Abstract
Coal gangue is a fine-grained mineral with nutrient content, which can be used as a potential soil amendment. Nevertheless, current research on using coal gangue to improve soil water and support plant growth is still insufficient. In this study, coal gangue powder (CGP) was added to aeolian sandy soil. We compared the soil hydraulic properties and plant growth of original aeolian sandy soil (CK) and different CGP application rates (10% and 20%). The results indicated that the application of CGP transformed the soil texture from sandy to loamy, significantly reduced soil bulk density and saturated hydraulic conductivity (Ks) values, altered the soil water characteristic curve, enhanced soil water-holding capacity, and increased plant-available water. Compared with the CK group, the emergence rate of alfalfa seeds increased from approximately 50% to over 70% after CGP application. During the growth process, CGP application significantly elevated the net photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate, and stomatal conductance of alfalfa leaves. Rapid fluorescence kinetics monitoring of leaves demonstrated that alfalfa treated with CGP had a higher efficiency in light energy utilization. However, the photosynthetic capacity of leaves did not improve as the CGP application rate increased from 10% to 20%, suggesting that excessive CGP addition did not continuously benefit plant gas exchange. In conclusion, CGP application can improve the soil hydraulic properties of aeolian sandy soil and support plant growth and development, which is conducive to reducing the accumulated amount of coal gangue, alleviating plant water stress, and promoting ecological restoration in arid mining areas. We recommend a 10% addition of coal gangue powder as the optimal amount for similar soils.
1. Introduction
Soil serves as the primary and essential source of nutrients and water for plant growth [1,2]. Its hydraulic characteristics play a crucial role in supporting plant growth and environmental sustainability, particularly in regions with limited water resources like arid and semi-arid areas [3]. Most of the arid and semi-arid lands globally are facing an increasing risk of desertification [4,5]. In these regions, most soils, particularly aeolian sandy soils, have a coarse texture and poor hydraulic properties, which are not conducive to water retention, making it extremely difficult for plants to survive in such soils [6]. Therefore, improving the soil hydraulic properties of aeolian sandy soils has become an urgent task.
The most direct approach to alter the soil hydraulic properties is through the use of additives. Currently, various types of soil additives are employed for soil amendment, including inorganic, organic, synthetic, and biological additives (e.g., wood ash, biochar, polyacrylamide) [5,7,8]. Among them, the addition of solid wastes like fly ash and fine gasification slag not only improves the physical and chemical properties of soil, including increasing specific surface area, pore size distribution, and nutrient and organic matter content [7,9,10], but also maximizes the utilization of waste resources, thus attracting widespread attention.
Coal is one of the main energy sources in China, accounting for approximately half of the global coal consumption [11,12]. Coal gangue is a solid waste generated during coal mining and washing processes, accounting for about 10–15% of the total coal production [11,13]. At present, the cumulative amount of coal gangue has exceeded 5 × 109 tons, becoming one of the most serious environmental problems [11]. Over the past 20 years, many methods have been actively explored to utilize coal gangue in various industries to address this environmental challenge, including in building materials, energy, and soil development [13,14,15]. However, compared with the production volume of coal gangue, its utilization rate is still insufficient.
Coal gangue is a fine-grained mineral with high nutrient and carbon content, which can be used as a potential soil amendment [11,13]. Nevertheless, current research on using coal gangue to improve soil and support plant growth is still insufficient, especially regarding coal gangue powder (CGP). Meanwhile, China’s coal production bases are concentrated in arid and semi-arid regions, and coal mining has made the risk of land desertification more prominent in these areas [16]. Using coal gangue to improve soil and inhibit desertification according to local conditions in mining areas is of great significance for maintaining vegetation and promoting the sustainable development of the ecosystem in mining areas.
Given this context, we propose the following hypotheses: (1) the addition of CGP will change soil texture; (2) applied CGP will significantly amend soil hydraulic properties; (3) CGP addition will have a positive impact on plant growth. This study aims to evaluate the potential of CGP obtained from coal mining areas for amending aeolian sandy soil, by applying different concentrations of CGP to compare the effects on soil hydraulic properties and plant growth. This application may achieve the in situ reuse of this solid waste, thus mitigating its environmental and economic impacts.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Coal Gangue and Soil Sampling
The Shendong mining area underwent an intensive process of coal mining throughout its history, resulting in the degradation of surface land [17,18,19] and substantial accumulation of coal gangue [20,21]. The coal gangue materials used in this study were sourced from the Daliuta mine (39.23° N, 110.15° E) in the Shendong mining area and characterized by its non-spontaneous combustion properties. The coal gangue is mainly composed of 59.5% SiO2, 22.4% Al2O3, 3.92% Fe2O3, 0.46% CaO, and 0.75% MgO, with a combustion loss of 14%. Prior to usage, the coal gangue samples were subjected to thorough washing procedures for dust removal. After drying, they were crushed and passed through a 2 mm sieve. A composite aeolian sandy soil sample was collected from the 0–30 cm depth in a field near the coal gangue sampling location. Soil subsamples were randomly taken from five points, each with a sampling volume of approximately 1920 cm3. The subsamples were combined, air-dried, homogenized, and passed through a 2 mm sieve before use. The soil particle composition of coal gangue powder (CGP) and aeolian sandy soil is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Soil particle composition of CGP and aeolian sandy soil.
2.2. Plant Growth Experiments
The plant growth experiment was conducted in the greenhouse of Northwest A&F University on 6 March 2024. Three different soil treatments were set up, including the Shendong mining area sandy soil culture group (CK), soil with 10% CGP added by weight, and soil with 20% CGP added by weight. In order to perform sterilization, alfalfa (Medicago sativa) seeds were soaked in a 30% (by volume) hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) solution for 5 min. After rinsing with distilled water, they were placed in different soil environments for cultivation. For each treatment, 16 pots were set as repetitions with completely random placement. Each pot contained 0.3 kg of soil, and 10 seeds were sown in each pot. The experimental pots had a square base with side lengths of 7 cm and a height of 8 cm, featuring drainage holes at the bottom. Before soil filling, a layer of filter paper was carefully placed at the base of each pot to prevent the leakage of soil and root systems. The greenhouse was illuminated with natural light. During the cultivation, all treatments were maintained under the same suitable temperature (25–30 °C) and relative humidity (40–50%) conditions. Alfalfa seeds were continuously cultivated in different soil environments for 65 days, determining the germination rate and photosynthetic characteristics of the plants.
2.3. Laboratory Measurements for Soil
After the plant growth experiment, a ring knife (100 cm3) was used to obtain undisturbed soil from the flowerpot to determine the soil properties. Bulk density (BD) was calculated as the ratio of the oven-dry weight to the volume of the cutting ring. The particle size distribution of the soil sample was determined using the Laser Particle Size Analyzer (Long Bench Controller 2000, Malvern Instrument, Malvern, UK), following the classification standards for soil texture established in America: particles ranging from 0.02 to 2 mm were classified as sand particles, those between 0.002 and 0.02 mm were classified as powder particles, and those smaller than 0.002 mm were classified as clay particles.
Saturated hydraulic conductivity (Ks) was determined using the constant head method [22,23,24]. The soil was filled in the ring stainless steel cutting ring, and it was found that the soil sample remained saturated at a 5 cm constant water head, and the water flow per unit time was recorded to calculate the saturated hydraulic conductivity. Three duplicate samples were measured in each treatment.
The soil–water retention curve (SWRC) was determined using a high-speed freezing centrifuge (CR22G II, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan). The samples were centrifuged at speeds of 310, 690, 980, 1700, 2190, 2590, 3100, 5370, 6930, and 8200 rpm. The corresponding matrix suction values were 10, 51, 102, 306, 510, 714, 1020, 3060, 5100, and 7140 cm water head. After centrifugation at each speed, the samples were weighed and then dried in an oven until reaching constant weight. This allowed for calculation of the water content corresponding to different suction values. Three duplicate samples were measured in each treatment. The van Genuchten (VG) model was used to fit the data [25]:
where θ is volumetric soil water content (cm3 cm−3), h is soil water pressure head in cm, θr is residual volumetric soil water content in cm3 cm−3, θs is volumetric soil water content at zero pressure head in cm3 cm−3, α is inversely related to the air-entry pressure in cm−1, and n and m are positive fitting parameters (n > 1, m = −1/n). The correlation coefficient (R2) was used to evaluate the model.
Field capacity (FC) and permanent wilting point (PWP) were determined based on the measured results of the SWRC, and the soil water content under 330 cm water head pressure (33 kPa) and 15,000 cm water head pressure (1500 kPa) was considered as FC and PWP, respectively [26,27]. And the available water content (AWC) was the difference between the FC and PWP.
2.4. Measurements of Plant Characteristics
The disinfected and rinsed Alfalfa seeds were placed in different treatments and cultivated in a warm and humid environment. On the 4th, 7th, 8th, 9th, 13th, 16th, 17th, 20th, and 22nd days of sowing, the number of emerging seedlings was counted until no new seedlings were produced.
Determination of gas exchange parameters was performed using the Li-6400 portable photosynthesis system (Li-6400, LI-Cor, Lincoln, NE, USA), on a cloudless morning between 9:00 and 11:00 a.m. Before the measurement began, the instrument was placed in the measurement environment and preheated for half an hour. During the measurement, through the instrument settings, the light quantum flux density was adjusted to 1000 µmol m−2 s−1, and the CO2 concentration was around 400 ppm. We selected fully unfolded leaves that had the same growth period and similar growth conditions, and five repeated leaves were measured in each treatment. Each gas exchange parameter was recorded after the data stabilized, including net photosynthetic rate (Pn,. µmol m−2 s−1), stomatal conductance (gs, mol m−2 s−1), and transpiration rate (Tr, mmol m−2 s−1). After the data collection was completed, the instantaneous water use efficiency was calculated. The calculation formula is as follows:
The fluorescence characteristics of plant leaves were determined by using rapid chlorophyll fluorescence induction dynamic technology and a portable modulated chlorophyll fluorescence meter (PAM-2500, WALZ, Effeltrich, Germany) from 6:00 to 8:00 p.m. For each treatment, 15 fully developed leaves were selected. After 20 min of dark adaptation, the rapid chlorophyll fluorescence induction kinetic curve (O-I-J-P) was determined using the poly—300 ms program. The O-I-J-P curve can reflect photochemical information about PSII, including the states of electrons on the donor side, on the recipient side, and at the reaction center of PSII. Further through JIP-test analysis, the following fluorescence parameters were obtained: (1) reaction center parameters—absorption per unit reaction center (ABS/RC), capture (TR0/RC), energy for electron transfer (ET0/RC), and energy for heat dissipation (DI0/RC); (2) parameters of the electron transfer process—the probability of electron transfer to the electron acceptor downstream of QA in the electron transfer chain (ET0/TR0), the quantum yield used for electron transfer (ET0/ABS), and the maximum quantum efficiency of PSII (TR0/ABS); (3) photosynthetic performance index—the maximum photochemical efficiency (FV/FM) and performance index (PI).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The differences in soil hydraulic properties among different treatments were evaluated using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS 22.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA), while all graphs were generated in Origin 2024 (Origin Lab Corporation, Northampton, MA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Soil Particle Composition and Bulk Density
The particle distribution curves of different materials are shown in Figure 1. The particle size of the original aeolian sandy soil (CK) was predominantly greater than 50 μm, presenting a frequency distribution curve with a narrow peak shape. In contrast, the particle size of CGP was distributed over a wide range (0.3–100 μm), with a gentle and broad peak between 2 and 10 μm (Figure 1). After applying CGP to the aeolian sandy soil, the frequency distribution curve transformed from a sharp peak to a smooth one. Meanwhile, the content of coarse particles decreased, while that of fine particles increased. With application rates of 10% and 20% CGP, the soil texture changed from sandy loam to loam and silty loam.
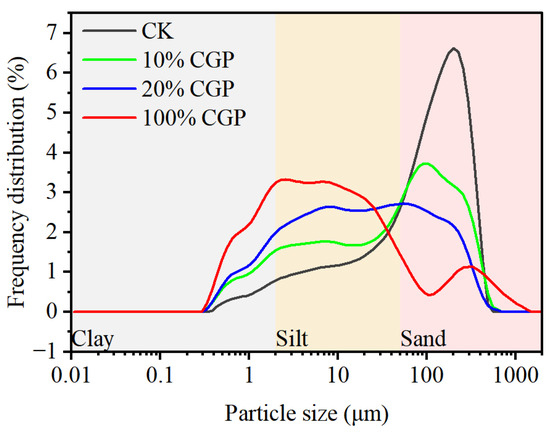
Figure 1.
Particle size distribution curves of CGP (100%), aeolian sandy soil (CK), and the mixture of the two materials (10% and 20%).
The bulk density (BD) of the soil was altered by the addition of CGP (Figure 2). The BD of the original soil (CK) was 1.55 ± 0.01 g cm−3. After adding 10% and 20% of CGP, the BD values of the soil decreased to 1.49 ± 0.03 g cm−3 and 1.44 ± 0.05 g cm−3, respectively. These results indicate that soil bulk density decreased significantly with the increase in CGP addition from 0% to 10% (p < 0.05), but there was no significant difference in bulk density between the 10% and 20% treatments, suggesting that further CGP addition beyond 10% did not cause an additional significant reduction in bulk density.
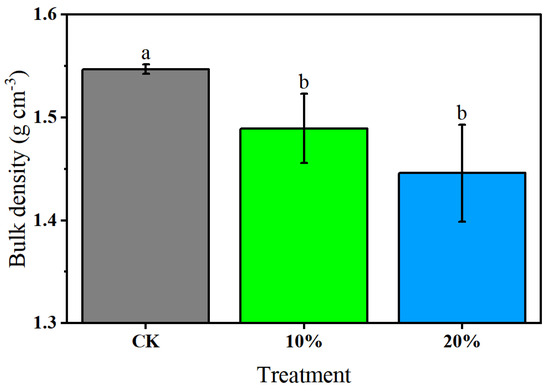
Figure 2.
Soil bulk density of different treatments. Different lowercase letters indicate a significant difference between means at p < 0.05.
3.2. Soil Hydraulic Properties
The hydraulic conductivity (Ks) of the saturated soil was changed by the addition of CGP (Figure 3). The Ks of the original soil (CK) was relatively high, reaching 11.85 ± 1.53 cm h−1, which indicated a strong water infiltration velocity. After adding 10% and 20% of CGP, the Ks values of the soil decreased to 1.76 ± 0.17 cm h−1 and 0.31 ± 0.10 cm h−1, respectively. These results clearly demonstrate that with the addition of CGP, the water infiltration rate decreased significantly.
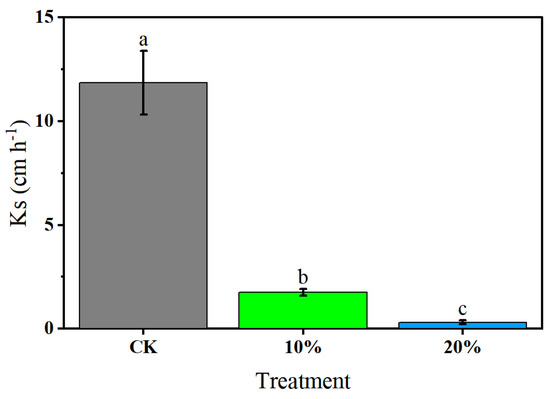
Figure 3.
Saturated soil hydraulic conductivity of different treatments. Different lowercase letters indicate a significant difference between means at p < 0.05.
The soil–water retention curves (SWRCs) for the experimental soils are shown in Figure 4. The effect of CGP application on soil water-holding capacity varied under high matric suction (>100 cm) and low matric suction (<100 cm). Notably, a consistent and significant increase in water content was observed at high matric suction with increasing CGP application. On the other hand, the treatment of the low-suction section was weak, and the change in water content was relatively unordered. This was attributed to the rapid water loss of sandy soil at this stage, which rendered the centrifuge method unable to accurately measure this stage. The VG model effectively described the SWRCs of all experimental soils, with coefficients of determination (R2) greater than 0.99 (Table 2). The values of θr, θs, n, and m increased with the increase in the application rate of CGP. In contrast, the value of α showed an opposite trend. These findings indicate that the application of CGP can enhance soil water-holding capacity. Moreover, it effectively increases the soil water loss threshold and the rate of water loss.
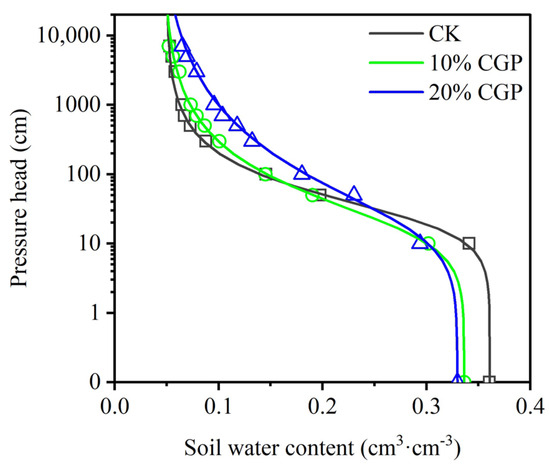
Figure 4.
Soil–water retention curves of aeolian sandy soil modified by coal gangue powder (CGP) at different treatments.

Table 2.
The VG model parameters of aeolian sandy soil modified by coal gangue powder (CGP) at different treatments.
The changes in the availability of soil water after the application of CGP were further quantified, as shown in Figure 5. After the application of CGP, the field capacity (FC) and the available water capacity (AWC) of the soil increased significantly (p < 0.05), while the permanent wilting point (PWP) remained almost unchanged in the CGP-treated soil. Compared with the original aeolian sandy soil (CK), the treatments with 10% and 20% CGP increased the FC by 1.4 and 5.0 cm3 cm−3, respectively, and the corresponding AWC increased by 1.3 and 4.0 cm3 cm−3, respectively. Overall, these results indicate that the application of CGP has improved the availability of soil water.
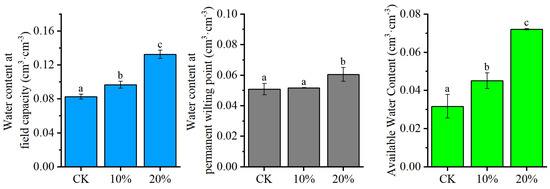
Figure 5.
Water availability parameters of aeolian sandy soil modified by coal gangue powder (CGP) at different treatments. For each parameter, different lowercase letters indicate a significant difference between means at p < 0.05.
3.3. Plant Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics
As shown in Figure 6, within 24 days after sowing, the emergence rate of alfalfa seeds increased with the progression of cultivation days. The emergence rates of seeds in the original aeolian sandy soil group (CK) and the 10% CGP treatment group were similar, both around 50%. In contrast, the emergence rate of seeds under the 20% CGP treatment increased significantly (p < 0.05), exceeding 70%.
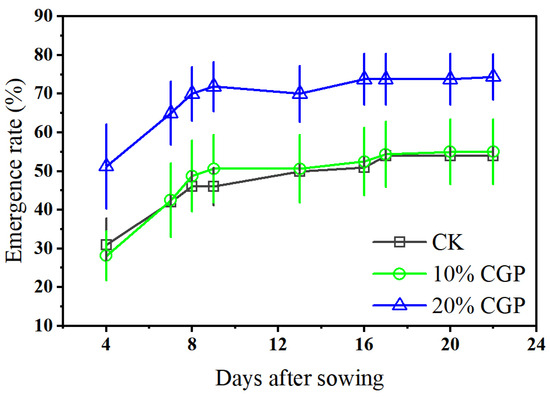
Figure 6.
Variation in alfalfa seeds emergence rate after sowing at different treatments.
The changes in gas exchange parameters during the growth of alfalfa under different treatments are shown in Figure 7. After the application of CGP, the net photosynthetic rate (Pn) and transpiration rate (Tr) of alfalfa increased significantly compared with those of the CK group (Figure 7a,b) (p < 0.05). The variation in stomatal conductance (gs) was consistent with that of Pn and Tr (Figure 7c), indicating that the enhancement of Pn and Tr after CGP application was related to the degree of stomatal opening. However, with the increase in the amount of CGP applied, Pn, Tr, and gs did not continue to rise, suggesting that excessive addition of CGP was not beneficial to plant water metabolism. Additionally, there was no significant difference in water use efficiency (WUE) among different treatments (Figure 7d).
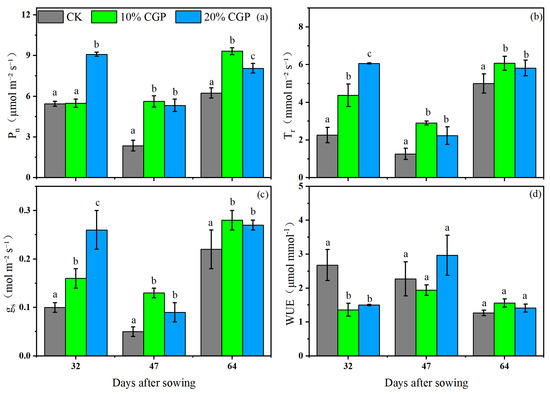
Figure 7.
Variation in gas exchange parameters of alfalfa leaves during the growth at different treatments, including net photosynthetic rate (a), transpiration rate (b), stomatal conductance (c), and water use efficiency (d). Different lowercase letters indicate a significant difference between means at p < 0.05.
The changes in rapid fluorescence kinetics monitoring of alfalfa leaves under different treatments are shown in Figure 8. The rapid fluorescence kinetics curves of alfalfa under the three treatments did not deform and exhibited a distinct O-J-I-P four-phase pattern. However, compared with the CK group, the relative fluorescence values of the J-I-P segments in the curves of the treatment groups with 10% and 20% CGP addition were higher (Figure 8a). Furthermore, JIP-test analysis was conducted on the rapid fluorescence kinetics curves of each group, and a series of fluorescence parameters reflecting the performance of PSII were calculated (Figure 8b). The values of light energy absorbed by the reaction center (ABS/RC), light energy captured by the reduced plastoquinone A (TR0/RC), energy captured by electron transfer (ET0/RC), and energy dissipated as heat (DI0/RC) did not vary with the treatments (p > 0.05), indicating no difference in the light energy absorption capacity of alfalfa PSII under CGP application. Additionally, in the electron transfer chain, there was no significant difference in the probability of leaf electrons transferring to the electron acceptors downstream of plastoquinone A (ET0/TR0) (p > 0.05). The quantum yield for electron transfer (ET0/ABS) and the maximum quantum efficiency of PSII (TR0/ABS) were at the same level, suggesting that the electron transfer process of PSII remained unchanged. The maximum photochemical efficiency FV/FM of leaves under different treatments was greater than 0.8. Nevertheless, the performance index (PI) of the 10% and 20% CGP treatments was higher than that of CK, implying better PSII activity, electron transfer status, and light energy utilization efficiency.
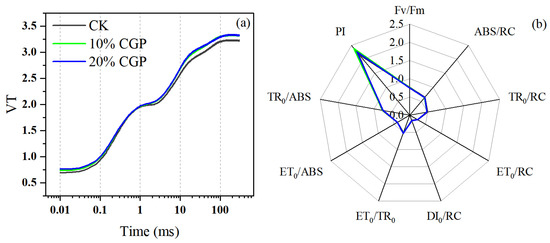
Figure 8.
Rapid fluorescence kinetics curves (a) and fluorescence parameters (b) at different treatments.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Applying CGP on Soil Hydraulic Properties
The poor soil hydraulic properties of aeolian sandy soil restrict the growth and restoration of vegetation, and improving these properties is crucial for controlling land desertification [3,28]. Our results indicate that with the increase in the application rate of CGP, the content of fine particles increases (Figure 1), the BD and Ks values decrease significantly (Figure 2 and Figure 3), the soil water-holding capacity is significantly enhanced (Figure 4), and the amount of plant-available water rises (Figure 5). The mineral composition of coal gangue mainly consists of quartz, clay minerals, and a certain amount of carbon, with clay minerals accounting for 50–70% [3,28]. Therefore, the utilization of CGP can directly increase the content of fine particles in the soil. Meanwhile, the addition of loose and porous materials can increase the extra pore volume and improve the soil pore structure [9,29]. As a result, the addition of CGP significantly reduced the soil bulk density (Figure 2). Soil texture and structure directly affect the soil’s hydraulic properties [30,31]. The increase in fine particles fills the soil’s pores to some extent, hindering the movement of soil water. At the same time, the increased attraction to water makes it less likely to be lost. Many studies have also confirmed that fine-particle additives can improve the soil’s hydraulic properties and effectively reduce deep percolation in sandy soils [32,33,34]. Therefore, CGP is expected to be a potential amendment for improving the hydraulic properties in arid sandy environments and helping plants resist water stress.
Feldspar sandstone, fly ash, and biochar exhibit comparable effects on soil properties to those of coal gangue. Among these soil additives, CGP demonstrates comparable efficacy. The peak particle-size distribution of feldspar sandstone amendment is about 20 μm [32], and that of fly-ash amendment is about 10 μm [35]. The peak particle-size distribution of biochar, which has attracted much attention in recent years, is about 5.4 μm [36]. The particle-size distribution of CGP is concentrated in the range of 2–10 μm (Figure 2), which is in the same order of magnitude as common soil additives currently used. The available water capacity (AWC) represents the amount of water available to plants, and changes in its value can directly reflect the effectiveness of soil amendments [34,37,38]. The addition of CGP significantly increased the AWC of the sandy soil in the study area. When the application rate of CGP was 20%, the AWC increased by 4 cm3 cm−3 (Figure 5). In contrast, in some studies on sandy soil improvement, the AWC increased by 1.3, 1.5, and 4 cm3 cm−3 for feldspar sandstone [32], attapulgite [26], and biochar [8], respectively. These findings indicate that CGP has a good effect on improving soil water availability. Therefore, we believe that the addition of CGP can provide plants with more available water resources while consuming a portion of coal gangue.
4.2. Effect of Applying CGP on Plant Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics
Our research results indicate that the addition of CGP effectively increases the emergence rate of plants (Figure 6) and enhances their photosynthetic capacity (Figure 7 and Figure 8). The soil water condition is an important factor restricting seed germination and plant growth [39,40]. Adequate soil water can promote seed emergence by facilitating seed coat softening, maintaining cell turgor pressure, and participating in the internal material transport of seeds [41,42]. After the seedlings emerge, sufficient soil water helps enhance the physiological metabolism of plants. By promoting the opening of stomata, carbon dioxide can enter the interior of leaves more smoothly, ensuring the supply of photosynthetic raw materials [43]. In addition, sufficient soil water enhances the activity of photosynthesis-related enzymes, thereby improving the photosynthetic efficiency of plants [44]. In our experiment, the addition of CGP enhanced the water retention capacity of the soil, increased the available water volume of plants, and thus improved the seed germination rate and the photosynthetic efficiency of plants.
In sandy soil areas, the soil has poor water retention capacity and is prone to soil erosion. Local plants are exposed to drought stress, which leads to a decrease in photosynthetic efficiency and a reduction in the synthesis of organic matter in their bodies, putting them at potential risk of death [45,46]. Therefore, we believe that adding CGP to the soil in these areas can effectively enhance the growth and metabolic capacity of vegetation, further improving their sustainability. However, we also found that excessive addition of CGP does not have a sustained promoting effect on plant growth (Figure 7 and Figure 8). This might be due to the fine particles of CGP. Excessive addition will reduce soil porosity and deteriorate its air permeability and water permeability. Plant roots require sufficient oxygen for respiration. Lack of oxygen can lead to poor root growth, affect the absorption of water and nutrients by the roots, and therefore inhibit the growth of the above-ground parts of the plant [47,48]. Overall, considering both expenses and benefits, we recommend adding 10% CGP to improve soil water conditions to promote plant growth and enhance plant photosynthetic capacity.
5. Conclusions
This study compared the effects of different application rates of CGP (10% and 20%) on soil hydraulic properties, plant growth, and photosynthetic characteristics. The application of CGP transformed the soil texture from sandy to loamy, significantly decreased soil bulk density and saturated hydraulic conductivity values, altered the soil water characteristic curve, enhanced soil water-holding capacity, and increased plant-available water. Compared with the original aeolian sandy soil group, the emergence rate of alfalfa seeds increased from approximately 50% to over 70% after CGP application. During the growth process, CGP application significantly elevated the net photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate, and stomatal conductance of alfalfa leaves. Rapid fluorescence kinetics monitoring of leaves revealed that alfalfa treated with CGP exhibited higher efficiency in light energy utilization. However, as the CGP application rate increased from 10% to 20%, the photosynthetic capacity of leaves did not improve, indicating that excessive CGP addition does not continuously promote plant gas exchange. Utilizing CGP as a soil amendment provides a promising approach for improving soil hydraulic properties, supporting plant growth, and facilitating the reuse of solid waste. Based on the above results, we recommend a 10% addition of coal gangue powder as the optimal amount for similar soils. Although large-scale application of CGP may incur high costs, these expenses are negligible when considering the substantial funds spent by coal mine-related enterprises on coal gangue disposal.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.L. and H.W.; methodology, X.D., Z.X., and H.W.; software, X.D. and R.H.; validation, X.D., J.N., and S.C.; formal analysis, X.D. and R.H.; investigation, S.C. and Z.X.; resources, S.C. and Z.X.; data curation, X.D.; writing—original draft preparation, X.D. and H.W.; writing—review and editing, H.W.; visualization, X.D.; supervision, M.L.; project administration, M.L.; funding acquisition, J.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Water Resource Protection and Utilization in Coal Mining, grant number GJNY-20-113-16.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the technical help from Jingjing Jin and Min Wang, Institute of Water-saving Agriculture in Arid Areas of China, Northwest A&F University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Yuen, D.; Xu, M. Effects of Near-Surface Complexities on Differential Travel Times and Amplitude Ratios Between PP and Its Precursors. JGR Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2019JB019139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Shangguan, Z. Stoichiometric Homeostasis in Response to Variable Water and Nutrient Supply in a Robinia Pseudoacacia Plant–Soil System. J. Plant Ecol. 2022, 15, 991–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Chen, G.; Meng, T.; Li, C.; Feng, H.; Si, B.; Siddique, K.H.M. Effect of Different Vegetation Restoration on Soil Properties in the Semi-Arid Loess Plateau of China. CATENA 2023, 220, 106630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, D.; Prajapat, G.; Goyal, S.; Agrawal, A. Modification of Desert Sand to Soil Using Polymers for Its Agricultural Potential. J. Arid Environ. 2023, 209, 104899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, Y.; Si, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Bai, Y.; et al. Optimizing Biochar Application to Improve Soil Physical and Hydraulic Properties in Saline-Alkali Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 144802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zhang, Z.; Su, R.; Dong, Z.; Zhen, Q.; Pang, J.; Lambers, H.; He, H.; Zhang, Z.; Su, R.; et al. Amending Aeolian Sandy Soil in the Mu Us Sandy Land of China with Pisha Sandstone and Increasing Phosphorus Supply Were More Effective than Increasing Water Supply for Improving Plant Growth and Phosphorus and Nitrogen Nutrition of Lucerne (Medicago Sativa). Crop Pasture Sci. 2020, 71, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Peng, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Fu, X.; Zhang, R.; Hu, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q. Advanced Coal Fly Ash Modification by Using Corrosive Microorganisms as Alternative Filler-Reinforcing Fluororubbers. Mater. Lett. 2019, 246, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Qiu, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Zang, F.; Zhao, C. The Role of Biochar Particle Size and Application Rate in Promoting the Hydraulic and Physical Properties of Sandy Desert Soil. CATENA 2021, 207, 105607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Miao, S.; Xue, B.; Jiang, Y.; Wei, C. Effect of Coal Gasification Fine Slag on the Physicochemical Properties of Soil. Water Air Soil Poll. 2019, 230, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamanaka, A.; Sasaoka, T.; Shimada, H.; Matsumoto, S. Amelioration of Acidic Soil Using Fly Ash for Mine Revegetation in Post-Mining Land. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2022, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J. Comprehensive Utilization and Environmental Risks of Coal Gangue: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 117946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholod, N.; Evans, M.; Pilcher, R.C.; Roshchanka, V.; Ruiz, F.; Coté, M.; Collings, R. Global Methane Emissions from Coal Mining to Continue Growing Even with Declining Coal Production. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, B.; Zhao, Z.; Deng, X.; Fang, C.; Dong, B.; Zhang, B. Sustainable and Clean Utilization of Coal Gangue: Activation and Preparation of Silicon Fertilizer. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2022, 24, 1579–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Z. Recycling Utilization Patterns of Coal Mining Waste in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motesharezadeh, B.; Ahmadiyan, E.; Alikhani, H.A.; Azarnivand, H. The Use of Coal Gangue as a Cultivation Bed Conditioner in Forage Maize Inoculated with Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2017, 48, 1266–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Lu, Y.; Bai, L.; Niu, J.; Chen, S.; Mojid, M.A.; Yang, Y.; Li, M. Water Uptake Characteristics of Stipa Bungeana Trin: Affected by Subsidence in the Coal Mining Areas of Northwest China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Li, T.; Xiang, M.; He, W.; Wu, B.; Peng, J.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Zheng, M.; Chen, J.; et al. Effect of Coal Mining on Springs in the Yushenfu Mining Area of China. Geofluids 2018, 2018, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, W.; Qiao, W.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z. Effect of Natural Conditions and Mining Activities on Vegetation Variations in Arid and Semiarid Mining Regions. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 103, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Fang, Z.; Zhao, B.; Tao, Y.; Liu, L.; Sun, W.; Sun, J. Study on Rheological and Mechanical Properties of Aeolian Sand-Fly Ash-Based Filling Slurry. Energies 2020, 13, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Mu, X.; Li, K.; Shao, H. Soil Characterization and Differential Patterns of Heavy Metal Accumulation in Woody Plants Grown in Coal Gangue Wastelands in Shaanxi, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 13489–13497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Guan, X. Effect and Mechanism of Coal Gangue Concrete Modification by Fly Ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 294, 123563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoozegar, A. Examination of Models for Determining Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity by the Constant Head Well Permeameter Method. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 200, 104572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Canqui, H.; Ruis, S.J. Cover Crop Impacts on Soil Physical Properties: A Review. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 1527–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libohova, Z.; Schoeneberger, P.; Bowling, L.C.; Owens, P.R.; Wysocki, D.; Wills, S.; Williams, C.O.; Seybold, C. Soil Systems for Upscaling Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity for Hydrological Modeling in the Critical Zone. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Genuchten, M.T. A Closed-Form Equation for Predicting the Hydraulic Conductivity of Unsaturated Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Xing, X.; Gao, Y.; Ma, X. An Environmentally Friendly Soil Amendment for Enhancing Soil Water Availability in Drought-Prone Soils. Agronomy 2022, 12, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangiabadi, M.; Gorji, M.; Shorafa, M.; Khavari Khorasani, S.; Saadat, S. Effect of Soil Pore Size Distribution on Plant-Available Water and Least Limiting Water Range as Soil Physical Quality Indicators. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Qin, Q.; Wang, H. The Effects of Land Subsidence and Rehabilitation on Soil Hydraulic Properties in a Mining Area in the Loess Plateau of China. CATENA 2017, 159, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xu, L.; Yang, H.; Ma, X. Effects of Biochar Addition or Grass Planting on Infiltrations into a Sandy Soil in the Loess Plateau in China. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 2024, 49, 3789–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Ren, L. Estimation of Effective Hydraulic Parameters in Heterogeneous Soils at Field Scale. Geoderma 2016, 264, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, P.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Lu, B.; Chen, W.; Wu, Y.; Li, G.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, G.; et al. Soil Texture Is an Important Factor Determining How Microplastics Affect Soil Hydraulic Characteristics. Environ. Int. 2022, 165, 107293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Han, J. Improving Water Retention Capacity of an Aeolian Sandy Soil with Feldspathic Sandstone. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belviso, C.; Satriani, A.; Lovelli, S.; Comegna, A.; Coppola, A.; Dragonetti, G.; Cavalcante, F.; Rivelli, A.R. Impact of Zeolite from Coal Fly Ash on Soil Hydrophysical Properties and Plant Growth. Agriculture 2022, 12, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarebanadkouki, M.; Hosseini, B.; Gerke, H.H.; Schaller, J. Amorphous Silica Amendment to Improve Sandy Soils’ Hydraulic Properties for Sustained Plant Root Access under Drying Conditions. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 935012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asante, B.; Schmidt, G.; Teixeira, R.; Krause, A.; Savastano Junior, H. Influence of Wood Pretreatment and Fly Ash Particle Size on the Performance of Geopolymer Wood Composite. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 2021, 79, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleszczuk, P.; Ćwikła-Bundyra, W.; Bogusz, A.; Skwarek, E.; Ok, Y.S. Characterization of Nanoparticles of Biochars from Different Biomass. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 121, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Yang, Y.; An, S.; Zhu, Z. Effects of Different Vegetation Restoration Measures on Soil Aggregate Stability and Erodibility on the Loess Plateau, China. CATENA 2020, 185, 104294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, R.; Plaza-Bonilla, D.; Cantero-Martínez, C.; Wendroth, O.; Lampurlanés, J. Soil Hydraulic Properties and Pore Dynamics under Different Tillage and Irrigated Crop Sequences. Geoderma 2023, 430, 116293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Huo, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Li, M.; Xu, B. Effects of Nitrogen Addition and Watering on Soil Seed Bank Germination in a Semiarid Grassland on the Loess Plateau of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Lu, Y.; Guo, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Qin, D.; Huo, J. Effects of Drought Stress on Photosynthesis and Chlorophyll Fluorescence in Blue Honeysuckle. Plants 2024, 13, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, T.C.; Deckard, E.L.; Goos, R.J.; Enz, J.W. Soil Moisture, Temperature, and Drying Influence on Soybean Emergence. Agron. J. 1996, 88, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, N.M.; Palta, J.A.; Berger, J.D.; Siddique, K.H.M. Sowing Soil Water Content Effects on Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): Seedling Emergence and Early Growth Interaction with Genotype and Seed Size. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1732–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoffoni, C.; Chatelet, D.S.; Pasquet-kok, J.; Rawls, M.; Donoghue, M.J.; Edwards, E.J.; Sack, L. Hydraulic Basis for the Evolution of Photosynthetic Productivity. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 16072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Hui, W.; Zhao, F.; Wang, P.; Su, C.; Gong, W. Physiology of Plant Responses to Water Stress and Related Genes: A Review. Forests 2022, 13, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zait, Y.; Shemer, O.E.; Cochavi, A. Dynamic Responses of Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters to Drought across Diverse Plant Families. Physiol. Plant. 2024, 176, e14527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, T.; Fang, L.; Peng, X.; Liu, F. CO2 Elevation Modulates the Response of Leaf Gas Exchange to Progressive Soil Drying in Tomato Plants. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 268, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelaar, W.; Vanbruggen, M.; Vandenhoek, W.; Huyser, M.; Blom, C. Root Porosities and Radial Oxygen Losses of Rumex and Plantago Species as Influenced by Soil Pore Diameter and Soil Aeration. New Phytol. 1993, 125, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wong, M.H. Effects of Air-Filled Soil Porosity and Aeration on the Initiation and Growth of Secondary Roots of Maize (Zea Mays). Plant Soil 1996, 186, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).