Abstract
Some tropical species—such as the domesticated Xanthosoma sagittifolium (L.) Schott (Taioba) and Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott (Taro)—have similar phenotypic characteristics, especially in the shape and color of the leaves and petioles which generate uncertainty in their identification for use in human food. This study aimed to analyze the morphological and molecular characteristics of X. sagittifolium and C. esculenta that may help in the popular and scientific identification of these species. The principal morphological characteristics of X. sagittifolium were as follows: leaves with subcoriaceous textures, basal insertion of the petiole, green pseudo-stem in the basal portion with exudate being white and the presence of two collector veins. Distinctive morphological characteristics of C. esculenta were as follows: leaves with velvety textures, peltate insertion of the petiole, pink pseudo-stem in the basal portion with pink exudate and presence of one collector vein. The morphological characteristics that can be used to distinguish Taioba from Taro are the basal petiole insertion of the first, against the petiole insertion near the center of the blade of the latter. Molecular analyses using eight Inter-Simple Sequence Repeat (ISSR) molecular markers simultaneously showed distinctive fingerprints for each of the species. These results contribute to the proper identification of the species used as a food source.
1. Introduction
The Araceae is a family that consists of 109 genera and approximately 2830 species that are widely distributed, mostly in the tropical, subtropical, and temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere [1]. The Araceae family is divided into several subfamilies based on the variation of habitats, disposition, and leaf morphology, the structure of the inflorescence and pollen, floral morphology, anatomy, and chromosome number [2]. Economically, the genera Alocasia, Colocasia, and Xanthosoma of this family are important due to their ornamental use or for the starch obtained from their corms [1]. The species Xanthosoma sagittigolium (L.) Schott is exclusively of Neotropical origin; however, it has been introduced in many tropical areas and cultivated as a food plant in developing countries, and it is found naturalized in many places. Approximately 400 million people worldwide now consume its leaves or corms as a staple food [3,4]. On the other hand, Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott is a cultivated species native to tropical Asia and naturalized throughout the tropics, and is valued as a rich source of easily digestible protein [3,5].
In Brazil, the leaves of the species X. sagittifolium (taioba) and the rhizomes of C. esculenta (taro), both cultivated by family farmers, are used as food in the states of Minas Gerais and Rio de Janeiro [6]. Despite their importance as an energy-rich food and its increased use, there are only a handful of efforts to market their products in the Americas and West and Central Africa, showing the marginalization of these cultivated species and therefore their status as two neglected crops [3,7]. C. esculenta has been traditionally grown in South and Southeast Asia and the Pacific region as a valuable staple food, where it is commonly known as taro, dasheen, eddoe [5,7], true cocoyam, old cocoyam [8], and poi [9]. X. sagittifolium is referred as yautia and tannia (Caribbean), malanga (Cuba), and cocoyam [9]. In sub-Saharan Africa, both species are known as cocoyam, where their staple root/tuber production ranks third in importance after yam and cassava [7].
There is little information regarding the taxonomy of the above-mentioned cultivated species [3]. Lately, a huge database has been developed aiming at improving the taxonomy of Araceae, including data on chromosome number, morphology, and molecular biology [10]. Molecular studies have been useful in establishing genetic differences between species. One mechanism that has had considerable success in helping to identify different taxa is the use of Inter-Simple Sequence Repeat (ISSR) markers [11].
X. sagittifolium (Taioba) and C. esculenta (Taro) are popularly mistaken for one another [5,7] because of their similar phenotypic characteristics, especially in the form and color of the leaves and petioles, which create uncertainty when they are collected for use as food by humans. The research hypothesis is that both species have enough morphological and molecular features that will aid in their characterization. Therefore, this study aimed at the following: (1) to analyze the morphological characteristics of X. sagittifolium and C. esculenta (Araceae) taxa and highlight those that allow easy differentiation in the field, (2) to evaluate and identify molecular ISSR markers that may help in the identification of these species, and (3) to compare these two species morphologically and molecularly with two additional taxa, Xanthosoma violaceum Schott and Xanthosoma undipes (K.Koch & C.D.Bouché) K.Koch.
2. Materials and Methods
Samples of X. sagittifolium and C. esculenta species were obtained from urban (1, 8, 11–14), natural (6, 7), and cultivated (2–5) populations from the states of São Paulo and Minas Gerais (Brazil) (Table 1, Figure 1). Sample data included the sample number, location where they were collected, georeferenced data (GPS), and collection date (Table 1). Additionally, X. violaceum and X. undipes species were also collected from two urban populations to compare morphology and the genetic profile to the target species (Figure 1). For molecular analysis, 150 mg of leaf tissue was sampled from each of the 14 specimens and stored at −20 °C. DNA was extracted following the protocol proposed by Alzate-Marin et al. [12].

Table 1.
Data of specimens studied.
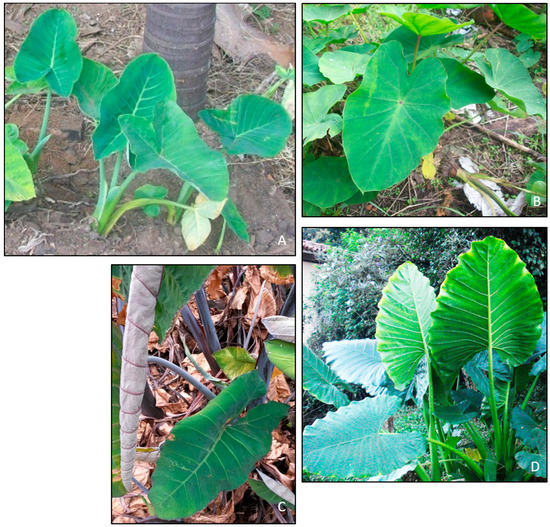

Figure 1.
Images of populations of X. sagittifolium (A), C. esculenta (B), X. violaceum (C), and X. undipes (D), which correspond to samples 11, 12, 10 and 9, respectively (Source: Laboratory of Plant Genetics/University of São Paulo, Campus of Ribeirão Preto, Brazil).
Subsequently, plants were described morphologically according to Acevedo-Rodriguez and Strong [13] (data not shown) and prepared for herbarium material. The exsiccates were deposited in the reference collection of the Herbarium SPFR University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, with the following labels: C. Faleiros, P. Sepulveda, and F. Bonifacio (Table 1).
For the molecular analyses, 15 ISSR markers were evaluated (UBC 1, 2, 813, 820, 834, 845, 851, 858, 860, 862, 864, 866, 885, 886, 897) according to the official list published by the University of British Columbia in Canada (UCB). The amplification products were separated by electrophoresis on 8% polyacrylamide gel. The results were visualized by staining with silver nitrate according to the protocol of Sanguinetti et al. [14]. Fragments of different mobilities were considered as different alleles. Estimates of the size of the resulting amplification products were performed by comparison with a DNA ladder of 50 base pairs (GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK). The polymorphism obtained by the ISSR technique was tabulated as binary according to the presence (1) or absence (0) of bands. Each polymorphic ISSR band was considered a biallelic locus, with an amplifiable allele and a null allele. GenAlEx 6.5 software [15] was used to generate a matrix of genetic distances according to Nei [16] and Nei’s genetic diversity (Ĥe). MEGA 5 software [17] was used to generate a dendrogram of genetic similarity based on the UPGMA algorithm.
3. Results and Discussion
X. sagittifolium exhibited white exudate from the vegetative parts (Figure 2A), green pseudostem (Figure 2B), basal petioles (Figure 2C), leaves with a sagittate form (Figure 2D), two collecting veins at the leaf margin (Figure 2E), and subcoriaceus leaf blades. C. esculenta displayed pink or purple exudates from the vegetative parts (Figure 3A), pink pseudostem (Figure 3B), peltate petioles (Figure 3C), velvety leaf blades (Figure 3D), and one collecting vein in the margin of the leaf (Figure 3E).
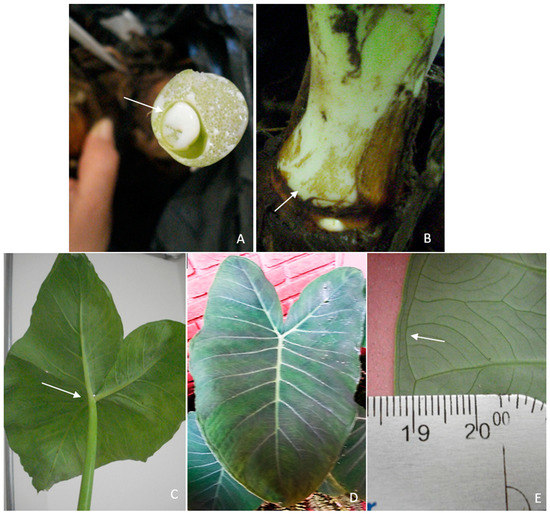

Figure 2.
Images of X. sagittifolium. (A) The white color of exudate in stem (arrow); (B) The green color of the pseudostem (arrow); (C) The basal insertion of the petiole in leaf (arrow); (D) The upper leaf and its sagittate form; (E) The two collecting veins at the leaf margin (arrow) (Source: Laboratory of Plant Genetics/University of São Paulo, Campus of Ribeirão Preto, Brazil).
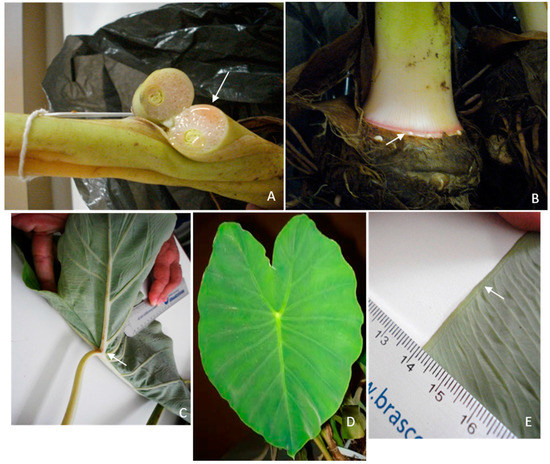

Figure 3.
Images of C. esculenta. (A) The pink color of exudate in stem (arrow); (B) The pink color of the pseudostem (arrow); (C) The position of the petiole near the center of the leaf blade (arrow); (D) The upper leaf with a velvety texture; (E) the collecting vein (arrow). (Source: Laboratory of Plant Genetics/University of São Paulo, Campus of Ribeirão Preto, Brazil).
Insertion of the petiole and the purple underside of the leaf blade, the leaves with revolute margins, purple petioles, and markedly subtriangular basal lobes were characteristics of X. violaceum (Figure 1C). Leaves with involute margins, the apex broadly obtuse to mucronate, and green petioles were features of X. undipes (Figure 1D).
For folk taxonomy, the morphological characteristics that can be used to distinguish Xanthosoma from Colocasia species are from the appreciation of the basal petiole insertion of the first (Figure 2C), against the petiole insertion near the center of the blade of the latter (Figure 3C). The results of the molecular analyses with the 15 ISSR markers show that only one primer did not have any amplification products (UBC 813), while eight primers (UBC 2, 834, 845, 851, 858, 860, 864, 866) produced high-resolution profiles that were selected for the next stage (Figure 4A). From these amplifications, 334 loci were obtained, with an average of 41.75 loci, varying between 22 (UBC 866) and 73 (UBC 2) (Table 2). Of these, 321 (96.11%) exhibited polymorphism and 13 (3.89%) were monomorphic. The results indicated an average of 26.52% genetic diversity among the specimens that were analyzed (Table 2).
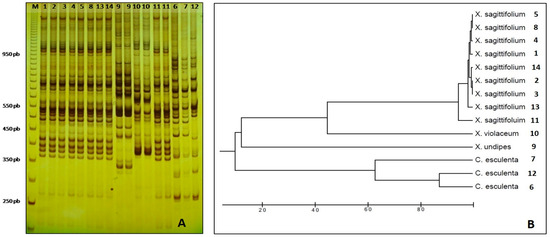
Figure 4.
(A) Non-denatured polyacrylamide gel (8%) showing the amplification products related to the ISSR UBC2. The distinctive fingerprint of each species studied is shown. Column M corresponds to a molecular weight marker (GE Healthcare 50 pb). Lanes 1–5, 8–14, and 11 (amplified in duplicate) correspond to the taxon X. sagittifolium; channel 9 corresponds to X. undipes (amplified in duplicate), channel 10 corresponds to X. violaceum (amplified in duplicate). Lanes 6, 7, and 12 correspond to C. esculenta. (Source: Laboratory of Plant Genetics/University of São Paulo, Campus of Ribeirão Preto, Brazil); (B) Dendrogram based on the UPGMA algorithm showing the genetic similarity of the specimens of the four analyzed species.

Table 2.
Characteristics and sequences of the inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) primers used in the genetic analysis of specimens of four species of Araceae. PL = polymorphic loci, ML = monomorphic loci. Ĥe = Nei Genetic Diversity. R = (A,G), Y = (C,T).
A UPGMA dendrogram was generated based on a genetic similarity matrix (data not shown) which showed groupings of the different species tested (Figure 4B). The analysis by ISSR molecular markers showed low polymorphism among specimens of X. sagittifolium, which originated from various collection sites, suggesting that these individuals have a common origin, possibly due to vegetative propagation by producers (Table 3). This result can be illustrated by observing specimens 2–3 and 5–8, which came from different localities, (see Table 1, Figure 4A) but showed identical band profiles for all the primers used. Additionally, three specimens of C. esculenta appeared to have higher polymorphism than the nine specimens of species X. sagittifolium (Table 3). X. undipes exhibited different electrophoretic profiles regarding the other individuals of the same gender. Therefore, it was grouped separately from X. violaceum and X. sagittifolium.

Table 3.
Genetic diversity of specimens of X. sagittifolium and C. esculenta analyzed using ISSR molecular markers.
X. sagittifolium and C. esculenta are the most important species of Araceae, with a nutritional value similar to the potato, with exceptional value for food security [3,4,7,18,19]. The usable parts in both species are the subterranean tuberous stems and the young leaves, especially from X. sagittifolium [3,4,19]. While there are numerous reports with different molecular markers for C. esculenta (e.g., [20,21,22,23]), a smaller number were found for X. sagittifolium [24,25,26,27] and for both species [25,27]. In this work, we characterized for the first time eight ISSR markers that can be used simultaneously in the genetic analysis of X. sagittifolium and C. esculenta and other related taxa such as X. violaceum and X. undipes, which can aid in characterization and identification.
C. esculenta has high genetic diversity with diploid and triploid genotypes spread throughout tropical regions [23,28]. As an allogamous and heterozygous species, natural pollination occurs between C. esculenta diploid plants; however, its asexual propagation by farmers generates clonal lineages [23]. Similarly, despite being an outcrossing species, X. sagittifolium is mostly cultivated by vegetative propagation due to the low viability of seeds produced from natural crosses [3]. Thus, our observations on the diversity of these species are according to their reproductive and cultivation characteristics (Table 3).
The morphologic and genetic characterization of X. sagittifolium and C. esculenta generated in this study can contribute to their proper identification in field and germplasm banks in Brazil and other places where these species are used as a food source.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Provost for Research of São Paulo University (Ana Lilia Alzate-Marin) and CAPES-PROEX grants. Maria del Pilar Sepulveda Nieto was supported by Universidad del Quindio (Colombia). Romulo Maciel de Moraes-Filho was supported by a graduate and a post-doctoral fellowship from CAPES, and Fernando Bonifacio-Anacleto was supported by scientific initiation scholarship from CNPq (134699/2012-2). Ana Lilia Alzate-Marin was supported by a research assistantship from CNPq (PV 300140/2011-8).
Author Contributions
All authors have contributed equally towards the research and the writing of the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Judd, W.S.; Campbell, C.S.; Kellog, E.A.; Stevens, P.F.; Donoghue, M.J. Plant Systematics: A Phylogenetic Approach, 3rd ed.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 249–251. [Google Scholar]
- Grayun, M.H. Evolution and phylogeny of the Araceae. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1990, 77, 628–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacometti, D.C.; Leon, J. Tannia, Yautia. In Neglected Crops: 1492 from a Different Perspective; Hernando Bermejo, J.E., León, J., Eds.; Plant Production and Protection Series No. 26; Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1994; pp. 253–258. [Google Scholar]
- Onokpise, O.U.; Wutoh, J.G.; Ndzana, X.; Tambong, J.T.; Meboka, M.M.; Sama, A.E.; Nyochemberg, L.; Guecia, A.; Nzietchueng, S.; Wilson, J.G.; et al. Evaluation of Macabo cocoyam germplasm in Cameroon. In Perspectives on New Crops and New Uses; Janick, J., Ed.; ASHS Press: Alexandria, VA, USA, 1999; pp. 394–396. [Google Scholar]
- Onwueme, I. Taro Cultivation in Asia and the Pacific; FAO: Bangkok, Thailand, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- MAPA—Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento. Manual de Hortaliças Não-Convencionais; Secretaria de Desenvolvimento Agropecuário e Cooperativismo: Brasília, Brasil, 2010.
- Onyeka, J. Status of Cocoyam (Colocasia esculenta and Xanthosoma spp) in West and Central Africa: Production, Household Importance and the Threat from Leaf Blight. Lima (Peru); CGIAR Research Program on Roots, Tubers and Bananas (RTB): Lima, Peru, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Obidiegwu, J.E.; Kendabie, P.; Obidiegwu, O.; Amadi, C. Towards an Enhanced Breeding in Cocoyam: A Review of Past and Future Research Perspectives. Res. Rev. J. Bot. Sci. 2016, 5, 22–33. [Google Scholar]
- O’Hair, S.K. Tropical Root and Tuber Crops. In Advances in New Crops; Janick, J., Simon, J.E., Eds.; Timber Press: Portland, OR, USA, 1990; pp. 424–428. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, E.G. The Commonly Cultivated Species of Xanthosoma Schott (Araceae), including Four New Species. Aroideana 2011, 34, 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zietkiewicz, E.; Rafalski, A.; Labuda, D. Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Genomics 1994, 20, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzate-Marin, A.L.; Guidugli, M.C.; Soriani, H.H.; Martinez, C.A.H.; Mestriner, M.A.A. DNA minipreparation procedure suitable for PCR/SSR and RAPD analyses in tropical forest tree species. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2009, 52, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Rodriguez, P.; Strong, T.M. Monocotiledons and Gymnosperm of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Island; National Museum of Natural History: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 30–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sanguinetti, C.J.; Dias, E.N.; Simpson, A.J.G. Rapid silver staining and recovery of PCR products separated on polyacrylamide gels. Biotechniques 1994, 17, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research-an update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nei, M. Genetic distance between populations. Am. Nat. 1972, 106, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S.; Nei, M.; Anil, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebot, V. Tropical Root and Tuber Crops: Cassava, Sweet Potato, Yams, Aroids; Crop Production Science in Horticulture, 17; CABI: Oxfordshire, UK, 2009; p. 432. [Google Scholar]
- Wada, E.; Asfaw, Z.; Feyissa, T.; Tesfaye, K. Farmers’ perception of agromorphological traits and uses of cocoyam (Xanthosoma sagittifolium (L.) Schott) grown in Ethiopia. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2017, 12, 2681–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, T.; Nguyen, V.X.; Tahara, M.; Yoshino, H. Geographical differentiation of Asian taro, Colacasia esculenta (L.) Schott, detected by RAPD and isozyme analyses. Euphytica 2001, 122, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, P.J. Genetic Diversity in Taro, and the Preservation of Culinary Knowledge. Ethnobot. Res. Appl. 2004, 2, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, D.R.; Faseela, F.; Kumar, N.; Damodaran, V.; Srivastava, R.C. Diversity of 21 taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott) accessions of Andaman Islands. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2012, 59, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaïr, H.; Traore, R.E.; Duval, M.F.; Rivallan, R.; Mukherjee, A.; Aboagye, L.M.; van Rensburg, W.J.; Andrianavalona, V.; de Carvalho, M.A.A.P.; Saborio, F.; et al. Genetic Diversification and Dispersal of Taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offei, S.K.; Asante, I.K.; Danquah, E.Y. Genetic structure of seventy cocoyam (Xanthosoma sagittifolium, Linn, Schott) accessions in Ghana based on RAPD. Hereditas 2004, 140, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osawaru, M.E.; Ogwu, M.C. Molecular Characterization of 36 Accessions of Two Genera of Cocoyam (Colocasia [Schott] and Xanthosoma [Schott], Araceae). Sci. Technol. Arts Res. J. 2015, 4, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathebras, C.; Traore, R.; Malapa, R.; Risterucci, A.M.; Chaïr, H. Characterization of microsatellites in Xanthosoma sagittifolium (Araceae) and cross-amplification in related species. Appl. Plant Sci. 2014, 2, 1400027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doungous, O.; Kalendar, R.; Adiobo, A.; Schulman, A.H. Retrotransposon molecular markers resolve cocoyam (Xanthosoma sagittifolium) and taro (Colocasia esculenta) by type and variety. Euphytica 2015, 206, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, D.J.; Yen, D.E.; Gaffey, P.M. Chromosome variation in taro, Colocasia esculenta: Implications for origin in the Pacific. Cytologia 1988, 53, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




