Squash Yield, Water-Use Efficiency and Nitrate Accumulation as Influenced by the Application of Humic Acid, Geobacillus stearothermophilus SSK-2018 and Wheat Straw in an Arid Land Condition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Planting Material, Field Preparation, Experimental Layout and Design
2.2. Soil Incorporation of Wheat Straw
2.3. Planting, Crop Irrigation and Other Cultural Practices
2.4. Application of Humic Acid and NPK Fertilizer
2.5. Determination of Squash Water-Use Efficiency
2.6. Nitrate Determination in Squash Fruits
2.7. Data Collection
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
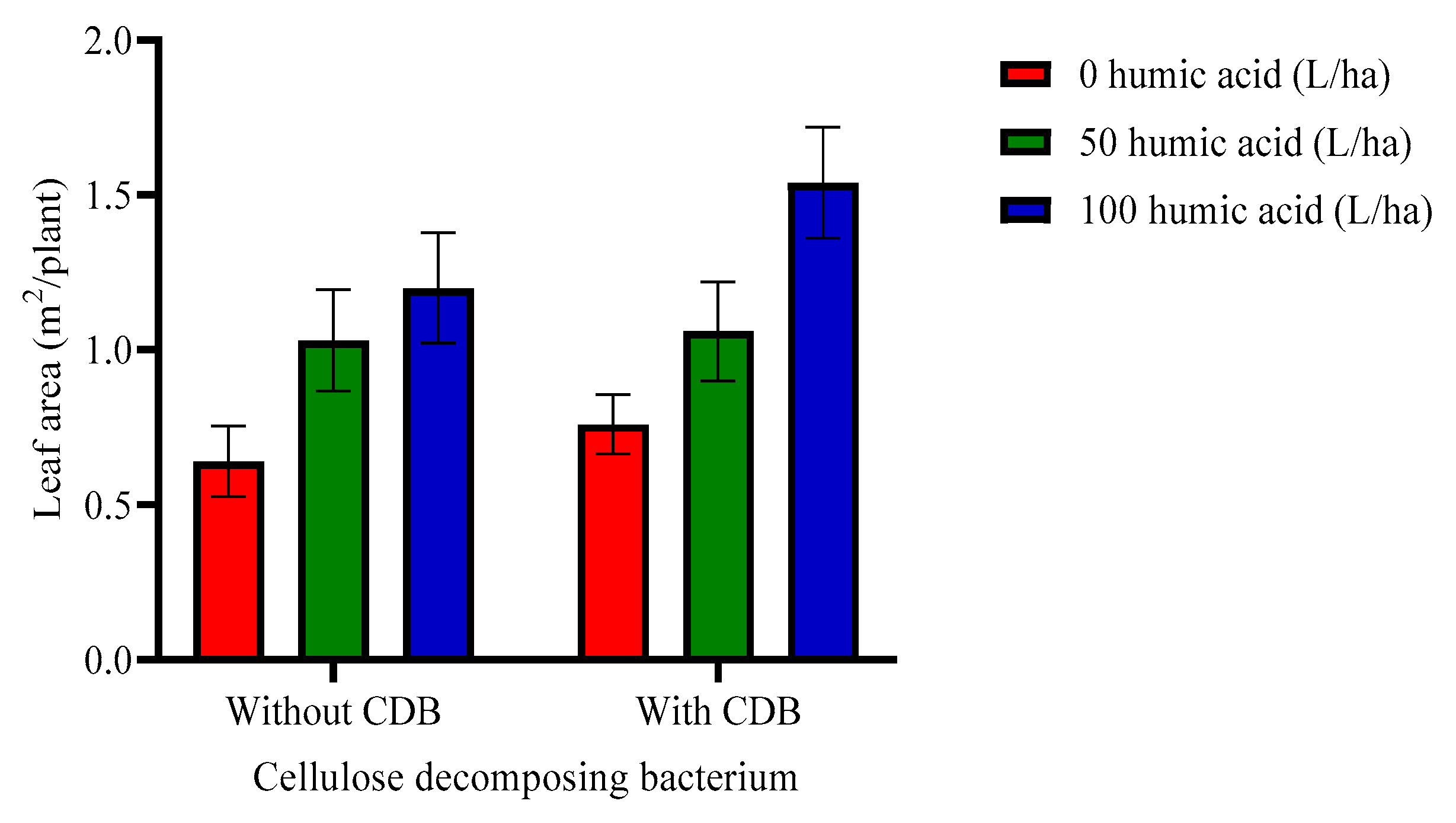
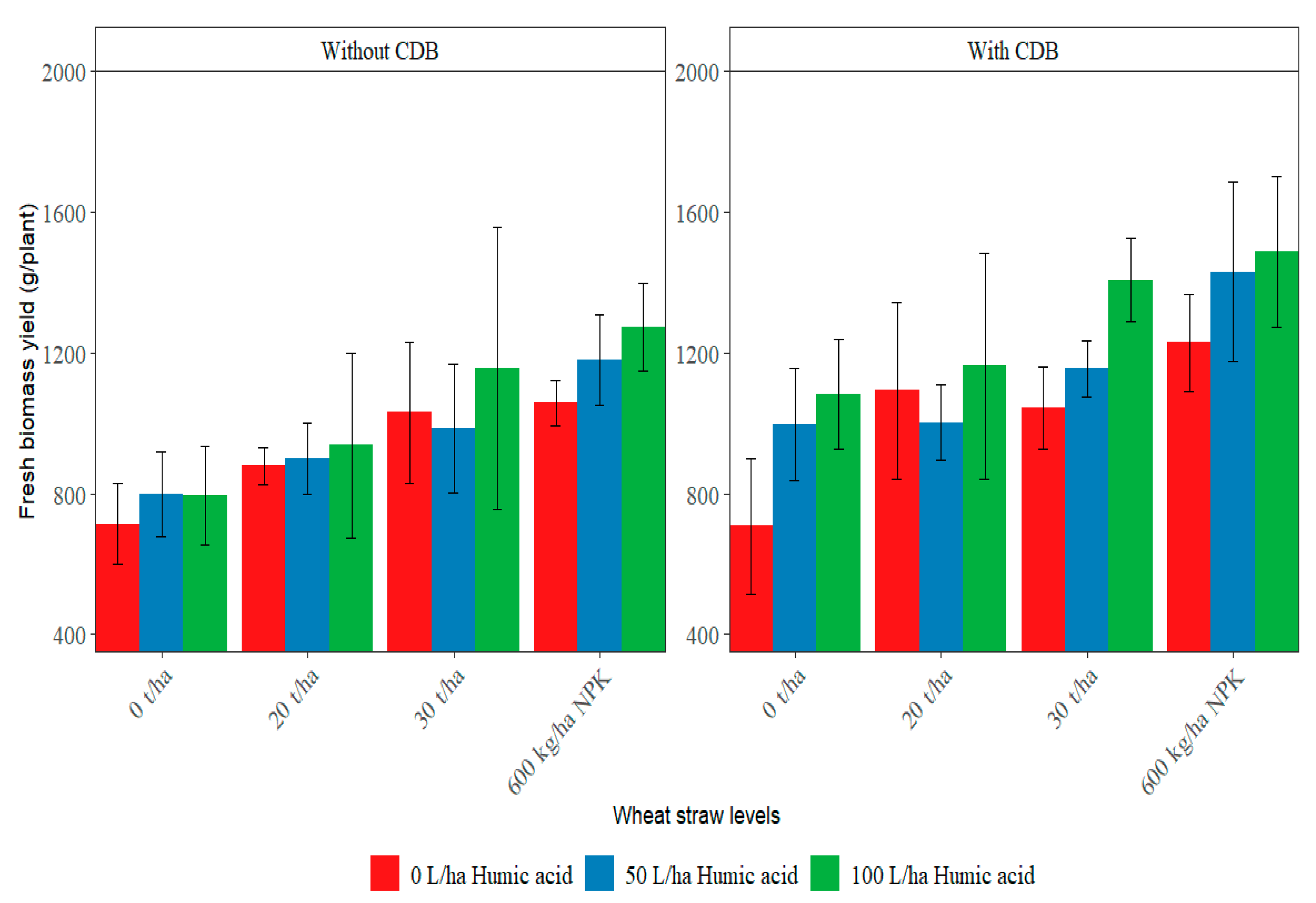
3.1. Effect of Humic Acid, Geobacillus stearothermophilus SSK-2018 and Wheat Straw on Leaf Area, Fresh and Dry Biomass Yield of Squash
3.2. Effect of Humic Acid, Geobacillus stearothermophilus SSK-2018 and Wheat Straw on Fruit Yield and Water-Use Efficiency of Squash
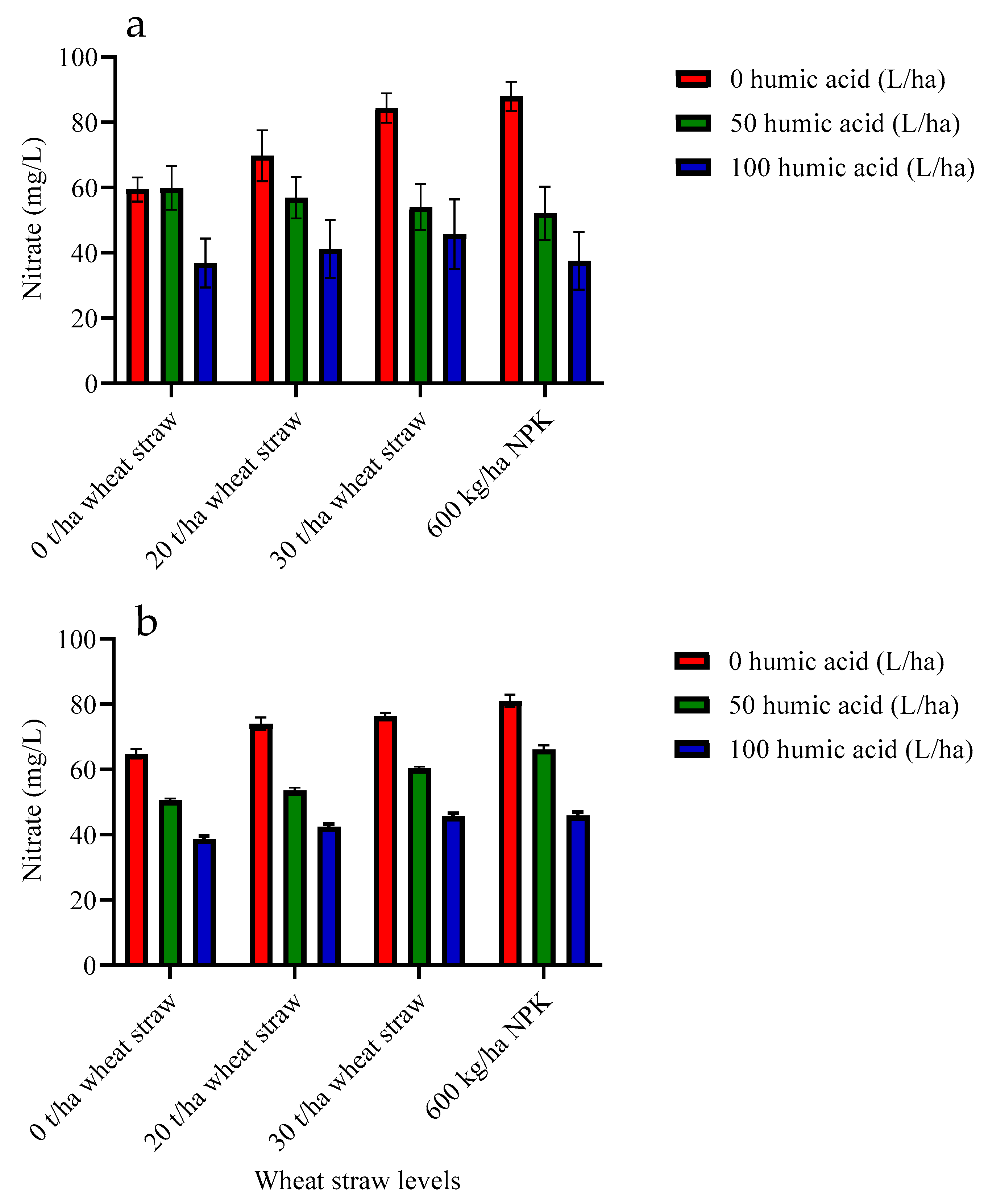
3.3. Effect of Humic Acid, Geobacillus stearothermophilus SSK-2018 and Wheat Straw on Nitrate Accumulation in Squash Fruits
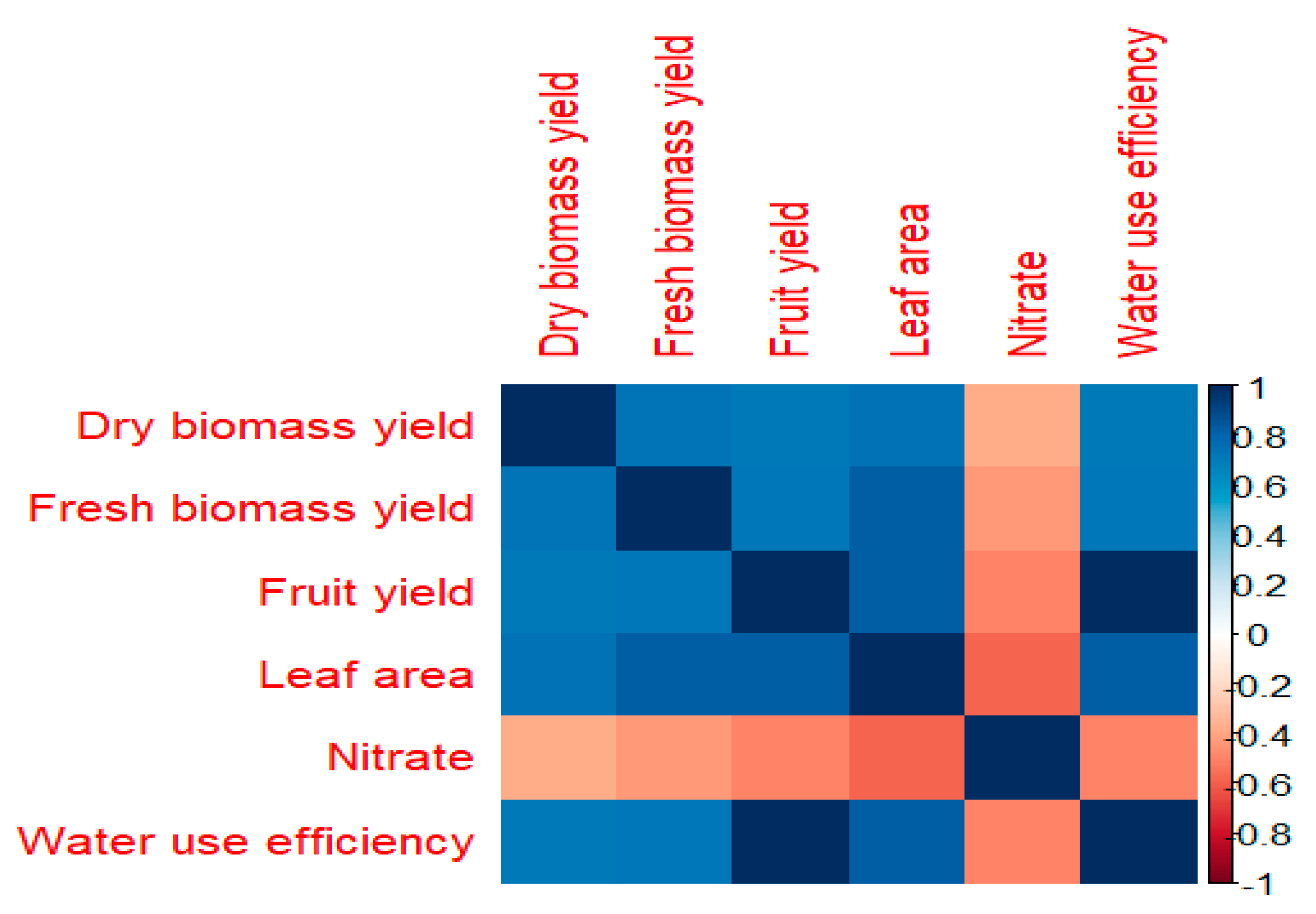
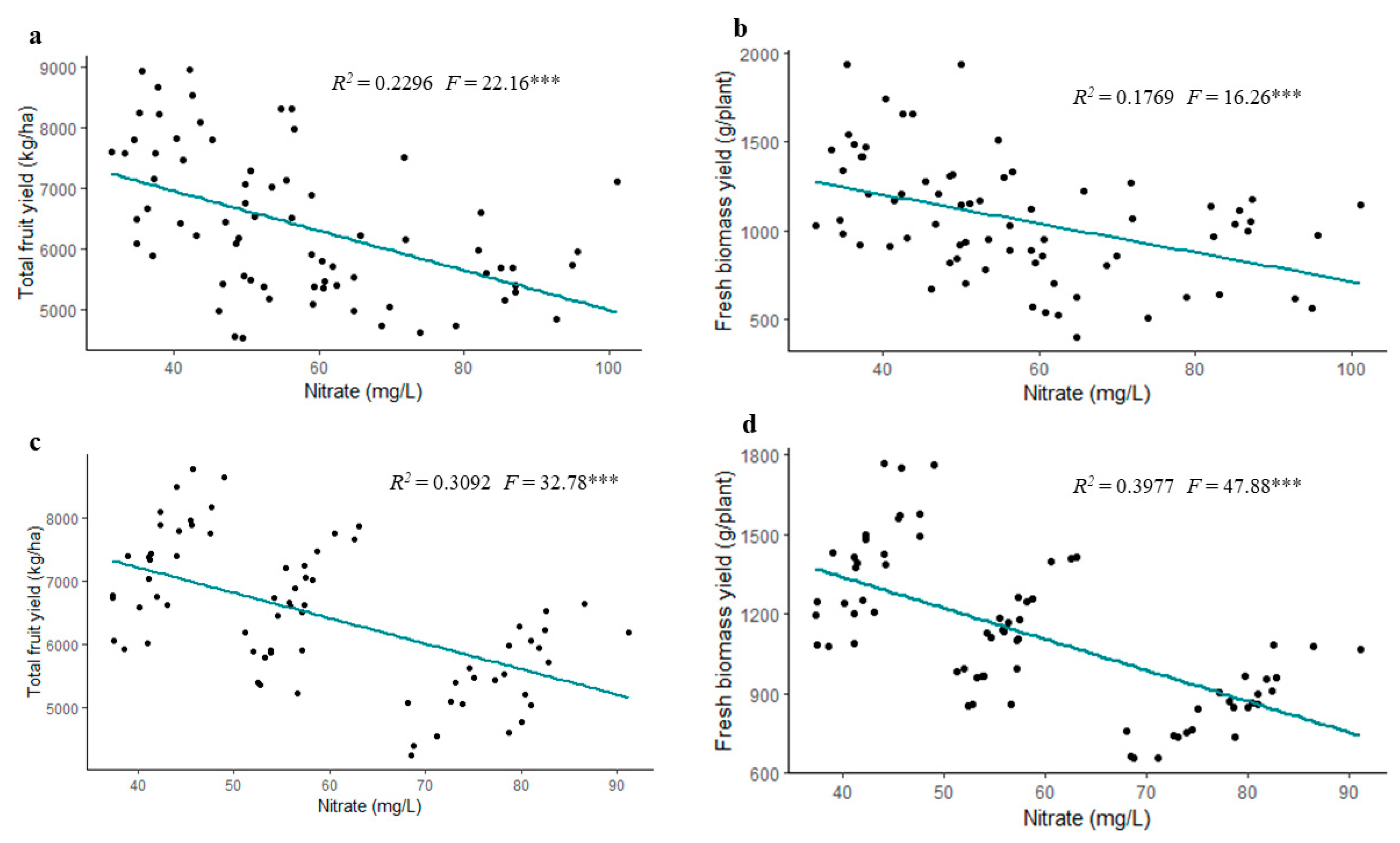
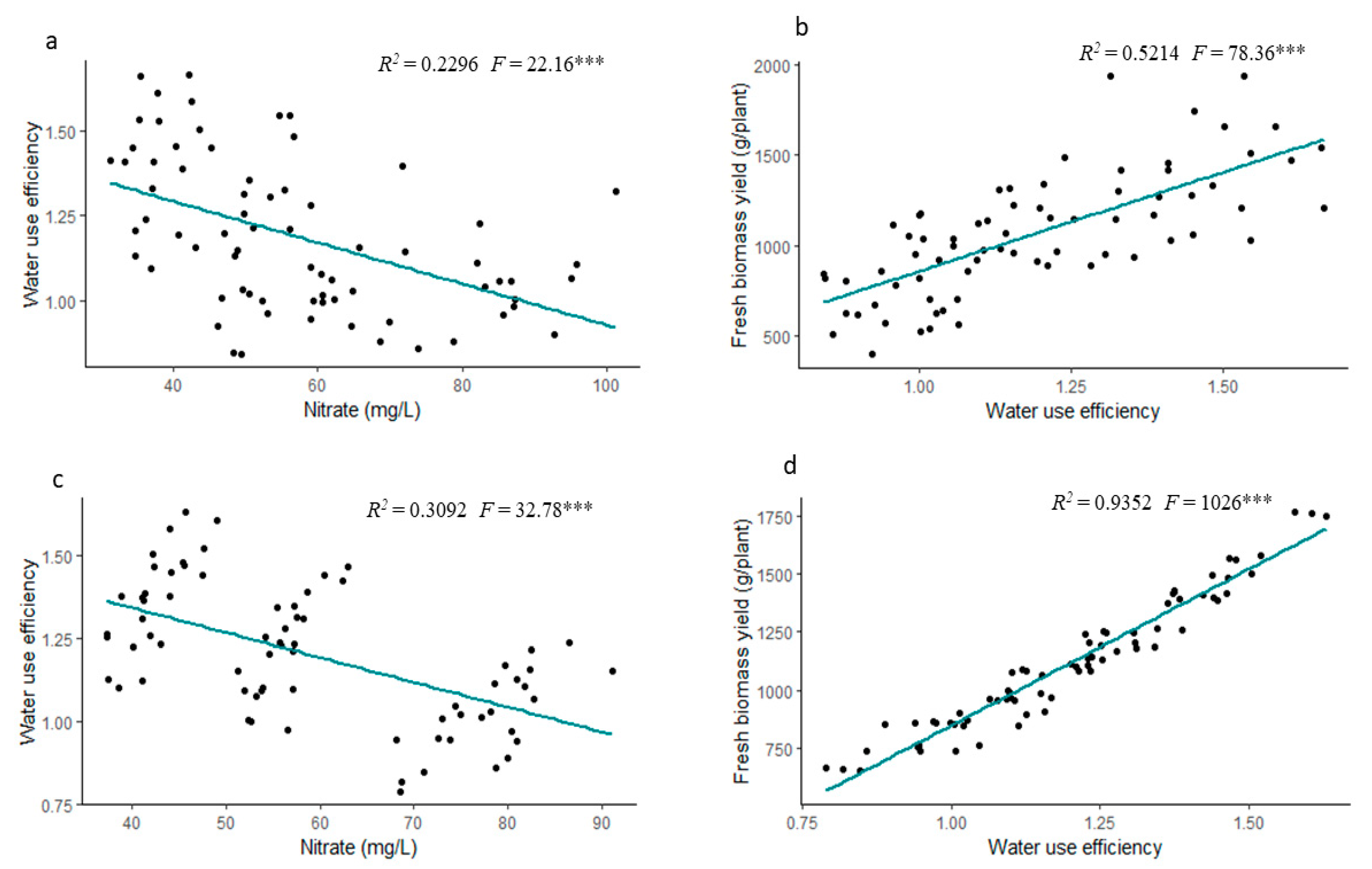
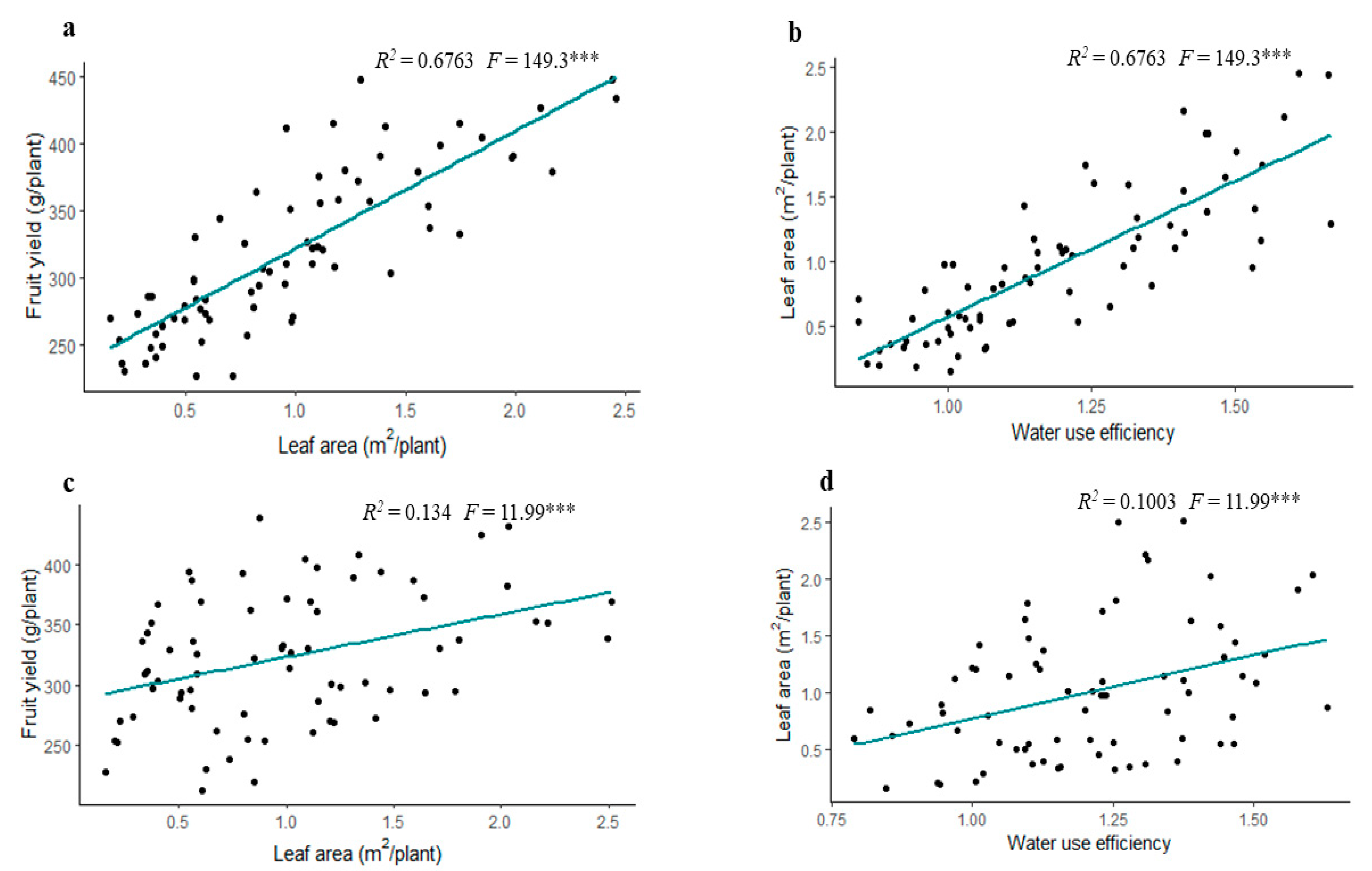
3.4. Correlation Analysis
3.5. Regression Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gichana, Z.; Liti, D.; Wakibia, J.; Ogello, E.; Drexler, S.; Meulenbroek, P.; Ondiba, R.; Zollitsch, W.; Waidbacher, H. Efficiency of pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo), sweet wormwood (Artemisia annua) and amaranth (Amaranthus dubius) in removing nutrients from a smallscale recirculating aquaponic system. Aquacult. Int. 2019, 27, 1767–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paksoy, M.; Aydin, C. Some physical properties of edible squash (Cucurbita pepo L.) seeds. J. Food. Eng. 2004, 65, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.A.; El-Sherbini, M.A.A.; Selim, E.M. Effects of biochar on soil properties, heavy metal availability and uptake, and growth of summer squash grown in metal-contaminated soil. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 301, 111097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, T.Z.; Mohammed, G.H.; Teli, J.A. Effect of bio and organic fertilizers on growth yield and fruit quality of summer squash. Sarhad. J. Agric. 2011, 27, 377–383. [Google Scholar]
- Kuslu, Y.; Sahin, U.; Kiziloglu, F.M.; Memis, S. Fruit yield and quality, and irrigation water use efficiency of summer squash drip-irrigated with different irrigation quantities in a semi-arid agricultural area. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 2518–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siswoyo, W.M.B. Response of Squash Crop to Sulphur and Pozzolan as Soil Conditioners under Different Irrigation Water Salinity Levels. Master’s Thesis, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture. Ministry of Agriculture Statistical Year Book for 2013, General Authority for Statistics Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia; Ministry of Agriculture: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, J.; Lima, A.; Suassuna, C.; Figueiredo, F.; da Silva, T.; Mesquita, E.; Cavalcante, L.; Mesquita, F. Growth and gas exchange of Cucurbita pepo L. under nitrogen and silicon fertilization. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.A.; AL-Huqail, A.A.; Ali, E.F.; Majrashi, A. Organic amendment and mulching enhanced the growth and fruit quality of squash plants (Cucurbita pepo L.) grown on silty loam soils. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.; Iqbal, J.; Ahmad, M.A. Comparative study of inorganic fertilizers and organic manures on yield and yield components of squash (Cucurpita pepo L.). J. Agric. Soc. Sci. 2006, 4, 227–229. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, T.; Zhang, P.; Wang, K.; Ding, R.; Yang, B.; Nie, J.; Jia, Z.; Han, Q. Effects of wheat straw incorporation on the availability of soil nutrients and enzyme activities in semiarid areas. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumhardt, R.L.; Jones, O.R. Residue management and tillage effects on soil-water storage and grain yield of dry land wheat and sorghum for a clay loam in Texas. Soil. Till Res. 2002, 68, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, N.M. Nitrate: Nutrient and signal for plant growth. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mensinga, T.T.; Speijers, G.J.A.; Meulenbelt, J. Health implications of exposure to environmental nitrogenous compounds. Toxicol. Rev. 2003, 22, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA. Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain on a request for the European Commission to perform a scientific risk assessment on nitrate in vegetables. EFSA J. 2008, 689, 1–79. Available online: http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/doc/689.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- Liu, C.W.; Sung, Y.; Chen, B.C.; Lai, H.Y. Effects of nitrogen fertilizers on the growth and nitrate content of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 4427–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Grundy, S.; Yang, Q.; Cheng, R. A review of environment effects on nitrate accumulation in leafy vegetables grown in controlled environments. Foods 2020, 9, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Semida, W.M.; Abd El-Wahed, M.H. Effect of mulching on plant water status, soil salinity and yield of squash under summer-fall deficit irrigation in salt affected soil. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 173, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, S.K.; Alayafi, A.H.; AL-Solaimani, S.G.; Abo-Elyousr, K.A. Mitigating Soil Salinity Stress with Gypsum and Bio-Organic Amendments: A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Solaimani, S.G.; Alghabari, F.; Ihsan, M.Z.; Fahad, S. Water deficit irrigation and nitrogen response of sudan grass under arid land drip irrigation conditions. Irrig. Drain. 2017, 66, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop evapotranspiration guidelines for computing crop water requirements. Irrig. Drain. 1998, 56, 300. [Google Scholar]
- Hafez, Y.M.; El-Nagar, A.S.; Elzaawely, A.A.; Kamel, S.; Maswada, H.F. Biological control of Podosphaera xanthii the causal agent of squash powdery mildew disease by upregulation of defense-related enzymes. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2018, 28, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistical Analysis System Institute Incorporation. SAS, Software Version 9.3; Statistical Analysis System Institute Incorporation: Cary, NC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Fontes, P.C.R.; Dias, E.N.; Solva, D.J.H. Dinâmica do crescimento, distribuição de matéria seca na planta e produção de pimentão em ambiente protegido. Hortic. Bras. 2005, 23, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, C.P.; Kawakami, J. Efficiency of the leaf disc method for estimating the leaf area index of soybean plants. Acta Sci. 2013, 35, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkmen, Ö.; Bozkurt, M.A.; Yıldız, M.; Çimrin, K.M. Effects of nitrogen and humic acid applications on the head weight, nutrient and nitrate contents in lettuce. Adv. Food Sci. 2004, 26, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Solaimani, S.G.; El-Nakhlawy, F.S.; Al-Fassi, F.A.; Dazzo, F.B.; Gomaa, A.M. Improving yield and decreasing leaf nitrate content of lettuce via application of the bio-organic agriculture. Wulfenia J. 2015, 22, 566–575. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, R.O.; Berlyn, G.P. The use of organic biostimulants to help low input sustainable agriculture. J. Sustain. Agric. 1990, 1, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.A.; Mirwise, M.; Ahmed, N.; Shah, S.A. Effect of humic acid on fruit yield attributes, yield and leaf nutrient accumulation of apple trees under calcareous Soil. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2018, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ma, Z.; Ren, B.; Zhao, B.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J. Effects of humic acid added to controlled-release fertilizer on summer maize yield, nitrogen use efficiency and greenhouse gas emission. Agriculture 2022, 12, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwanto, B.H.; Wulandari, P.; Sulistyaningsih, E.; Utami, S.N.H.; Handayani, S. Improved corn yields when humic acid extracted from composted manure is applied to acid soils with phosphorus fertilizer. Appl. Environ. Soil. Sci. 2021, 2021, 8838420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Xia, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, R.; Fan, Z.; Chen, F.; Liu, Y. Interactions between N, P and K fertilizers affect the environment and the yield and quality of satsumas. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 19, e00663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyaya, N.; Mukherjee, D. Effect of mulching on the changes in the microbial population in soil and nodulation of lentil (Lens culinaris). Environ. Ecol. 1990, 8, 435–437. [Google Scholar]
- Abou El-Magd, M.M.; Zaki, M.F.; Abou-Hussein, S.D. Effect of organic manure and different levels of saline irrigation water on growth: Green yield and chemical content of sweet fennel. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2008, 2, 90–98. [Google Scholar]
- Salehzadeh, H.; Maleki, A.; Rezaee, R.; Shahmoradi, B.; Ponnet, K. The nitrate content of fresh and cooked vegetables and their healthrelated risks. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santamaria, P.; Eliab, A.; Seriob, F. Effect of solution nitrogen concentration on yield, leaf element content, and water and nitrogen use efficiency of three hydroponically-grown rocket salad genotypes. J. Plant Nutr. 2002, 25, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anon. Commission Regulation (EU) No 1258/2011 of 2 December 2011 amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 as regards maximum levels for nitrates in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2011, L320, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Amro, A. Nitrate and nitrite content of some vegetables grown in central Jordan valley. Agric. Sci. 2000, 27, 410–419. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, R.A.; Muhammad, K.A.; Qadir, O.K. A survey of nitrate and nitrite contents in vegetables to assess the potential health risks in Kurdistan, Iraq. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 910, 012065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, S.I.M.; Glala, A.A.; Abdalla, A.M.; El-Sayed, A.E.A.; Darwish, M.A. Effect of biofertilizer and organic fertilization on growth, nutrient contents and fresh yield of dill (Anethum graveolens). Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2020, 44, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weightman, R.M.; Hudson, E.M. Noxious or nutritious? Progress in controlling nitrate as a contaminant in leafy crop species. Food Energy Secur. 2013, 2, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, D.; Malcolm, R.E.; Ord, B.G. Influences of humic substances on biochemical process in plant. In Soil Organic Matter and Biological Activity; Vaughan, D., Malcolm, R.E., Eds.; Martinus Nijhoff/Junk W: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti, A.; Figliolia, A.; Izza, C.; Canali, S.; Rossi, G. Some thoughts on the physiological effects of humic acid: Interactions with mineral fertilizers. Agrochimica 1996, 40, 229–240. [Google Scholar]
- Naserzadeh, Y.; Nafchi, A.M.; Mahmoudi, N.; Nejad, D.K.; Gadzhikurbanov, A.S. Effect of combined use of fertilizer and plant growth stimulating bacteria Rhizobium, Azospirillum, Azotobacter and Pseudomonas on the quality and components of corn forage in Iran. RUDN J. Agron. Anim. Indust. 2019, 14, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weightman, R.M.; Buxton, J.; Dyer, C.; Farrington, D. Investigation of sampling and sources of variation in nitrate levels in lettuce and spinach. In Final Report on Project CO3030 for the UK Food Standards Agency; UK Food Standards Agency: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]

| Treatments | Leaf Area (m2/plant) | Fresh Biomass Yield (g/plant) | Dry Biomass Yield (g/plant) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 Season | 2021 Season | 2020 Season | 2021 Season | 2020 Season | 2021 Season | |
| Humic acid (L/ha) | ||||||
| 0 | 0.454 c | 0.702 b | 807.09 c | 899.11 c | 134.80 c | 137.13 c |
| 50 | 0.981 b | 1.051 ab | 1053.38 b | 1149.40 b | 169.00 b | 175.78 b |
| 100 | 1.483 a | 1.377 a | 1327.67 a | 1420.58 a | 220.02 a | 225.33 a |
| LSD0.05 | 0.44 | 0.36 | 212.43 | 105.56 | 17.03 | 3.08 |
| Cellulose-decomposing bacterium (CDB) | ||||||
| Without | 0.857 b | 0.96 b | 975.49 b | 1053.15 b | 157.57 b | 163.58 b |
| With | 1.088 a | 1.12 a | 1149.94 a | 1259.58 a | 191.64 a | 195.25 a |
| LSD0.05 | 0.22 | 0.11 | 139.4 | 50.79 | 26.66 | 7.18 |
| Wheat straw (t/ha) | ||||||
| 0 | 0.657 d | 0.57 c | 848.50 d | 1023.31 d | 130.04 d | 139.80 d |
| 20 | 0.868 c | 0.93 b | 995.55 c | 1146.37 b | 160.08 c | 165.25 c |
| 30 | 1.083 b | 1.17 b | 1130.05 b | 1189.83 b | 188.49 b | 189.72 b |
| 600 kg/ha NPK | 1.265 a | 1.48 a | 1276.75 a | 1265.95 a | 219.82 a | 222.88 a |
| LSD0.05 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 100.29 | 69.53 | 23.14 | 15.03 |
| Interactions | ||||||
| HA × CDB | NS | * | NS | NS | NS | * |
| HA × Straw | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| CDB × Straw | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| HA × CDB × Straw | NS | NS | * | NS | NS | NS |
| Treatments | Fruit Yield (g/plant) | Total Fruit Yield (kg/ha) | Water-Use Efficiency (kg/m3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 Season | 2021 Season | 2020 Season | 2021 Season | 2020 Season | 2021 Season | |
| Humic acid (L/ha) | ||||||
| 0 | 274.68 c | 278.11 c | 5493.57 c | 5562.20 c | 1.02 c | 1.03 c |
| 50 | 320.28 b | 322.54 b | 6405.59 b | 6450.82 b | 1.19 b | 1.20 b |
| 100 | 363.86 a | 363.26 a | 7277.26 a | 7265.30 a | 1.35 a | 1.35 a |
| LSD0.05 | 39.19 | 25.15 | 783.88 | 503.2 | 0.14 | 0.095 |
| Cellulose-decomposing bacterium (CDB) | ||||||
| Without | 303.92 b | 312.78 b | 6078.40 b | 6255.75 b | 1.13 b | 1.16 b |
| With | 335.29 a | 329.82 a | 6705.87 a | 6596.47 a | 1.24 a | 1.22 a |
| LSD0.05 | 29.24 | 10.03 | 584.85 | 200.63 | 0.1 | 0.036 |
| Wheat straw (t/ha) | ||||||
| 0 | 282.09 d | 297.35 d | 5641.98 d | 5947.16 d | 1.04 d | 1.10 d |
| 20 | 308.49 c | 310.40 c | 6169.19 c | 6208.06 c | 1.14 c | 1.15 c |
| 30 | 332.4 b | 329.01 b | 6649.73 b | 6580.22 b | 1.23 b | 1.22 b |
| 600 kg/ha NPK | 355.34 a | 348.44 a | 7106.93 a | 6968.99 a | 1.32 a | 1.29 a |
| LSD0.05 | 20.98 | 11.51 | 419.78 | 230.21 | 0.07 | 0.042 |
| Treatments | Nitrate (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|
| Humic Acid (L/ha) | 2020 Season | 2021 Season |
| 0 | 75.38 a | 74.06 a |
| 50 | 55.73 b | 57.64 b |
| 100 | 40.32 c | 43.17 c |
| LSD0.05 | 8.69 | 7.73 |
| Cellulose-decomposing bacterium (CDB) | ||
| Without | 55.58 a | 56.72 b |
| With | 58.70 a | 59.86 a |
| LSD0.05 | 3.95 | 1.59 |
| Wheat straw (t/ha) | ||
| 0 | 52.06 b | 51.36 d |
| 20 | 55.92 ab | 56.67 c |
| 30 | 61.38 a | 60.77 b |
| 600 kg/ha NPK | 59.22 a | 64.35 a |
| LSD0.05 | 5.64 | 3.13 |
| Interactions | ||
| HA × CDB | NS | NS |
| HA × Straw | ** | ** |
| CDB × Straw | NS | NS |
| HA × CDB × Straw | NS | NS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bello, S.K.; AL-Solaimani, S.G.; Abo-Elyousr, K.A.M. Squash Yield, Water-Use Efficiency and Nitrate Accumulation as Influenced by the Application of Humic Acid, Geobacillus stearothermophilus SSK-2018 and Wheat Straw in an Arid Land Condition. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8070588
Bello SK, AL-Solaimani SG, Abo-Elyousr KAM. Squash Yield, Water-Use Efficiency and Nitrate Accumulation as Influenced by the Application of Humic Acid, Geobacillus stearothermophilus SSK-2018 and Wheat Straw in an Arid Land Condition. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(7):588. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8070588
Chicago/Turabian StyleBello, Suleiman K., Samir G. AL-Solaimani, and Kamal A. M. Abo-Elyousr. 2022. "Squash Yield, Water-Use Efficiency and Nitrate Accumulation as Influenced by the Application of Humic Acid, Geobacillus stearothermophilus SSK-2018 and Wheat Straw in an Arid Land Condition" Horticulturae 8, no. 7: 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8070588
APA StyleBello, S. K., AL-Solaimani, S. G., & Abo-Elyousr, K. A. M. (2022). Squash Yield, Water-Use Efficiency and Nitrate Accumulation as Influenced by the Application of Humic Acid, Geobacillus stearothermophilus SSK-2018 and Wheat Straw in an Arid Land Condition. Horticulturae, 8(7), 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8070588







