Bacillus safensis P1.5S Exhibits Phosphorus-Solubilizing Activity Under Abiotic Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Culture Media
2.2. Bioinformatic Analysis of the Draft Genome of Strain P1.5S
2.3. Evaluation of Bacterial Growth Under Abiotic Stress Conditions
2.4. Phosphate Solubilization Under Abiotic Stress Conditions
2.5. Determination of Organic Acids Production
2.6. Acid and Alkaline Phosphatase Activity Assessment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
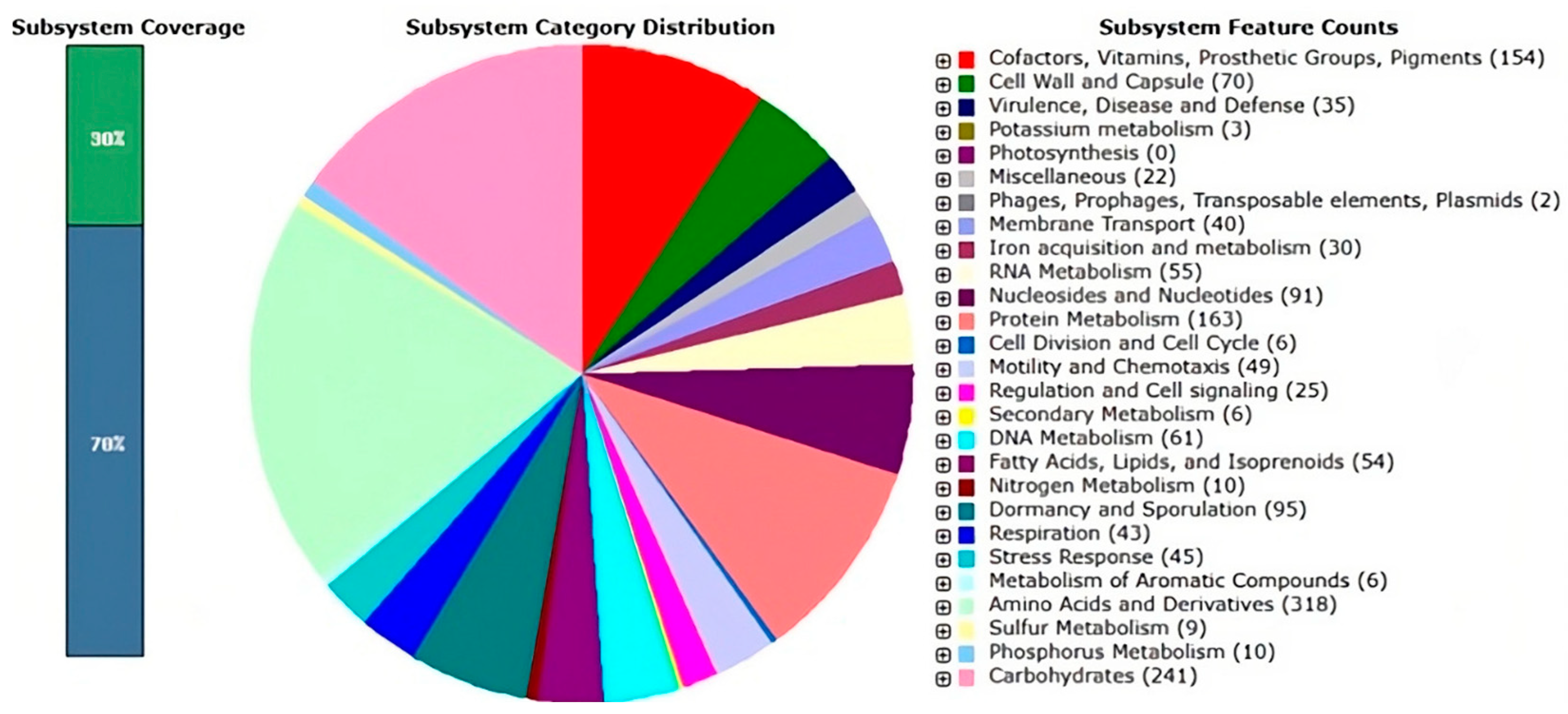
3.1. Functional Genome Analysis of Bacillus safensis P1.5S
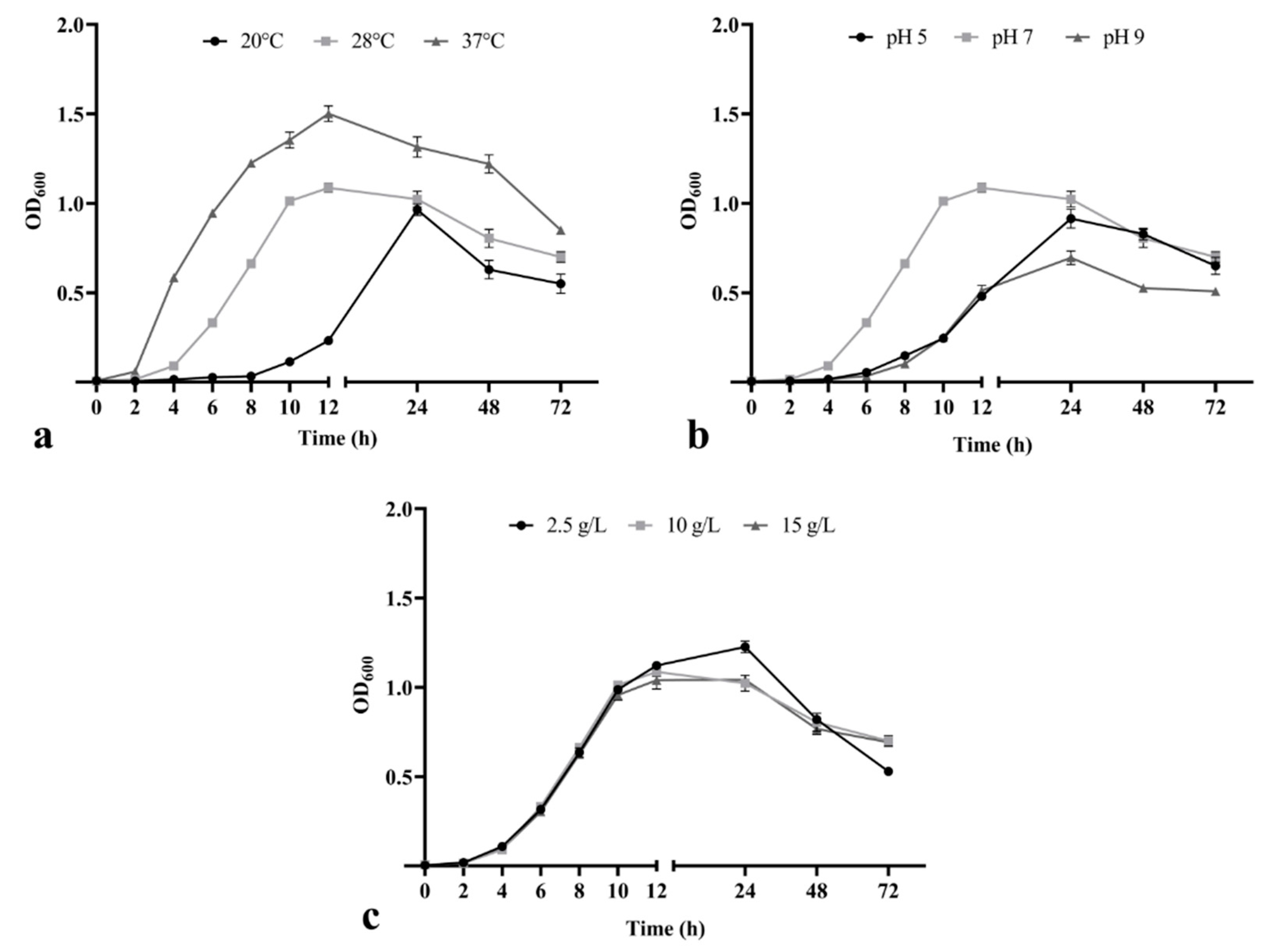
3.2. Effect of Temperature, pH and Salinity on Bacillus safensis P1.5S Growth
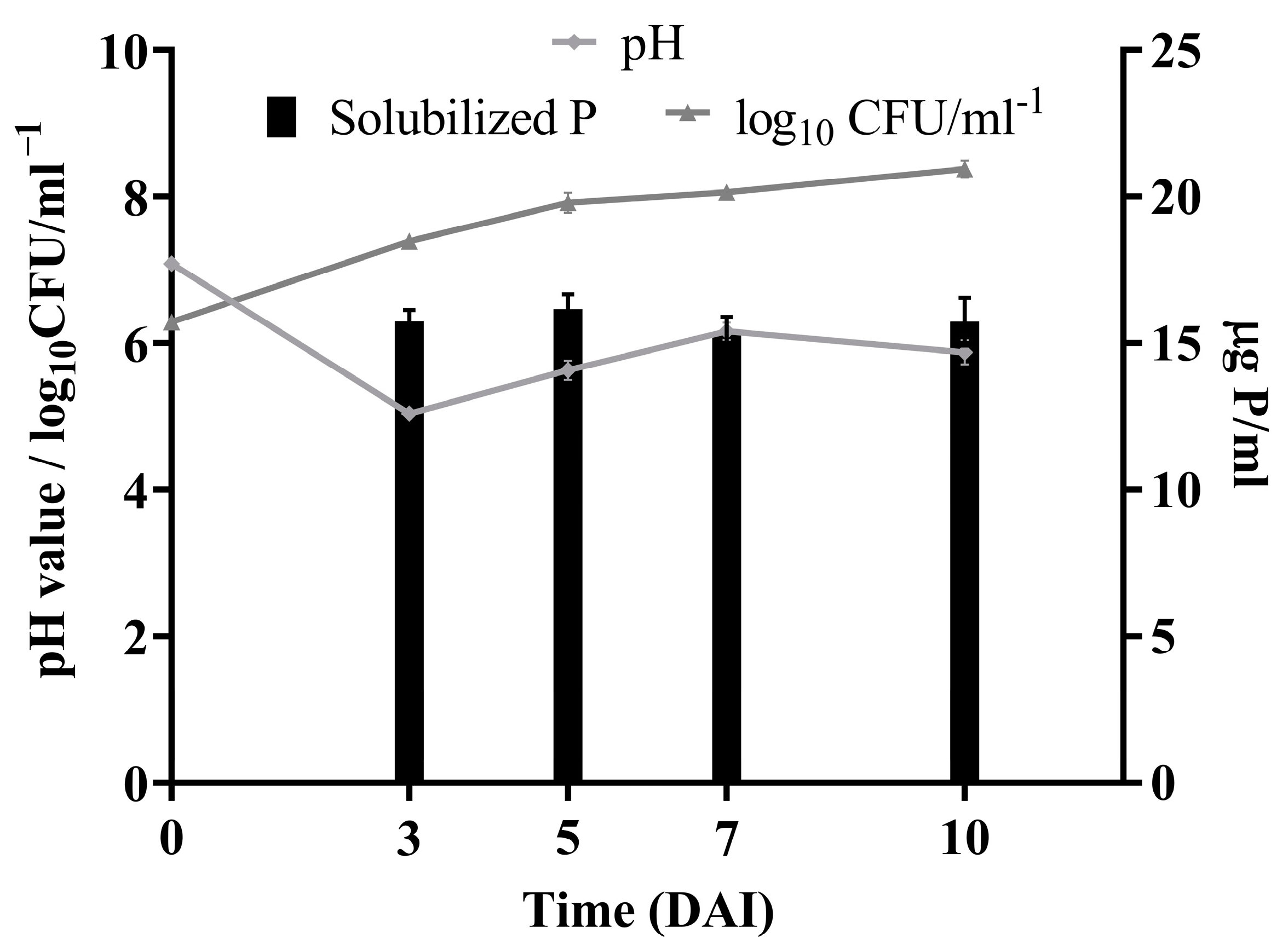
3.3. Phosphorus Solubilization Potential of Bacillus safensis P1.5S
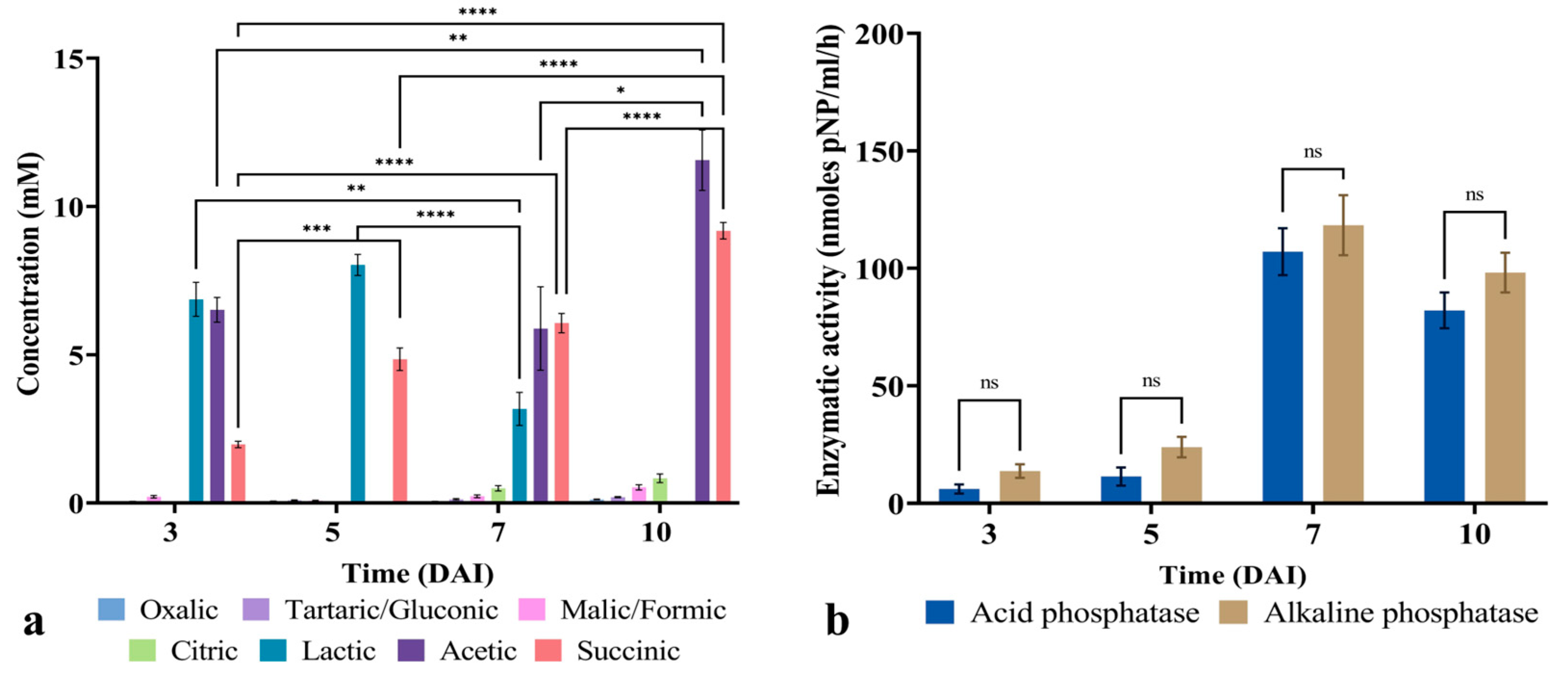
3.4. Bacillus safensis P1.5S Released Organic Acids and Phosphatases During P Solubilization
3.5. Effect of Abiotic Stress Conditions on Bacillus safensis P1.5S P Solubilization Ability
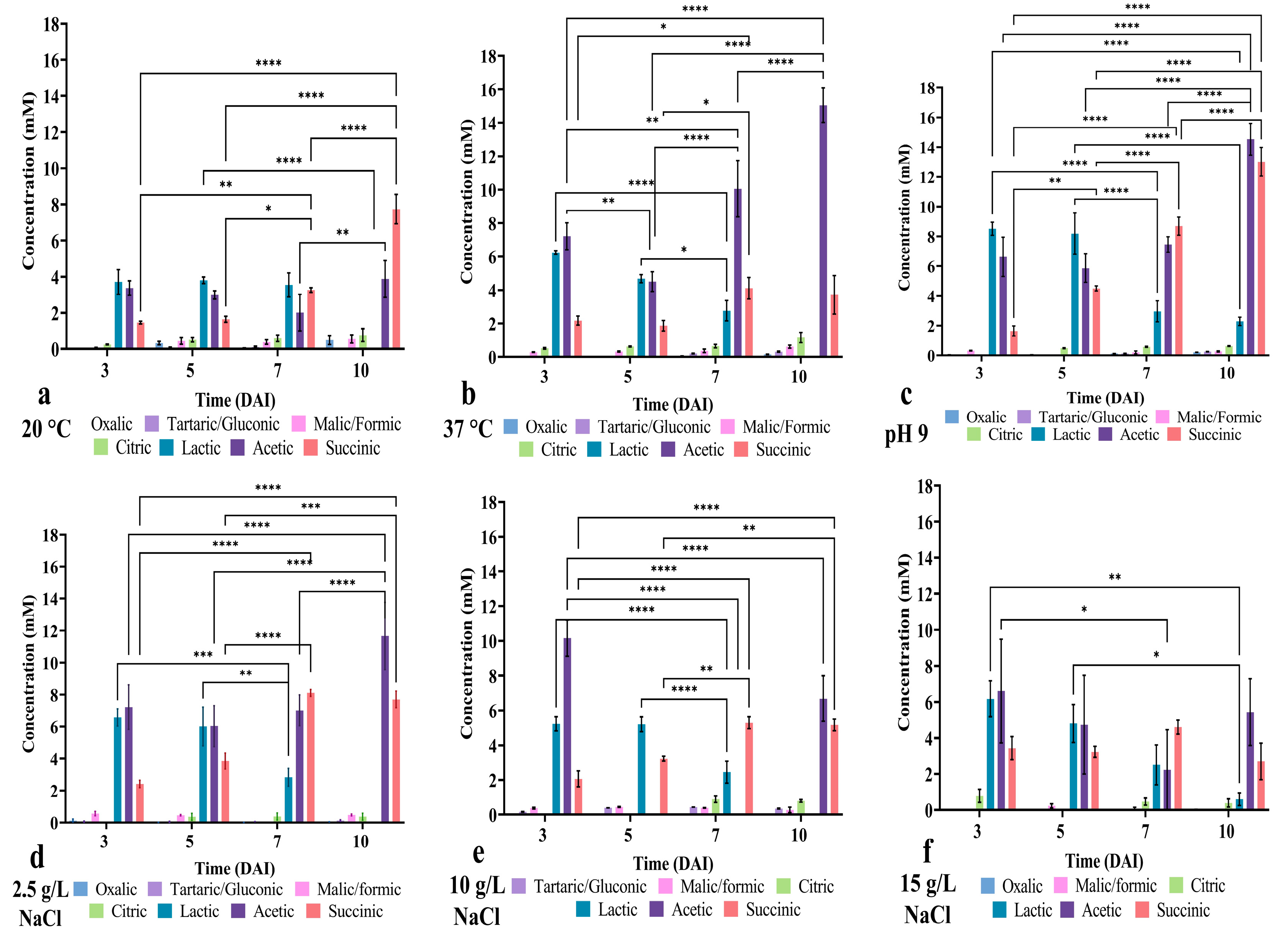
3.6. Bacillus safensis P1.5S Displayed a Distinct Pattern of Organic Acid Production Under Stress Conditions
3.7. Temperature Induces Changes in Acid and Alkaline Phosphatase Activity During Phosphorus Solubilization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PSM | Phosphorus-Solubilizing Microorganisms |
| PSB | Phosphorus-Solubilizing Bacteria |
| P | Phosphorus |
| LB | Luria Bertani agar/broth |
| PVK | Pikovskaya agar/broth |
| RAST | Rapid Annotations using Subsystems Technology |
| BLAST | Basic Local Alignment Search Tool |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| TYGS | Type (Strain) Genome Server |
| OD | Optical Density |
| TCP | Tri-Calcium Phosphate |
| CFU | Colony Forming Units |
| DAI | Days After Inoculation |
| pNP | ρ-Nitrophenol |
| SEM | Standard Error of the Mean |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| dDDH | Digital DNA-DNA Hybridization |
References
- Kumar, L.; Chhogyel, N.; Gopalakrishnan, T.; Hasan, M.K.; Jayasinghe, S.L.; Kariyawasam, C.S.; Kogo, B.K.; Ratnayake, S. Chapter 4—Climate change and future of agri-food production. In Future Foods; Bhat, R., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 49–79. [Google Scholar]
- Furtak, K.; Wolińska, A. The impact of extreme weather events as a consequence of climate change on the soil moisture and on the quality of the soil environment and agriculture—A review. CATENA 2023, 231, 107378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, G.S.; Kaur, M.; Kaushik, P. Impact of climate change on agriculture and its mitigation strategies: A review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Bermúdez, M.; del Pozo, J.C.; Pernas, M. Effects of combined abiotic stresses related to climate change on root growth in crops. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 918537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kour, D.; Yadav, A.N. Stress adaptive phosphorus solubilizing microbiomes for agricultural sustainability. Appl Biol Biotech 2022, 10, i–iii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, H.; Dutta, A. The microbial aspect of climate change. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2016, 1, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Qin, Y.; Wu, H.; Zuo, W.; He, H.; Tan, J.; Wang, Y.; He, D. Isolation and characterization of phosphorus solubilizing bacteria with multiple phosphorus sources utilizing capability and their potential for lead immobilization in soil. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesme, T.; Metson, G.S.; Bennett, E.M. Global phosphorus flows through agricultural trade. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2018, 50, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantigoso, H.A.; Manter, D.K.; Fonte, S.J.; Vivanco, J.M. Root exudate-derived compounds stimulate the phosphorus solubilizing ability of bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S. Plant-microbe interactions ameliorate phosphate-mediated responses in the rhizosphere: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1074279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, H.; Fraga, R.; Gonzalez, T.; Bashan, Y. Genetics of phosphate solubilization and its potential applications for improving plant growth-promoting bacteria. Plant Soil. 2006, 287, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeeva, A.; Galyamova, M.; Sedykh, S. Prospects for using phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms as natural fertilizers in agriculture. Plants 2022, 11, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, G.; Wei, Y.; Dong, Y.; Hou, L.; Jiao, R. Isolation and screening of multifunctional phosphate solubilizing bacteria and its growth-promoting effect on Chinese fir seedlings. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Pan, G.; Lu, X.; Qi, W. Phosphorus solubilizing microorganisms: Potential promoters of agricultural and environmental engineering. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1181078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Rahman, N.S.N.; Abdul Hamid, N.W.; Nadarajah, K. Effects of abiotic stress on soil microbiome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.K.; Kumar, M.; Chakdar, H.; Anuroopa, N.; Bagyaraj, D.J. Bacillus species in soil as a natural resource for plant health and nutrition. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etesami, H.; Jeong, B.R.; Glick, B.R. Potential use of Bacillus spp. as an effective biostimulant against abiotic stresses in crops—A review. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2023, 5, 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, T.; Ali, F.; Rafique, M.; Ali, J.; Afridi, M.S.; Smith, D.; Mehmood, S.; Amna; Souleimanov, A.; Jellani, G.; et al. Biochemical characterization and potential of Bacillus safensis strain SCAL1 to mitigate heat stress in Solanum lycopersicum L. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 42, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altimira, F.; Godoy, S.; Arias-Aravena, M.; Vargas, N.; González, E.; Dardón, E.; Montenegro, E.; Viteri, I.; Tapia, E. Reduced fertilization supplemented with Bacillus safensis RGM 2450 and Bacillus siamensis RGM 2529 promotes tomato production in a sustainable way. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1451887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebotar, V.K.; Zaplatkin, A.N.; Chizhevskaya, E.P.; Gancheva, M.S.; Voshol, G.P.; Malfanova, N.V.; Baganova, M.E.; Khomyakov, Y.V.; Pishchik, V.N. Phytohormone production by the endophyte Bacillus safensis ts3 increases plant yield and alleviates salt stress. Plants 2024, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, M.B.; Dal’Rio, I.; Rodrigues Coelho, M.R.; Seldin, L. Response of sweet potato cultivars to Bacillus velezensis T149-19 and Bacillus safensis T052-76 used as biofertilizers. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lateef, A.; Adelere, I.A.; Gueguim-Kana, E.B. The biology and potential biotechnological applications of Bacillus safensis. Biologia 2015, 70, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, M.A.; Shah, F.H.; Ullah, A.; Ali, K.; Jones, D.A.; Khan, M.E.H.; Ashraf, A. Biochemical characterization of halotolerant Bacillus safensis PM22 and its potential to enhance growth of maize under salinity stress. Plants 2022, 11, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, N.; Khan, M.; Rehman, F.u.; Mahrukh; Room, S.; Ahmad, M.A.; Iftikhar, M.; Munis, M.F.H.; Chaudhary, H.J. Harnessing Bacillus safensis as biofertilizer for sustainable drought alleviation in Brassica juncea L. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2024, 61, 103388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Dubey, R.C.; Maheshwari, D.K. Bacillus strains isolated from rhizosphere showed plant growth promoting and antagonistic activity against phytopathogens. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 167, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid Annotations using Subsystems Technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Göker, M. TYGS is an automated high-throughput platform for state-of-the-art genome-based taxonomy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apweiler, R.; Bairoch, A.; Wu, C.H.; Barker, W.C.; Boeckmann, B.; Ferro, S.; Gasteiger, E.; Huang, H.; Lopez, R.; Magrane, M.; et al. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2025. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D609–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nautiyal, C.S. An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 170, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzuay, M.S.; Ciancio, M.G.R.; Ludueña, L.M.; Angelini, J.G.; Barros, G.; Pastor, N.; Taurian, T. Growth promotion of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) and maize (Zea mays L.) plants by single and mixed cultures of efficient phosphate solubilizing bacteria that are tolerant to abiotic stress and pesticides. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 199, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, J.R.; Banerjee, M.R.; Germida, J.J. Phosphate-solubilizing rhizobacteria enhance the growth and yield but not phosphorus uptake of canola (Brassica napus L.). Biol. Fertil. Soils 1997, 24, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantea, L.E.; El-Sabeh, A.; Mihasan, M.; Stefan, M. JGCA_029930515.1—Genome sequencing and assembly of Bacillus safensis P1.5S—A salt-tolerant rhizobacteria with phosphorus solubilization potential. GenBank 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, D.A.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D36–D42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeek, R.; Olson, R.; Pusch, G.D.; Olsen, G.J.; Davis, J.J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Gerdes, S.; Parrello, B.; Shukla, M.; et al. The SEED and the Rapid Annotation of microbial genomes using Subsystems Technology (RAST). Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D206–D214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owino, V.; Kumwenda, C.; Ekesa, B.; Parker, M.E.; Ewoldt, L.; Roos, N.; Lee, W.T.; Tome, D. The impact of climate change on food systems, diet quality, nutrition, and health outcomes: A narrative review. Front. Clim. 2022, 4, 941842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, A.A.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Srivastava, A.K.; Bhojiya, A.A. Biofertilizers: A Nexus between soil fertility and crop productivity under abiotic stress. Curr. Res. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 3, 100063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozo, J.; Danojević, D.; Jovanović, Ž.; Nenadović, Ž.; Fira, D.; Stanković, S.; Radović, S. Genotype-dependent antioxidative response of four sweet pepper cultivars to water deficiency as affected by drought-tolerant Bacillus safensis Ss-2.7 and Bacillus thuringiensis Ss-29.2 strains. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, W. Regulation of bacterial heat shock stimulons. Cell Stress Chaperones 2016, 21, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Esawi, M.A.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Ali, H.M.; Alayafi, A.A. Azospirillum lipoferum FK1 confers improved salt tolerance in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) by modulating osmolytes, antioxidant machinery and stress-related genes expression. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 159, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleator, R.D.; Hill, C. Bacterial osmoadaptation: The role of osmolytes in bacterial stress and virulence. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 26, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, L.F.; López, M.G.; Straube, L.; Passaglia, L.M.P.; Wendisch, V.F. Inorganic phosphate solubilization by rhizosphere Bacterium paenibacillus sonchi: Gene expression and physiological functions. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 588605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengel, Z. Soil pH, soil health and climate change. In Soil Health and Climate Change; Singh, B.P., Cowie, A.L., Chan, K.Y., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 69–85. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, S.A.; Rahman, K. Soil salinity development, classification, assessment and management in irrigated agriculture. In Handbook of Plant and Crop Stress; Pessarakli, M., Ed.; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 23–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.S.; Ullrich, M.S. Characterization of salt tolerant phosphate and zinc solubilizing Bacillus isolates for plant protection and plant stimulation use in sustainable agriculture in Myanmar. Int. J. Plant Biol. Res. 2021, 9, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Ahmad, M.; Hussain, A.; Jamil, M. Integrated use of phosphate-solubilizing Bacillus subtilis strain IA6 and zinc-solubilizing Bacillus sp. strain IA16: A promising approach for improving cotton growth. Folia Microbiol. 2021, 66, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, G.-C.; Tian, S.-J.; Cai, M.-Y.; Xie, G.-H. Phosphate-solubilizing and -mineralizing abilities of bacteria isolated from soils. Pedosphere 2008, 18, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouas, S.; Djedidi, S.; Ben Slimene Debez, I.; Sbissi, I.; Alyami, N.M.; Hirsch, A.M. Halotolerant phosphate solubilizing bacteria isolated from arid area in Tunisia improve P status and photosynthetic activity of cultivated barley under P shortage. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, M.M.; Deivaraj, S.; Benson, A.; Henry, A.J.; Narendrakumar, G. Soil extract calcium phosphate media for screening of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2018, 52, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagah, A.; El-Sheekh, M.M.; Arief, O.M.; Alqahtani, M.D.; Alharbi, B.M.; Dawwam, G.E. Endophytic Bacillus vallismortis and Bacillus tequilensis bacteria isolated from medicinal plants enhance phosphorus acquisition and fortify Brassica napus L. vegetative growth and metabolic content. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1324538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakki, M.; Banane, B.; Marhane, O.; Esmaeel, Q.; Hatimi, A.; Barka, E.A.; Azim, K.; Bouizgarne, B. Phosphate solubilizing Pseudomonas and Bacillus combined with rock phosphates promoting tomato growth and reducing bacterial canker disease. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1289466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, U.C.; Cuadros-Orellana, S.; Silva, D.R.C.; Freitas-Júnior, L.F.; Fernandes, A.C.; Leite, L.R.; Oliveira, C.A.; Dos Santos, V.L. Genomic and phenotypic insights into the potential of rock phosphate solubilizing bacteria to promote millet growth in vivo. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 574550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Gonzalez, M.E.; Mora-Herrera, M.E.; Wong-Villarreal, A.; De La Portilla-López, N.; Sanchez-Paz, L.; Lugo, J.; Vaca-Paulín, R.; Del Aguila, P.; Yañez-Ocampo, G. Effect of pH and carbon source on phosphate solubilization by bacterial strains in Pikovskaya medium. Microorganisms 2022, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Tan, C.; Li, W.; Lin, L.; Liao, T.; Fan, X.; Peng, H.; An, Q.; Liang, Y. Phosphorus-, potassium-, and silicon-solubilizing bacteria from forest soils can mobilize soil minerals to promote the growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2024, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, H.; Fraga, R. Phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion. Biotechnol. Adv. 1999, 17, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Fahad, S.; Saleem, M.H.; Ali, B.; Mussart, M.; Ullah, R.; Amanullah, J.; Arif, M.; Ahmad, M.; Shah, W.A.; et al. Comparative efficacy of phosphorous supplements with phosphate solubilizing bacteria for optimizing wheat yield in calcareous soils. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Torres, M.; Romero-Perdomo, F.; Mendoza-Labrador, J.; Gutiérrez, A.Y.; Vargas, C.; Castro-Rincon, E.; Caro-Quintero, A.; Uribe-Velez, D.; Estrada-Bonilla, G.A. Genomic and phenotypic analysis of rock phosphate-solubilizing rhizobacteria. Rhizosphere 2021, 17, 100290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitriatin, B.N.; Mulyani, O.; Herdiyantoro, D.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Pellegrini, M. Metabolic characterization of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms and their role in improving soil phosphate solubility, yield of upland rice (Oryza sativa L.), and phosphorus fertilizers efficiency. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 1032708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Cai, B. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria: Advances in their physiology, molecular mechanisms and microbial community effects. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Sanchez, M.; Bertrand, I.; Barakat, A.; Zeroual, Y.; Oukarroum, A.; Plassard, C. Improved rock phosphate dissolution from organic acids is driven by nitrate assimilation of bacteria isolated from nitrate and CaCO3-rich soil. PLoS One 2023, 18, e0283437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, S.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Wang, L.; Zheng, B. Genome-based identification of phosphate-solubilizing capacities of soil bacterial isolates. AMB Express 2024, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhanja, E.; Das, R.; Begum, Y.; Mondal, S.K. Study of pyrroloquinoline quinine from phosphate-solubilizing microbes responsible for plant growth: In silico approach. Front. Agron. 2021, 3, 667339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, F.; Harvey, P.R.; Wang, L.; Fan, S.; Xie, X.; Li, F.; Zhou, H.; et al. Identification of the phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria strain JP233 and its effects on soil phosphorus leaching loss and crop growth. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 892533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, F.; Li, Q.; Solanki, M.K.; Wang, Z.; Xing, Y.-X.; Dong, D.-F. Soil phosphorus transformation and plant uptake driven by phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1383813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Ahmad, M.; Raza, M.A.; Hilger, T.; Rasche, F. Phosphate-solubilizing Bacillus sp. modulate soil exoenzyme activities and improve wheat growth. Microb. Ecol. 2024, 87, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Mohapatra, N.P.; Schlesinger, L.S.; Gunn, J.S. The acid phosphatase AcpA is secreted in vitro and in macrophages by Francisella spp. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, J.; Arora, N.K. Phosphate-solubilizing Bacillus sp. enhances growth, phosphorus uptake and oil yield of Mentha arvensis L. 3 Biotech. 2019, 9, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Galeana, J.A.; Castro-Martínez, C.; Fierro-Coronado, R.A.; Armenta-Bojórquez, A.D.; Maldonado-Mendoza, I.E. Characterization of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria exhibiting the potential for growth promotion and phosphorus nutrition improvement in maize (Zea mays L.) in calcareous soils of Sinaloa, Mexico. Ann. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalache, G.; Mihasan, M.; Zamfirache, M.M.; Stefan, M.; Raus, L. Phosphate solubilizing bacteria from runner bean rhizosphere and their mechanism of action. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2018, 23, 13853–13861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Narayanan, M.; Shi, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Ma, Y. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria: Their agroecological function and optimistic application for enhancing agro-productivity. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 166468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alori, E.T.; Glick, B.R.; Babalola, O.O. Microbial phosphorus solubilization and its potential for use in sustainable agriculture. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, G.; Banerjee, P.; Sharma, R.K.; Maity, J.P.; Etesami, H.; Shaw, A.K.; Huang, Y.-H.; Huang, H.-B.; Chen, C.-Y. Management of phosphorus in salinity-stressed agriculture for sustainable crop production by salt-tolerant phosphate-solubilizing bacteria—A review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmoteleb, A.; Gonzalez-Mendoza, D. Isolation and identification of phosphate solubilizing Bacillus spp. from Tamarix ramosissima rhizosphere and their effect on growth of Phaseolus vulgaris under salinity stress. Geomicrobiol. J. 2020, 37, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini Hajiabadi, A.; Mosleh Arani, A.; Ghasemi, S.; Rad, M.H.; Etesami, H.; Shabazi Manshadi, S.; Dolati, A. Mining the rhizosphere of halophytic rangeland plants for halotolerant bacteria to improve growth and yield of salinity-stressed wheat. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 163, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalache, G.; Zamfirache, M.; Marius, M.; Ivanov, I.; Stefan, M.; Raus, L. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria associated with runner bean rhizosphere. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2015, 67, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mantea, L.-E.; El-Sabeh, A.; Mihasan, M.; Stefan, M. Bacillus safensis P1.5S Exhibits Phosphorus-Solubilizing Activity Under Abiotic Stress. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11040388
Mantea L-E, El-Sabeh A, Mihasan M, Stefan M. Bacillus safensis P1.5S Exhibits Phosphorus-Solubilizing Activity Under Abiotic Stress. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(4):388. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11040388
Chicago/Turabian StyleMantea, Loredana-Elena, Amada El-Sabeh, Marius Mihasan, and Marius Stefan. 2025. "Bacillus safensis P1.5S Exhibits Phosphorus-Solubilizing Activity Under Abiotic Stress" Horticulturae 11, no. 4: 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11040388
APA StyleMantea, L.-E., El-Sabeh, A., Mihasan, M., & Stefan, M. (2025). Bacillus safensis P1.5S Exhibits Phosphorus-Solubilizing Activity Under Abiotic Stress. Horticulturae, 11(4), 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11040388






