Exogenous Melatonin Affects Fruit Enlargement and Sugar Metabolism in Melt Peach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fruit Material and Experimental Design
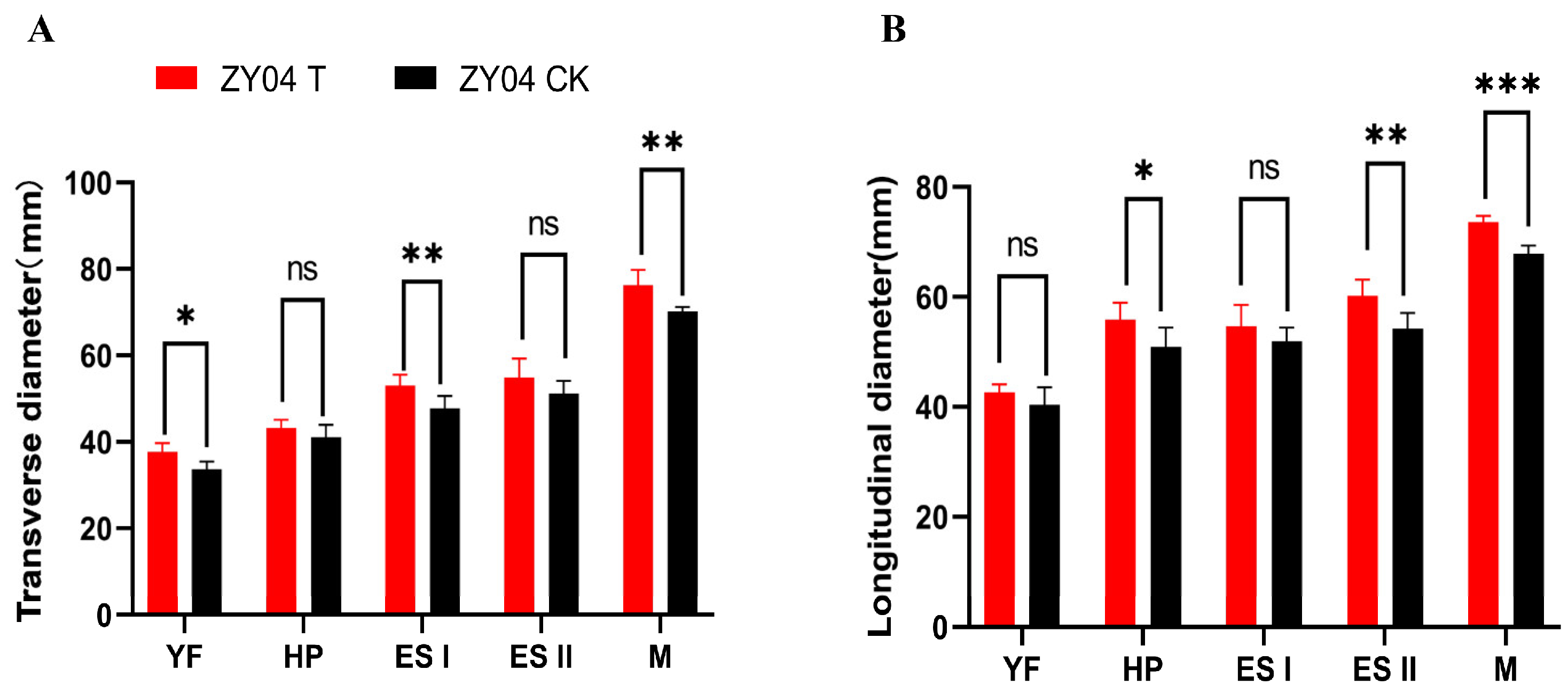
2.2. Measurement of the Transverse Diameter and Total Diameter of Peach Fruits
2.3. Determination of Total Soluble Solids and TA Contents in Peach Fruits
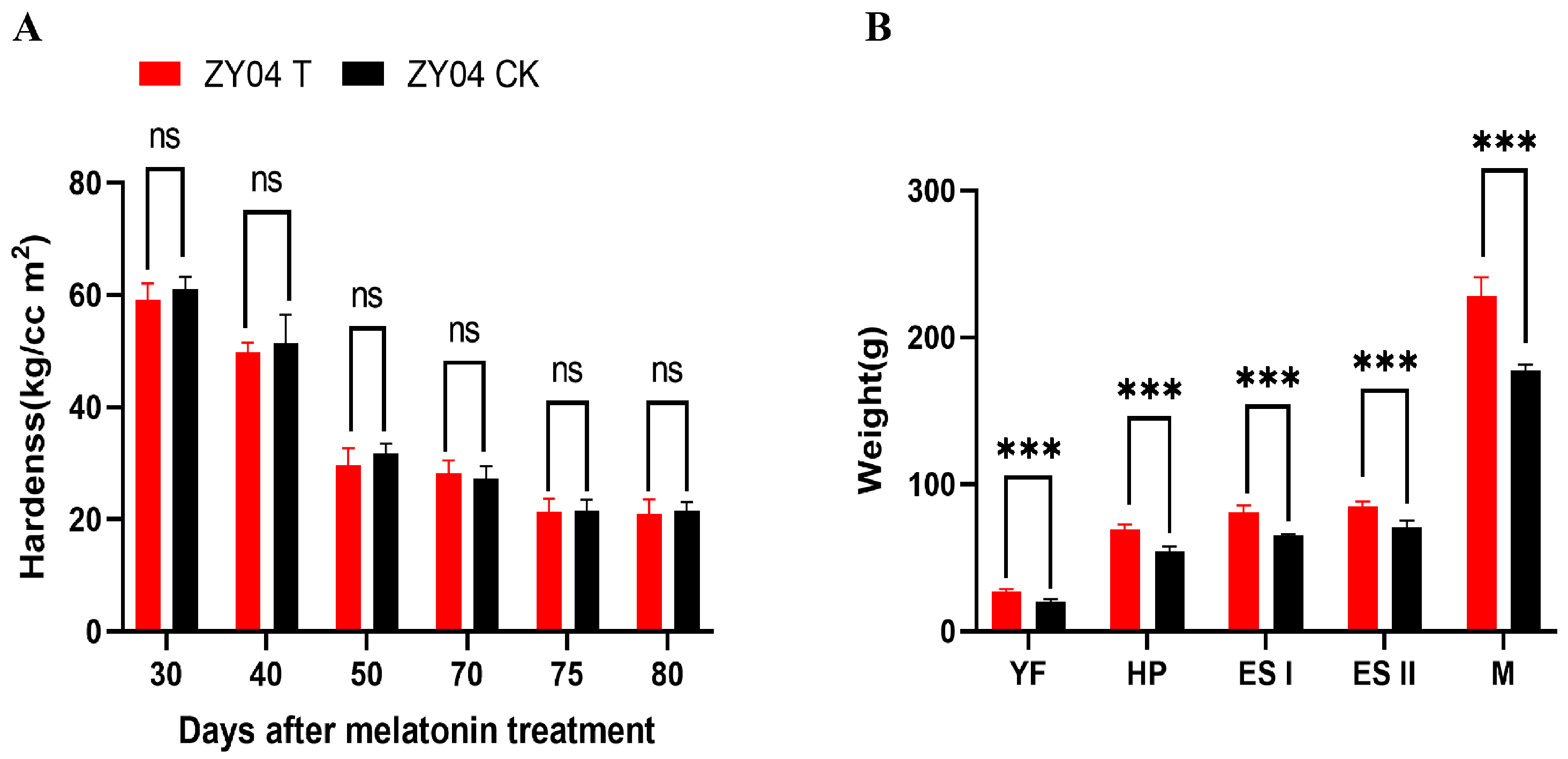
2.4. The Hardness and Individual Weight of Peach Fruits
2.5. Determination of Sugar Content in Peach Fruits
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Exogenous Treatment of Melatonin Increases the Fruit Shape of Peaches
3.2. The Effect of Exogenous Treatment of Melatonin on Soluble Solids and Titratable Acids in Peach Fruits
3.3. The Effect of Exogenous Melatonin Treatment on the Weight and Firmness of Peach Fruits
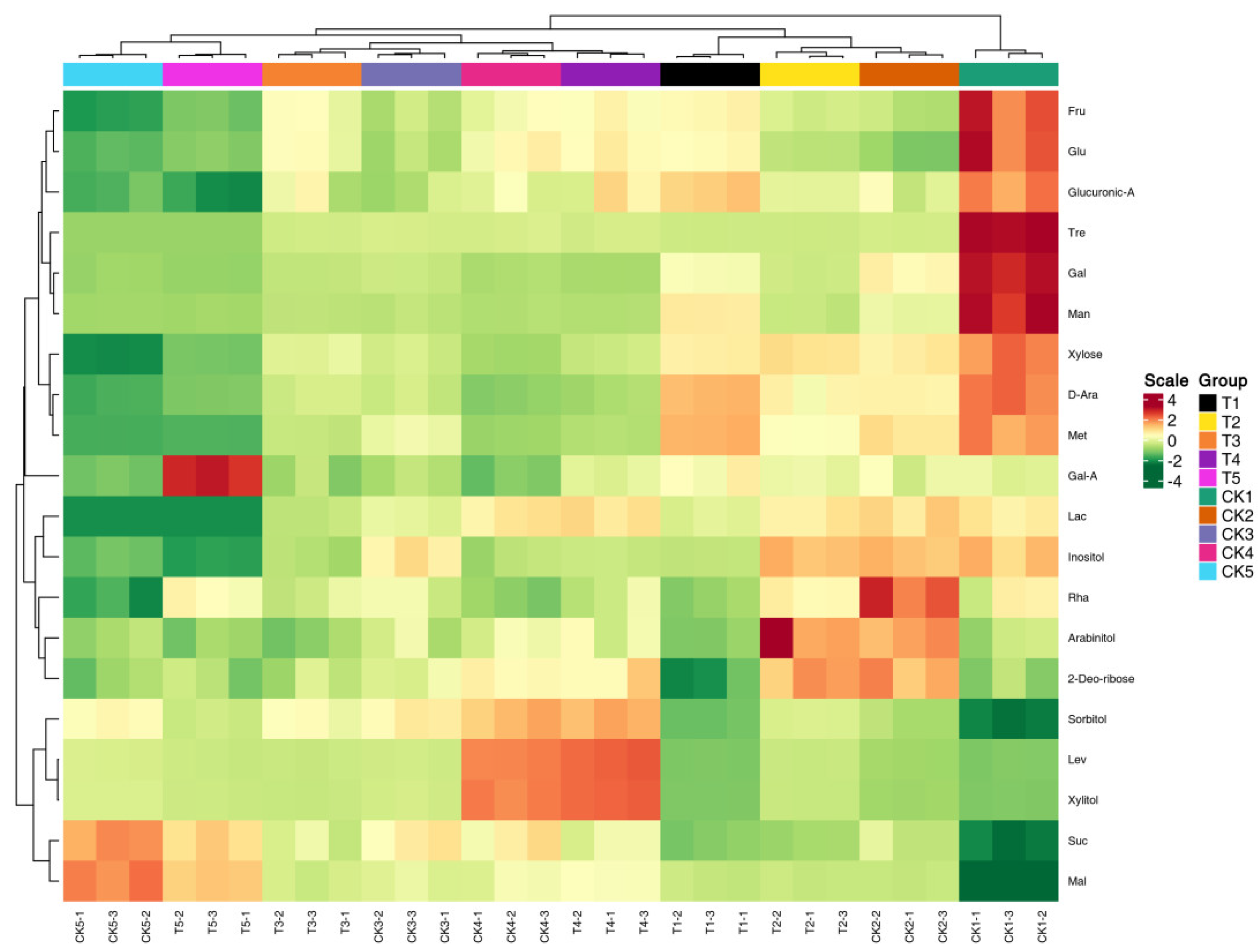
3.4. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
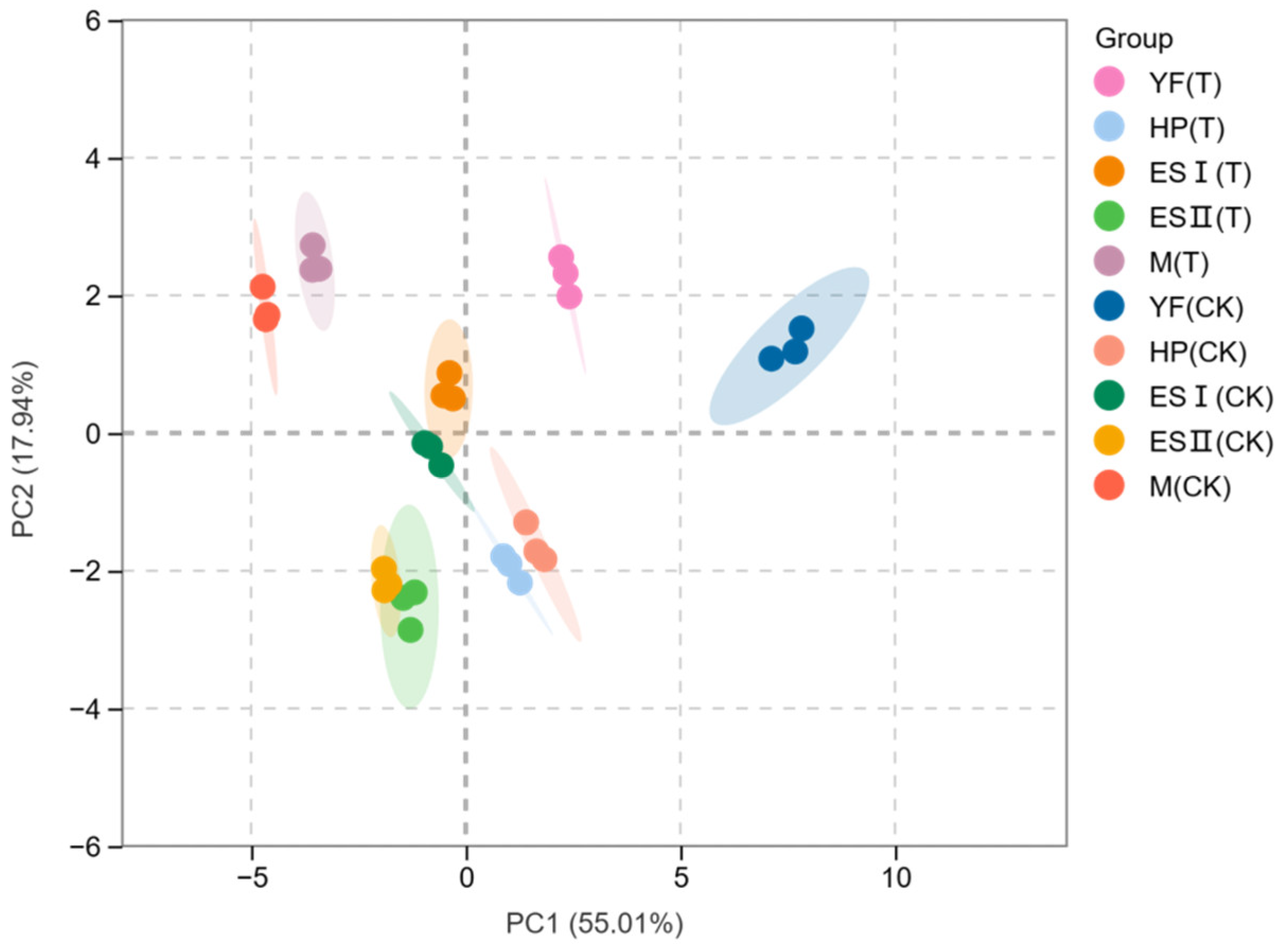
3.5. Principal Component Analysis
3.6. The Influence of Exogenous Treatment of Melatonin on the Sugar Components of Peach Fruits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cirilli, M.; Baccichet, I.; Chiozzotto, R.; Silvestri, C.; Rossini, L.; Bassi, D. Genetic and phenotypic analyses reveal major quantitative loci associated to fruit size and shape traits in a non-flat peach collection (P. persica L. Batsch). Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, K.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhu, G.; Fang, W.; Cheng, S.; Zeng, P.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; et al. Comparative population genomics reveals the domestication history of the peach, Prunus persica, and human influences on perennial fruit crops. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Fu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ren, F.; Zhao, H.; Tian, S.; Guo, W.; Tu, X.; Zhao, J.; et al. Genome re-sequencing reveals the evolutionary history of peach fruit edibility. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, A.M.; Ezzat, A.; El-Ramady, H.; Alam-Eldein, S.M.; Okba, S.K.; Elmenofy, H.M.; Hassan, I.F.; Illés, A.; Holb, I.J. Temperate Fruit Trees under Climate Change: Challenges for Dormancy and Chilling Requirements in Warm Winter Regions. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, D.; Selli, R. Evaluation of fruit quality in peach and apricot. Adv. Hortic. Sci. 1990, 2, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, B.M.; Andrade, P.B.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Seabra, R.M.; Oliveira, M.B.; Ferreira, M.A. Influence of jam processing upon the contents of phenolics, organic acids and free amino acids in quince fruit (Cydonia oblonga Miller). Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2004, 218, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yue, Q.; Bian, F.; Zhai, H.; Yao, Y. Effects of melatonin treatment on grape berry ripening and contents of ethylene and ABA. Plant Physiol. J. 2017, 53, 2181–2188. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemi, S.M.B.; Jafarpour, D.; Jouki, M. Improving bioactive properties of peach juice using Lactobacillus strains fermentation: Antagonistic and anti-adhesion effects, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, and Maillard reaction inhibition. J. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawa-Miszczak, L.; Węgrzynowicz-Lesiak, E.; Gabryszewska, E.; Saniewski, M. Effect of different sucrose and nitrogen levels in the medium on chlorophyll and anthocyanin content in Clematis pitcheri shoots cultured in vitro at different temperatures. Fruit Ornam. Plant Res. 2009, 17, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, X.; Ye, Z.; Su, M.; Zhang, X.; Du, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Huan, C. Transcriptome Co-Expression Network Analysis of Peach Fruit with Different Sugar Concentrations Reveals Key Regulators in Sugar Metabolism Involved in Cold Tolerance. Foods 2023, 12, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Shao, X. PpCBF6 is a low-temperature-sensitive transcription factor that binds the PpVIN2 promoter in peach fruit and regulates sucrose metabolism and chilling injury. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 181, 11681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcada, C.F.; Gogorcena, Y.; Moreno, M.A. Fruit sugar profile and antioxidants of peach and nectarine cultivars on almond × peach hybrid rootstocks. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 164, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, G.; Liu, J.; Younas, M.U.; Zhu, Y. Melatonin Role in Plant Growth and Physiology under Abiotic Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shilo, L.; Dagan, Y.; Smorjik, Y.; Weinberg, U.; Dolev, S.; Komptel, B.; Shenkman, L. Effect of melatonin on sleep quality of copd intensive care patients: A pilot study. Chronobiol. Int. J. Biol. Med. Rhythm. Res. 2000, 17, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezinski, A.; Vangel, M.; Wurtman, R.; Norrie, G.; Zhdanova, I.; Ben-Shushan, A.; Ford, I. Effects of exogenous melatonin on sleep: A Meta-analysis. Chin. J. Clin. Healthc. 2005, 9, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Xing, Q.; Ahammed, G.J.; Zhou, J. Functions and prospects of melatonin in plant growth, yield, and quality. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 5928–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; An, B.; Shi, H.; Luo, H.; He, C. High Concentration of Melatonin Regulates Leaf Development by Suppressing Cell Proliferation and Endoreduplication in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, K.; Vara, E.; García, C.; Ariznavarreta, C.; Escames, G.; Tresguerres, J.A. Effect of exogenous administration of melatonin and growth hormone on pro-antioxidant functions of the liver in aging male rats. J. Pineal Res. 2010, 42, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Huang, H.; Huber, D.; Pan, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Z. Delay of ripening and softening in ‘Guifei’ mango fruit by postharvest application of melatonin. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 163, 111–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Ren, X.; Wei, L.; Cao, X.; Ge, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, J. Collaborative analysis on difference of apple fruits flavour using electronic nose and electronic tongue. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 260, 108879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.; Shahzad, K.; Saqib, S.; Shahzad, A.; Nasrullah Younas, M.; Afridi, M.I. The Solanum melongena COP1LIKE manipulates fruit ripening and flowering time in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 96, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jin, W.; Sun, Y. The beneficial effects of exogenous melatonin on tomato fruit properties. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 207, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Luo, Z.; Ban, Z.; Jiang, N.; Yang, M.; Li, L. Role of exogenous melatonin involved in phenolic metabolism of Zizyphus jujuba fruit. Food Chem. 2021, 341, 128268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, B.; Xia, C.; Tian, S.; Shi, H. Melatonin reduces pesticide residue, delays senescence, and improves antioxidant nutrient accumulation in postharvest jujube fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 173, 111419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Tao, X.; Ai, X.; Luo, Z.; Mao, L.; Ying, T.; Li, L. Effect of exogenous auxin on aroma volatiles of cherry tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) fruit during postharvest ripening. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 146, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monforte, A.J.; Diaz, A.; Caño-Delgado, A.; Van Der Knaap, E. The genetic basis of fruit morphology in horticultural crops: Lessons from tomato and melon. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 4625–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, D.; Gambardella, M.; Negri, P. Date of ripening and two morphological fruit traits in peach progenies. Acta Hortic. 1988, 34, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, G.I.; Wani, A.W.; Dar, S.Q.; Wani, M.Y.; Sofi, J.A.; Baba, T.R.; Parray, E.; Rasool, A. Physiology of Fruit Set and Development in Apple under Temperate conditions: A Review. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2020, 9, 618–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, J.L.; Hanson, J.B.; Bils, R.F. Effect of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid Application on Activity and Composition of Mitochondria from Soybeans. Plant Physiol. 1960, 35, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, M.; Khan, F.; Shah, A.H.; Fahad, S.; Wahid, F.; Ali, J.; Adnan, M.; Ahmad, M.; Irfan, M.; Zafar-ul-Hye, M.; et al. Effect of micronutrients foliar supplementation on the production and eminence of plum (Prunus domestica L.). Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2020, 12, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Vimolmangkang, S.; Zheng, H.; Peng, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, H.; Fang, T.; Liao, L.; Wang, L.; He, H.; Han, Y. Assessment of Sugar Components and Genes Involved in the Regulation of Sucrose Accumulation in Peach Fruit. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6723–6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsani, J.; Budde, C.O.; Porrini, L.; Lauxmann, M.A.; Lombardo, V.A.; Murray, R.; Andreo, C.S.; Drincovich, M.F.; Lara, M.V. Carbon metabolism of peach fruit after harvest: Changes in enzymes involved in organic acid and sugar level modifications. J. Exp. Botany. 2009, 60, 1823–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.; Wang, J.; Tang, Z.; Yu, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Tian, Q. Application of Exogenous Melatonin Improves Tomato Fruit Quality by Promoting the Accumulation of Primary and Secondary Metabolites. Foods 2022, 24, 4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Kou, F.; Zhang, M.; Jin, X.; Ren, C.; Yu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M. Effect of Exogenous Melatonin on the Quality of Soybean and Natto Products under Drought Stress. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 8847698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Rengel, Z. Phytomelatonin: Biosynthesis, Signaling, and Functions. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2025, 76, 171–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Cheng, Q.; Dai, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, R.; Wang, J.; Hu, R.; Lin, L. Effects of exogenous melatonin on sugar and organic acid metabolism in early-ripening peach fruits. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0292959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Jiang, B.; Wang, Q.; Xu, H.; Zhang, W. Exogenous Melatonin Affects Fruit Enlargement and Sugar Metabolism in Melt Peach. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080964
Guo Y, Jiang B, Wang Q, Xu H, Zhang W. Exogenous Melatonin Affects Fruit Enlargement and Sugar Metabolism in Melt Peach. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(8):964. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080964
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yanfei, Baoxin Jiang, Qinghao Wang, Huilian Xu, and Wangshu Zhang. 2025. "Exogenous Melatonin Affects Fruit Enlargement and Sugar Metabolism in Melt Peach" Horticulturae 11, no. 8: 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080964
APA StyleGuo, Y., Jiang, B., Wang, Q., Xu, H., & Zhang, W. (2025). Exogenous Melatonin Affects Fruit Enlargement and Sugar Metabolism in Melt Peach. Horticulturae, 11(8), 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080964




