Comparative Evaluation of Yield and Fruit Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Five Commercial Cultivars of Pomegranate Grown in Southeastern Italy in Two Consecutive Years
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site and Fruit Collection
2.2. Yield and Morpho-Pomological Analyses
2.3. Color of Fruit Skin, Arils and Juice Evaluation
2.4. Physical and Chemical Analyses of Juice
2.5. Total Polyphenols Determination
2.6. Antioxidant Activity
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Weather Data
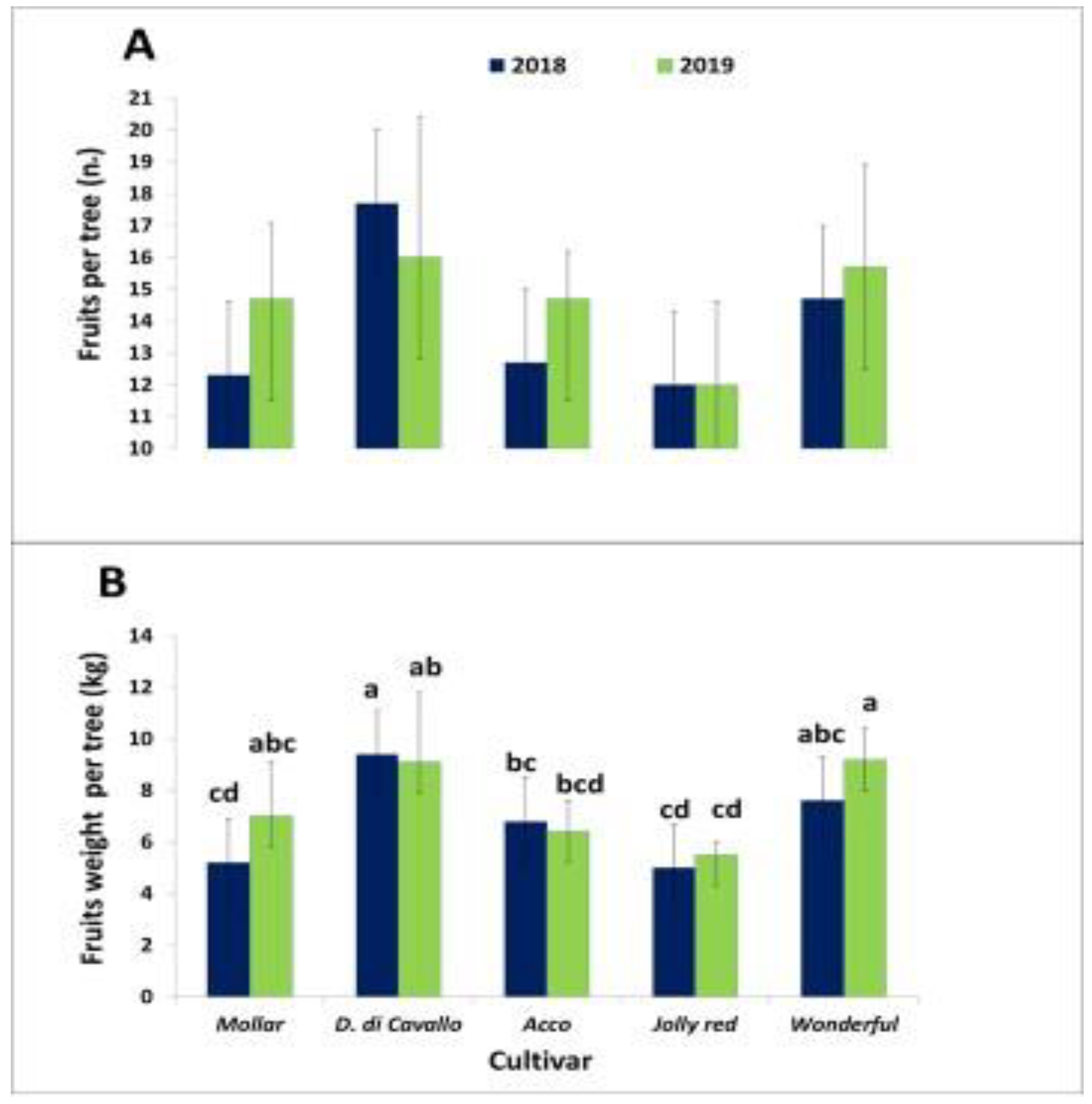
3.2. Yield and Morpho-Pomological Characteristics
3.3. Color of Fruit’s Skin, Arils and Juice
3.4. Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Juice
3.5. Total Phenol Content and Antioxidant Activity
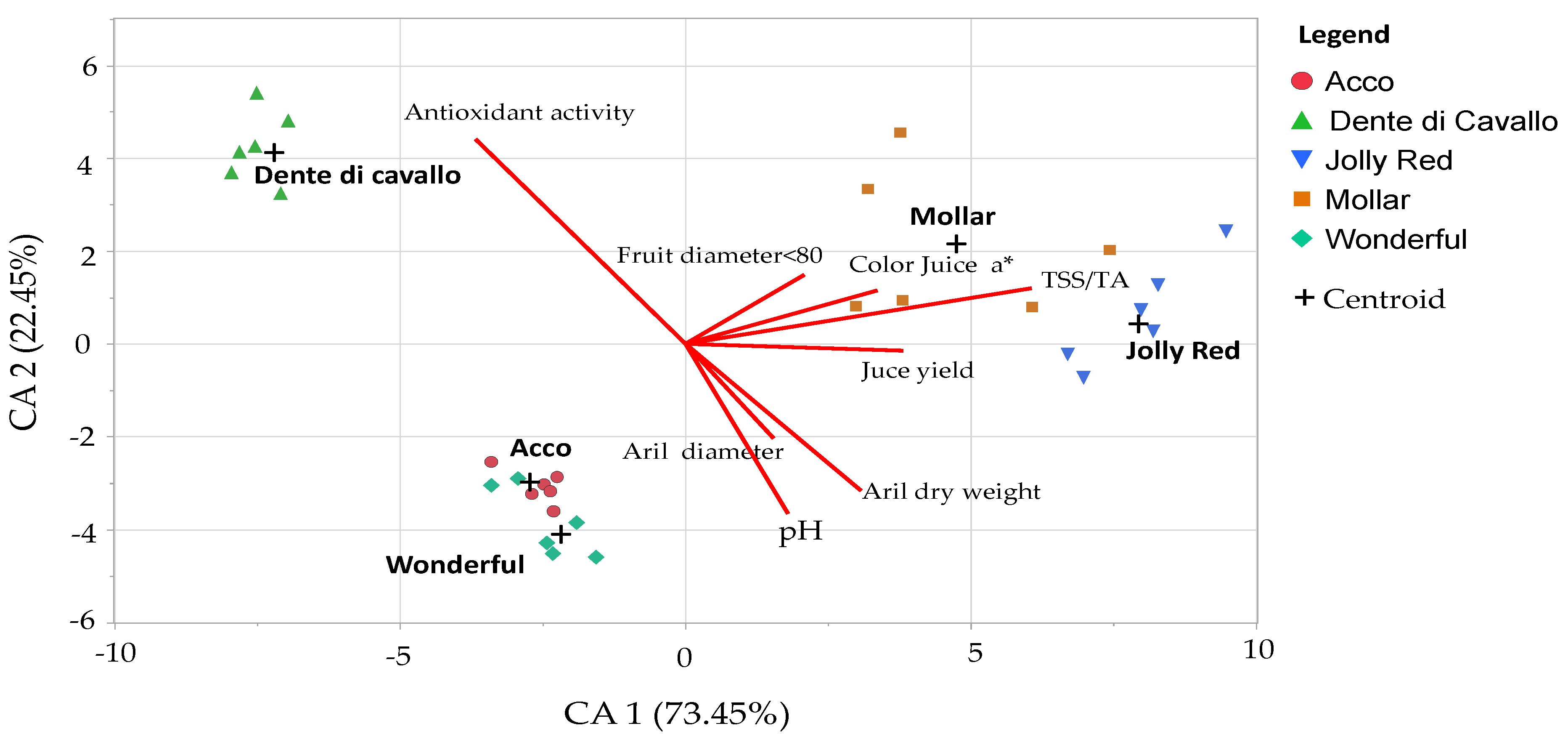
3.6. Multivariate Analysis on the Morpho-Qualitative Parameters
3.7. Correlation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Stepwise Discriminant Analysis (SDA)
| Test | Value | Fisher’s Test Value | DF † | Prob > F ‡ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wilks’ Lambda | 0.0006 | 13.77 | 32 | <0.0001 |
| Pillai’s Trace | 2.81 | 6.27 | 32 | <0.0001 |
| Hotelling–Lawley Trace | 49.7 | 26.25 | 32 | <0.0001 |
| Roy’s Largest Root | 36.50 | 95.82 | 8 | <0.0001 |
| Parameter Selected | F-Ratio Value | Prob F † |
|---|---|---|
| Aril diameter (mm) | 4.44 | 0.009 |
| Aril dry weight (%) | 6.28 | 0.0019 |
| pH (-) | 5.11 | 0.005 |
| TSS/TA ratio (°Brix/% citric acid) | 18.28 | <0.0001 |
| Antioxidant activity (mmol TE100 L−1) | 33.99 | <0.0001 |
| Juice color a* | 4.24 | <0.012 |
| Fruit diameter ≤ 80 mm (%) | 3.53 | 0.025 |
| Juice yield (cm3 100 g arils) | 3.41 | 0.035 |
References
- Holland, D.; Hatib, K.; Bar-Ya’akov, I. Pomegranate: Botany, horticulture, breeding. Hortic. Rev. 2009, 35, 127–191. [Google Scholar]
- Stover, E.D.; Mercure, E.W. The pomegranate: A new look at the fruit of paradise. HortScience 2007, 42, 1088–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossio, F. Melograno, potenzialità e limiti di un antico frutto italiano. Riv. Fruttic. Ortofloric. 2017, 81, 52–63. [Google Scholar]
- Pontonio, E.; Montemurro, M.; Pinto, D.; Marzani, B.; Trani, A.; Ferrara, G.; Mazzeo, A.; Gobbetti, M.; Rizzello, C.G. Lactic acid fermentation of pomegranate juice as a tool to improve antioxidant activity. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karapetsi, L.; Pantelidis, G.; Pratsinakis, E.D.; Drogoudi, P.; Madesis, P. Fruit quality traits and genotypic characterization in a pomegranate ex situ (Punica granatum L.) collection in Greece. Agriculture 2021, 11, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefusco, A.; Durante, M.; Migoni, D.; De Caroli, M.; Ilahy, R.; Pék, Z.; Helyes, L.; Panizzi, F.P.; Mita, G.; Piro, G.; et al. Analysis of the phytochemical composition of pomegranate fruit juices, peels and kernels: A comparative study on four cultivars grown in southern Italy. Plants 2021, 10, 2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, A.; Calin-Sànchez, A.; Rodriguez, P.; Cruz, Z.N.; Giròn, I.F.; Correl, M.; Martinez-Font, R.; Moriana, A.; Carbonell-Barrachina, A.A.; Torrecillas, A. Water stress and the end of pomegranate fruit ripening produces earlier harvesting and improves fruit quality. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 226, 28–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, A.; Frabboni, L.; Disciglio, G. Water-yield relationship and vegetative growth of wonderful young pomegranate trees under deficit irrigation conditions in southeastern Italy. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiba, A.; Hssaini, L.; Haddioui, A.; Hamdani, A.; Charafi, J.; El Iraqui, S.; Razouk, R. Pomegranate plasticity to water stress: Attempt to understand interactions between cultivar, year and stress level. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISTAT. Electronic Information System on Agriculture and Livestock; Italian National Statistical Institute (ISTAT): Rome, Italy, 2020; Available online: http://agri.istat.it/ (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Harel-Beja, R.; Sherman, A.; Rubinstein., M.; Eshed. R.; Bar-Ya’akov., I.; Trainin., T.; Ophir, R.; Holland., D. A novel genetic map of pomegranate based on transcript markers enriched with QTLs for fruit quality traits. Tree Genet. Genomes 2015, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, E.; Tzulker, R.; Glazer, I.; Bar-Ya’Akov, I.; Wiesman, Z.; Tripler, E.; Bar-Ilan, I.; Fromm, H.; Borochov-Neori, H.; Holland, D.; et al. Environmental conditions affect the color, taste, and antioxidant capacity of 11 pomegranate accessions’ fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9197–9209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikdel, K.; Seifi, E.; Babaei, H. Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of five Iranian pomegranate cultivars (Punica granatum) in maturation stage. Acta Agric. Slov. 2016, 107, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jamali, B.; Bonyanpour, A.R. Comparison of fruit quality characteristics and polyphenolic compounds in seven Iranian pomegranate cultivars. Hortic. Int. J. 2018, 2, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athmaselvi, K.A.; Jenney, P.; Pavithra, C.; Roy, I. Physical and biochemical properties of selected tropical fruits. Int. Agrophys. 2014, 28, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. Textural soil classification. In Study Guide Revised; United States Department of Agriculture, Soil Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1987; p. 48. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO/FAO. Bioclimatic Map of the Mediterranean Zone; Explanatory Notes, Arid Zone Research; UNESCO/FAO: Rome, Italy, 1963; p. 2217. [Google Scholar]
- Ventrella, D.; Charfeddine, M.; Moriondo, M.; Rinaldi, M.; Bindi, M. Agronomic adaptation strategies under climate change for winter durum wheat and tomato in southern Italy: Irrigation and nitrogen fertilization. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2012, 12, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maiman, S.A.; Ahmad, D. Changes in physical and chemical properties during pomegranate (Punica granatum) fruit maturation. Food Chem. 2002, 76, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UPOV. Guidelines for the Conduct of Tests for Distinctness, Uniformity and Stability. Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.); TG/PGRAN/3; UPOV: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kader, A. Increasing food availability by reducing postharvest losses of fresh produce. In Acta Horticulturae, Proceedings of the V International Postharvest Symposium, Verona, Italy, 6–11 June 2004; International Society for Horticultural Science: Leuven, Belgium, 2005; pp. 2169–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis; Association of Official Analytical Cereal Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Difonzo, G.; Vollmer, K.; Caponio, F.; Pasqualone, A.; Carle, R.; Steingass, C.B. Characterisation and classification of pineapple (Ananas comosus [L.] Merr.) juice from pulp and peel. Food Control 2019, 96, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, M.; Di Mise, A.; Difonzo, G.; Centrone, M.; Venneri, M.; Pellegrino, T.; Russo, A.; Mastrodonato, M.; Caponio, F.; Valenti, G.; et al. Green olive leaf extract (OLE) provides cytoprotection in renal cells exposed to low doses of cadmium. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Roteggente, A.; Pannola, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved radicalcation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.R.; Box, G.E.P. An analysis of transformations (with discussion). J. R. Stat. Soc. 1964, 26, 211–225. [Google Scholar]
- Rencher, A.C. Interpretation of canonical discriminant functions, canonical variates, and principal components. Am. Stat. 1992, 46, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Guo, B.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, B.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Yan, J. Determining the geographic origin of wheat using multielement analysis and multivariate statistics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4397–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliardi, A.; Giuliani, M.M.; Carucci, F.; Francavilla, M.; Gatta, G. Effects of the irrigation with treated wastewaters on the proximate composition, mineral, and polyphenolic profile of the globe artichoke heads [Cynara cardunculus (L.)]. Agronomy 2020, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazare, S.; Lyu, Y.; Yermiyahu, U.; Heler, Y.; Ben-Gal, A.; Holland, D.; Dag, A. Optimizing nitrogen application for growth and productivity of pomegranates. Agronomy 2020, 10, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Porat, R.; Yermiyahu, U.; Heler, Y.; Holland, D.; Dag, A. Effects of nitrogen fertilization on pomegranate fruit, aril and juice quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 1678–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojir, F.; Schübl, E.; Elmadfa, I. The origins of a global standard for food quality and safety: Codex Alimentarius Austriacus and FAO/WHO Codex Alimentarius. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2013, 82, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, G.; Giancaspro, A.; Mazzeo, A.; Giove, S.L.; Matarrese, A.M.S.; Pacucci, C.; Punzi, R.; Trani, A.; Gambacorta, G.; Blanco, A.; et al. Characterization of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) genotypes collected in Puglia region, Southeastern Italy. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 178, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiletta, G.; Petriccione, M.; Liguori, L.; Pizzolongo, F.; Romano, R.; Di Matteo, M. Study of pomological traits and physico-chemical quality of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) genotypes grown in Italy. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 1427–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.; Pereira, J.A.; Lopez-Cortes, I.; Salazar, D.M.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, J.; Ramalhosa, E. Physicochemical composition and antioxidant activity of several pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) cultivars grown in Spain. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 1799–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usanmaz, S.; Kahramanoglu, I.; Yilmaz, N. Yield and pomological characteristics of three pomegranate (Punica granatum L) cultivars: Wonderful, Acco and Herskovitz. Am. J. Agric. For. 2014, 2, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, E.; Caruso, T.; Marra, F.P.; Sottile, F. Preliminary observations on some Sicilian pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) varieties. J. Am. Pomol. Soc. 2001, 55, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Passafiume, R.; Perrone, A.; Sortino, G.; Gianguzzi, G.; Saletta, F.; Gentile, C. Chemical–physical characteristics, polyphenolic content and total antioxidant activity of Italian-grown pomegranate cultivars. NFS J. 2019, 16, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opara, L.U.; Al-Ani, M.R.; Al-Shuaibi, Y.S. Physicochemical properties, vitamin C content, and antimicrobial properties of pomegranate fruit (Punica granatum L.). Food Bioprocess Technol. 2009, 2, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naing, A.H.; Kim, C.K. Abiotic stress-induced anthocyanins in plants: Their role in tolerance to abiotic stresses. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 172, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Said, F.; Opara, U.L.; Al-Yahyai, R. Physico-chemical and textural quality attributes of pomegranate cultivars (Punica granatum L.) grown in the Sultanate of Oman. J. Food Eng. 2009, 90, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, G.; Cavoski, I.; Pacifico, A.; Tedone, L.; Mondelli, D. Morpho-pomological and chemical characterization of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) genotypes in Apulia region, Southeastern Italy. Sci. Hort. 2011, 130, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaouay, F.; Mena, P.; Garcia-Viguera, C.; Mars, M. Antioxidant activity and physico-chemical properties of Tunisian grown pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) cultivars. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2012, 40, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.J.; Melgarejo, P.; Hernandez, F.; Salazar, D.M.; Martinez, R. Seed characterization of five new pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) varieties. Sci. Hortic. 2006, 110, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampem, G. Physico-chemical and textural properties relevant to processing of pomegranate fruit and arils. In Quality Attributes of Pomegranate Fruit and Co-Products Relevant to Processing and Nutrition. Ph.D. Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2017; pp. 12–51. Available online: https://scholar.sun.ac.za (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Hernandez, F.; Melgarejo., P.; Tomás-Barberán., F.A.; Artés, F. Evolution of juice anthocyanins during ripening of new selected pomegranate (Punica granatum) clones. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 1999, 210, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbè, M.; Ulloa, P.A.; Lòpez, F.; Sàenz, C.; Pena, A.; Salazar, F.N. Characterization of chimical composition and bioactive compounds in juice from pomegranate (‘Wonderful’, ‘Chaca’ and ‘Copda’) at different maturity stages. Chilean JAR 2016, 76, 479–486. [Google Scholar]
- Attanayake, R.R.; Eeswaran, R.; Rajapaksha, R.; Weerakkody, P.; Bandaranayake, P.C.G. Biochemical composition and expression analysis of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes of a yellow peeled and pinkish ariled pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) cultivar are differentially regulated in response to agro-climatic conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 8761–8771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Month | Tmax | Tmin | RHmax | RHmin | Ws | Rad | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (°C) | (°C) | (%) | (%) | (m s −1) | (Wm−2) | (mm) | |
| 2018 | |||||||
| April | 21.3 | 12.9 | 94.6 | 37.6 | 2.8 | 235.3 | 54.0 |
| May | 26.1 | 13.4 | 95.2 | 49.1 | 2.4 | 275.8 | 58.3 |
| June | 30.0 | 12.1 | 89.5 | 40.3 | 3.4 | 289.6 | 88.2 |
| July | 33.3 | 19.6 | 83.6 | 35.4 | 3.0 | 318.7 | 16.8 |
| Aug | 32.7 | 20.1 | 71.3 | 28.3 | 2.1 | 285.7 | 39.1 |
| Sept | 29.1 | 17.1 | 81.3 | 30.0 | 3.7 | 193.6 | 80.0 |
| Mean | 28.7 | 15.9 | 85.9 | 36.8 | 2.9 | 266.5 | |
| Total | 366.4 | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| April | 20.6 | 8.2 | 94.4 | 51.0 | 3.7 | 190.2 | 40.3 |
| May | 21.3 | 10.2 | 95.3 | 56.3 | 4.0 | 232.9 | 86.7 |
| June | 33.2 | 17.5 | 85.9 | 35.1 | 3.7 | 252.2 | 9.2 |
| July | 33.7 | 19.5 | 84.0 | 33.9 | 3.7 | 258.8 | 30.0 |
| Aug | 34.8 | 20.3 | 79.9 | 33.9 | 3.6 | 225.6 | 5.7 |
| Sept | 29.5 | 16.8 | 88.7 | 42.6 | 3.6 | 175.5 | 3.8 |
| Mean | 28.8 | 15.4 | 88.0 | 42.5 | 3.7 | 222.5 | |
| Total | 175.7 |
| Cultivar Parameter | Mollar | D. Cavallo | Acco | Jolly Red | Wonderful |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fruit weight (g) | |||||
| 2018 | 415.1 ± 91.8 abc | 542.1 ± 91.7 ab | 559.2 ± 147.3 a | 361.1 ± 88.4 bc | 499.8 ± 78.9 abc |
| 2019 | 473.7 ± 40.4 abc | 498.2 ± 139.8 abc | 332.8 ± 110.3 c | 375.0 ± 45.3 abc | 447.9 ± 122.1 abc |
| Fruit diameter (mm) | |||||
| 2018 | 91.3 ± 5.5 | 97.3 ± 5.8 | 96.6 ± 5.1 | 87.0 ± 5.0 | 94.0 ± 5.5 |
| 2019 | 96.2 ± 9.1 | 92.4 ± 11.2 | 82.6 ± 3.9 | 90.0 ±18.8 | 96.02 ± 9.0 |
| Fruit length (mm) | |||||
| 2018 | 84.3 ± 5.5 a | 88.6 ± 6.1 a | 87.6 ± 8.7 a | 77.0 ± 4.3 ab | 85.5 ± 5.8 a |
| 2019 | 81.5 ± 9.8 ab | 81.2 ± 4.0 a | 73.1 ± 4.9 b | 78.8 ± 3.7 ab | 84.2 ± 7.5 a |
| Fruit diameter ≤ 80 mm (%) | |||||
| 2018 | 26.2 ± 4.9 a | 13.7 ± 5.2 b | 15.3 ± 2.3 b | 30.8 ± 10.1 a | 14.7 ± 2.2 b |
| 2019 | 21.1 ± 5.2 ab | 12.1 ± 6.2 b | 19.1 ± 11.9 ab | 22.6 ± 6.9 ab | 13.6 ± 1.5 b |
| Cultivar Parameter | Mollar | D. Cavallo | Acco | Jolly Red | Wonderful |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aril portion (%) | |||||
| 2018 | 50.7 ± 0.7 b | 47.9 ± 0.9 c | 44.7 ± 4.5 c | 58.7 ± 2.5 a | 50.2 ± 1.2 b |
| 2019 | 49.7 ± 1.0 b | 49.3 ± 2.4 bc | 50.2 ± 1.1 b | 58.3 ± 2.7 a | 53.7 ± 4.2 ab |
| Aril length (mm) | |||||
| 2018 | 9.6 ± 0.5 | 9.5 ± 1.2 | 8.6 ± 0.8 | 9.1 ± 0.9 | 9.5 ± 1.8 |
| 2019 | 9.6 ± 0.8 | 9.2 ± 1.7 | 8.2 ± 0.7 | 9.0 ± 0.9 | 9.6 ± 1.4 |
| Aril width (mm) | |||||
| 2018 | 8.1 ± 1.0 | 8.1 ± 1.2 | 7.5 ± 0.6 | 7.9 ± 0.9 | 8.3 ± 0.7 |
| 2019 | 8.1 ± 1.1 | 8.1 ± 1.2 | 7.3 ± 0.6 | 7.9 ± 0.8 | 8.4 ± 0.8 |
| Fresh weight of 100 arils (g) | |||||
| 2018 | 31.7 ± 3.9 bc | 30.3 ± 1.6 c | 33.8 ± 2.5 bc | 31.8 ± 5.1 bc | 30.8 ± 3.1 c |
| 2019 | 37.1 ± 2.8 ab | 31.0 ± 1.5 c | 31.5 ± 3.2 bc | 41.9 ± 4.2 a | 32.9 ± 3.0 bc |
| Aril dry weight (%) | |||||
| 2018 | 20.4 ± 0.6 c | 21.6 ± 1.1 bc | 22.2 ± 0.9 ab | 19.4 ± 1.0 c | 22.6 ± 0.6 ab |
| 2019 | 20.5 ± 0.6 c | 19.2 ± 1.0 c | 23.8 ± 1.2 ab | 19.8 ± 1.4 c | 23.3 ± 0.3 a |
| Cultivar Parameter | Mollar | D. Cavallo | Acco | Jolly Red | Wonderful |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skin colorL* | |||||
| 2018 | 53.8 ± 4.5 a | 40.0 ± 3.0 b | 39.8 ± 3.5 b | 54.8 ± 7.4 a | 39.5 ± 4.3 b |
| 2019 | 50.4 ± 2.6 a | 41.0 ±2.6 b | 42.0 ± 2.3 b | 55.7 ± 3.5 a | 43.6 ± 5.2 ab |
| Skin colora* | |||||
| 2018 | 35.0 ± 9.4 ab | 38.4 ± 3.1 ab | 39.6 ± 3.3 ab | 29.3 ± 0.3 b | 34.4 ± 3.5 ab |
| 2019 | 36.4 ± 5.0 ab | 43.8 ± 4.3 a | 40.4 ± 3.1 ab | 33.0 ± 6.3 b | 39.1 ± 4.6 ab |
| Skin colorb* | |||||
| 2018 | 31.7 ± 5.3 ab | 17.5 ± 1.7 c | 17.5 ± 2.6 c | 30.9 ± 5.6 ab | 16.3 ± 4.1 c |
| 2019 | 29.6 ± 1.7 ab | 27.8 ± 1.9 ab | 25.8 ± 2.2 b | 32.7 ± 3.3 a | 26.3 ± 3.0 b |
| Arilcolor L* | |||||
| 2018 | 35.0 ± 5.8 a | 19.6 ± 3.5 c | 25.0 ± 2.7 bc | 34.2 ± 8.5 ab | 24.8 ± 3.2 bc |
| 2019 | 30.0 ± 4.8 ab | 24.4 ± 3.8 bc | 24.4 ± 3.4 bc | 30.7 ± 6.0 ab | 24.8 ± 4.2 bc |
| Arilcolor a* | |||||
| 2918 | 10.2 ± 2.3 c | 13.3 ± 4.5 bc | 18.2 ± 3.7 ab | 22.3 ± 5.1 ab | 18.0 ± 4.4 ab |
| 2019 | 23.5 ± 4.5 a | 25.5 ± 4.0 a | 23.5 ± 3.0 a | 23.7 ± 6.0 a | 19.4 ± 7.0 ab |
| Aril colorb* | |||||
| 2018 | 11.8 ± 1.2 cd | 6.4 ± 1.8 e | 7.9 ± 1.0 e | 10.1 ± 1.7 cde | 8.3 ± 1.4 e |
| 2019 | 17.4 ± 2.2 a | 12.9 ± 1.7 bc | 11.9 ± 1.2 cd | 16.7 ± 2.8 ab | 9.7 ± 2.0 de |
| Juicecolor L* | |||||
| 2018 | 13.5 ± 1.5 de | 20.3 ± 0.3 b | 20.8 ± 0.5 b | 24.4 ± 2.1 a | 20.5 ± 0.2 b |
| 2019 | 20.9 ± 2.0 ab | 16.5 ± 1.0 c | 17.9 ± 2.2 bc | 15.3 ± 1.9 cd | 12.2 ± 2.0 e |
| Juicecolor a* | |||||
| 2018 | 6.1 ± 0.8 a | 1.3 ± 0.1 c | 1.9 ± 0.7 bc | 12.3 ± 6.1 a | 1.4 ± 0.1 c |
| 2019 | 7.4 ± 1.9 a | 3.1 ± 0.8 b | 3.6 ± 1.0 b | 11.2 ± 5.0 a | 5.1 ± 2.0 ab |
| Juice colorb* | |||||
| 2018 | 1.0 ± 0.1 c | 0.2 ± 0.1 d | 0.2 ± 0.1 d | 3.3 ± 2.7 ab | 0.2 ± 0.1 d |
| 2919 | 1.3 ± 0.2 bc | 2.1 ± 0.2 b | 1.8 ± 0.6 b | 2.7 ± 1.5 ab | 4.0 ± 1.4 a |
| Cultivar Parameter | Mollar | D. Cavallo | Acco | Jolly Red | Wonderful |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Juice yield (cm3 100−1 g arils) | |||||
| 2018 | 78.5 ± 13.4 ab | 74.5 ± 10.8 ab | 85.5 ± 6.4 a | 85.6 ± 4.8 a | 78.3 ± 3.4 ab |
| 2019 | 61.0± 1.7 c | 73.7 ± 3.2 b | 69.0 ± 4.4 b | 62.7 ± 4.9 bc | 68.7 ± 4.5 b |
| TSS (°Brix) | |||||
| 2018 | 14.7 ± 0.3 c | 16.8 ± 0.2 b | 16.2 ± 0.1 b | 14.6 ± 0.4 c | 17.7 ± 0.2 a |
| 2019 | 16.1 ± 0.8 b | 16.1 ± 0.7 b | 16.6 ± 0.3 b | 15.0 ± 0.4 bc | 16.6 ± 0.5 b |
| pH | |||||
| 2018 | 3.0 ± 0.1 c | 2.8 ± 0.1 c | 2.8 ± 0.1 c | 3.6 ± 0.3 ab | 3.3 ± 0.1 b |
| 2019 | 3.7 ± 0.1 a | 3.3 ± 0.1 b | 3.3 ± 0.1 b | 3.8 ± 0.1 a | 3.2 ± 0.1 b |
| TA (g citric acid 100 mL−1) | |||||
| 2018 | 0.6 ± 0.1 c | 1.6 ± 0.1 b | 1.7 ±0.2 b | 0.6 ± 0.1 c | 2.3 ± 0.2 a |
| 2019 | 0.5 ± 0.1 c | 1.2 ± 0.2 b | 1.6 ± 0.1 b | 0.5 ± 0.1 c | 2.6 ± 0.2 a |
| TSS/TA (°Brix/%citric acid) | |||||
| 2018 | 26.0 ± 4.2 ab | 10.8 ± 0.5 c | 9.4 ± 0.9 cd | 23.4 ± 1.4 b | 7.8 ± 1.0 d |
| 2019 | 31.1 ± 4.5 a | 13.4 ± 0.8 c | 10.3 ± 0.1 c | 30.8 ± 6.5 a | 6.2 ± 0.9 d |
| Parameters | Standardized Coefficients | Pearson’s Correlation Coefficients | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivar parameter | CA1 | CA2 | CA1 | CA2 |
| Aril diameter (mm) | 0.38 | −0.50 | 0.08 ns | −0.53 ** |
| Aril dry weight (%) | 0.77 | −0.79 | 0.59 ** | −0.70 *** |
| pH (-) | 0.46 | −0.91 | 0.51 ** | −0.19 ns |
| TSS/TA ratio (°Brix/% citric acid) | 1.62 | 0.34 | 0.88 *** | 0.49 ** |
| Antioxidant activity (mmol TE100 L−1) | −0.92 | 1.10 | −0.61 *** | 0.67 *** |
| Juice color a* | 0.84 | 0.28 | 0.81 *** | 0.14 ns |
| Fruit diameter ≤ 80 mm (%) | 0.52 | 0.37 | 0.71 *** | 0.36 * |
| Juice yield (cm3 100 g arils) | 0.95 | −0.04 | 0.10 ns | −0.12 ns |
| % variance explained | 73.45 | 22.45 | ||
| Parameter | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fruit weight | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||
| 2 | Fruit diameter | 0.66 ** | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||
| 3 | Fruit length | 0.44 * | 0.55 * | 1.00 | |||||||||||||
| 4 | Aril portion | ns | ns | ns | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| 5 | Aril lenght | ns | 0.51 * | 0.57 * | ns | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| 6 | Aril diameter | ns | ns | 0.45 * | ns | 0.78 ** | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| 7 | Fresh weight of 100 arils | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | 1.00 | |||||||||
| 8 | Aril dry weight | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | 1.00 | ||||||||
| 9 | Fruit diameter ≤ 80 mm | ns | ns | ns | 0.56 * | ns | ns | ns | −0.58 * | 1.00 | |||||||
| 10 | Juice yield | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | −0.44 * | ns | ns | 1.00 | ||||||
| 11 | TSS | 0.37 * | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | 0.59 * | −0.58 * | ns | 1.00 | |||||
| 12 | pH | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | 0.40 * | ns | ns | −0.40 * | ns | 1.00 | ||||
| 13 | TA | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | −0.37 * | 1.00 | |||
| 14 | TSS/TA | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | 0.46 * | −0.67 * | 0.66 ** | ns | −0.70 * | 0.36 * | ns | 1.00 | ||
| 15 | TPC | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | −0.39 * | ns | 0.50 * | −0.12 | ns | −0.52 * | 1.00 | |
| 16 | AA | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | 0.67 * | 1.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarantino, A.; Frabboni, L.; Mazzeo, A.; Ferrara, G.; Disciglio, G. Comparative Evaluation of Yield and Fruit Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Five Commercial Cultivars of Pomegranate Grown in Southeastern Italy in Two Consecutive Years. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060497
Tarantino A, Frabboni L, Mazzeo A, Ferrara G, Disciglio G. Comparative Evaluation of Yield and Fruit Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Five Commercial Cultivars of Pomegranate Grown in Southeastern Italy in Two Consecutive Years. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(6):497. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060497
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarantino, Annalisa, Laura Frabboni, Andrea Mazzeo, Giuseppe Ferrara, and Grazia Disciglio. 2022. "Comparative Evaluation of Yield and Fruit Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Five Commercial Cultivars of Pomegranate Grown in Southeastern Italy in Two Consecutive Years" Horticulturae 8, no. 6: 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060497
APA StyleTarantino, A., Frabboni, L., Mazzeo, A., Ferrara, G., & Disciglio, G. (2022). Comparative Evaluation of Yield and Fruit Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Five Commercial Cultivars of Pomegranate Grown in Southeastern Italy in Two Consecutive Years. Horticulturae, 8(6), 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8060497









