Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of RR-Type MYB-Related Transcription Factors in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Search and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.2. Collinearity Analysis
2.3. Analysis of the Physical and Chemical Properties
2.4. Analysis of Gene Structure and Conserved Motifs
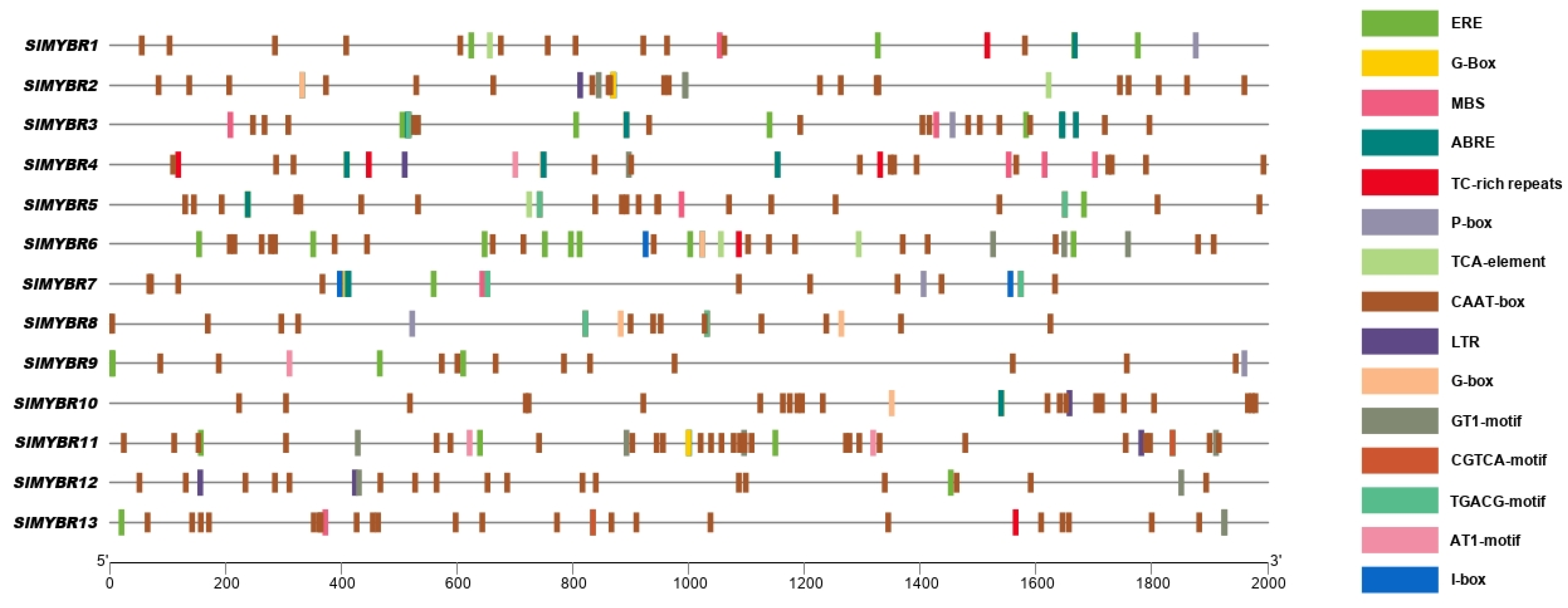
2.5. Cis-Acting Elements of Gene Promoter
2.6. Expression Pattern Analysis
2.7. Plant Materials and Growth Condition
2.8. Exogenous Hormone Treatment
2.9. RNA Isolation and qRT-PCR Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Characteristics of RR-Type MYB-Related TFs in Tomato
3.2. Phylogenetic and Synteny Analysis of RR-Type MYB-Related TFs
3.3. Gene Structure and Conserved Motifs Analysis of RR-Type SlMYBR Genes
3.4. Cis-Acting Elements of SlMYBR Promoters
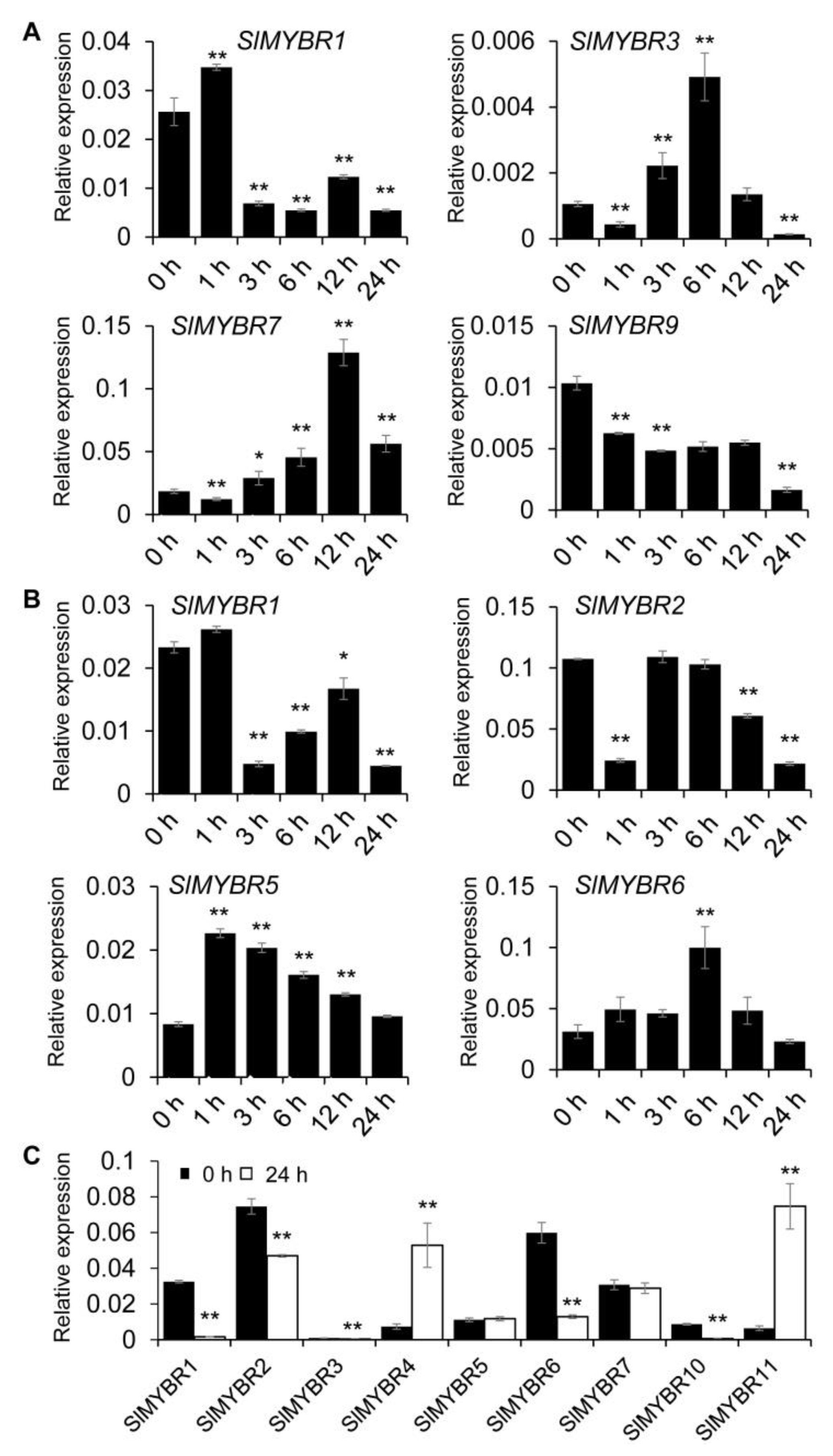
3.5. Expression Profiles Analysis of SlMYBR Genes
3.6. Expression Pattern of SlMYBRs under Different Hormones Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, C.; Yao, L.; You, C.; Wang, S.; Cui, J.; Ge, X.; Ma, H. MID1 plays an important role in response to drought stress during reproductive development. Plant J. 2016, 88, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ptashne, M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature 1988, 335, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, G.A.; Hahn, M.W.; Abouheif, E.; Balhoff, J.P.; Pizer, M.; Rockman, M.V.; Romano, L.A. The evolution of transcriptional regulation in eukaryotes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 1377–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dubos, C.; Stracke, R.; Grotewold, E.; Weisshaar, B.; Martin, C.; Lepiniec, L. MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klempnauer, K.H.; Gonda, T.J.; Bishop, J.M. Nucleotide sequence of the retroviral leukemia gene v-myb and its cellular progenitor c-myb: The architecture of a transduced oncogene. Cell 1982, 31, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, K. Myb proteins in life, death and differentiation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1998, 8, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, J.; Ghosal, D.; Wienand, U.; Peterson, P.A.; Saedler, H. The regulatory c1 locus of Zea mays encodes a protein with homology to myb proto-oncogene products and with structural similarities to transcriptional activators. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 3553–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldoni, E.; Genga, A.; Cominelli, E. Plant MYB transcription factors: Their role in drought response mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 15811–15851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambawat, S.; Sharma, P.; Yadav, N.R.; Yadav, R.C. MYB transcription factor genes as regulators for plant responses: An overview. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2013, 19, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Millard, P.S.; Kragelund, B.B.; Burow, M. R2R3 MYB transcription factors—Functions outside the DNA-binding domain. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielsen, O.S.; Sentenac, A.; Fromageot, P. Specific DNA binding by c-Myb: Evidence for a double helix-turn-helix-related motif. Science 1991, 253, 1140–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.; Paz-Ares, J. MYB transcription factors in plants. Trends Genet. 1997, 13, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.H.; Zhou, Y.W.; Ma, Z.X.; Lu, X.Q.; Li, Y.L.; Chen, H. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of MYB transcription factors and their responses to abiotic stresses in woodland strawberry (Fragaria vesca). Horticulturae 2021, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; He, J.; Dong, J.H.; Hou, X.J.; Zhang, X. Genomic survey and expression profiling of the MYB gene family in watermelon. Hortic. Plant J. 2018, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Peng, R.; Tian, Y.; Han, H.; Xu, J.; Yao, Q. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the MYB transcription factor superfamily in Solanum lycopersicum. Plant Cell Physiol. 2016, 57, 1657–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galego, L.; Almeida, J. Role of DIVARICATA in the control of dorsoventral asymmetry in Antirrhinum flowers. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 880–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howarth, D.G.; Donoghue, M.J. Duplications and expression of DIVARICATA-like genes in dipsacales. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1245–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W. Evolution of RAD- and DIV-like genes in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raimundo, J.; Sobral, R.; Bailey, P.; Azevedo, H.; Galego, L.; Almeida, J.; Coen, E.; Costa, M.M. A subcellular tug of war involving three MYB-like proteins underlies a molecular antagonism in Antirrhinum flower asymmetry. Plant J. 2013, 75, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrigal, Y.; Alzate, J.F.; Gonzalez, F.; Pabon-Mora, N. Evolution of RADIALIS and DIVARICATA gene lineages in flowering plants with an expanded sampling in non-core eudicots. Am. J. Bot. 2019, 106, 334–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Mao, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, H.; He, S.; Tu, J.; Cheng, C.; Tian, G.; et al. AtDIV2, an R-R-type MYB transcription factor of Arabidopsis, negatively regulates salt stress by modulating ABA signaling. Plant Cell Rep. 2018, 37, 1499–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ju, H.W.; Chung, M.S.; Huang, P.; Ahn, S.J.; Kim, C.S. The R-R-type MYB-like transcription factor, AtMYBL, is involved in promoting leaf senescence and modulates an abiotic stress response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.S.; Chao, Y.C.; Tseng, T.W.; Huang, C.K.; Lo, P.C.; Lu, C.A. Two MYB-related transcription factors play opposite roles in sugar signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2017, 93, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Shi, M.; Yu, J.; Guo, C. SPL9 mediates freezing tolerance by directly regulating the expression of CBF2 in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Xu, Y.; Shi, M.; Lai, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Poethig, R.S.; Wu, G. Repression of miR156 by miR159 regulates the timing of the juvenile-to-adult transition in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sengupta, A.; Hileman, L.C. A CYC-RAD-DIV-DRIF interaction likely pre-dates the origin of floral monosymmetry in Lamiales. EvoDevo 2022, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.; Meier, I.; Wienand, U. The tomato I-box binding factor LeMYBI is a member of a novel class of Myb-like proteins. Plant J. 1999, 20, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machemer, K.; Shaiman, O.; Salts, Y.; Shabtai, S.; Sobolev, I.; Belausov, E.; Grotewold, E.; Barg, R. Interplay of MYB factors in differential cell expansion, and consequences for tomato fruit development. Plant J. 2011, 68, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, B.; Gao, S.; Lercher, M.J.; Hu, S.; Chen, W.H. Evolview v3: A webserver for visualization, annotation, and management of phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W270–W275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodstein, D.M.; Shu, S.; Howson, R.; Neupane, R.; Hayes, R.D.; Fazo, J.; Mitros, T.; Dirks, W.; Hellsten, U.; Putnam, N.; et al. Phytozome: A comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1178–D1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, K.; Shen, H. Cell-PLoc 2.0: An improved package of web-servers for predicting subcellular localization of proteins in various organisms. Nat. Sci. 2010, 2, 1090–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nystrom, S.L.; McKay, D.J. Memes: A motif analysis environment in R using tools from the MEME Suite. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1008991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lescot, M.; Dehais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouze, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Tabata, S.; Hirakawa, H.; Asamizu, E.; Shirasawa, K.; Isobe, S.; Kaneko, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Shibata, D.; Aoki, K.; et al. The tomato genome sequence provides insights into fleshy fruit evolution. Nature 2012, 485, 635–641. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, M.; Wu, X.; Wu, G. ABI5 acts downstream of miR159 to delay vegetative phase change in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2021, 231, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; He, K.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Gao, Z.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Qiu, X.; et al. The MYB transcription factor superfamily of Arabidopsis: Expression analysis and phylogenetic comparison with the rice MYB family. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 60, 107–124. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Dairi, M.; Pathare, P.B.; Al-Yahyai, R. Effect of postharvest transport and storage on color and firmness quality of tomato. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayenan, M.A.T.; Danquah, A.; Hanson, P.; Asante, I.K.; Danquah, E.Y. Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) genotypes respond differently to long-term dry and humid heat stress. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Aslam, M.; Yao, L.A.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Huang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Niu, X. Genomic analysis of SBP gene family in Saccharum spontaneum reveals their association with vegetative and reproductive development. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Bai, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; Hu, S.; He, Y. BnA.JAZ5 attenuates drought tolerance in rapeseed through mediation of ABA-JA crosstalk. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aysha, J.; Noman, M.; Wang, F.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Li, X. Synthetic promoters: Designing the cis regulatory modules for controlled gene expression. Mol. Biotechnol. 2018, 60, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azeez, A.; Sane, A.P.; Tripathi, S.K.; Bhatnagar, D.; Nath, P. The gladiolus GgEXPA1 is a GA-responsive alpha-expansin gene expressed ubiquitously during expansion of all floral tissues and leaves but repressed during organ senescence. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2010, 58, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gačnik, S.; Veberič, R.; Hudina, M.; Koron, D.; Mikulič-Petkovšek, M. Salicylate treatment affects fruit quality and also alters the composition of metabolites in strawberries. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
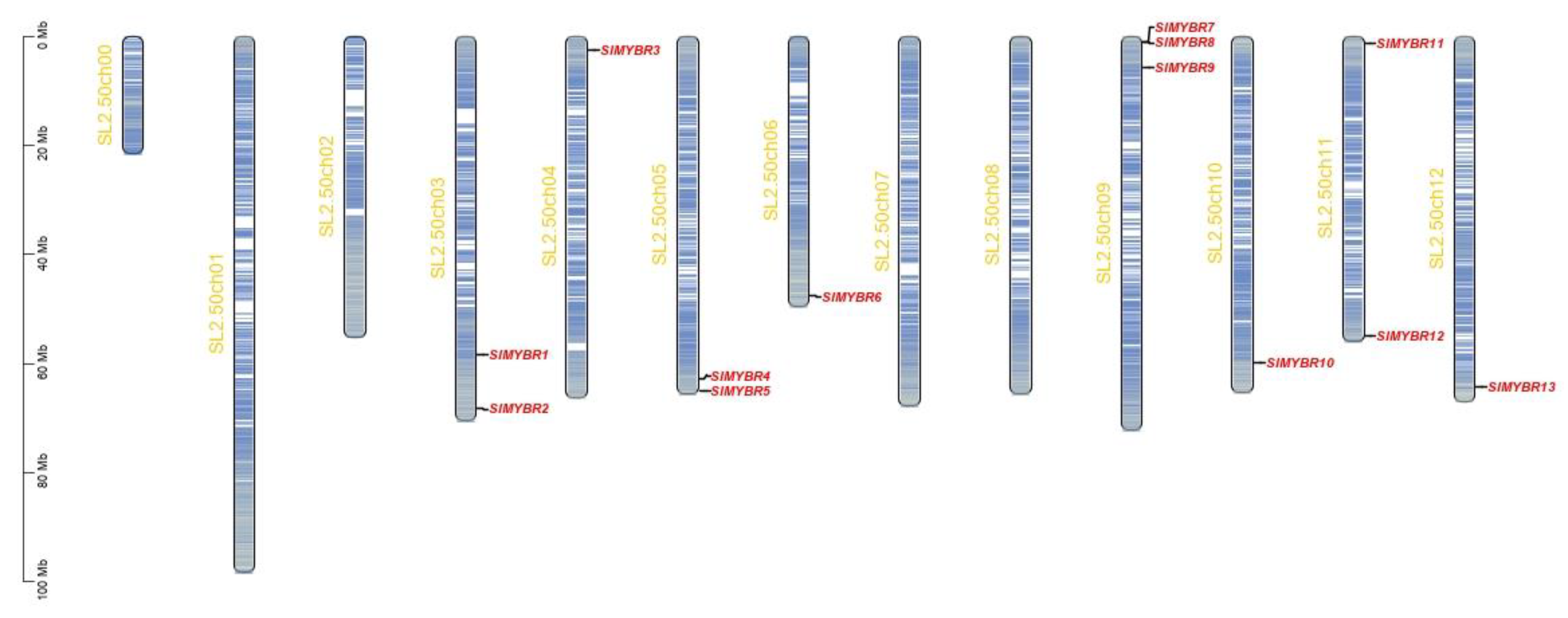
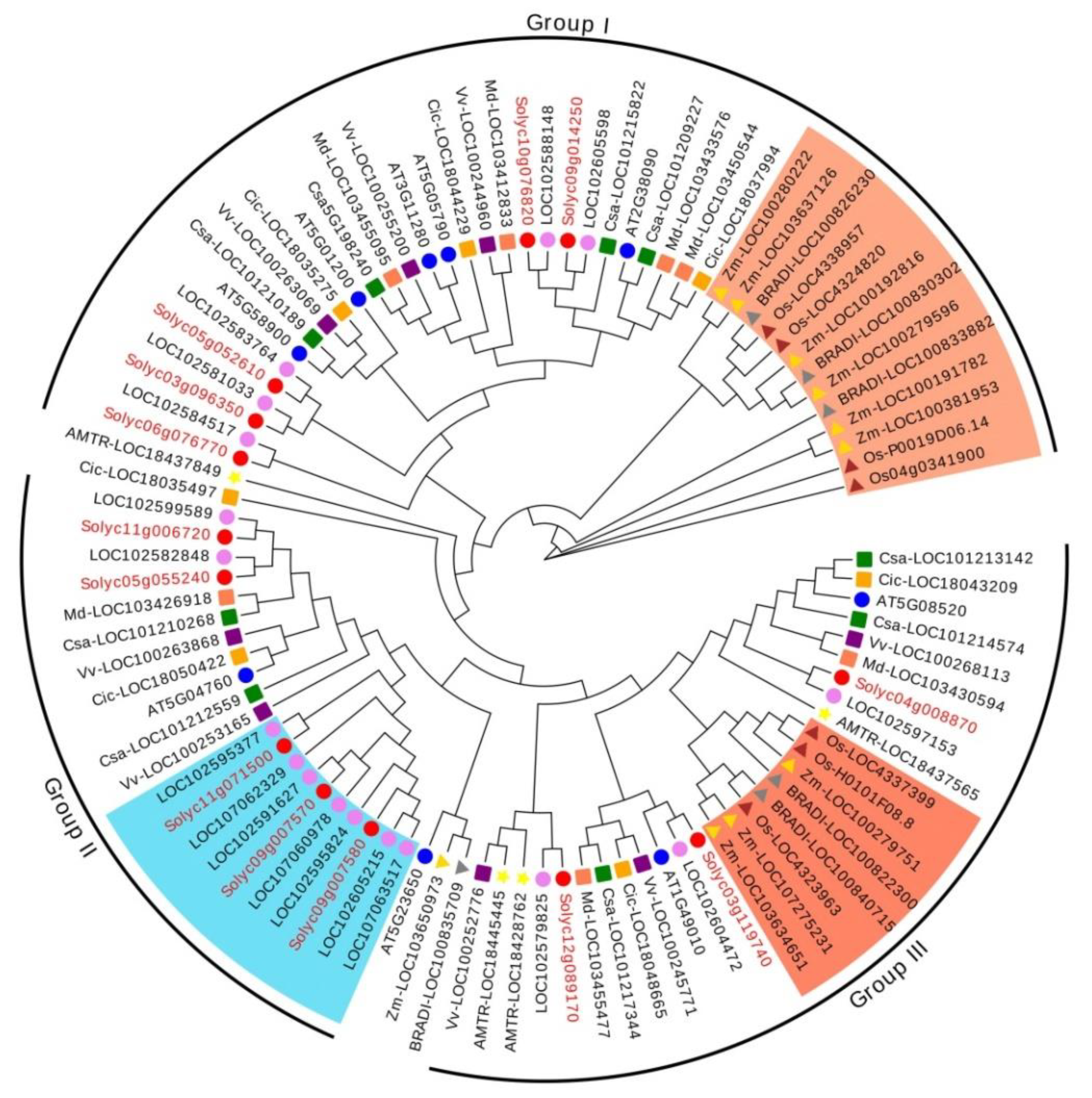

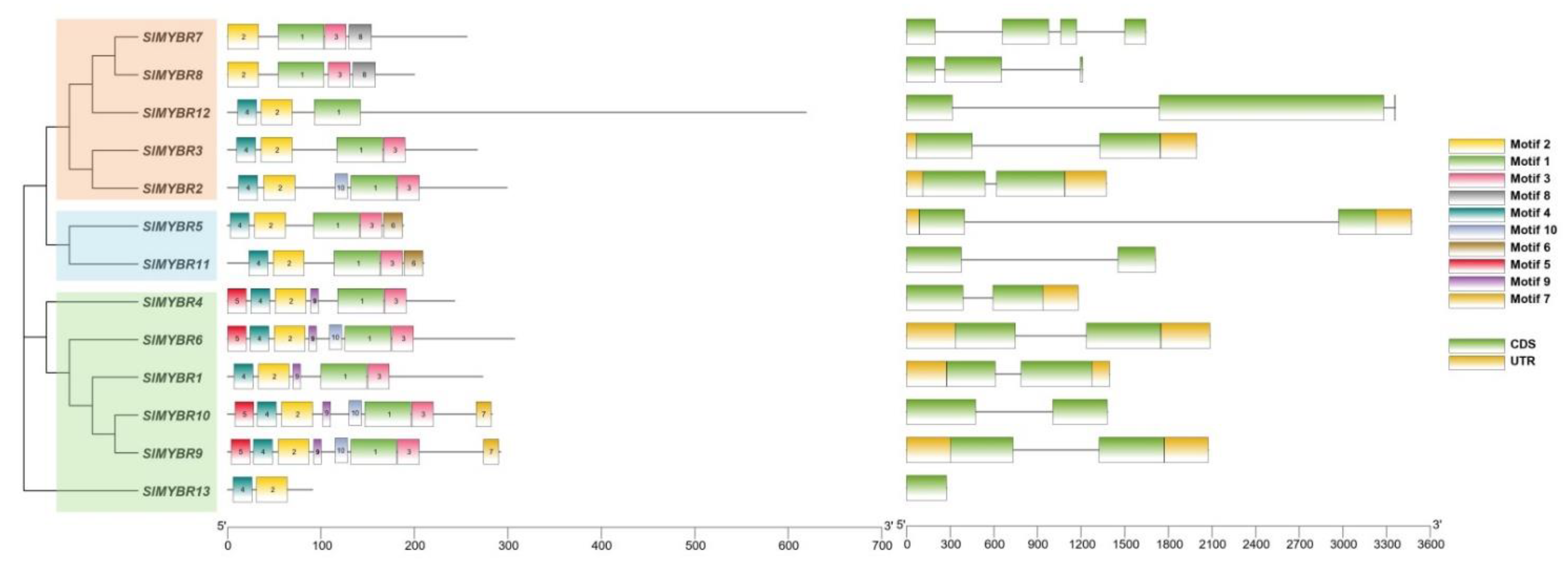
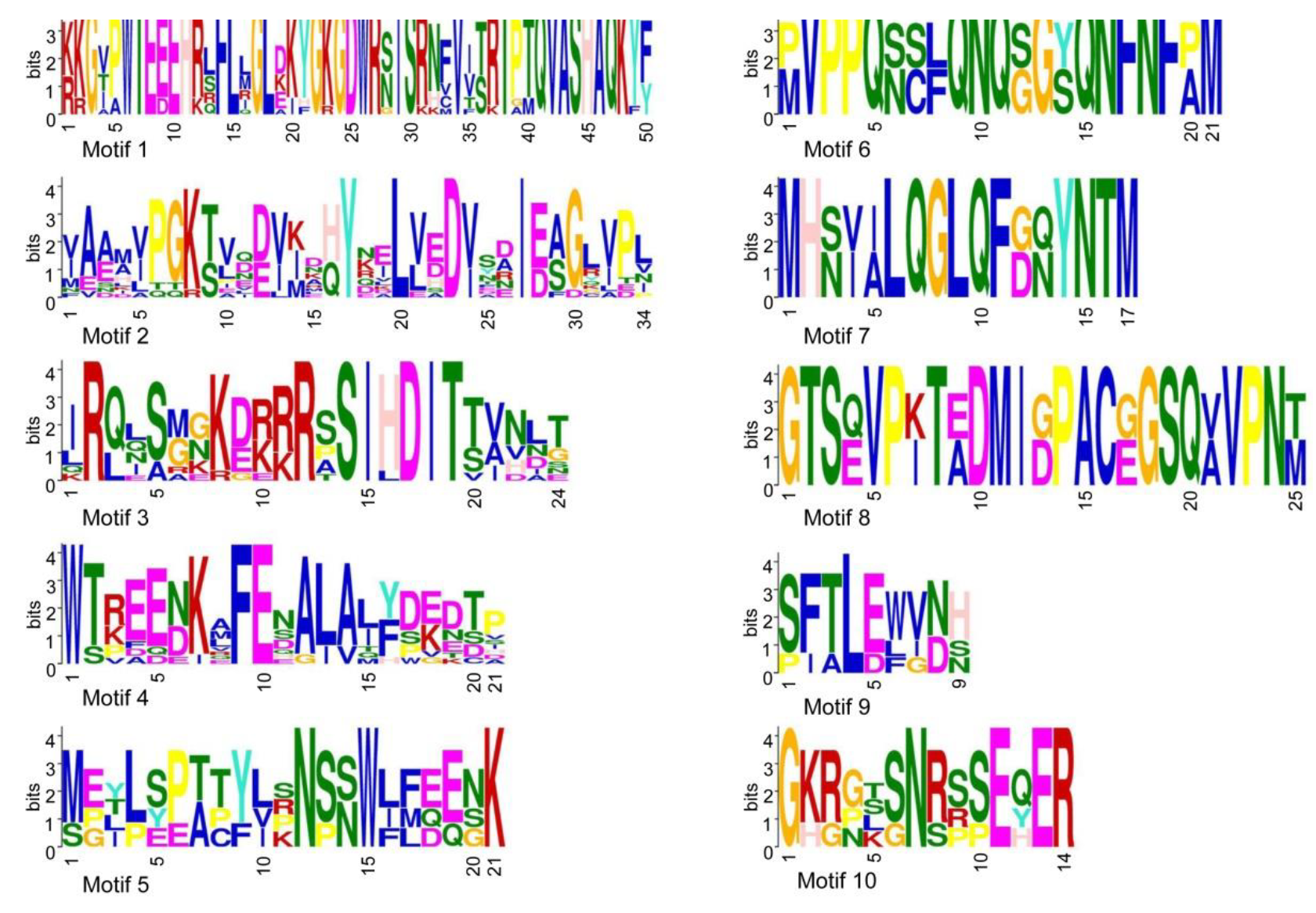


| Gene Name | Gene ID | Location | No. of Amino Acids | pI | Mw (Da) | Instability Index | Subcellular Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SlMYBR1 | Solyc03g096350 | SL2.50ch03:58394818..58396214 | 273 | 7.1 | 31,417.08 | 49.9 | Nucleus |
| SlMYBR2 | Solyc03g119740 | SL2.50ch03:68293180..68294554 | 299 | 6.59 | 32,825.52 | 59.72 | Nucleus |
| SlMYBR3 | Solyc04g008870 | SL2.50ch04:2492192..2494187 | 267 | 6.92 | 29,774.28 | 46.4 | Nucleus |
| SlMYBR4 | Solyc05g052610 | SL2.50ch05:62818453..62819634 | 243 | 7.02 | 28,526.07 | 49.59 | Nucleus |
| SlMYBR5 | Solyc05g055240 | SL2.50ch05:64968898..64972370 | 188 | 5.46 | 21,500.77 | 40.46 | Nucleus |
| SlMYBR6 | Solyc06g076770 | SL2.50ch06:47685103..47687190 | 307 | 9.14 | 34,693.9 | 54.45 | Nucleus |
| SlMYBR7 | Solyc09g007570 | SL2.50ch09:1163232..1164877 | 256 | 4.98 | 28,668.4 | 58.34 | Nucleus |
| SlMYBR8 | Solyc09g007580 | SL2.50ch09:1176695..1177907 | 200 | 4.88 | 21,988.46 | 56.06 | Nucleus |
| SlMYBR9 | Solyc09g014250 | SL2.50ch09:5739856..5741930 | 292 | 8.35 | 33,064.86 | 56.42 | Nucleus |
| SlMYBR10 | Solyc10g076820 | SL2.50ch10:59788934..59790315 | 283 | 8.96 | 32,916.82 | 58.57 | Nucleus |
| SlMYBR11 | Solyc11g006720 | SL2.50ch11:1335551..1337261 | 210 | 6.45 | 24,593.63 | 54.75 | Nucleus |
| SlMYBR12 | Solyc11g071500 | SL2.50ch11:54954825..54958185 | 619 | 5.69 | 65,667.07 | 57.76 | Nucleus |
| SlMYBR13 | Solyc12g089170 | SL2.50ch12:64288495..64288771 | 91 | 5.51 | 10,469.7 | 54.49 | Nucleus |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Guo, C. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of RR-Type MYB-Related Transcription Factors in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Horticulturae 2022, 8, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8050399
Sun J, Guo C. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of RR-Type MYB-Related Transcription Factors in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Horticulturae. 2022; 8(5):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8050399
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jiaying, and Changkui Guo. 2022. "Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of RR-Type MYB-Related Transcription Factors in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.)" Horticulturae 8, no. 5: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8050399
APA StyleSun, J., & Guo, C. (2022). Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of RR-Type MYB-Related Transcription Factors in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Horticulturae, 8(5), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8050399






