Abstract
Citrus canker is a quarantined disease caused by the bacterial plant pathogen Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri (Xcc), which causes persistent surface damage, leaf and fruit drop, and tree decline in citrus plants. The citrus cultivar Citron C-05 (Citrus medica L.) is a disease-resistant genotype identified after years of screening at the National Center for Citrus Improvement (Changsha), which displays allergic, necrotic, and disease-resistant responses to Xcc. In this study, the BAK1 gene was identified in this cultivar to be a disease resistance gene involved in plant-microbe interaction between citrus and Xcc. Functional investigations of this gene revealed that both CsBAK1 (C. sinensis BAK1) or CmBAK1(C. medica BAK1) could inhibit the growth of Xcc to some extent when transiently expressed in the susceptible ‘Bingtang’ genotype of sweet orange. Critical regions of the CmBAK1 promoter sequence were identified by creating downstream deletions and exposing mutants to Xcc to determine effects on the resistance phenotype; a 426 bp region (−2000~–1574) was identified as a key functional region responsible for eliciting the hypersensitive response in plants. Through screening arrayed Citron C-05 cDNA libraries by yeast one-hybrid assays, a basic APETALA2/ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR (AP2/ERF) transcription factor of CmRAP2-13 that binds directly to the 426 bp key sequence and activates expression of CmBAK1 was identified. Moreover, transcriptional analysis revealed an obvious increase in transcript levels of CsRAP2-13 in Citron C-05, American citron, and Finger citron. In this study, we present the identification of transcriptional activators that are found to interact with BAK1 proteins in response to Xcc. These results reveal a coordinated regulatory mechanism of RAP2-13, which may be involved in defence responses through the regulation of BAK1.
1. Introduction
Citrus canker is a devastating disease caused by the Gram-negative bacterium Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri (Xcc). The main symptoms of citrus canker are the formation of crater-like disease spots on the surface of branches, leaves, and fruits, which can lead to leaf and fruit drop, retardation of tree growth and development, decreased yield, and cosmetic damage that makes fruit unmarketable [1,2]. At present, the control of citrus canker relies primarily on chemical applications; however, disease eradication using this method is challenging and potentially environmentally damaging. Breeding resistant citrus varieties is widely considered a more effective and safe control measure [3]. Investigating the interactions between citrus plants and Xcc to identify molecular components underpinning the resistance of citrus to this pathogen greatly helps inform breeding program efforts aimed at developing disease resistant cultivars.
Plants have a variety of strategies to defend against invading plant pathogens, including increasing the strength of their cell walls, producing specific metabolites to kill pathogens, and regulating defence-related gene expression in plant cells. It is now widely recognized that plants possess a system of innate immunity. When plants are exposed to potential pathogens, they are able to resist many diseases. Plants can become susceptible lose such disease resistance when a pathogen produces a specific effector that can bypass the plant defence system [4]. Extracellular recognition of microbial and host damage associated molecular patterns (MAMPs and DAMPs, respectively) by plants induces the first layer defence known as pattern-triggered immunity (PTI).
Citrus has several reproductive characteristics, such as long juvenility, self-incompatibility, nucellar embryony, heterozygosity, and apomixis, which hinder efforts to develop resistant varieties through conventional breeding. Genetic modification of plants involves the intentional alteration of the plant genome through the insertion of foreign DNA sequences [5]. Resistance genes from the same or different species can be transgenically integrated into susceptible citrus cultivars and have the potential to improve the PTI response and resistance to citrus canker of these susceptible species [6]. FLS2 is a good candidate resistance gene for integration into citrus improvement programs. For example, overexpression of Xa21 in the sweet orange cultivar ‘Dark’ resulted in increased tolerance to Xcc [7].
A common coreceptor found in plants involved in the regulation of specific cellular mechanisms such as growth, development, and defence against pathogens is the membrane-bound brassinosteroid-insensitive associated receptor kinase BAK1. BAK1 attaches to ligand stimulated transmembrane receptors, thereby stimulating their kinase domains through transphosphorylation [8]. Additionally, BAK1 plays a common role in several pathways responsible for PTI signal transduction in Arabidopsis thaliana [9]. BAK1 is a leucine rich repeat receptor-like kinase (LRR-RLK). The extracellular LRR domain of BAK1 consists of five repeat sequences, and serine-rich and proline-rich domains are located after these LRR domains [10]. BAK1 also has a transmembrane domain, a cytoplasmic kinase domain, and a short C-terminal tail. As a member of the serine protein family, BAK1 has four homologues. Somatic embryogenic receptor kinase 1 (SERK1) is the first member of this family to be identified, which is why BAK1 is also known as SERK3 [10]. In plant innate immunity, BAK1 plays an important role in communication with the receptor FLS2 [11,12]. Thus, BAK1 plays a crucial role in the control and management of some LRR-RLKs by cooperating with certain LRR-RLKs in multiple stimulus-dependent systems [13,14]. The important role of BAK1 in citrus response to invasion by Xcc remains unclear.
After years of screening, the cultivar Citron C-05 (Citrus medica L.) was identified as a resistant germ plasm that developed no obvious disease and produced hypersensitivity reaction after inoculation with ulcerative bacteria [15,16]. In order to utilize Citron C-05 in breeding for resistance to canker disease, it is necessary to identify the resistance-related genes and explore its resistance mechanism to the disease. This study aims to analyze the expression profiles of the gene BAK1, and to better understand the resistant mechanism of citron C-05, which may provide a theoretical basis for disease resistance molecular breeding. In this study, the BAK1 gene and its promoter were cloned and analyzed in both Citron C-05 and ‘Bingtang’ sweet orange genotypes, and transcription factors regulating BAK1 gene expression were screened by yeast monoclonal screening, so as to understand whether BAK1 is involved in the transcriptional regulation of the defence response to canker disease in the Citron C-05 cultivar.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
Both susceptible citrus genotypes (‘Bingtang’ sweet orange, Pomelo, Nanchuan citron, Wild citron, and Round citron) and resistant ones (American citron, Finger citron, and Citron C-05) were used in the present study. Plants of all the tested genotypes were grafted onto trifoliate orange (Poncirus trifoliata) rootstock and grown for two years in a greenhouse maintained at 28 ± 1 °C, 80% relative humidity (RH), and natural photoperiod. Fully expanded young leaves with light green coloration were selected for Xcc inoculation.
2.2. Bacterial Pathogen Preparation
The Xcc strain DL509, previously isolated and stored at −80 °C in the laboratory, was cultured in LB medium (10 g/L peptone; 10 g/L sodium chloride; 5 g/L yeast extract) at 28 °C for 72 h, and single colonies were selected and cultured in 100 mL liquid LB medium at 28 °C with shaking at 200 rpm/min for 24 h. The bacterial solution was centrifuged at 7000× g for 10 min. The bacterial pellet was rinsed 3 times with sterile water, and then resuspended in sterile water. The OD600 of the bacterial suspension was adjusted to 0.75 (about 109 CFU/mL). After a 10-fold gradient dilution, the 10−7, 10−8 and 10−9 dilution gradients were selected for plate counting, and the 10−4 (2.01 × 105 CFU/mL) dilution gradient was selected for inoculum. Control plants were simultaneously inoculated with the same concentration of Xoo (Xanthomonasoryzae pv. oryzae). Xcc was injected on one side of the main vein of the sampled fully expanded young leaves and Xoo on the other side of the same leaf as a control. Inoculated leaves were sampled at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 days post inoculation (dpi) for successive RT-PCR.
2.3. RNA Isolation and Quantitative RT-PCR
Total RNA was isolated from sampled leaves using the RNA prep pure plant kit (Tiangen) based on the manufacturer’s instructions. cDNA was synthesized from 1 μg of RNA using the PrimeScript RT reagent Kit (Takara, Dalian, China). Quantitative PCR was performed on a Bio-Rad CFX 96 quantitative PCR instrument using SYBR Green I SuperMix (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). The reaction procedure was as follows: pre-denaturation at 94 °C for 5 min followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 94 °C for 5 s, annealing at 59 °C for 15 s, and extension at 72 °C for 20 s. EF1-α (Table 1) was used as the reference gene [17], and the 2−△△Ct algorithm was used for data calculation.

Table 1.
BAK1 and EF1-α gene primer sequences for qPCR.
2.4. Isolation and Bioinformatic Analysis of the CsBAK1 Gene in Citrus
BAK1 was ampyfied from cDNA by homologous recombination using specific primers (Table 1). The target fragment was cloned into the pCAMBIA1301 vector (named 35S:: BAK1) and then transformed into E.coli strain DH5α (TransGen Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) using heat shock. Positive clones identified by colony PCR were confirmed with Sanger Sequencing (Springen Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China). To isolate CsBAK1 from genomic DNA, gene-specific primers were designed based on the gDNA sequence of the gene (Table 2). CsBAK1 isolated from gDNA was verified and named gCsBAK1. The gCsBAK1 PCR product was likewise cloned into the pCAMBIA1301 vector (named 35S:: gCsBAK1).

Table 2.
Cloning primer sequences for BAK1 amplification from genomic DNA.
The CDS sequence of the BAK1 gene was translated into putative protein sequences. The homology of the gene sequence and cDNA sequence were analyzed by DNAMAN5.0. The transmembrane domain (http://smart.embl.de/, accessed on 26 May 2021) of BAK1 was further analyzed.
2.5. Transient Expression of CsBAK1 in’Bingtang’ Sweet Orange Leaves
For transient expression, the full length ORF of CsBAK1 was amplified and cloned into the pCAMBIA1301-sGFP vector, under the control of the 35S promoter. Recombinant plasmids were transformed into the Agrobacterium strain EHA105 and then agroinfiltrated into ‘Bingtang’ sweet orange leaves, as described previously.
Leaves inoculated by injection of Xcc (105 cfu/mL) were randomly sampled for quantification 1 day after infiltration with EHA105. Xcc injected leaves (Xcc 105 cfu/mL) were co-infiltrated with EHA105 1, 4, and 6 dpi, and leaves were sampled. Sampled leaves were surface disinfected with 75% ethanol, then eight leaf disc samples were collected from within the infiltration areas of each of the three inoculated leaves and homogenized in 1 mL of sterile distilled water. The suspension was then serially diluted with sterile distilled water. 20 μL of the diluted suspension from each sample was incubated on plates of solid LB medium at 28 °C for 48 h. The bacteria were quantified according to the formation of colonies on the LB agar plates. Quantifications were repeated three times.
2.6. Construction of BAK1 Promoter Vectors and ‘Bingtang’ Sweet Orange Leaf Transformation
The CmBAK1 promoter CmP1 (−2000 bp~+0 bp) was amplified from genomic DNA with primers CmP1-F and CmP1-R. Then, a series of nested deletion fragments—CmP1 (−2000 bp~+0 bp), CmP2 (−1571 bp~−0 bp), CmP3 (−839 bp~−0 bp), CmP4 (−560 bp~−0 bp), and CmP5 (−2000 bp~−1574 bp) were amplified from PCX-CSP1 using ordinary reverse primers −1161 bp (Table 3), and the full-length promoter and 5 ‘-deleted derivative were cloned into PCX-GUS upstream of β-glucuronidase. Empty PCX-GUS vector was used as a negative control. All constructs were transformed into Agrobacterium EHA105 then infiltrated into ‘Bingtang’ sweet orange leaves according to the previously described protocol. One day after infiltration, Xcc (105 CFU/mL) was randomly selected to inject leaves for quantification.

Table 3.
Primers used for promoter cloning.
GUS expression was detected according to the method described by Jefferson et al. [18]. Citrus leaves carrying different promoter CmP fragments were treated with GUS staining solution (50 mM PBS, pH 7.0, 10 mM EDTA, pH 8.0, 20% methanol, 0.1% Triton X-100, 0.1% sodium lauryl sarcosine and 10 mM β-mercaptoethanol). The samples were vacuumized for 1–2 h and incubated at 37 °C for 12–16 h. The dye was decolorized with 70% ethanol for 1–2 day, and then the staining was observed and photographed.
2.7. Yeast One-Hybrid (Y1H) Screening
Y1H screening was conducted with the Matchmaker Gold OneHybrid Library Screening System (Takara, Clontech, Cat. Nos. 630491, Dalian, China). A 426 bp fragment of the bait sequence was cloned into the pAbAi vector containing the AUR1-Cgene, conferring resistance to Aureobasidin A (AbA, acyclic depsipeptide used to select yeast). A bait-specific reporter strain was then generated by homologous recombination using the resulting pAbAi-Bait construct (Table 4). Aureobasidin A was found to inhibit the bait-specific reporter strain at a minimal inhibitory concentration. Along with screening a cDNA library generated from Citron C-05 leaves using the strain, transformants grown on selective medium (SD/Leu/AbA 250 ng/mL) were screened and positive colonies were identified by PCR. DNA sequence retransformation assays were carried out by amplifying full-length CDSs from cDNA using the primers listed in Table 5. PCR products were cloned into the pGADT7 vector, and a bait reporter yeast strain was used to transfer the constructs. After being cultured on SD/Leu and (SD/Leu/AbA 250 ng/mL) plates for 3 day at 30 °C, the cells were resuspended in liquid media to an OD600 of 0.1 (10−1) and diluted in a 10-fold dilution series (10−2 to 10−3). Each dilution was spotted seven times on AbA media selective for the respective plasmids (SD/−Leu)) and interactions (SD/−Leu)/AbA 250 ng/mL), complemented with 100 ng/mL AbA to suppress background growth.

Table 4.
Primer sets used in bait promoter cloning.

Table 5.
Primer sets used in RAP2-13 cloning.
2.8. Expression Profiling of Transcription Factors
The expression of defence genes (CmRAP2-13) induced by Xcc was evaluated. Primer sequences for RAP2-13 was selected from Table 6.

Table 6.
The primer sequences of RAP2-13.
2.9. Data Processing
Microsoft Excel 2016 Software (16.0.4266.1001) was used for data processing, GraphPad Prism 7 Statistical Analysis Software was used for variance analysis and significant difference analysis, and the Duncan method was used for multiple comparisons.
3. Results
3.1. Canker Symptom Development on Leaves of Susceptible and Resistant Sweet Orange Cultivars
Fully expanded young leaves were infiltrated with 105 cfu/mL of Xcc on the left of the main vein and with the same concentration of Xoo on the right, and the incidence of citrus germplasm was observed regularly (Figure 1). At 6 days after Xcc inoculation, the leaf of Citron C-05 began to show tissue depression, which was the disease resistance reaction, while the leaf symptoms of the susceptible genotypes (Nanchuan citron, Round citron, Wild citron, sweet orange, and pomelo) were obviously observed. Leaves of Finger citron and American citron appeared some reaction points. On the 8th and 10th day after Xcc inoculation, the tissue sag of Citron C-05 increased, and the symptoms of susceptible cultivars increased were aggravated, and the callus swelling developed, which was the typical symptom of citrus canker disease (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
Leaf symptom development of tested citrus cultivars following inoculation with Xcc. Citron C-05, American Citron, Nanchuan Citron, Round citron, sugar orange, Shatian pomelo, and wild citron. Citron fully expanded young leaves were infiltrated with 105 cfu/mL of Xcc on the left of the main vein and with the same concentration of Xoo on the right. Symptoms were observed at 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 dpi.
3.2. Analysis of CsBAK1 Expression Levels in Citrus Leaves
Quantitative PCR (qPCR) results showed that BAK1 was up regulated after Xcc inoculation in both resistant and susceptible genotypes. However, while BAK1 was significantly up-regulated in resistant genotypes, while only weakly up-regulated occurred in the susceptible genotypes. Crucially, BAK1 in the resistant Citron C-05, Finger citron, and American citron began to be highly expressed at 4 dpi and its expression level peaked at 8 dpi. In susceptible citrus cultivars, BAK1 was not significantly up-regulated until 10 dpi (Figure 2). These results indicated that BAK1 was specifically upregulated by the citrus canker bacteria in the resistant germplasm, and thus might play a key role in the resistance response to Xcc.

Figure 2.
Relative expression levels of BAK1. *** indicate significant differences (p < 0.05, respectively). BTC: ‘Bingtang’ sweet orange; STY: Pomelo; NCXY: Nanchuan citron; YSJY: Wild citron; YXY: Round citron; MGJY: American citron; FS: Finger citron; JY C-05: Citron C-05.
3.3. Isolation and Phylogenetic Analysis of the BAK1 Gene from the Citron C-05 Cultivar
To verify whether there was an association between the BAK1 protein structure and resistance of Citron C-05 to Xcc, the BAK1 amino acid sequences were compared across the resistant Citrons (Citron C-05, Common citron, American citron, Aiguo citron) and the susceptible citrus genotypes (‘Bingtang’ sweet orange, Danna citron, Nanchuan citron, Wild citron, Round citron, and Small citron) obtained by resequencing. The results suggested that BAK1 had 6 amino acid site differences, but there was no obvious correlation between these differences and resistance. The BAK1 protein structure, predicted by SMART online software, inferred that its secondary structure likely consists of two transmembrane regions, six leucine repeats, one low repetition region, and one protein kinase domain (Figure 3). The secondary protein structure of the tested citrus taxa did not reveal significant differences. Phylogenetic analysis showed that CsBAK1 shared high homology with BAK1 (Figure 4).

Figure 3.
Secondary structure of BAK1. LRR: leucine-rich repeats motif; S_TKc: Tyrosine kinase, catalytic domain.

Figure 4.
Phylogenetic analysis of BAK1 in different citrus species.
3.4. Transient Expression of CsBAK1 in ‘Bingtang’ Sweet Orange Leaves
Disease symptom development was observed in CsBAK1 leaves every day after inoculation with Xcc, and the bacterial load of Xcc in inoculated leaves was quantified at 4 and 6 dpi. The most severe symptoms appeared around the injection site, producing a large number of disease spots. When A. tumefaciens containing the BAK1 gene expression vector was infiltrated into inoculated leaves, the symptoms were much reduced, with only sporadic disease spots developing on the leaf surface. The pathogen load in leaves was consistent with the observed symptom severity. The number of canker bacteria per unit leaf area was highly correlated with the severity of symptoms at 4 and 6 dpi. The leaves infiltrated with the BAK1 expression vector presented mild symptoms and the bacterial content was significantly lower than that of the control, indicating that BAK1 likely induced a bacteriostatic effect (Figure 5 and Figure 6).
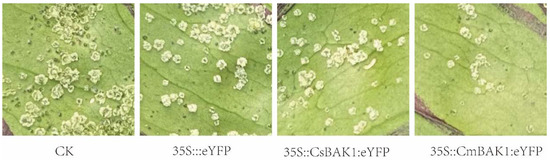
Figure 5.
Leaf symptoms after transient expression of BAK1. CK: control injected with buffer solution. 35S::eYFP: control injected with Agrobacterium of empty vector. 35S::CsBAK1::eYFP: leaves injected with Agrobacterium of empty vector 35S:: CsBAK1::eYFP. 35S::CmBAK1::eYFP leaves injected with Agrobacterium of empty vector 35S::CmBAK1::eYFP.
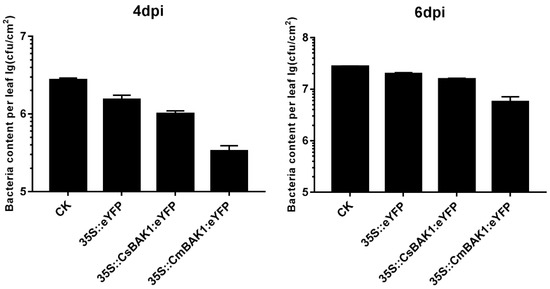
Figure 6.
Xcc growth in each leaf after transient overexpression of BAK1. CK: control injected with buffer solution. 35S::eYFP: control injected with Agrobacterium of empty vector. 35S::CsBAK1::eYFP: leaves injected with Agrobacterium of empty vector 35S::CsBAK1::eYFP. 35S::CmBAK1::eYFP leaves injected with Agrobacterium of empty vector 35S::CmBAK1::eYFP.
3.5. Analysis of the BAK1 Promoter Region
To analyze the crucial regions of the BAK1 gene promoter, BAK1 gene promoter sequences were retrieved from resequencing data. 2000 bp upstream of the ATG start codon was considered to contain the promoter sequence. Comparative analysis showed that the promoter sequences were quite different. Moreover, there were correlative differences between the different promoter sequences and Xcc resistance.
Using PLACE (http://www.dna.affrc.go.jp/PLACE/, accessed on 21 October 2021) software, possible cis-acting elements in the BAK1 gene promoter were predicted. Here, we used the susceptible citrus germplasm (‘Bingtang’ sweet orange) and wild citron, resistant citrus (American citron and citron C-05). Sweet orange is a commercial variety cultivated in large quantities and is susceptible to disease. American citrate and wild citrate are closely related to citrate C-05, and thus can eliminate the influence of differences in genetic background. To analyze the crucial regions of the BAK1 gene promoter, we identified differences in the cis-acting elements of the promoter. The cis-acting element TCT-motif was different between resistant and susceptible citrus (Table 7).

Table 7.
Cis-acting elements and functions of the BAK1 promoter. BTC: ‘Bingtang’ sweet orange; YSJY: Wild citron; MGJY: American citron; JY C-05: Citron C-05.
The BAK1 gene promoter can be induced by the citrus canker bacteria. In GUS reporter assays, it was observed that when the promoter pCs-BAK1 of ‘Bingtang’ sweet orange was expressed, no blue spots developed in the leaves of citrus inoculated with Xcc, whereas when that of Citron C-05 was expressed, a large number of blue spots appeared on the leaves (Figure 7), suggesting that the promoter pCs-BAK1 of sweet orange could not be activated by Xcc, while that of Citron C-05 could. To identify the core region of promoter driven activity, plant expression vectors with truncated 5 ends were designed and constructed according to the distribution of promoter core elements (Figure 7). The constructed vectors were transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens EHA105. The promoter activity was verified by GUS staining after transient expression in citrus leaves. From test of promoter 5′ deletions, it was found that the core region of BAK1 promoter activity was located between 2000 bp and 1161 bp.
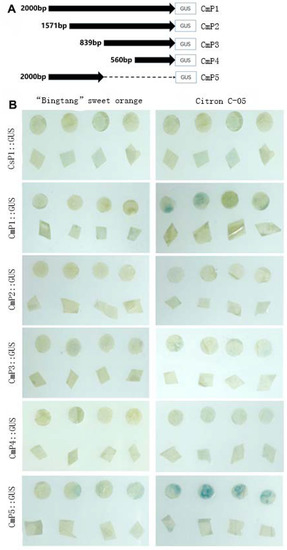
Figure 7.
GUS expression analysis of transiently expressed truncated BAK1 promoters. (A) Schematic representation of the deletion promoter constructs. (B) GUS staining assay of sweet orange leaves upon ectopic expression of the promoter: GUS post inoculation with Xcc. Circular section: treatment; Triangle: control. CmP1: The full-length CmBAK1 gene promoter (−2000 bp to +0 bp); CmP2: (−1571 bp to −0 bp); CmP3: (−839 bp to −0 bp); CmP4: (−560 bp to −0 bp); CmP5: (−2000 bp to −1161 bp).
3.6. Identification of BAK1 Promoter Binding Proteins
To identify proteins that can bind to the BAK1 promoter region, the 426 bp fragment mentioned above was used as a bait to screen transformants from a cDNA library generated from the leaves of plants infected with PGADT for 24 h by the yeast one-hybrid (Y1H) screening system (Figure 8). The monoclonal yeast plasmid of primary screening sequencing was retransformed into baited yeast. Most of the primary screening clones could not produce single colonies on the screening medium, but the plasmid of the growing colony was sequenced. After comparing the sequences in the NCBI database, these genes were named respectively. The transcription factor found to interact with the BAK1 promoter was CmRAP2-13.

Figure 8.
Screening of cDNA library of Citron C-05. (A) Y1HGold[pBait-AbAi] yeast cells were transformed with a prey vector (CmP5); (B) Y1HGold[pBait-AbAi] yeast cells were transformed with a prey vector containing the transcription factor fused to a GAL4 activation domain; (C) Preliminary screening and rescreening; (D) PCR was used to detect the inserted fragment (containing the transcription factor) in the product sequencing alignment.
All the selected transcription factors and promoters grew well on medium free of basiditin, but differences were found after addition of the selected concentration of basiditin. Among the promoter fragments of BAK1, the fragment of Citron C-05 could interact with transcription factor CmRAP2-13 and permit colony growth, whereas the fragment of the ‘Bingtang’ sweet orange promoter could not (Figure 9).
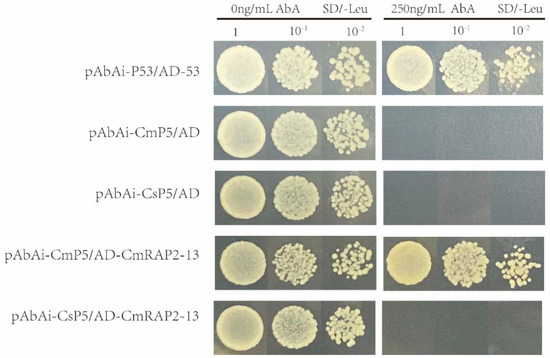
Figure 9.
Promoter interactions with selected transcription factors. TFs (RAP2-13) bind to the BAK1 promoter in yeast. Bait strain Y1HGold[pBait-AbAi] yeast cells were transformed with a prey vector containing RAP2-13 fused to a GAL4 activation domain. Cells were grown in liquid media to OD600 of 1 (100) and diluted in a 10× dilution series (10−1 to 10−3). For each dilution, 10 μL was spotted on media selecting for both plasmids (SD/−Leu) and selecting for the interaction (SD/−Leu/AbA250), supplemented with 100 ng mL−1 AbA to suppress background growth.
3.7. RAP2-13 Gene Expression in Citrus Leaves
Quantitative analysis showed that the expression of RAP2-13 was significantly up-regulated in resistant germplasm at 6 dpi with Xcc and peaked at 10 dpi, whereas it was not significantly up-regulated in susceptible genotypes (Figure 10). The expression of RAP2-13 induced by the citrus canker pathogen indicated that RAP2-13 plays a role in the resistance of Citron C-05 and other resistant germplasm to Xcc.
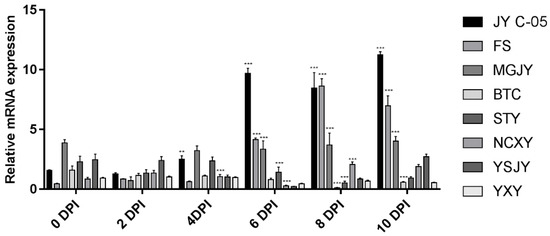
Figure 10.
Relative expression levels of transcription factor RAP2-13. ** and *** indicated significant differences (p < 0.05, respectively). BTC: ‘Bingtang’ sweet orange; STY: Pomelo; NCXY: Nanchuan citron; YSJY: Wild citron; YXY: Round citron; MGJY: American citron; FS: Finger Citron; JY C-05: Citron C-05.
4. Discussion
Plants have developed a sophisticated innate immune response that can quickly sense and defend against pathogens and limit their proliferation [19,20]. Compared to the immune systems of animals, plants lack mobile defence cells and adaptive immune systems. Instead, plants have evolved their innate immune systems to recognize various molecules produced by pathogens or plant cells infected with pathogens, and subsequently activate defensive responses. These microbial molecules are called pathogen-associated molecular patterns PAMPs [21,22,23]. The receptor kinase BAK1/SERK3 and its approximate BAK1-like protein 1 (BKK1/SERK4) act as receptors for LRR-RLK type pattern recognition responses (PRRs), such as flagellin receptor FLS2 [8] and the bacterial extension factor EF-TU receptor EFR [24]. Biochemical and structural analysis showed that bacterial flagellin epitopes flg22 induced the formation of the FLS2-BAK1 heterocomplex within seconds through direct interaction with LRR domains of FlS2 and BAK1. The C-terminal fragment of flg22 seems to be the molecular glue of the FLS2-BAK1 complex [25]. In this study, BAK1 in the resistant citrus cultivars Citron C-05, Finger citron, and American citron became highly expressed at 4 dpi with Xcc, with expression peaking at 8 dpi. Leaves injected with BAK1 expression vector harboring Agrobacterium presented mild symptoms and the bacterial content of inoculated Xcc was significantly lower than that of the control, indicating that BAK1 exerted a bacteriostatic effect. Sequence analysis and protein structural analysis showed that both BAK1 proteins contained multiple LRR structures, which may be involved in the PTI response. Formation of this core receptor recognized by flg22 leads to trans-phosphorylation of both proteins, which is critical for mediating downstream signaling [25,26]. For BAK1 and CERK1 coreceptors, their kinase activity is essential for mediating downstream signals [27,28].
The induced plant defence response is the result of the combined action of inducer promoters, various relevant cis-regulatory elements, signal transduction pathways, and pathogen-specific responses [29]. Gene promoters induced by pathogen elicitors or pathogen attack are heretofore referred to as “pathogen-sensitive promoters” or “pathogen-induced promoters” [30]. The regulatory mechanisms of these promoters also differ depending on the presence of pathogens and specific regulatory elements. Several genes and their promoters play crucial roles in jasmonic acid-mediated defence signaling pathways against pathogen attack. The findings of Zhou et al. [31] showed that Xoo stimulated the inhibition of JA biosynthesis through “SAPK10-WRKY72-AOS1” module infection, leading to increased susceptibility to Xoo. The key to promoter regulation lies in the transcriptional levels of downstream regulatory gene expression, and the role of promoters in the process of acquiring resistance in plants infected with pathogenic microorganisms has been studied. In this study, we cloned the BAK1 gene promoter of the susceptible ‘Bingtang’ and resistance Citron C-05 sweet orange cultivars, analyzed the sequence of the promoter in the resistant germplasm, and analyzed the cis-acting elements of the promoter, including WRE3, CCAAT-box, MYB recognition site, G-box, W box and ABRE. The cis-acting element TCT-motif was different between resistant and susceptible citrus. However, whether the differences in these components cause the differences in promoter activity needs to be further investigated.
In the present study, CmRAP2-13 was identified as a transcriptional activator of CmBAK1. CmRAP2-13 is a member of the AP2/ERF transcription factor family, which directly interacts with cis-acting elements such as GCC-box on target gene promoters [32]. Studies have shown that ERF2 promoter-binding transferrin transcription factors can positively regulate the production of plant disease resistance proteins in Streptomyces attenuatum, and this protein plays an important role in Streptomyces infection [33]. The AP2/ERF superfamily transcription factors regulate many processes in plant development and play an important role in hormone regulation and stress responses. The spatiotemporal expression of the CmRAP2-13 transcription factor regulated by the citrus canker pathogen exhibited differences between ‘Bingtang’ and Citron C-05 sweet orange cultivars, and our promoter analysis also found that there were different loci.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we identified the transcription factor CmRAP2-13 plays an important role in resistance to the citrus canker pathogen Xanthomonas citri subspecies citri (Xcc). In response to Xcc invasion, CmRAP2-13 stimulates a resistance response by directly binding to the CmBAK1 promoter to activate CmBAK1 expression. Our findings help to elucidate the regulatory mechanism of BAK1 gene in Xcc resistance and expand the current understanding of the function of BAK1 in plant pathogen defences.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.W., M.Z., Y.L., D.L., X.M. and Z.D.; Data curation, Q.W., M.Z., Y.L., D.L., X.M. and Z.D.; Formal analysis, Q.W., M.Z. and Y.L.; Investigation, Q.W., M.Z. and Y.L.; Methodology, Q.W., M.Z. and Y.L.; Resources, Q.W., M.Z. and Y.L.; Software, Q.W.; Supervision, Q.W. and M.Z.; Visualization, Q.W., M.Z. and Y.L.; Writing—original draft, Q.W., M.Z. and Y.L.; Writing—review & editing, Q.W., M.Z., Y.L., D.L., X.M. and Z.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Project of International Cooperation and Ex-change of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31720103915).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rukshana, N.; Popy, B.; Medhi, K.K. Citrus Canker: Developments down the lane. Ann. Plant Soil Res. 2020, 22, 396–404. [Google Scholar]
- Gottwald, T.R.; Hughes, G.; Graham, J.H.; Sun, X.; Riley, T. The citrus canker epidemic in Florida: The scientific basis of regulatory eradication policy for an invasive species. Phytopathology 2001, 91, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lúcia, B.C.; Caio FC, Z.; Luiz, L.S.; Carlos, R.P. Hexyl gallate for the control of citrus canker caused by Xanthomonas citri subsp citri. Microbiol. Open 2020, 9, e1104. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, J.D.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 23–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.; Nicholas, P.; Nicholas, N.; Xiao, L.J.; John, M.H.; Xing, H.Z. Genomic Analysis for Citrus Disease Detection. OBM Genet. 2021, 5, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Febres, V.J.; Jones, J.B.; Moore, G.A. A survey of FLS2 genes from multiple citrus species identifies candidates for enhancing disease resistance to Xanthomona scitri ssp. citri. Hortic. Res. 2016, 3, 16022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding-li, L.; Xiao, X.; Guo, W. Production of transgenic ‘anliucheng’ sweet orange (Citrus sinensis Osbeck) with Xa21 gene for potential canker resistance. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 2370–2377. [Google Scholar]
- Domínguez-Ferreras, A.; Kiss-Papp, M.; Jehle, A.K.; Felix, G.; Chinchilla, D. An Overdose of the Arabidopsis Coreceptor Brassinosteroid Insensitive1-Associated Receptor Kinase1 or Its Ectodomain Causes Autoimmunity in a Suppressor of Bir1-1-Dependent Manner. Plant Physiol. 2015, 168, 1106–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.A.; Prochnik, S.; Jenkins, J.; Salse, J.; Hellsten, U.; Murat, F.; Perrier, X.; Ruiz, M.; Scalabrin, S.; Terol, J. Sequencing of diverse mandarin, pummelo and orange genomes reveals complex history of admixture during citrus domestication. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, V.; Vielle-Calzada, J.P.; Hartog, M.V.; Schmidt, E.D.; Boutilier, K.; Grossniklaus, U.; de Vries, S.C. The Arabidopsis somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 1 gene is expressed in developing ovules and embryos and enhances embryogenic competence in culture. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinchilla, D.; Zipfel, C.; Robatzek, S.; Kemmerling, B.; Nurnberger, T.; Jones, J.D.; Felix, G.; Boller, T. A flagellin-induced complex of the receptor FLS2 and BAK1 initiates plant defence. Nature 2007, 448, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heese, A.; Hann, D.R.; Gimenez-Ibanez, S.; Jones, A.M.; He, K.; Li, J.; Schroeder, J.I.; Peck, S.C.; Rathjen, J.P. The receptor-like kinase SERK3/BAK1 is a central regulator of innate immunity in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12217–12222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmerling, B.; Nürnberger, T. Brassinosteroid-independent functions of the BRI1-associated kinase BAK1/SERK3. Plant Signal Behav. 2008, 3, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vert, G. Plant signaling: Brassinosteroids, immunity and effectors are BAK1. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, R963–R965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.N.; Hu, C.H.; Xu, L.; Zhang, J.Y.; Yang, L.; Li, D.Z.; Li, N.; Liu, L.P. Strategies for citrus to acquire resistance to canker disease. Proc. Int. Soc. Citric. 2010, 2, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H.Y.; Zhao, M.M.; Xu, J.; Tan, L.M.; Han, J.; Li, D.Z.; Wang, M.J.; Xiao, S.Y.; Ma, X.F.; Deng, Z.N. Citron C-05 inhibits both the penetration and colonization of Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri to achieve resistance to citrus canker disease. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang Jl Ji, H.G.; Sossod, D.; Lie, T.; Frommerd, W.B.; Bing, Y.; Frank FWhiteb Wang, N.; Jones, J.B. Lateral organ boundaries 1 is a disease susceptibility gene for citrus bacterial canker disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 114, E521–E529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, R.A.; Kavanagh, T.A.; Bevan, M.W. GUS fusions: Beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 3901–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, P.N.; Rathjen, J.P. Plant immunity: Towards an integrated view of plant-pathogen interactions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangl, J.L.; Horvath, D.M.; Staskawicz, B.J. Pivoting the plant immune system from dissection to deployment. Science 2013, 341, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, H.; Albert, I.; Reinhard, A. Nurnberger, Immune receptor complexes at the plant cell surface. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 20, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couto, D.; Zipfel, C. Regulation of pattern recognition receptor signalling in plants. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 16, 537–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saijo, Y.; Loo, E.P.; Yasuda, S. Pattern recognition receptors and signaling in plant-microbe interactions. Plant J. 2018, 93, 592–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, M.; Schwessinger, B.; Albrecht, C.; Chinchilla, D.; Jones, A.; Holton, N.; Malinovsky, F.G.; Tor, M.; de Vries, S.; Zipfel, C. The A rabidopsis leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinases BAK1/SERK3 and BKK1/SERK4 are required for innate im m unity to hem ibiotrophic and biotrophic pathogens. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 2440–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Han, Z.; Tang, J.; Hu, Z.; Chai, C.; Zhou, B.; Chai, J. Structure reveals that BAK1 as a co-receptor recognizes the BRI1-bound brassinolide. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, B.; Mentzel, T.; Jehle, A.K.; Mueller, K.; Beeler, S.; Boller, T.; Felix, G.; Chinchilla, D. Rapid heteromerization and phosphorylation of ligand-activated plant transmembrane receptors and their associated kinase BAK1. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 9444–9451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwessinger, B.; Bahar, O.; Thomas, N.; Holton, N.; Nekrasov, V.; Ruan, D.; Canlas, P.E.; Daudi, A.; Petzold, C.J.; Singan, V.R.; et al. Transgenic expression of the dicotyledonous pattern recognition receptor EFR in rice leads to ligand dependent activation of defense responses. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004809. [Google Scholar]
- Petutschnig, E.K.; Jones, A.M.; Serazetdinova, L.; Lipka, U.; Lipka, V. The lysin motif receptor-like kinase (LysM-RLK) CERK1 is a major chitin-binding protein in Arabidopsis thaliana and subject to chitin-induced phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 28902–28911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazarei, M.; Teplova, I.; Hajimorad, M.R.; Stewart, C.N. Pathogen phytosensing: Plants to report plant pathogens. Sensors 2008, 8, 2628–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, O.G.; Ibragimova, S.S.; Kochetov, A.V. Simple data base to select promoters for plant transgenesis. Transgenic Res. 2012, 21, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.M.; Zhang, Y. Plant immunity: Danger perception and signaling. Cell 2020, 181, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakoby, M.; Weisshaar, M.J.B.; Dröge-Laser, W.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J.; Tiedemann, J.; Kroj, T.; Parcy, F. bZIP transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Ma, L.; Wang, W.; Sun, H.; Wang, L.; Baldwin, I.T.; Wu, J. An ERF2-like transcription factor regulates production of the defense sesquiterpene capsidiol upon Alternaria alternata in-fection. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 5895–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).