Differential Responses of Spinach Cultivars to Micro-Nanoplastic Stress Under Hydroponic and Soil Cultivation Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurement Indices and Methods
2.4. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
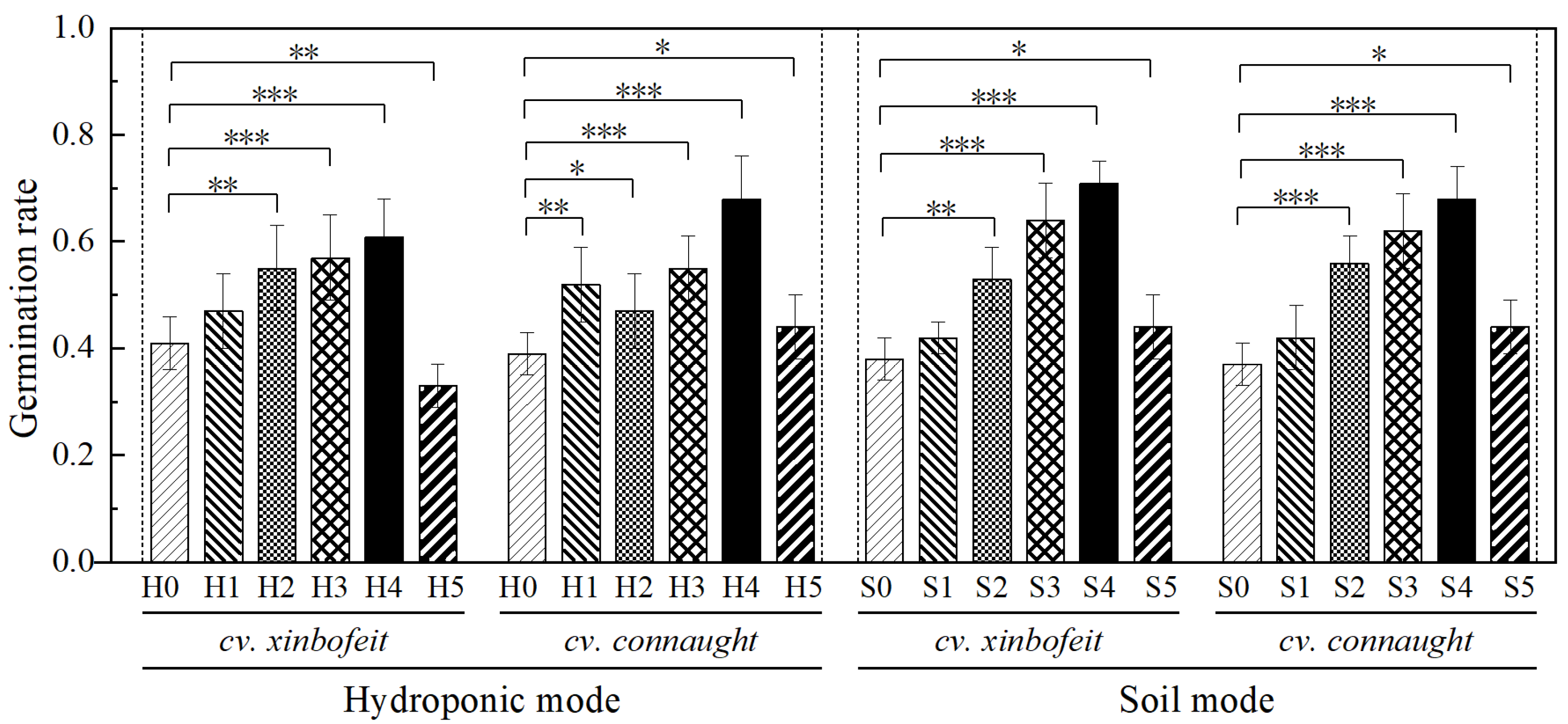
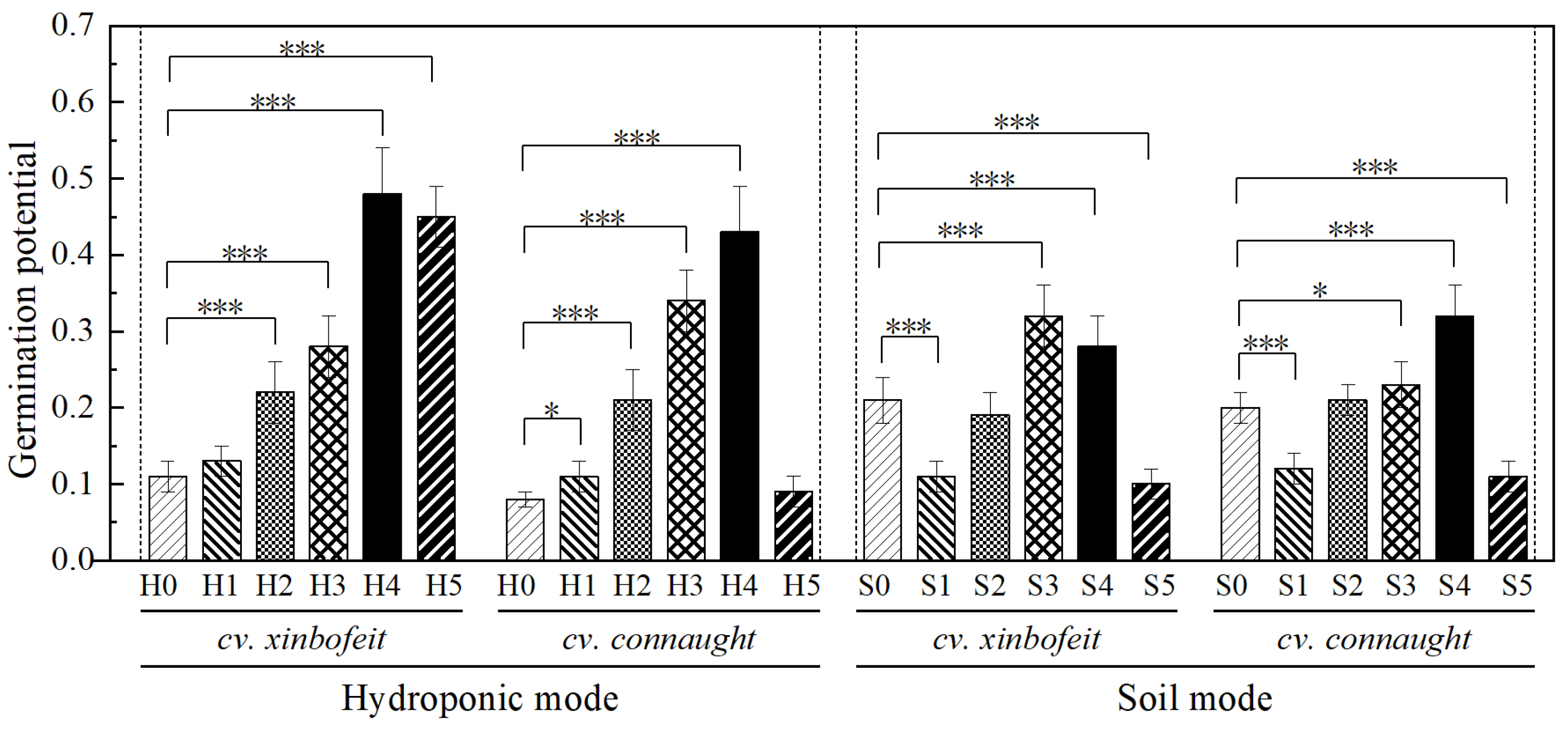
3.1. Effects of PVC-MNPs on Spinach Seed Germination
3.2. Effect of PVC-MNPs on the Growth of Spinach Sprouts
3.3. Effect of PVC-MNPs on the Antioxidant Properties of Spinach Sprouts
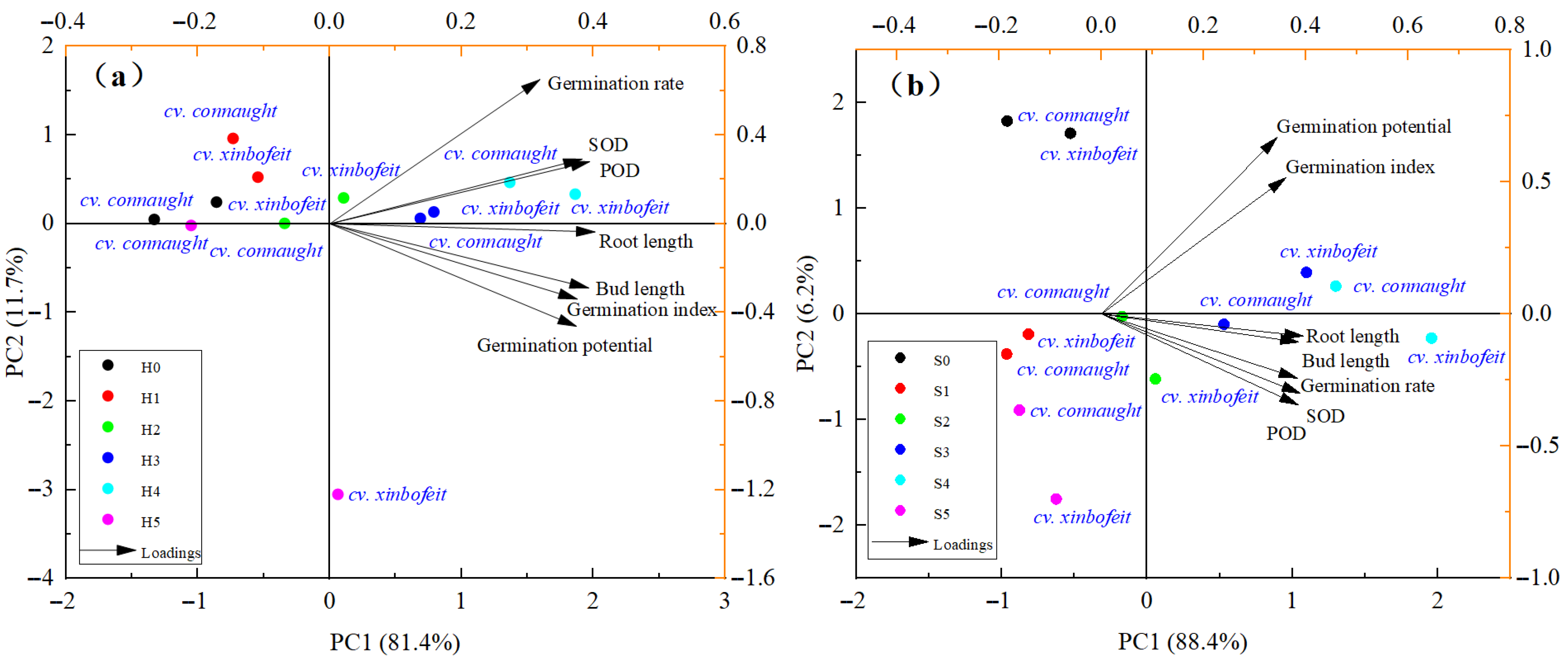
3.4. Principal Component Analysis of Spinach Sprout Growth
4. Discussion
4.1. Seed Germination Characteristics
4.2. Morphological Characteristics of Sprout Growth
4.3. Antioxidant Capacity of Sprouts
4.4. Principal Component Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, I.; Tariq, M.; Alabbosh, K.F.; Rehman, A.; Jalal, A.; Khan, A.A.; Farooq, M.; Li, G.; Iqbal, B.; Ahmad, N.; et al. Soil microplastics: Impacts on greenhouse gasses emissions, carbon cycling, microbial diversity, and soil characteristics. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 197, 105343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.Y.; Tang, Y.; Cheng, P.; Song, Y.; Li, X.; Lou, J.; Iqbal, B.; Zhao, X.; Hameed, R.; Li, G.; et al. Effects of degradable and non-degradable microplastics and oxytetracycline co-exposure on soil N2O and CO2 emissions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 197, 105331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, R.; Dai, W.; Luan, Y.; Li, J. Impacts of Micro(nano)plastics on terrestrial plants: Germination, growth, and litter. Plants 2023, 12, 3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Yu, Y.; Huang, S.; Chen, R.; Jia, X.; Chen, Y.; Xue, S.; Liu, M.; Yang, X. Effect of polyethylene microplastic concentration on the characteristics and stability of black soil aggregates. Soil Sci. 2023, 54, 56–66. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zuo, Z.; Hao, W.; Deng, L.; Xu, M. Effects of microplastics on soil aggregate stability and soil organic carbon mineralization. J. Northwest AF Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 51, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, B.; Zhao, T.; Yin, W.; Zhao, X.; Xie, Q.; Khan, K.Y.; Zhao, X.; Nazar, M.; Li, G.; Du, D. Impacts of soil microplastics on crops: A review. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 181, 104680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, G.; Qi, S.; Khan, I.U.; Li, G.; Dai, Z.; Du, D. The degradability of microplastics may not necessarily equate to environmental friendliness: A case study of cucumber seedlings with disturbed photosynthesis. Agriculture 2024, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payanthoth, N.S.; Mut, N.N.N.; Samanta, P.; Li, G.; Jung, J. A review of biodegradation and formation of biodegradable microplastics in soil and freshwater environments. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2024, 67, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodor, A.; Feigl, G.; Kolossa, B.; Mészáros, E.; Laczi, K.; Kovács, E.; Perei, K.; Rákhely, G. Soils in distress: The impacts and ecological risks of (micro)plastic pollution in the terrestrial environment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 269, 115807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Li, H. A review of trends in the use of sewage irrigation technology from the livestock and poultry breeding industries for farmlands. Irrig. Sci. 2022, 40, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hong, T.; Fang, W.; Chen, X. Optimized design for vibration reduction in a residual film recovery machine frame based on modal analysis. Agriculture 2024, 14, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, G.; Guo, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; Hamoud, Y.; Javed, Q. Response of fertigation under buried straw layer on growth, yield, and water-fertilizer productivity of Chinese cabbage under greenhouse conditions. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2019, 50, 1030–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, C.; Akhlaq, M. Effects of film mulching on the physiological and morphological parameters and yield of cucumber under insufficient drip irrigation. Irrig. Drain. 2022, 71, 897–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Luo, X.; Xu, J.; Yao, X.; Fan, J.; Mao, Y.; Song, Y.; Yang, J.; Pan, J.; Khattak, W.A. Dry-wet cycle changes the influence of microplastics (MPs) on the antioxidant activity of lettuce and the rhizospheric bacterial community. J. Soils Sedim. 2023, 23, 2189–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Xu, J.; Allen, S.; Khan, S.; Nadir, S.; Arif, M.; Yasmeen, T. Unraveling consequences of soil micro- and nano-plastic pollution on soil-plant system: Implications for nitrogen (N) cycling and soil microbial activity. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.; Zheng, H.; Liu, Y.; Zaib, A.; Rehman, S.; Riaz, N.; Eliw, M.; Hayat, F.; Li, H.; Wang, F. Effects of micro(nano)plastics on soil nutrient cycling: State of the knowledge. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cai, H.; Wen, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. Research progress on degradation of biodegradable micro-nano plastics and its toxic effect mechanism on soil ecosystem. Environ. Res. 2024, 262, 119979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Li, X.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.; Tang, S. Recent advances on multilevel effects of micro(nano)plastics and coexisting pollutants on terrestrial soil-plants system. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Xu, X.; Guo, L.; Jin, R.; Lu, Y. Uptake and transport of micro/nanoplastics in terrestrial plants: Detection, mechanisms, and influencing factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 907, 168155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, I.; Adeel, M.; Ahmad, M.A.; Shakoor, N.; Jiangcuo, G.D.; Azeem, K.; Ishfaq, M.; Shakoor, A.; Ayaz, M.; Xu, M.; et al. Uptake and accumulation of nano/microplastics in plants: A critical review. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosker, T.; Bouwman, L.; Brun, N.; Behrens, P.; Vijver, M. Microplastics accumulate on pores in seed capsule and delay germination and root growth of the terrestrial vascular plant Lepidium sativum. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Wu, J.; Xiong, H.; Zeb, A.; Yang, T.; Su, X.; Su, L.; Liu, W. Impact of polystyrene nanoplastics (PSNPs) on seed germination and seedling growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zantis, L.; Borchi, C.; Vijver, M.; Peijnenburg, W.; Di Lonardo, S.; Bosker, T. Nano- and microplastics commonly cause adverse impacts on plants at environmentally relevant levels: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 867, 161211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Shen, X.; Niu, Q.; Duan, H.; Tang, C.; Tao, B.; Chen, S.; Shangguan, Q.; Feng, B.; Yu, H.; et al. Thermally and chemically stable Fe/Mg-layered double oxides-biochar for enhanced polystyrene nanoplastic adsorption and sustainable recycling. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 508, 160918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yuan, W.; Xu, E.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y. Uptake, translocation, and biological impacts of micro(nano)plastics in terrestrial plants: Progress and prospects. Environ. Res. 2021, 203, 111867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, A.; Javed, Q.; Sun, J.; Ullah, I.; Buttar, N.A.; Saifullah, M.; Du, D. Effect of salt stress on seed germination and seedling vigour in okra. Indian. J. Hortic. 2020, 77, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, C.; Bian, Z.; Ye, Z.; Meng, L.; Xia, L.; Bao, E.; Cao, K. Abscisic acid and reactive oxygen species were involved in slightly acidic electrolyzed water-promoted seed germination in watermelon. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 291, 110581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, Y.; Landt, L.; Rillig, M. Plastic particles and their additives promote plant invasion through physicochemical mechanisms on seed germination. J. Ecol. 2025, 113, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhang, R.; Fan, J.; He, Y.; Mao, X. Comprehensive transformative profiling of nutritional and functional constituents during germination of soybean sprouts. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, N.; Feng, L. Toxic effects of microplastics and nanoplastics on plants: A global meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 337, 122593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanò, C.; Muccifora, S.; Castiglione, R.; Bellani, L.; Bottega, S.; Giorgetti, L. Polystyrene nanoplastics affect seed germination, cell biology and physiology of rice seedlings in-short term treatments: Evidence of their internalization and translocation. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 172, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, S.; Guchhait, R.; Sarkar, M.; Pramanick, K. Occurrence and distribution of micro/nanoplastics in soils and their phytotoxic effects: A review. Plant Cell Environ. 2022, 45, 1011–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Yang, X.; Tang, X.; Xu, L.; Hu, J.; Wang, M.; Wang-Pruski, G.; Zhang, Z. The Effect of microplastics with different types, particle sizes, and concentrations on the germination of non-heading chinese cabbage seed. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorobi, F.; Vyavahare, G.; Seok, Y.; Park, J. Effect of polypropylene microplastics on seed germination and nutrient uptake of tomato and cherry tomato plants. Chemosphere 2023, 329, 138679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahasa, R.; Dhevagi, P.; Poornima, R.; Ramya, A.; Moorthy, P.; Alagirisamy, B.; Karthikeyan, S. Effect of polyethylene microplastics on seed germination of Blackgram (Vigna mungo L.) and Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Environ. Adv. 2023, 11, 100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, M.M.; Ahmed, Z.; Ahmad, N.; Karrar, E.; Rehman, A.; Muhammad, A.R.; Al-Farga, A.; Waheed, I.M.; Rahaman, A.; Zeng, X. Probing the combined impact of pulsed electric field and ultra-sonication on the quality of spinach juice. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15475. [Google Scholar]
- Waseem, M.; Akhtar, S.; Manzoor, M.F.; Mirani, A.A.; Ali, Z.; Ismail, T.; Ahmad, N.; Karrar, E. Nutritional characterization and food value addition properties of dehydrated spinach powder. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yu, S.; Xu, H.; Aheto, J.H.; Bonah, E.; Ma, M.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X. Rapid and nondestructive detection of freshness quality of postharvest spinaches based on machine vision and electronic nose. J. Food Saf. 2019, 39, e12708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, M.; Lv, Y.; Wang, Q.; Qu, B.; Shao, M. Effects of temperature on seed germination of invasive plant Rorippa amphbia (L.) Besser. Biotechnol. J. Int. 2018, 22, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Luo, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, H.; Li, P. Effects of hydrogen-rich water combined with vacuum precooling on the senescence and antioxidant capacity of pakchoi (Brassica rapa subsp. Chinensis). Sci. Hortic. 2021, 289, 110469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Qu, C.; Wang, L. Cerium improves growth of maize seedlings via alleviating morphological structure and oxidative damages of leaf under different stresses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 9022–9030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethanis, J.; Golia, E. Micro- and nano-plastics in agricultural soils: A critical meta-analysis of their impact on plant growth, nutrition, metal accumulation in plant tissues and crop yield. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 194, 105202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galahitigama, H.; Sandamali, P.; Jayapra, T.; Abesinghe, N.; Senavirathna, M.; Diola, M.; Tanchuling, M. Assessing the impact of micro and nanoplastics on the productivity of vegetable crops in terrestrial horticulture: A comprehensive review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, G.; Guo, X.; Wang, Z.; Ali, M.U.; Chen, S.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Q.; Ullah, M.S. Coupling fertigation and buried straw layer improves fertilizer use efficiency, fruit yield, and quality of greenhouse tomato. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 239, 106239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Feng, X.; Liu, Y.; Adams, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, S. Micro(nano)plastics and terrestrial plants: Up-to-date knowledge on uptake, translocation, and phytotoxicity. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 185, 106503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y. Unveiling the impact of microplastics and nanoplastics on vascular plants: A cellular metabolomic and transcriptomic review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 279, 116490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Zhao, F.; Tian, L.; Ni, K.; Lu, Y.; Borah, P. Effects of polystyrene microplastics on the seed germination of herbaceous ornamental plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 809, 151100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, M.; Meng, F.; Xiao, Y.; Dai, W.; Luan, Y. Effect of polystyrene microplastics on rice seed germination and antioxidant enzyme activity. Toxics 2021, 9, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Yu, C.; Lei, X.; Xing, X.; Ma, X.; Sun, Y. The impact of microplastic concentration and particle size on the germination and seedling growth of Pisum sativum L. Agronomy 2024, 14, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, J.; Zu, J.; Wang, P.; Yang, Y. Effects of microplastics on seed germination and seedling physiological characteristics of Spinacia oleracea under alkali stress. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 2536–2544. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, C.; Kang, H.; Lee, Y.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.; Seo, J.; Wang, M.; Lee, J. Nanoplastic ingestion enhances toxicity of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the monogonont rotifer Brachionus koreanus via multixenobiotic resistance (MXR) disruption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11411–11418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, M.; Li, S.; Liang, G.; Bu, Q.; Xu, L.; Zhu, H.; Lu, A. Species-dependent response of food crops to polystyrene nanoplastics and microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Ding, L.; Wang, S.; Ding, R.; Qiu, X.; Li, J.; Hua, Z.; Liu, S.; Wu, R.; Liang, X.; et al. Metabolomics reveals how spinach plants reprogram metabolites to cope with intense stress responses induced by photoaged polystyrene nanoplastics (PSNPs). J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zima, H.; Clark, K.; Poudel-Ward, B.; Slinski, S.; Klosterman, S.; Correll, J. Evaluation of spinach cultivars for downy mildew resistance in Yuma, AZ, 2023. Plant Health Prog. 2025, 26, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Xu, X.; Guo, L.; Yuzuak, S.; Lu, Y. Physiological and biochemical effects of polystyrene micro/nano plastics on Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Zu, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, B. Effects of the combination of polystyrene nanoplastics and lead on seed germination and seedling growth of spinach (Spinacia oleracea). Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2023, 31, 967–975. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Chen, C.; Pang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, W.; Kan, H. Effects of microplastics concentration on plant root traits and biomass: Experiment and meta-analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 285, 117038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, Y.; Rajagopalan, U.; Kadono, H.; Li, D. Effects of microplastics on lentil (Lens culinaris) seed germination and seedling growth. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Weert, S.; Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.; Diepens, N.; Koelmans, A. Effects of nanoplastics and microplastics on the growth of sediment-rooted macrophytes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Cao, X.; Zhao, R.; Cui, Z. Stress response to nanoplastics with different charges in Brassica napus L. during seed germination and seedling growth stages. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2023, 17, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z. Impacts of micro/nanoplastics combined with graphene oxide on Lactuca sativa seeds: Insights into seedling growth, oxidative stress, and antioxidant gene expression. Plants 2024, 13, 3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatment | Cultivation Mode | PVC-MNP Concentration | |
|---|---|---|---|
| cv. xinbofeit | cv. connaught | ||
| H0 | Hydroponic | 0 mg·L−1 | |
| H1 | 1 mg·L−1 | ||
| H2 | 10 mg·L−1 | ||
| H3 | 50 mg·L−1 | ||
| H4 | 100 mg·L−1 | ||
| H5 | 200 mg·L−1 | ||
| S0 | Soil | 0.00% | |
| S1 | 0.10% | ||
| S2 | 0.20% | ||
| S3 | 0.50% | ||
| S4 | 1.00% | ||
| S5 | 2.00% | ||
| Treatment | Bud Length (mm) | Root Length (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cv. xinbofeit | cv. connaught | cv. xinbofeit | cv. connaught | |
| H0 | 12.36 ± 2.04 d | 9.65 ± 1.93 d | 13.52 ± 1.12 d | 10.54 ± 1.24 c |
| H1 | 13.96 ± 1.88 cd | 11.35 ± 2.38 cd | 13.12 ± 1.07 d | 11.42 ± 1.12 bc |
| H2 | 14.85 ± 2.03 c | 13.42 ± 2.36 c | 15.62 ± 1.56 c | 12.57 ± 1.40 b |
| H3 | 18.42 ± 1.21 ab | 15.74 ± 1.62 b | 18.22 ± 1.82 b | 16.81 ± 1.93 a |
| H4 | 20.36 ± 1.92 a | 18.22 ± 2.40 a | 20.35 ± 1.27 a | 17.42 ± 1.77 a |
| H5 | 17.73 ± 1.77 b | 12.05 ± 2.50 cd | 14.95 ± 1.37 c | 10.87 ± 1.29 c |
| Treatment | Bud Length (mm) | Root Length (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cv. xinbofeit | cv. connaught | cv. xinbofeit | cv. connaught | |
| S0 | 10.63 ± 2.96 c | 7.63 ± 2.09 d | 8.87 ± 1.75 d | 6.52 ± 1.09 d |
| S1 | 10.96 ± 1.96 c | 7.41 ± 2.03 d | 7.63 ± 1.33 d | 6.49 ± 1.57 d |
| S2 | 12.74 ± 2.94 c | 9.62 ± 2.26 c | 10.7 ± 1.45 c | 8.74 ± 1.38 c |
| S3 | 15.85 ± 2.39 b | 14.25 ± 1.68 b | 13.48 ± 1.86 b | 11.03 ± 1.30 b |
| S4 | 19.63 ± 1.85 a | 16.74 ± 1.85 a | 17.52 ± 1.50 a | 13.72 ± 1.61 a |
| S5 | 11.32 ± 2.23 c | 7.85 ± 2.48 d | 9.06 ± 1.53 d | 7.06 ± 1.41 d |
| Treatment | SOD (U/g) | POD (U/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cv. xinbofeit | cv. connaught | cv. xinbofeit | cv. connaught | |
| H0 | 576.32 ± 28.52 c | 549.24 ± 12.63 c | 74.63 ± 8.78 c | 71.51 ± 8.98 c |
| H1 | 589.41 ± 34.62 bc | 567.65 ± 25.62 bc | 78.41 ± 12.28 c | 84.63 ± 17.56 bc |
| H2 | 588.14 ± 24.32 bc | 576.74 ± 22.48 b | 86.92 ± 15.01 bc | 90.42 ± 12.47 b |
| H3 | 602.85 ± 25.47 b | 599.32 ± 32.41 ab | 104.60 ± 17.37 b | 111.98 ± 14.25 a |
| H4 | 657.92 ± 32.63 a | 615.47 ± 19.57 a | 132.54 ± 11.06 a | 119.44 ± 17.03 a |
| H5 | 564.57 ± 26.95 c | 552.14 ± 24.74 c | 75.96 ± 12.76 c | 69.51 ± 17.69 c |
| Treatment | SOD (U/g) | POD (U/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cv. xinbofeit | cv. connaught | cv. xinbofeit | cv. connaught | |
| S0 | 555.62 ± 12.63 c | 537.63 ± 19.47 d | 69.32 ± 12.74 d | 66.34 ± 14.63 d |
| S1 | 554.65 ± 14.54 c | 557.95 ± 20.65 cd | 68.41 ± 9.07 d | 74.85 ± 13.02 cd |
| S2 | 596.32 ± 24.68 b | 584.25 ± 15.48 b | 84.96 ± 11.85 bc | 82.41 ± 11.70 c |
| S3 | 625.74 ± 22.57 a | 598.90 ± 26.96 ab | 99.74 ± 14.39 b | 93.52 ± 10.85 b |
| S4 | 639.57 ± 18.64 a | 626.45 ± 28.45 a | 121.33 ± 10.74 a | 105.87 ± 12.16 a |
| S5 | 572.63 ± 21.07 bc | 562.38 ± 19.52 c | 82.54 ± 12.71 c | 78.85 ± 12.21 cd |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.; Zhang, R.; Bao, X.; Ji, F.; Zuo, Z.; Geng, W. Differential Responses of Spinach Cultivars to Micro-Nanoplastic Stress Under Hydroponic and Soil Cultivation Conditions. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091062
Song J, Zhang R, Bao X, Ji F, Zuo Z, Geng W. Differential Responses of Spinach Cultivars to Micro-Nanoplastic Stress Under Hydroponic and Soil Cultivation Conditions. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(9):1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091062
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Jinxiu, Rong Zhang, Xiaotong Bao, Fang Ji, Zhiyu Zuo, and Wei Geng. 2025. "Differential Responses of Spinach Cultivars to Micro-Nanoplastic Stress Under Hydroponic and Soil Cultivation Conditions" Horticulturae 11, no. 9: 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091062
APA StyleSong, J., Zhang, R., Bao, X., Ji, F., Zuo, Z., & Geng, W. (2025). Differential Responses of Spinach Cultivars to Micro-Nanoplastic Stress Under Hydroponic and Soil Cultivation Conditions. Horticulturae, 11(9), 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091062






