Cherry Tomato Bunch and Picking Point Detection for Robotic Harvesting Using an RGB-D Sensor and a StarBL-YOLO Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
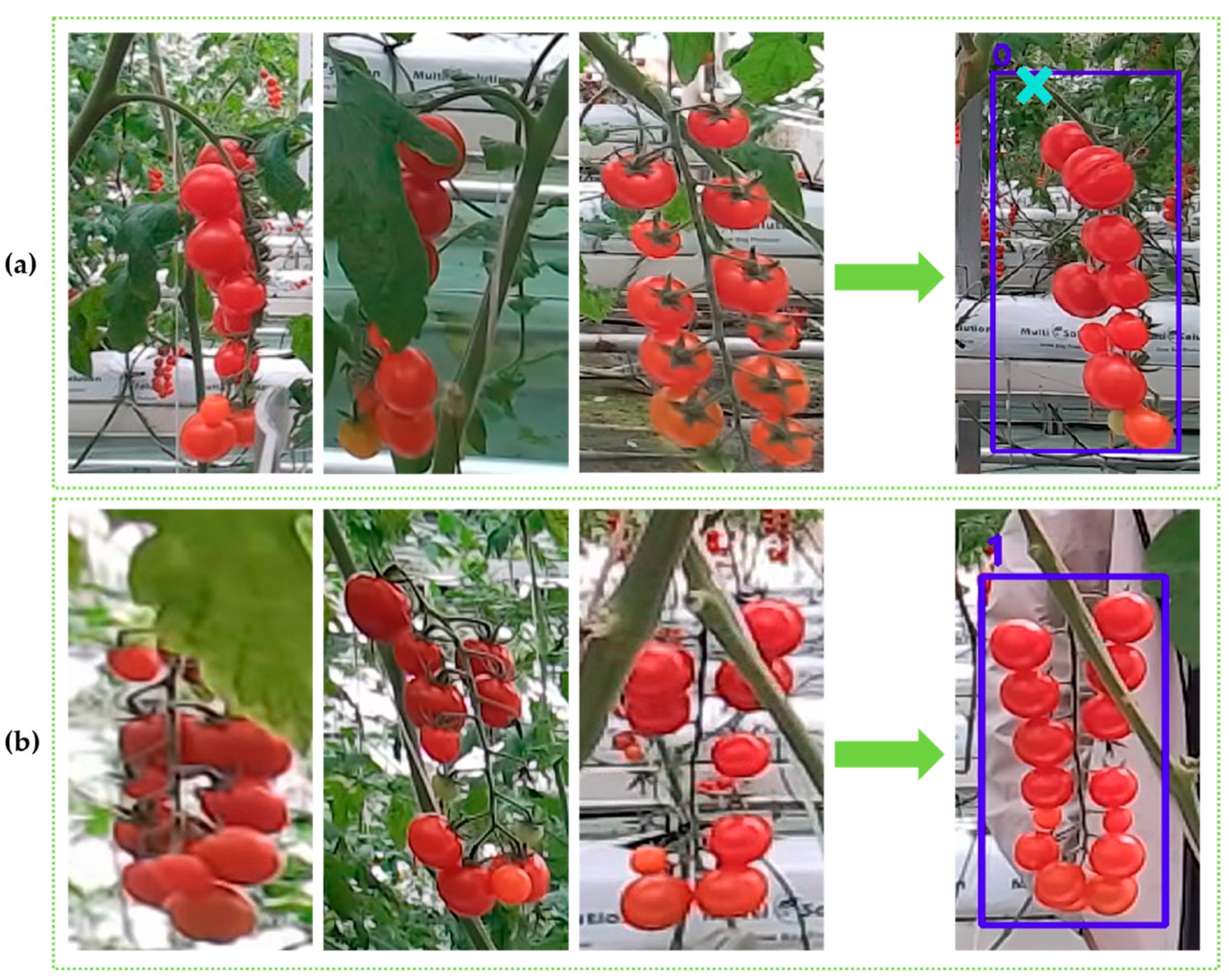
- A practical classification and detection framework for cherry tomato harvesting: We propose StarBL-YOLO, which explicitly divides cherry tomato bunches into pickable and non-pickable categories. This design addresses the limitations of previous works where fully occluded stems often lead to unreliable picking point predictions, improving the practical applicability of automated harvesting.
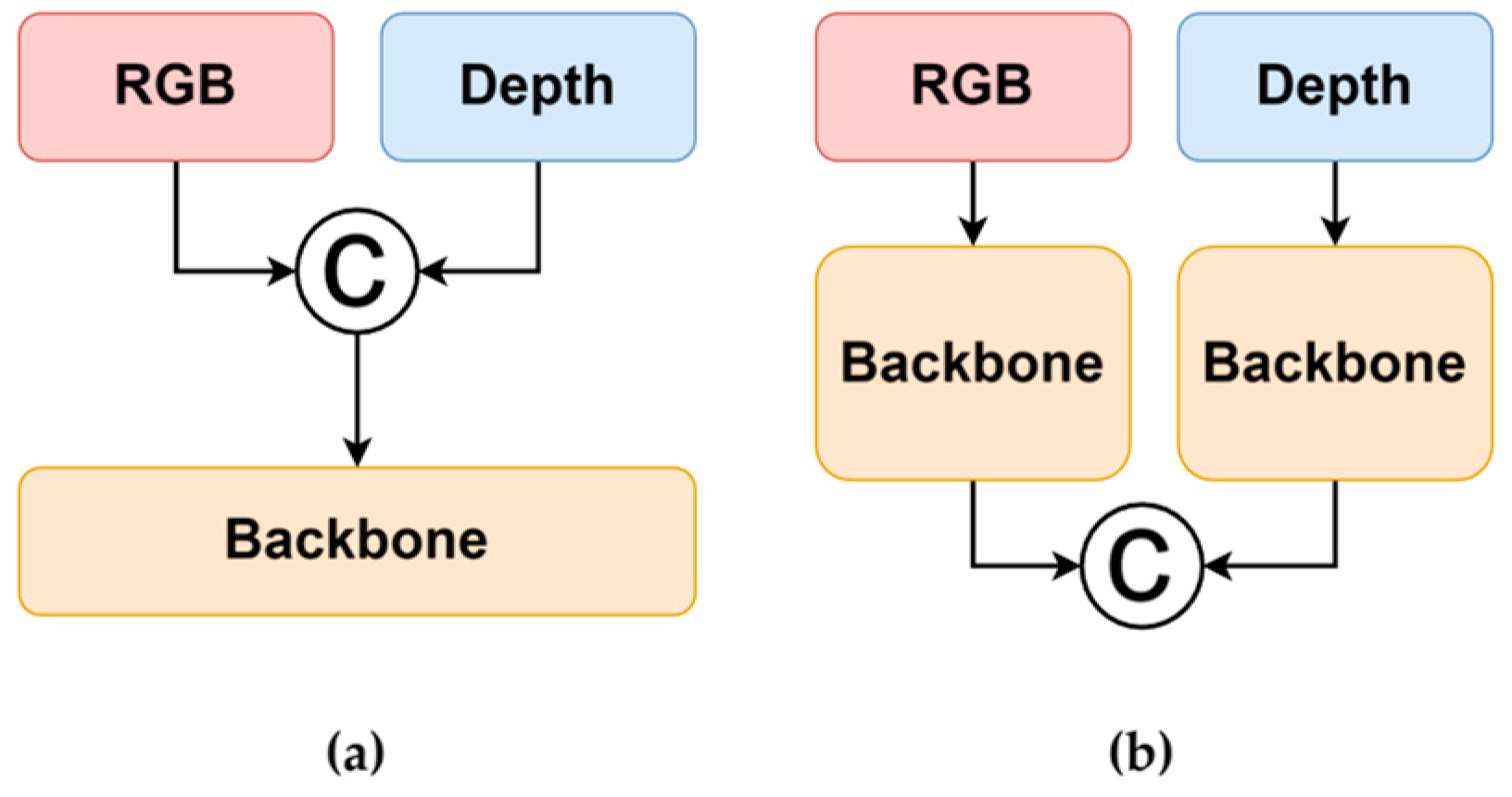
- Single-stream RGB-D integration for efficient occlusion-aware detection: To balance accuracy and efficiency, we employ a single-stream RGB-D fusion strategy, directly combining color and depth data. This approach enables robust detection of occluded bunches while avoiding dual-stream complexity.
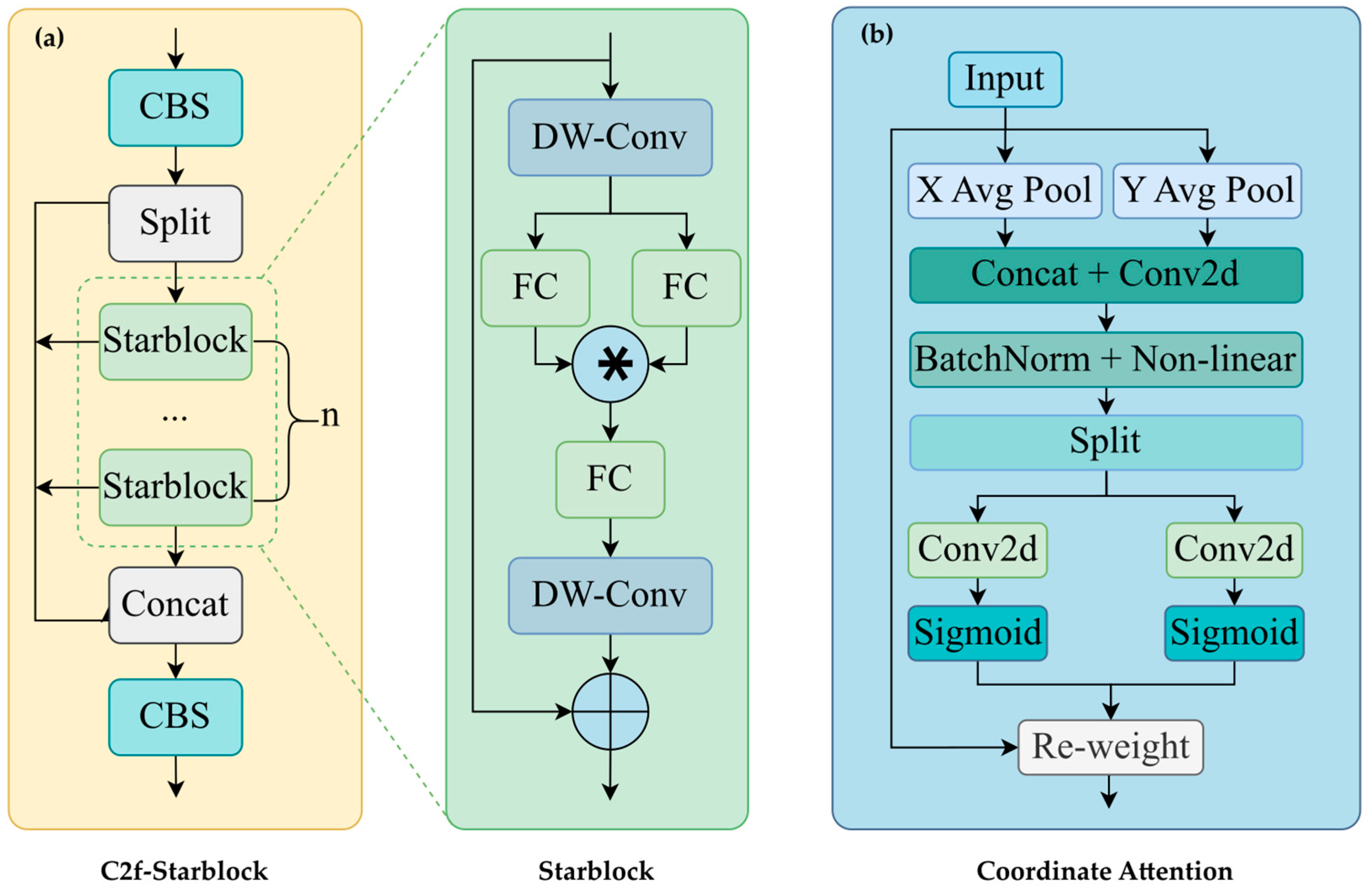
- Lightweight architecture with enhanced spatial feature representation: The Starblock from StarNet [26] is used to replace the Bottleneck in the C2f structure in YOLOv8-Pose, and the coordinate attention mechanism [27] is integrated into the backbone network. These two components work synergistically to enhance detection robustness in complex backgrounds by efficiently extracting features and reinforcing spatial information, delivering enhanced detection accuracy with reduced computational complexity.
- Task-specific loss optimization for accurate picking point localization: We replace the original OKS loss function with the L1 loss function, better suited for the requirements of single-point robotic picking.
2. Materials and Methods
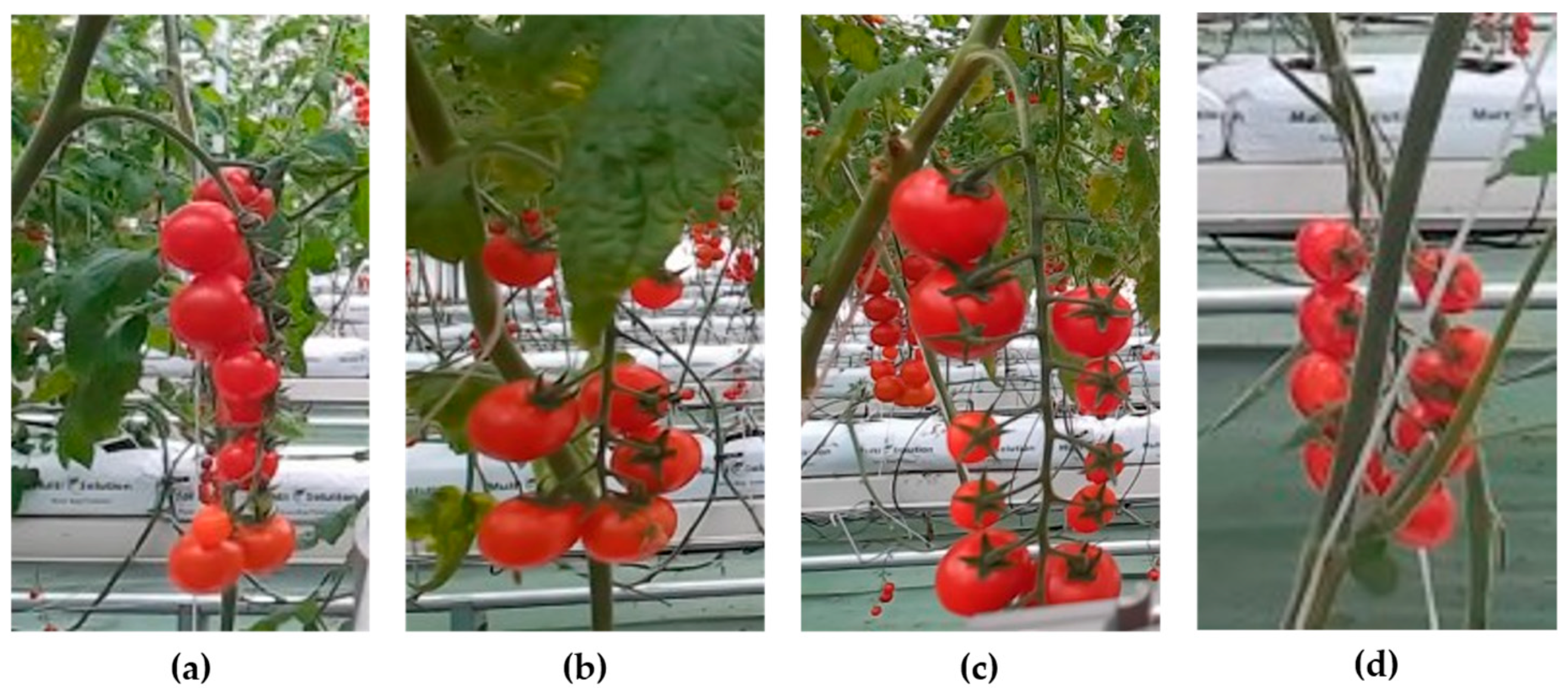
2.1. Datasets
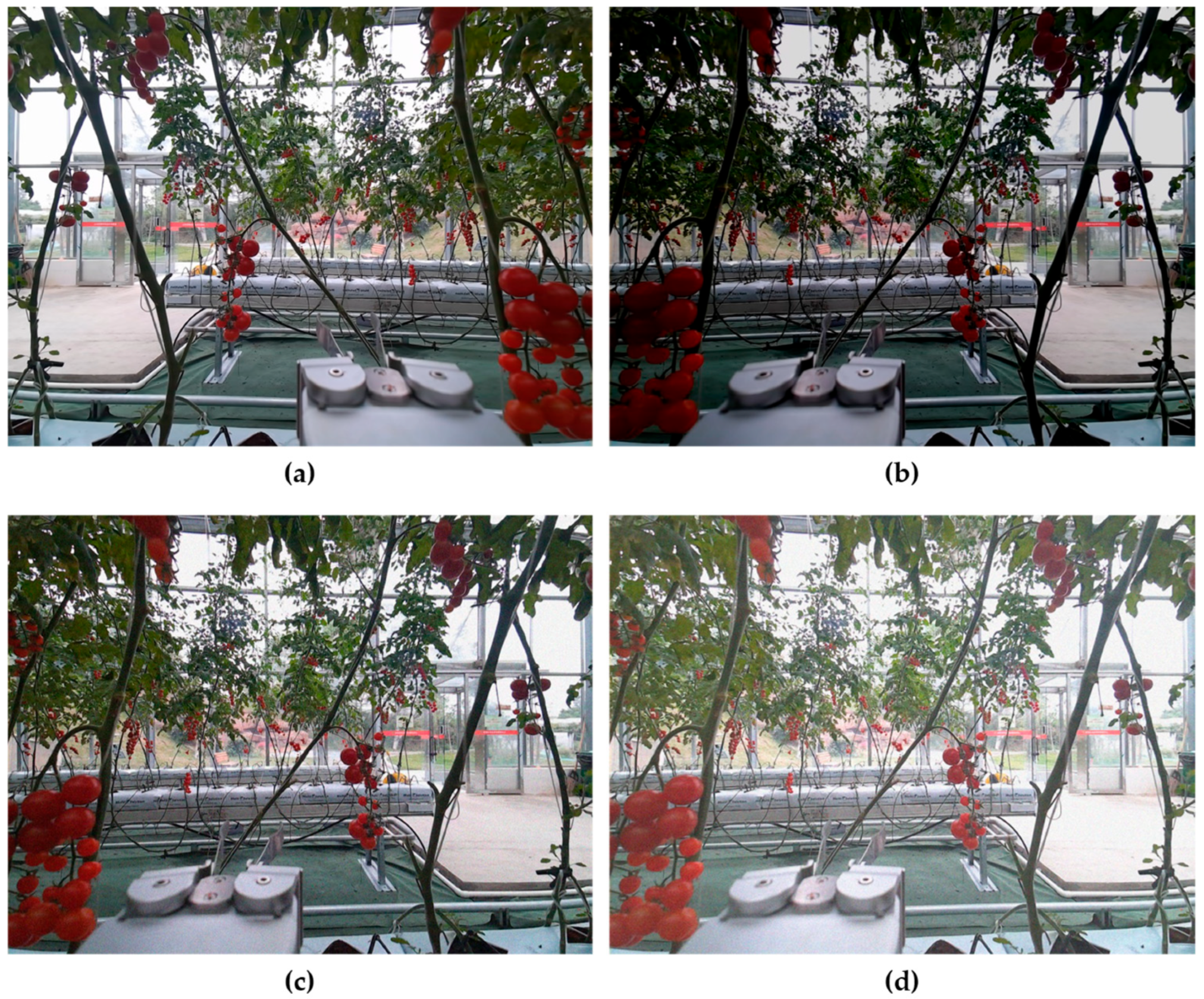
2.1.1. Data Acquisition
2.1.2. Data Augmentation Methods and Data Split
2.1.3. Data Labeling Strategy
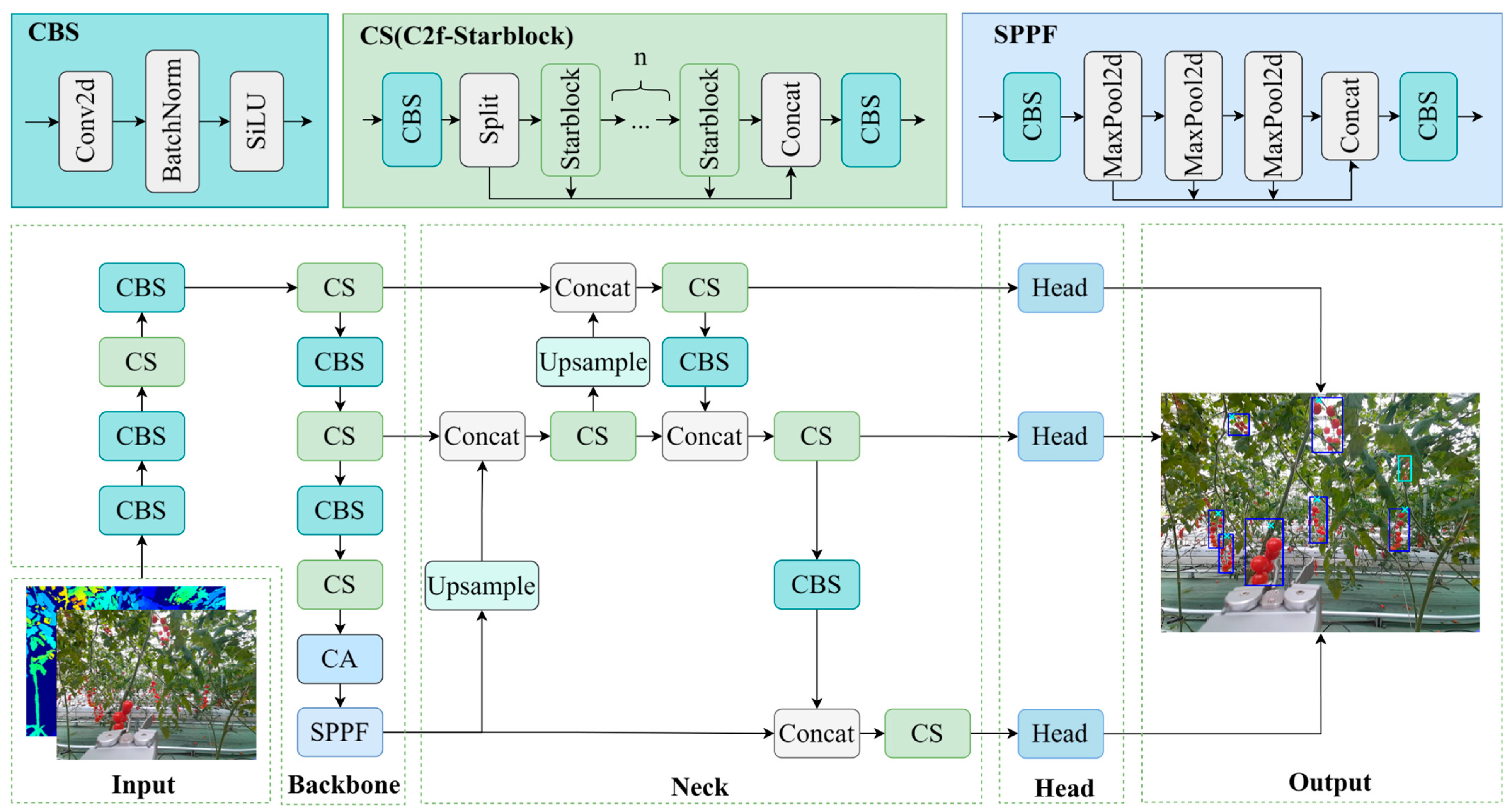
2.2. Improved YOLOv8-Pose: StarBL-YOLO
2.2.1. The Single-Stream Fusion of RGB and Depth Images
2.2.2. Starblock in StarNet
2.2.3. Coordinate Attention
2.2.4. Loss Function
2.3. Evaluations of Model Performance
3. Results
3.1. Experiment Environment
3.2. Ablation Experiments
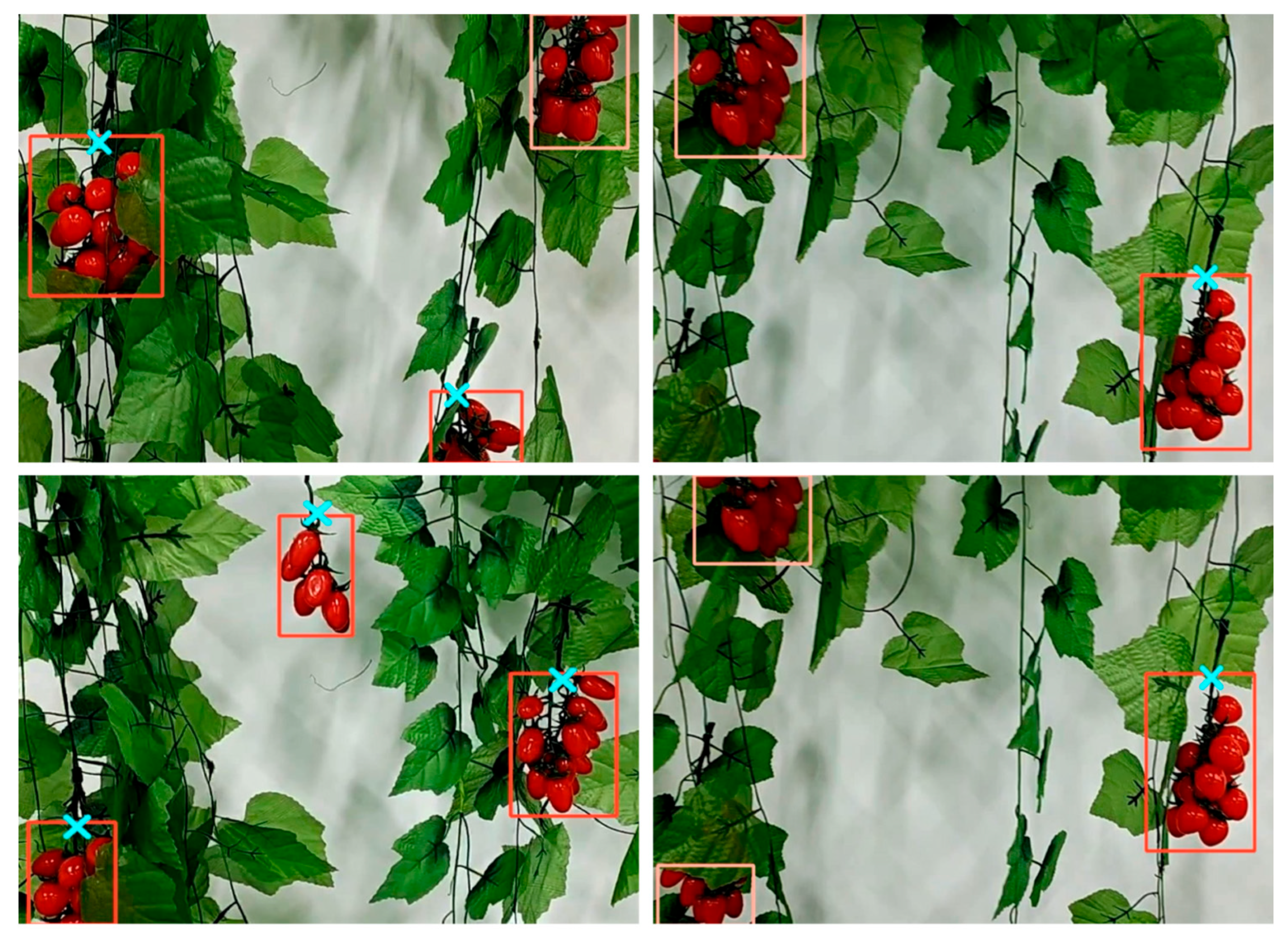
3.3. Comparison of Cherry Tomato Bunch and Picking Point Detection
3.4. Model Generalization Validation Experiments
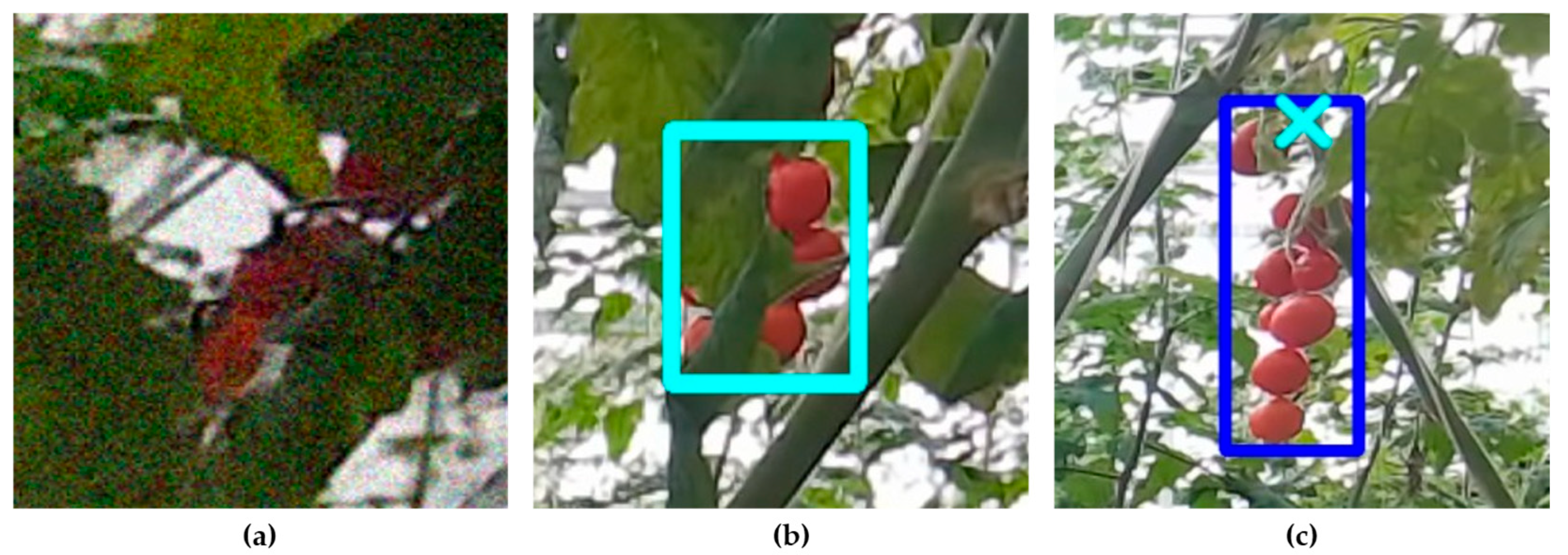
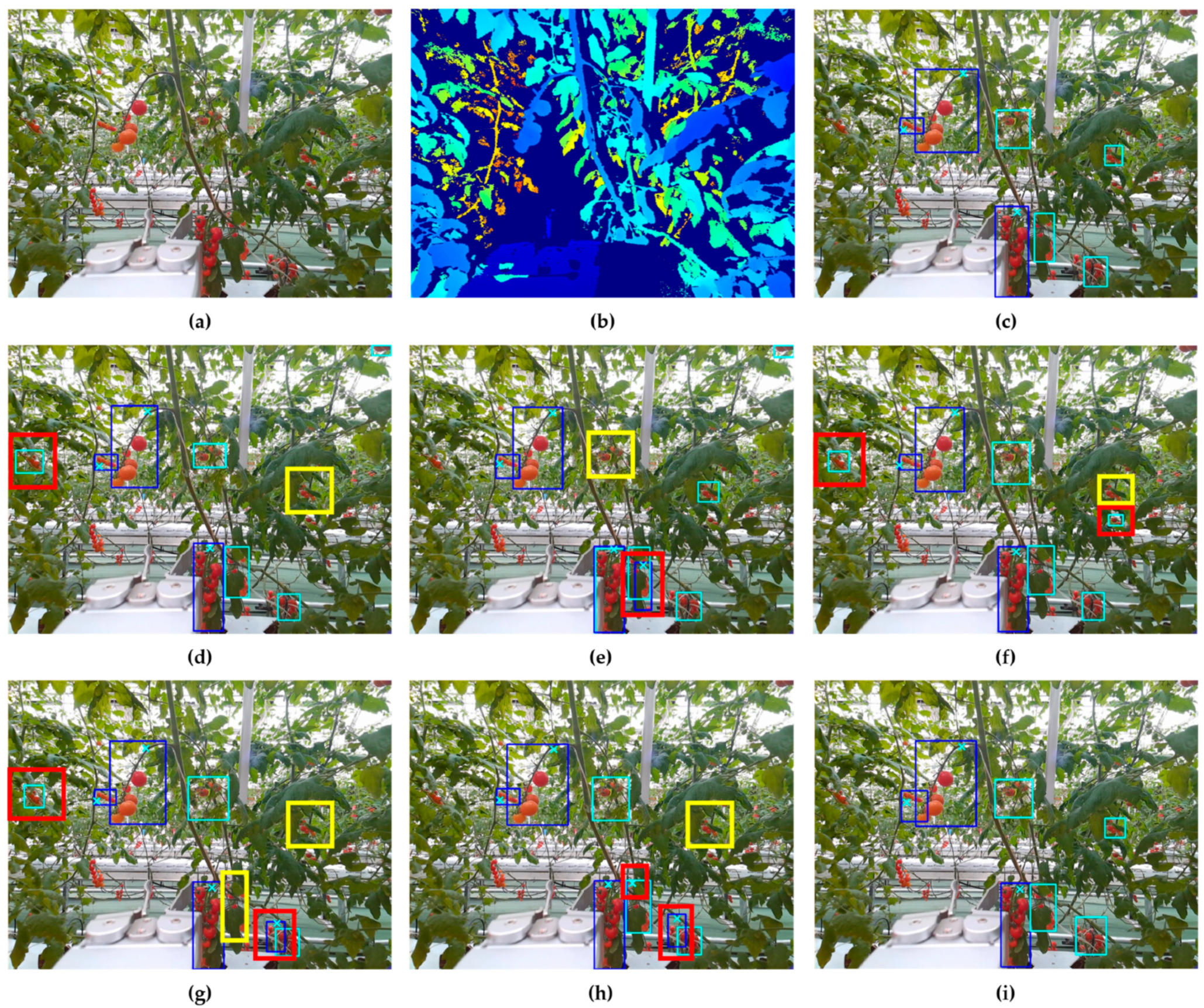
3.5. Failure Case Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agarwal, S.; Rao, A.V. Tomato lycopene and its role in human health and chronic diseases. CMAJ Can. Med. Assoc. J. J. De L Assoc. Medicale Can. 2000, 163, 739–744. [Google Scholar]
- Taqi, F.; Al-Langawi, F.; Abdulraheem, H.; El-Abd, M. A cherry-tomato harvesting robot. In Proceedings of the 2017 18th International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR), Hong Kong, China, 10–12 July 2017; pp. 463–468. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, P.; Ergu, D.; Liu, F.; Cai, Y.; Ma, B. A Review of Yolo Algorithm Developments. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 199, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozzi, M.; Cantalamessa, S.; Cogato, A.; Kayad, A.; Marinello, F. Automatic Bunch Detection in White Grape Varieties Using YOLOv3, YOLOv4, and YOLOv5 Deep Learning Algorithms. Agronomy 2022, 12, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Tang, Y.; Zou, X.; Cheng, J.; Xiong, J. Fruit detection in natural environment using partial shape matching and probabilistic Hough transform. Precis. Agric. 2020, 21, 160–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Qiu, J. Ultralytics YOLO, 8.0.0; 2023. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- OĞUztÜRk, G.E. AI-driven irrigation systems for sustainable water management: A systematic review and meta-analytical insights. Smart Agric. Technol. 2025, 11, 100982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, K.; Mirzakhani Nafchi, A.; Mirzaee, S.; Abdalla, A. AI-Driven Future Farming: Achieving Climate-Smart and Sustainable Agriculture. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.; Li, R.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Fan, R.; Liu, S. Green Citrus Detection and Counting in Orchards Based on YOLOv5-CS and AI Edge System. Sensors 2022, 22, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Xue, Y.; Zheng, C.; Qi, Y.; Wan, H.; Mao, L. Detection of passion fruits and maturity classification using Red-Green-Blue Depth images. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 175, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Guo, Z.; Feng, Q.; Xie, F.; Zuo, Y.; Li, T. MSOAR-YOLOv10: Multi-Scale Occluded Apple Detection for Enhanced Harvest Robotics. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaukab, S.; Komal; Ghodki, B.M.; Ray, H.; Kalnar, Y.B.; Narsaiah, K.; Brar, J.S. Improving real-time apple fruit detection: Multi-modal data and depth fusion with non-targeted background removal. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 82, 102691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tian, Y.; Zeng, Z. LEFF-YOLO: A Lightweight Cherry Tomato Detection YOLOv8 Network with Enhanced Feature Fusion. In Proceedings of the Advanced Intelligent Computing Technology and Applications, Ningbo, China, 26–29 July 2025; pp. 474–488. [Google Scholar]
- Aguiar, A.S.; Magalhães, S.A.; dos Santos, F.N.; Castro, L.; Pinho, T.; Valente, J.; Martins, R.; Boaventura-Cunha, J. Grape Bunch Detection at Different Growth Stages Using Deep Learning Quantized Models. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Lv, L.; Zhang, F.; Fu, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W. Robust Cherry Tomatoes Detection Algorithm in Greenhouse Scene Based on SSD. Agriculture 2020, 10, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Zeng, Z.; Tian, Y. A Yolov7 Cherry Tomato Identification Method That Integrates Depth Information; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2023; Volume 12747. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Cui, B.; Deng, H.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Q.; Lu, D.; Cui, Y.; Tian, Y. Cherry Tomato Detection for Harvesting Using Multimodal Perception and an Improved YOLOv7-Tiny Neural Network. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, T.; Wang, P. Tomato cluster detection and counting using improved YOLOv5 based on RGB-D fusion. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 207, 107741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.; Wen, M.; Li, P.; Zeng, Z.; Tian, Y. DCFA-YOLO: A Dual-Channel Cross-Feature-Fusion Attention YOLO Network for Cherry Tomato Bunch Detection. Agriculture 2025, 15, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, N.; Han, Y.; Yang, S.; Zheng, S. AHPPEBot: Autonomous Robot for Tomato Harvesting based on Phenotyping and Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 13–17 May 2024; pp. 18150–18156. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Lan, Y. Fast and precise detection of litchi fruits for yield estimation based on the improved YOLOv5 model. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 965425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, T.; Cao, H. Development of an Optimized YOLO-PP-Based Cherry Tomato Detection System for Autonomous Precision Harvesting. Processes 2025, 13, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Yu, X.; Li, N.; Zhang, Z.; He, C.; Li, Z.; Deng, C.; Sun, T. Efficient tomato harvesting robot based on image processing and deep learning. Precis. Agric. 2023, 24, 254–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Cao, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Zhao, A.; Zou, X.; Wang, H. YOLOv8n-DDA-SAM: Accurate Cutting-Point Estimation for Robotic Cherry-Tomato Harvesting. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohan, M.; Sai Ram, T.; Rami Reddy, C.V. A Review on YOLOv8 and Its Advancements. In Proceedings of the Data Intelligence and Cognitive Informatics, Tirunelveli, India, 18–20 November 2024; pp. 529–545. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Dai, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y. Rewrite the Stars. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 5694–5703. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13708–13717. [Google Scholar]
- Pande, B.; Padamwar, K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Roshan, S.; Bhamare, M. A Review of Image Annotation Tools for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Applied Artificial Intelligence and Computing (ICAAIC), Salem, India, 9–11 May 2022; pp. 976–982. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path Aggregation Network for Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, J.; Zheng, W.; Qi, Z.; Yuan, T.; Wang, P. RTMFusion: An enhanced dual-stream architecture algorithm fusing RGB and depth features for instance segmentation of tomato organs. Measurement 2025, 239, 115484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Wang, F.; Li, B.; Tang, R.; Wei, R.; Deng, H.; Tian, Y. Adaptive Automotive Chassis Welding Joint Inspection Using a Cobot and a Multi-modal Vision Sensor: Adaptive welding joint inspection robotic vision system. In Proceedings of the 2024 Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area International Conference on Digital Economy and Artificial Intelligence, Hongkong, China, 19–21 January 2024; pp. 841–849. [Google Scholar]
- Sifre, L.; Mallat, S.J.A. Rigid-Motion Scattering for Texture Classification. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1403.1687. [Google Scholar]
- Maji, D.; Nagori, S.; Mathew, M.; Poddar, D. Yolo-pose: Enhancing yolo for multi person pose estimation using object keypoint similarity loss. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference On Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2637–2646. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable Bag-of-Freebies Sets New State-of-the-Art for Real-Time Object Detectors. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M.J.A. YOLOv11: An Overview of the Key Architectural Enhancements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17725. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Ye, Q.; Doermann, D.S.J.A. YOLOv12: Attention-Centric Real-Time Object Detectors. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.12524. [Google Scholar]


| Model | Pickable Butch | Non-Pickable Butch | Picking Point | Para (M) | GFLOPs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP50 | mAP50-95 | mAP50 | mAP50-95 | mAP50 | mAP50-95 | RMSE | R2 | |||
| Baseline | 0.864 | 0.618 | 0.659 | 0.406 | 0.885 | 0.879 | 26.1529 | 0.9966 | 3.078 | 8.3 |
| +D | 0.891 | 0.663 | 0.695 | 0.442 | 0.914 | 0.909 | 24.6129 | 0.9969 | 3.078 | 8.4 |
| +S | 0.877 | 0.632 | 0.676 | 0.42 | 0.9 | 0.896 | 25.9661 | 0.9964 | 2.715 | 7.7 |
| +C | 0.866 | 0.629 | 0.666 | 0.419 | 0.881 | 0.877 | 26.9815 | 0.9962 | 3.084 | 8.3 |
| +L | 0.872 | 0.626 | 0.67 | 0.409 | 0.909 | 0.901 | 21.7415 | 0.9972 | 3.078 | 8.3 |
| +D+S | 0.883 | 0.654 | 0.704 | 0.451 | 0.914 | 0.909 | 24.6129 | 0.9969 | 2.715 | 7.7 |
| +S+C | 0.86 | 0.64 | 0.692 | 0.45 | 0.891 | 0.882 | 24.6863 | 0.9969 | 2.721 | 7.7 |
| +D+C | 0.887 | 0.666 | 0.729 | 0.478 | 0.911 | 0.906 | 21.9219 | 0.9975 | 3.085 | 8.4 |
| +D+S+C | 0.901 | 0.667 | 0.701 | 0.45 | 0.921 | 0.918 | 26.2862 | 0.9965 | 2.721 | 7.7 |
| Full model | 0.908 | 0.665 | 0.739 | 0.468 | 0.928 | 0.925 | 19.8810 | 0.9979 | 2.721 | 7.7 |
| Model | Pickable Butch | Non-Pickable Butch | Picking Point | Para (M) | GFLOPs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP50 | mAP50-95 | mAP50 | mAP50-95 | mAP50 | mAP50-95 | RMSE | R2 | |||
| YOLOv5-Pose | 0.872 | 0.592 | 0.667 | 0.36 | 0.903 | 0.888 | 29.1726 | 0.9949 | 14.91 | 19.8 |
| YOLOv7-Pose | 0.887 | 0.612 | 0.684 | 0.41 | 0.919 | 0.911 | 29.3693 | 0.9951 | 79.82 | 100.7 |
| YOLOv8-Pose | 0.864 | 0.618 | 0.659 | 0.406 | 0.885 | 0.879 | 26.1529 | 0.9966 | 3.08 | 8.3 |
| YOLOv11-Pose | 0.873 | 0.652 | 0.703 | 0.452 | 0.894 | 0.89 | 23.2803 | 0.9971 | 2.65 | 6.6 |
| YOLOv12-Pose | 0.89 | 0.653 | 0.702 | 0.444 | 0.91 | 0.907 | 25.9420 | 0.9965 | 2.63 | 6.6 |
| StarBL-YOLO | 0.908 | 0.665 | 0.739 | 0.468 | 0.928 | 0.925 | 19.8810 | 0.9979 | 2.72 | 7.7 |
| Model | Pickable Butch | Non-Pickable Butch | Picking Point | Para (M) | GFLOPs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP50 | mAP50-95 | mAP50 | mAP50-95 | mAP50 | mAP50-95 | RMSE | R2 | |||
| YOLOv11s-Pose | 0.888 | 0.678 | 0.714 | 0.472 | 0.914 | 0.907 | 21.7525 | 0.9975 | 9.69 | 22.3 |
| YOLOv12s-Pose | 0.886 | 0.676 | 0.71 | 0.47 | 0.909 | 0.905 | 21.9349 | 0.9975 | 9.51 | 22.2 |
| StarBL-YOLO | 0.908 | 0.665 | 0.739 | 0.468 | 0.928 | 0.925 | 19.8810 | 0.9979 | 2.72 | 7.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Wen, M.; Zeng, Z.; Tian, Y. Cherry Tomato Bunch and Picking Point Detection for Robotic Harvesting Using an RGB-D Sensor and a StarBL-YOLO Network. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080949
Li P, Wen M, Zeng Z, Tian Y. Cherry Tomato Bunch and Picking Point Detection for Robotic Harvesting Using an RGB-D Sensor and a StarBL-YOLO Network. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(8):949. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080949
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Pengyu, Ming Wen, Zhi Zeng, and Yibin Tian. 2025. "Cherry Tomato Bunch and Picking Point Detection for Robotic Harvesting Using an RGB-D Sensor and a StarBL-YOLO Network" Horticulturae 11, no. 8: 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080949
APA StyleLi, P., Wen, M., Zeng, Z., & Tian, Y. (2025). Cherry Tomato Bunch and Picking Point Detection for Robotic Harvesting Using an RGB-D Sensor and a StarBL-YOLO Network. Horticulturae, 11(8), 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080949






