Lightweight YOLOv11n-Based Detection and Counting of Early-Stage Cabbage Seedlings from UAV RGB Imagery
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Designing an adaptive dual-path downsampling module (ADown), which effectively suppresses background noise and enhances target edge features through parallel average and maximum pooling operations. The merged feature representation improves the ability to distinguish targets in complex field environments.
- (2)
- The illumination-robust contrastive learning head (IRCLHead) dynamically adjusts contrast loss parameters through a temperature-adaptive network. It also combines a dual-output supervision mechanism to extract features with strong discriminative ability and illumination invariance. This effectively enhances the model’s adaptability under complex illumination conditions.
- (3)
- A lightweight spatial-channel attention convolution module (LAConv) has been developed, combining multi-scale feature extraction and a deep decomposition structure to integrate spatial pyramid pooling with channel attention mechanisms effectively. This reduces computational complexity while achieving adaptive capture of seedling morphological features and suppression of background interference. This meets the computational resource requirements of drone edge computing platforms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
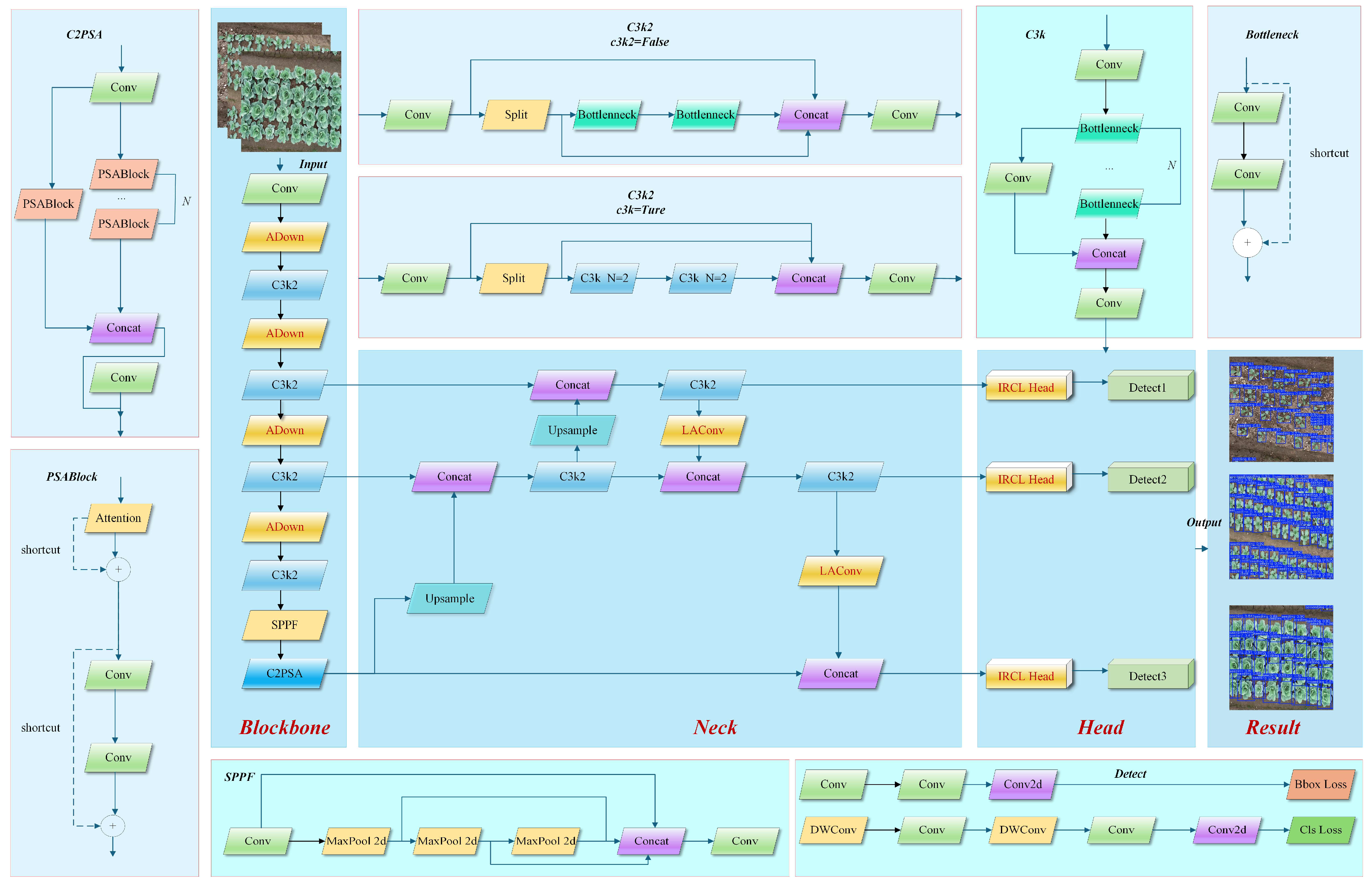
2.2. Improved Model Architecture
2.2.1. Adaptive Dual-Path Downsampling
2.2.2. Illumination-Robust Contrastive Learning Head
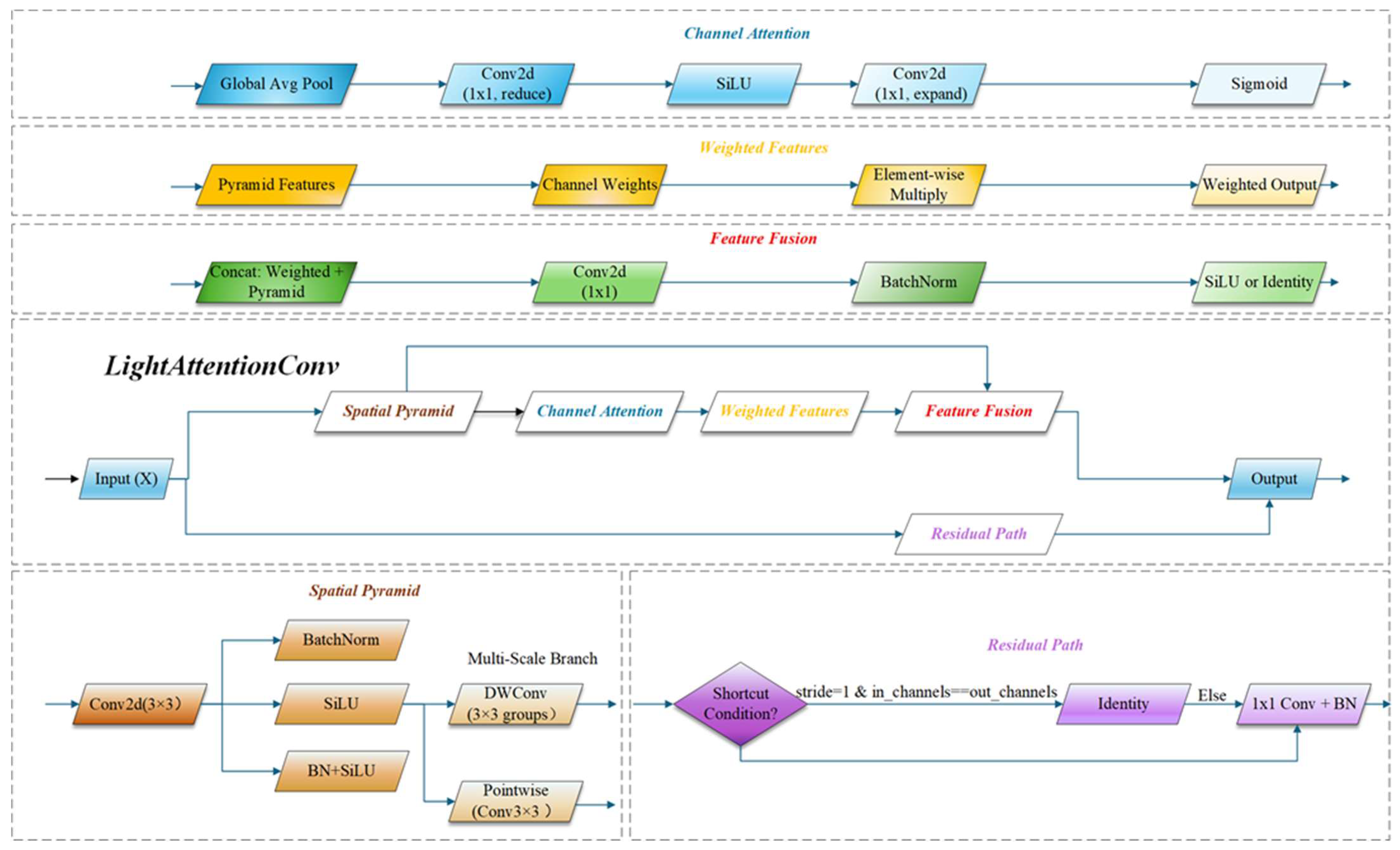
2.2.3. Light Attention Conv
2.2.4. Real-Time Cabbage Seedling Counting Model
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Environment
3.2. Evaluation Metrics
3.3. Comparison Experiments
3.3.1. Comparison of the Improved Model with the Baseline Model
3.3.2. Comparison of the Improved Model with Other Network Models
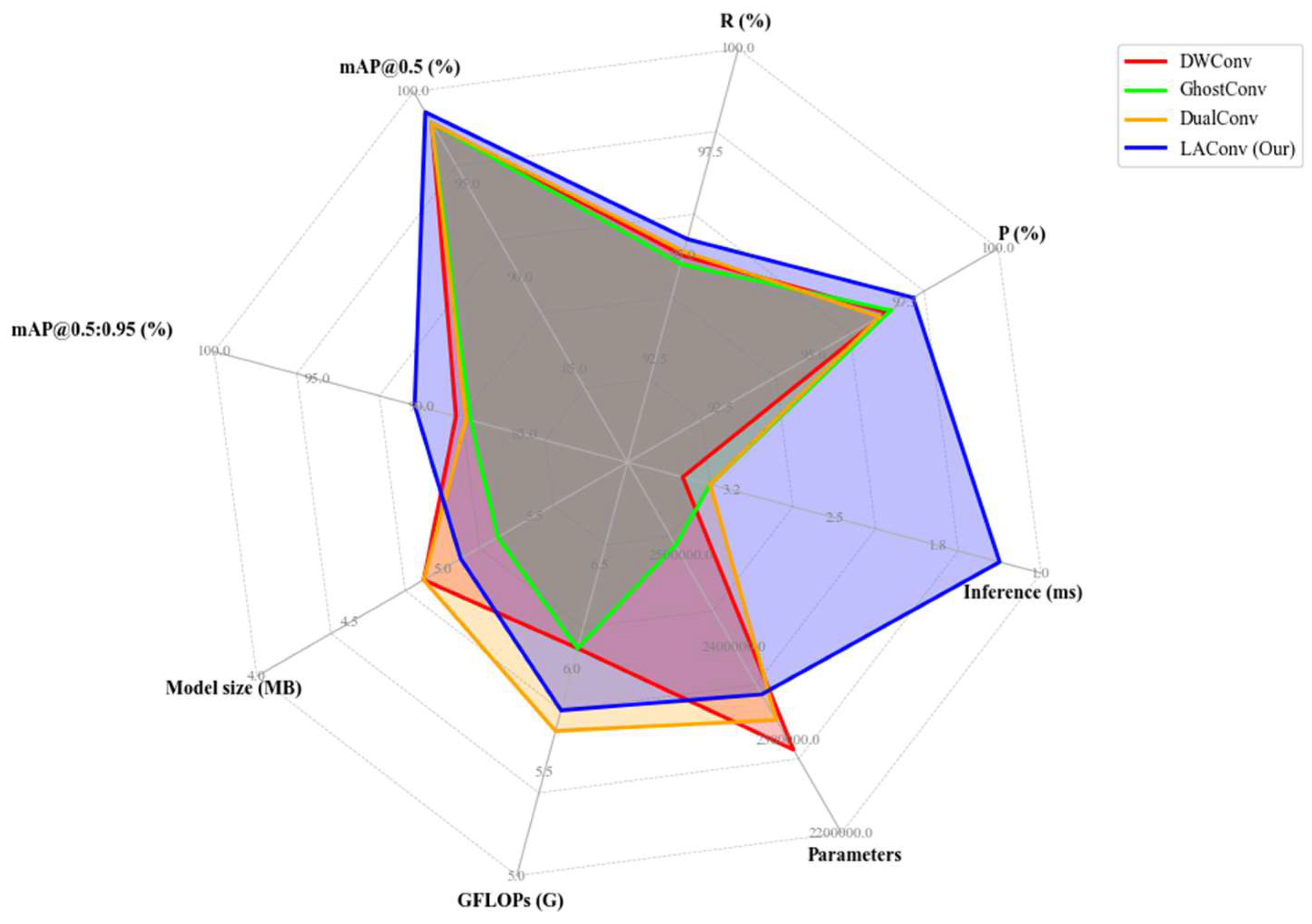
3.3.3. Radar Chart Comparing Different Convolutions
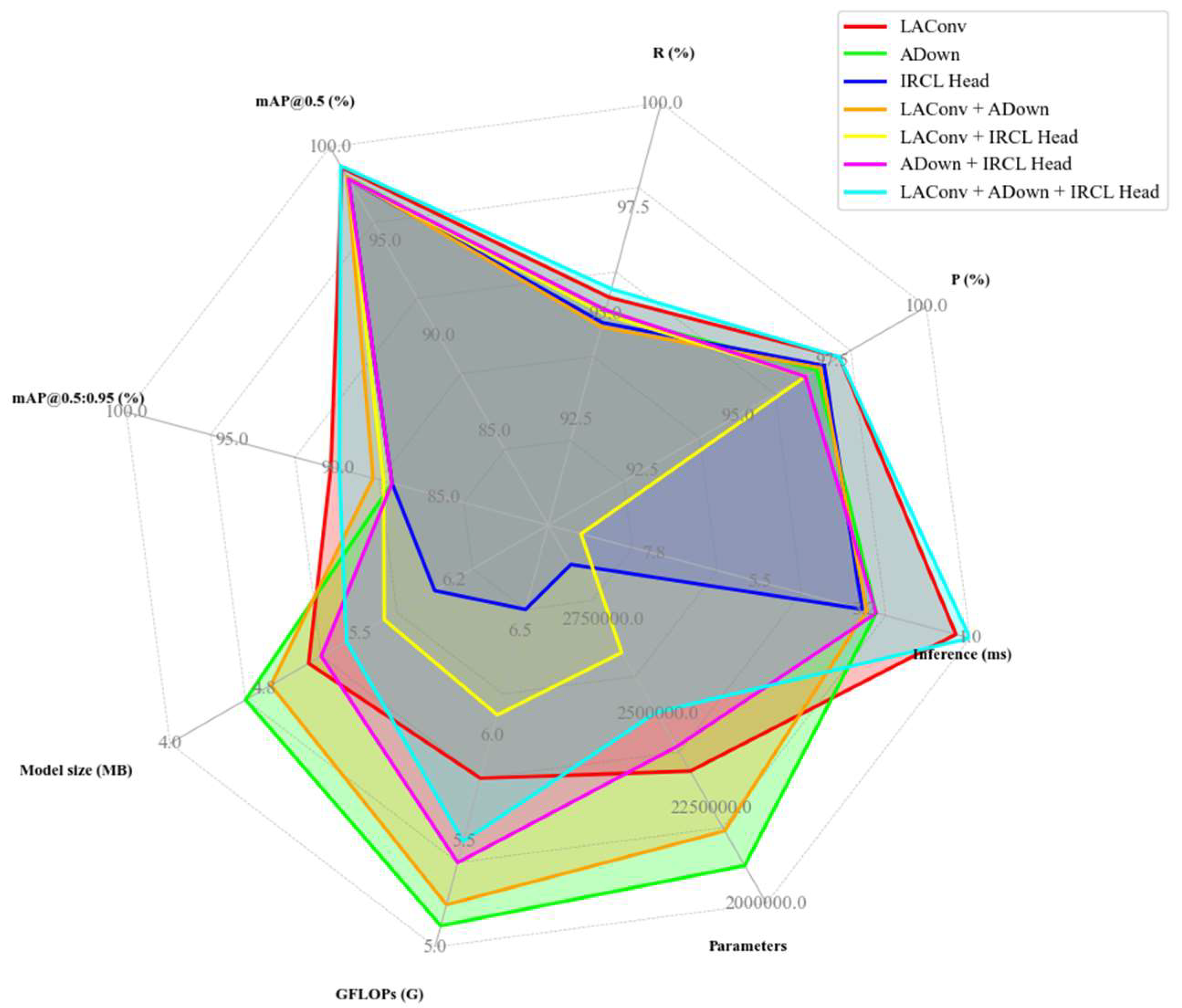
3.4. Ablation Experiment
3.5. Counting Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mostafa, S.; Mondal, D.; Panjvani, K.; Kochian, L.; Stavness, I. Explainable deep learning in plant phenotyping. Front. Artif. Intell. 2023, 6, 1203546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, L.; Wei, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, M.; Luo, S. DualSeg: Fusing transformer and CNN structure for image segmentation in complex vineyard environment. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 206, 107682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreb, N.; Murphy, A.; Jaiswal, S.; Jaiswal, A.K. Cabbage. In Nutritional Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Fruits and Vegetables; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 33–54. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Miao, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhu, H.; Wu, H. Cabbage Transplantation State Recognition Model Based on Modified YOLOv5-GFD. Agronomy 2024, 14, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, T.; Wu, H.; Zhao, Y. Recognition Method of Cabbage Heads at Harvest Stage under Complex Background Based on Improved YOLOv8n. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; He, Y.; Song, J.; Wang, J.; Xi, D.; Shao, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G. Smart UAV-assisted blueberry maturity monitoring with Mamba-based computer vision. Precis. Agric. 2025, 26, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, E.; Liang, Z. Apple detection during different growth stages in orchards using the improved YOLO-V3 model. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 157, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Lv, S.; Jiang, M.; Song, H. Using channel pruning-based YOLO v4 deep learning algorithm for the real-time and accurate detection of apple flowers in natural environments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 178, 105742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Shao, C.; Zhou, C.; Yao, L. A method for cabbage root posture recognition based on YOLOv5s. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, R.; Ahmed, D.; Karkee, M. Comparing YOLOv8 and Mask R-CNN for instance segmentation in complex orchard environments. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2024, 13, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luling, N.; Reiser, D.; Straub, J.; Stana, A.; Griepentrog, H.W. Fruit Volume and Leaf-Area Determination of Cabbage by a Neural-Network-Based Instance Segmentation for Different Growth Stages. Sensors 2022, 23, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, R.; Flores-Calero, M.; Qureshi, R.; Badgujar, C.; Nepal, U.; Poulose, A.; Zeno, P.; Vaddevolu, U.B.P.; Khan, S.; Shoman, M.; et al. YOLO advances to its genesis: A decadal and comprehensive review of the You Only Look Once (YOLO) series. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2025, 58, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Wang, B. Recognition Model for Tea Grading and Counting Based on the Improved YOLOv8n. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongdee, P.; Teeyapan, K. A Comparative Study of Deep Learning Models for Cabbage Detection and Counting in Drone Imagery. In Proceedings of the 2025 17th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST), Bangkok, Thailand, 26 February–1 March 2025; pp. 260–265. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhang, T.; Wu, H.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, Y. CabbageNet: Deep Learning for High-Precision Cabbage Segmentation in Complex Settings for Autonomous Harvesting Robotics. Sensors 2024, 24, 8115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Qin, C.; Choi, D. YOLO-SDLUWD: YOLOv7-based small target detection network for infrared images in complex backgrounds. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2025, 11, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, D.; Tao, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhang, D. SR-YOLO: Spatial-to-Depth Enhanced Multi-Scale Attention Network for Small Target Detection in UAV Aerial Imagery. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Shao, C.; Cheng, D.; Yao, L.; Zhou, C. YOLOv5-POS: Research on cabbage pose prediction method based on multi-task perception technology. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1455687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Zhao, X.; Tan, H.; Zheng, S.; Zhai, C.; Chen, L. Effective methods for mitigate the impact of light occlusion on the accuracy of online cabbage recognition in open fields. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2025, 15, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Keypoint detection and diameter estimation of cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.) heads under varying occlusion degrees via YOLOv8n-CK network. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 226, 109428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, T.; Han, K.; Jin, X.; Wang, J.; Kong, X.; Yu, J. TSP-yolo-based deep learning method for monitoring cabbage seedling emergence. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 157, 127191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Li, A.; Liu, T.; Han, K.; Jin, X.; Chen, X.; Yu, J. Lightweight cabbage segmentation network and improved weed detection method. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 226, 109403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Yuan, K.; Shui, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Z. A Lightweight Method for Ripeness Detection and Counting of Chinese Flowering Cabbage in the Natural Environment. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Cai, D.; Jin, Z.; Xu, T.; Yu, F. Research on unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) rice field weed sensing image segmentation method based on CNN-transformer. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 229, 109719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Y. Detecting soybean leaf disease from synthetic image using multi-feature fusion faster R-CNN. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 183, 106064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, A.; Moncada, C.; Crespo, F.; Morocho-Cayamcela, M.E. An efficient strawberry segmentation model based on Mask R-CNN and TensorRT. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2025, 15, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhao, J.; Bi, C.G.; Shi, L.; Chen, H. A Lightweight YOLOv5 Target Detection Model and Its Application to the Measurement of 100-Kernel Weight of Corn Seeds. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousafzai, S.N.; Nasir, I.M.; Tehsin, S.; Fitriyani, N.L.; Syafrudin, M. FLTrans-Net: Transformer-based feature learning network for wheat head detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 229, 109706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Cao, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Feng, S.; Xu, T. Study on lightweight rice blast detection method based on improved YOLOv8. Pest Manag. Sci. 2025, 81, 4300–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, J.; Liu, W.; Yue, R.; Yao, M.; Shi, J.; Hu, J. Seedling-YOLO: High-Efficiency Target Detection Algorithm for Field Broccoli Seedling Transplanting Quality Based on YOLOv7-Tiny. Agronomy 2024, 14, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, F.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, C.; Peng, X. Detection of Camellia oleifera fruit maturity in orchards based on modified lightweight YOLO. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 226, 109471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Z.; Li, J.; Song, K.; Qi, J. Performance and speed optimization of DLV3-CRSNet for semantic segmentation of Chinese cabbage (Brassica pekinensis Rupr.) and weeds. Crop Prot. 2025, 195, 107236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Fang, N.; Liu, N.; Lin, F.; Yang, S.; Ning, J. Visual recognition of cherry tomatoes in plant factory based on improved deep instance segmentation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 197, 106991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M. Yolov11: An overview of the key architectural enhancements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Chen, X.; Duan, Z. LCDDN-YOLO: Lightweight Cotton Disease Detection in Natural Environment, Based on Improved YOLOv8. Agriculture 2025, 15, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Yang, K.; Lin, Y.; Guo, S.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Lai, R.; Zhang, H. A comparison between Pixel-based deep learning and Object-based image analysis (OBIA) for individual detection of cabbage plants based on UAV Visible-light images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 209, 107822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Liu, C.; Wu, M.; Zhang, H.; Song, H.; Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Hu, J. Real-time detection of Chinese cabbage seedlings in the field based on YOLO11-CGB. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1558378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Wang, G.; Qi, J.; Wang, Q.; Xiang, M.; Song, K.; Zhou, Z. Improved YOLO v7 for Sustainable Agriculture Significantly Improves Precision Rate for Chinese Cabbage (Brassica pekinensis Rupr.) Seedling Belt (CCSB) Detection. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Qi, A.; Zhong, J.; Luo, Y.; Hu, W.; Shi, Y.; Liu, T. Field cabbage detection and positioning system based on improved YOLOv8n. Plant Methods 2024, 20, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
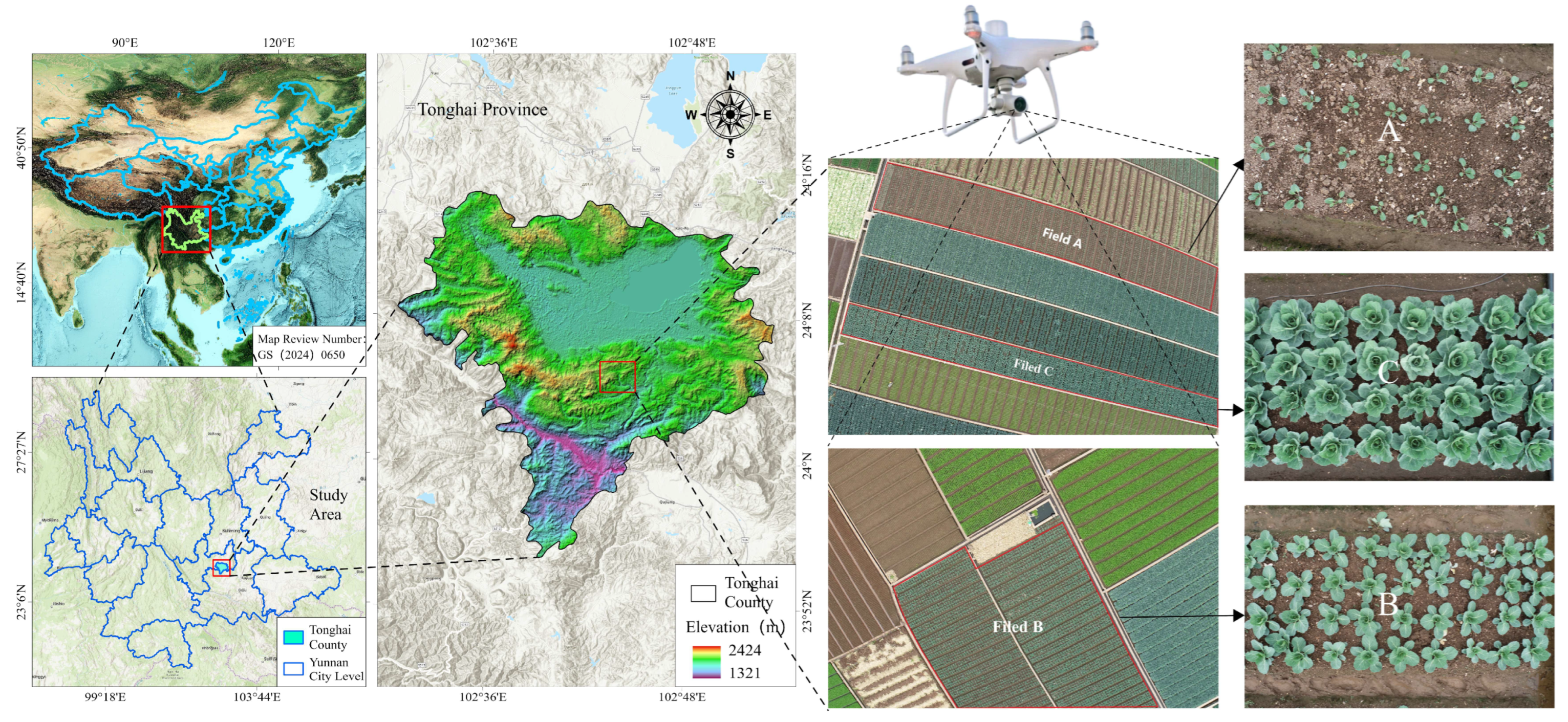

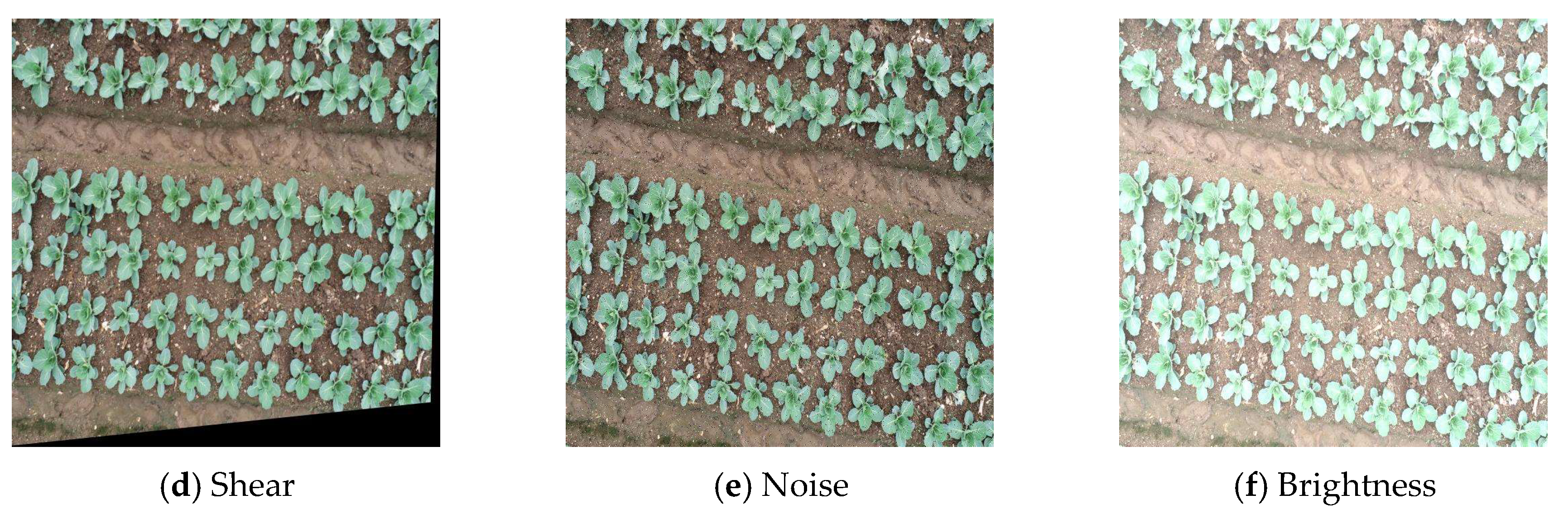


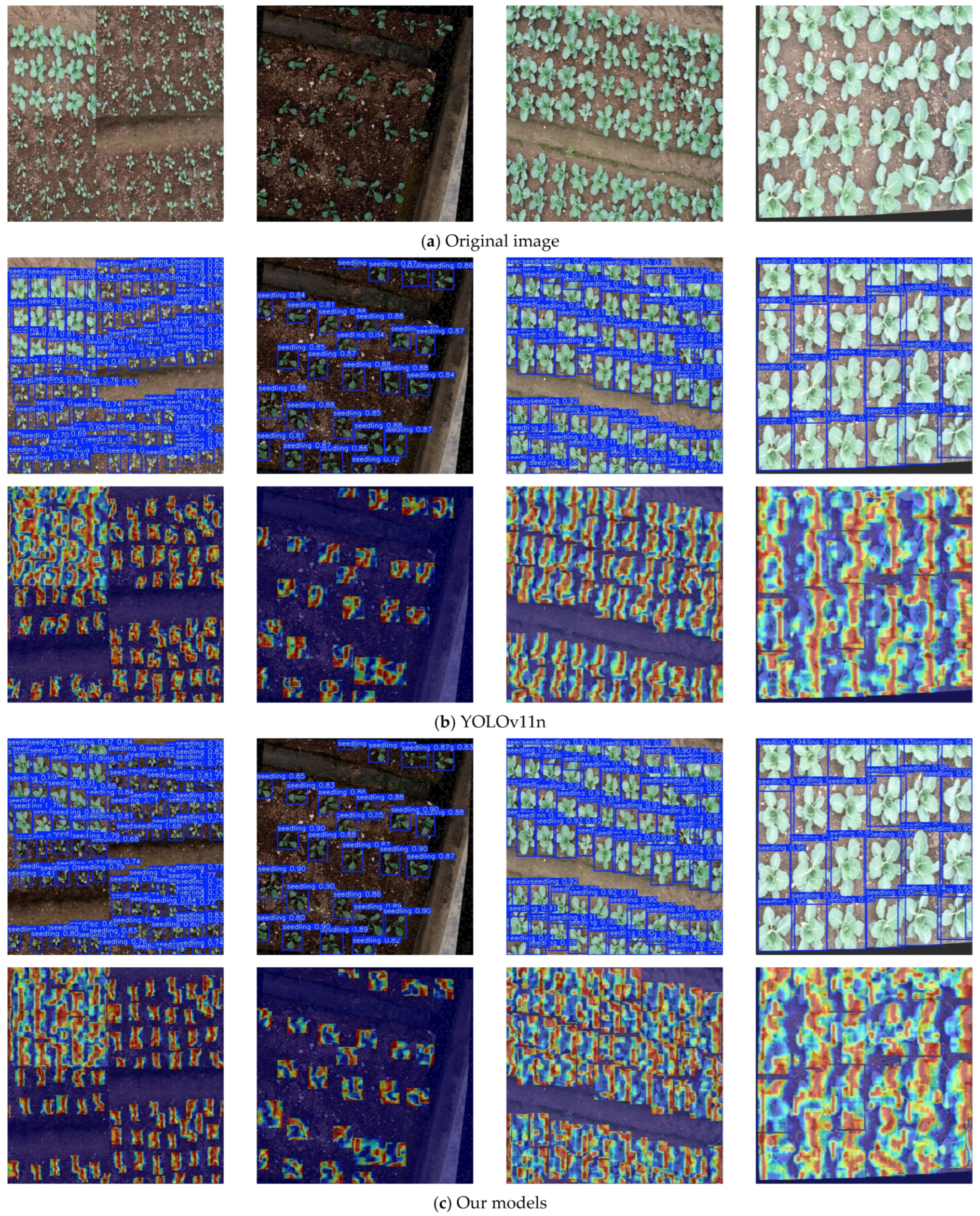

| Dataset | Total Number of Pictures | Training Set | Validation Set | Test Set |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original image | 820 | 574 | 164 | 82 |
| Data enhancement | 4669 | 3268 | 934 | 467 |
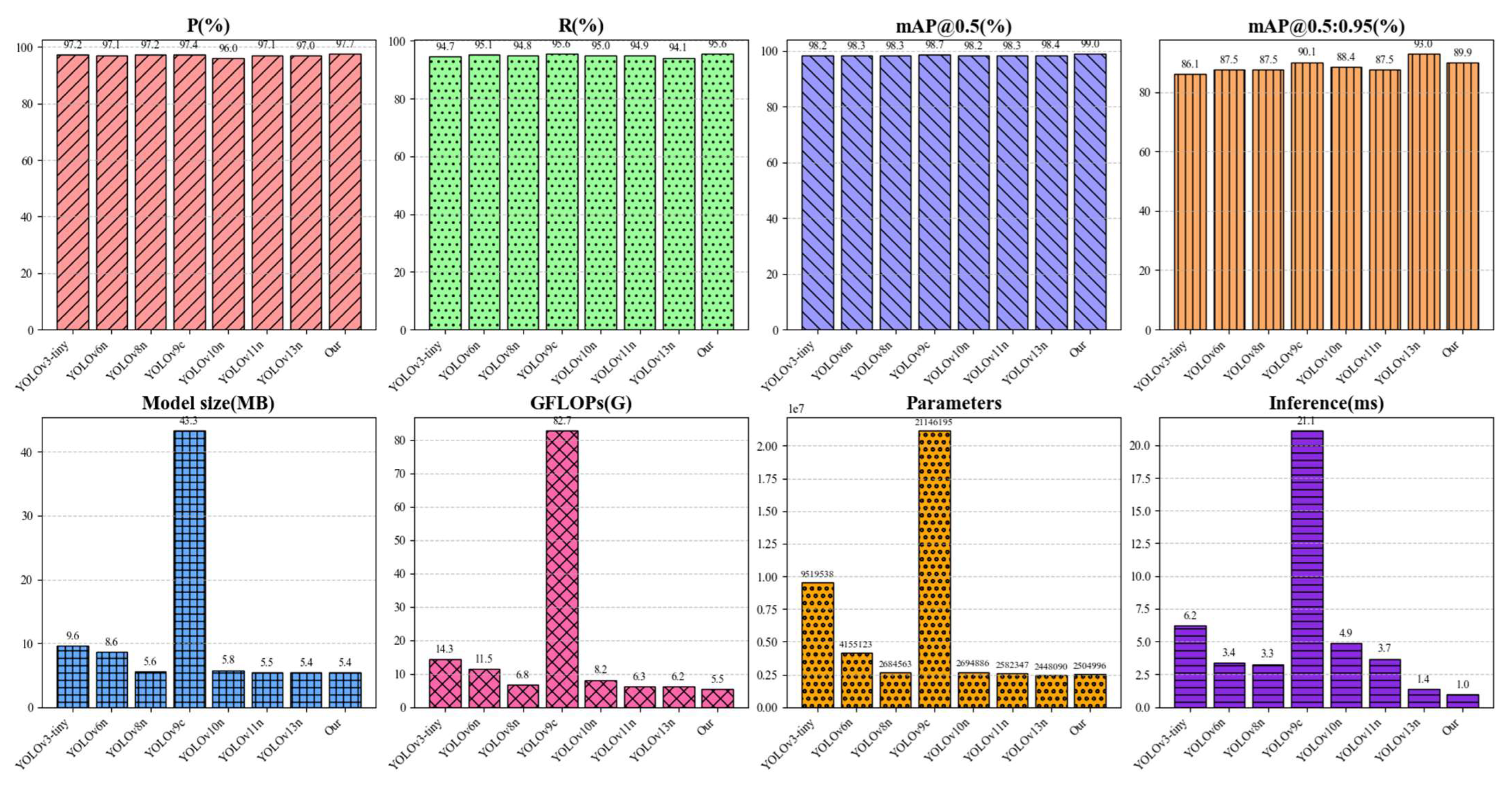
| Models | P (%) | R (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.5:0.95 (%) | Model Size (MB) | GFLOPs (G) | Parameters | Inference (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv11n | 97.1 | 94.9 | 98.3 | 87.5 | 5.5 | 6.3 | 2,582,347 | 3.7 |
| Our | 97.7 | 95.6 | 99.0 | 89.9 | 5.4 | 5.5 | 2,504,996 | 1.0 |
| Models | P (%) | R (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.5:0.95 (%) | Model Size (MB) | GFLOPs (G) | Parameters | Inference (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv3-tiny | 97.2 | 94.7 | 98.2 | 86.1 | 9.6 | 14.3 | 9,519,538 | 6.2 |
| YOLOv6n | 97.1 | 95.1 | 98.3 | 87.5 | 8.6 | 11.5 | 4,155,123 | 3.4 |
| YOLOv8n | 97.2 | 94.8 | 98.3 | 87.5 | 5.6 | 6.8 | 2,684,563 | 3.3 |
| YOLOv9c | 97.4 | 95.6 | 98.7 | 90.1 | 43.3 | 82.7 | 21,146,195 | 21.1 |
| YOLOv10n | 96.0 | 95.0 | 98.2 | 88.4 | 5.8 | 8.2 | 2,694,886 | 4.9 |
| YOLOv11n | 97.1 | 94.9 | 98.3 | 87.5 | 5.5 | 6.3 | 2,582,347 | 3.7 |
| Our | 97.7 | 95.6 | 99.0 | 89.9 | 5.4 | 5.5 | 2,504,996 | 1.0 |
| Models | P (%) | R (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.5:0.95 (%) | Model Size (MB) | GFLOPs (G) | Parameters | Inference (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSP-yolo Chen et al. [21] | 98.5 | 97.8 | 99.4 | 90.3 | \ | \ | \ | 1.0 |
| YOLO11CGB Shi et al. [37] | \ | \ | 97.0 | \ | \ | 4.1 | 3.2 | \ |
| YOLOv7 Gao et al. [38] | 94.3 | \ | 83.4 | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ |
| YOLOv8n Jiang et al. [39] | 95.5 | 85.1 | 93.9 | \ | \ | \ | \ | 26.3 |
| Models | P (%) | R (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.5:0.95 (%) | Model Size (MB) | GFLOPs (G) | Parameters | Inference (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DWConv | 97.0 | 95.0 | 98.3 | 88.3 | 4.9 | 6.1 | 2,289,739 | 3.6 |
| GhostConv | 97.1 | 94.8 | 98.3 | 87.6 | 5.3 | 6.1 | 2,510,219 | 3.4 |
| DualConv | 96.8 | 95.1 | 98.3 | 87.8 | 4.9 | 5.7 | 2,321,838 | 3.4 |
| LAConv (Our) | 97.7 | 95.4 | 98.9 | 90.3 | 5.1 | 5.8 | 2,349,443 | 1.3 |
| ADown | IRCLHead | LAConv | P(%) | R(%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.5:0.95 (%) | Model Size (MB) | GFLOPs (G) | Parameters | Inference (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✕ | ✕ | ✓ | 97.7 | 95.4 | 98.9 | 90.3 | 5.1 | 5.8 | 2,349,443 | 1.3 |
| ✓ | ✕ | ✕ | 97.1 | 95.0 | 98.4 | 87.4 | 4.6 | 5.1 | 2,099,787 | 3.0 |
| ✕ | ✓ | ✕ | 97.3 | 94.8 | 98.3 | 87.4 | 6.1 | 6.6 | 2,895,940 | 3.3 |
| ✓ | ✕ | ✓ | 97.2 | 94.7 | 98.4 | 88.3 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 2,191,403 | 3.2 |
| ✕ | ✓ | ✓ | 96.8 | 95.0 | 98.3 | 87.8 | 5.7 | 6.1 | 2,663,036 | 9.3 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✕ | 96.8 | 95.1 | 98.3 | 87.4 | 5.2 | 5.4 | 2,413,380 | 3.0 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 97.7 | 95.6 | 99.0 | 89.9 | 5.4 | 5.5 | 2,504,996 | 1.0 |
| Method | Number of Instances | Number of Detection Boxes | Accuracy (%) | Time (Min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real-time counting model based on YOLOv11n | 820 | 27,650 | 99.6 | 27.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, R.; Luo, R.; Ding, X.; Cui, J.; Yi, B. Lightweight YOLOv11n-Based Detection and Counting of Early-Stage Cabbage Seedlings from UAV RGB Imagery. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080993
Zhao R, Luo R, Ding X, Cui J, Yi B. Lightweight YOLOv11n-Based Detection and Counting of Early-Stage Cabbage Seedlings from UAV RGB Imagery. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(8):993. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080993
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Rongrui, Rongxiang Luo, Xue Ding, Jiao Cui, and Bangjin Yi. 2025. "Lightweight YOLOv11n-Based Detection and Counting of Early-Stage Cabbage Seedlings from UAV RGB Imagery" Horticulturae 11, no. 8: 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080993
APA StyleZhao, R., Luo, R., Ding, X., Cui, J., & Yi, B. (2025). Lightweight YOLOv11n-Based Detection and Counting of Early-Stage Cabbage Seedlings from UAV RGB Imagery. Horticulturae, 11(8), 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080993






