2.2. Domain Identification and Gene Structure Analysis of AP2/ERF Family Members
Motif predictive analysis was performed through the website tool MEME (http://meme-suite.org accessed on 29 July 2022) [19], with Motif set to 20 and other parameters as default. The results of Motif prediction, CDD domain identification, and evolutionary tree analysis were combined with TBtools software [18].
2.3. AP2/ERF Gene Family Cluster Analysis
The MUSCLE method was used for multiple sequence alignment. Basing on the obtained multiple sequence alignments, an ML phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA-X [20] software with complete deletion, the JTT amino acid substitution model, and 1000 bootstrap replicates.
2.4. Prediction of cis-Acting Sites of AP2/ERF Gene Family
The upstream 2000 bp sequence of the family members was extracted. cis-acting elements were predicted by Using PlantCARE [21] (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/ accessed on 30 August 2022).
2.5. Chromosomal Distribution and Duplication of AP2/ERF Gene
The distribution of the AP2/ERF genes on chromosomes was drafted with the Tbtools software. MCScan [22] was used to conduct the analysis of gene duplication events. The Synteny analysis was performed between Oily persimmon and the other plant species also using MCScanX. The Arabidopsis genome was downloaded from EnsemblPlants (https://plants.ensembl.org/Arabidopsis_thaliana/Info/Index accessed on 8 August 2021). The Diospyros lotus (D. lotus) genome was retrieved from PersimmonDB (http://persimmon.kazusa.or.jp accessed on 1 August 2022).
2.6. Tissue-Specific Expression Analysis and Real-Time QUANTITATIVE Fluorescence PCR (qRT-PCR) Expression Detection
Gene expression data (Reads/kb/Million, RPKM) from different tissue parts of persimmon were provided by Suo et al. [16]. AP2/ERF gene expression analysis by qRT-PCR under the treatment of polyamines was studied in the tissue culture plantlet of ‘Xiaoguotianshi’. The tissue parts were stem segment (pre-rooting) cultivated for 20 days and roots (post-rooting) cultivated for 35 days. The polyamine type was putrescine, and 5 concentrations, including 20 mg/L, 40 mg/L, 80 mg/L, 120 mg/L, and 200 mg/L, were set. The qRT-PCR primers were designed according to the sequences of AP2/ERF, SAMD, and CYCD genes of Oily persimmon. SAMD and CYCD gene sequences were obtained by using Arabidopsis SAMD and CYCD gene as queries to retrieve in Oily persimmon genome. The primer sequences are shown in Table S1. RNA extraction, reverse transcription, and fluorescent quantitative PCR kit were all made by Beijing Tiangen Biological Co., Ltd. The internal reference was DkActin. The qRT-PCR used the SYBR-green dye method, and the PCR instrument was LightCycler 480 (Roche) real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR instrument. Three biological replicates and three technical replicates were used for qRT-PCR, with distilled water as the negative control. The PCR procedure was: 95 °C for 30 s; 95 °C for 5 s, 55 °C for 30 s, and 35 cycles. The relative gene expression was calculated by 2-ΔΔct. Correlation analysis of differential gene expressions was performed by Corrplot R package. TAU-index value was introduced to evaluate the tissue specificity of gene expression [18].
2.7. GO Enrichment and Protein Interaction (PPI) Analysis of AP2/ERF
The GO number of the AP2/ERF family was obtained by local annotation with Linux using the eggNOG database. GO Enrichment was performed and visualized by the TBtools software [18]. The STRING program, with the number of interactions 5 and the confidence parameter 0.15, was used to predict the interaction of AP2/ERF proteins, and the regulatory map was drawn. Species parameter chose Arabidopsis. Cytoscape 3.8.2 [20] was used for visualizing the results of PPI.
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Sequence Information of AP2/ERF Gene Family Members in Oily Persimmon
A total of 157 genes with AP2/ERF domain were identified, accounting for 0.51% of the total number of genes in the Oily persimmon genome. The AP2 domain consists of about 65~70 amino acid residues, with highly conserved YRG and RAYD motifs in the N-terminal and C-terminal, respectively (Figure 1A). The gene ID was named Dk1gERF001~Dk15gERF160 according to their location on the chromosome. As shown in Table S2, the predicted results on physicochemical properties of DkAP2/ERF protein presented that the numbers of amino acids (No.AA) was between 118 and 639, with an average of 281. The molecular weight (MW) of the proteins varied greatly, ranging from 13,067 Da to 70,680 Da, with an average of 31,049 Da. The average value of PI was 7.30. 52.23% of the genes were higher than 7, and 47.77% of the genes were less than 7, indicating that the DkAP2/ERFs were basically neutral. Except Dk12gERF127, Grand Average of Hydropathicity (GRAVY) was all negative, suggesting that DkAP2/ERFs mainly were hydrophilic proteins. The instability index (II) ranged from 34.23 to 83.67, with an average of 57.16. Only nine proteins had II less than 40. When the II value was above 40, the proteins were unstable, indicating that most DkAP2/ERFs proteins were unstable proteins. Subcellular localization (Sclo) predicted that 76% of AP2/ERF proteins were distributed in the nucleus, 14% in extracellular distribution, and 10% in other multipoint distribution. Among the prediction results of the transmembrane region, only Dk8gERF101 and Dk12gERF127 were predicted the transmembrane region, and only one and three transmembrane helixes (TMHs) were detected, respectively, indicating that they might be membrane receptor proteins related to cell signal transduction. Of the remaining proteins, 152 were located on the surface of cell membrane, indicating that DkAP2/ERFs mainly were membrane proteins. Dk8gERF101, Dk12gERF126, and Dk13gERF128 were located in the membrane Signal peptide (SigIP) prediction analysis, which showed that, except Dk2gERF020, DkAP2/ERF family proteins almost had no signal peptide, which implied they might be mainly non-secreted proteins.
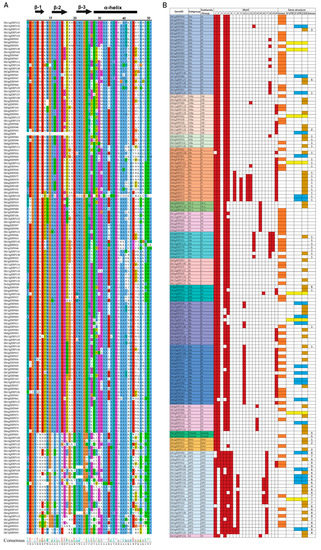
Figure 1.
Alignment of the DkAP2/ERF domains (A) and summary of gene structure (B). For (A), colorful shadings indicate conserved and identical amino acid residues. The black bar and arrows represent predicted α-helix and β-sheet regions, respectively, within the AP2/ERF domain [25]. For (B), the different shadings in columns 1 to 3 represent different subfamilies/groups/subgroups to which the DkAP2/ERF belong. Columns 4 to 24 represent 20 conserved motifs (Motif 1–Motif 20) obtained by MEME analysis, in which the colored grids represent Motifs owned by a single gene. The last four columns are descriptions on gene structure, in which, colored grids display the structural part that a single gene has, and the numbers indicate the number of introns that a gene contains. Blank grinds indicate none.
The amino acid sequences of 26 deposited DkERF genes [21,22,23,24] in NCBI GenBank were used as queries to retrieve the highest homologous ERF genes in our 157 DkAP2/ERF genes through BLAST. As shown in Table S3, the homology between Oily persimmon DkAP2/ERF and 26 cultivated persimmon ERF ranged from 87.05% to 100%, with an average of 96.12%, reflecting the potentially high similarity of the ERF gene family between Oily persimmon and cultivated persimmon.
3.2. DkAP2/ERF Gene Family Classification and Evolutionary Analysis
Referring to the classification of Nakano et al., 2006 [3], as revealed in Figure 2, DkAP2/ERF could be assigned into four subfamilies, including ERF (126), AP2 (25), RAV (4), and Soloist (2). The ERF subfamily was further divided into 11 groups (Group I-X and Group VI-L), among which Group IX had the most members, followed by Group II (18), Group X (16) and Group VI (15). Group VI-L has the smallest members. Each subgroup contained similar exon number and intron-exon structure, implying their close evolutionary relationship and similar functions.
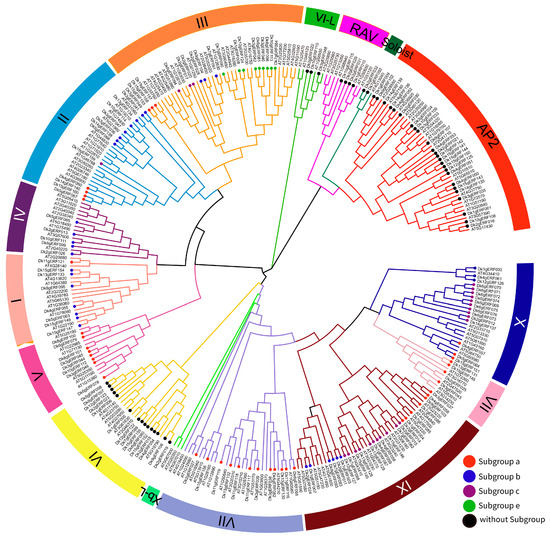
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree displaying the relationships among AP2/ERF amino acid sequences of Oily persimmon and Arabidopsis. The different colored arcs indicate different subfamilies/groups of the AP2/ERF family. The members of subgroups of ERF genes in Oily persimmon that inferred according to the cluster results with ERF subgroups gene members are marked in colorful dots. Lowercase letters a, b, c, and e indicate the subgroups of ERF genes corresponding to Arabidopsis.
A total of 157 DkAP2/ERF genes were positioned according to their physical location (Figure 3). DkAP2/ERF genes were distributed on all 15 chromosomes. The most distribution was displayed on Chr2 (22), followed by Chr15 (20), Chr9 (5), and Chr 11 (5) (Figure 4A). The distribution of ERF, AP2, RAV, and Soloist subfamilies was exhibited variable in the genome (Figure 4C). The AP2 subfamily was located on nine chromosomes, more on Chr15 and Chr4, and the least on Chr12. The ERF subfamily existed on all 15 chromosomes, among which, Ch2, Chr15, Ch3, and Ch6 contained the most. The RAV was only found on Chr1, Chr2, and Chr3 chromosomes. The Soloist was distributed on Chr2 and Chr7. In addition, as revealed from Figure 3, DkAP2/ERF genes were associated with chromosome gene density to some extent; moreover, they were more in regions with high gene density. Most were located at both ends.
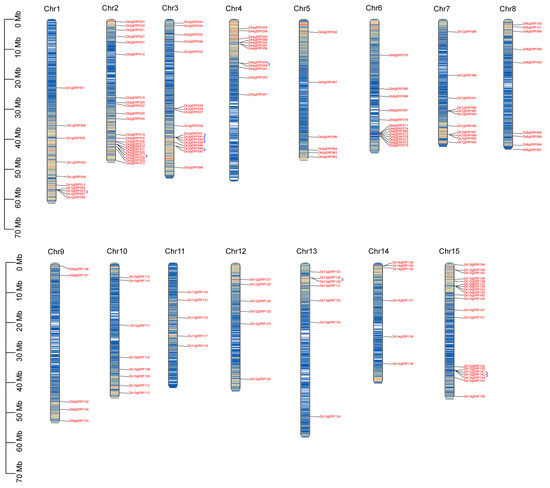
Figure 3.
The distribution of the DkAP2/ERF gene on the 15 chromosomes. The blue arcs represent gene family members with duplication relationships.
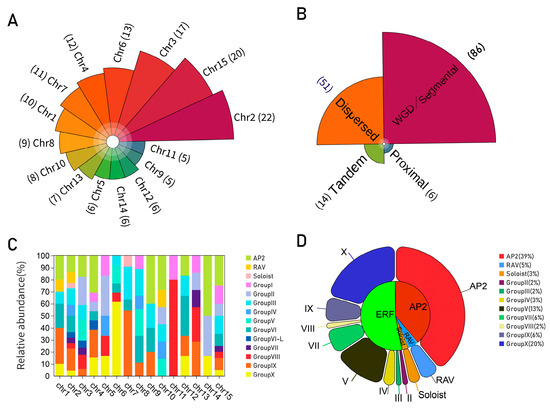
Figure 4.
Distribution (A) and proportion (C) of DkAP2/ERF genes on persimmon chromosomes, duplication events between different gene members (B), and summary of genes with introns in subfamilies and different groups (D).
Gene duplication is one of the patterns in the acquisition of new genes. Through gene duplication events, new functions can be evolved without the loss of the old functions or functional fine-tuning of a gene. It has been well reported that WGD/segmental duplication, tandem, proximal, and dispersed were the four main types of gene duplication. As shown in Figure 4B, among 157 DkAP2/ERF genes, the largest number of genes (86) resulted from whole-genome replication or fragment replication, accounting for 54.8%, followed by Dispersed (51; 32.5%). Proximal replication was the least. A total of of 14 genes of Tandem duplication (8.9%) were detected, which existed on the chromosomes of Ch1, 2, 3, 4, 13, and 15. Multiple tandem duplication events were found on Ch3. Tandem repetition, fragment replication, and translocation are the main gene replication events that promote gene family expansion. The results of this study suggested that fragment replication contributed more to AP2/ERF gene replication in Oily persimmon.
To further study the evolutionary mechanism of DkAP2/ERF, the collinearity analysis of the genome of the D. oleifera, A. thaliana, and another commonly used related species in Diospyros genus D. lotus was conducted. A total of 88 (56.05%) and 4 (2.56%) homologous genes were detected in A. thaliana and D. lotus, respectively. The four DkAP2/ERF genes homologous to that of the D. lotus were: Dk1gERF010, Dk10gERF115, Dk12gERF122, and Dk15gERF148, belonging to RAV, RAV subfamily, Group VI, and Group VII, respectively.
3.3. Gene Conserved Motif and Structure Analysis of the DkAP2/ERF Family
A total of 20 conservative motifs were identified (Figure 5). On the whole, Motif 1, 2, 4, and 5 were the four highest sharing motifs in DkAP2/ERF family. The overlapping regions analysis between motifs and domains (Figure S1) showed that these motifs were right located in the AP2 domain. Hence, due to their high conservation and general existence in the AP2 domain, they could be a classic feature that distinguishes the AP2/ERF family from other families. Motif 3, 6, and 17 were unique to the AP2 subfamily that could be used for distinguishing this family from other subfamilies. In addition, the absence of Motif 2 was also a characteristic of the AP2 subfamily. The RAV and the Soloist subfamily had no unique motifs. The absence of Motif 4 and motif 5 simultaneously could be used as a marker to distinguish them from other subfamilies to some extent. In the DkERF subfamily, each group basically contained similar conservative motif components and was basically consistent in arrangement order. Additionally, some groups had their own characteristic motifs, such as Motif 7, 9, 11, and 12 in Subgroup Xc; Motif 14, 15 in Group VI; and Motif 19 in Group V, whereby they could be used as feature sequences that were different from other Groups or Subgroups. In motifs that occur less frequently, some individual motifs were shared by several subgroups, for example, Motif 10 was shared by Group II and Group III, and Motif 20 was shared by Subgroup IIa, Subgroup VIIIa, and Group III. The motif features shared by different families reflected their functional and evolutionary relevance. Those motifs that occurred less frequently indicated that the member of the corresponding gene was special in a certain function. Interestingly, three copies of Motif 15 were found in Dk15gERF155 in Group VI, suggesting that it may have gained a new function.
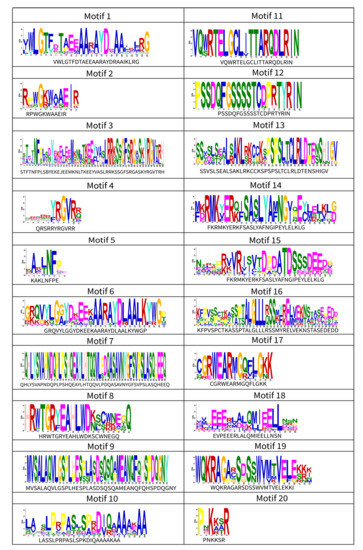
Figure 5.
SeqLogo diagrams and sequences of 20 motifs.
The results of gene structure analysis showed that most genes in the same cluster had common exon/intron structures, especially in terms of the number of introns, such as Group V and Group VI, and so on (Figure S1). Nevertheless, there were a few notable exceptions. The number of gene subfamilies/Groups with introns is shown in Figure 4D. In total, 64 DkAP2/ERF genes were detected to contain intron structure (accounting for less than 40.76% of the total DkAP2/ERF genes), and the number of introns ranged from 1 to 9, among which, the number of genes containing one intron was the largest (39.06%). DkAP2/ERF genes with intron structure mainly existed in several subfamilies. All members of the AP2 subfamily had multiple introns, and the number of introns was higher than that of the other three subfamilies (6–9). Three-quarters of RAV subfamily members (1–3) and two soloist genes (2) also had introns. Most DkERF subfamily members had no intron structure. Among the DkERF subfamily members, three groups were completely intron-free (Group VI, Group VI-L, Group I). All Subgroup Xc members in Group V, Group VII, and Group X had intron structure (1). In addition, there were sporadic individual sequences with intron in Group I, Group II, Group V, Group IX, and Group VIII. In general, genes containing intron structure accounted for 26.98% of the total DkERF genes.
In the whole DkAP2/ERF family, 71 members had complete gene structures. Eight members only had 5′-UTR and CDS regions; twenty-two members had 3′-UTR and CDS regions; and the remaining members only contained CDS (Figure 1B).
3.4. Analysis of cis-Acting Elements of DkAP2/ERF Gene Family
PlantCare was used to predict cis-acting elements for 2000 bp upstream of 157 DkAP2/ERF. Twenty-five kinds of cis-acting elements with clear functional records were detected, with a total of 4541 cis-acting elements (Table S4). The 25 cis-elements could be generally assigned to four categories, including 5 major hormone response elements, 6 stress response elements, 11 growth and development-related elements, and 3 light-responsive elements. Light-responsive elements were the most, accounting for 45.76% of the total deduced cis-elements. Among the five kinds of major hormone-responsive elements, methyl jasmonate (MeJA, 572) and abscisic acid (ABA, 441) were exhibited as the largest, which was about 4 times that of the other three. The predicted binding sites of cis-acting elements in stress response included those affected by stress factors such as anaerobic, low temperature, drought, pathogenic microorganisms, and defense response, among which anaerobic stress (366) and drought-induced MYB binding sites (169) had the most elements, and wound-induced cis-acting elements had the least (6). The meristem-specific expression of growth and development-related elements accounted for the highest proportion. The number of cis-acting elements in a single gene ranged from 9 to 59, with an average of 28. The types of cis-acting elements are between 3 and 14, with an average of 8. No significant difference existed in the type and quantity of cis-acting elements among different DkAP2/ERF subfamilies (Figure 6). Overall, this gene family contained abundant cis-acting elements that correlated with hormone action, indicating that DkAP2/ERF has the potential to respond to multiple hormone induction.
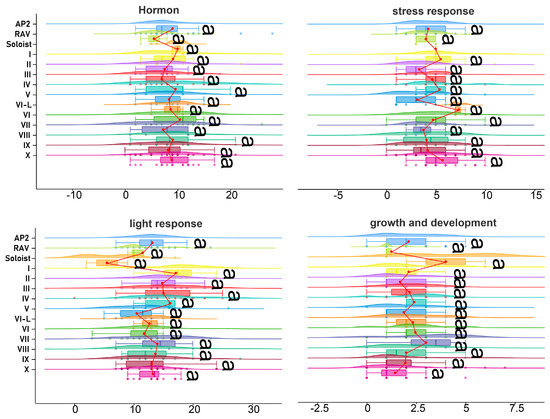
Figure 6.
Data visualization and difference significance analysis of the 4 major categories of predicted cis--acting elements in the DkAP2ERF subfamily and Groups. “a” means no significant difference existed (p > 0.5).
3.5. GO Analysis of DkAP2/ERF
We selected and visualized the top 30 GO terms (Figure 7). DkAP2/ERF could be annotated into three main ontologies, namely, molecular function, cell component, and biological process. Among them, the items annotated to the biological process were the most, followed by molecular function. The number of entries annotated to the cell component body was minimal (only 1). In molecular functions, it was mainly DNA-binding activity, including sequence-specific DNA-binding activity and transcription factor DNA-binding activity. In the cellular component annotation, the DkAP2/ERF protein was annotated primarily in the nucleus. In biological processes, DkAP2/ERF members were annotated in the ethylene response and its signal transduction pathway, and are also widely involved in RNA biosynthesis, nucleic acid metabolism, phosphorylation signal transduction, nitrogen compound metabolism, and other processes.
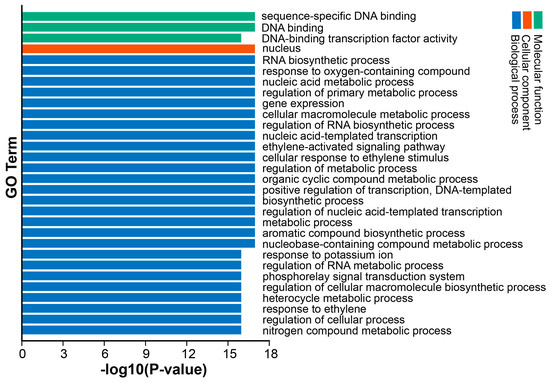
Figure 7.
GO term analysis result of DkAP2/ERF protein sequences.
3.6. PPI Protein Prediction
The protein pattern of the String protein interaction database (A. thaliana) was used to predict the interaction of 157 DkAP2/ERF proteins. The interaction network was mapped (Figure 8A). The size of the dots on the network diagram indicated the number of lines connecting the proteins and the extent of interaction with other proteins in the network. Nine DkAP2/ERF proteins had more than 10 interactions with other proteins, and Dk4gERF052 detected the most interactions with other proteins (38). A total of 72 DkAP2/ERF proteins were mapped to the Arabidopsis genome, 49 of which predicted protein interactions. Arabidopsis homologous genes corresponding to the 49 interacting proteins included AP2, RAV, ESR1, CBF1, CBF2, CRF2, CRF4, CRF5, ERF1, ERF4, ABI4, SHN1/2/3, etc., which played an important role in stress response, ABA, Cytokinins, lignin, waxy, keratins and cell wall metabolism, tissue, and organ meristem, as well as auxin and ethylene synthesis, and signal transduction. The interaction network between each Arabidopsis homologous protein and other proteins in the database was further analyzed, from which 20 Arabidopsis proteins were screened, which were closely related to biological processes such as root meristem, induction, elongation, and metabolism (Table 1, Figure 9). The corresponding 20 DkAP2/ERF genes belonged to seven subfamily/Groups, including AP2 subfamily, Group III, Group IV, Group V, Group VI, Group VIII, and Group IX, and accounted for a relatively large proportion in the AP2 subfamily and Group VI (Figure 8B).
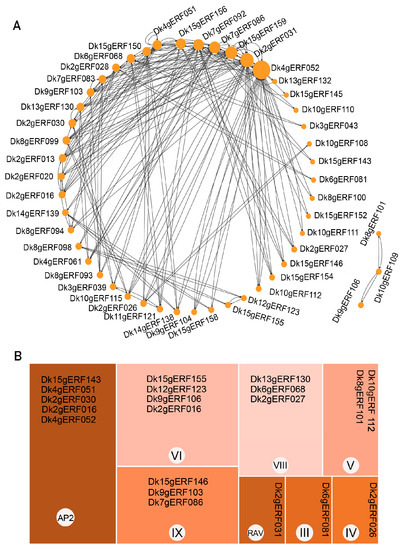
Figure 8.
The interaction network of AP2/ERF in Oily persimmon according to the orthologs in Arabidopsis (A) and distribution tree of 20 important DkAP2/ERF in different families (B).

Table 1.
Twenty important predicted DkAP2/ERF and their interactions with root growth and development-related protein genes and functional annotation.
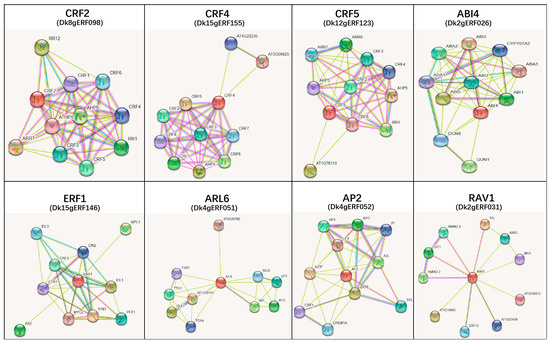
Figure 9.
Several of the proteins predicted to be involved in rooting processes in Arabidopsis and their interaction networks. The genes in parentheses are the corresponding AP2/ERF homologous genes in Oily persimmon.
3.7. Tissue-Specific Expression Analysis of DkAP2/ERF
The expression of DkAP2/ERF in different tissues of persimmon was investigated based on the transcriptome data of different Oily persimmon tissues. FPKM ≥ 1 was used as the effective expression level to initially screen the genes. A total of 116 DkAP2/ERF genes were included in the analysis (Figure 10B).
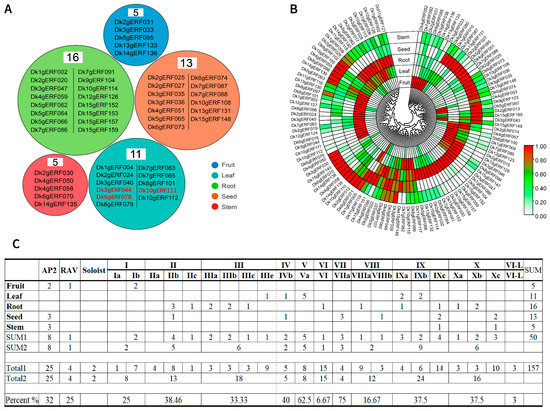
Figure 10.
DkAP2/ERF gene expression in different persimmon tissues. (A) Genes with preference (in black) and specific expression (highlighted in red) in different tissues. (B) Heat maps of DkAP2/ERF expression in five tissues with FPKM value greater than or equal to 1. (C) The number and proportion of family distribution of tissue preference expressed genes.
Based on the expression data of each DkAP2/ERF gene in different tissue parts, the TAU-index value was calculated to analyze the tissue-specific expression of the gene: TAU-index = 1, indicating the specific expression of the gene in a certain tissue; TAU-index is close to 1, indicating the expression of tissue bias. When the TAU-index is close to 0, it tends to be a compositional expression. DkAP2/ERF gene expression was detected in all five tissues tested (Figure 10B), and the genes with tissue preference expression were detected in each tissue (47). The number of DkAP2/ERF genes was the highest in the root (16). Few tissue-specific genes were expressed (3) and detected only in leaves (Figure 10A). No constitutive expression genes were detected. The highest number of tissue preference and specific expression genes were detected in the AP2 subfamily and Group IX. Relative to the number of genes in each subfamily/group/subgroup, a higher number of members with organizational preference and specific expression were detected in Group V and Group VII, accounting for 62.50% and 75.00%, respectively (Figure 10C).
After the standardization of gene expression data, an expression heat map was drawn and expression clustering was performed. Figure 10B clearly showed the specificity and preference of DkAP2/ERF gene expression in different tissues. The overlapped color blocks in the highlighted color labeling indicated that some genes might be highly expressed in multiple tissues at the same time. The expression pattern of DkAP2/ERF gene is extensive and diverse, indicating that DkAP2/ERF gene had multiple functions in persimmon growth and development. DkAP2/ERF genes expressed specifically or preferentially in different tissues might be related to the occurrence, development, and function of specific organs.
3.8. Expression Analysis of DkAP2/ERF Genes during Rooting and Development in Tissue Culture SEEDLINGS Treated with Polyamine
The representative DkAP2/ERF gene was selected for qRT-PCR to preliminarily study the expression of adventitious root generation and elongation under the action of polyamines. The results showed that DkAP2/ERF showed different responses to polyamines. Compared with the control, some AP2/ERF genes showed up-regulated expression and some showed down-regulated expression. With the change of polyamine concentration, the expression pattern of the DkAP2/ERF gene also showed different trends.
In the occurrence of adventitious roots, five expression trend profiles were detected for the 20 tested genes, of which one profile showed a significant expression trend (p = 0.01), including eight DkAP2/ERF genes, whose expression was continuously up-regulated with the increase of polyamine concentration (Figure 11A), indicating that they might have similar functions in the occurrence of adventitious root under the treatment of polyamines. Further correlation analysis of gene expression detected seven and five pairs with significant (p < 0.05) and extremely significant (p < 0.001) expression, respectively (Figure S2; Figure 11B). As shown in Figure 11B, significant positive and negative correlations between genes were both revealed, among which six pairs of genes were positively correlated. Moreover, in these six pairs of genes, four pairs were significantly correlated (with 1 star mark), and two pairs were extremely significantly correlated (with 2 stars mark). Additionally, five pairs of negatively correlated genes were detected, among which two pairs of genes were significantly correlated (with 2 stars). In all, these results implied that there should be multiple DkAP2/ERF involved in adventitious root generation under the treatment of polyamines, which had bidirectional functions of promotion and inhibition.
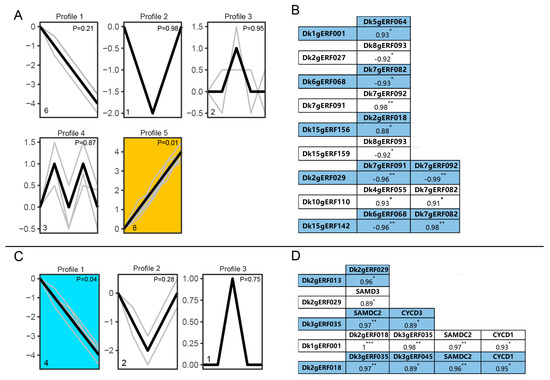
Figure 11.
Expression patterns of DkAP2/ERF genes in response to polyamines in rooting biological process of tissue culture seedlings and the correlation between different genes. (A) DkAP2/ERF gene expression pattern before adventitious roots formation. (B) Correlation of DkAP2/ERF gene expression before adventitious roots. (C) DkAP2/ERF gene expression pattern after adventitious root occurrence. (D) Correlation between DkAP2/ERF gene expression after adventitious root occurrence.
Three asterisks, two asterisks, and one asterisk represent the significant levels of p < 0. 001, p < 0. 01, and p < 0. 05, respectively. In the process of adventitious root elongation, four genes with the same gene expression trend were detected under different polyamine concentrations (p < 0.05) (Figure 11C). Correlation analysis of gene expression (Figure S3; Figure 11D) showed that among the seven tested DkAP2/ERF genes, two and three pairs were detected to be significantly (p < 0.05) and extremely significantly correlated (p < 0.01), respectively. Further study on the expression correlation of six genes related to polyamine synthesis, cell circulation, and root development showed that three DkAP2/ERF genes exhibited extremely significant correlation with one polyamine synthesis gene (SAMDC2) and two cell circulation genes (CYCD1, CYCD2) (p < 0.01) (Figure S3; Figure 11D). These results implied that DkAP2/ERF gene might play an important role in adventitious root elongation by cooperating with polyamine synthesis and cell metabolism genes.
4. Discussion
In this study, we systematically identified and analyzed the structure of DkAP2/ERF genes in Diospyros for the first time in the whole genome. A total of 157 DkAP2/ERF genes were identified, including 25 AP2 subfamily genes, 4 RAV subfamily genes, 2 soloist genes, and 136 ERF subfamily genes. They contained at least one AP2 conserved domain composed of about 60 amino acid residues, which is consistent with the structural characteristics of AP2/ERF family genes. The DkERF subfamily contained the most gene family members, and all the protein sequences had the AP2 conserved domain. All DkAP2 subfamily sequences contained two AP2 conserved domains except Dk9gERF107. Three of four sequences of the RAV subfamily had a conserved B3 domain. DkERF genes in Oily persimmon could be divided into 11 groups, whose phylogenetic tree structure was basically consistent with that of Arabidopsis [3]. This phenomenon was also found in grape [26] and other species. The similarity of AP2 sequences in the same family implies the similarity of gene functions in the same AP2/ERF family. The above results indicated that the AP2/ERF gene family has a relatively conservative evolutionary trend in different species, which is consistent with that in other species [3,5,27,28].
The member numbers of the AP2/ERF gene family identified in oily persimmon accounted for 0.51% of the genome annotation genes. A total of 229 AP2/ERF members were screened in the chrysanthemum genome (2.53 Gb), which accounted for 0.40% of the total chrysanthemum hypothesized protein bank [29]. In dicots, 147 members (0.54%) were screened in the Arabidopsis genome (125 MB) [27]; 288 members (0.55%) were identified in the sunflower (Helianthus annuus) genome (3.6 Gb) [7]. In monocots, a total of 163 members (0.43%) were found in the rice genome (430 Mb) [30]. A total of 218 members (0.61%) were discovered in the sugar cane (Saccharum officinarum) genome (3.13 Gb) [31]. Therefore, it could be implied that although the AP2/ERF family has a large number of members in all plant species, the number of members of this family seemed no obvious relationship with the size of the genome. In addition, it was also found that the proportion of members of this family in the putative protein library is basically between 0.40% and 0.60%, so it is speculated that the number of members of this family is positively correlated with the size of the entire protein library. Altogether, these results suggested that the number of members of the AP2/ERF family is relatively stable and there is no absolute correlation with genome size.
Although the Motif distribution of DkAP2/ERF subfamily proteins located in the same subgroup had high similarity, some differences in the type, quantity, and distribution of conserved motifs still existed, suggesting that there may be functional differentiation of DkAP2/ERF proteins in the same subgroup. However, DkAP2/ERF proteins in different groups have the same Motif distribution, suggesting that DkAP2/ERF proteins in different groups may also have functional redundancy. Existing studies have confirmed that AP2/ERF family members are widely active in various plant organs, such as roots, stems, leaves, etc. [2]. In this study, DkAP2/ERF gene expression was detected in all examined five tissues, further strengthening this conclusion, indicating that DkAP2/ERF family members are correlated with every tissue and organ. Rice AP2 subfamily CRL5 [32], ERN1, ERN2, and ERN3 of alfalfa (Medicago Sativa) [33], and the PUCHI gene of the Arabidopsis ERF subfamily [12] all indicated that root growth requires the participation of multiple AP2/ERF subfamily members. In this study, the result of gene expression tests in different tissues showed that multiple AP2/ERF expressions were mostly found in roots, so it can be inferred that DkAP2/ERF family members would involve in the growth and development of cultivated persimmon roots, which supports the above conclusion.
Roots are crucial for plant anchor and for the absorption of water and nutrients from the soil [34]. As the first sensing organ, the root has developed an effective response mechanism to drought, salt, alkali, waterlogging, and other adverse events over the long term [35]. Compared with other tissue parts, it is supposed to have more abundant gene expression. In this study, more preferentially expressed genes were detected in the roots than in other tissues, which could be explained by this. Although AP2/ERF genes are widely involved in plant growth and development, different subfamilies or subgroups of the same group usually have certain functional advantages. For example, the AP2 subfamily mainly regulates the growth and development of flowers, ovule, and seeds [36,37] and recognition of leaf epidermal cells [38]. The ERF subfamily regulates ethylene response and hormone signal transduction [39,40], and the expression function of disease-resistance-related genes, which play an important role in the process of stress resistance and resistance to biological stress [41,42]. The RAV subfamily plays an important role in regulating ethylene, brassinosteroids, biological and abiotic stresses in plants [43]. Additionally, in the ERF subfamily, Group III was often reported involving in the regulation of cell wall anabolic processes [44], and cytokinin response factors were usually from the Group VI group. Therefore, all in all, this study detected that the different expressions of AP2/ERF in tissues and organs might be explained by their functional preference.
Hormone types and proportions play a key role in root generation and development of tissue culture seedlings. Generally, most plants can achieve an ideal rooting rate by using appropriate IAA and IBA ratios. Persimmon is a woody fruit tree that is thought to be hard to root. In order to improve the rooting rate, many attempts have been made, but the effect of IAA and IBA on the rooting of persimmon was limited. As an exogenous hormone, polyamines can promote the induction and elongation of roots [45]. However, no relevant application has been reported in cultivated persimmon, and studies on its mechanism are lacking too. In our previous experiments, we found that putrescine could significantly promote the root generation and development of persimmon seedlings in tissue culture (unpublished). In this study, DkAP2/ERF gene expression analysis was performed on the mixed stem samples sampled before the root appeared under the treatment of putrescine. Different levels of DkAP2/ERF gene expression were detected, and different expression patterns were observed with different concentrations of polyamines, indicating that AP2/ERF gene could respond to the rooting process under the treatment of putrescine. Moreover, we found different gene members had different external conditions to be induced expression. Additionally, different DkAP2/ERF genes were found to have co-expression or reverse co-expression interaction, indicating that there might be some coordination or restriction relationship between DkAP2/ERF genes in function. Our study of DkAP2/ERF gene expression during root elongation showed similar results as well. Furthermore, the expression analyses of several enzyme genes related to polyamine synthesis and auxin were also conducted. A significant correlation of gene expression between AP2/ERF and these genes was demonstrated, indicating possible interaction between AP2/ERF gene and other metabolic processes during the rooting process under the treatment of polyamine.
Genome sequencing is tough for cutivated persimmon due to its high ploidy level and high genetic/genomic complexity. Oily persimmon is a diploidy with a relatively simple genome in the Diospyros genus. Its genome was released in 2019 [16]. Previous reports using a variety of molecular markers and comparative transcriptome studies revealed that Oily persimmon was one of the closest relatives to D. kaki, and may be one of its candidate ancestors [46,47,48]. Hence, in theory, the genomic information of Oily persimmon could be well used for cultivated persimmon research. In this study, the primers for gene expression on ‘Xiaoguotianshi (2n = 6X)’ were all based on the genomic design of Oily persimmon. The q-RT PCR results showed very good amplification, indicating that the AP2/ERF gene identified on the related Oily persimmon should have high conservation in cultivated persimmon, supporting the conclusion that the pioneering research resolved a possible close relationship between these two species. Additionally, it also shows that it is feasible to utilize the genes identified in Oily persimmon to carry out the study in cultivated persimmon. This study was only a preliminary exploration of gene expression, and more DkAP2/ERF genes and functions related to the occurrence and development of persimmon adventitious roots will be further studied systematically in the future.
Through homologous mapping with Arabidopsis AP2/ERF genes and interactions predicted by the PPI protein database, 49 protein interactions were revealed in this study, confirming the correlation of gene expression between DkAP2/ERFs in the above expression analysis. We also predicted Arabidopsis homologous genes, including AP2, RAV, ESR1, CBF1, CBF2, CRF2, CRF4, CRF5, ERF1, ERF4, ABI4, SHN1/2/3, etc., which corresponded to these 49 interacting DkAP2/ERF. It has been demonstrated that CTK acted on root development by affecting vascular tissue development, root cell extension, geotropism formation, adventitious root and lateral root development, root meristem activity, etc. [49,50,51], and AHK2, AHK3, AHK4 [52], AHPs, and ARRs [53,54] were thought as receptor genes for CTK. In the protein network, CRF1-7, AHK2, AHK3, AHK4, and other CTK receptor proteins displayed a close interaction relationship, and all participated in the cell cytokinin metabolism network. The CRF gene itself has also been reported to be involved in regulating lateral root development [55]. In this study, Dk8gERF098, Dk15gERF155, and Dk12gERF123 were detected to have remarkable homology with CRF2, CRF4, and CRF5, respectively, indicating that they might play roles in root growth and development. Auxin is a recognized dominant regulator of rooting, while ethylene is a stimulating factor of adventitious root occurrence [10]. It has been reported that the synthesis of ethylene was regulated by endogenous IAA, and ethylene could also in turn regulate IAA transport and signal transduction [56]. Moreover, it usually affected the process of adventitious roots by affecting auxin [57]. In this study, it was predicted that Dk4gERF051 and Dk2gERF027 had good homologous similarity with AIL6 and ESR1 in Arabidopsis, and that, in the protein network, AIL6 and ESR1 showed solid interaction relationship with auxin signaling responsive genes, such as WUS, MP, TG4, etc. Thus, it could be inferred that Dk4gERF051 and Dk2gERF027 might also be involved in the regulation of root growth and development. In addition, some of our DkAP2/ERF were also mapped to Arabidopsis homologs ABI4 (Dk2gERF026), RAV1 (Dk2gERF026), and ERF1 (Dk15gERF146), among which ABI4 and RAV1 are predicted to coexist in the same regulatory network responding to ABA signaling, which implied that these genes might participate in ABA metabolism. The network relationship between ERF1 and EIN2, EIN3, EIL1, and CTR1, which are the key proteins in the ethylene response, meant that Dk15gERF146 could be involved in the ethylene response (Table 1).
In summary, the growth and development of plant adventitious is a comprehensive process of the synthesis and signal transduction of various hormones such as ABA, IAA, cytokinin, salicylic acid, and ethylene, as well as important physiological and biochemical processes such as cell meristem and cell wall metabolism (Tahir et al., 2022). In this study, multiple DkAP2/ERF genes were predicted homologous or having derivational interactions with genes related to hormone signaling pathways and physiological and biochemical processes in Arabidopsis. Therefore, it is speculated that these genes may also regulate the growth and development of adventitious roots in cultivated persimmon. The prediction of cis-elements in DkAP2/ERF gene and their expression during rooting in tissue culture seedlings under polyamines also supported the above conclusion. In the future, these genes can be used as the focus to explore rooting mechanism and breeding. This part of the work is ongoing.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae9020191/s1. Figure S1: Clustering of DkAP2/ERF family members and Motif arrangements in Oily persimmon. The overlay of Domains on Motifs is marked with colored dotted boxes to visually present the overlapping relationship between motif and domain; Figure S2: Correlations between DkAP2/ERF gene expression in adventitious root generation; Figure S3: Correlations between DkAP2/ERF gene expression in adventitious root elongation. Table S1: The primer sequences used in qRT-PCR assay; Table S2: The predicted physicochemical properties and duplication events of 157 DkAP2/ERF proteins; Table S3: The highest homologous ERF in our 157 DkAP2/ERFs corresponding to the cultivated persimmon ERFs deposited in NCBI GenBank; Table S4: cis-acting elements in DkAP2/ERF gene.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.D., J.X., and X.Y.; methodology, L.C. and Y.W.; software, Y.W. and X.D.; validation, X.D. and J.X.; formal analysis, Y.W. and D.L.; investigation, X.D. and L.C.; resources, X.D.; data curation, X.Y. and Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, X.D. and Y.W.; writing—review and editing, L.S., L.Z., S.Z., and Y.S.; visualization, Y.W. and X.D.; supervision, M.L. and X.L.; project administration, M.L. and X.L.; funding acquisition, J.X. and X.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by open-end fund of Hubei Key Laboratory of Economic Forest Germplasm Improvement and Resources Comprehensive Utilization, Hubei Collaborative Innovation Center for the Characteristic Resources Exploitation of Dabie Mountain (202019804), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31460509), and National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFD1000603).
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the manuscript and in Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Pingxian Zhang (from Agricultural Genomics Institute at Shenzhen, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences) for his technical support and improvement of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Akagi, T.; Katayama-Ikegami, A.; Yonemori, K. Proanthocyanidin biosynthesis of persimmon (Diospyros Kaki Thunb). Fruit. Sci. Hortic--Amst. 2011, 130, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Hou, X.L.; Xing, G.M.; Liu, J.X.; Duan, A.Q.; Xu, Z.S.; Li, M.Y.; Zhuang, J.; Xiong, A.S. Advances in AP2/ERF super-family transcription factors in plant. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 750–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Suzuki, K.; Fujimura, T.; Shinshi, H. Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and Rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 411–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licausi, F.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Perata, P. APETALA2/Ethylene responsive factor (AP2/ERF) transcription factors: Mediators of stress responses and developmental programs. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanja, B.K.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Tang, M.; M’mbone Muleke, E.; Dong, J.; Liu, L. Genome-wide characterization of the AP2/ERF gene family in Radish (Raphanus Sativus L.): Unveiling evolution and patterns in response to abiotic stresses. Gene 2019, 718, 144048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, K.; Peterson, K.; Jack, T. The plant B3 superfamily. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, S.; Sorkheh, K.; Nasernakhaei, F. Characterization of the APETALA2/Ethylene-responsive factor (AP2/ERF) transcription factor family in Sunflower. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagale, S.; Rozwadowski, K. EAR motif-mediated transcriptional repression in plants: An underlying mechanism for epigenetic regulation of gene expression. Epigenetics 2011, 6, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.B.; Belachew, A.; Ma, S.F.; Young, M.; Ade, J.; Shen, Y.; Marion, C.M.; Holtan, H.E.; Bailey, A.; Stone, J.K.; et al. The EDLL motif: A potent plant transcriptional activation domain from AP2/ERF transcription factors. Plant J. 2012, 70, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.M.; Mao, J.; Li, S.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X. Insights into factors controlling adventitious root formation in Apples. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trupiano, D.; Yordanov, Y.; Regan, S.; Meilan, R.; Tschaplinski, T.; Scippa, G.S.; Busov, V. Identification, characterization of an AP2/ERF transcription factor that promotes adventitious, lateral root formation in Populus. Planta 2013, 238, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, A.; Kato, T.; Fukaki, H.; Aida, M.; Tasaka, M. The auxin-regulated AP2/EREBP gene PUCHI is required for morphogenesis in the early lateral root primordium of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2156–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neogy, A.; Garg, T.; Kumar, A.; Dwivedi, A.K.; Singh, H.; Singh, U.; Singh, Z.; Prasad, K.; Jain, M.; Yadav, S.R. Genome-wide transcript profiling reveals an auxin-responsive transcription factor, OsAP2/ERF-40, promoting rice adventitious root development. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 2343–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigal, A.; Yordanov, Y.S.; Perrone, I.; Karlberg, A.; Tisserant, E.; Bellini, C.; Busov, V.B.; Martin, F.; Kohler, A.; Bhalerao, R.; et al. The AINTEGUMENTA LIKE1 homeotic transcription factor PtAIL1 controls the formation of adventitious root primordia in Poplar. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 1996–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bais, H.P.; Ravishankar, G.A. Role of polyamines in the ontogeny of plants and their biotechnological applications. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult. 2002, 69, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, Y.; Sun, P.; Cheng, H.; Han, W.; Diao, S.; Li, H.; Mai, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, F.; Fu, J. A high-quality chromosomal genome assembly of Diospyros Oleifera Cheng. Gigascience 2020, 9, giz164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.A.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview version 2—A multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Elkan, C. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proc. Int. Conf. Intell. Syst. Mol. Biol. 1994, 2, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.R.; Shi, Y.N.; Min, T.; Luo, Z.R.; Yao, Y.C.; Xu, Q.; Ferguson, I.; Chen, K.S. Expression of ethylene response genes during persimmon fruit astringency removal. Planta 2012, 235, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, T.; Yin, X.R.; Shi, Y.N.; Luo, Z.R.; Yao, Y.C.; Grierson, D.; Ferguson, I.B.; Chen, K.S. Ethylene-responsive transcription factors interact with promoters of ADH and PDC involved in persimmon (Diospyros kaki) fruit de-astringency. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 6393–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, T.; Fang, F.; Ge, H.; Shi, Y.N.; Luo, Z.R.; Yao, Y.C.; Grierson, D.; Yin, X.Y.; Chen, K.S. Two novel anoxia-induced ethylene response factors that interact with promoters of deastringency-related genes from persimmon. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e7043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.; Choi, S.C.; Jung, S.; Cho, B.K.; Ahn, G.H.; Ryu, S.B. A transcriptome approach towards understanding fruit softening in persimmon. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1556. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, M.D.; Yamasaki, K.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Tateno, M.; Suzuki, M. A novel mode of DNA recognition by a beta-sheet revealed by the solution structure of the GCC-box binding domain in complex with DNA. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 5484–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licausi, F.; Giorgi, F.M.; Zenoni, S.; Osti, F.; Pezzotti, M.; Perata, P. Genomic and transcriptomic analysis of the AP2/ERF superfamily in Vitis Vinifera. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Han, Z.; Yuan, J.; Chen, C.; Song, W.; Wang, C. Genome-Wide identification of AP2/ERF transcription factors in Cauliflower and expression profiling of the ERF Family under salt and drought stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Sun, W.; Ma, Z.; Zheng, T.; Huang, L.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, G.; Tang, Z.; Bu, T.; Li, C.; et al. Genome-wide investigation of the AP2/ERF gene family in tartary buckwheat (Fagopyum Tataricum). BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Y.; Han, J.J.; You, Q.; Chai, M.J.; Li, Y.; Tian, C.F.; Yang, Q.S.; Lu, J.X. Genome-wide analysis of AP2/ERF gene family in Chrysanthemums. Mol. Plant Breed. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Sharoni, A.M.; Nuruzzaman, M.; Satoh, K.; Shimizu, T.; Kondoh, H.; Sasaya, T.; Choi, I.R.; Omura, T.; Kikuchi, S. Gene structures, classification and expression models of the AP2/EREBP transcription factor family in Rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 344–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chai, Z.; Lin, P.; Huang, C.; Huang, G.; Xu, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of AP2/ERF transcription factors in Sugarcane (Saccharum Spontaneum L.). BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitomi, Y.; Ito, H.; Hobo, T.; Aya, K.; Kitano, H.; Inukai, Y. The Auxin responsive AP2/ERF transcription factor CROWN ROOTLESS5 is involved in crown root initiation in rice through the Induction of OsRR1, a type-A response regulator of cytokinin signaling. Plant J. 2011, 67, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andriankaja, A.; Boisson-Dernier, A.; Frances, L.; Sauviac, L.; Jauneau, A.; Barker, D.G.; de Carvalho-Niebel, F. AP2-ERF Transcription factors mediate nod factor dependent Mt ENOD11 activation in root hairs via a novel Cis-regulatory motif. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2866–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.W. Molecular bases for the regulation of adventitious root generation in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 614072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Bullock, D.A.; Alonso, J.M.; Stepanova, A.N. To fight or to grow: The balancing role of ethylene in plant abiotic stress responses. Plants 2021, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aukerman, M.J.; Sakai, H. Regulation of flowering time and floral organ identity by a microRNA and its APETALA2-like aarget genes. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2730–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jofuku, K.D.; Omidyar, P.K.; Gee, Z.; Okamuro, J.K. Control of seed mass and Seed yield by the floral homeotic gene APETALA2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3117–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moose, S.P.; Sisco, P.H. Glossy15, an APETALA2-like gene from maize that regulates leaf epidermal cell identity. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 3018–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinshi, H.; Usami, S.; Ohme-Takagi, M. Identification of an ethylene-responsive region in the promoter of a tobacco class I chitinase gene. Plant Mol. Biol. 1995, 27, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Munné-Bosch, S. Ethylene Response Factors: A key regulatory hub in hormone and stress signaling. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Sarai, A. Unique Mode of GCC box recognition by the DNA-binding domain of ethylene-responsive element-binding factor (ERF domain) in plant. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 26857–26861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutterson, N.; Reuber, T.L. Regulation of disease resistance pathways by AP2/ERF transcription factors. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, K.H.; Lee, S.C.; Jung, H.W.; Hong, J.K.; Hwang, B.K. Expression and functional roles of the pepper pathogen-induced transcription factor RAV1 in bacterial disease resistance, and drought and salt Stress tolerance. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 61, 897–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, S.; Somssich, M.; Nakata, M.T.; Unda, F.; Atsuzawa, K.; Kaneko, Y.; Wang, T.; Bågman, A.M.; Gaudinier, A.; Yoshida, K.; et al. Complete substitution of a secondary cell wall with a primary cell wall in Arabidopsis. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsafouros, A.; Denaxa, N.K.; Roussos, P.A. Chapter 12—Role of Polyamines in Adventitious root formation. In Environmental, Physiological and Chemical Controls of Adventitious Rooting in Cuttings; Plant Biology, Sustainability and Climate Change; Husen, A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 289–313. ISBN 978−0−323−90636−4. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.L.; Luo, Z.R. Comparison of four molecular markers for genetic analysis in Diospyros L. (Ebenaceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 2009, 281, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.M.; Liu, H.M.; Hu, J.J.; Liang, Y.Q.; Liang, J.J.; Wuyun, T.N.; Tan, X.F. Five complete chloroplast genome sequences from Diospyros: Genome organization and comparative analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, C.F.; Liu, S.Y.; Wang, M.K.; Ji, H.; Ruan, X.F.; Wang, R.Z.; Yang, Y. Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveals genetic divergence and domestication genes in Diospyros. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, T.; Motyka, V.; Laucou, V.; Smets, R.; Van Onckelen, H.; Schmülling, T. Cytokinin-deficient transgenic Arabidopsis plants show multiple developmental alterations indicating opposite functions of cytokinins in the regulation of shoot and root meristem activity. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2532–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohar, D.P.; Schaff, J.E.; Laskey, J.G.; Kieber, J.J.; Bilyeu, K.D.; Bird, D.M. Cytokinins play opposite roles in lateral root formation, and nematode and rhizobial symbioses. Plant J. 2004, 38, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riefler, M.; Novak, O.; Strnad, M.; Schmülling, T. Arabidopsis cytokinin receptor mutants reveal functions in shoot growth, leaf senescence, seed size, germination, root development, and cytokinin metabolism. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Sakurai, K.; Ueguchi, C.; Mizuno, T. Two types of putative nuclear factors that physically interact with histidine-containing phosphotransfer (hpt) domains, signaling mediators in Histo-asp phosphorelay, in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2001, 42, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, L.; Chen, H.C.; Sheen, J. Two-component signal transduction pathways in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 500–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaller, G.E.; Kieber, J.J.; Shiu, S.H. Two-component signaling elements and histidyl-aspartyl phosphorelays. Arab. Book 2008, 6, e0112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Cho, C.; Lee, M.R.; Van Binh, N.; Kim, J. CYTOKININ RESPONSE FACTOR2 (CRF2) and CRF3 regulate lateral root development in response to cold stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 1828–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druege, U.; Franken, P.; Lischewski, S.; Ahkami, A.H.; Zerche, S.; Hause, B.; Hajirezaei, M.R. Transcriptomic analysis reveals ethylene as stimulator and auxin as regulator of adventitious root formation in Petunia cuttings. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druege, U.; Franken, P.; Hajirezaei, M.R. Plant hormone homeostasis, signaling, and function during adventitious root formation in cuttings. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).