Hydraulic Performance of Horticultural Substrates—1. Method for Measuring the Hydraulic Quality Indicators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Samples and Preparation
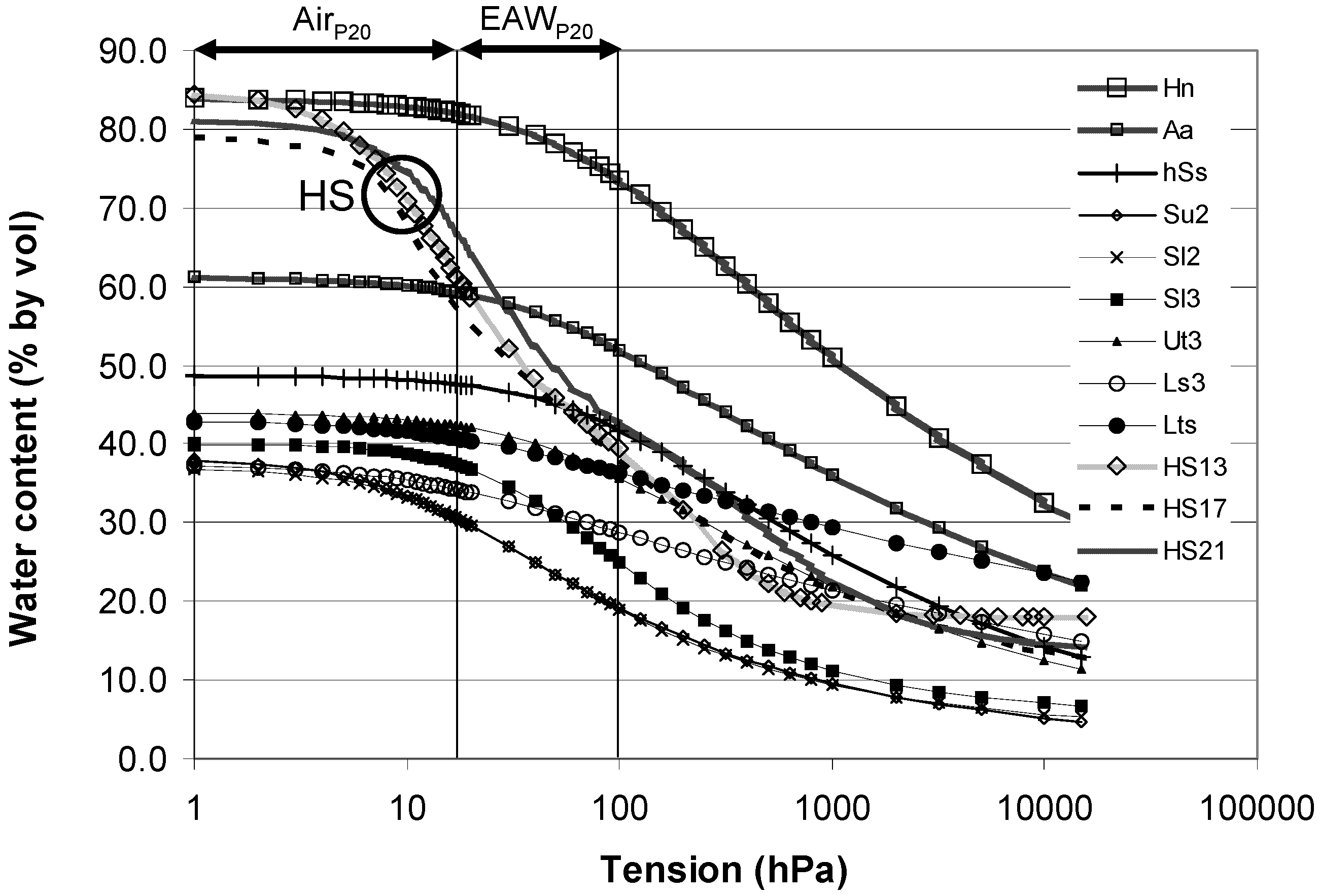
2.2. Hydraulic Criteria
2.3. Measurement of the Water Retention Curve and the Unsaturated Hydraulic Conductivity Function
2.3.1. Short Description of the Procedure
2.4. Rewetting Properties
2.5. Shrinkage Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raviv, M.; Lieth, J.H. Soilless Culture; Elsevier Publications: London, UK, 2008; p. 608. [Google Scholar]
- Caron, J.; Pepin, S.; Periard, Y. Physics of growing media in green future. International Symposium on Growing Media and Soilless Cultivation. Acta Hortic. 2014, 1034, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlovich, P.T.; Fonteno, W.C. Effect of soil moisture tension and soil water content on the growth of chrysanthemum in 3 container media. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1986, 111, 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Milks, R.R.; Fonteno, W.C.; Larson, R.A. Hydrology of horticultural substrates: I. Mathematical models for moisture characteristic curves of horticultural container media. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1989, 114, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Milks, R.R.; Fonteno, W.C.; Larson, R.A. Hydrology of horticultural substrates: II. Predicting physical properties of media in containers. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1989, 114, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Milks, R.R.; Fonteno, W.C.; Larson, R.A. Hydrology of horticultural substrates: III. Predicting air and water content in limited-volume plug cells. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1989, 114, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Ritsema, C.J.; Dekker, L.W. Water repellency and its role in forming preferred flow paths in soils. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1996, 34, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Naddafa, O.; Livieratos, I.; Stamatakisa, A.; Tsirogiannisb, I.; Gizasb, G.; Savvasc, D. Hydraulic characteristics of composted pig manure, perlite, and mixtures of them, and their impact on cucumber grown on bags. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 129, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN 13041. Bodenverbesserungsmittel und Kultursubstrate—Bestimmung der Physikalischen Eigenschaften—Rohdichte (Trocken), Luftkapazität; Wasserkapazität, Schrumpfungswert, und Gesamtporenvolumen, Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, U.; Durner, W.; von Unold, G.; Mueller, L.; Wieland, R. The evaporation method—Extending the measurement range of soil hydraulic properties using the air-entry pressure of the ceramic cup. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2010, 173, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiskanen, J. Physical properties of two-component growth media based on Sphagnum peat and their implications for plant-available water and aeration. Plant Soil 1995, 172, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibbiani, C.; Campiotti, C.A.; Incrocci, L. Estimation of hydraulic properties of growing media with a one-step outflow technique. International Symposium on Growing Media and Soilless Cultivation. Acta Hortic. 2014, 1034, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UMS GmbH Munich, HYPROP©—Laboratory Evaporation Method for the Determination of pF-Curves and Unsaturated Conductivity. Available online: http://www.ums-muc.de/en/products/soil_laboratory.html (accessed on 29 August 2011).
- Von Post, L. Sveriges Geologiska Undersöknings torvinventering och nogra av des hittils vunna resultat (SGU peat inventory and some preliminary results). Svenska Mosskulturforeningens Tidskrift Jonköping 1922, 36, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Boden, A.G. Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung. 5. Aufl. (KA 5); 438 S.; Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe: Hannover, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Verdonck, O.; Gabriels, R.I. Reference method for the determination of physicalproperties of plant substrates. II. Reference method for the determination of chemical properties of plant substrates. Acta Hortic. 1992, 302, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, U.; Doerner, J.; Müller, L. Simplified method for quantifying the hydraulic properties of shrinking soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2015, 178, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letey, J. Measurement of contact angle, water drop penetration time, and critical surface tension. In Water-Repellent Soils; DeBano, L.F., Letey, J., Eds.; University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1968; pp. 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco-Canqui, H.; Lal, R. Extent of soil water repellency under long-term no-till soils. Geoderma 2009, 149, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| HS No. | Ingredients, Texture Class | Ash Content (%) | Corg (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Horticultural substrates | |||
| 1 | Hh (H3–H8), R, G | 68.1 | |
| 2 | Hh (H2–H4) H7–H9, G, R | 16.8 | |
| 3 | Hh (H2–H5), P, C, K | 35.1 | |
| 4 | Hh (H3–H8), R, G, P, C, K | 21.4 | |
| 5 | 95% Hh (H3–H7), P, Co | 24.4 | |
| 6 | R, C, Co, Guano | 25.3 | |
| 7 | 90% Hh (H4–H8), 10% C, K | 41.0 | |
| 8 | Hh (H3–H8), C,P | 35.9 | |
| 9 | 75% Hh (H3–H5 and H6–H7), Co, C, K | 25.1 | |
| 10 | 80% Hh (H3–H5 and H6–H7), Co, C | 39.9 | |
| 11 | Hh (H2–H5), G, R, P, C, K | 48.3 | |
| 12 | Hh (H3–H8), G, R, P, C, C | 42.7 | |
| 13 | Hh (H3–H5 and H7–H9) | 15.1 | |
| 14 | Hh (H2–H5), G, R, K | 35.8 | |
| 15 | Hh (H3–H8), G, P, K | 10.8 | |
| 16 | 60% Hh (H3–H5 and H6–H7), R, G, Co, K | 25.5 | |
| 17 | 60% Hh (H3–H5 and H6–H7), Co, C, P | 42.8 | |
| 18 | 50% Hh (H3–H5), G, R, C | 36.2 | |
| Natural organic and mineral soils | |||
| 19 | Fen peat (Hn, H7) | 55.0 | |
| 20 | Half-fen (Aa) | 11.6 | |
| 21 | Sand (Ss, strong humic | 2.9 | |
| 22 | Weak silty sand (Su2) | 0.9 | |
| 23 | Weak loamy sand Sl2 | 1.0 | |
| 24 | Medium loamy sand (Sl3) | 1.1 | |
| 25 | Strong loamy sand (Sl4) | 1.2 | |
| 26 | Medium clayey silt (Ut3) | 1.3 | |
| 27 | Medium sandy loam (Ls3) | 1.5 | |
| 28 | Sandy clayey loam (Lts) | 1.6 | |
| No. | Θs | FC | AirP20 | EAWP20 | S | DBD | CR5 | WDPT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vol. % | g·cm−3 | cm | Sec. | |||||
| Horticultural substrates | ||||||||
| 1 | 71.8 | 38.7 | 9.3 | 28.2 | 2.1 | 0.43 | 10.1 | 0.1 |
| 2 | 86.0 | 48.0 | 6.5 | 36.6 | 6.2 | 0.17 | 45.7 | 1 |
| 3 | 79.6 | 46.4 | 9.4 | 27.9 | 5.4 | 0.30 | 54.7 | 0.1 |
| 4 | 79.0 | 46.2 | 11.8 | 26.7 | 3.3 | 0.26 | 26.7 | 15 |
| 5 | 86.2 | 45.1 | 11.7 | 34.4 | 2.1 | 0.20 | 42.9 | 2 |
| 6 | 87.1 | 31.6 | 31.7 | 26.7 | 0.4 | 0.18 | 17.9 | 0.1 |
| 7 | 84.2 | 53.8 | 4.5 | 31.1 | 9.1 | 0.21 | 24.4 | 1 |
| 8 | 81.2 | 50.6 | 5.7 | 29.1 | 6.6 | 0.25 | 45.7 | 0.1 |
| 9 | 80.7 | 38.8 | 13.9 | 33.5 | 0.8 | 0.22 | 29.3 | 0.1 |
| 10 | 84.4 | 44.1 | 13.6 | 31.4 | 6.2 | 0.18 | 29.3 | 0.1 |
| 11 | 83.1 | 54.7 | 7.2 | 26.5 | 6.2 | 0.31 | 13.1 | 2 |
| 12 | 75.8 | 40.8 | 6.8 | 32.8 | 1.0 | 0.30 | 26.7 | 6 |
| 13 | 84.5 | 55.1 | 2.7 | 32.5 | 0.6 | 0.21 | 47.7 | 1 |
| 14 | 78.8 | 43.2 | 11.6 | 29.2 | 0.8 | 0.28 | 15.9 | 6 |
| 15 | 83.4 | 52.0 | 6.9 | 29.6 | 7.0 | 0.19 | 36.4 | 2 |
| 16 | 81.1 | 39.8 | 13.7 | 31.5 | 3.3 | 0.19 | 12.7 | 1 |
| 17 | 80.8 | 48.8 | 13.8 | 32.1 | 6.2 | 0.23 | 29.3 | 0.1 |
| 18 | 81.0 | 47.3 | 7.6 | 30.6 | 7.0 | 0.26 | 79.9 | 2 |
| Natural organic and mineral soils | ||||||||
| 19 | 84.0 | 77.2 | 1.1 | 9.4 | 7.2 | 0.43 | 80 | 6 |
| 20 | 61.3 | 54.9 | 1.1 | 8.2 | 4.1 | 1.05 | 56 | 9 |
| 21 | 48.7 | 44.3 | 0.6 | 20.7 | 2.1 | 1.35 | 51 | 3 |
| 22 | 38.2 | 22.2 | 4.6 | 14.5 | nm | 1.63 | 32 | nm |
| 23 | 36.9 | 22.2 | 3.6 | 14.4 | nm | 1.66 | 46 | nm |
| 24 | 40.0 | 29.4 | 1.4 | 13.8 | nm | 1.58 | 123 | nm |
| 25 | 34.5 | 25.6 | 3.0 | 7.6 | nm | 1.72 | 30 | nm |
| 26 | 43.9 | 38.4 | 0.9 | 7.3 | nm | 1.48 | 61 | nm |
| 27 | 37.5 | 30.5 | 2.0 | 6.7 | nm | 1.64 | 4 | nm |
| 28 | 43.0 | 37.8 | 1.4 | 5.4 | 1.9 | 1.50 | 17 | nm |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schindler, U.; Müller, L.; Eulenstein, F. Hydraulic Performance of Horticultural Substrates—1. Method for Measuring the Hydraulic Quality Indicators. Horticulturae 2017, 3, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae3010005
Schindler U, Müller L, Eulenstein F. Hydraulic Performance of Horticultural Substrates—1. Method for Measuring the Hydraulic Quality Indicators. Horticulturae. 2017; 3(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae3010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchindler, Uwe, Lothar Müller, and Frank Eulenstein. 2017. "Hydraulic Performance of Horticultural Substrates—1. Method for Measuring the Hydraulic Quality Indicators" Horticulturae 3, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae3010005
APA StyleSchindler, U., Müller, L., & Eulenstein, F. (2017). Hydraulic Performance of Horticultural Substrates—1. Method for Measuring the Hydraulic Quality Indicators. Horticulturae, 3(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae3010005





