Comprehensive Genome-Wide Characterization of the GRAS Gene Family and Their Role in Salt Stress Tolerance in Punica granatum L.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genome-Wide Identification of GRAS in Pomegranate
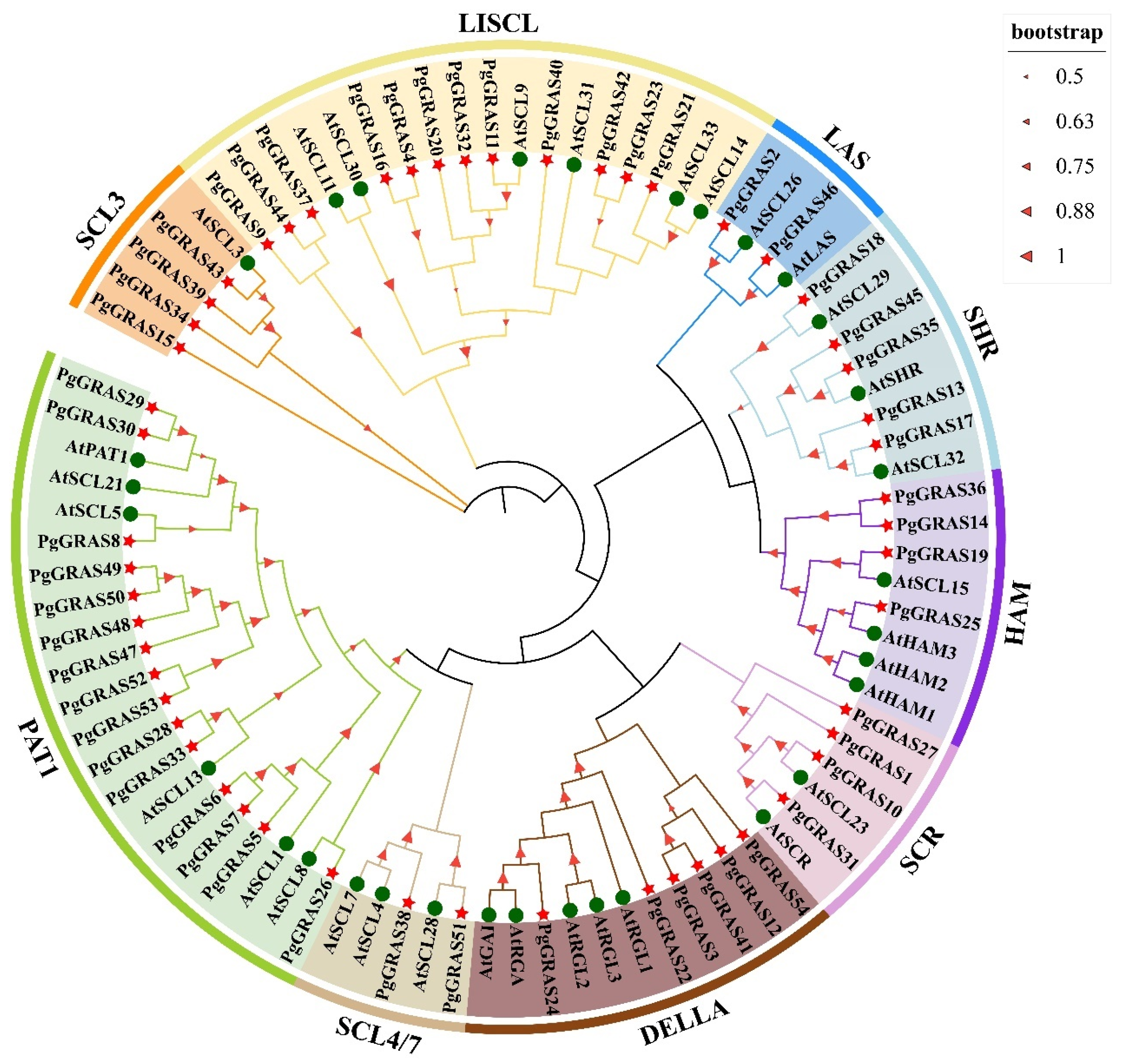
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of PgGRAS Gene Family Members
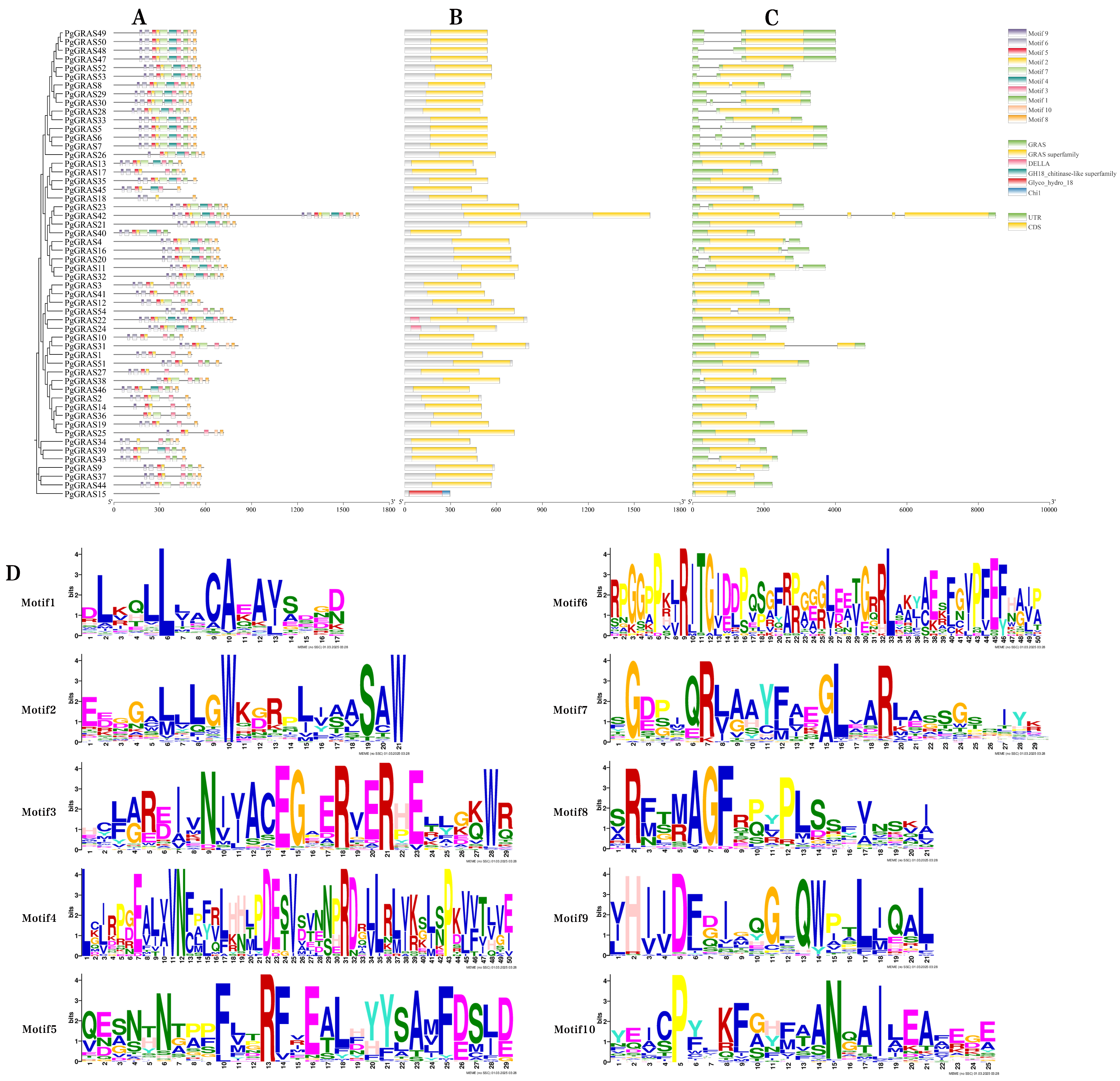
2.3. Conserved Motifs, Structural Domains, and Gene Structure Analysis of PgGRAS
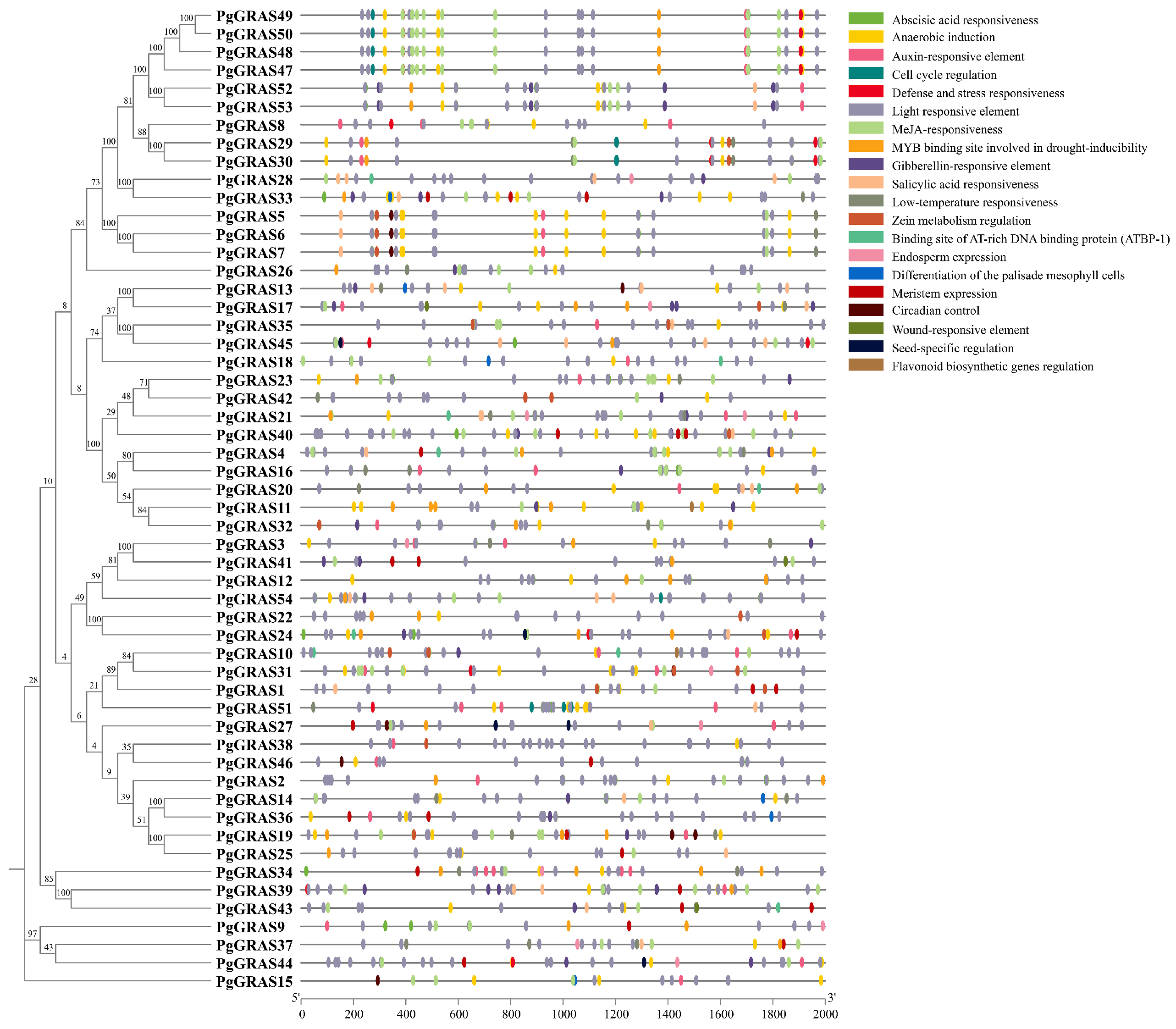
2.4. Cis-Regulatory Elements Analysis of the PgGRAS Promoter
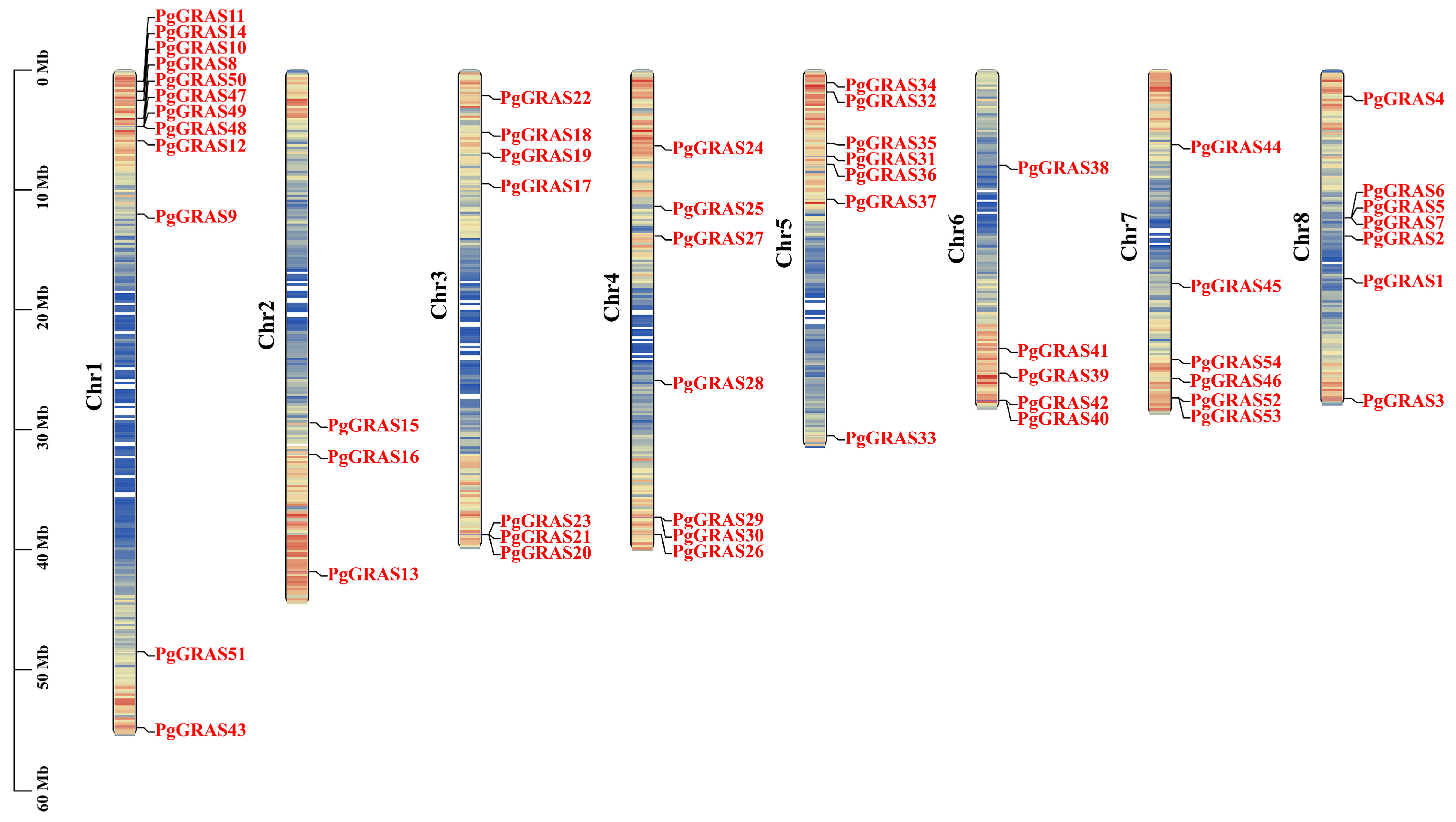
2.5. PgGRAS Chromosome Distribution and Collinearity Analysis
2.6. Plant Materials and Salt Stress Treatment
2.7. Cloning of Target Genes and Construction of Expression Vectors
2.8. qRT-PCR Analysis
2.9. Stable Genetic Transformation in Arabidopsis thaliana
2.10. Physiological Measurements of Transgenic Arabidopsis Under Salt Stress
2.11. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Sequence Analysis of Pomegranate GRAS Gene Family
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Pomegranate GRAS Gene Family
3.3. Conserved Motif and Gene Structure Analysis of PgGRAS Proteins
3.4. Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements in PgGRAS Promoters
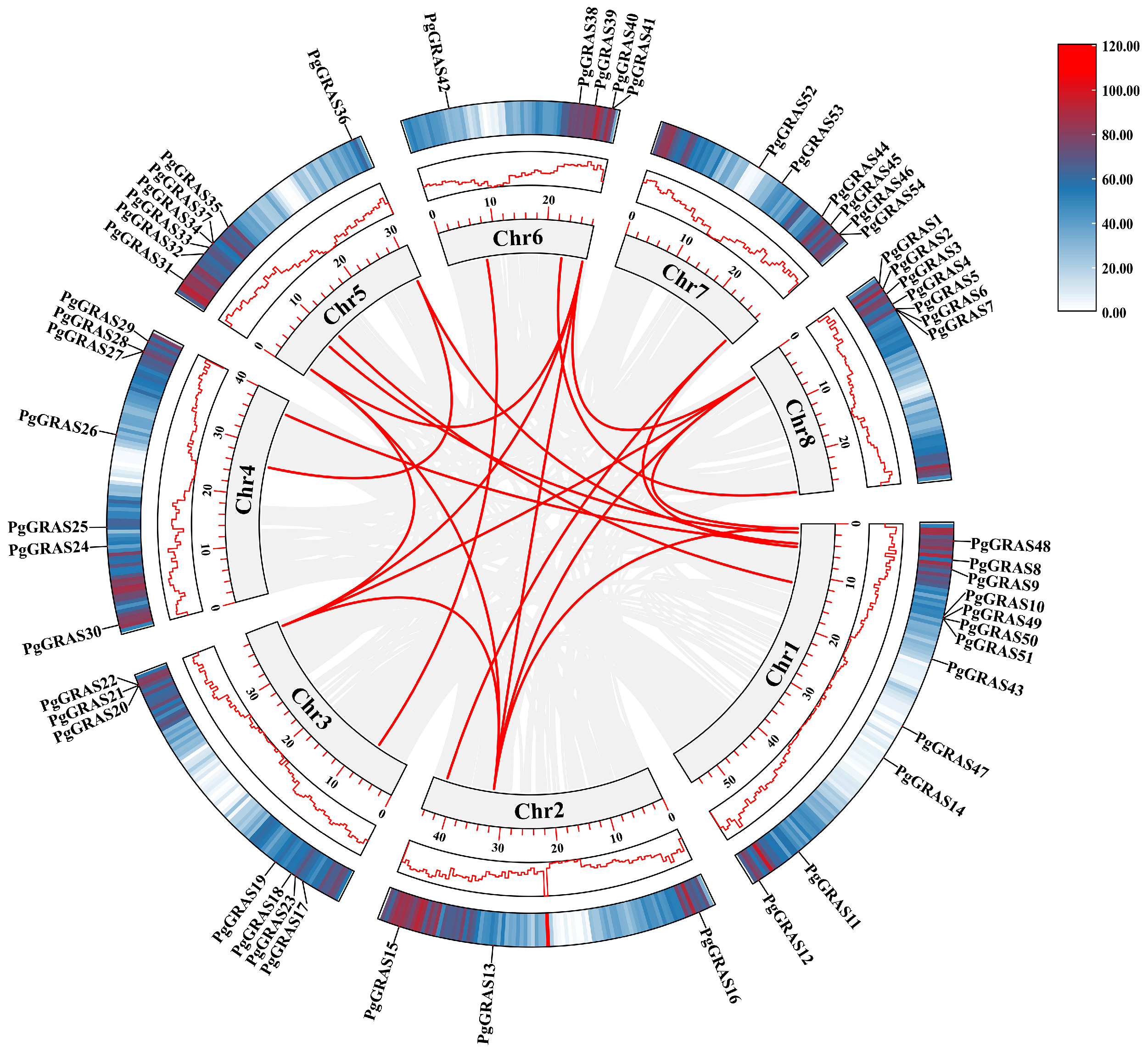
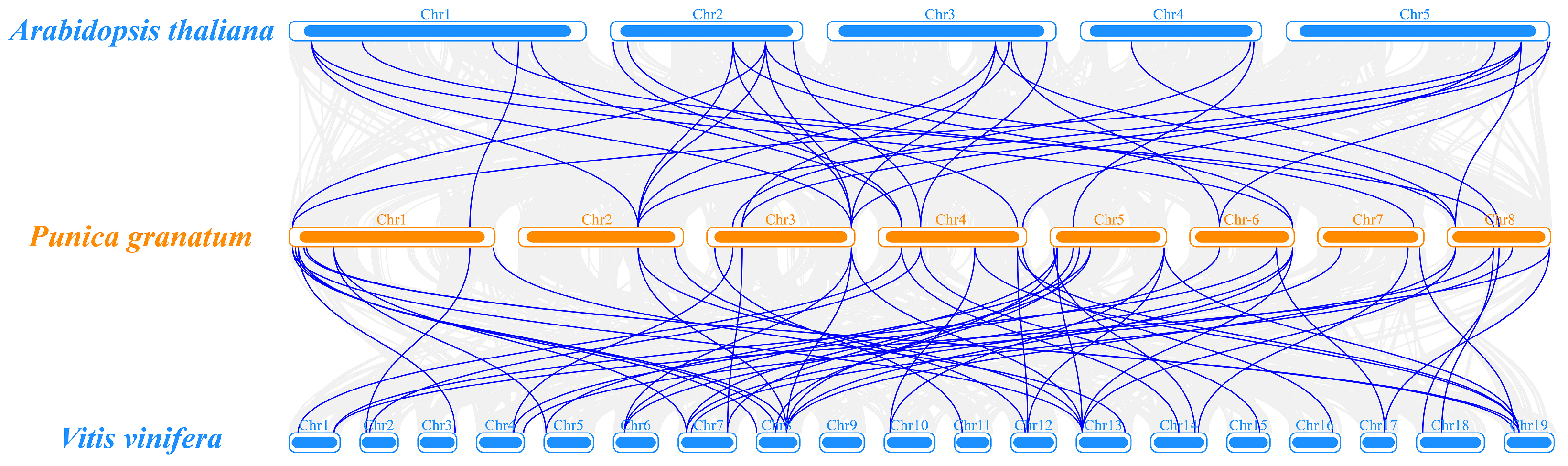
3.5. Chromosomal Localization and Collinearity Analysis of PgGRAS Genes
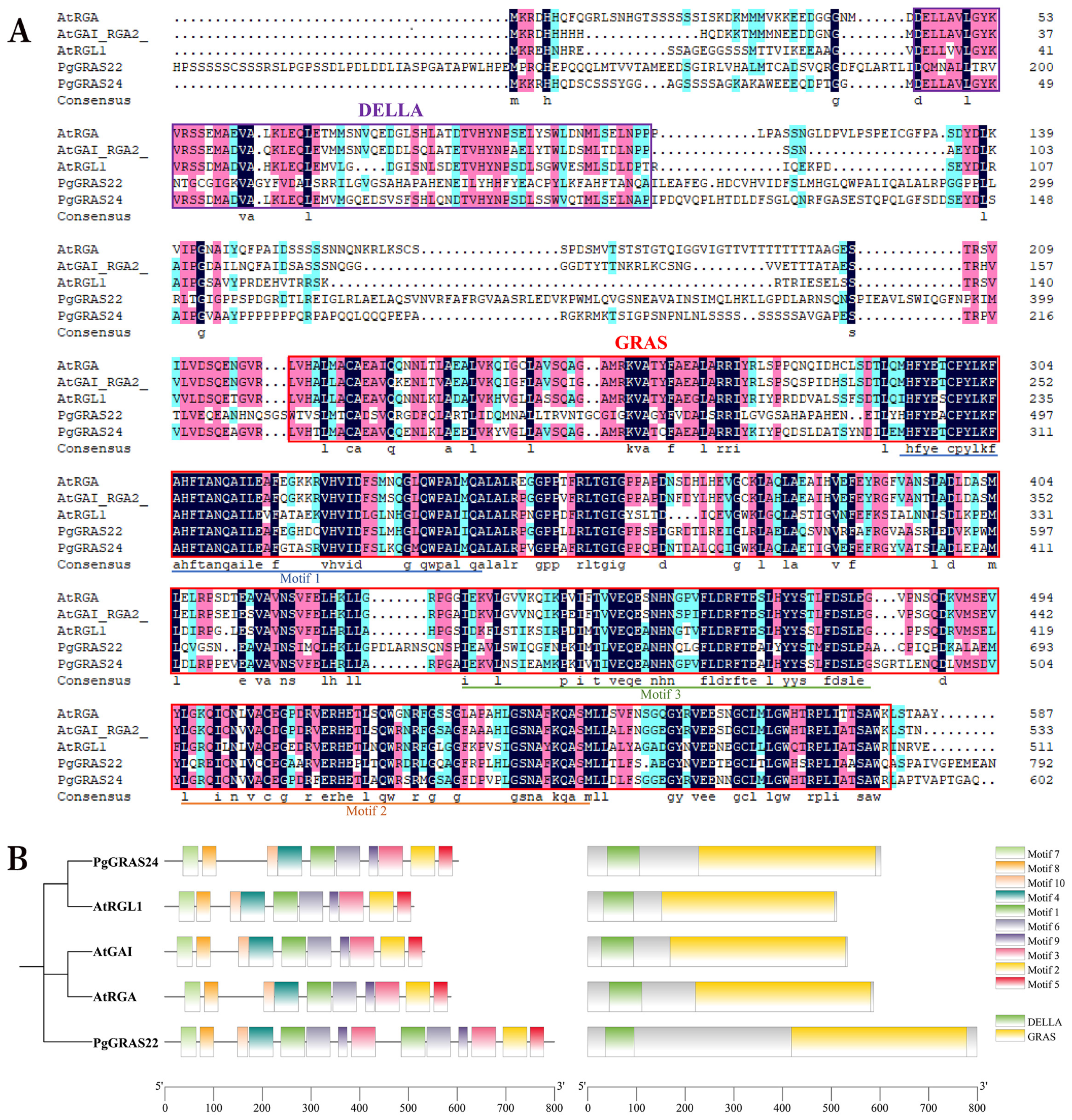
3.6. Sequence Comparison, Conserved Motifs, and Structural Domains of Pomegranate DELLA Proteins
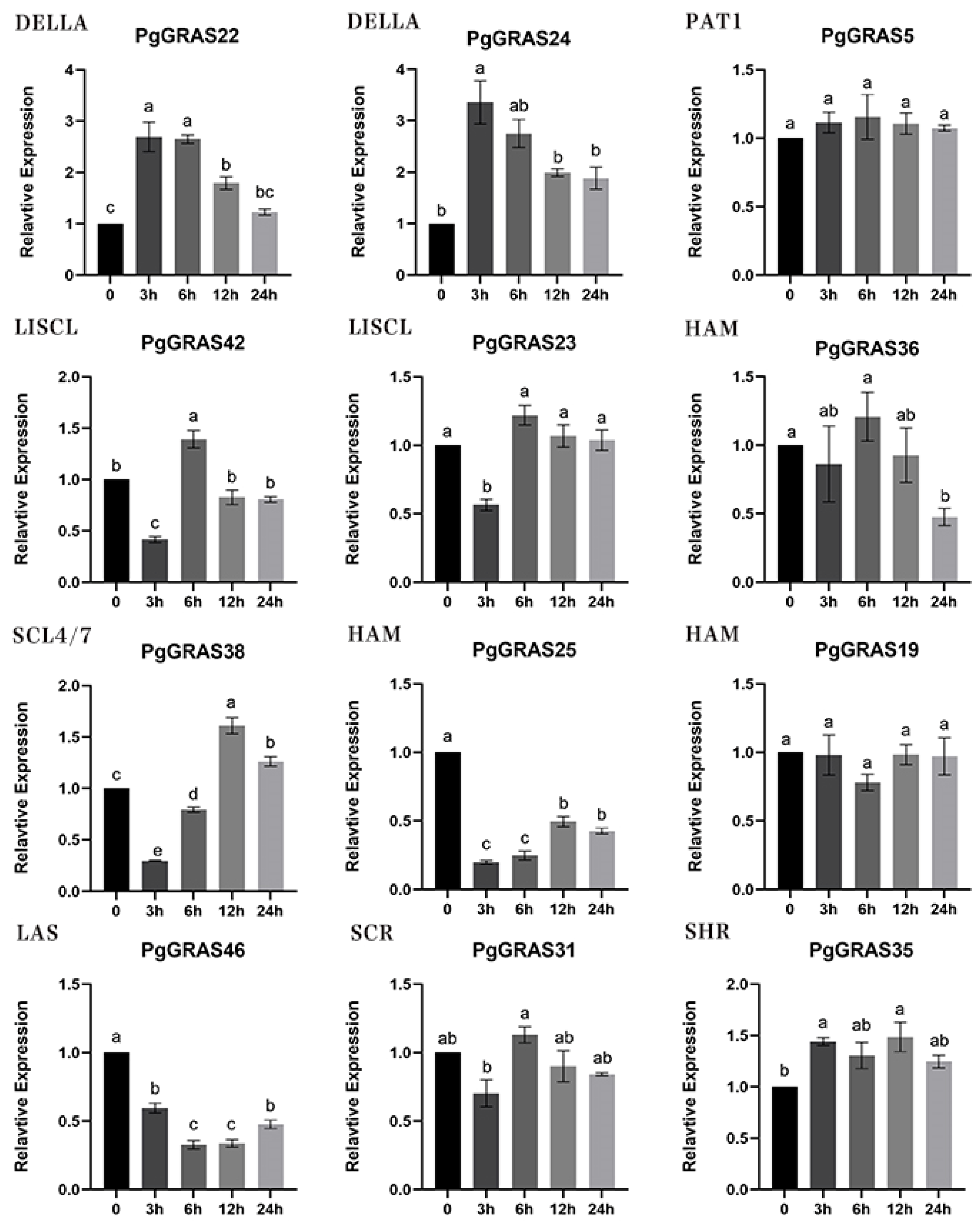
3.7. Expression Pattern Analysis of PgGRAS Under Saline Stress in Pomegranate
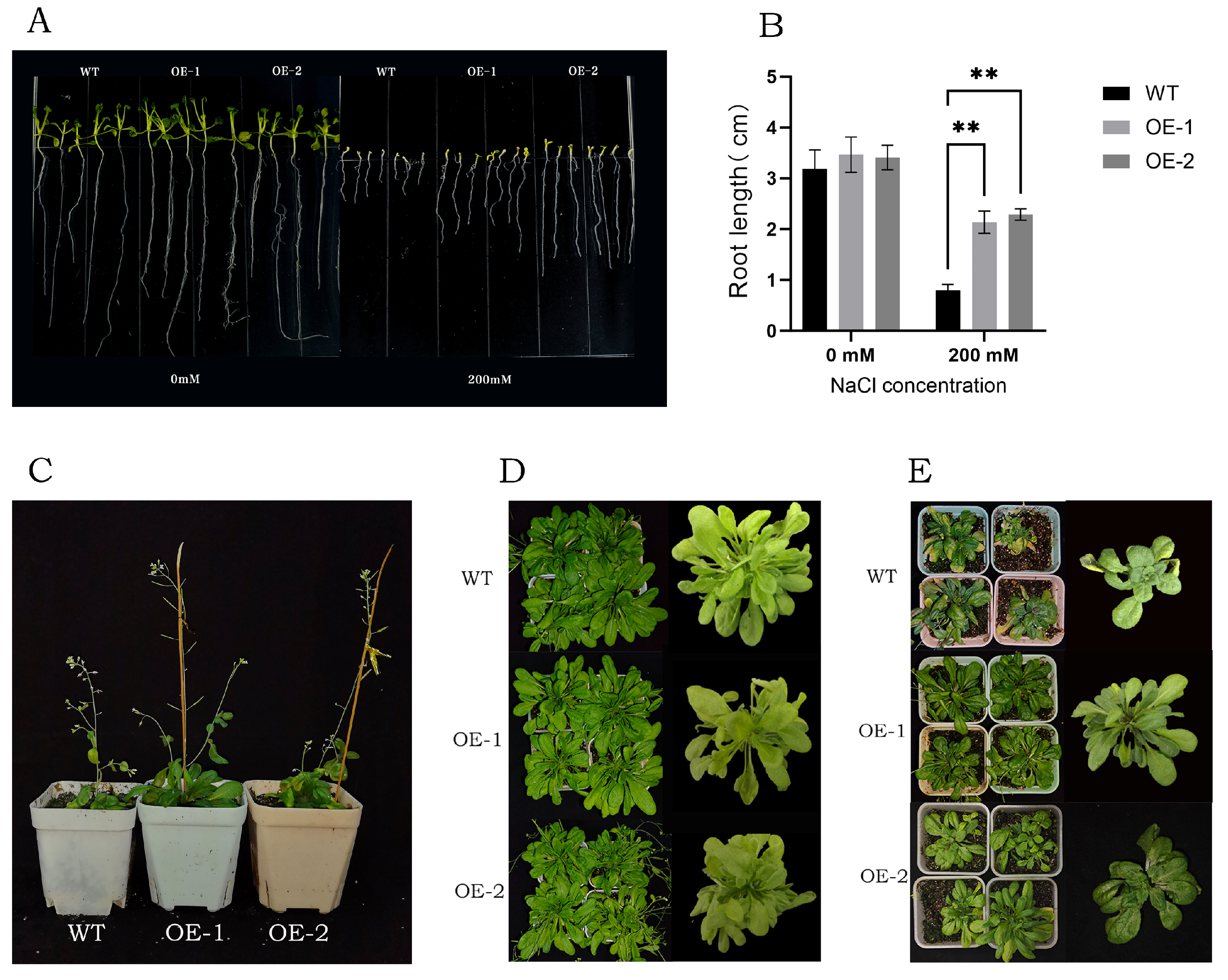
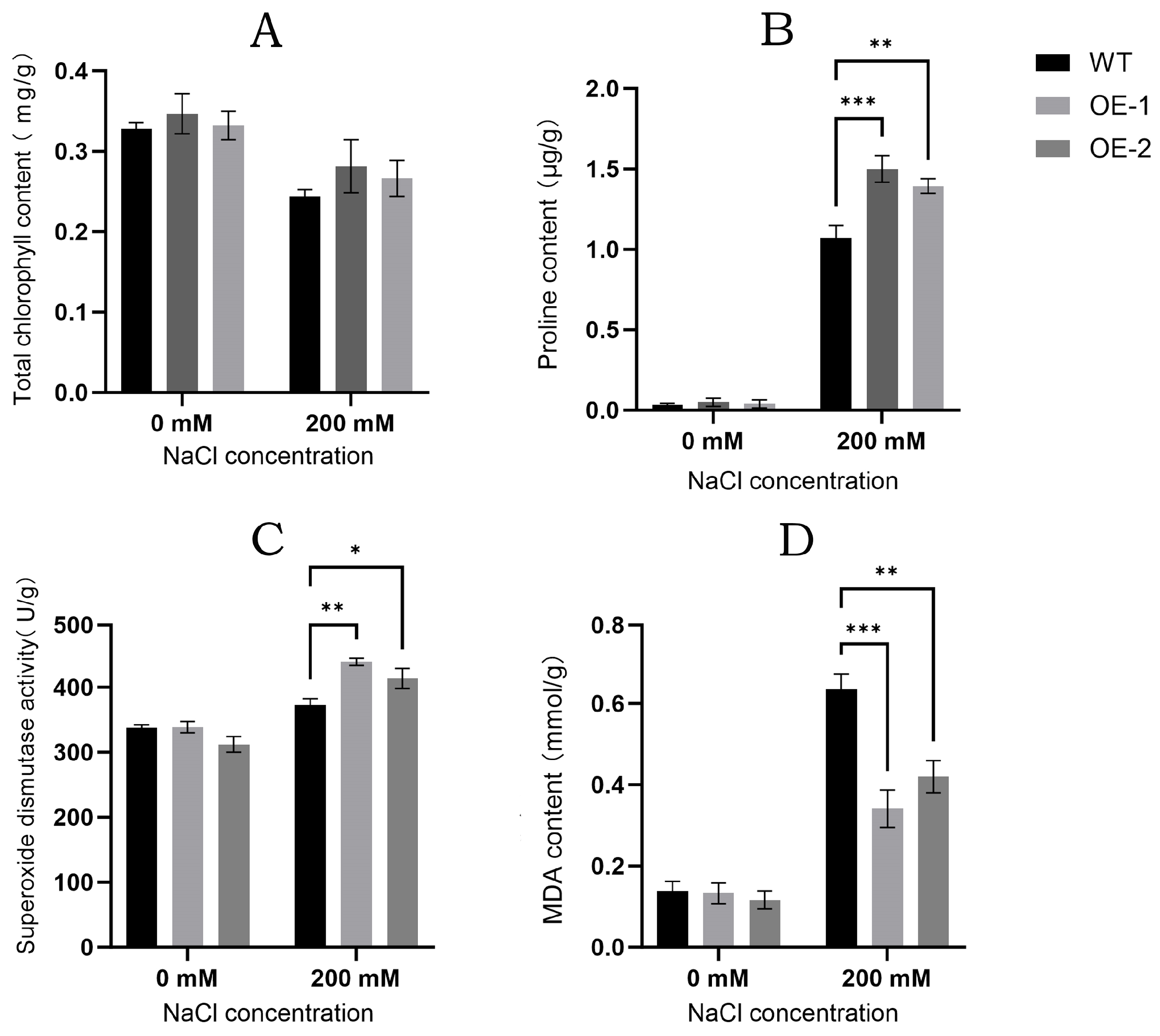
3.8. Salt Tolerance Analysis of Transgenic Arabidopsis
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, X.; Xue, B.; Jones, W.T.; Rikkerink, E.; Dunker, A.K.; Uversky, V.N. A Functionally Required Unfoldome from the Plant Kingdom: Intrinsically Disordered N-Terminal Domains of GRAS Proteins Are Involved in Molecular Recognition during Plant Development. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 77, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Liu, Z.-W.; Wu, Z.-J.; Li, H.; Wang, W.-L.; Cui, X.; Zhuang, J. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of GRAS Family Transcription Factors in Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho-Plágaro, T.; Molinero-Rosales, N.; Fariña Flores, D.; Villena Díaz, M.; García-Garrido, J.M. Identification and Expression Analysis of GRAS Transcription Factor Genes Involved in the Control of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Development in Tomato. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Carol, P.; Richards, D.E.; King, K.E.; Cowling, R.J.; Murphy, G.P.; Harberd, N.P. The Arabidopsis GAI Gene Defines a Signaling Pathway That Negatively Regulates Gibberellin Responses. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 3194–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Laurenzio, L.; Wysocka-Diller, J.; Malamy, J.E.; Pysh, L.; Helariutta, Y.; Freshour, G.; Hahn, M.G.; Feldmann, K.A.; Benfey, P.N. The SCARECROW Gene Regulates an Asymmetric Cell Division That Is Essential for Generating the Radial Organization of the Arabidopsis Root. Cell 1996, 86, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolle, C. The Role of GRAS Proteins in Plant Signal Transduction and Development. Planta 2004, 218, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Widmer, A. Genome-Wide Comparative Analysis of the GRAS Gene Family in Populus, Arabidopsis and Rice. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 32, 1129–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, M.; Nkurikiyimfura, O.; Niyitanga, S.; Jakada, B.H.; Shaheen, I.; Aslam, M.M. GRAS Transcription Factors Emerging Regulator in Plants Growth, Development, and Multiple Stresses. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 9673–9685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, J.; Tang, X. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of GRAS Transcription Factors in Sacred Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera). PeerJ 2016, 4, e2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pysh, L.D.; Wysocka-Diller, J.W.; Camilleri, C.; Bouchez, D.; Benfey, P.N. The GRAS Gene Family in Arabidopsis: Sequence Characterization and Basic Expression Analysis of the SCARECROW-LIKE Genes. Plant J. 1999, 18, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Meng, J.; Wang, C.; Du, J.; Guo, Y. Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the GRAS Transcription Factor Gene Family in Theobroma cacao. Genes 2022, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Anwar, A.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; He, L.; Wang, F.; Gao, J. The Fundamental Role of DELLA Protein and Regulatory Mechanism during Plant Growth and Development. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2021, 49, 12561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Galea, P.; Hirtreiter, B.; Bolle, C. Two GRAS Proteins, SCARECROW-LIKE21 and PHYTOCHROME A SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION1, Function Cooperatively in Phytochrome a Signal Transduction. Plant Physiol. 2012, 161, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M. DELLA and SCL3 Balance Gibberellin Feedback Regulation by Utilizing INDETERMINATE DOMAIN Proteins as Transcriptional Scaffolds. Plant Signal. Behav. 2014, 9, e29726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z.E.; Chen, E.Y.; Zhang, C.J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, F.G. Genome-Wide Analysis of GRAS Transcription Factor Gene Family in Gossypium hirsutum L. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, N.M.; Hinde, E.; Winter, C.M.; Fisher, A.P.; Crosti, G.; Blilou, I.; Gratton, E.; Benfey, P.N.; Sozzani, R. Tracking Transcription Factor Mobility and Interaction in Arabidopsis Roots with Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy. eLife 2016, 5, e14770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, J.; Kim, B.; Yoon, E.K.; Jang, S.; Kim, G.; Dhar, S.; Lee, S.A.; Lim, J. Characterization of the GRAS Transcription Factor SCARECROW-LIKE 28’s Role in Arabidopsis Root Growth. J. Plant Biol. 2017, 60, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, M.; Saha, A.; Moin, M.; Kirti, P.B. Genome-Wide Identification, Transcript Profiling and Bioinformatic Analyses of GRAS Transcription Factor Genes in Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 777285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Abiotic Stress Responsive GRAS Family Genes in Oat (Avena sativa). PeerJ 2023, 11, e15370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Z.; Luo, X.; Wu, M.; Wei, L.; Fan, Z.; Zhu, Y. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression of GRAS Gene Family Members in Cassava. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, H.; Yang, L. Genome-Wide Characterization of DELLA Gene Family in Blueberry (Vaccinium darrowii) and Their Expression Profiles in Development and Response to Abiotic Stress. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.-S.; Liang, D.; Shuai, P.; Xia, X.-L.; Yin, W.-L. The Salt- and Drought-Inducible Poplar GRAS Protein SCL7 Confers Salt and Drought Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 4011–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Huang, R.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Ji, X. Genome-Wide Identification, Expression and Salt Stress Tolerance Analysis of the GRAS Transcription Factor Family in Betula platyphylla. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1022076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Xu, C.; Ming, R.; Tang, H.; Guyot, R.; Kramer, E.M.; Hu, Y.; Yi, X.; Qi, Y.; Xu, X.; et al. The Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) Genome and the Genomics of Punicalagin Biosynthesis. Plant J. 2017, 91, 1108–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.; Yaich, H.; Cheikhrouhou, S.; Khemakhem, I.; Bouaziz, M.; Attia, H.; Ayadi, M.A. Antioxidant Properties and Phenolic Profile Characterization by LC–MS/MS of Selected Tunisian Pomegranate Peels. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 2890–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, A.; Barbarossa, A.; Tassone, A.; Ceramella, J.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A.; Basile, G.; Fazio, A.; Iacopetta, D.; Franchini, C.; et al. Pomegranate: Nutraceutical with Promising Benefits on Human Health. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, X.; Yan, J.; Yuan, Z.; Gu, M. Effects of Salt Stress on Growth, Photosynthesis, and Mineral Nutrients of 18 Pomegranate (Punica granatum) Cultivars. Agronomy 2020, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Clements, J.; Eddy, S.R. HMMER Web Server: Interactive Sequence Similarity Searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W29–W37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X Version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Nei, M.; Dudley, J.; Tamura, K. MEGA: A Biologist-Centric Software for Evolutionary Analysis of DNA and Protein Sequences. Brief. Bioinform. 2008, 9, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v5: An Online Tool for Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME Suite: Tools for Motif Discovery and Searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An Upgraded Gene Feature Visualization Server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombauts, S.; Déhais, P.; Van Montagu, M.; Rouzé, P. PlantCARE, a Plant Cis-Acting Regulatory Element Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 295–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; DeBarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A Toolkit for Detection and Evolutionary Analysis of Gene Synteny and Collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Urano, D.; Liao, K.-L.; Hedrick, T.L.; Gao, Y.; Jones, A.M. A Nondestructive Method to Estimate the Chlorophyll Content of Arabidopsis Seedlings. Plant Methods 2017, 13, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabnam, N.; Tripathi, I.; Sharmila, P.; Pardha-Saradhi, P. A Rapid, Ideal, and Eco-Friendlier Protocol for Quantifying Proline. Protoplasma 2016, 253, 1577–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leon, J.A.D.; Borges, C.R. Evaluation of Oxidative Stress in Biological Samples Using the Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances Assay. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2020, 159, e61122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.G.; Wan, P.; Sun, S.H.; Li, J.Y.; Chen, M.S. Genome-Wide Analysis of the GRAS Gene Family in Rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2004, 54, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Zhao, X.; Duan, X.; An, Y.; Lv, W.; An, H. Identification and Expression of GRAS Family Genes in Maize (Zea mays L.). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.-T.; Yu, T.-F.; Fu, J.-D.; Su, H.-G.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.-B.; Chen, M.; Guo, J.; Ma, Y.-Z.; Wei, W.-L.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of the GRAS Gene Family and Functional Identification of GmGRAS37 in Drought and Salt Tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 604690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, C.; Mu, Q.; Wu, W.; Wang, B.; Fang, J. A Characterization of Grapevine of GRAS Domain Transcription Factor Gene Family. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2016, 16, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Yin, T.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X.; Wu, J.; Cai, H.; Yang, N.; Li, X.; Wen, K.; Chen, D.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Pattern Analysis of the Kiwifruit GRAS Transcription Factor Family in Response to Salt Stress. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Xian, Z.; Kang, X.; Tang, N.; Li, Z. Genome-Wide Identification, Phylogeny and Expression Analysis of GRAS Gene Family in Tomato. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Dong, S.; Liu, X.; Bo, K.; Miao, H.; Beckles, D.M.; Zhang, S.; Gu, X. Genome-Wide Characterization of Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) GRAS Genes and Their Response to Various Abiotic Stresses. Horticulturae 2020, 6, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Jin, M.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Guo, R.; Luo, H.; Guo, T.; Xu, J. Genome-Wide Identification of GRAS Gene Family in Cunninghamia lanceolata and Expression Pattern Analysis of ClDELLA Protein Under Abiotic Stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhu, K.; Cheng, Z.-M. Evolution and Functional Analysis of the GRAS Family Genes in Six Rosaceae Species. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Xu, J.; Li, G.; Zhong, T.; Chen, D.; Lv, J. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of GRAS Gene Family in Eucalyptus grandis. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Chen, X.; Hao, Z.; Lu, L.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Shi, J.; Chen, J. Genome-Wide Analysis of the GRAS Gene Family in Liriodendron chinense Reveals the Putative Function in Abiotic Stress and Plant Development. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1211853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Xu, Y.; He, G.; He, K.; Xiao, L.; Hu, R.; Li, S. Genome-Wide Characterization and Expression Profiling of the GRAS Gene Family in Salt and Alkali Stresses in Miscanthus sinensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wu, S.; Hua, J.; Liu, L.; Yin, Y.; Li, H.; Gu, C. Genome-Wide Study of the GRAS Gene Family in Hibiscus hamabo Sieb. et Zucc and Analysis of HhGRAS14-Induced Drought and Salt Stress Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 2022, 319, 111260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, L.; Yan, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, B.; Ma, X. Cloning and Characterization of an ABA-Independent DREB Transcription Factor Gene, HcDREB2, in Hemarthria compressa. Hereditas 2016, 153, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Fan, D.; Lan, S.; Cheng, S.; Chen, S.; Lin, Y.; Cao, S. Genome-Wide Identification, Expression and Stress Analysis of the GRAS Gene Family in Phoebe bournei. Plants 2023, 12, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arain, S.; Meer, M.; Sajjad, M.; Yasmin, H. Light Contributes to Salt Resistance through GAI Protein Regulation in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 159, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Chen, S.; Li, T.; Ma, X.; Liang, X.; Ding, X.; Liu, H.; Luo, L. OsGRAS23, a Rice GRAS Transcription Factor Gene, Is Involved in Drought Stress Response through Regulating Expression of Stress-Responsive Genes. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Xu, X.; Li, J. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of GRAS Transcription Factors in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). PeerJ 2017, 5, e3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achard, P.; Cheng, H.; Grauwe, L.D.; Decat, J.; Schoutteten, H.; Moritz, T.; Straeten, D.V.D.; Peng, J.; Harberd, N.P. Integration of Plant Responses to Environmentally Activated Phytohormonal Signals. Science 2006, 311, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Gong, Y.; Chen, S.; Ma, C.; Duanmu, H. Genome-Wide Identification of GRAS Transcription Factors and Their Functional Analysis in Salt Stress Response in Sugar Beet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T. The Molecular Mechanism and Evolution of the GA–GID1–DELLA Signaling Module in Plants. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, R338–R345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Tu, Q.; Lyu, X.; Cheng, Q.; Ji, R.; Qin, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Li, H.; Zhao, T. GmSTF Accumulation Mediated by DELLA Protein GmRGAs Contributes to Coordinating Light and Gibberellin Signaling to Reduce Plant Height in Soybean. Crop J. 2024, 12, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Jones, W.T.; Harvey, D.; Edwards, P.J.B.; Pascal, S.M.; Kirk, C.; Considine, T.; Sheerin, D.J.; Rakonjac, J.; Oldfield, C.J.; et al. N-Terminal Domains of DELLA Proteins Are Intrinsically Unstructured in the Absence of Interaction with GID1/Gibberellic Acid Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 11557–11571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganie, S.A.; Molla, K.A.; Henry, R.J.; Bhat, K.V.; Mondal, T.K. Advances in Understanding Salt Tolerance in Rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Xu, N.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Yan, F.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, Q. Identification and Expression Pattern Analysis of BpGRAS Gene Family in Bergenia purpurascens and Functional Characterization of BpGRAS9 in Salt Tolerance. Plant Mol. Biol. 2025, 115, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene ID | Gene Name | mRNA Sequence ID | Protein Sequence ID | Length (aa) | kDa | pI | Instability Index | Aliphatic Index | GRAVY | Subcellular Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 116187514 | PgGRAS1 | XM_031516257.1 | XP_031372117.1 | 510 | 56.79 | 5.95 | 43.05 | 87.82 | −0.244 | Cytoplasmic |
| 116187891 | PgGRAS2 | XM_031516894.1 | XP_031372754.1 | 500 | 54.61 | 5.53 | 36.12 | 81.98 | −0.159 | Cytoplasmic |
| 116188025 | PgGRAS3 | XM_031517128.1 | XP_031372988.1 | 498 | 55.94 | 6.51 | 57.13 | 96.71 | −0.071 | Cytoplasmic |
| 116188061 | PgGRAS4 | XM_031517177.1 | XP_031373037.1 | 683 | 76.63 | 7.58 | 45.58 | 77.82 | −0.445 | Nuclear |
| 116188620 | PgGRAS5 | XM_031518092.1 | XP_031373952.1 | 541 | 60.94 | 4.99 | 50.35 | 82.01 | −0.389 | Nuclear |
| 116188711 | PgGRAS6 | XM_031518093.1 | XP_031373953.1 | 541 | 60.94 | 4.99 | 50.35 | 82.01 | −0.389 | Nuclear |
| 116189521 | PgGRAS7 | XM_031518094.1 | XP_031373954.1 | 541 | 60.94 | 4.99 | 50.35 | 82.01 | −0.389 | Nuclear |
| 116190128 | PgGRAS8 | XM_031519789.1 | XP_031375649.1 | 524 | 58.39 | 5.93 | 47.7 | 85.04 | −0.223 | Chloroplast |
| 116192510 | PgGRAS9 | XM_031521068.1 | XP_031376928.1 | 587 | 67.24 | 5.21 | 46.1 | 88.82 | −0.376 | peroxidase |
| 116192682 | PgGRAS10 | XM_031521295.1 | XP_031377155.1 | 454 | 48.87 | 5.07 | 54.65 | 88.57 | −0.147 | Chloroplast |
| 116192866 | PgGRAS11 | XM_031521552.1 | XP_031377412.1 | 743 | 83.75 | 6.48 | 42.64 | 78.12 | −0.445 | Chloroplast |
| 116193265 | PgGRAS12 | XM_031522080.1 | XP_031377940.1 | 582 | 64.52 | 5.06 | 46.45 | 82.34 | −0.304 | Nuclear |
| 116194169 | PgGRAS13 | XM_031522921.1 | XP_031378781.1 | 449 | 50.23 | 5.13 | 48.23 | 88.62 | −0.169 | Chloroplast |
| 116194523 | PgGRAS14 | XM_031523342.1 | XP_031379202.1 | 502 | 56.36 | 4.69 | 50.03 | 78.11 | −0.33 | Cytoplasmic |
| 116195364 | PgGRAS15 | XM_031524504.1 | XP_031380364.1 | 297 | 31.57 | 4.67 | 37.88 | 83.2 | −0.014 | Chloroplast |
| 116196333 | PgGRAS16 | XM_031526002.1 | XP_031381862.1 | 694 | 77.27 | 6.04 | 55.28 | 76.9 | −0.441 | Nuclear |
| 116198598 | PgGRAS17 | XM_031528783.1 | XP_031384643.1 | 468 | 52.54 | 5.61 | 44.88 | 87.76 | −0.177 | Cytoplasmic |
| 116198662 | PgGRAS18 | XM_031528866.1 | XP_031384726.1 | 542 | 59.71 | 6.09 | 42.46 | 73.51 | −0.5 | peroxidase |
| 116199139 | PgGRAS19 | XM_031529433.1 | XP_031385293.1 | 549 | 59.34 | 5.91 | 45.46 | 84.08 | −0.107 | Nuclear |
| 116199452 | PgGRAS20 | XM_031529799.1 | XP_031385659.1 | 697 | 78.26 | 5.66 | 54.04 | 70.92 | −0.483 | Nuclear |
| 116200022 | PgGRAS21 | XM_031530678.1 | XP_031386538.1 | 799 | 88.90 | 4.99 | 54.15 | 72.6 | −0.504 | Nuclear |
| 116200713 | PgGRAS22 | XM_031531571.1 | XP_031387431.1 | 799 | 87.17 | 5.73 | 46.14 | 90.66 | −0.118 | Cytoplasmic |
| 116201968 | PgGRAS23 | XM_031533456.1 | XP_031389316.1 | 746 | 84.23 | 6 | 58.18 | 68.4 | −0.489 | Nuclear |
| 116203867 | PgGRAS24 | XM_031535825.1 | XP_031391685.1 | 602 | 65.63 | 5.03 | 51.89 | 81.23 | −0.263 | Nuclear |
| 116204084 | PgGRAS25 | XM_031536147.1 | XP_031392007.1 | 717 | 77.85 | 6.18 | 60.15 | 81.23 | −0.23 | Nuclear |
| 116204827 | PgGRAS26 | XM_031537145.1 | XP_031393005.1 | 594 | 64.04 | 7.61 | 52.14 | 82.19 | −0.272 | Nuclear |
| 116204912 | PgGRAS27 | XM_031537281.1 | XP_031393141.1 | 488 | 55.68 | 5.98 | 46.68 | 79.73 | −0.455 | Nuclear |
| 116205051 | PgGRAS28 | XM_031537492.1 | XP_031393352.1 | 492 | 55.12 | 5.53 | 45.99 | 77.89 | −0.272 | Nuclear |
| 116206171 | PgGRAS29 | XM_031538964.1 | XP_031394824.1 | 510 | 57.40 | 6.04 | 48.23 | 83.96 | −0.293 | Nuclear |
| 116206537 | PgGRAS30 | XM_031538965.1 | XP_031394825.1 | 510 | 57.40 | 6.04 | 48.23 | 83.96 | −0.293 | Nuclear |
| 116206862 | PgGRAS31 | XM_031539687.1 | XP_031395547.1 | 812 | 86.50 | 5.8 | 55.47 | 82.57 | −0.206 | Nuclear |
| 116207812 | PgGRAS32 | XM_031540907.1 | XP_031396767.1 | 718 | 81.26 | 6.24 | 49.65 | 78.23 | −0.506 | Nuclear |
| 116207917 | PgGRAS33 | XM_031541038.1 | XP_031396898.1 | 541 | 60.90 | 5.72 | 47.83 | 76.97 | −0.377 | Nuclear |
| 116208367 | PgGRAS34 | XM_031541757.1 | XP_031397617.1 | 427 | 47.78 | 7.61 | 46.55 | 92.9 | −0.103 | Nuclear |
| 116208829 | PgGRAS35 | XM_031542392.1 | XP_031398252.1 | 545 | 61.09 | 5.81 | 52.66 | 63.39 | −0.526 | Chloroplast |
| 116208927 | PgGRAS36 | XM_031542502.1 | XP_031398362.1 | 502 | 55.95 | 4.76 | 44.28 | 70.76 | −0.359 | Chloroplast |
| 116208955 | PgGRAS37 | XM_031542532.1 | XP_031398392.1 | 573 | 64.61 | 5.66 | 35.78 | 88.45 | −0.213 | Cytoplasmic |
| 116209919 | PgGRAS38 | XM_031543677.1 | XP_031399537.1 | 621 | 68.02 | 5.46 | 62.4 | 72.8 | −0.417 | Nuclear |
| 116209979 | PgGRAS39 | XM_031543751.1 | XP_031399611.1 | 470 | 52.35 | 5.99 | 49.38 | 90.72 | −0.183 | Nuclear |
| 116211438 | PgGRAS40 | XM_031545827.1 | XP_031401687.1 | 369 | 42.49 | 9.54 | 38.91 | 88.75 | −0.328 | Cytoplasmic |
| 116211781 | PgGRAS41 | XM_031546293.1 | XP_031402153.1 | 523 | 57.91 | 5.81 | 45.33 | 87.09 | −0.107 | Chloroplast |
| 116212322 | PgGRAS42 | XM_031546873.1 | XP_031402733.1 | 1604 | 181.47 | 5.73 | 50.91 | 72.19 | −0.535 | Nuclear |
| 116212548 | PgGRAS43 | XM_031547221.1 | XP_031403081.1 | 475 | 53.67 | 5.86 | 56.11 | 94.91 | −0.187 | Nuclear |
| 116213071 | PgGRAS44 | XM_031547880.1 | XP_031403740.1 | 567 | 63.85 | 5.66 | 42.88 | 79.28 | −0.345 | Cytoplasmic |
| 116213118 | PgGRAS45 | XM_031547939.1 | XP_031403799.1 | 437 | 49.22 | 5.11 | 43.96 | 87.51 | −0.231 | Cytoplasmic |
| 116213186 | PgGRAS46 | XM_031548035.1 | XP_031403895.1 | 423 | 47.36 | 7.08 | 53.13 | 84.68 | −0.326 | Nuclear |
| 116213207 | PgGRAS47 | XM_031548059.1 | XP_031403919.1 | 540 | 60.60 | 5.29 | 51.27 | 81.28 | −0.396 | Cytoplasmic |
| 116213387 | PgGRAS48 | XM_031548069.1 | XP_031403929.1 | 540 | 60.60 | 5.29 | 51.27 | 81.28 | −0.396 | Cytoplasmic |
| 116213541 | PgGRAS49 | XM_031548074.1 | XP_031403934.1 | 540 | 60.60 | 5.29 | 51.27 | 81.28 | −0.396 | Cytoplasmic |
| 116213862 | PgGRAS50 | XM_031548083.1 | XP_031403943.1 | 540 | 60.60 | 5.29 | 51.27 | 81.28 | −0.396 | Cytoplasmic |
| 116214098 | PgGRAS51 | XM_031549390.1 | XP_031405250.1 | 704 | 77.60 | 5.82 | 56.74 | 75.82 | −0.382 | Cytoplasmic |
| 116214877 | PgGRAS52 | XM_031550360.1 | XP_031406220.1 | 568 | 63.77 | 6.31 | 49.59 | 79.52 | −0.427 | Cytoplasmic |
| 116214902 | PgGRAS53 | XM_031550361.1 | XP_031406221.1 | 568 | 63.77 | 6.31 | 49.59 | 79.52 | −0.427 | Cytoplasmic |
| 116214918 | PgGRAS54 | XM_031550419.1 | XP_031406279.1 | 717 | 78.44 | 5.79 | 66.95 | 78.97 | −0.3 | Nuclear |
| Sequence1 | Sequence2 | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PgGRAS8 | PgGRAS30 | 0.3062 | 2.1813 | 0.1404 |
| PgGRAS8 | PgGRAS33 | 0.4344 | 2.4413 | 0.1779 |
| PgGRAS9 | PgGRAS37 | 0.4714 | 1.8863 | 0.2499 |
| PgGRAS11 | PgGRAS4 | 0.3735 | 2.4969 | 0.1496 |
| PgGRAS11 | PgGRAS16 | 0.3228 | 3.5733 | 0.0903 |
| PgGRAS14 | PgGRAS36 | 0.4781 | 2.0015 | 0.2389 |
| PgGRAS16 | PgGRAS4 | 0.3222 | 1.7630 | 0.1828 |
| PgGRAS16 | PgGRAS23 | 0.4394 | 3.6614 | 0.1200 |
| PgGRAS16 | PgGRAS42 | 0.4236 | 2.2801 | 0.1858 |
| PgGRAS19 | PgGRAS38 | 0.8156 | 1.2933 | 0.6307 |
| PgGRAS23 | PgGRAS32 | 0.4497 | 3.8821 | 0.1158 |
| PgGRAS23 | PgGRAS42 | 0.3100 | 1.6736 | 0.1853 |
| PgGRAS28 | PgGRAS33 | 0.3250 | 1.9666 | 0.1653 |
| PgGRAS32 | PgGRAS40 | 0.4410 | 2.2815 | 0.1933 |
| PgGRAS41 | PgGRAS3 | 0.2558 | 1.4911 | 0.1715 |
| PgGRAS42 | PgGRAS4 | 0.4592 | 2.4760 | 0.1855 |
| PgGRAS47 | PgGRAS52 | 0.2459 | 3.5683 | 0.0689 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Ren, H.; Cheng, F.; Teng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, Z. Comprehensive Genome-Wide Characterization of the GRAS Gene Family and Their Role in Salt Stress Tolerance in Punica granatum L. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11050504
Huang J, Ren H, Cheng F, Teng Y, Zhao X, Yuan Z. Comprehensive Genome-Wide Characterization of the GRAS Gene Family and Their Role in Salt Stress Tolerance in Punica granatum L. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(5):504. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11050504
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jingyi, Hongfang Ren, Fan Cheng, Yingfen Teng, Xueqing Zhao, and Zhaohe Yuan. 2025. "Comprehensive Genome-Wide Characterization of the GRAS Gene Family and Their Role in Salt Stress Tolerance in Punica granatum L." Horticulturae 11, no. 5: 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11050504
APA StyleHuang, J., Ren, H., Cheng, F., Teng, Y., Zhao, X., & Yuan, Z. (2025). Comprehensive Genome-Wide Characterization of the GRAS Gene Family and Their Role in Salt Stress Tolerance in Punica granatum L. Horticulturae, 11(5), 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11050504






