1. Introduction
Chrysanthemum is a traditional and famous flower originating in China with high ornamental value and has more than 3000 years of cultivation history [
1]. As a typical representative of medicinal and food plants, it has functions of clearing heat, detoxification, and brightening eyesight, and is widely used in traditional Chinese medicine, food, cosmetics, and other fields [
2,
3]. Pharmacological tests have confirmed that chrysanthemum flavonoids possess a variety of physiological activities such as anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, hypoglycemic, and hypolipidemic activities [
4,
5,
6].
Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat. (Jinsi Huangju) is a historic ornamental variety characterized by its large, graceful blooms. When processed, the dried flowers create a delightful beverage with a sweet aroma, often described as “flowers blooming in the cup”. Additionally, Jinsi Huangju is valued for its medicinal properties, being rich in flavonoids and other bioactive compounds that contribute to health benefits, like lowering blood lipids, alleviating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and providing antioxidant effects [
4,
7,
8,
9,
10]. In the context of Jinsi Huangju, flavonoids are significant secondary metabolites that serve as the foundation for tea product development [
11,
12,
13]. Recent studies indicate that during the flowering phase, the flavonoid levels in Jinsi Huangju are relatively low, highlighting the necessity to enhance these levels to produce high-value flavonoids through synthetic biology and other innovative approaches.
Flavones are derived from the flavonoid metabolic pathway, which begins with phenylalanine. This process involves several enzymes, including phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL), cinnamate-4-hydroxylase (C4H), 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL), chalcone synthase (CHS), and chalcone isomerase (CHI), ultimately leading to the production of naringenin [
9,
14]. One pathway converts naringenin into eriodyctiol through the action of flavonoid-3′-hydroxylase (F3′H), after which eriodyctiol is transformed into luteolin by flavone synthase (FNS). Alternatively, naringenin can be directly converted into apigenin by FNS, which is subsequently changed into luteolin by F3′H (
Figure S1) [
15,
16]. In this process, FNS and F3′H play crucial roles in the synthesis of flavone compounds.
The metabolism of flavonoids differs across various plant tissues and stages of reproduction, with these variations often attributed to transcription factors that attach to the promoters of structural genes to modulate their expression [
17]. MYB transcription factors play a crucial role in a range of plant activities, including the signaling pathways of phytohormones, developmental and morphological gene regulation, responses to biotic and abiotic stresses, and metabolic pathways, especially those involved in secondary metabolism [
18,
19,
20]. In the medicinal plant
Scutellaria baicalensis, SbMYB3 enhances the transcriptional activity of SbFNSII-2 by directly binding to cis-acting elements in its promoter region, thereby positively regulating the biosynthesis of root-specific flavonoids such as baicalein and baicalin. RNAi-mediated knockdown of SbMYB3 results in significantly reduced levels of these compounds [
21]. Similarly, AgMYB12 specifically binds to the
AgFNS promoter, inducing up-regulation of
AgFNS gene expression and consequently increasing the accumulation of luteolin and apigenin in celery [
22].
In recent times, researchers have utilized metabolomic and transcriptomic data to investigate secondary metabolites, determine gene roles, and clarify metabolic pathways involved in plant growth. This study focused on the variations in flavonoids and genes throughout floral development, employing ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) and RNA sequencing techniques. Through the integration of metabolomic and transcriptomic evaluations, the candidate gene CmMYB8a, closely linked to flavonoid production, was identified, and the molecular processes governing flavonoid biosynthesis in Jinsi Huangju flowers were examined. Future research will further validate the interaction between CmMYB8a and structural gene promoters, exploring the molecular mechanisms by which CmMYB8a regulates flavonoid synthesis. This will provide an important theoretical basis for the breeding and genetic improvement of high-level flavonoid plants in Jinsi Huangju.
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
Chrysanthemum morifolium (Jinsi Huangju) was acquired from the Jiangxi Oil-tea Camellia Institute located in Jiujiang, Jiangxi, China (116°0′36.14″ E, 29°40′35.98″ N). Samples were gathered at three distinct flowering phases based on the varying characteristics of the chrysanthemum: S1 (initial flowering stage, where the outer florets of the capitulum begin to open), S2 (intermediate flowering stage, where the capitulum’s size doubles compared to S1), and S3 (full bloom stage, where the tongue florets are completely open). All samples were flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C for subsequent transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses. Uniformly growing cuttings were chosen and planted in soil blocks containing a 1:1 (v/v) mixture of vermiculite and peat soil. The seedlings were maintained in an illuminated incubator at 25/18 °C under long-day conditions (light/dark: 16 h/8 h, relative humidity: 70%). Agrobacterium transformation was carried out when the seedlings grew to the 6–8 leaf stage.
2.2. Metabolome Data Analysis
Groups S1, S2, and S3 were subjected to metabolomics analysis, each consisting of three biological replicates. The biological samples were flash-frozen via vacuum lyophilization (Scientz-100F) and ground to a fine powder (30 Hz, 1.5 min) using a tissue homogenizer (MM 400, Retsch). Subsequently, 50 mg of powdered sample was weighed and mixed with 1200 μL of −20 °C pre-cooled 70% methanolic aqueous solution containing internal standard extract. After centrifuging at 12,000 rpm for 3 min, the supernatant was removed. Subsequently, the sample underwent filtration through a 0.22 μm microporous membrane and it was then transferred to an injection vial for UPLC-MS/MS analysis.
The analysis using UPLC-MS/MS (ExionLC™ system) utilized a temperature-controlled C18 column (Agilent SB-C18, 2.1 × 100 mm, 1.8 µm) set at 40 °C, with two mobile phases: Phase A consisting of 0.1% formic acid in water and Phase B containing 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile. A multi-step gradient was implemented: 95% A (0–9 min linear transition to 5% A), 1 min isocratic elution at 95% B, followed by 1.1 min re-equilibration to initial conditions and 2.9 min column stabilization, all at 0.35 mL/min flow rate. Samples (2 μL injection volume) were analyzed under these optimized conditions.
The parameters for the ESI source were set as follows: a thermal block temperature of 500 °C; dual-polarity spray voltages of +5500 V and −4500 V; gas pressures of 50 psi for GSI, 60 psi for GSII, and 25 psi for CUR; along with a high CAD setup. For MRM acquisition on the triple quadrupole system, nitrogen was used as the collision gas at medium pressure, with transition-specific DP/CE values being optimized in real-time during the method development phase. Monitoring was conducted in time-segmented elution to ensure the precise detection of metabolites that were chromatographically separated.
Compound identification leveraged the commercially available MetWare metabolomics database (Wuhan, China). In the context of differential metabolite screening, univariate statistical analysis methods encompass hypothesis testing and fold change (FC) analysis. Conversely, multivariate statistical analysis methods include principal component analysis (PCA) and orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA), among others. Utilizing the variable importance in projection (VIP) derived from the OPLS-DA model, we initially screened for metabolites exhibiting significant differences between groups. Ultimately, differential metabolites were further refined by integrating the p-value and FC value obtained from the univariate analysis. Differential metabolite screening implemented strict thresholds: VIP > 1 from multivariate analysis combined with bidirectional fold-change criteria (FC ≥ 2 for up-regulation, ≤0.5 for down-regulation).
2.3. RNA Sequencing
Total RNA was extracted from C. morifolium using three biological replicates at each developmental stage. The concentration and purity of the extracted RNA were assessed with the Invitrogen Qubit 4. RNA integrity was evaluated using a Qsep400 bioanalyzer and agarose gel electrophoresis. Sequencing libraries were generated using the NEBNext® UltraTM Kit (Illumina®-compatible, NEB, Ipswich, MA, USA), in accordance with the manufacturer’s protocol. Index codes were added to attribute sequences to each sample. The quality of the library was verified via Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer capillary electrophoresis. Sequencing was performed on the Illumina platform by Metware Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China) to generate raw data. The raw data, provided in fastq format, underwent quality control using the fastp (version 0.23.2) software. This process included filtering raw data, checking the sequencing error rate, and analyzing GC content distribution, resulting in the generation of clean reads.
2.4. Transcriptome Data Analysis
De novo assembly of the cleaned reads was conducted using Trinity (version 2.13.2) software. The quality of the assembly results was evaluated using Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs (BUSCOs). Hierarchical clustering was performed using Corset (version 1.09) software. Gene expression was quantified using Expectation Maximization (RSEM, version 1.3.1). The expression value for each unigene was normalized to fragments per kilobase of transcripts per million fragment-mapped reads (FPKM). Unigene sequences were aligned against six databases by DIAMOND BLASTX, including NCBI-Nr (non-redundant proteins), Swiss-Prot (curated sequences), TrEMBL (automated annotations), KEGG pathways, GO terms, and KOG/COG orthologs. Following the prediction of the amino acid sequences for the unigenes, further alignment was conducted against the Pfam database using HMMER for annotation purposes. Enrichment analysis was performed utilizing the hypergeometric test; for KEGG, the test was conducted at the pathway level, while for GO, it was based on the GO term. Differential expression analysis between sample groups was conducted using DESeq2. Subsequently, multiple hypothesis testing correction of the p-values was performed using the Benjamini–Hochberg method to obtain the False Discovery Rate (FDR). The criteria for screening differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were set as |log2Fold Change| ≥ 1 and FDR < 0.05. What is more, KEGG, GO, and KOG annotation and enrichment of DEGs were performed.
2.5. Determination of Total Flavonoid Content
Fresh leaves from infected plants were gathered and processed into a fine powder. An aliquot of the powder (0.2 g) was extracted in 3 mL of 70% methanol for 30 min at 60 °C in an ultrasonication bath (power: 400 W, frequency: 40 kHz). After centrifugation at 12,000 rpm for 10 min, the OD510 of the supernatant was quantitatively analyzed using an ultraviolet spectrophotometer (INESA L6, Shanghai, China). The total flavonoid content was determined using the aluminum nitrate colorimetric method with rutin as the standard [
23]. The calibration curve was established as y = 0.0058x + 0.0308 (R
2 = 0.9991).
2.6. Flavone Extraction and HPLC Analysis
Petals of Jinsi Huangju were collected at five different blooming stages and immediately ground into a fine powder using liquid nitrogen. Subsequently, 0.2 g of the powdered sample was accurately weighed and transferred into a glass tube. Then, 5 mL of an 80% methanol solution was added, and the mixture was extracted at a stable temperature of 4 °C for 4 h. Following centrifugation, the resulting extract was filtered through a 0.22 μm microporous membrane to obtain a purified sample for further analysis. The method was adapted and optimized from an earlier established method [
24,
25]. The FLD-3x00 (RS) fluorescence detector, with a C18 column 100 × 2.1 mm, 1.7 µm (Syncronis, Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA), was used to analyze the components of the extracts. The column temperature was 35 °C, the flow rate was 1.0 mL/min, and the sample volume was 10 μL. The mobile phase consisted of two components: phase A (ultra-pure water containing 0.1% formic acid) and phase B (acetonitrile containing 0.1% formic acid). The gradient elution program was as follows: 0 min, 8% B; 10 min, 18% B; 20 min, 23% B; 45 min, 40% B; 48 min, 50% B; 52 min, 8% B; and 62 min, 8% B. The detection wavelength was 280 nm and there were five biological replicates per sample.
2.7. Virus Vector Construction and Agroinfiltration
pCVA plasmid vectors can be used to insert target gene fragments for in vitro recombination of silenced fragments. We used the Web MicroRNA Designer (WMD) (
http://wmd3.weigelworld.org/cgi-bin/webapp.cgi, accessed on 18 December 2023) to design 21-nt mature amiRNA-
FNS and amiRNA-
MYB8a sequences. Four oligonucleotide sequences were suggested by the WMD tool and two primer sequences, oligo A and oligo B, which were used to PCR amplify the designed amiRNA-
FNS and amiRNA-
MYB8a based on the pRS300 plasmid. The PCR products containing amiRNA-
FNS and amiRNA-
MYB8a were digested using KpnI and XbaI and cloned into the pCVA vector to obtain pCVA-amiRNA-
FNS and pCVA-amiRNA-
MYB8a. All primers are listed in
Table S1.
pCVA, pCVB, pCVA-amiRNA-FNS, and pCVA-amiRNA-MYB8a were transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101. PCR-confirmed monoclonal colonies were aseptically transferred into 5 mL Luria–Bertani (LB) liquid medium supplemented with dual antibiotics (50 μg/mL kanamycin and 25 μg/mL rifampicin), and cultured overnight at 28 °C. The cultures were transferred into 100 mL LB liquid medium containing kanamycin, rifampicin, 10 mM MES buffer, and 20 μM acetosyringone, and cultured to an OD600 of about 1.0. Thereafter, the bacteria were collected by centrifugation at 6000 rpm for 10 min, and an appropriate amount of resuspension buffer (10 mM MgCl2, 10 mM MES buffer, and 200 μM acetosyringone) was added to reach a final OD600 of about 1.0. The cultures were then incubated at 25 °C for 3 h under dark conditions. Finally, pCVB was mixed 1:1 (v/v) with pCVA-amiRNA-FNS and pCVA-amiRNA-MYB8a resuspensions, respectively (experimental group); pCVB and pCVA resuspensions were mixed 1:1 (v/v) (mock group); and the chrysanthemum seedlings were infected using vacuum infiltration. More specifically, the beakers containing the seedlings and infective solution were placed in a vacuum dryer for about 10 min. After releasing the vacuum, the seedlings were deposited in a plastic bag and cultured in the dark for 2 d at 10 °C. The seedlings were then transplanted to soil for culturing and water was sprayed on the leaves during the maintenance process. After 2 weeks, samples of the middle and upper parts of leaves appearing in good condition were taken for DNA identification.
2.8. DNA and RNA Isolation and PCR Analysis
Total DNA was isolated from the leaves of pCVA-amiRNA-
FNS-infected, pCVA-amiRNA-
MYB8a-infected, mock-infected, and control plants (CK) using the FastPure Plant DNA Isolation Mini Kit (Vazyme, Nanjing, China). Primers pCVA and pCVB were used to amplify CaLCuV (
Table S1). To identify the silencing efficiency of
FNS and
MYB8a in chrysanthemum, total RNA was extracted from new leaves of
Agrobacterium infiltration plants.
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
Total RNA was extracted from flower buds at the non-chromogenic stage (S0a), initial chromogenic stage (S0b), full chromogenic stage I (S1), full chromogenic stage II (S2, initial blooming stage), and full chromogenic stage III (S3, blooming stage) of Jinsi Huangju. Total RNA was isolated from samples using a Universal Plant Total RNA Isolation Kit (Vazyme), followed by cDNA synthesis with HiScript III RT SuperMix (Vazyme). Gene expression levels were quantified via qPCR using SYBR qPCR Master Mix (Vazyme). In chrysanthemum, CmEF1α served as the reference gene for normalization. Primer sequences are listed in
Table S1. The qPCR reaction mixture comprised 1 µL of cDNA, 10 µL of 2 × ChamQ Universal SYBR qPCR master mix, and 4 pmol of each primer. Thermal cycling parameters were set as follows: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 3 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s, 55 °C for 15 s, and 72 °C for 30 s. Each sample was analyzed in three technical replicates, and relative gene expression levels were calculated using the 2
−ΔΔCt method.
2.10. Statistical Analysis
Student’s t-test was applied to determine significant differences in the expression levels of key genes and the outcomes of transient transformation in Jinsi Huangju seedlings. For other statistical analyses, Duncan’s multiple-range test was conducted at a significance level of p < 0.05 to evaluate significant variations in the data. All data analyses were conducted using SPSS v.20 software (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Flavonoid Metabolites at Different Opening Stages of Jinsi Huangju Flowers
To investigate the alterations in metabolites throughout the growth phases of Jinsi Huangju, we employed the UPLC-MS/MS method for comprehensive targeted metabolomics analysis across three developmental stages (S1, S2, and S3). The platform detected 2146 metabolites, including 517 flavonoids, 146 amino acids and their derivatives, 68 nucleotides and their derivatives, 132 organic acids, 186 lipids, 300 phenolic acids, 93 lignans and coumarins, 10 tannins, 149 alkaloids, 259 terpenoids, 28 quinones, and 258 other substances. Within the 517 flavonoid compounds, there were 216 flavones, 158 flavonols, 19 chalcones, 54 dihydroflavones, 10 dihydroflavonols, 11 flavanols, 28 isoflavones, 6 orange ones, 1 anthocyanin, and 14 other types of flavonoids. Among the 10 types of tannin, there were 7 tannins and 3 proanthocyanidins. Among the 149 identified alkaloids, there were 16 pyrrole alkaloids, 26 phenolic amines, 11 piperidine alkaloids, 2 isoquinoline alkaloids, 29 indole alkaloids, and 65 other alkaloids. Among the 259 terpenoids, there were 178 sesquiterpenes, 35 diterpenes, 18 triterpenes, 22 triterpenoids, and 6 other terpenoids. Among the 186 lipids, there were 16 glycerides, 1 phosphatidylcholine, 5 sphingolipids, 25 lysophosphatidylcholines, 29 lysophosphatidylethanolamines, and 110 free fatty acids.
Pearson correlation analysis confirmed the authenticity of the metabolomics data (
Figure S2). PCA results showed (
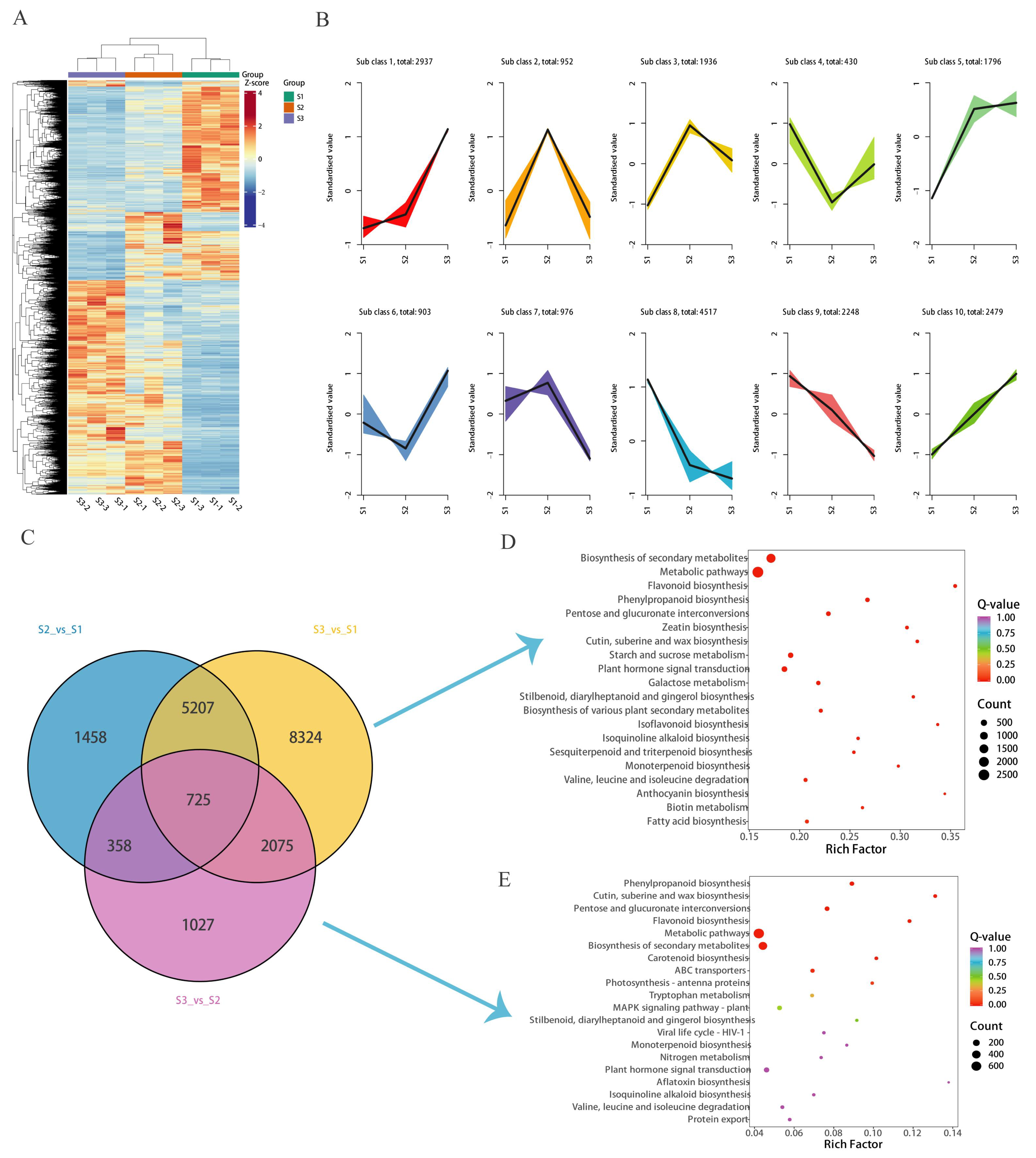
Figure 1A) that there was a clear separation of flower samples at different developmental stages, with samples clustered together within each of the S1, S2, and S3 groups.
Figure 1B shows that heat maps are drawn according to the proportional content of each metabolite for further hierarchical cluster analysis. As anticipated, the replicates for each flower development stage grouped closely, demonstrating minimal variation among them. The heat map analysis indicated that over fifty percent of the metabolites were more abundant in the S1 stage compared to the other stages. Additionally, certain metabolites exhibited a gradual increase in accumulation from S2 to S3, suggesting that their accumulation is linked to the flower development process.
Differential metabolites (DAMs) were screened with variable importance in projection VIP > 1, fold change ≥ 2, and fold change ≤ 0.5 in order to detect the changes in flower metabolites at different developmental stages. The findings revealed that there were 236 distinct metabolites when comparing S2 to S1, 454 when comparing S3 to S1, and 185 when comparing S3 to S2 (
Figure 2). Flavones were the major differential metabolites (
Table S2). In the comparison between S2 and S1, there were 67 flavone differential metabolites, which represented approximately 28.39% of the total differential metabolites. In the comparison between S3 and S1, 114 flavone differential metabolites were identified, accounting for roughly 25.11% of the total differential metabolites. Lastly, the comparison between S3 and S2 revealed 46 flavone differential metabolites, constituting about 24.86% of the total differential metabolites (
Figure 1C). A total of 10 flavones were noted, including Apigenin-7-O-(2′-glucurosyl) glucuronide, Luteolin, 2′-Hydroxygenistein, Artocarpanone, 3,5,7,2′-Tetrahydroxyflavone, Isoscutellarein, Norartocarpetin, 6-Hydroxyluteolin, Aureusidin, and 1,2,4,5-tetrahydroxy-7-(hydroxymethyl) anthracene-9,10-dione (
Table S3). The S3 vs. S1 comparison exhibited a significant number of unique flavonoid metabolites, with 31 flavonoids being exclusive to this comparison (
Table S4).
3.2. Determination of Flavonoid Content in the Developmental Process of Jinsi Huangju Flowers
The total flavonoid content of flowers in flower buds at the no color developing stage (S0a), initial color developing stage (S0b), full color developing stage I (S1), full color developing stage II (S2), and full color developing stage III (S3) (blooming stage) (
Figure 3A) were detected, respectively. A characteristic rise-and-fall profile was observed for total flavonoid accumulation during Jinsi Huangju flowering, suggesting stage-specific metabolic regulation (
Figure 3B). This result was consistent with the total flavonoid content in petals of ‘Anastasia Pink’ during the flowering process [
26]. Additionally, both lutein (
Figure 3C) and apigenin (
Figure 3D) exhibited a similar trend of rising and falling across the various stages of flower opening, and peaked at the full color development stage I (S1).
3.3. Transcriptome Analyses at Different Opening Stages of Jinsi Huangju Flowers
To investigate the synthesis of flavonoids during the development of chrysanthemum flowers, RNA-seq analysis was performed using the Illumina platform. Transcriptome sequencing was performed on nine libraries of three samples using three bioreplicates. A total of nine samples were analyzed by transcriptome sequencing, and 62.9 Gb of clean data were obtained; the number of raw reads in the samples ranged between 44,696,370 and 51,167,108 (
Table S5). After the removal of low-quality reads, the Q20 and Q30 base call accuracy rates were found to exceed 97.40% and 92.81%, respectively. The average GC content was 42.82%. These results indicate that the sequencing results were of high quality and were suitable for downstream analysis (
Table S5). By cluster analysis of DEGs, the tissue-specific transcriptome analysis of the development process of the flower was completed. Differential genes were filtered using |log2FC| ≥ 1 and FDR < 0.05 as the screening criteria (
Figure 4A). We used the K-means DEG clustering algorithm to obtain 10 clusters based on similar expression patterns (
Figure 4B). Venn diagram analysis showed that S2 vs. S1, S3 vs. S1, and S3 vs. S2 expressed 7748, 16,331, and 4185 DEGs, wherein 4807, 8984, and 2059 up-regulated genes and 2941, 7347, and 2126 down-regulated genes were expressed, respectively (
Figure 4C). KEGG enrichment analysis showed that flavonoid biosynthesis was enriched at DEGs (S3 vs. S1 and S3 vs. S2) (
Figure 4D,E).
Based on the results of metabolomic analyses, flavonoids were the major metabolites in the flower development process of Jinsi Huangju, and the flavonoid content of the Jinsi Huangju flower development process was determined, so the transcriptome analyses also focused on the biosynthesis of flavonoids. Thirty-eight flavonoid structural genes were differentially expressed during the S1 to S3 stages of Jinsi Huangju flower development, and all genes were down-regulated with the flower development process (
Figure 5,
Table S6).
MYB transcription factors, bHLH transcription factors, and WD40 repeat proteins play important roles in the regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis. Between S2 and S1, 180 flavonoid regulatory genes were differentially expressed: 104 up-regulated in S2 (30 MYB, 44 bHLH, 30 WD40) and 77 down-regulated (47 MYB, 21 bHLH, 9 WD40). Comparing S3 vs. S1, 360 genes showed differential expression: 184 up-regulated in S3 (68 MYB, 56 bHLH, 60 WD40) and 174 down-regulated (76 MYB, 47 bHLH, 51 WD40). In the S3 vs. S2 comparison, 65 genes were differentially expressed: 21 up-regulated in S3 (5 MYB, 5 bHLH, 11 WD40) and 44 down-regulated (22 MYB, 5 bHLH, 17 WD40).
To validate the transcriptome analysis, six flavonoid structural genes and six regulatory genes were randomly selected for qRT-PCR verification. The qRT-PCR results showed consistent expression patterns with RNA-seq data for all 12 genes (
Figure 6). Notably, while
CmBBX19 exhibited up-regulated expression in both S2 and S3, all other genes displayed down-regulated trends in these stages.
3.4. Combined Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis of Flavonoid Biosynthesis Pathways
Combined with metabolomic and transcriptomic data, we mapped all structural genes involved in the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway (
Figure 5). A total of 38 flavonoid structural genes were labeled as flavonoid biosynthesis pathways in the S1 to S3 stages of development of Jinsi Huangju flowers, including
CmPAL (9),
CmC4H (5),
Cm4CL (5),
CmCHS (3),
CmCHI (8), and
CmFNS (8). The analysis results showed that the expression levels of most differentially expressed genes decreased with flower development (
Figure 5). The reduction in the expression levels of key genes led to low flavonoid production, which is consistent with the metabolomics data. Both metabolomics and transcriptomics data indicated that the generation of flavonoids affected the color of Jinsi Huangju flowers. Because several structural genes lead to the difference in flavonoid content in flowers at different opening stages, it is speculated that these differences may be regulated by upstream transcription factors. The main differentially expressed transcription factors between different flowering periods are shown in
Table S7 (FPKM values > 1.0).
The expression characteristics of MYB family genes and
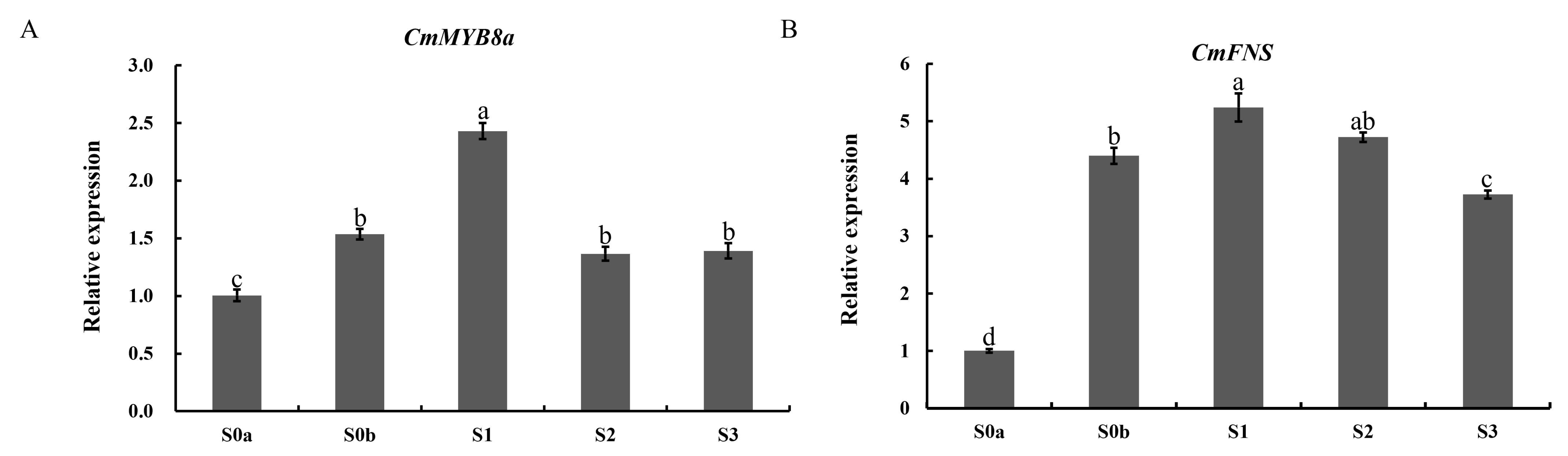
CmFNS in Jinsi Huangju were investigated by qRT-PCR analysis at five stages of flower opening. The expression patterns of
CmFNS during the flowering process were consistent with those in ‘Pink Anna’ [
14]. The spatiotemporal expression pattern of
CmMYB8a was positively correlated with the expression of the flavonoid accumulation marker gene
CmFNS, and correlated with the change pattern of the flavonoid content at different opening stages of the flower; that is, it showed a tendency to increase and then decrease, and the highest expression was found at the S1 stage (
Figure 7), suggesting that
CmMYB8a may be involved in the regulation of flavonoid synthesis in flowers.
3.5. CmMYB8a Regulates Flavonoid Biosynthesis
Previous studies indicated that CmMYB8a may play a role in the regulation of flavonoid production in chrysanthemum blooms, so the function of
CmMYB8a was further analyzed. According to the
CmMYB8a gene sequence annotated in the chrysanthemum transcriptome database, specific primers were designed and the full-length cDNA sequence of the
CmMYB8a gene was cloned. A phylogenetic analysis comparing CmMYB8a with 93 members of the
Arabidopsis MYB family revealed that it shared the closest relationship with AtMYB11 and AtMYB12, forming a clade and being clustered into the SG7 subfamily (
Figure 8A). CmMYB8a contains conserved R2 and R3 domains at its N-terminus, along with SG7 domains at the C-terminus (
Figure 8B).
qRT-PCR demonstrated predominant expression in roots, followed by flowers and leaves, with minimal expression in stems (
Figure S3). The spatiotemporal and temporal expression patterns of
CmMYB8a were found to have the same expression trend as that of the flavonoid accumulation marker gene
CmFNS and the transient transformation of Jinsi Huangju seedlings with
CmMYB8a and
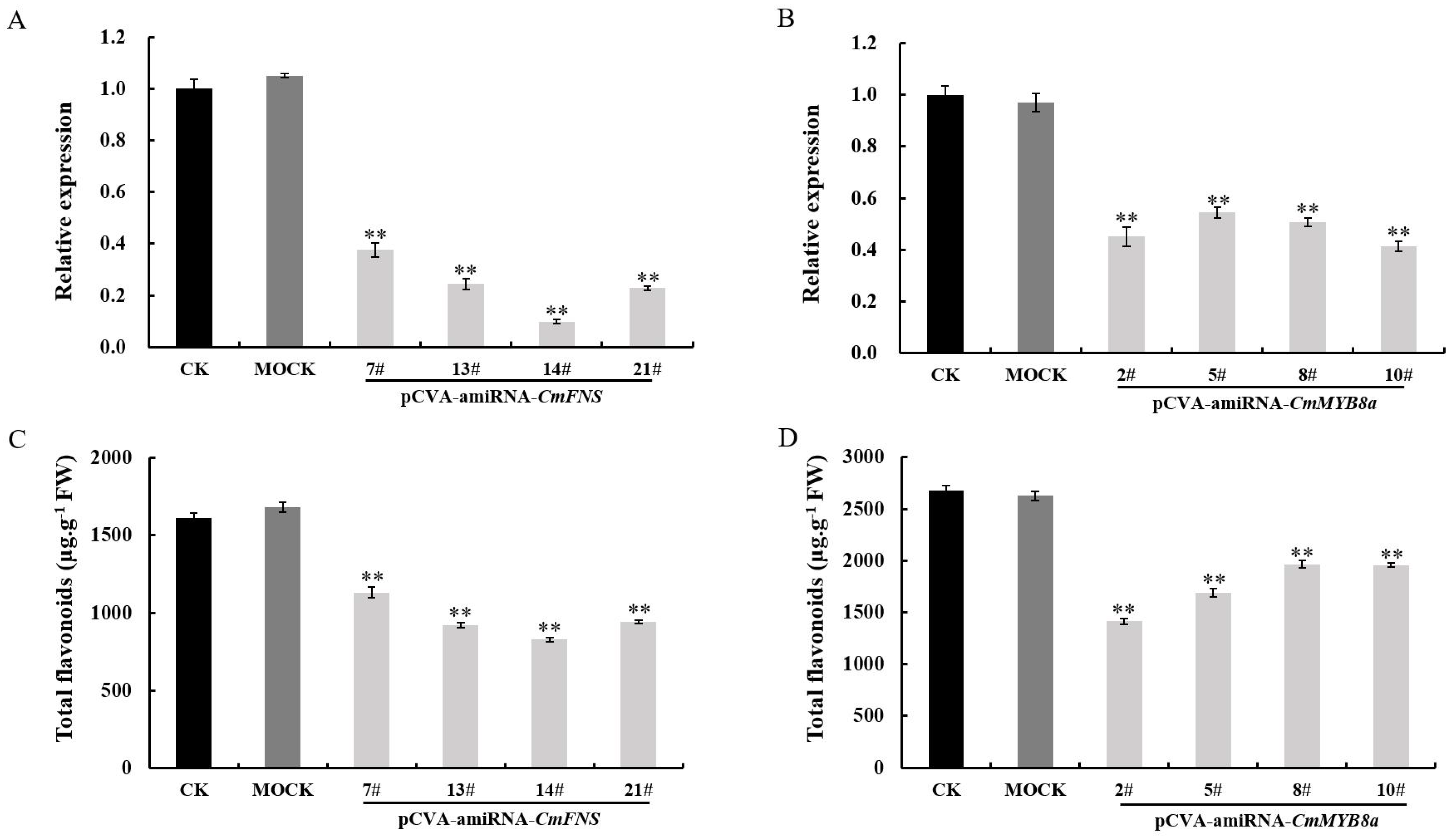
CmFNS, respectively. A total of 56 and 38 Jinsi Huangju plants were infected with
A. tumefaciens GV3101 carrying pCVA-amiRNA-
CmFNS and pCVA-amiRNA-
CmMYB8a constructs, respectively. The transformation efficiency reached 85.7% and 84.2% (
Tables S8 and S9). qRT-PCR analysis revealed that the expression of
CmFNS was reduced by 62.4–90% in the pCVA-amiRNA-
CmFNS-infected plants compared to the mock-infected and control plants, and the expression of
CmMYB8a decreased by 45.6–58.5% (
Figure 9A,B). In
CmMYB8a-silenced lines, the expression levels of
CmCHS,
CmFNS, and
CmCHI were all significantly reduced (
Figure S4). These results suggest that
CmMYB8a likely functions as a transcriptional activator that directly or indirectly promotes the expression of these structural genes. Additionally, the total flavonoid content was also measured in the transiently transformed pCVA-amiRNA-
CmFNS-infected and pCVA-amiRNA-
Cm MYB8a plants, and it was revealed that the flavonoid content of the chrysanthemum leaves was reduced, suggesting that
CmMYB8a serves as a key regulator to regulate flavonoid biosynthesis (
Figure 9C,D).
4. Discussion
Secondary metabolites are essential for the survival of plants, their adaptation to the environment, and their ecological roles [
27,
28]. In this study, a total of 2146 metabolites were detected, including 517 flavonoids. During the floral development of Jinsi Huangju, flavonoid metabolites reach their peak concentration at the S1 stage (full chromogenic stage), indicating this phase as the critical period for flavonoid biosynthesis. This pattern aligns closely with the total flavonoid dynamics observed in petals of the ‘Pink Anna’ chrysanthemum [
14], indicating that the early stages of full bloom may be a common phase for flavonoid accumulation in Asteraceae species. The enrichment of flavonoids during the initial pigmentation phase is likely linked to their dual physiological roles: on the one hand, flavonoids act as UV-absorbing screens and antioxidants, shielding delicate petals from photooxidative damage [
29]; on the other hand, flavonoids indirectly affect the accumulation and stability of anthocyanins through the metabolic network, thereby regulating flower color formation [
14,
30]. The MYB–bHLH–WDR (MBW) complex is a core transcriptional activation module that regulates flavonoid biosynthesis in plants by precisely controlling the expression of structural genes, thereby modulating the spatiotemporal accumulation of flavonoids [
31]. Epigenetic modifications significantly influence the accumulation trends of flavonoids by regulating the spatiotemporal expression of genes associated with flavonoid biosynthesis [
32]. Xu et al. found that high levels of methylation in the promoter regions of genes involved in flavonoid biosynthesis correlate with reduced gene expression and flavonoid content [
33]. Pandey et al. [
34] demonstrated that UV-B radiation induces genome-wide DNA demethylation in
Artemisia annua, resulting in enhanced transcriptional activation of key regulatory factors AaMYB1, AaMYC, and AaWRKY, which drive the overexpression of the
AaPAL1 gene and subsequently activate the entire phenylpropanoid–flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. Emerging evidence indicates that epigenetic regulation plays a crucial role in controlling both flower color and flowering time in chrysanthemums. Specifically, the methylation level of
CmMYB6 promoter exhibits a negative correlation with anthocyanin content, determining flower color variation in chrysanthemums [
35]. Further mechanistic studies by Li et al. [
36] revealed that three distinct DNA methyltransferases (CmDRM2a, CmDRM2b, and CmCMT2) differentially modulate the methylation status of the
CmMYB6 promoter, thereby precisely regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis and floral coloration. Additionally, research has identified that the
Chrysanthemum lavandulifolium DNA demethylase ClROS1 accelerates flowering by reducing the methylation level of CONSTANS (CO) promoter in
Arabidopsis thaliana [
37].
The significant reduction in flavonoid metabolites at the S3 stage (full flowering stage) may be related to the reprogramming of the metabolic pathway during the senescence of petals [
38,
39]. Studies have shown that during the process of senescence, flowers undergo a metabolic shift from sink organs to source organs [
39]. Transcriptional activation during petal senescence predominantly coordinates catabolic pathways targeting cellular macromolecules, including nucleic acid hydrolysis, proteolysis, lipid mobilization, and structural polymer disassembly [
38]. The 31 flavonoid metabolites uniquely identified in the S3 vs. S1 comparison may reflect stage-specific metabolic adaptations during late flowering. Importantly, many of these metabolites are glycosylated flavonoids, which may function as signaling molecules within the regulatory framework of petal senescence. In
Oenothera, it was found that the contents of cyanidin 3-glucoside and isosalipurposide increase in senescent petals [
40].
As a branch of the phenylalanine metabolic pathway, flavonoid metabolism is most commonly regulated by R2R3-MYB transcription factor. Initially discovered in maize, R2R3-MYB plays a crucial role in the metabolism of anthocyanin glycosides, leading to the identification of numerous MYB genes across various plant species [
41]. In pear (
Pyrus bretschneideri),
PpMYB17 increased the contents of flavonols, flavonoids, isoflavones, and anthocyanins in calli through up-regulated flavonoid biosynthesis pathway structure genes [
42].
DcMYB113 is specifically expressed in the epidermis and phloem of carrot (
Daucus carota) root, promoting anthocyanin accumulation and showing a purple color [
43].
CmMYB012 reduces the accumulation of flavonoids and anthocyanins by inhibiting the expression of
CmFNS,
CmCHS,
CmDFR,
CmANS, and
CmUFGT, which in turn regulates the formation of floral colors in
Chrysanthemum morifolium [
30]. These studies suggest that MYB transcription factors regulate flavonoid metabolism at the transcriptional level.
CmMYB8a clusters with
Arabidopsis AtMYB11/12 in the SG7 subfamily of MYB transcription factors (
Figure 8). Its expression pattern is highly synchronized with flavonoid content and the expression of the structural gene
CmFNS (
Figure 3 and
Figure 7). In
CmMYB8a-silenced lines, the expression levels of
CmCHS,
CmFNS, and
CmCHI are all significantly reduced (
Figure S1). These results suggest that
CmMYB8a likely functions as a transcriptional activator that directly or indirectly promotes the expression of these structural genes. The silencing of
CmMYB8a may lead to loss of activation signals, ultimately resulting in down-regulation of these flavonoid biosynthetic genes. Transient transformation assays further demonstrated that CmMYB8a positively regulates flavonoid biosynthesis. While the direct binding between CmMYB8a and the promoters of these structural genes has not yet been experimentally validated, our subsequent investigation will employ these assays to characterize these molecular interactions. Previous studies have reported that MYB proteins can activate or repress downstream gene expression by forming regulatory complexes with other proteins.
In
Camellia sinensis, the protein CsMYB67 boosts the transcription of CsANS through its interaction with CsTTG1, thereby facilitating the production of anthocyanins [
44]. In strawberry (
Fragaria ananassa), FaMYB123 interacts with FabHLH3 to regulate the expression of FaMT1, thereby regulating the synthesis of anthocyanins and flavonols in fruit [
45]. In apple (
Malus domestica), the application of brassinolide prompts MdMYB60 to interact with MdBEH2.2, which further enhances the inhibitory effect of MdBEH2.2 or MdMYB60 on the transcription of genes associated with flavonoid biosynthesis, which in turn reduces the content of flavonoid compounds [
46]. This indicates that MYB proteins can interact with various protein factors to influence flavonoid metabolism at the post-transcriptional stage. In the medicinal plant
Scutellaria baicalensis, the overexpression of the transcription factor SbMYB3 led to a higher accumulation of specific inter-root flavonoids, including baicalein, baicalin, wogonin, and wogonoside [
21]. Conversely, plants with
SbMYB3-RNAi interference showed a decrease in the production of these compounds and it was observed that SbMYB3 interacts with the promoter of
SbFNSII-2, enhancing its activity, which indicates that SbMYB3 serves as a positive regulator in the biosynthesis of inter-root flavonoids [
21]. Similarly, in
Apium graveolens, AgMYB12 binds to the
AgFNS promoter, promoting the up-regulation of the
AgFNS gene, which results in increased levels of lignans and apigenin [
22]. Additionally, AgMYB1 positively regulates apigenin accumulation by up-regulating the structural genes
AgPAL,
AgCHS,
AgCHI, and
AgFNSI in
Apium graveolens [
47].
In the reported literature, transcription factors regulating the synthesis of flavonoids such as flavonols and anthocyanins are predominant. The growing global demand for plant-derived bioactive compounds, particularly in pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications, has intensified the search for multifunctional transcriptional regulators of flavonoid biosynthesis pathways. The direct interaction mechanism between CmMYB8a and its target gene promoters, as well as its specific function in flowers, requires further investigation. Additionally, integrating multi-omics data to identify additional regulatory factors will help comprehensively reveal the molecular basis of flavonoid metabolism in chrysanthemum, thereby advancing its applications in the pharmaceutical and nutritional fields.