Biocontrol of Large Patch Disease in Zoysiagrass (Zoysia japonica) by Bacillus subtilis SA-15: Identification of Active Compounds and Synergism with a Fungicide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
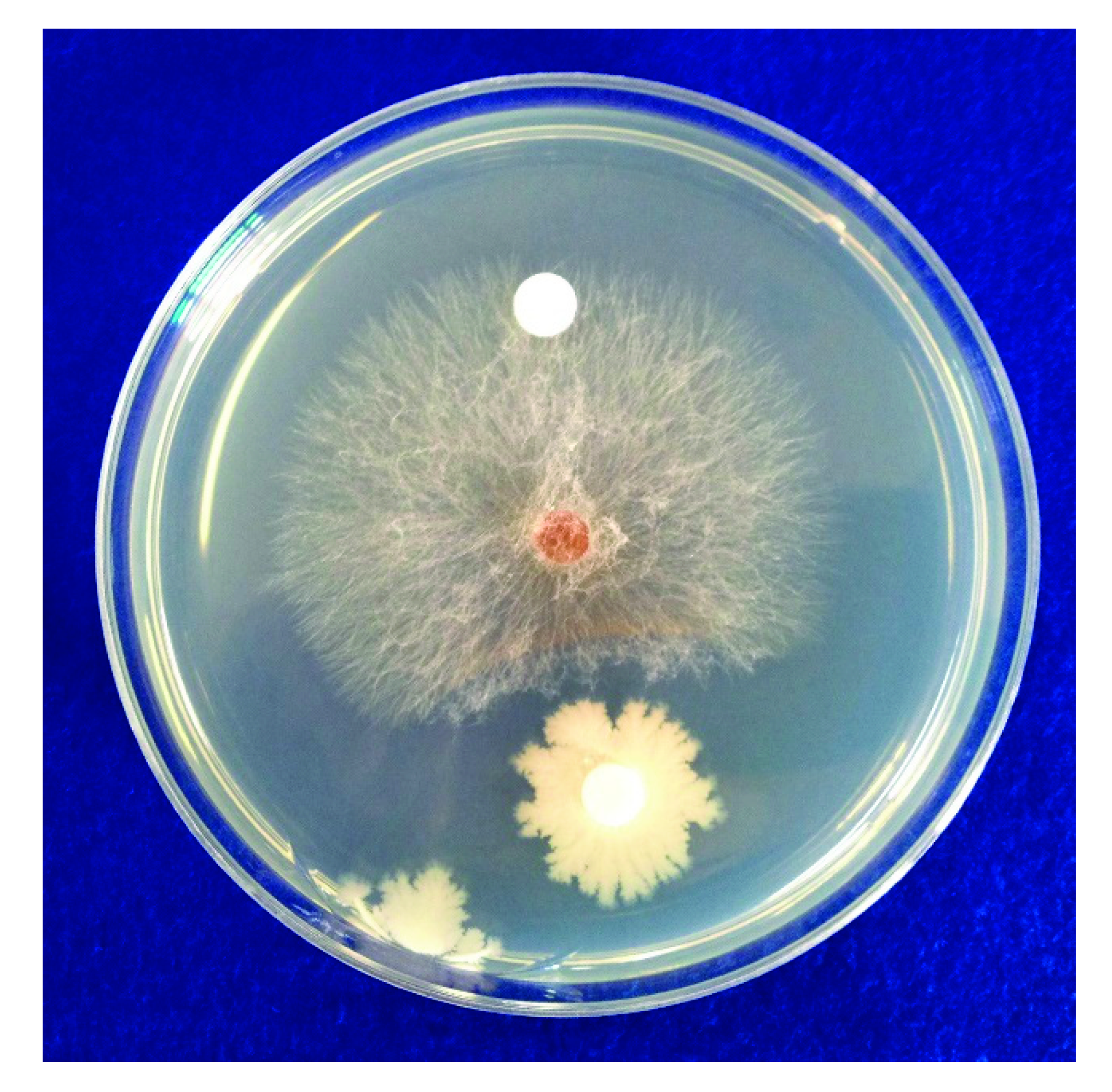
2.1. In Vitro Antifungal Activity of B. subtilis SA-15
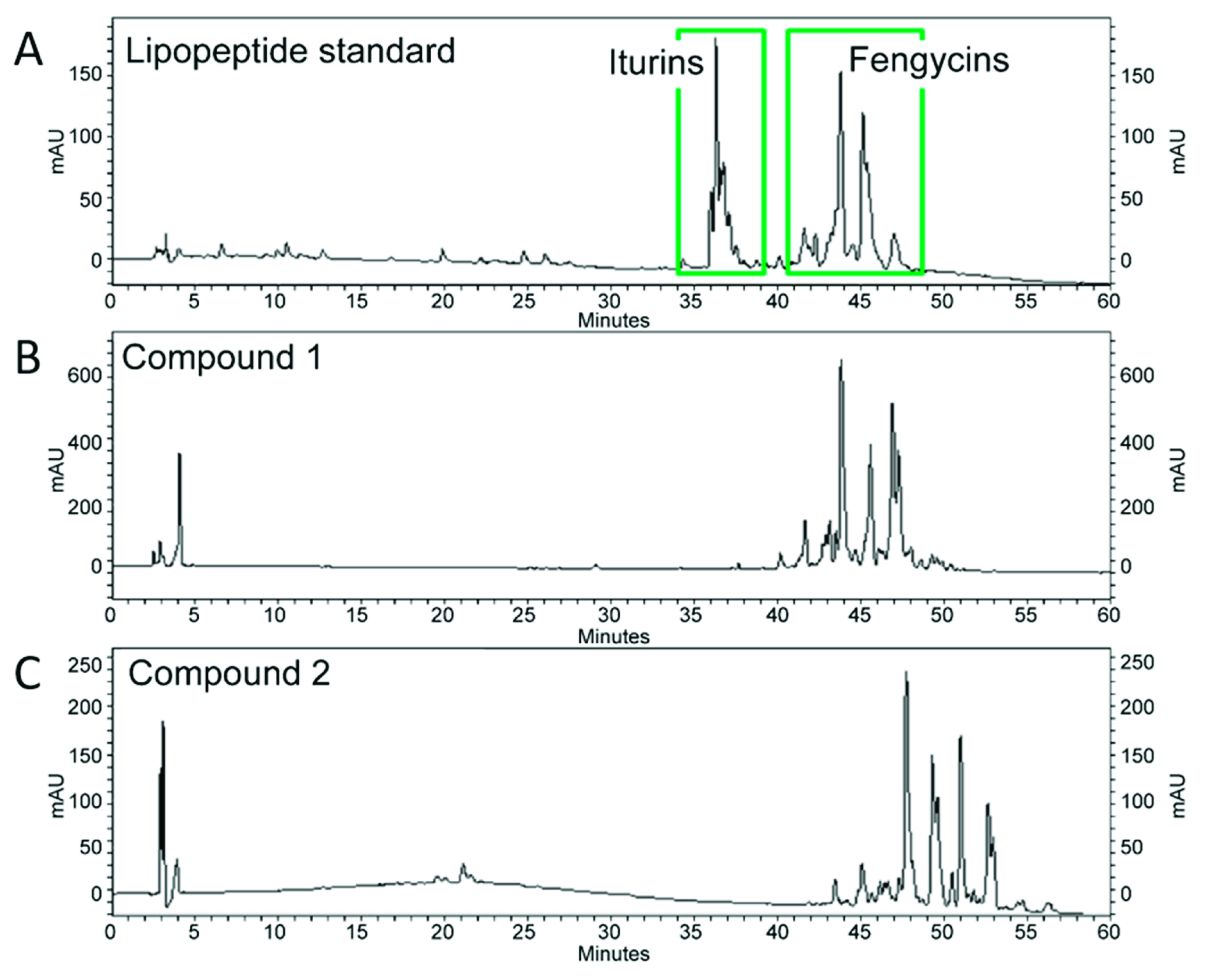
2.2. Purification of Antifungal Compound Fractions from B. subtilis SA-15
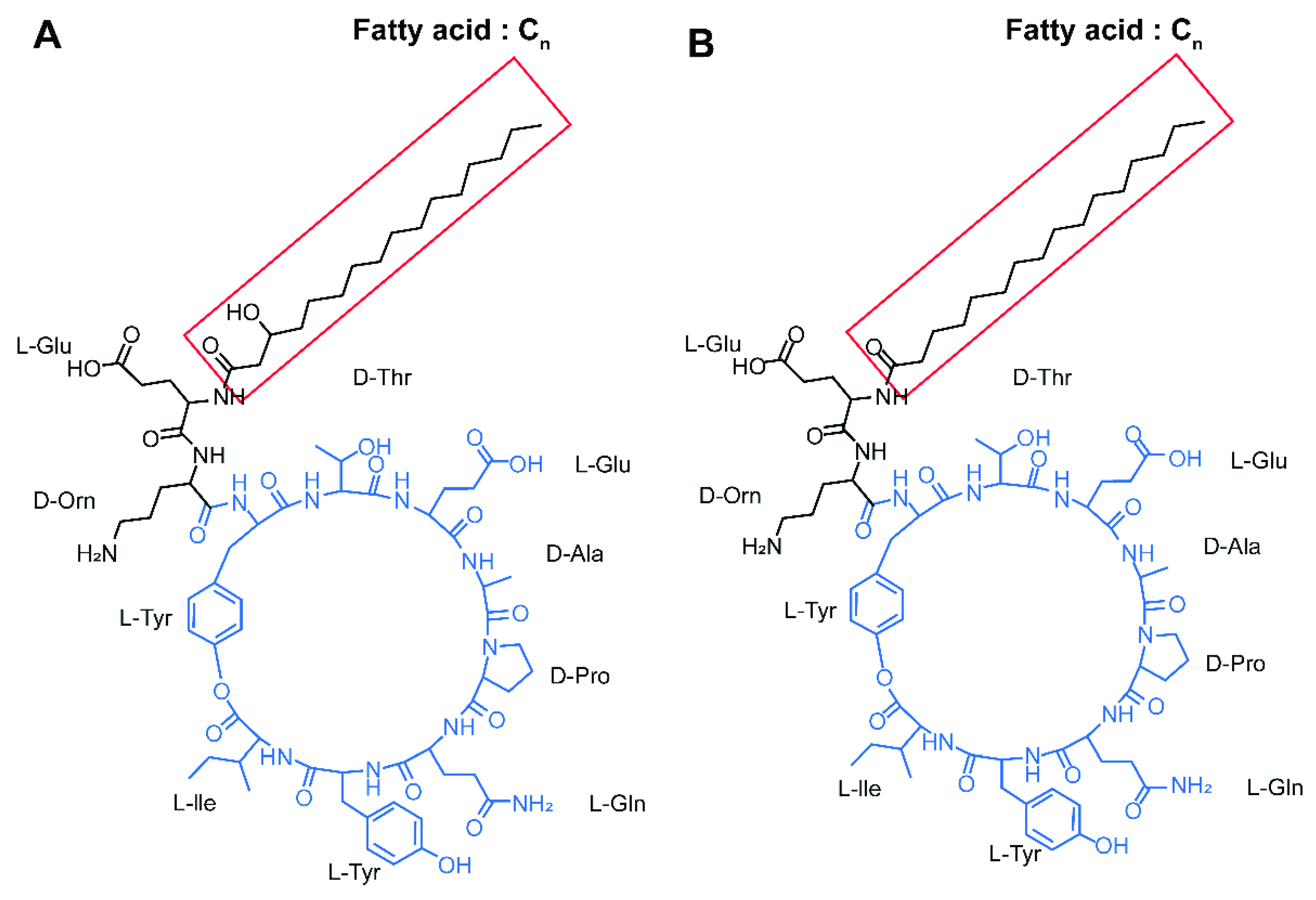
2.3. Identification of Lipopeptide Compounds from B. subtilis SA-15
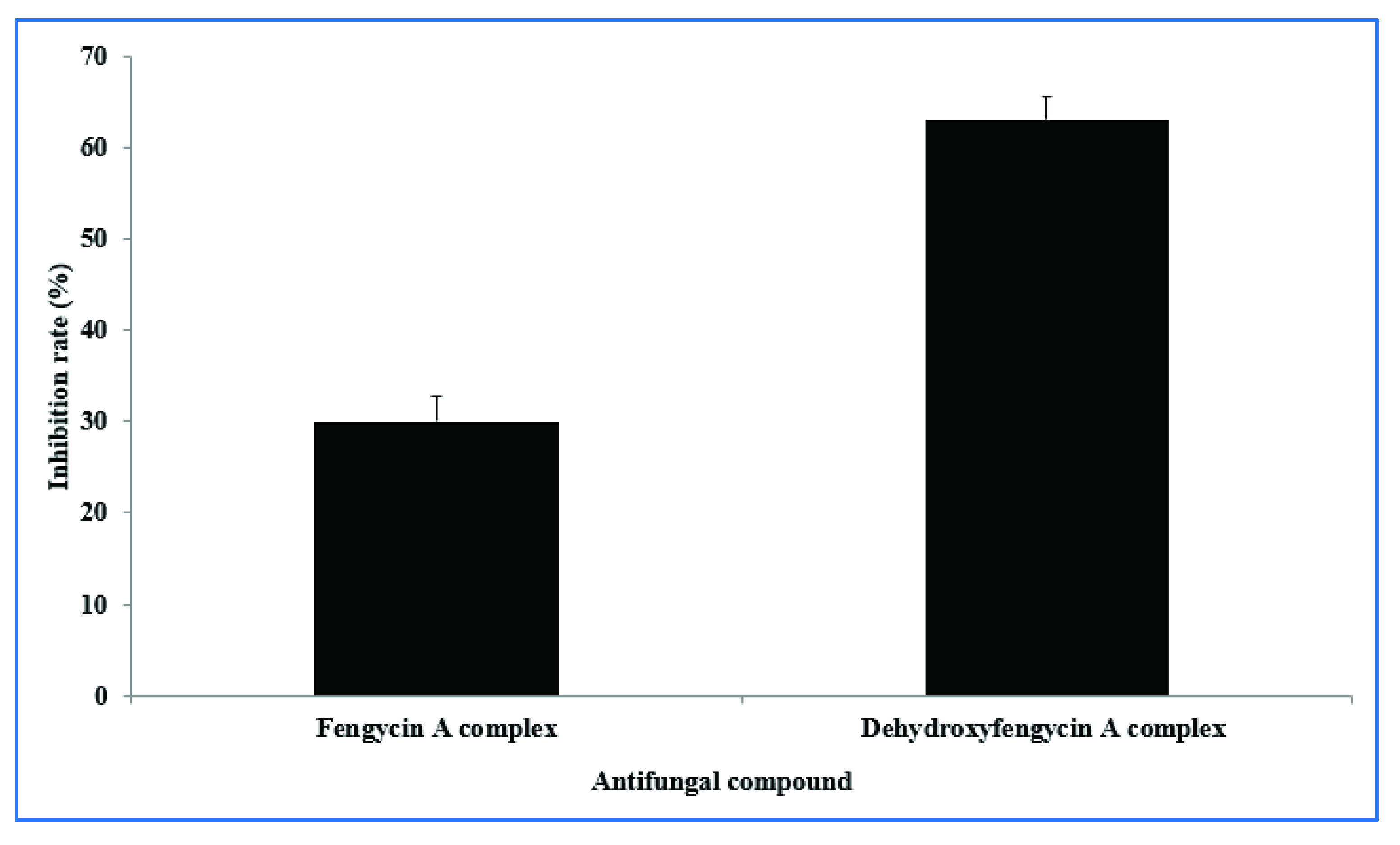
2.4. In Vitro Inhibition Effects of Compounds 1 and 2 on R. solani Growth
2.5. In Vivo Control of Large Patch Disease with B. subtilis SA-15
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Antifungal Activity of B. subtilis SA-15 and Identification of Antifungal Compounds
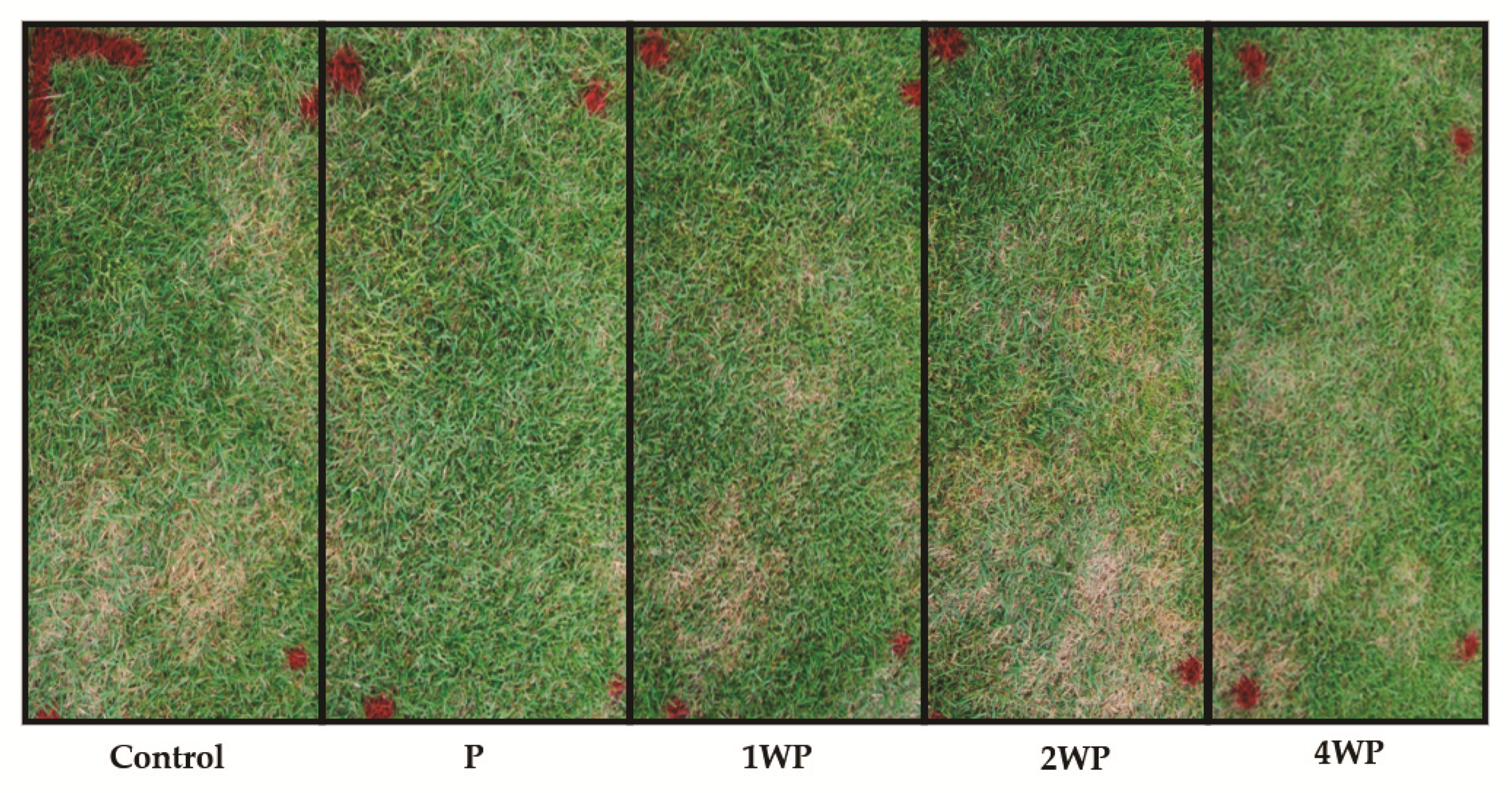
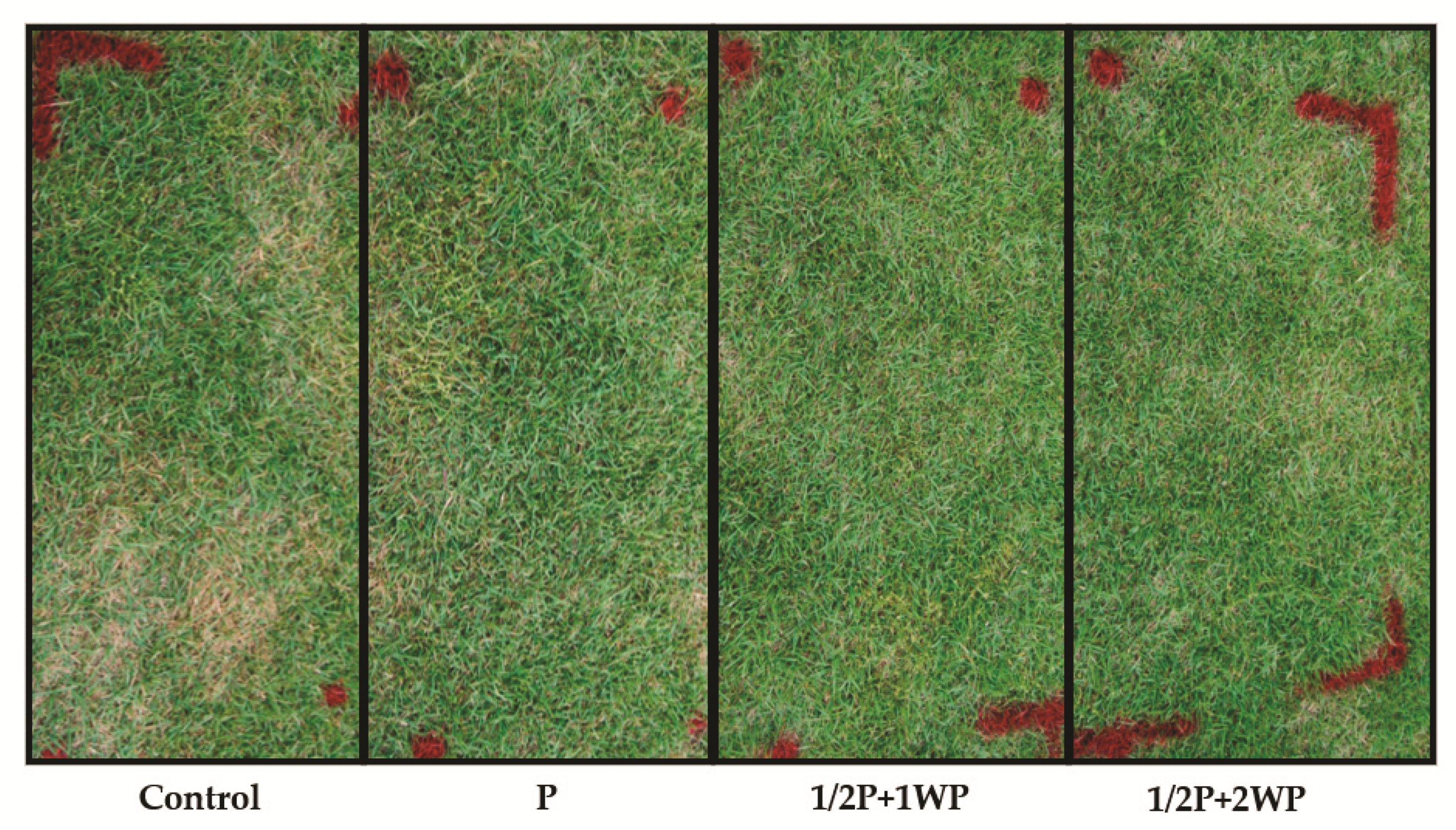
3.2. In Vivo Control of Large Patch Disease after Applying B. subtilis SA-15
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, D.H.; Park, N.I.; Choi, S.H.; Park, K.W.; Kim, J.W.; Kwak, Y.S.; Lee, J.J. Composition and invading problem of interspecies turfgrass on golf course. Korean J. Weed Sci. 2012, 32, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shim, G.Y.; Kim, H.K. Identification and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia spp. isolated from turfgrasses in golf course in Korea. Korean Turfgrass Sci. 1995, 9, 235–252. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, Y.T.; Kim, S.T.; Kim, I.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, H.J.; Shim, K.Y.; Yang, S.W.; Lee, J.J.; Ham, S.K. Standard and Practice for Management in Golf Course; KTRI: Seongnam, Korea, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, G.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, H.K. Occurrence of Rhizoctonia blight of zoysiagrass in golf course in Korea. Korean J. Plant Pathol. 1994, 10, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu, S.S.; Huang, Q.; Carrow, R.N.; Raymer, C.P. Laccase mediated changes in physical and chemical composition properties of thatch layer in creeping bentgrass (Agrostis stolonifera L.). Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 64, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Ham, S.K. Screening of cellulose decomposing microorganisms for functional improvement for SCB (slurry composting and biofiltering) liquid fertilizer. Asian J. Turfgrass Sci. 2011, 25, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Ma, K.W.; Lee, G.J. Antagonistic mechanisms and culture conditions of isolated microbes applied for controlling large patch disease in zoysiagrass. Hort. Sci. Technol. 2015, 33, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Borriss, R. Use of plant-associated Bacillus strains as biofertilizers and biocontrol agents. In Bacteria in Agrobiology: Plant Growth Response; Maheshwari, D.K., Ed.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 41–76. [Google Scholar]
- Borriss, R.; Chen, X.H.; Rückert, C.; Blom, J.; Becker, A.; Baumgarth, B.; Fan, B.; Pukall, R.; Schumann, P.; Sproer, C.; et al. Relationship of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens clades associated with strains DSM 7T and FZB42T: A proposal for Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. amyloliquefaciens subsp. nov. and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum subsp. nov. based on complete genome sequence comparisons. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 1786–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, B.Y.; Ahn, J.H.; Song, J.Y.; Seol, Y.J.; Kim, W.G.; Weon, H.Y. Draft genome sequence of the biocontrol bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain M27. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 6934–6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.I.; Ryu, J.; Kim, Y.H.; Chi, Y.T. Production of biosurfactant lipopeptides iturin A, fengycin, and surfactin A from Bacillus subtilis CMB32 for control of Colletotrichum gloeosprioides. J. Mirobio. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.H. Development and Application of New Microbial Agent Bacillus subtilis HSB904. Master’s Thesis, Korean National Open University, Seoul, Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Beard, J.B. Turfgrass: Science and Culture; Prentice Hall Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, G.Y.; Kim, H.K. Control of large patch caused by Rhyzoctonia solani AG 2-2 by combined application of antagonists and chemicals in golf course. Kor. Turfgrass Sci. 1999, 13, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Lee, K.S.; Lee, G.J. Strategies of eco-friendly turfgrass management and resource recycling for a sustainable golf course. Weed Turf. Sci. 2019, 8, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Shim, G.Y.; Kim, K.S. Inhibition of in vitro growth of three soil-borne turfgrass diseased by antagonistic bacteria from composted from liquid manure. Hort. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, G.J. Isolation and selection of functional microbes for eco-friendly turfgrass management in golf course from livestock manure compost. Weed Turf. Sci. 2017, 6, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.Y.; Kwark, S.N.; Lee, G.J. Isolation and selection of antagonistic microbes for biological control of zoysiagrass large patch disease. Hort. Sci. Thechnol. 2013, 31, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ryu, J.Y.; Jin, R.D.; Kim, Y.W.; Lee, H.B.; Kim, K.Y. Biocontrol of damping-off (Rhizoctonia solani) in cucumber by Trichoderma asperellum T-5. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fert. 2006, 39, 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y.; Mao, Z.C.; Wang, Y.H.; Wu, Y.X.; He, Y.Q.; Long, C.L. Diversity and active mechanism of fengycin-type cyclopetides from Bacillus subtilis XF-1 against Plasmodiophora brassicae. J. Mirobiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 23, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, P.; Hbid, C.; Destain, J.; Razafindralambo, H.; Paquot, M.; de Pauw, E.; Thonart, P. Optimization of biosurfactant lipopeptide production from Bacillus subtilis S499 by Placket-Burman design. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1999, 77–79, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Bie, X.M.; Lv, F.X.; Zhao, H.Z.; Lu, Z.X. Antifungal activity and mechanism of fengycin in the presence and absent of commercial surfactin against Rhizopus stolonifer. J. Microbial. 2011, 49, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimon, L.; Peypoux, F.; Wallach, J.; Michel, G. Effect of the lipopeptide antibiotic, iturin A, on morphology and membrane ultrastructure of yeast cells. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1995, 128, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeriouh, H.; de Vicente, A.; Pérez-García, A.; Romero, D. Surfactin triggers biofilm formation of Bacillus subtilis in melon phylloplane and contributes to the biocontrol activity. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2196–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Raza, W.; Shen, Q.; Huang, Q. Antifungal activity of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens NJN-6 volatile compounds against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 5942–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Li, Q.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, N.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R. Responses of beneficial Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9 to different soil borne fungal pathogens through the alteration of antifungal compounds production. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulimushi, P.Z.; Arias, A.A.; Franzil, L.; Steels, S.; Ongena, M. Stimulation of fengycin-type antifungal lipopeptides in Bacillus amyloliquefaciencs in the presence of the maize fungal pathogen Rhizomucor variabilis. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falardeau, J.; Wise, C.; Novitsky, L.; Avis, T.J. Ecological and mechanistic insights into the direct and indirect antimicrobial properties of Bacillus subtilis lipopeptides on plant pathogens. J. Chem. Ecol. 2013, 39, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deleu, M.; Paquot, M.; Mylander, T. Effect of fengycin, a lipopeptide produced by Bacillus subtilis, on model membranes. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eeman, M.; Pegado, L.; Dufrêne, Y.F.; Paquot, M.; Deleu, M. Influence of environmental conditions on the interfacial organization of fengycin, a bioactive lipopeptide produced by Bacillus subtilis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 329, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avis, T.J. Antifungal compounds that target fungal membranes: Applications in plant disease control. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2007, 29, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balleza, D.; Alessandrini, A.; Beltran Garcia, M.J. Role of lipid composition, physicochemical interactions, and membrane mechanics in the molecular actions of microbial cyclic lipopeptides. J. Membrane Biol. 2019, 252, 131–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebib, H.; Hedi, A.; Rousset, M.; Boudabous, A.; Limam, F.; Sadfi-Zouaoui, N. Biological control of Fusarium foot rot of wheat using fengycin-producing Bacillus subtilis isolated from salty soil. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 8464–8475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, S.P. Microbial detoxification of mycotoxins. J. Chem. Ecol. 2013, 39, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Lee, J.P.; Chang, S.W.; Lee, G.J. Synergistic suppression of bio-sulfur of pencycuron on large patch disease caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG 2-2 (IV) in Zoysia japonica. Weed Turf. Sci. 2019, 8, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Jee, H.J.; Shim, C.K.; Kim, M.J.; Park, J.H.; Han, E.J.; Goo, H.J.; Choi, M.J. Control efficacy of mixed application of microbial and chemical fungicides against powdery mildew of red-pepper. J. Korean Pestic. 2014, 18, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| Peak | Retention Time (min) | Mass (m/z) | Assignment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compound 1 | |||
| 1 | 37.53 | 725 [M+2H]2+, 1449 [M+H]+ | C15fengycinA |
| 2 | 38.91 | 739 [M+2H]2+, 1477 [M+H]+ | C17fengycinA |
| 3 | 39.66 | 732 [M+2H]2+, 1463 [M+H]+ | C16fengycinA |
| 4 | 40.04 | 739 [M+2H]2+, 1477 [M+H]+ | C17fengycinA |
| 5 | 40.98 | 746 [M+2H]2+, 1491 [M+H]+ | C18fengycinA |
| 6 | 42.12 | 753 [M+2H]2+, 1505 [M+H]+ | C19fengycinA |
| 7 | 43.67 | 760 [M+2H]2+, 1519 [M+H]+ | C20fengycinA |
| Compound 2 | |||
| 1 | 38.21 | 732 [M+2H]2+, 1462 [M+H]+ | C17dehydroxyfengycinA |
| 2 | 39.50 | 739 [M+2H]2+, 1476 [M+H]+ | C18dehydroxyfengycinA |
| 3 | 40.65 | 1477 [M+H]+, 1490 [M+H]+ | C18 & C19dehydroxyfengycinA |
| 4 | 41.48 | 746 [M+2H]2+, 1490 [M+H]+ | C19dehydroxyfengycinA |
| 5 | 42.35 | 753 [M+2H]2+, 1504 [M+H]+ | C20dehydroxyfengycinA |
| 6 | 42.96 | 753 [M+2H]2+, 1504 [M+H]+ | C20dehydroxyfengycinA |
| 7 | 44.08 | 760 [M+2H]2+, 1518 [M+H]+ | C21dehydroxyfengycinA |
| 8 | 45.30 | 767 [M+2H]2+, 1532 [M+H]+ | C22dehydroxyfengycinA |
| Treatment 1 | Diseased Area (%) | Control Efficiency (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 August | 7 October | 26 August | 7 October | |
| Control | 12.3 ± 5.1 a 2 | 35.8 ± 1.4 a | - | - |
| P | 2.5 ± 1.4 a | 4.1 ± 2.4 b | 79.9 a | 88.5 a |
| 1WP | 15.3 ±7.3 a | 2.8 ± 1.6 b | 0.0 b | 92.0 a |
| 2WP | 29.2 ± 11.4 a | 17.4 ± 2.2 b | 0.0 b | 51.2 a |
| 4WP | 7.1 ± 1.2 a | 10.7 ± 3.2 b | 41.9 ab | 70.0 a |
| Treatment 1 | Diseased Area (%) | Control Efficiency (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 August | 7 October | 26 August | 7 October | |
| Control | 12.3 ± 5.1 a 2 | 35.8 ± 1.4 a | - | - |
| P | 2.5 ± 1.4 a | 4.1 ± 2.4 b | 79.9 a | 88.5 a |
| 1/2P + WP | 0.5 ± 0.3 a | 0.0 ± 0.0 b | 95.6 a | 100.0 a |
| 1/2P + 2WP | 0.5 ± 0.3 a | 4.1 ± 2.3 b | 100.0 a | 88.6 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-S.; Lee, K.-S.; Kim, H.-G.; Lee, G.-J. Biocontrol of Large Patch Disease in Zoysiagrass (Zoysia japonica) by Bacillus subtilis SA-15: Identification of Active Compounds and Synergism with a Fungicide. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8010034
Kim Y-S, Lee K-S, Kim H-G, Lee G-J. Biocontrol of Large Patch Disease in Zoysiagrass (Zoysia japonica) by Bacillus subtilis SA-15: Identification of Active Compounds and Synergism with a Fungicide. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Young-Sun, Kyo-Suk Lee, Hong-Gi Kim, and Geung-Joo Lee. 2022. "Biocontrol of Large Patch Disease in Zoysiagrass (Zoysia japonica) by Bacillus subtilis SA-15: Identification of Active Compounds and Synergism with a Fungicide" Horticulturae 8, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8010034
APA StyleKim, Y.-S., Lee, K.-S., Kim, H.-G., & Lee, G.-J. (2022). Biocontrol of Large Patch Disease in Zoysiagrass (Zoysia japonica) by Bacillus subtilis SA-15: Identification of Active Compounds and Synergism with a Fungicide. Horticulturae, 8(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8010034







