Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Revealed Genes Associated with the Formation of Different Fruit Colors in Fragaria pentaphylla
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Metabolomic Analysis
2.3. Transcriptome Analysis
2.3.1. Construction of cDNA Library and Sequencing of the Transcriptome
2.3.2. DEG Analysis
2.3.3. Metabolomics and Transcriptomics Integrated Analysis
2.3.4. Real-Time Fluorescent Quantitative PCR
2.4. Data Statistics and Analysis
3. Results
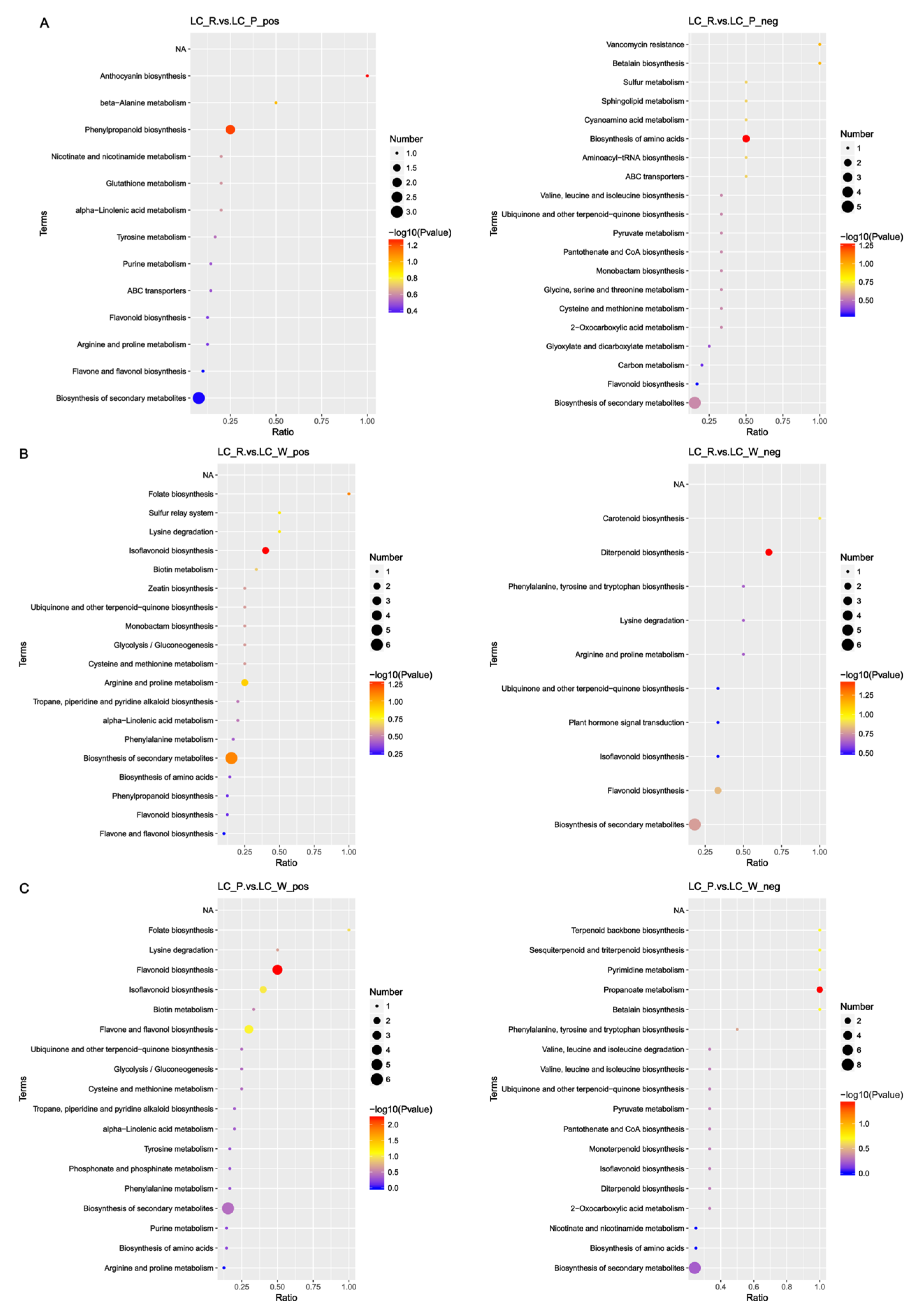
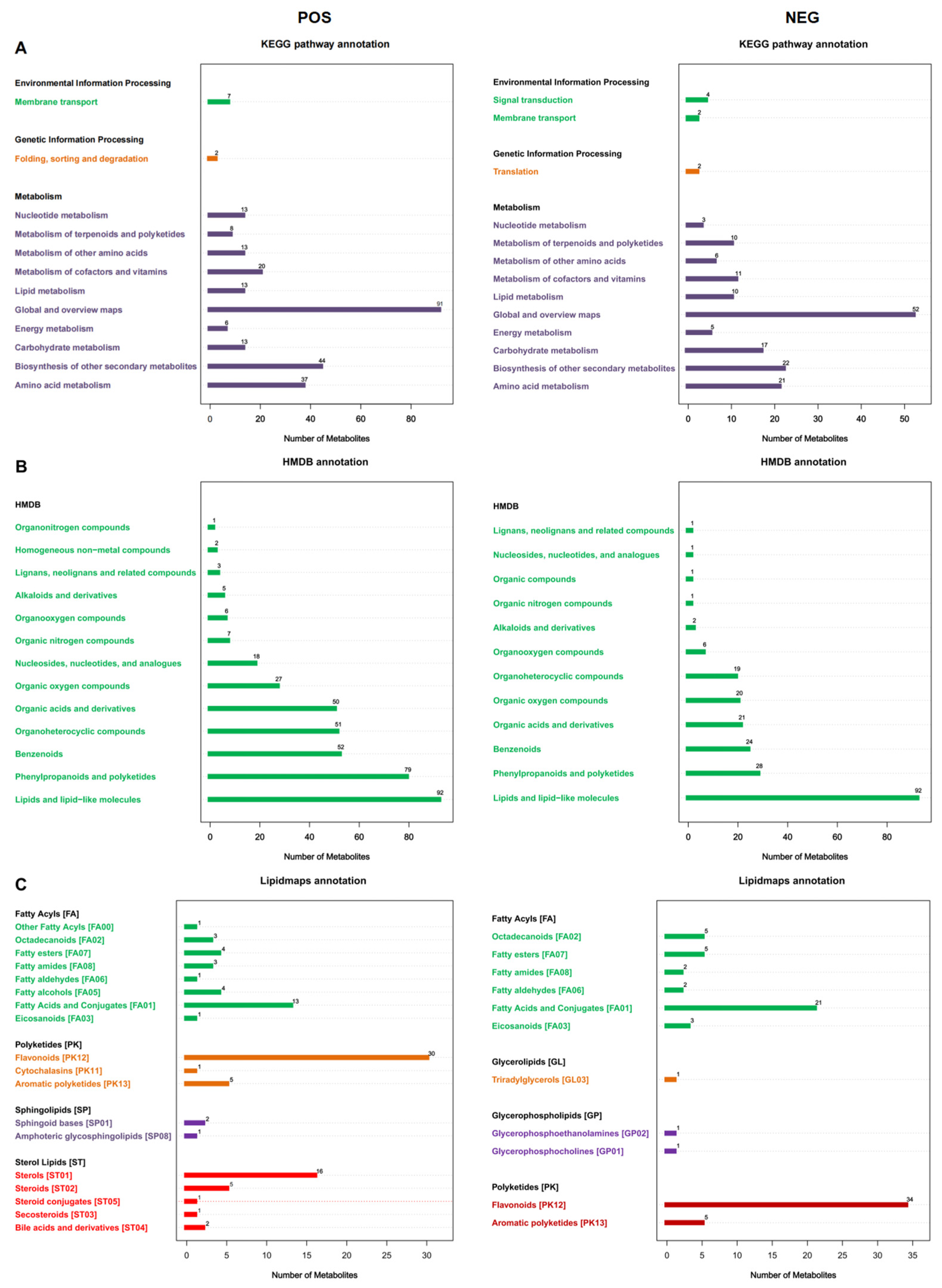
3.1. Metabolite Identification in F. pentaphylla Fruits with Different Colors
3.2. Analysis of Flavonoid-Derived Metabolites
3.3. RNA-Seq and Assembly
3.4. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) in F. pentaphylla
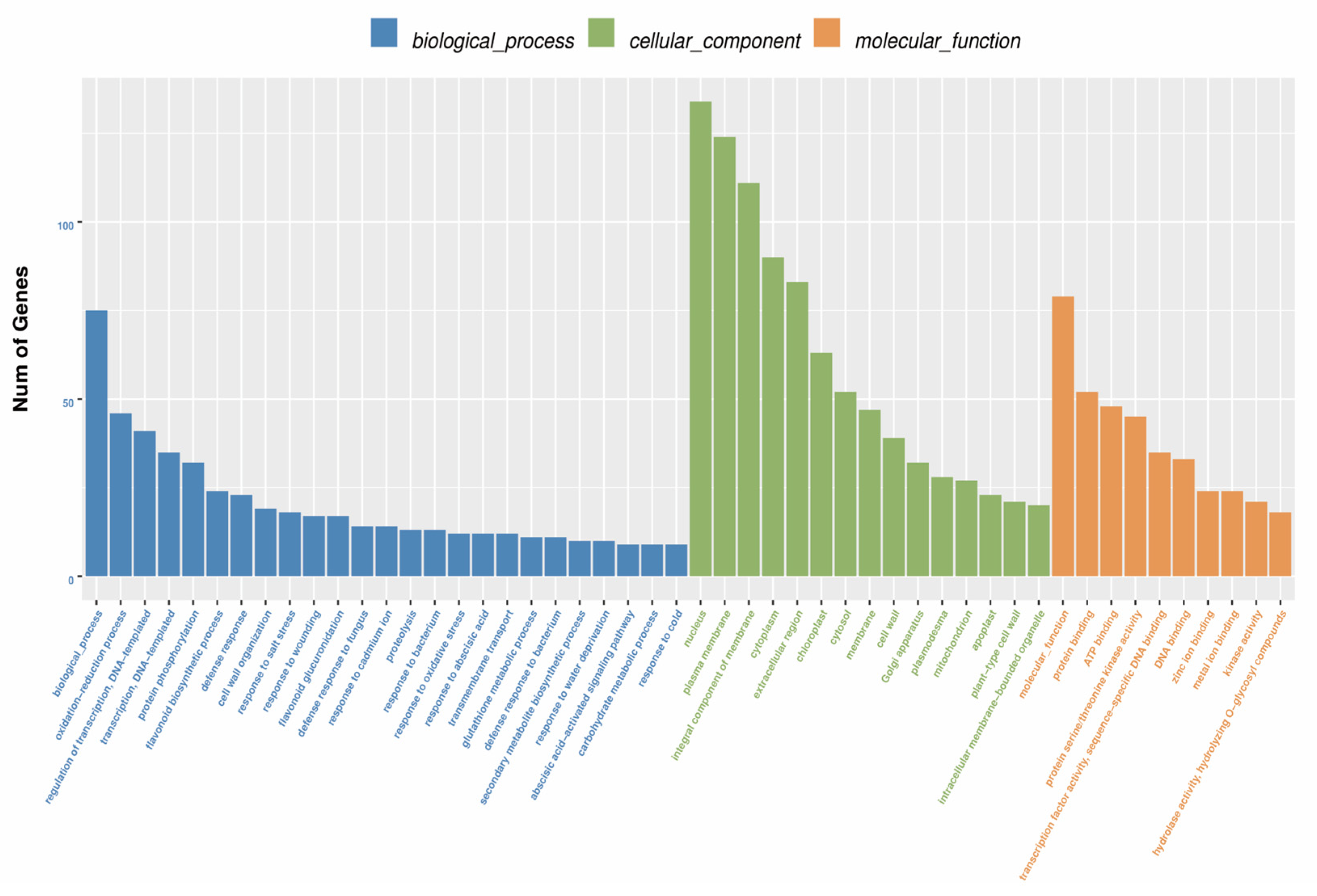
3.5. Functional Annotation of Unigenes
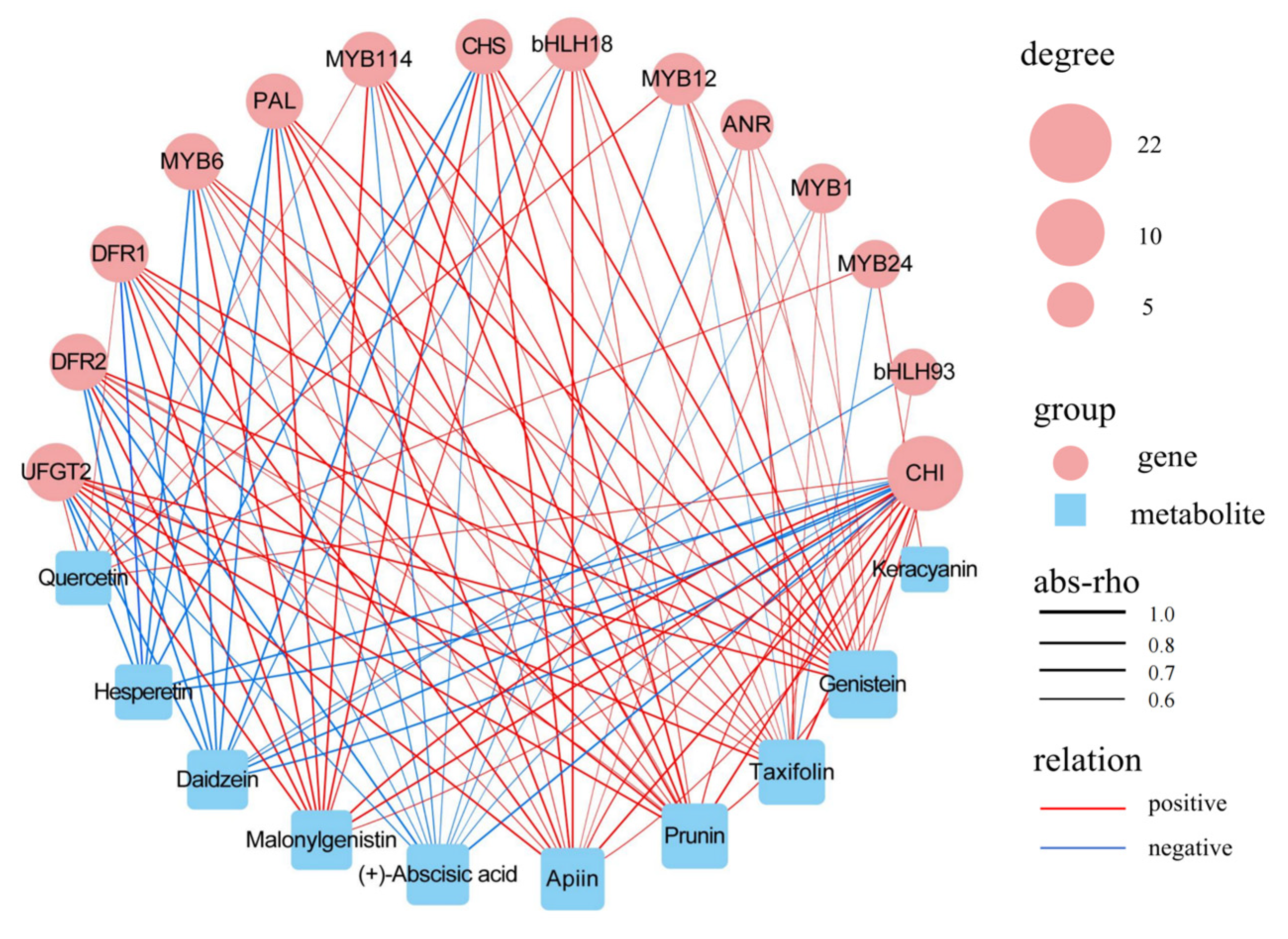
3.6. Combined Analysis of Transcriptomes and Metabolomes
3.7. qRT-PCR Validation of DEGs in Transcriptome Data
3.8. Fruit Color Change Involves Phenylpropanoid, Flavonoid, and Anthocyanidin Biosynthesis Pathways
4. Discussion
4.1. Metabolism Compounds Associated with Fruit Coloration in the Strawberry
4.2. The Genes Involved in Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in the Strawberry
4.3. Candidate Genes Involved in Regulating Fruit Coloration in F. pentaphylla
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saridas, A.M.; Guclu, G.; Selli, S.; Kelebek, H.; Kargi, P.S. The cross-breeding of Osmanli and Sabrina varieties to produce newly aroma-enriched strawberry genotypes. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 144, 107713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.H.; Chen, A.; Netzel, E.M.; O’Hare, J.T. Differences in the Anthocyanin Profile of Different Tissues of the Strawberry Fruit †. Proceedings 2020, 36, 74. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.X.; Xu, S.T.; Ding, W.H.; Peter, A. Genetic diversity and offspring fitness in the red and white fruit color morphs of the wild strawberry Fragaria pentaphylla. J. Plant Ecol. 2019, 13, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Li, S.G.; Chang, L.L.; Dong, J.; Zhong, C.F.; Zhang, H.L.; Wei, L.G.; Gao, Y.S.; Wang, G.X.; Zhang, Y.T.; et al. Chromosome-level genome assembly of Fragaria pentaphylla using PacBio and Hi-C technologies. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 873711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.Y.; Wang, K.; Tang, R.K.; Liu, J.Y.; Cheng, K.; Gao, G.T.; Wang, Y.Y.; Qin, G.Z. Recent advances in biosynthesis and regulation of strawberry anthocyanins. Hortic. Res. 2025, 12, uhaf135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, H.A.; Khan, R.A. Anthocyanins: Traditional Uses, Structural and Functional Variations, Approaches to Increase Yields and Products’ Quality, Hepatoprotection, Liver Longevity, and Commercial Products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, R.J.; Ye, Y.J.; Hu, Q.D.; Ma, X.H.; Zhang, X.L.; Zheng, J. Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses Reveal New Insights into the Role of Metabolites and Genes in Modulating Flower Colour of Clematis tientaiensis. Horticulturae 2022, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.K.; Wang, X.W.; Lin, X.Y.; Mostafa, S.; Zou, H.L.; Wang, L.; Jin, B. Plant anthocyanins: Classification, biosynthesis, regulation, bioactivity, and health benefits. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 217, 109268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Butelli, E.; Martin, C. Engineering anthocyanin biosynthesis in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 19, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Yang, S.; Ni, J.; Teng, Y.; Bai, S. Advances of anthocyanin synthesis regulated by plant growth regulators in fruit trees. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 307, 111476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharoni, A.; De Vos, C.H.R.; Wein, M.; Sun, Z.K.; Greco, R.; Kroon, A.; Mol, J.N.M.; O’Connell, A.P. The strawberry FaMYB1 transcription factor suppresses anthocyanin and flavonol accumulation in transgenic tobacco. Plant J. 2001, 28, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaart, J.G.; Dubos, C.; Romero De La Fuente, I.; van Houwelingen, A.M.M.L.; de Vos, R.C.H.; Jonker, H.H.; Xu, W.J.; Routaboul, J.-M.; Lepiniec, L.; Bovy, A.G. Identification and characterization of MYB-bHLH-WD40 regulatory complexes controlling proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) fruits. New Phytol. 2013, 197, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.R.; Kim, H.T.; Shanmugam, A.; Nath, U.K.; Goswami, G.; Song, J.Y.; Park, J.I.; Nou, I.S. Expression Profiling of Regulatory and Biosynthetic Genes in Contrastingly Anthocyanin Rich Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) Cultivars Reveals Key Genetic Determinants of Fruit Color. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.M.; Wang, Y.N.; Tao, Y.T.; Chen, L.X.; Lin, H.Y.; Qi, Z.C.; Li, J.M. Genome-wide identification and analysis of anthocyanin synthesis-related R2R3-MYB genes in Fragaria pentaphylla. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, M.; Zhao, C.; Wang, R.; Xue, L.; Lei, J. A novel bHLH transcription factor, FabHLH110, is involved in regulation of anthocyanin synthesis in petals of pink-flowered strawberry. Plant Physiol. Biochem. PPB 2025, 222, 109713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simirgiotis, M.J.; Theoduloz, C.; Caligari, P.D.S.; Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.S.H. Comparison of phenolic composition and antioxidant properties of two native Chilean and one domestic strawberry genotypes. Food Chem. 2008, 113, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Koyama, N.; Tamura, H. Color and Anthocyanin Composition of Strawberry Fruit: Changes during Fruit Development and Differences among Cultivars, with Special Reference to the Occurrence of Pelargonidin 3-malonylglucoside. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2002, 71, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.Z.; Pang, F.H.; Wang, J.; Cai, W.J.; Xia, J.; Zhao, M.Z. Identification of Anthocyanin Compositions and Expression Analysis of Key Related Genes in Fragaria × ananassa. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2023, 50, 791–801. [Google Scholar]
- Patricio, Z.; Makarena, G.; Igor, P.; Claudia, J.; Claudia, S.A.; Marco Isaac, G.; Rodrigo, I.; Juan Alfonso, S. Transcriptomic Analysis of Sex-Associated DEGs in Female and Male Flowers of Kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa [A. Chev] C. F. Liang & A. R. Ferguson). Horticulturae 2021, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.F.; Jing, Y.L.; Wang, Q.H.; Zhang, W.S. Identification and Quantification of Carotenoids in White and Yellow-Fleshed Peaches (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch) by QTRAP+ LC-MS/MS. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.B.; Xin, M.; Rothenberg, O.D.; Yang, Z.B.; Zhang, W.T.; Wan, S.H.; Yang, H.J.; Zhang, L.Y. Metabolome and Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Putative Genes Involved in Anthocyanin Accumulation and Coloration in White and Pink Tea (Camellia sinensis) Flower. Molecules 2020, 25, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.D.; Li, Y.L.; Lu, Q.W.; Lu, H.F.; Li, J.M. Combined Analysis of the Metabolome and Transcriptome Identified Candidate Genes Involved in Phenolic Acid Biosynthesis in the Leaves of Cyclocarya paliurus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.H.; Li, F.D.; Tong, W.; Li, P.H.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, H.J.; Ge, R.H.; Li, R.P.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.Z.; et al. Tea Plant Information Archive: A comprehensive genomics and bioinformatics platform for tea plant. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1938–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihaela, P.; Daehwan, K.; Geo, P.M.; Jeffrey, L.T.; Steven, S.L. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie, and Ballgown. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1650–1667. [Google Scholar]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Cheng, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basharat, Y.; Khalid, G.; Abas, A.W.; Preeti, S. Health Benefits of Anthocyanins and Their Encapsulation for Potential Use in Food Systems: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2223–2230. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.A.; Wang, W.X.; Li, J.P.; Ding, Y.H.; Tian, J.L.; Wang, Z.H.; Xiong, B.; Xu, T.; Kou, G.Q.; Zheng, Y.Y.; et al. Analysis of Anthocyanin Accumulation and Related Gene Expression During Fig Fruit Development. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 41, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Liu, X.; Liang, R.; Li, J.; Bi, M.G.; Li, J.; Mu, C.; Yang, Y.D.; Li, S.J.; Yang, P.P.; et al. LlbZIP11 promotes anthocyanin accumulation in raised spots of Lilium leichtlinii by inducing LlMYB19S expression. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 320 Pt 3, 146085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, D.J.; Olson, B.J.; Clemente, T.E.; Smith, S.D. A novel R3 MYB transcriptional repressor associated with the loss of floral pigmentation in Iochroma. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 1346–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zhao, Q.; Song, Y.; Jin, H.C.; Seymour, D.; Liu, Y.Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, D.; Liu, D.F. Evaluation of pigment composition and antioxidant properties in the flesh of seven colored pummelo cultivars. Food Chem. X 2025, 29, 102705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Y.; Hua, W.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, R.H.; Li, P.P.; Deng, M.H. Bioactive Components and Color Variation Mechanism Among Three Differently Colored Peppers Based on Transcriptomics and Non-Targeted Metabolomics. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Maor, C.L.; Haro, D.A.L.; Jozwiak, A.; Gharat, S.A.; Kazachkova, Y.; Cai, J.H.; Vainer, A.; Toppino, L.; Sehrawat, U.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms Driving the Unusual Pigmentation Shift in Eggplant Fruit Development. Plant Commun. 2025, 6, 101321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaakola, L.W. Insights into the regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in fruits. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfranco, D.; Xin, J.; Teresa, C.; Zhu, C.F.; Lourdes, G.G. Differential accumulation of pelargonidin glycosides in petals at three different developmental stages of the orange-flowered gentian (Gentiana lutea L. var. aurantiaca). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212062. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, B.; Li, S.S.; Yang, Y.; Xu, W.Z.; Wang, L.S. Functional identification of anthocyanin glucosyltransferase genes: A Ps3GT catalyzes pelargonidin to pelargonidin 3-O-glucoside, painting the vivid red flower color of Paeonia. Planta 2023, 257, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvia, G.; Pierdomenico, P. Fruit Colour and Novel Mechanisms of Genetic Regulation of Pigment Production in Tomato Fruits. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, A.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Yang, Q.; Liu, F.; Han, T.; Tang, X. Integrated metabolome and transcriptome analysis provides clues to fruit color formation of yellow, orange, and red bell pepper. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, S.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.J.; Bai, W.Q.; Lin, H. New insights into the transcription factor regulatory networks driving peel coloration under hormone induction, analyzed by transcriptomics and metabolomics in tangor ‘Murcot’. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1526733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tikunov, Y.; Schouten, R.E.; Marcelis, L.F.M.; Visser, R.G.F.; Bovy, A. Anthocyanin Biosynthesis and Degradation Mechanisms in Solanaceous Vegetables: A Review. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhong, F.; Tian, R.R.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.M.; Li, T.H. Comparative study of phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity in different species of cherries. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, C633–C638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, C.; Kuhn, N.; Arellano, M.; Time, A.; Multari, S.; Martens, S.; Carrera, E.; Sagredo, B.; Donoso, J.M.; Meisel, L.A. Differential Phenolic Compounds and Hormone Accumulation Patterns between Early- and Mid-Maturing Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) Cultivars during Fruit Development and Ripening. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8850–8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvatierra, A.; Pimentel, P.; Moya-Leon, M.A.; Caligari, P.D.; Herrera, R. Comparison of transcriptional profiles of flavonoid genes and anthocyanin contents during fruit development of two botanical forms of Fragaria chiloensis ssp. chiloensis. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.C.; Shao, W.L.; Du, Z.K.; Lu, H.F.; Li, J.M. Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses reveal differences in the biosynthetic pathway of anthocyanins in Fragaria nilgerrensis and Fragaria pentaphylla. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 271, 109476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.L.F.; Escribano-Bailón, T.M.; Alonso, P.J.J.; Rivas-Gonzalo, J.C.; Santos-Buelga, C. Anthocyanin pigments in strawberry. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.X.; Jiang, L.Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.T.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, B.; Wang, X.R.; Tang, H.R. Comparative Transcriptome Profiling Analysis of Red- and White-Fleshed Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) Provides New Insight into the Regulation of the Anthocyanin Pathway. Plant Cell Physiol. 2018, 59, 1844–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Y.; Yue, M.L.; Liu, Y.Q.; Ye, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.T.; Lin, Y.X.; Wang, X.R.; Chen, Q.; Tang, H.R. Alterations of Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis Lead to the Natural Formation of Pinkish-Skinned and White-Fleshed Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, L.D.; Zúñiga, P.E.; Figueroa, N.E.; Pastene, E.; Escobar-Sepúlveda, H.F.; Figueroa, P.M.; Garrido-Bigotes, A.; Figueroa, C.R. Application of a JA-Ile Biosynthesis Inhibitor to Methyl Jasmonate-Treated Strawberry Fruit Induces Upregulation of Specific MBW Complex-Related Genes and Accumulation of Proanthocyanidins. Molecules 2018, 23, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Yin, Y.J.; Gao, H.S.; Sheng, L.X. Identification of MYB Transcription Factors Involved in Fruit Quality Regulation of Fragaria × ananassa Duch. Genes 2022, 14, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lin, A.Q.; Zhou, Y.K.; Liu, Z.; Bai, P.; Zhu, Y.X.; Fan, J.M.; Bi, X.Y.; Kuang, H.Y.; Lian, H.L.; et al. Mutation in FvPAL2 leads to light red strawberry fruits and yellow-green petioles. Plant Sci. Int. J. Exp. Plant Biol. 2024, 352, 112370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.R.; Sun, M.; Hui, J.T.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.B.; Lin, G.C. Combined Transcriptome and Metabolome Analyses Provide New Insights into the Changes in the Flesh Color of Anthocyanins in Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa (Weston) Duchesne ex Rozier). Genes 2024, 15, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, H.; Gregor, K. Wilfried S RNAi-induced silencing of gene expression in strawberry fruit (Fragaria × ananassa) by agroinfiltration: A rapid assay for gene function analysis. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 48, 818–826. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.; Wang, J.Y.; Jia, H.F.; Jia, W.S.; Wang, H.Q.; Xiao, M. RNAi-Mediated Silencing of the Flavanone 3-Hydroxylase Gene and Its Effect on Flavonoid Biosynthesis in Strawberry Fruit. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2013, 32, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Li, W.J.; Dou, Y.J.; Zhang, J.X.; Jiang, G.H.; Miao, L.X.; Han, G.F.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.H. Transcript Quantification by RNA-Seq Reveals Differentially Expressed Genes in the Red and Yellow Fruits of Fragaria vesca. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giampieri, F.; Gasparrini, M.; Forbes-Hernandez, T.Y.; Mazzoni, L.; Capocasa, F.; Sabbadini, S.; Alvarez-Suarez, M.J.; Afrin, S.; Rosati, C.; Pandolfini, T.; et al. Overexpression of the Anthocyanidin Synthase Gene in Strawberry Enhances Antioxidant Capacity and Cytotoxic Effects on Human Hepatic Cancer Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Q.; Han, T.Y.; Lyu, L.F.; Li, W.L.; Wu, W.L. Research progress in understanding the biosynthesis and regulation of plant anthocyanins. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 321, 112374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.B.; Wu, L.; Cao, M.H.; Ma, C.; Xiao, K.; Li, Y.B.; Lian, H.L. Identification of MBW Complex Components Implicated in the Biosynthesis of Flavonoids in Woodland Strawberry. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 774943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Sun, P.; Li, J. Expression of genes involved in the anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway in white and red fruits of Fragaria pentaphylla and genetic variation in the dihydroflavonol-4-reductase gene. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2017, 72, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadomura-Ishikawa, Y.; Miyawaki, K.; Takahashi, A.; Noji, S. RNAi-mediated silencing and overexpression of the FaMYB1 gene and its effect on anthocyanin accumulation in strawberry fruit. Biol. Plant. 2015, 59, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.T.; Mirbeth, B.; Rentsch, J.; Sutter, C.; Ring, L.; Flachowsky, H.; Habegger, R.; Hoffmann, T.; Hanke, M.; Schwab, W. Premature and ectopic anthocyanin formation by silencing of anthocyanidin reductase in strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa). New Phytol. 2014, 201, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.B.; Li, M.B.; Ma, C.; Li, X.Y.; Bai, P.; Lin, A.Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.Q.; Kuang, H.Y.; Lian, H.L. Loss-of-function mutation in anthocyanidin reductase activates the anthocyanin synthesis pathway in strawberry. Mol. Hortic. 2024, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Huang, D.; Peng, B.Y.; Zhang, P.P.; Zhan, W.Y.; Xu, Z.Q.; Lv, J.B. Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression profiling of bHLH genes under different development and abiotic stress conditions in Carya illinoinensis. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2025, 184, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatierra, A.; Pimentel, P.; Moya-León, M.A.; Herrera, R. Increased accumulation of anthocyanins in Fragaria chiloensis fruits by transient suppression of FcMYB1 gene. Phytochemistry 2013, 90, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavel, S.; Jurgita, P.; Vaiva, K.; Erna, D.; Vidmantas, S.; Vidmantas, B.; Tadeušas, S.; Aušra, R.; Raimundas, R. Expression and Anthocyanin Biosynthesis-Modulating Potential of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) MYB10 and bHLH Gene. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126991. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.L.; Li, G.; Hu, P.P.; Zhao, X.; Li, L.J.; Wei, W.; Feng, J.Y.; Zhou, H.C. Identification of fundamental/helix-loop-helix transcription factors reveals candidate genes involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis from the strawberry white-flesh mutant. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2721. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Xu, R.; Chang, K.Z.; Yuan, S.; Huang, C.X.; Wang, J.W.; Li, S.H.; Liu, F.Z.; Zhong, F.L. Identification of PAL Gene in Purple Cabbage and Functional Analysis Related to Anthocyanin Synthesis. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Genes | Forward Primer (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer (3′–5′) |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | GCCACCCAGAAGACTGTTGATG | CCAGTGCTGCTAGGAATGATGTTG |
| FpbHLH18 | CTTCATCAACCAGTGGCACAT | AGAATCGGGTGACAGTGAGAG |
| FpbHLH91 | GGTGCCAGAGACGACGATGA | GCTCCTCAGAGACCCATTGTTGTA |
| FpbHLH93 | GAGTGCTCACAGTCCCATCT | ACTCCTCATCCTCCACCATTG |
| FpMYB1 | CCAGACGAAGACGACCTAATAATC | GGTGTTCCAGTAGTTCTTGATCTC |
| FpMYB24 | CGACAAGCAAGACACGAACAAAGG | TGAGGAAGGGTACGCCAACAAC |
| FpMYB114 | GTGTTCTGGTCTTATTGGTTTGGA | GACTAGATCATTGCTTGCCGATT |
| FpDFR1 | GAAGGCGGCGACTCACTTG | CATAGGTGTGGCGACATGGAAC |
| FpDFR2 | CGAGCCACCGTGCGAGAC | GCCTTCCACAGCGTCAGTAGC |
| FpLAR | GGCTCCATCGGCAAGTTCATAG | AGGGTCATTGACAGTGGTCTCTCT |
| FpUFGT | CCTCCAGACTCCGTACTATTC | TATGAACCGCTGCTGACT |
| FpANR | AAGTCTGCTTGTGTCATCGG | TGGGTCTCTAACAGTGGTTCT |
| FpPAL | CCACAGACGAACCAAGCAAGG | GGTGAGGCAGAGTGTGAGACT |
| FpCHS | CGTCGAGACCGTTGTGCTTCA | AGTTGGGTGGTGTCGCTGTC |
| FpCHI | TCGGAGTCTACTTGGAGGATAAGG | CCTGTAACGATCTCCCTGAAGAAC |
| Compounds | Molecular Weight | RT (min) | Relative Quantification | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | PF | WF | |||
| keracyanin | 594.15837 | 7.578 | 1.02 × 107 | 5.72 × 104 | 2.88 × 105 |
| cyanidin3-O-rutinoside 5-O-beta-D-glucoside betaine | 756.20857 | 7.935 | 4.20 × 105 | 3.88 × 104 | 2.65 × 105 |
| Procyanidin A2 | 576.12904 | 9.391 | 1.01 × 106 | 1.49 × 106 | 1.01 × 106 |
| Procyanidin B1 | 578.14221 | 6.305 | 4.40 × 106 | 5.06 × 106 | 9.58 × 106 |
| Procyanidin B2 | 578.14194 | 6.45 | 1.35 × 106 | 1.41 × 106 | 2.93 × 106 |
| Procyanidin C1 | 866.2036 | 1.371 | 1.05 × 105 | 3.13 × 105 | 4.42 × 105 |
| Myricetin | 318.03984 | 7.825 | 7.35 × 105 | 5.42 × 105 | 2.34 × 106 |
| Quercetin | 302.04234 | 8.733 | 1.68 × 107 | 3.94 × 107 | 1.53 × 107 |
| Dihydromyricetin | 320.05226 | 7.849 | 4.11 × 104 | 2.86 × 104 | 5.34 × 104 |
| Taxifolin | 304.05744 | 8.816 | 2.80 × 107 | 3.55 × 107 | 2.59 × 107 |
| Catechin | 290.07843 | 6.934 | 4.41 × 107 | 5.83 × 107 | 6.94 × 107 |
| Hesperetin | 302.0779 | 7.677 | 5.52 × 105 | 3.83 × 105 | 9.57 × 104 |
| Prunin | 434.1212 | 8.119 | 9.22 × 106 | 2.22 × 106 | 1.15 × 105 |
| Apiin | 564.14743 | 7.921 | 1.12 × 106 | 1.62 × 106 | 4.29 × 105 |
| Sample | Raw Reads | Raw Bases | Valid Reads | Valid Bases | Valid (%) | Q20% | Q30% | GC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF1 | 47,908,194 | 7.19 G | 44,887,508 | 6.73 G | 93.69 | 99.95 | 97.20 | 47 |
| RF2 | 44,473,914 | 6.67 G | 41,528,038 | 6.23 G | 93.38 | 99.95 | 97.17 | 47 |
| RF3 | 53,874,228 | 8.08 G | 49,677,842 | 7.45 G | 92.21 | 99.95 | 97.06 | 47 |
| PF1 | 54,261,864 | 8.14 G | 50,135,926 | 7.52 G | 92.40 | 99.95 | 97.08 | 47 |
| PF2 | 41,872,844 | 6.28 G | 37,341,402 | 5.60 G | 89.18 | 99.95 | 96.80 | 47 |
| PF3 | 61,661,466 | 9.25 G | 57,837,044 | 8.68 G | 93.80 | 99.95 | 97.05 | 47 |
| WF1 | 51,405,642 | 7.71 G | 48,344,662 | 7.25 G | 94.05 | 99.95 | 97.15 | 47 |
| WF2 | 64,389,242 | 9.66 G | 61,227,906 | 9.18 G | 95.09 | 99.95 | 96.96 | 47 |
| WF3 | 53,240,280 | 7.99 G | 49,899,752 | 7.48 G | 93.73 | 99.95 | 97.00 | 47 |
| Pathway Name | Pathway ID | KEGG Annotated |
|---|---|---|
| Caffeine metabolism | ko00232 | 3 |
| Aflatoxin biosynthesis | ko00254 | 1 |
| Indole alkaloid biosynthesis | ko00901 | 1 |
| Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis | ko00940 | 30 |
| Flavonoid biosynthesis | ko00941 | 18 |
| Anthocyanin biosynthesis | ko00942 | 4 |
| Isoflavonoid biosynthesis | ko00943 | 7 |
| Flavone and flavonol biosynthesis | ko00944 | 1 |
| Stilbenoid, diarylheptanoid, and gingerol biosynthesis | ko00945 | 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Tian, S.; Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Tang, X.; Guo, R. Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Revealed Genes Associated with the Formation of Different Fruit Colors in Fragaria pentaphylla. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091097
Yang X, Tian S, Zhao C, Li J, Wang L, Tang X, Guo R. Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Revealed Genes Associated with the Formation of Different Fruit Colors in Fragaria pentaphylla. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(9):1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091097
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xianan, Shiqi Tian, Chenxue Zhao, Jianxin Li, Lianjun Wang, Xuedong Tang, and Ruixue Guo. 2025. "Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Revealed Genes Associated with the Formation of Different Fruit Colors in Fragaria pentaphylla" Horticulturae 11, no. 9: 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091097
APA StyleYang, X., Tian, S., Zhao, C., Li, J., Wang, L., Tang, X., & Guo, R. (2025). Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Revealed Genes Associated with the Formation of Different Fruit Colors in Fragaria pentaphylla. Horticulturae, 11(9), 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091097






