Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Key Pathways and Candidate Genes for Resistance to Plasmodiophora brassicae in Radish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and P. brassica Inoculation
2.2. RNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.3. Analysis of the RNA-Seq Data
2.4. Real-Time qPCR Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Investigation of the Resistance to P. brassicae in 52 Radish Lines
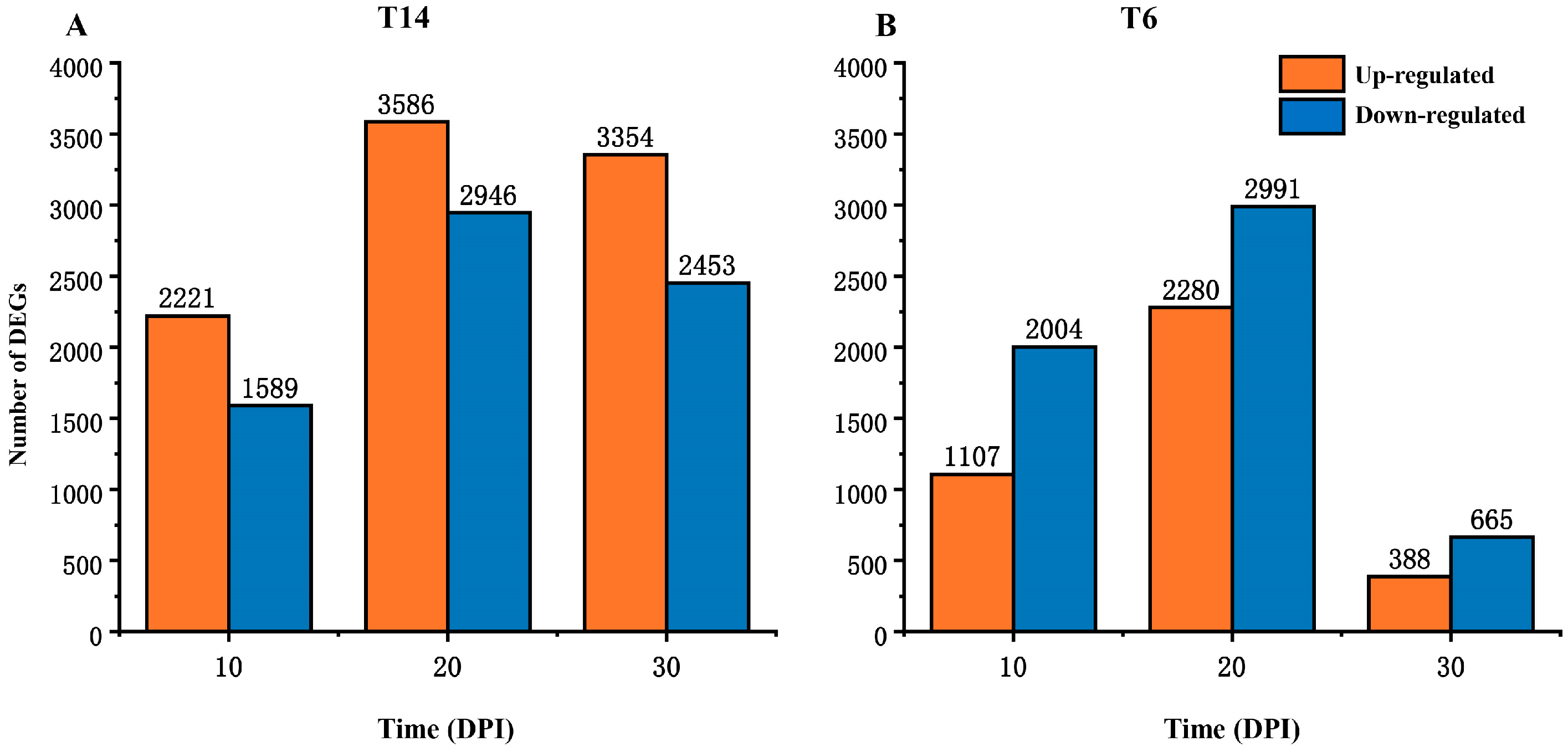
3.2. Sequencing Data Analysis
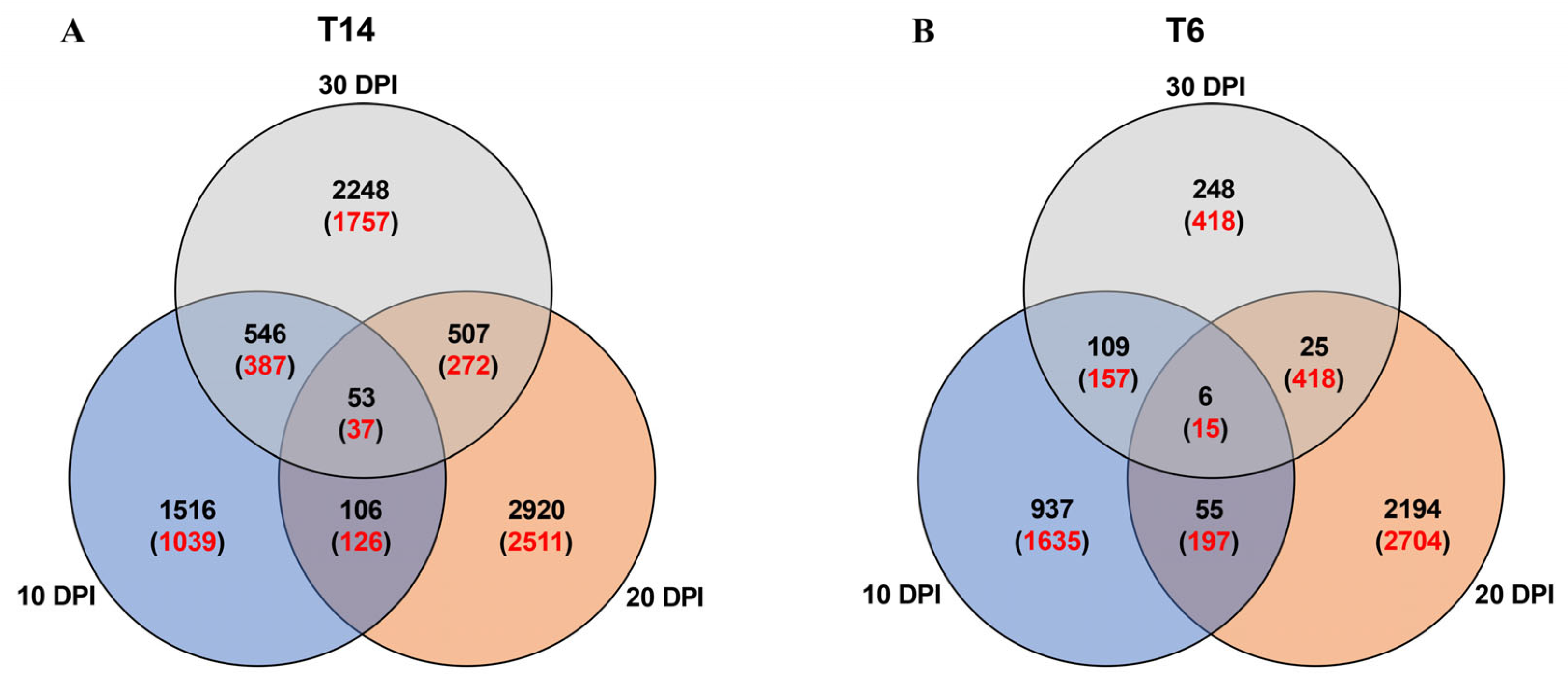
3.3. DEGs Between Resistant and Susceptible Radish Lines in Uninoculated or Inoculated Conditions
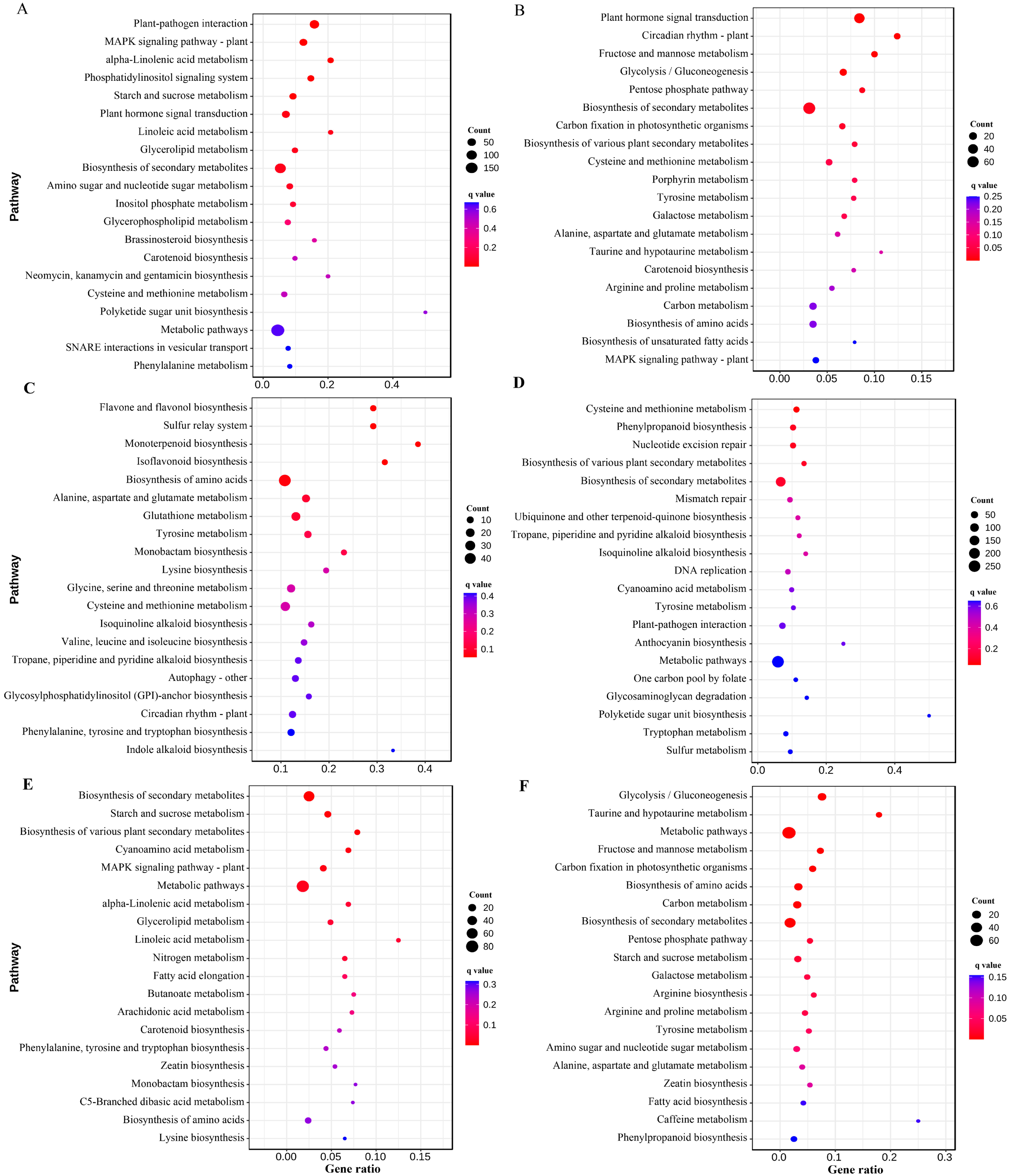
3.4. Differential Enrichment of Metabolic Pathways in Resistant and Susceptible Lines
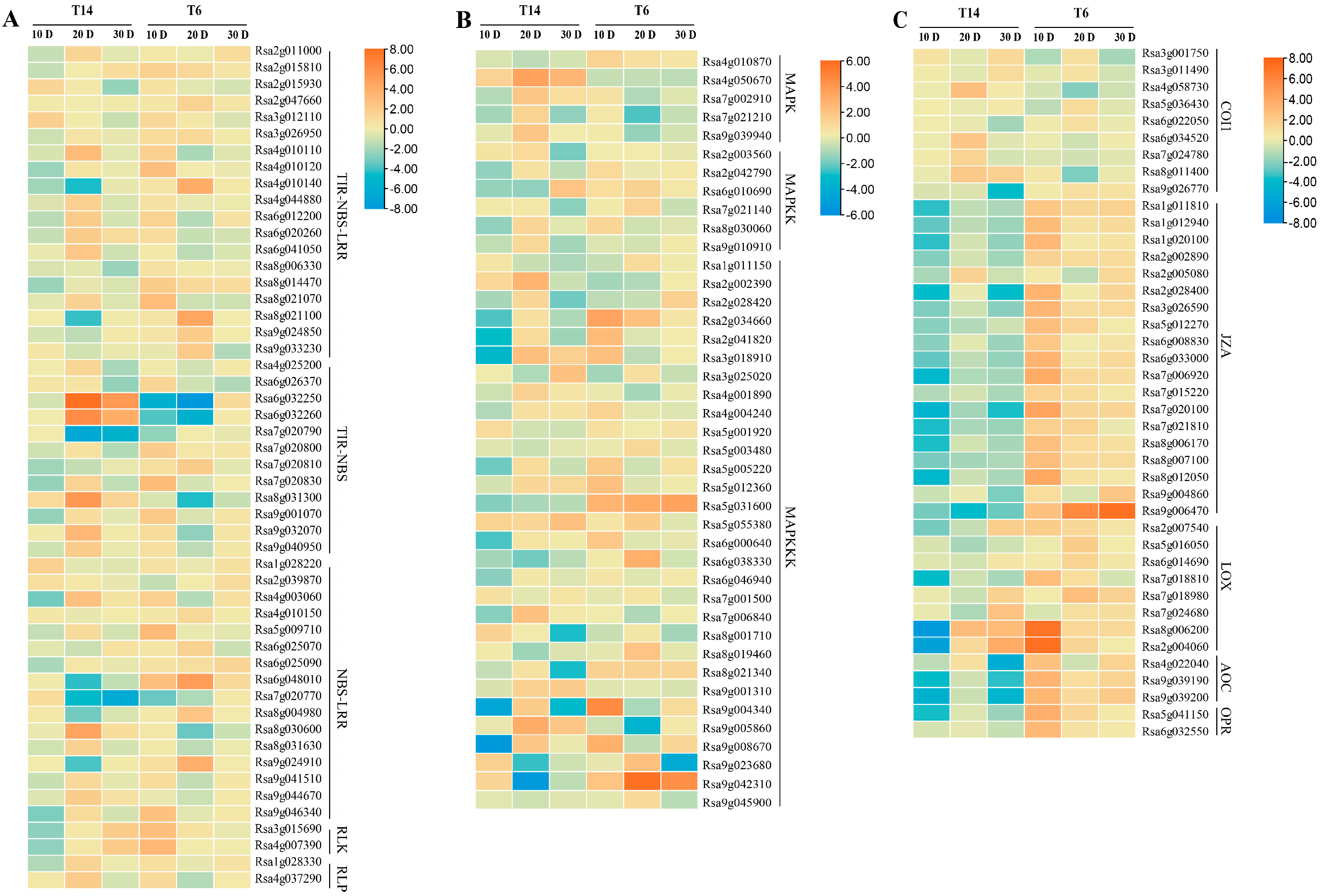
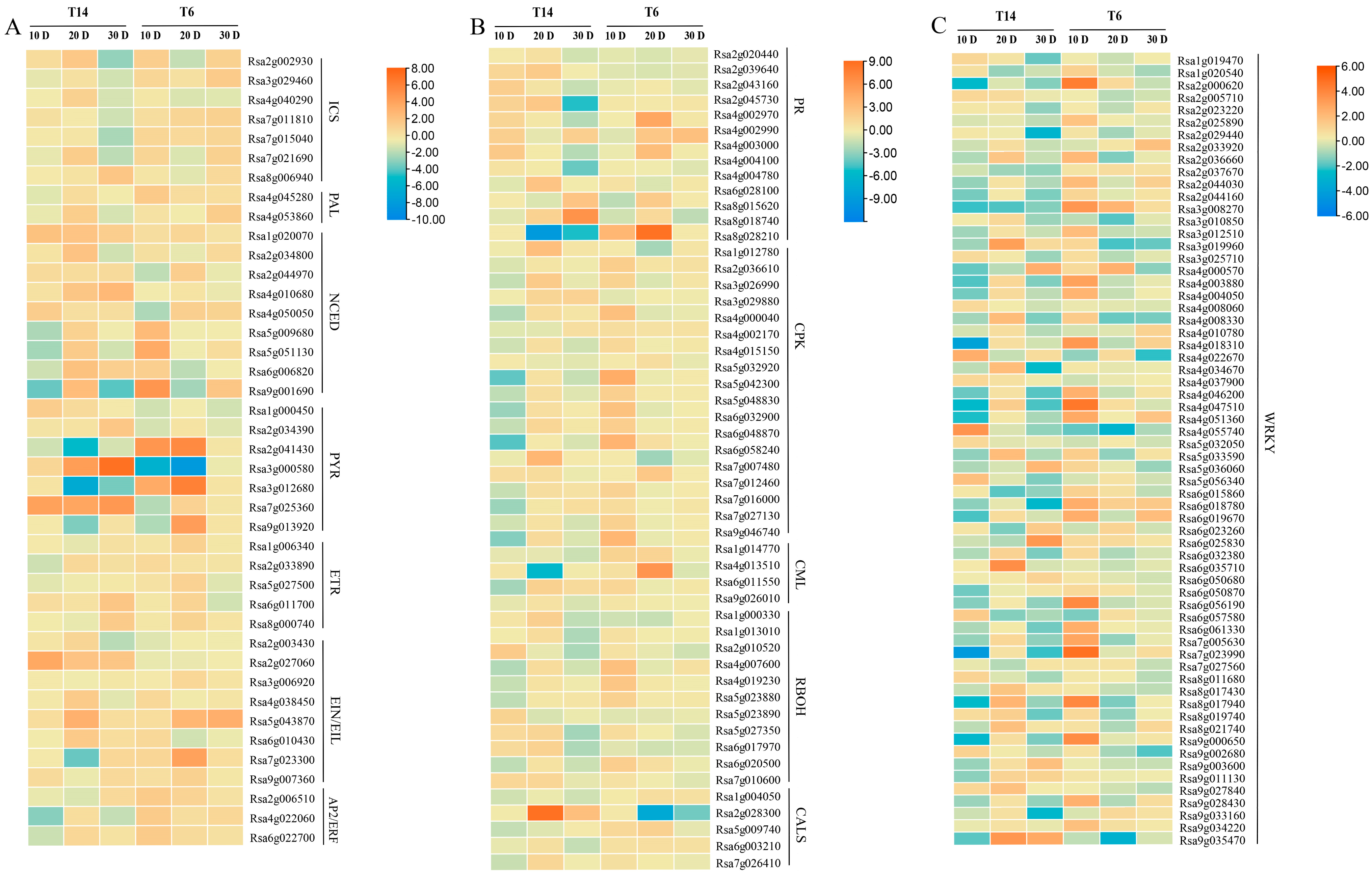
3.5. Differential Gene Ontology Enrichment and Expression Patterns Between Resistant and Susceptible Lines
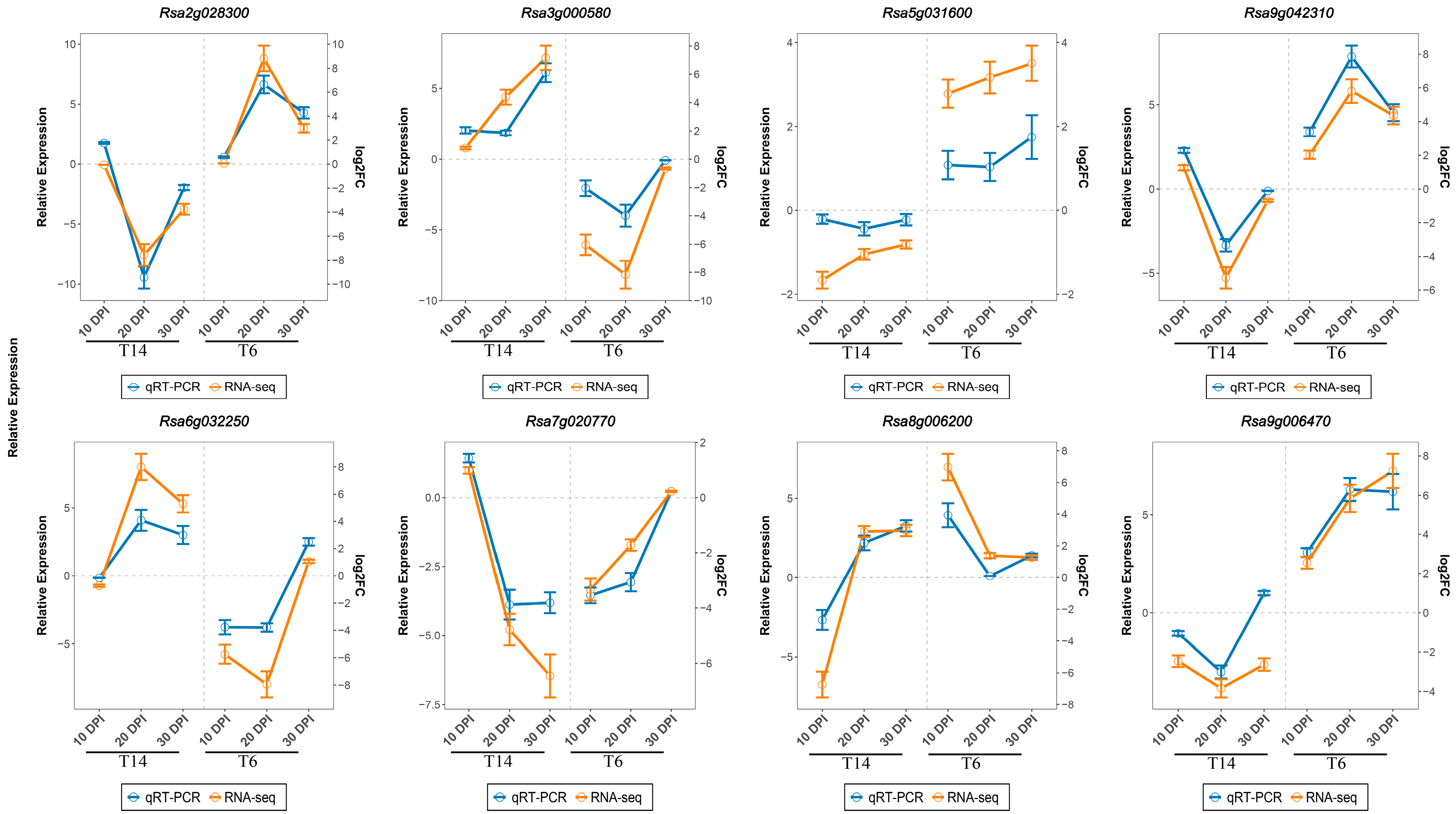
3.6. Validation of RNA-Seq Data by RT-qPCR
4. Discussion
- Transcriptomic analysis in susceptible and resistant lines during P. brassicae infection
- Multilayered defense activation in resistant and susceptible lines
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swaamy, K. Origin, distribution, genetic diversity and breeding of radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Int. J. Dev. Res. 2023, 13, 61657–61673. [Google Scholar]
- Nishio, T. Economic and academic importance of radish. In The Radish Genome; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gaba, J.; Bhardwaj, G.; Sharma, A.; Nayik, G.; Gull, A. Antioxidants in Vegetables and Nuts-Properties and Health Benefits; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Goyeneche, R.; Roura, S.; Ponce, A.; Vega-Gálvez, A.; Quispe-Fuentes, I.; Uribe, E.; Di Scala, K. Chemical characterization and antioxidant capacity of red radish (Raphanus sativus L.) leaves and roots. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 16, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baenas, N.; Piegholdt, S.; Schloesser, A.; Moreno, D.A.; García-Viguera, C.; Rimbach, G.; Wagner, A.E. Metabolic activity of radish sprouts derived isothiocyanates in Drosophila melanogaster. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, M.; Kakizaki, T.; Morimitsu, Y.; Ohara, T.; Hatakeyama, K.; Yoshiaki, H.; Kohori, J.; Nishio, T. Novel glucosinolate composition lacking 4-methylthio-3-butenyl glucosinolate in Japanese white radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 2037–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, M.S.; Riley, M.B.; Norsworthy, J.K.; Bridges, W., Jr. Variation of glucosinolates in wild radish (Raphanus raphanistrum) accessions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11626–11632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 188–189. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, S.; Chatterji, S.; Mehta, S.; Rai, P.K.; Singh, R.K.; Yadav, D.K.; Watal, G. Antidiabetic effect of Raphanus sativus root juice. Pharm. Biol. 2011, 49, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, F.; Yao, J.; Fan, L.; Liu, Z.; Yao, Y. Comprehensive review of Plasmodiophora brassicae: Pathogenesis, pathotype diversity, and integrated control methods. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1531393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharan, G.S.; Mehta, N.K.; Meena, P.D. The pathogen: Plasmodiophora brassicae. In Clubroot Disease of Crucifers: Biology, Ecology and Disease Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 87–120. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Wei, X.; Li, B.; et al. Research progress on clubroot disease in Brassicaceae crops–advances and perspectives. Veg. Res. 2024, 4, e022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.A.; Schwelm, A.; Zamani-Noor, N.; Salih, R.; Vañó, M.S.; Wu, J.; García, M.G.; Heick, T.M.; Luo, C.; Prakash, P. The clubroot pathogen Plasmodiophora brassicae: A profile update. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2022, 24, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, G.C. Introduction to the History of Plant Pathology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Karling, J.S. The Plasmodiophorales, 2nd ed.; Hafner Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, G.R. The occurrence and economic impact of Plasmodiophora brassicae and clubroot disease. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2009, 28, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, J.; Strelkov, S.; Orchard, D.; Hartman, M.; Lange, R.; Turkington, T. Identification of clubroot of crucifers on canola (Brassica napus) in Alberta. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2005, 27, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, A.; Xie, X.; Shi, Y.; Li, B. Research status of clubroot (Plasmodiophora brassicae) on cruciferous crops in China. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 36 (Suppl. S1), 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engqvist, L. Distribution of clubroot (Plasmodiophora brassicae Wor) in Sweden and the effect of infection on oil content of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Sver. Utsädesförenings Tidskr. 1994, 104, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.; Ahmed, H.; Zhou, Q.; Turnbull, G.; Strelkov, S.; Gossen, B.; Peng, G. Effect of host and non-host crops on Plasmodiophora brassicae resting spore concentrations and clubroot of canola. Plant Pathol. 2015, 64, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botero-Ramirez, A.; Kirk, B.; Strelkov, S.E. Optimizing clubroot management and the role of canola cultivar mixtures. Pathogens 2024, 13, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.; Li, Q.; Xu, Q.; Liu, J.; Huang, F.; Zhan, Z.; Qin, P.; Zhou, X.; Yu, W.; Zhu, L. CRb and PbBa8. 1 synergically increases resistant genes expression upon infection of Plasmodiophora brassicae in Brassica napus. Genes 2020, 11, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, K.; Suwabe, K.; Tomita, R.N.; Kato, T.; Nunome, T.; Fukuoka, H.; Matsumoto, S. Identification and characterization of Crr1a, a gene for resistance to clubroot disease (Plasmodiophora brassicae Woronin) in Brassica rapa L. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatakeyama, K.; Yuzawa, S.; Tonosaki, K.; Takahata, Y.; Matsumoto, S. Allelic variation of a clubroot resistance gene (Crr1a) in Japanese cultivars of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L.). Breed. Sci. 2022, 72, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Gong, J.; Li, Q.; Dun, B.; Liu, D.; Yin, F.; Yuan, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H. R gene triplication confers European fodder turnip with improved clubroot resistance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qin, L.; Zhang, W.; Tang, L.; Zhang, C.; Dong, X.; Miao, P.; Shen, M.; Du, H.; Cheng, H. WeiTsing, a pericycle-expressed ion channel, safeguards the stele to confer clubroot resistance. Cell 2023, 186, 2656–2671.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, A.; Tsuro, M.; Kubo, N.; Hayashi, T.; Wang, N.; Fujimura, T.; Hirai, M. QTL mapping of clubroot resistance in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2010, 120, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, C.; Deng, X.; Cui, L.; Yu, X.; Yuan, W.; Dai, Z.; Yao, M.; Pang, W.; Ma, Y.; Yu, X. Construction of a high-density genetic linkage map and identification of quantitative trait loci associated with clubroot resistance in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Mol. Breed. 2019, 39, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Yan, C.; Pang, W.; Cui, L.; Fu, P.; Yu, X.; Qiu, Z.; Zhu, M.; Piao, Z.; Deng, X. Identification of novel locus RsCr6 related to clubroot resistance in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 866211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Zhang, Y. MAP kinase cascades in plant development and immune signaling. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e53817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, S. Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plant signaling. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 301–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Wang, Z.; Wei, C.; Amo, A.; Ahmed, B.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X. Phenylpropanoid pathway engineering: An emerging approach towards plant defense. Pathogens 2020, 9, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Jia, M.; Hou, Z.; Dou, D.; Yu, J. Phenylalanine metabolism-dependent lignification confers rhizobacterium-induced plant resistance. Plant Physiol. 2025, 197, kiaf016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, K.; Gogoi, H.; Borgohain, M.; Saikia, R.; Chikkaputtaiah, C.; Hiremath, S.; Basu, U. The molecular dynamics between reactive oxygen species (ROS), reactive nitrogen species (RNS) and phytohormones in plant’s response to biotic stress. Plant Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; He, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhong, X.; Yan, B.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Zhai, K.; Huang, Y. Ca2+ sensor-mediated ROS scavenging suppresses rice immunity and is exploited by a fungal effector. Cell 2021, 184, 5391–5404.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Nat. Preced. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Ultrafast one-pass FASTQ data preprocessing, quality control, and deduplication using fastp. Imeta 2023, 2, e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Dong, J.; Zhang, W.; Tang, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, K.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; He, Q. A chromosome-level genome assembly of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) reveals insights into genome adaptation and differential bolting regulation. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 990–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. The Subread aligner: Fast, accurate and scalable read mapping by seed-and-vote. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.; Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential analysis of count data–the DESeq2 package. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 10–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G. Thirteen years of clusterProfiler. Innovation 2024, 5, 100722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taj, G.; Giri, P.; Tasleem, M.; Kumar, A. MAPK signaling cascades and transcriptional reprogramming in plant–pathogen interactions. In Approaches to Plant Stress and Their Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 297–316. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, M.A.; Jones, J.D.; Dangl, J.L. Reactive oxygen species signaling in response to pathogens. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, J.; Fan, B.; Yu, J.-Q.; Chen, Z. Protein–protein interactions in the regulation of WRKY transcription factors. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorang, J. Necrotrophic exploitation and subversion of plant defense: A lifestyle or just a phase, and implications in breeding resistance. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huot, B.; Yao, J.; Montgomery, B.L.; He, S.Y. Growth–defense tradeoffs in plants: A balancing act to optimize fitness. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 1267–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Does, D.; Leon-Reyes, A.; Koornneef, A.; Van Verk, M.C.; Rodenburg, N.; Pauwels, L.; Goossens, A.; Körbes, A.P.; Memelink, J.; Ritsema, T. Salicylic acid suppresses jasmonic acid signaling downstream of SCFCOI1-JAZ by targeting GCC promoter motifs via transcription factor ORA59. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 744–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Choi, S.R.; Wang, Y.; Chhapekar, S.S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, M.; Liu, D.; Zuo, Z. Starch content changes and metabolism-related gene regulation of Chinese cabbage synergistically induced by Plasmodiophora brassicae infection. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhab071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
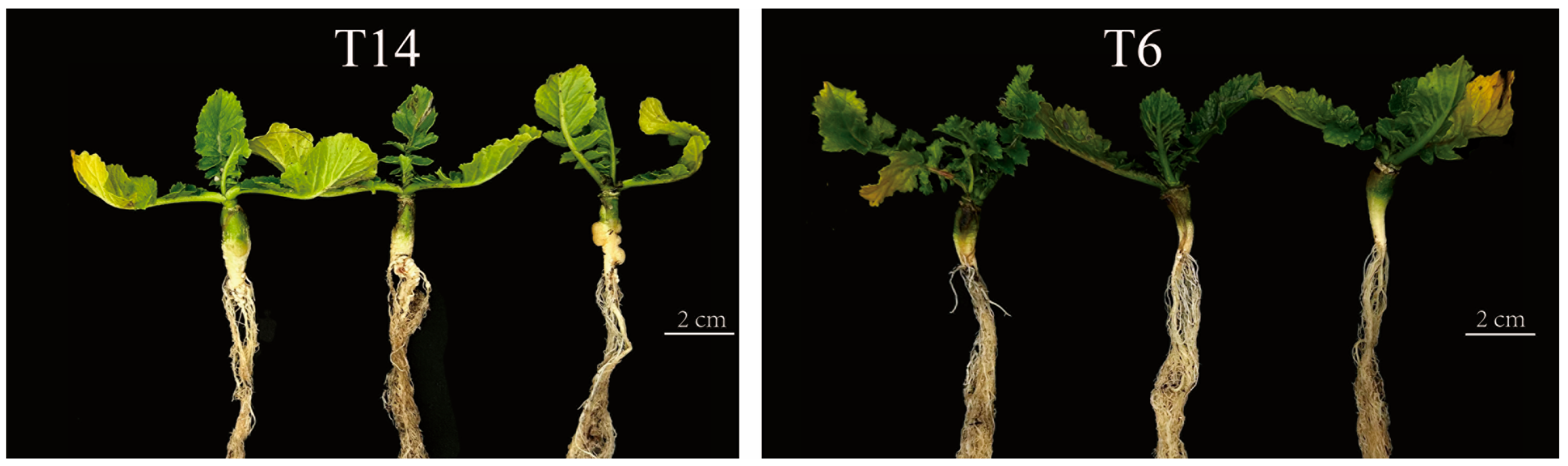


| Name | Plant NO. a | DI b | Phenotype c | Name | Plant NO. | DI | Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 10 | 3.40 ± 1.34 | S | 19_12 | 9 | 1.33 ± 0.82 | S |
| T2 | 10 | 0.67 ± 1.63 | S | 19_16 | 10 | 3.83 ± 0.41 | S |
| T3 | 10 | 2.00 ± 2.83 | S | MYB01 | 9 | 1.80 ± 1.48 | S |
| T5 | 10 | 3.17 ± 1.60 | S | MYB02 | 10 | 3.60 ± 0.89 | S |
| T6 | 9 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | R | YZ-1 | 10 | 3.22 ± 1.39 | S |
| T7 | 10 | 4.00 ± 0.00 | S | YZ-2 | 10 | 2.27 ± 1.74 | S |
| T8 | 9 | 4.00 ± 0.00 | S | YZ-3 | 8 | 3.40 ± 1.26 | S |
| T9 | 10 | 2.67 ± 2.07 | S | YZ-4 | 10 | 3.10 ± 1.66 | S |
| T10 | 8 | 3.25 ± 1.50 | S | YZ-5 | 10 | 2.88 ± 1.81 | S |
| T11 | 10 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | R | YZ-6 | 10 | 4.00 ± 0.00 | S |
| T13 | 10 | 2.25 ± 1.71 | S | YZ-7 | 10 | 3.83 ± 0.41 | S |
| T14 | 10 | 4.00 ± 0.00 | S | YZ-8 | 10 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | R |
| T15 | 10 | 2.00 ± 1.90 | S | YZ-9 | 10 | 1.23 ± 1.92 | S |
| T16 | 10 | 2.83 ± 1.47 | S | YZ-10 | 9 | 2.88 ± 1.81 | S |
| T17 | 10 | 3.60 ± 0.55 | S | YZ-11 | 10 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | R |
| T20 | 8 | 3.50 ± 1.00 | S | YZ-12 | 10 | 2.62 ± 1.76 | S |
| T21 | 10 | 3.20 ± 1.79 | S | YZ-13 | 9 | 2.14 ± 1.68 | S |
| T22 | 9 | 3.40 ± 1.34 | S | YZ-14 | 10 | 3.82 ± 0.60 | S |
| T23 | 10 | 2.67 ± 2.07 | S | YZ-15 | 10 | 3.86 ± 0.38 | S |
| T24 | 10 | 0.20 ± 0.45 | S | YZ-16 | 9 | 2.56 ± 1.51 | S |
| T25 | 9 | 0.80 ± 1.79 | S | YZ-17 | 10 | 3.40 ± 0.97 | S |
| T26 | 10 | 0.20 ± 0.45 | S | YZ-18 | 9 | 4.00 ± 0.00 | S |
| T30 | 9 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | R | YZ-19 | 10 | 3.43 ± 1.13 | S |
| T31 | 10 | 0.83 ± 1.60 | S | YZ-20 | 9 | 4.00 ± 0.00 | S |
| T33 | 9 | 0.67 ± 1.63 | S | YZ-21 | 10 | 4.00 ± 0.00 | S |
| T35 | 10 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | R | YZ-22 | 10 | 3.17 ± 1.33 | S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Cui, F.; Yu, Q.; Liu, B.; Guo, X.; Liu, L. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Key Pathways and Candidate Genes for Resistance to Plasmodiophora brassicae in Radish. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11070777
Ma Y, Li X, Cui F, Yu Q, Liu B, Guo X, Liu L. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Key Pathways and Candidate Genes for Resistance to Plasmodiophora brassicae in Radish. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(7):777. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11070777
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yinbo, Xinyuan Li, Feng Cui, Qian Yu, Baoyang Liu, Xinyi Guo, and Liwang Liu. 2025. "Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Key Pathways and Candidate Genes for Resistance to Plasmodiophora brassicae in Radish" Horticulturae 11, no. 7: 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11070777
APA StyleMa, Y., Li, X., Cui, F., Yu, Q., Liu, B., Guo, X., & Liu, L. (2025). Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Key Pathways and Candidate Genes for Resistance to Plasmodiophora brassicae in Radish. Horticulturae, 11(7), 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11070777







