Full-Length Transcriptome and Transcriptome Sequencing Unveil Potential Mechanisms of Brassinosteroid-Induced Flowering Delay in Tree Peony
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. BR Treatment
2.3. RNA Preparation
2.4. PacBio Iso-Seq Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.5. Analysis of the Full-Length Transcriptome
2.6. BGISEQ-500 RNA-Seq
2.7. BGISEQ-500 Data Analysis
2.8. qRT-PCR Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Full-Length Transcriptome Sequencing and Functional Annotation
3.2. Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) Analysis from Transcriptome Sequencing
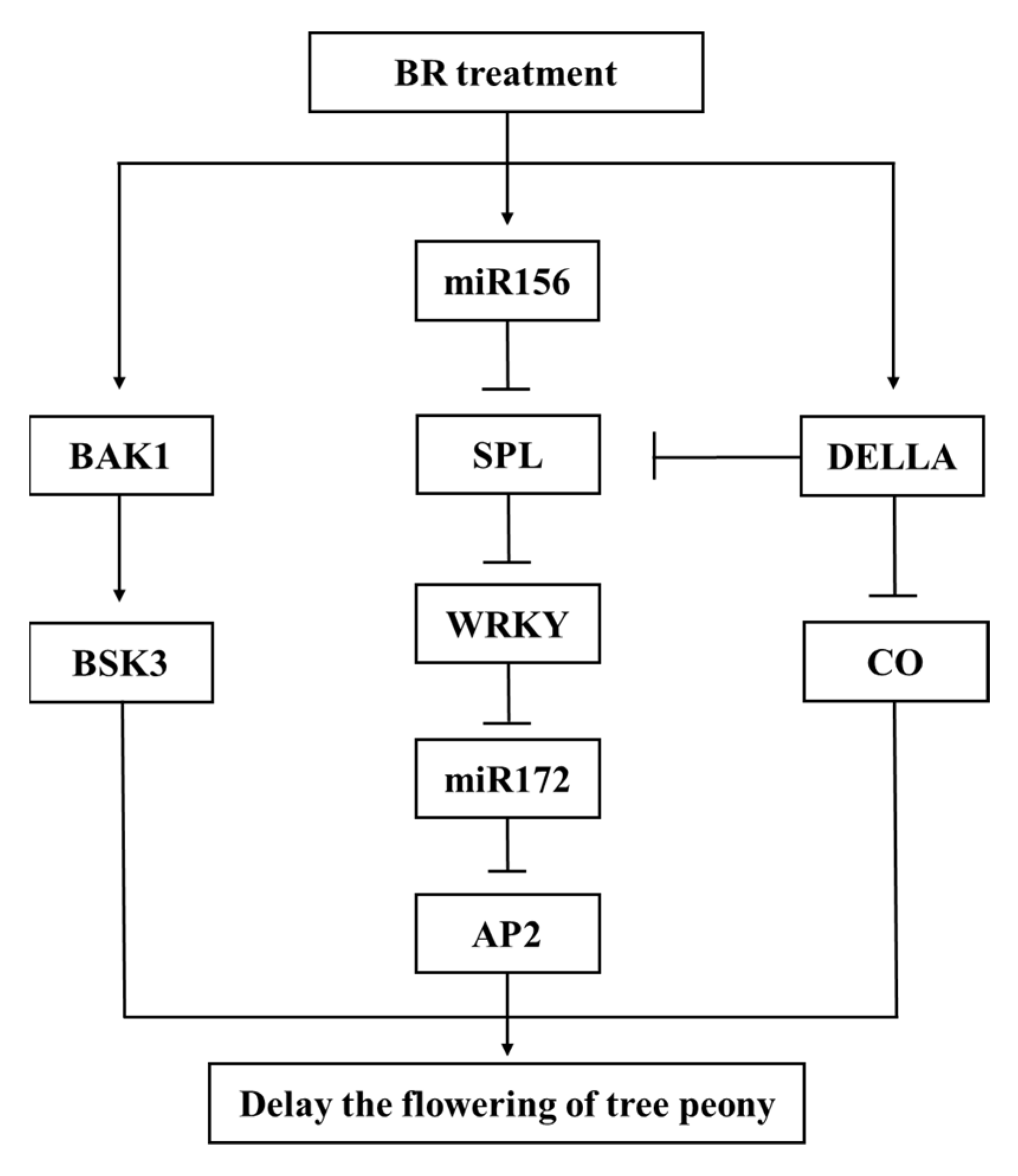
3.3. The Molecular Pathway of BR Regulating Tree Peony Flower Opening
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, D.; Hou, X.; Jia, T. Reverse transcriptase domain sequences from tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa) long terminal repeat retrotransposons: Sequence characterization and phylogenetic analysis. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2014, 28, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Han, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Hu, Y. Diversity in seed oil content and fatty acid composition in three tree peony species with potential as sources of omega-3 fatty acids. J. Pomol. Hortic. Sci. 2016, 91, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Han, J.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J. Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR during flower development in tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa Andr.). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Guo, D.; Zhao, W.; Hou, X. Newly developed SSR markers reveal genetic diversity and geographical clustering in Paeonia suffruticosa based on flower colour. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 292, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Cheng, F.; Zhong, Y.; Cai, C.; Wu, J.; Cui, H. Development of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers from Paeonia ostii to study the genetic relationships among tree peonies (Paeoniaceae). Sci. Hortic. 2013, 164, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xue, J.; Ahmadi, N.; Holloway, P.; Zhu, F.; Ren, X.; Zhang, X. Molecular characterization and expression patterns of PsSVP genes reveal distinct roles in flower bud abortion and flowering in tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa). Can. J. Plant Sci. 2017, 94, 1181–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Wang, S.; Xue, J.; Li, D.; Ren, X. Morphological and physiological changes, and the functional analysis of PdSPL9 in the juvenile-to-adult phase transition of Paeonia delavayi. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2018, 133, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Cheng, F.; Wang, R.; Zhong, Y.; He, C. Transcriptome comparison reveals key candidate genes responsible for the unusual reblooming trait in tree peonies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, S.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, P.; Liu, C.; Dong, L.; Zheng, G. Transcriptome analysis of tree peony during chilling requirement fulfillment: Assembling, annotation and markers discovering. Gene 2012, 497, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Guo, Q.; Wei, W.; Guo, L.; Guo, D.; Zhang, L. Screening of genes related to early and late flowering in tree peony based on bulked segregant RNA sequencing and verification by quantitative real-time PCR. Molecules 2018, 23, 689–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, D.; Guo, L.; Guo, Q.; Wang, H.; Hou, X. Construction of a high-density genetic map and QTLs mapping with GBS from the interspecific F1 population of P. ostii ‘Fengdan Bai’ and P. suffruticosa ‘Xin Riyuejin’. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 246, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y.; Yuan, J.; Guo, T.; Xu, L.; Mu, Z.; Han, L. Analysis of transcripts and splice isoforms in Medicago sativa L. by single-molecule long-read sequencing. Plant Mol. Biol. 2019, 99, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makita, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Lau, N.S.; Othman, A.S.; Matsui, M. Construction of Pará rubber tree genome and multi-transcriptome database accelerates rubber researches. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrarini, M.; Moretto, M.; Ward, J.A.; Šurbanovski, N.; Stevanovićet, V.; Giongo, L.; Viola, R.; Cavalieri, D.; Velasco, R.; Cestaro, A. An evaluation of the PacBio RS platform for sequencing and de novo assembly of a chloroplast genome. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Tang, X.; Ren, C.; Wei, B.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Jin, P. Full-length transcriptome sequences and the identification of putative genes for flavonoid biosynthesis in safflower. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 548–560. [Google Scholar]
- An, D.; Cao, H.; Li, C.; Humbeck, K.; Wang, W. Isoform sequencing and state-of-art applications for unravelling complexity of plant transcriptomes. Genes 2018, 9, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhu, C.; Tian, C.; Xu, K.; Huang, L.; Shi, B.; Lai, Z.; Lin, Y.; Guo, Y. Integrated volatile metabolome, multi-flux full-length sequencing, and transcriptome analyses provide insights into the aroma formation of postharvest jasmine (Jasminum sambac) during flowering. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 183, 111726–111740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, G.; Yuan, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Xu, L.; Li, L. Single-molecule real-time transcript sequencing identified flowering regulatory genes in Crocus sativus. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 857–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Tang, L.; Mei, X.; Liu, H.; Luo, H.; Deng, Y.; Su, J. Single-molecule long-read sequencing of the full-length transcriptome of Rhododendron lapponicum L. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6755–6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liaquat, F.; He, Y.; Munis, M.F.H.; Zhang, C. Functional annotation of a full-length transcriptome and identification of genes associated with flower development in Rhododendronsimsii (Ericaceae). Plants 2021, 10, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, C.; Guo, D.; Guo, L.; Hou, X.; Wang, H. Identification of differentially expressed miRNAs and their target genes in response to brassinolide treatment on flowering of tree peony (Paeonia ostii). Plant Signal. Behav. 2022, 17, 2056364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Feng, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. DEGseq: An R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhoads, A.; Au, K.F. PacBio sequencing and its applications. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Xi, F.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. Transcriptome characterization of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) seedlings in response to exogenous gibberellin applications. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, P.; Liang, F.; Ye, Z.; Li, J.; Shen, C.; Pei, L.; Wang, F.; Hu, J.; Tu, L.; et al. A global survey of alternative splicing in allopolyploid cotton: Landscape, complexity and regulation. New Phytol. 2017, 217, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, C.; Blow, M.; Sreedasyam, A.; Kuo, R.C.; Ramamoorthy, G.K.; Torres-Jerez, I.; Li, G.; Wang, M.; Dilworth, D.; Barry, K.; et al. Revealing the transcriptomic complexity of switchgrass by PacBio long-read sequencing. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, Y.; Chai, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z. Full-length transcript sequencing and comparative transcriptomic analysis to evaluate the contribution of osmotic and ionic stress components towards salinity tolerance in the roots of cultivated alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 32–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Harata-Lee, Y.; Denton, M.D.; Feng, Q.; Rathjen, J.R. Long read reference genome-free reconstruction of a full-length transcriptome from Astragalus membranaceus reveals transcript variants involved in bioactive compound biosynthesis. Cell Discov. 2017, 3, 17031–17043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, T.; Tao, J. Single molecule, full-length transcript sequencing provides insight into the TPS gene family in Paeonia ostii. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, T.K.; Rim, Y.; Jiang, H.J.; Kim, C.H.; Park, J.; Kumar, R.; Lee, S.; Kim, B.C.; Bhak, J.; Nguyen-Quoc, B. De novo transcriptome sequencing of Momordica cochinchinensis to identify genes involved in the carotenoid biosynthesis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2012, 79, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Yu, D. WRKY transcription factors WRKY12 and WRKY13 interact with SPL10 to modulate age-mediated flowering. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 1659–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujioka, S.; Sakurai, A. Biosynthesis and metabolism of brassinosteroids. Physiol. Plant. 1997, 100, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Giehl, R.F.H.; Meyer, R.C.; Altmann, T.; Wiren, N. Natural variation of BSK3 tunes brassinosteroid signaling to regulate root foraging under low nitrogen. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2378–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Abbas, S.; Lin, J. Dynamic spatial reorganization of BSK1 complexes in the plasma membrane underpins signal-specific activation for growth and immunity. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 588–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Willige, B.C.; Jaillais, Y.; Geng, S.; Park, M.Y.; Gray, W.M.; Chory, J.; Copenhaver, G.P. BRASSINOSTEROID-SIGNALING KINASE 3, a plasma membrane-associated scaffold protein involved in early brassinosteroid signaling. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1007904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, T.M.; Nemanja, V.; Liu, D.; Eugenia, R.; Yin, Y. Brassinosteroids: Multidimensional regulators of plant growth, development, and stress responses. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 295–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Pan, J.; Li, Y.; Lou, D.; Hu, Y.; Yu, D. The DELLA-CONSTANS transcription factor cascade integrates gibberellic acid and photoperiod signaling to regulate flowering. Plant Physiol. 2016, 172, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, V.C.; Horrer, D.; Küttner, F.; Schmid, M. Spatial control of flowering by DELLA proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 2012, 139, 4072–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Li, T.; Xu, P.; Li, L.; Du, S.; Lian, H.; Yang, H. DELLA proteins physically interact with CONSTANS to regulate flowering under long days in Arabidopsis. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
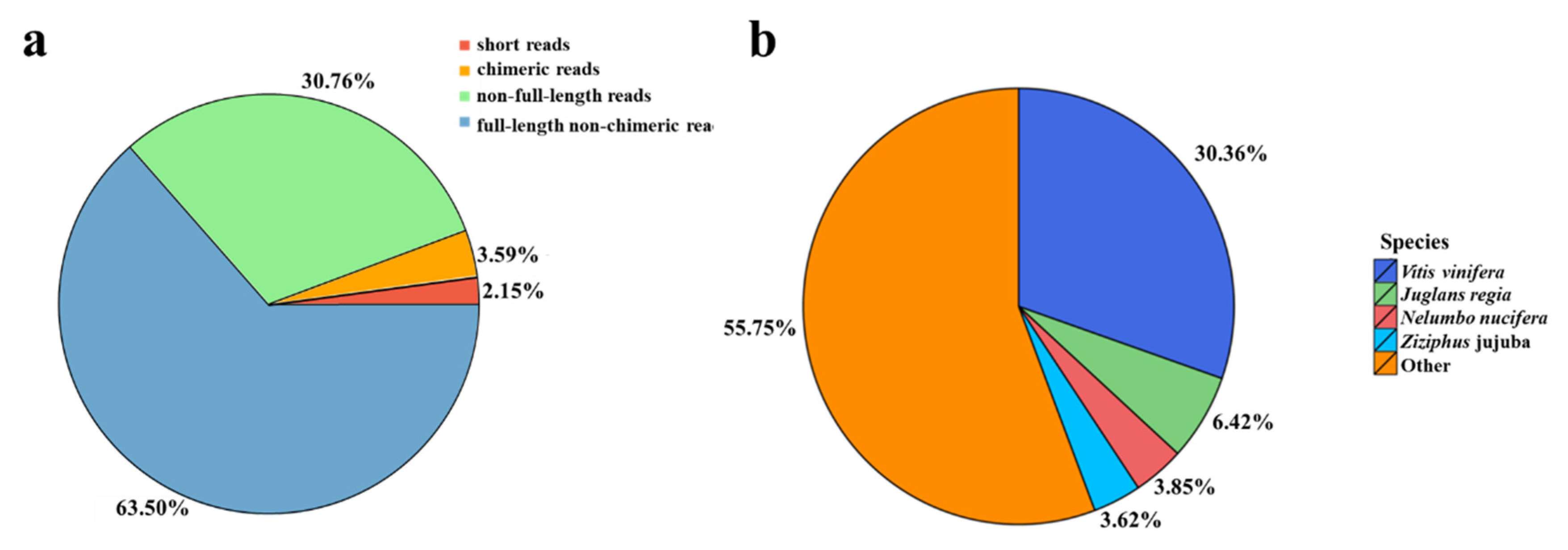


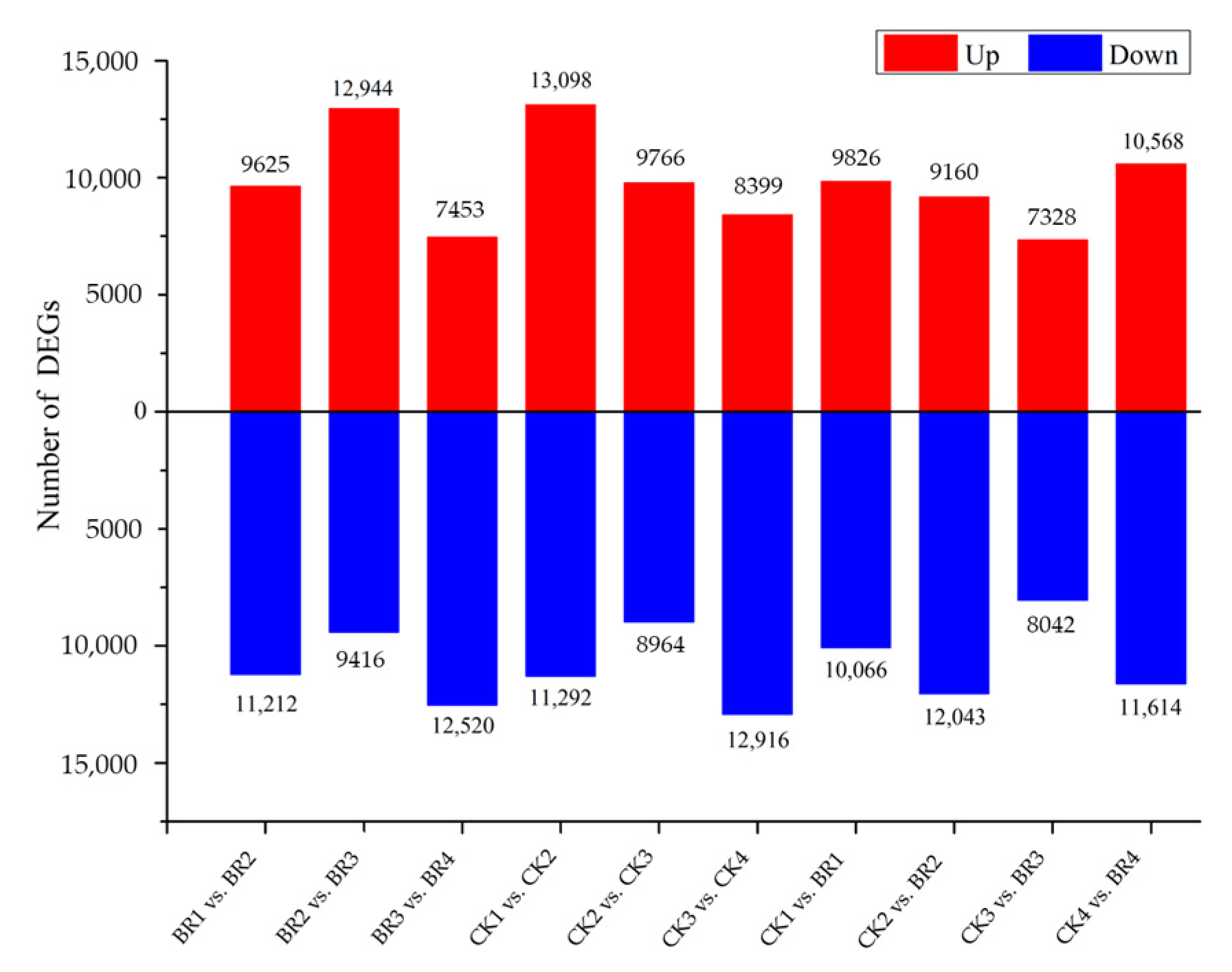
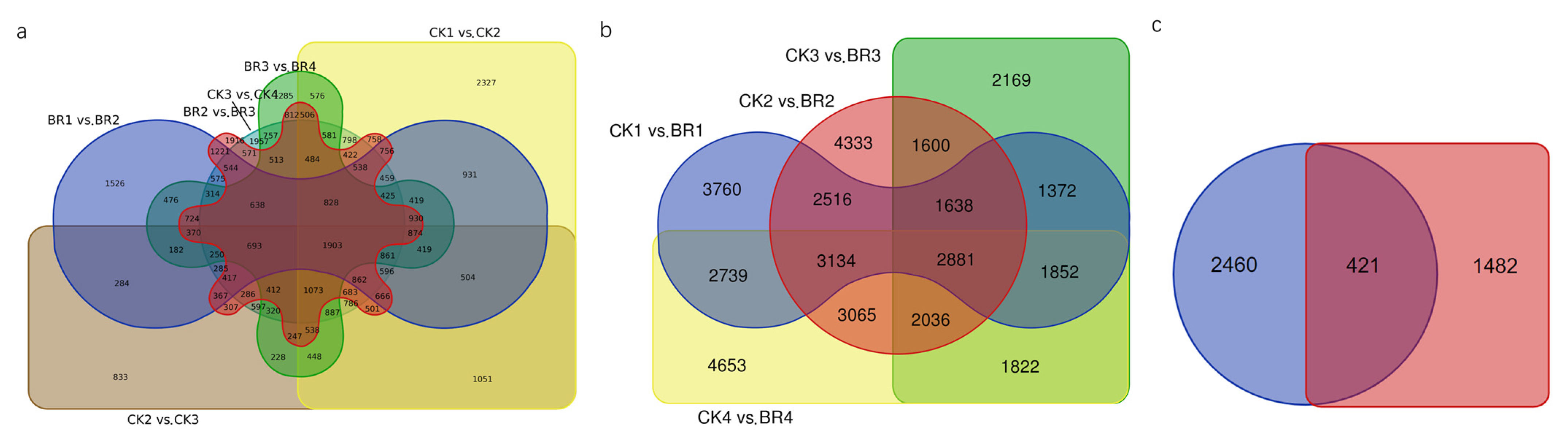
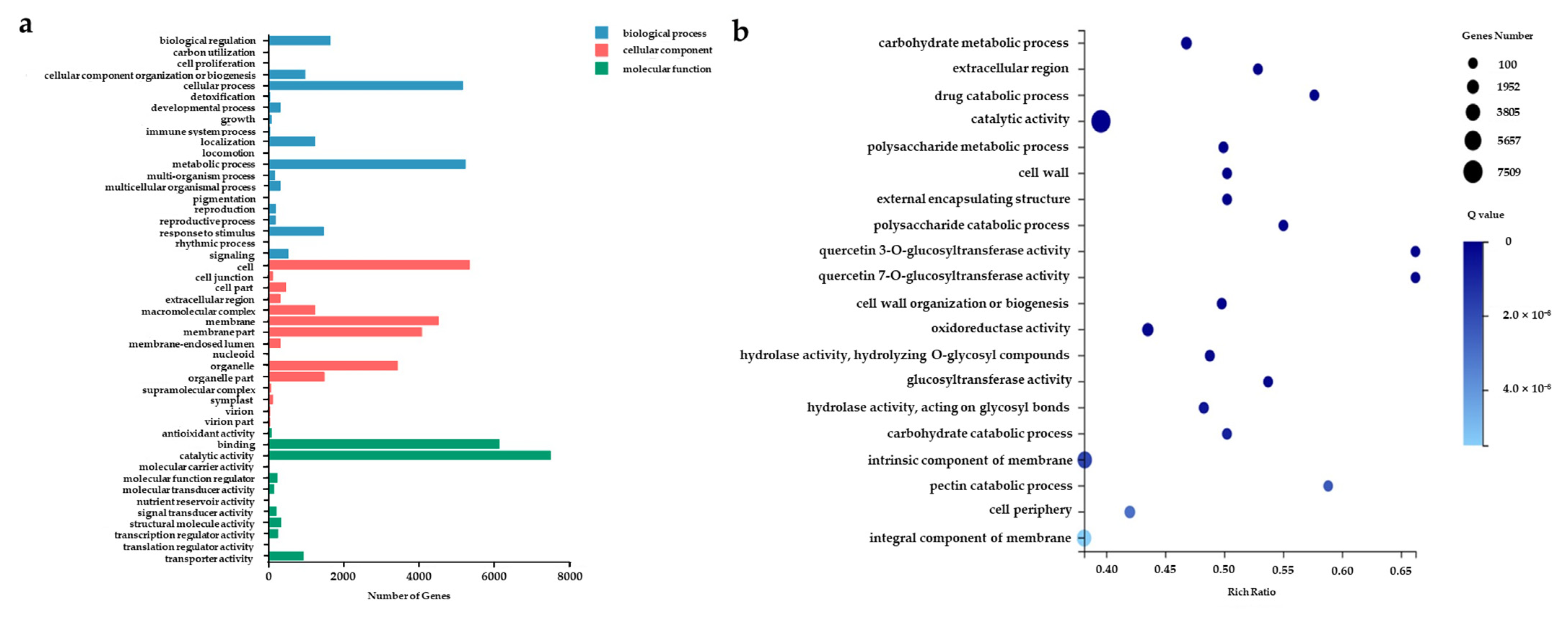


| Data | Total Reads | Total Base (GB) | Max Length (bp) | Mean Length (bp) | N50 Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymerase reads | 711,498 | 22.25 | 233,101 | 31,275.88 | 59,732 |
| Subreads | 13,978,732 | 21.27 | 149,197 | 1521.25 | 1764 |
| Cluster Type | Total Isoforms | Total Base (bp) | Mean Quality | Mean Isoform Length (bp) | Mean full-Length Coverage | Mean Non-Full-Length Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HQ | 135,541 | 218,900,453 | 0.9988 | 1615 | 2.18 | 16.18 |
| LQ | 132,075 | 212,109,968 | 0.3049 | 1606 | 1.11 | 5.34 |
| Total | NR | NT | SwissProt | KEGG | KOG | InterPro | GO | Intersection | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 62,229 | 57,193 | 51,080 | 46,622 | 47,429 | 48,398 | 51,967 | 35,643 | 25,090 | 58,218 |
| 100% | 91.91% | 82.08% | 74.92% | 76.22% | 77.77% | 83.51% | 57.28% | 40.32% | 93.55% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Song, C.; Guo, L.; Guo, D.; Xue, X.; Wang, H.; Hou, X. Full-Length Transcriptome and Transcriptome Sequencing Unveil Potential Mechanisms of Brassinosteroid-Induced Flowering Delay in Tree Peony. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8121136
Zhang L, Song C, Guo L, Guo D, Xue X, Wang H, Hou X. Full-Length Transcriptome and Transcriptome Sequencing Unveil Potential Mechanisms of Brassinosteroid-Induced Flowering Delay in Tree Peony. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(12):1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8121136
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lin, Chengwei Song, Lili Guo, Dalong Guo, Xian Xue, Huafang Wang, and Xiaogai Hou. 2022. "Full-Length Transcriptome and Transcriptome Sequencing Unveil Potential Mechanisms of Brassinosteroid-Induced Flowering Delay in Tree Peony" Horticulturae 8, no. 12: 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8121136
APA StyleZhang, L., Song, C., Guo, L., Guo, D., Xue, X., Wang, H., & Hou, X. (2022). Full-Length Transcriptome and Transcriptome Sequencing Unveil Potential Mechanisms of Brassinosteroid-Induced Flowering Delay in Tree Peony. Horticulturae, 8(12), 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8121136





