Tomato Fruit Growth and Nutrient Accumulation in Response to Blue and Red Light Treatments during the Reproductive Growth Stage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
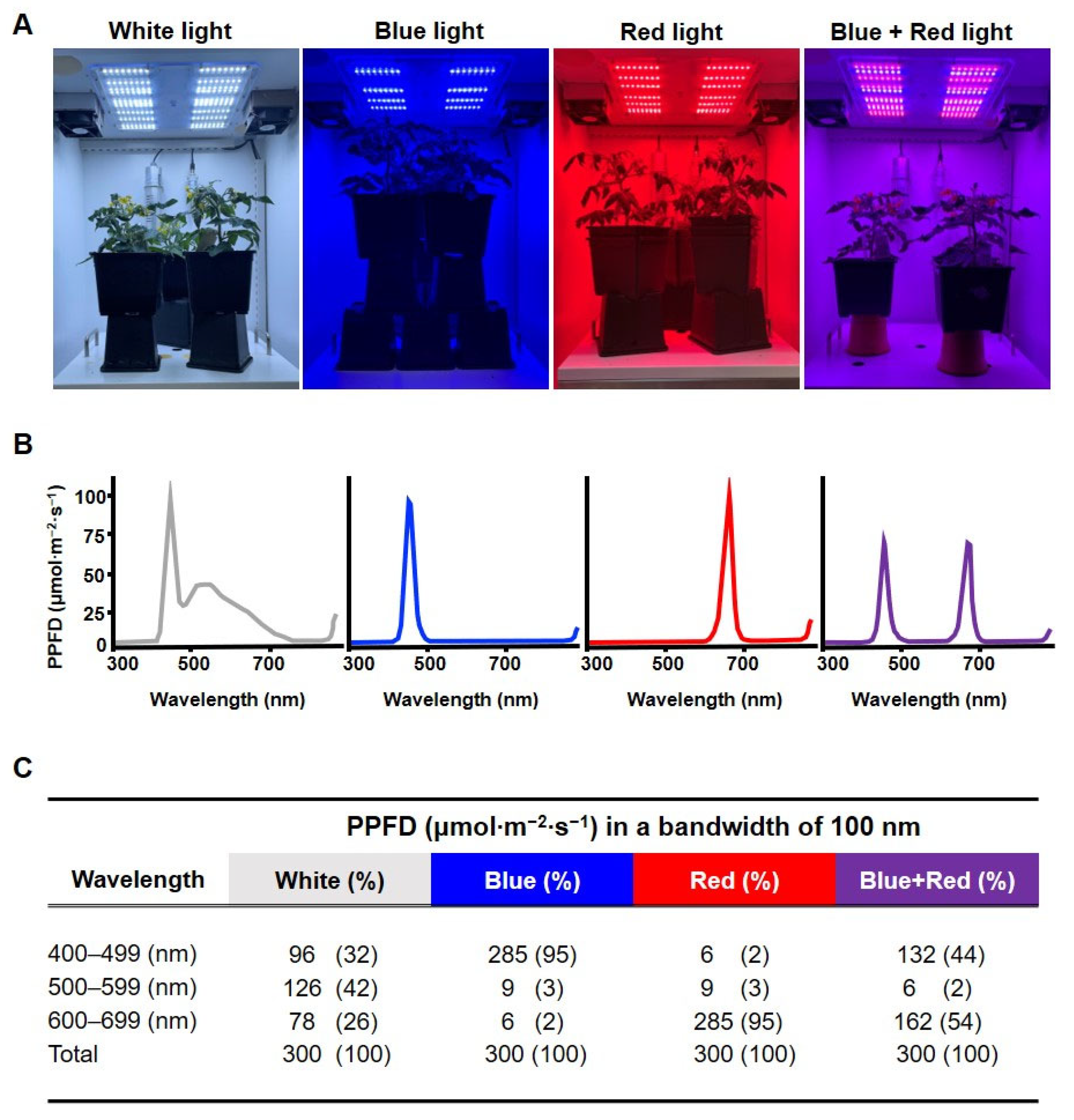
2.2. Experimental Design and Light Treatments
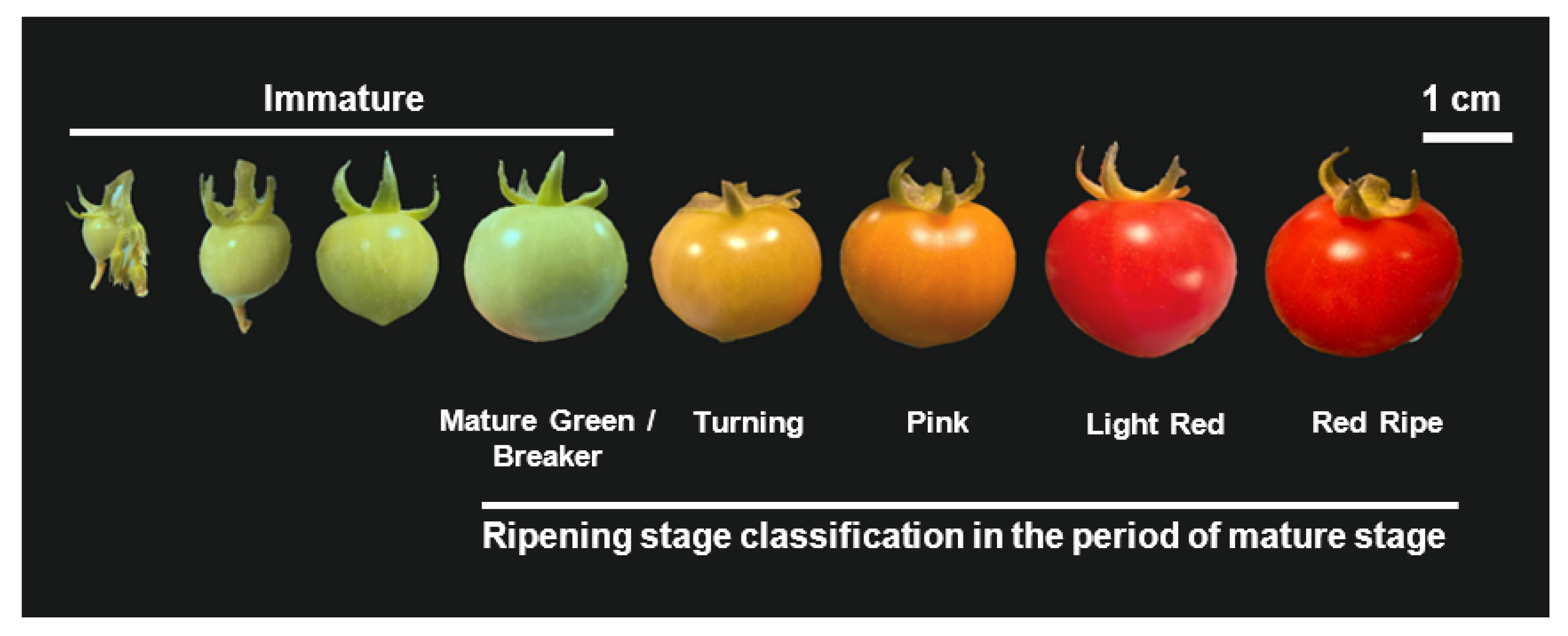
2.3. Investigating Tomato Fruit Development and Ripening
2.4. Investigating the Nutritional Characteristics of Tomato Fruits
2.5. Statistics Analysis and Graph Visualization
3. Results and Discussion
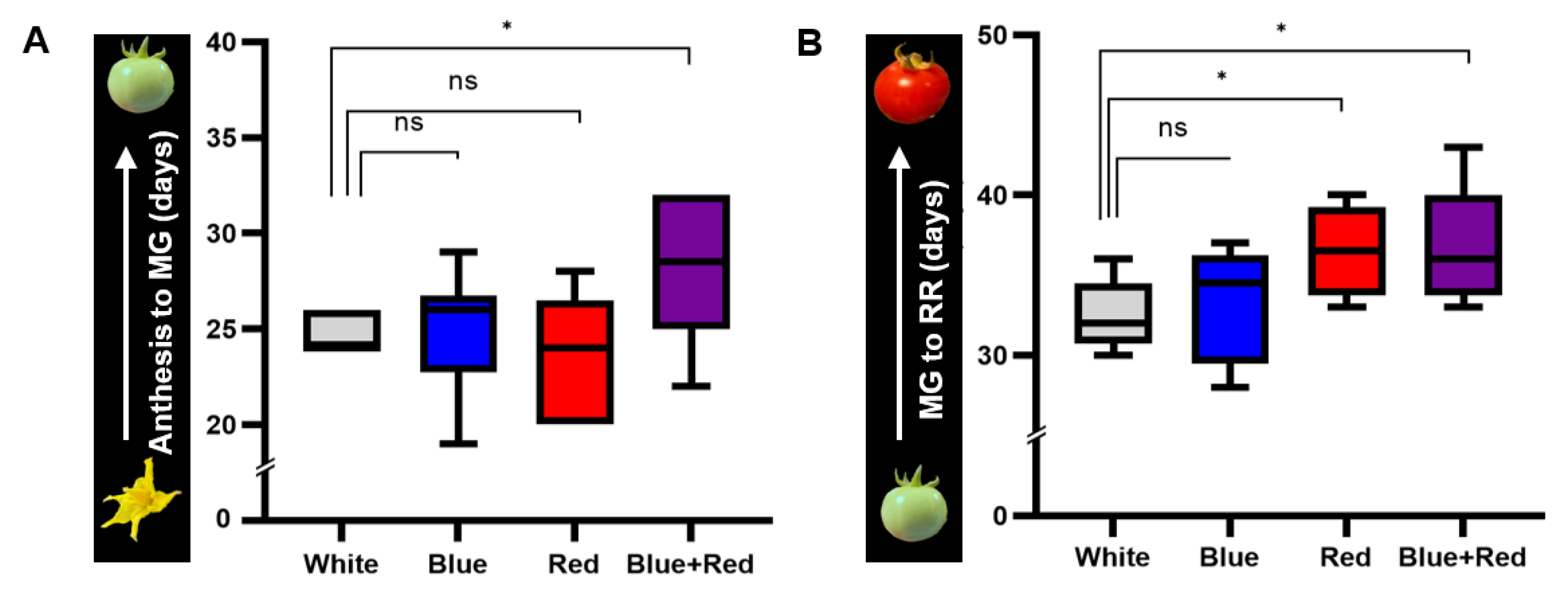
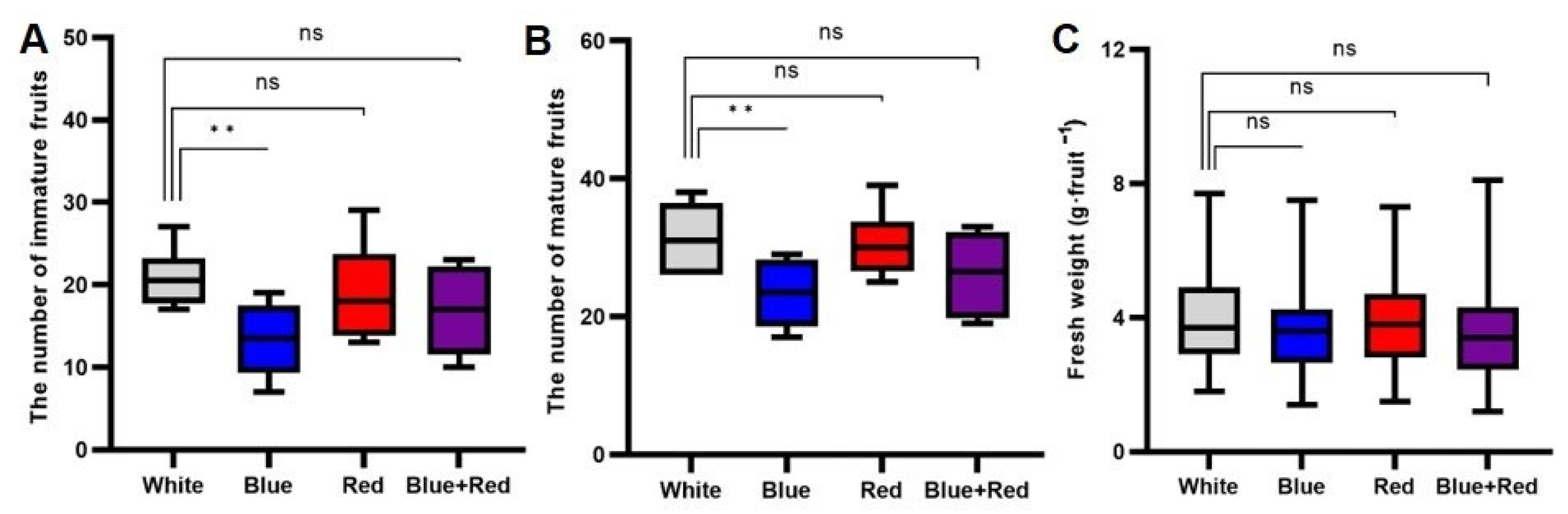
3.1. Effects of the Different Spectral Distributions of Light on Tomato Fruit Development and Ripening after Anthesis
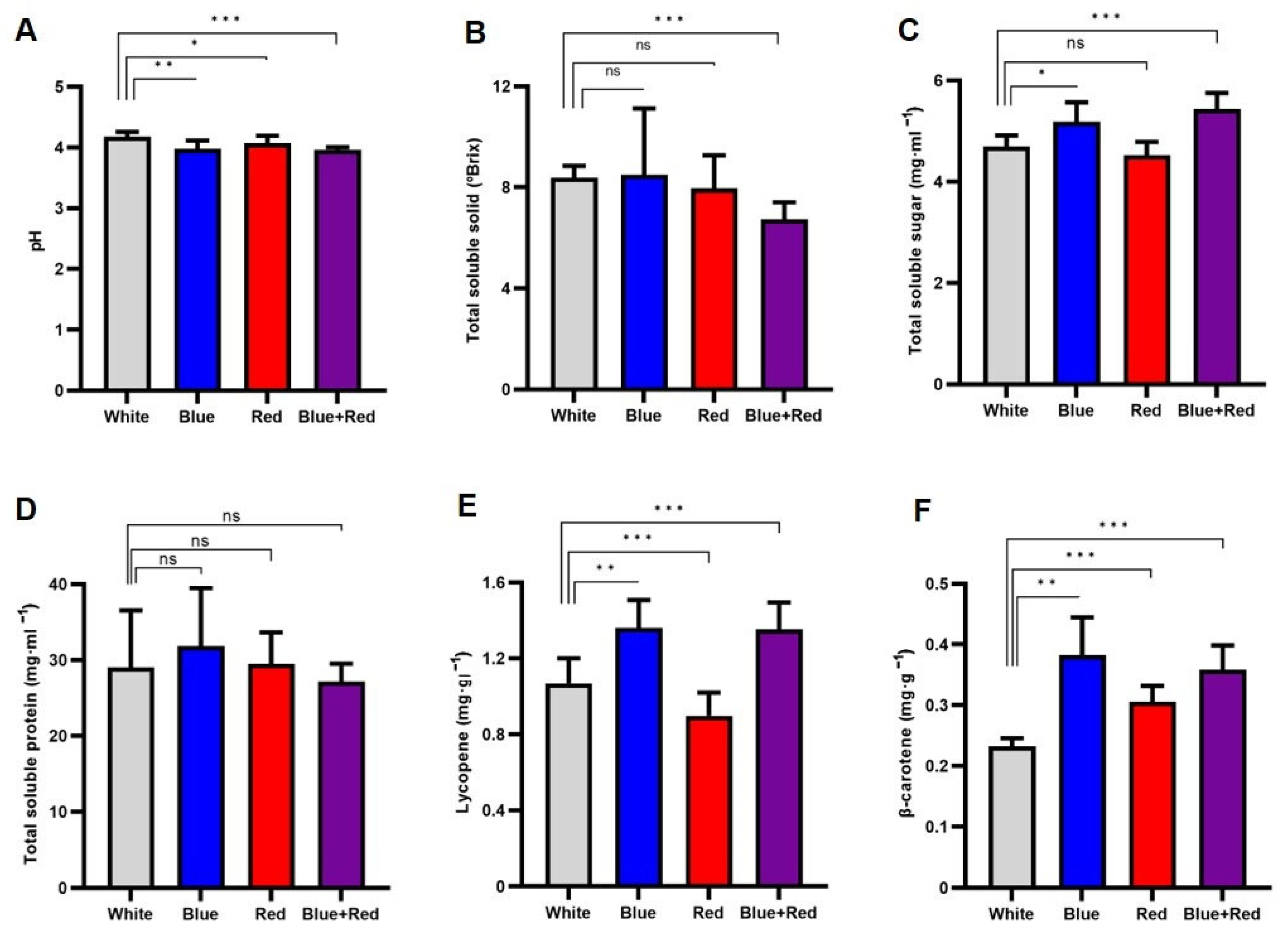
3.2. The Nutritional Characteristics of Tomato Fruits Developed and Matured under Different Light Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Folta, K.M.; Carvalho, S.D. Photoreceptors and Control of Horticultural Plant Traits. HortScience 2015, 50, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giliberto, L.; Perrotta, G.; Pallara, P.; Weller, J.L.; Fraser, P.D.; Bramley, P.M.; Fiore, A.; Tavazza, M.; Giuliano, G. Manipulation of the Blue Light Photoreceptor Cryptochrome 2 in Tomato Affects Vegetative Development, Flowering Time, and Fruit Antioxidant Content. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, E. Effects of Light Quality on Growth of Crop Plants under Artificial Lighting. Environ. Control Biol. 2003, 41, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.Y.; Park, S.A.; Park, B.J.; Lee, Y.; Oh, M.M. Growth and Antioxidant Phenolic Compounds in Cherry Tomato Seedlings Grown Under Monochromatic Light-Emitting Diodes. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2015, 55, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzounis, T. Spectral Effects of Artificial Light on Plant Physiology and Secondary Metabolism: A Review. HortScience 2015, 50, 1128–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannehl, D.; Schwend, T.; Veit, D.; Schmidt, U. Increase of Yield, Lycopene, and Lutein Content in Tomatoes Grown Under Continuous PAR Spectrum LED Lighting. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 611236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Wei, C.; Zhang, J.; Tan, X.; Li, T.; Gao, B.; Liu, B. Supplemental Blue Light Frequencies Improve Ripening and Nutritional Qualities of Tomato Fruits. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 888976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Yang, T.; Choi, S.; Wang, Y.J.; Lin, M.Y.; Liceaga, A.M. Supplemental Intracanopy Far-Red Radiation to Red LED Light Improves Fruit Quality Attributes of Greenhouse Tomatoes. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 261, 108985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmitessa, O.D.; Paciello, P.; Santamaria, P. Supplemental LED Increases Tomato Yield in Mediterranean Semi-Closed Greenhouse. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewolde, F.T.; Shiina, K.; Maruo, T.; Takagaki, M.; Kozai, T.; Yamori, W. Supplemental LED Inter-Lighting Compensates for a Shortage of Light for Plant Growth and Yield Under the Lack of Sunshine. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Türkay, A.; Rezzan, K.; Ufuk, K.M. Blue LED Lighting Improves the Postharvest Quality of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L. cv. Zahide F1) Fruits. Ege Üniversitesi Ziraat Fakültesi Derg. 2021, 58, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jin, N.; Jin, L.; Xiao, X.; Hu, L.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, W.; Lyu, J.; et al. Response of Tomato Fruit Quality Depends on Period of LED Supplementary Light. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 833723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, R.; Xu, L. Dynamic Control of Supplemental Lighting for Greenhouse. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1956, 020050. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, D.M.; Sina, A.A.; Khandker, S.S.; Neesa, L.; Tanvir, E.M.; Kabir, A.; Khalil, M.I.; Gan, S. Nutritional Composition and Bioactive Compounds in Tomatoes and Their Impact on Human Health and Disease: A Review. Foods 2020, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, P.; Sharma, A.; Singh, B.; Nagpal, A.K. Bioactivities of Phytochemicals Present in Tomato. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 2833–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Massa, G.D.; Kim, H.-H.; Wheeler, R.M.; Mitchell, C.A. Plant Productivity in Response to LED Lighting. HortScience 2008, 43, 1951–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appolloni, E.; Orsini, F.; Pennisi, G.; Durany, X.G.; Paucek, I.; Gianquinto, G. Supplemental LED Lighting Effectively Enhances the Yield and Quality of Greenhouse Truss Tomato Production: Results of a Meta-Analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 596927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devesh, S.; Chandrajit, B.; Merve, M.W.; Bernhard, R. LEDs for Energy Efficient Greenhouse Lighting. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 49, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorais, M.; Gosselin, A.; Trudel, M.J. Annual Greenhouse Tomato Production Under a Sequential Intercropping System Using Supplemental Light. Sci. Hortic. 1991, 45, 22–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Chang, L.; Qinghua, S.; Fengjuan, Y.; Min, W. Mixed Red and Blue Light Promotes Ripening and Improves Quality of Tomato Fruit by Influencing Melatonin Content. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 185, 104407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanwoua, J.; Vercambre, G.; Buck-Sorlin, G.; Dieleman, J.A.; de Visser, P.; Génard, M. Supplemental LED Lighting Affects the Dynamics of Tomato Fruit Growth and Composition. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 256, 108571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngcobo, B.L.; Bertling, I.; Clulow, A.D. Preharvest Illumination of Cherry Tomato Reduces Ripening Period, Enhances Fruit Carotenoid Concentration and Overall Fruit Quality. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. United States Standards for Grades of Fresh Tomatoes. 1991. Available online: https://www.ams.usda.gov/sites/default/files/media/Tomato_Standard%5B1%5D.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Jung, H.-A.; Hong, J.-Y. Change in Quality Characteristics of Yellow Paprika According to Drying Methods. Korean J. Food Preserv. 2017, 24, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kohyama, K.; Nishinari, K. Effect of Soluble Sugars on Gelatinization and Retrogradation of Sweet Potato Starch. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 1406–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilberg, V.C.; Rodriguez-Amaya, D.B. HPLC Quantitation of Major Carotenoids of Fresh and Processed Guava, Mango and Papaya. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, D.; Qin, M.; Xie, Z.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Supplemental Lighting on Potassium Transport and Fruit Coloring of Tomatoes Grown in Hydroponics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Song, S.; Su, W.; Hao, Y.; Liu, H. Supplementary Red Light Results in the Earlier Ripening of Tomato Fruit Depending on Ethylene Production. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 175, 104044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C. Plant Blue-Light Receptors. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Yang, Z.; Gomez, A.; Liu, B.; Lin, C.; Oka, Y. Signaling Mechanisms of Plant Cryptochromes in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Plant Res. 2016, 129, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanya, K.; Ishigami, Y.; Hikosaka, S.; Goto, E. Effects of Blue and Red Light on Stem Elongation and Flowering of Tomato Seedlings. Acta Hortic. 2012, 956, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Kafi, M.; Kalate-Jari, S.; Matinizadeh, M.; Karaj, I. Tulip Response to Different Light Sources. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2018, 28, 539–545. [Google Scholar]
- Moradi, S.; Kafi, M.; Aliniaeifard, S.; Salami, S.A.; Shokrpour, M.; Pedersen, C.; Moosavi-Nezhad, M.; Wróbel, J.; Kalaji, H.M. Blue Light Improves Photosynthetic Performance and Biomass Partitioning toward Harvestable Organs in Saffron (Crocus sativus L.). Cells 2021, 10, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naznin, M.T.; Lefsrud, M.; Gravel, V.; Azad, M.O.K. Blue Light Added with Red LEDs Enhance Growth Characteristics, Pigments Content, and Antioxidant Capacity in Lettuce, Spinach, Kale, Basil, and Sweet Pepper in a Controlled Environment. Plants 2019, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, E.A.; Scott, J.W.; Einstein, M.A.; Malundo, T.M.M.; Carr, B.T.; Shewfelt, R.L.; Tandon, K.S. Relationship between Sensory and Instrumental Analysis for Tomato Flavor. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. Jashs 1998, 123, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chang, T.; Guo, S.; Xu, Z.; Chen, W. Effect of Irradiation with Blue and Red LED on Fruit Quality of Cherry Tomato During Growth Period. China Veg. 2010, 22, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, F.; Wang, C.; Sun, X.; Bao, Z.; Dong, C.; Sun, C.; Ren, Y.; Liu, S. Sugar Metabolic Changes in Protein Expression Associated with Different Light Quality Combinations in Tomato Fruit. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 88, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q. Regulation of Carotenoid Metabolism in Tomato. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, N.A.; Erdman, J.W. Are Lycopene Metabolites Metabolically Active. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2012, 59, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingwan, M.; Pradhan, A.A.; Kushwaha, A.K.; Dar, M.A.; Bhagavatula, L.; Datta, S. Photoprotective Role of Plant Secondary Metabolites: Biosynthesis, Photoregulation, and Prospects of Metabolic Engineering for Enhanced Protection Under Excessive Light. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2023, 209, 105300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba, R.; Cordonnier-Pratt, M.M.; Pratt, L.H. Fruit-Localized Phytochromes Regulate Lycopene Accumulation Independently of Ethylene Production in Tomato. Plant Physiol. 2000, 123, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zabaras, D.; Bennett, L.; Aguas, P.; Woonton, B.W. Effects of UV-C, Red Light and Sun Light on the Carotenoid Content and Physical Qualities of Tomatoes During Post-Harvest Storage. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjai, L.; Noga, G.; Hunsche, M.; Fiebig, A. Optimal Red Light Irradiation Time to Increase Health-Promoting Compounds in Tomato Fruit Postharvest. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 251, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.H.; Won, H.J.; Ban, S.; Choi, H.; Jung, J.H. Tomato Fruit Growth and Nutrient Accumulation in Response to Blue and Red Light Treatments during the Reproductive Growth Stage. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9101113
Lee SH, Won HJ, Ban S, Choi H, Jung JH. Tomato Fruit Growth and Nutrient Accumulation in Response to Blue and Red Light Treatments during the Reproductive Growth Stage. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(10):1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9101113
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Su Hyeon, Hyo Jun Won, Seunghyun Ban, Hyelim Choi, and Je Hyeong Jung. 2023. "Tomato Fruit Growth and Nutrient Accumulation in Response to Blue and Red Light Treatments during the Reproductive Growth Stage" Horticulturae 9, no. 10: 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9101113
APA StyleLee, S. H., Won, H. J., Ban, S., Choi, H., & Jung, J. H. (2023). Tomato Fruit Growth and Nutrient Accumulation in Response to Blue and Red Light Treatments during the Reproductive Growth Stage. Horticulturae, 9(10), 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9101113





