Effect of Peat-Zeolite Substrates Used During Seedling Cultivation on the Growth, Physiology, and Yield of Sweet Peppers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Growing Conditions
2.2. Biometric Measurements
2.3. Determination of Dry Matter
2.4. Determination of Photosynthetic Parameters
2.5. Non-Destructive Measurements
2.6. Determination of Nitrogen (Ammonia/Ammonium) and Protein in Leaves
2.7. Yielding of Plants
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Radha, T.K.; Ganeshamurthy, A.; Mitra, D.; Sharma, K.; Rupa, T.; Selvakumar, G. Feasibility of Substituting Cocopeat with Rice Husk and Saw Dust Compost as a Nursery Medium for Growing Vegetable Seedlings. Bioscan 2018, 13, 659–663. [Google Scholar]
- Cantliffe, D.J.; Funes, J.; Jovicich, E.; Paranjpe, A.; Rodriguez, J.; Show, N. Media and containers for greenhouse soilless grown cucumbers, melons, peppers, and strawberry. Acta Hortic. 2003, 614, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathowa, T.; Tshegofatso, N.; Mojeremane, W.; Matsuane, C.; Legwaila, G.M.; Oagile, O. Effect of commercial growing media on emergence, growth and development of tomato seedlings. Int. J. Agron. Agric. Res. 2016, 9, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, A.; Ngouajio, M.; Biernbaum, J. Alfalfa-based organic amendment in peat compost growing medium for organic tomato transplant production. HortScience 2011, 46, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, S.F.; Deppe, N.A.; Palmquist, D.E.; Berhow, M.A. Extracted sweet corn tassels as renewable alternative to peat in greenhouse substrates. Ind. Crops Prod. 2011, 33, 514–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, N.R.; Suleiman, M.S.; Thomas, B.; Lekha, V.S.; George, P.; Ali, I.S. Growing substrate for organic lettuce production in Kuwait. World J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 9, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oagile, O.; Ramalekane, O.; Mojeremane, W.; Matsuane, C.; Legwaila, G.M.; Mathowa, T. Growth and development response of Kale (Brassica oleracea var. Acephala L.) seedlings to different commercial growing media. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2016, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argüello, B.M.; Reyes, I.V.; Flores, A.C.; De los Santos Villarreal, G.; Jiménez, L.I.; Saldivar, R.H.L. Water holding capacity of substrates containing zeolite and its effect on growth, biomass production and chlorophyll content of Solanum lycopersicum. Nova Sci. 2018, 10, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, F.M.S.; Al Labib, B.; Jabin, D.; Sayeed, M.S.R.; Islam, S.; Akter, S.; Eusufzai, T.K.; Khan, H.M.I.; Jahan, R.; Rahmatullah, M. Study of Zeolite application in soil on height and flowering of Solanum melongena L. (Solanaceae). Am.-Eurasian J. Sustain. Agric. 2012, 6, 271–275. [Google Scholar]
- Torma, S.; Vilcek, J.; Adamisin, P.; Huttmanova, E.; Hronec, O. Influence of natural zeolite on nitrogen dynamics in soil. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2014, 38, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolov, I.; Antonov, D.; Stoilov, G.; Tsareva, I.; Baev, M. Jordanian zeolitic tuff as a raw material for the preparation of substrates used for plant growth. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2005, 6, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazirska, V.; Simidtchiev, H.R.; Chakalov, K. Effect of zeolite on yield and fruit quality of greenhouse cucumbers. In Proceedings of the Natural Zeolite Conference, Sofia, Italy, 21–29 September 1997; pp. 109–110. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis, M.; Koukouzas, N.; Vassilatos, C.H.; Kamenou, E.; Samantouros, K. The zeolites from evros region, Northern Greece: A potential use as cultivation substrate in hydroponics. Acta Hortic. 2001, 548, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdak, P.; Mobli, M.; Khoshgoftarmanesh, A.H. Effects of different growing media on vegetative and reproductive growth of bell pepper. J. Plant Nutr. 2016, 39, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghtedary-Naeini, A.; Golabadi, M.; Hoodaji, M. Using enriched zeolite as a slow release iron fertilizer for soilless greenhouse cultivation of cucumber. J. Plant Nutr. 2015, 39, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djedidi, M.; Grasopoulos, D.; Maloupa, E. The effect of different substrates on the quality of f. Carmello tomatoes (Lycopersicon esculentum MILL) grown under protection in a hydroponic system. Cah. Options Mediterr. 1999, 31, 279–283. Available online: https://om.ciheam.org/ressources/om/pdf/c31/CI020860.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Markovic, V.; Takac, A.; Ilin, Z. Enriched zeolite as a substrate component in the production of pepper and tomato seedlings. Acta Hortic. 1995, 396, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayan, S.; Tillki, F. Morphological attributes of oriental spruce (Picea orientalis (L.) Link.) seedlings grown in peat–based amended with natural zeolite. Acta Agron. Hung. 2007, 55, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronikashvili, T.G.; Urushadze, T.F. To influence of zeolitcantaining substrates and fertilizers on some qualitative indices of agricultural products. Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2010, 8, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Laužikė, K.; Uselis, N.; Kviklys, D.; Samuolienė, G. Orchard planting density and tree development stage affects physiological processes of apple (Malus domestica Borkh.) tree. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, H.; Polat, E.; Sönmez, İ.; Yılmaz, E. Effects of different growing media on seedling quality and nutrient contents in pepper (Capsicum annuum L. var longum cv. Super Umut F1). J. Food Agric. Environ. 2010, 8, 894–897. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261251842_Effects_of_different_growing_media_on_seedling_quality_and_nutrient_contents_in_pepper_Capsicum (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Unal, M. Effect of organic media on the growth of vegetable seedlings. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 50, 517–522. Available online: https://api.pakjas.com.pk/downloadPaper/2187.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Yilmaz, E.; Sönmez, İ.; Demir, H. Effects of zeolite on seedlings quality and nutrient contents of cucumber plant (Cucumis sativus L. cv. Mostar F1) grown in different mixtures of growing media. Comm. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2014, 45, 2767–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, V.; Djurovka, M.; Ilin, Z.; Lazic, B. Effect of seedling quality on yield and characters of plant and fruits of sweet pepper. Acta Hortic. 2000, 533, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjoko, D.; Utami, R.S.; Arniputri, R.B. Hydroponic of Chili with substrates variation. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 200, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prisa, D. Study and evaluation of natural zeolite and dried zeolite for the cultivation of friggitello pepper. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2023, 19, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parandnia, M.; Najafi, P.; Tabatabaei, S.H. Effect of zeolite on germination and vegetative growth of bell pepper. Res. Crops 2011, 12, 796–799. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/287839443_Effect_of_zeolite_on_germination_and_vegetative_growth_of_bell_pepper (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Cattivello, C. Use of substrates with zeolites for seedling vegetables and pot plant production. Acta Hortic. 1995, 401, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravčević, D.; Simić, A.; Rakić, V.; Pavlović, N.; Ćosić, M.; Lipovac, A.; Kaludjerović, L. The effect of addition of different amounts of natural zeolites on the cucumber seedlings quality. In Proceedings of the 8th Serbian-Croatian-Slovenian Symposium on Zeolites, Belgrade, Serbia, 3–5 October 2019; pp. 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.H.; Wang, X.F.; Zang, J.B. Effects of application of zeolite on tomato seedling growth. China Veg. 2004, 3, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Fadillioğlu, G.; Başay, S. Effects of Different Growing Media on Seedling Quality in Organic Seedling Production. MAKUFEBED 2023, 14, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castronuovo, D.; Satriani, A.; Rivelli, A.R.; Comegna, I.; Belviso, C.; Coppola, A.; Di Prima, S.; Cavalcante, F.; Lovelli, S. Effects of Zeolite and Deficit Irrigation on Sweet Pepper Growth. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soval-Villa, M.; Wood, C.W.; Guertal, E.A. Tomato leaf chlorophyll meter readings as affected by variety, nitrogen form, and nighttime nutrient solution strength. J. Plant Nutr. 2002, 25, 2129–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddling, J.; Gelang-Alfredsson, J.; Piikki, K.; Pleijel, H. Evaluating the relationship between leaf chlorophyll concentration and SPAD-502 chlorophyll meter readings. Photosynth. Res. 2007, 91, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapałowska, A.; Matłok, N.; Piechowiak, T.; Szostek, M.; Puchalski, C.; Balawejder, M. Physiological and Morphological Implications of Using Composts with Different Compositions in the Production of Cucumber Seedlings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi, G.; Khosh-Khui, M.; Eshghi, S. Effects of Natural Zeolite on Growth and Flowering of Strawberry Fragariaxananassa. Duch. Int. J. Agric. Res. 2006, 1, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smedt, C.; Steppe, K.; Spanoghe, P. Beneficial effects of zeolites on plant photosynthesis. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2017, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, R.; Nawaz, A.; Ejaz, S.; Ali, S.; Saleem, M.S.; Hammad, H.M. Zeolite amendment reduces lead accumulation and improves growth and yield in tomato plants irrigated with sewage water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 41970–41982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Song, S.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y. Effects of mixed corn stalk substrates on growth and photosynthesis of tomato seedlings. Acta Hortic. 2018, 1227, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.S.; Mahmoud, A.M. Response of Adansonia digitata to compost and zeolite in replacement of chemical fertilization. Am.-Eurasian J. Agri. Environ. Sci. 2013, 13, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, F. Role of nitrogen (N) in plant growth, photosynthesis pigments, and N use efficiency: A review. Agrisost 2022, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sönmez, İ.; Kaplan, M.; Demır, H.; Yilmaz, E. Effects of zeolite on seedling quality and nutrient contents of tomato plant (Solanum lycopersicon cv. Malike F1) grown in different mixtures of growing media. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2010, 8, 1162–1165. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/266169406_Effects_of_zeolite_on_seedling_quality_and_nutrient_contents_of_tomato_plant_Solanum_ (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Assimakopoulou, A.; Dimitroulia, D.; Kosmidis, S.; Doula, M.K. Growth, yield and nutrient status of pepper plants grown on a soil substrate with olive mill waste sludge and natural zeolite addition. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankauskienė, J.; Brazaitytė, A.; Vaštakaitė Kairienė, V.; Zalatorius, V. Effects of peat and peat-zeolite substrates on quality, growth indices of cucumber seedlings and crop productivity. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2019, 18, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzistathis, T.; Tsaniklidis, G.; Papaioannou, A.; Koukounaras, A. Comparative Approach on the Effects of Soil Amendments and Controlled-Release Fertilizer Application on the Growth, Nutrient Uptake, Physiological Performance and Fruit Quality of Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Plants. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandapaka, M.; Murthy, A.N.G.; Shanker, A.K. Nitrogen Nutrition in Crops and Its Importance in Crop Quality. In The Indian Nitrogen Assessment; Abrol, Y.P., Adhya, T.K., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzarano, F.; Valentini, G.; Arfelli, G.; Seghetti, L.; Manetta, A.C.; Metruccio, E.G.; Di Marco, S. Activity of Italian natural chabazite-rich zeolitites against grey mould, sour rot and grapevine moth, and effects on grape and wine composition. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2019, 58, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lija, M.; Haruna, A.O.; Kasim, S. Maize (Zea mays L.) nutrient use efficiency as affected by formulated fertilizer with Clinoptilolite Zeolite. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2014, 26, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekian, R.; Abedi, K.J.; Eslamian, S.S. Influences of clinoptilolite and surfactant-modified clinoptilolite zeolite on nitrate leaching and plant growth. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leggo, P. An investigation of plant growth in an organo-zeolitic substrate and its ecological significance. Plant Soil. 2000, 219, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S. The effect of different substrates on the vegetative, productivity characters and relative absorption of some nutrient elements by the tomato plant. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2011, 5, 3091–3096. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/288408957_The_effect_of_different_substrates_on_the_vegetative_productivity_characters_and_relative_absorption_of_some_nutrient_elements_by_the_tomato_plant (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Berar, V.; Poşta, G. Research concerning the zeolites influence, used in the culture substratum, upon the quality of greenhouse grown tomato. J. Hortic. For. Biotech. 2011, 5, 45–47. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/77333090/Researches_Concerning_the_Use_of_Zeolites_in_the_Culture_Substrate_of_Tomatoes_in_Greenhouses (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Bozorgi, H.R.; Bidarigh, S.; Azarpour, E.; Danesh, R.K.; Moraditochaee, M. Effects of natural zeolite application under foliar spraying with humic acid on yield and yield components of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Int. J. Agri. Crop Sci. 2012, 4, 1485–1488. Available online: https://www.internationalscholarsjournals.com/archive/ijas-volume-2-issue-4-year-2012.html (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Bernardi, A.C.C.; Oliveira, P.P.A.; Monte, M.B.M.; Barros, F. Brazilian sedimentary zeolite use in agriculture. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 167, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girijaveni, V.; Sammi Reddy, K.; Srinivasarao, C.H.; Raju, B.M.K.; Balakrishnan, D.; Sumanta Kundu, S.; Pushpanjali Rohit, J.; Singh, V.K. Role of mordenite zeolite in improving nutrient and water use efficiency in Alfisols. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1404077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, K.; Biswas, A.K.; Somasundaram, J. Nanoporous zeolites in farming: Current status and issues ahead. Curr. Sci. 2010, 99, 760–764. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285535061_Nanoporous_zeolites_in_farming_Current_status_and_issues_ahead (accessed on 1 December 2025).
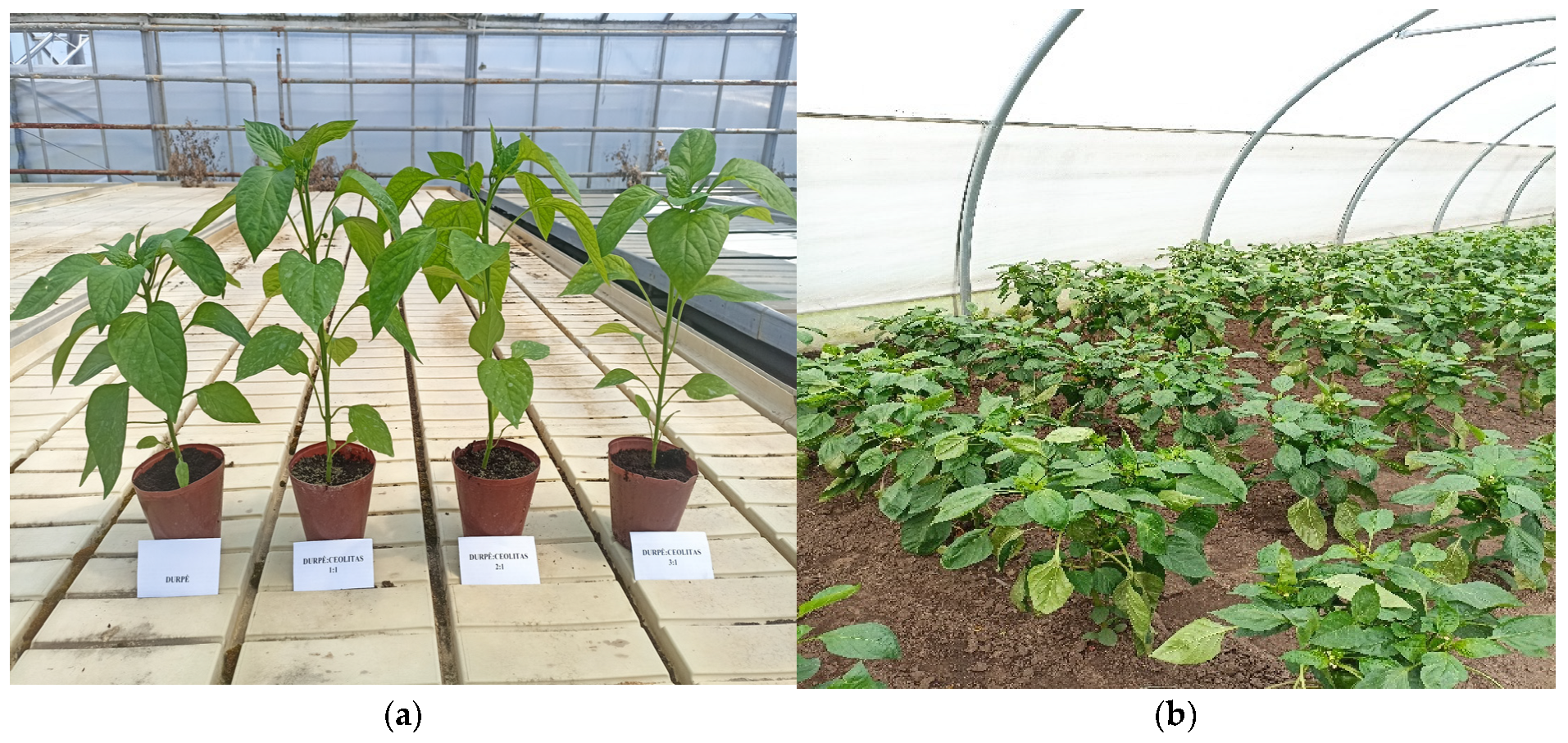

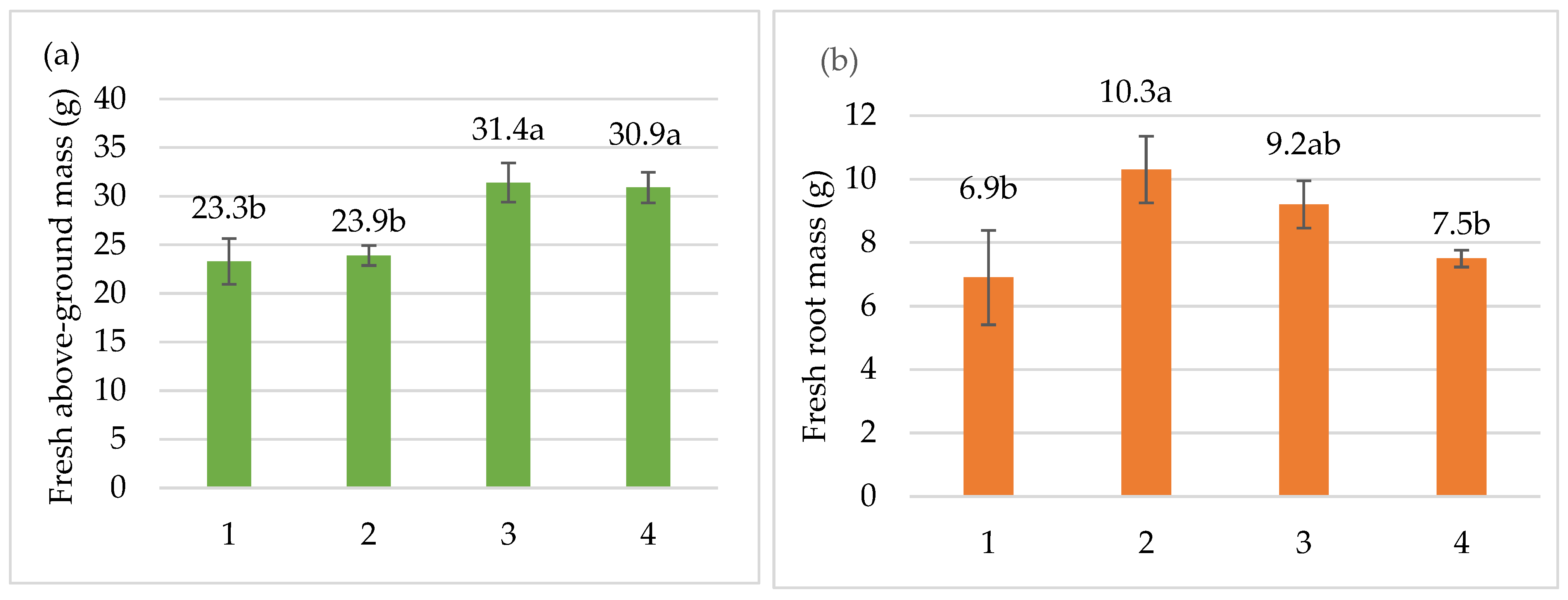
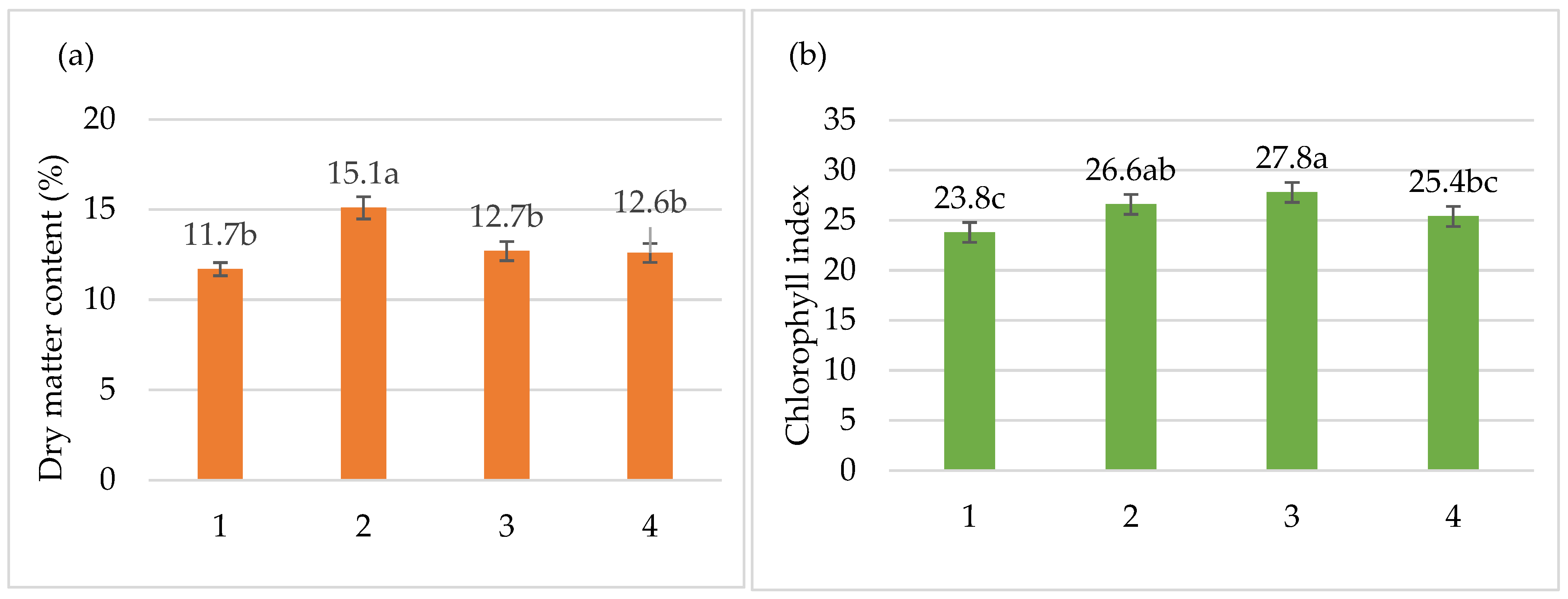

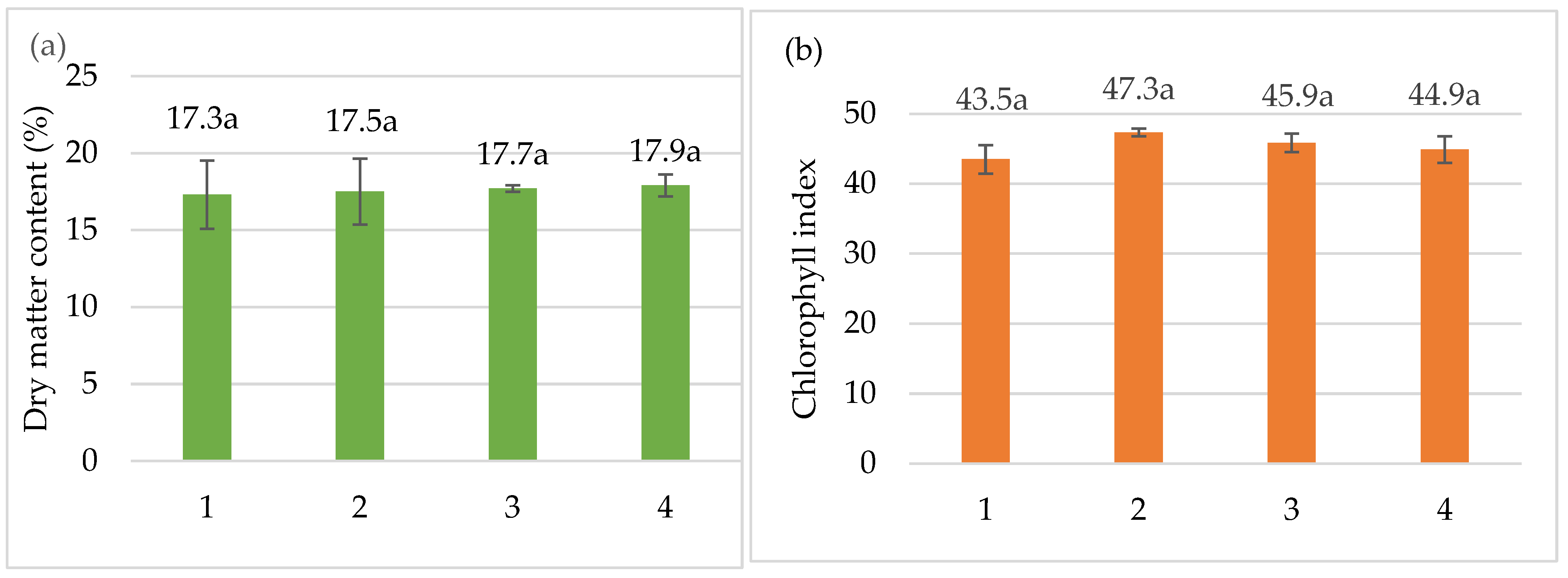
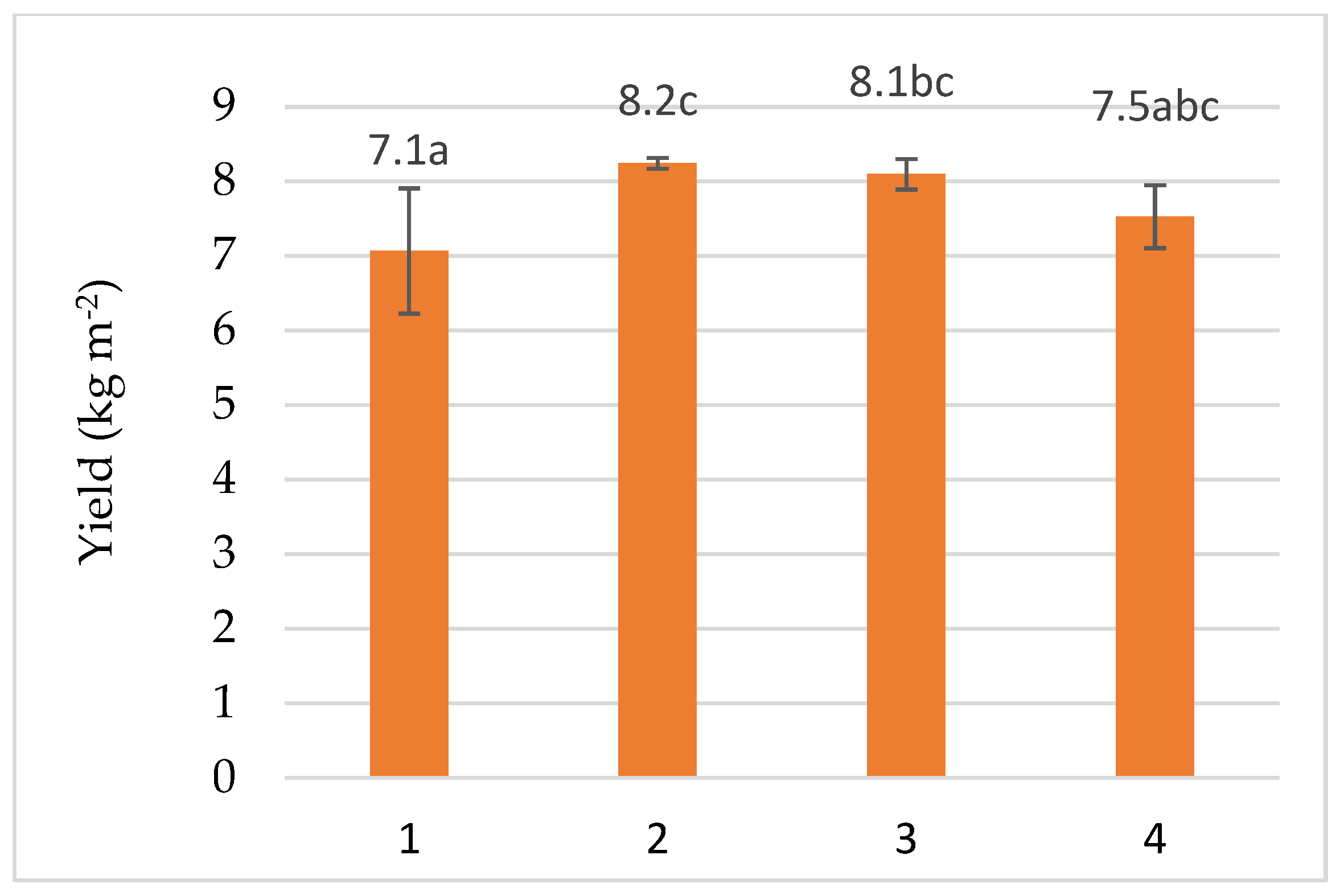
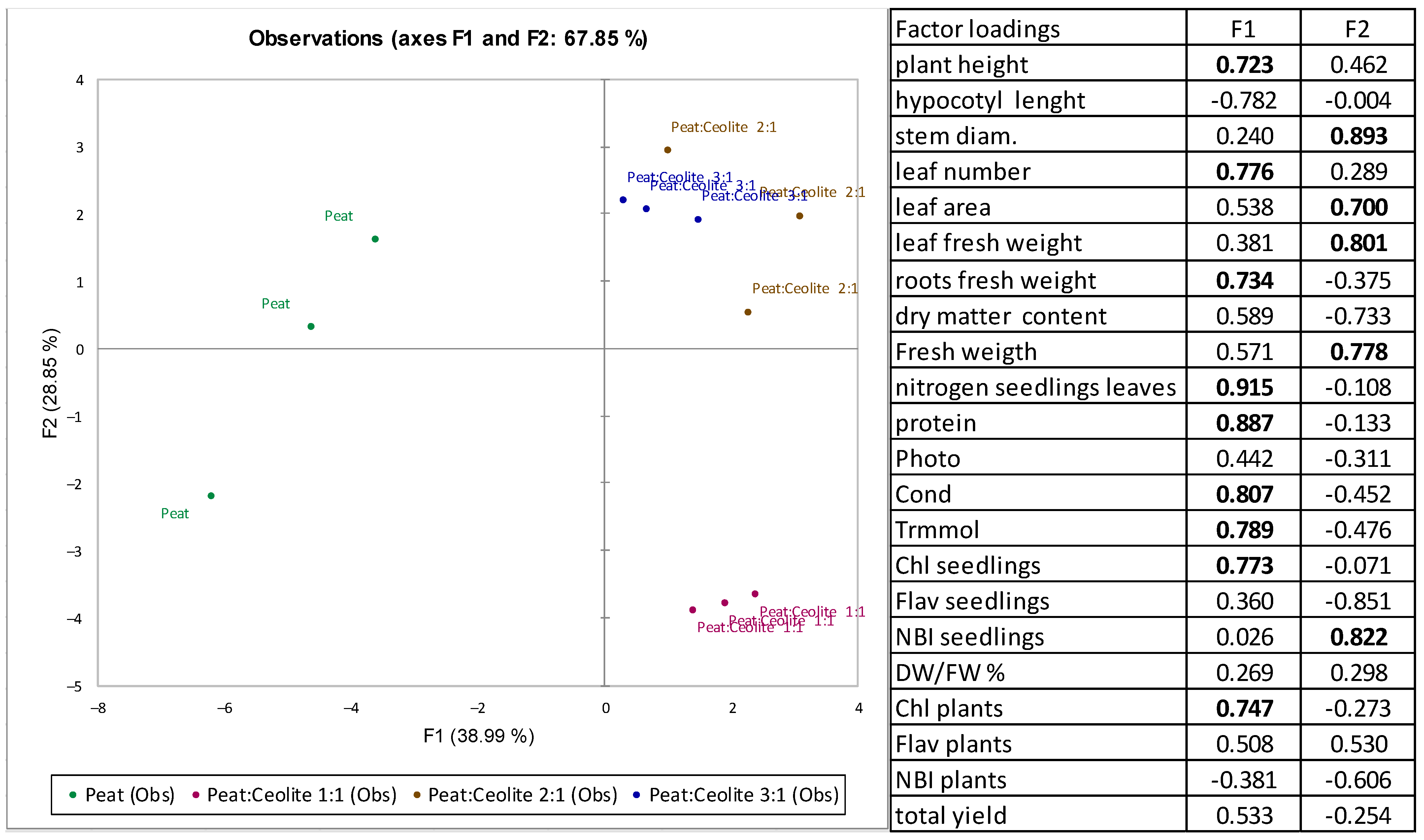
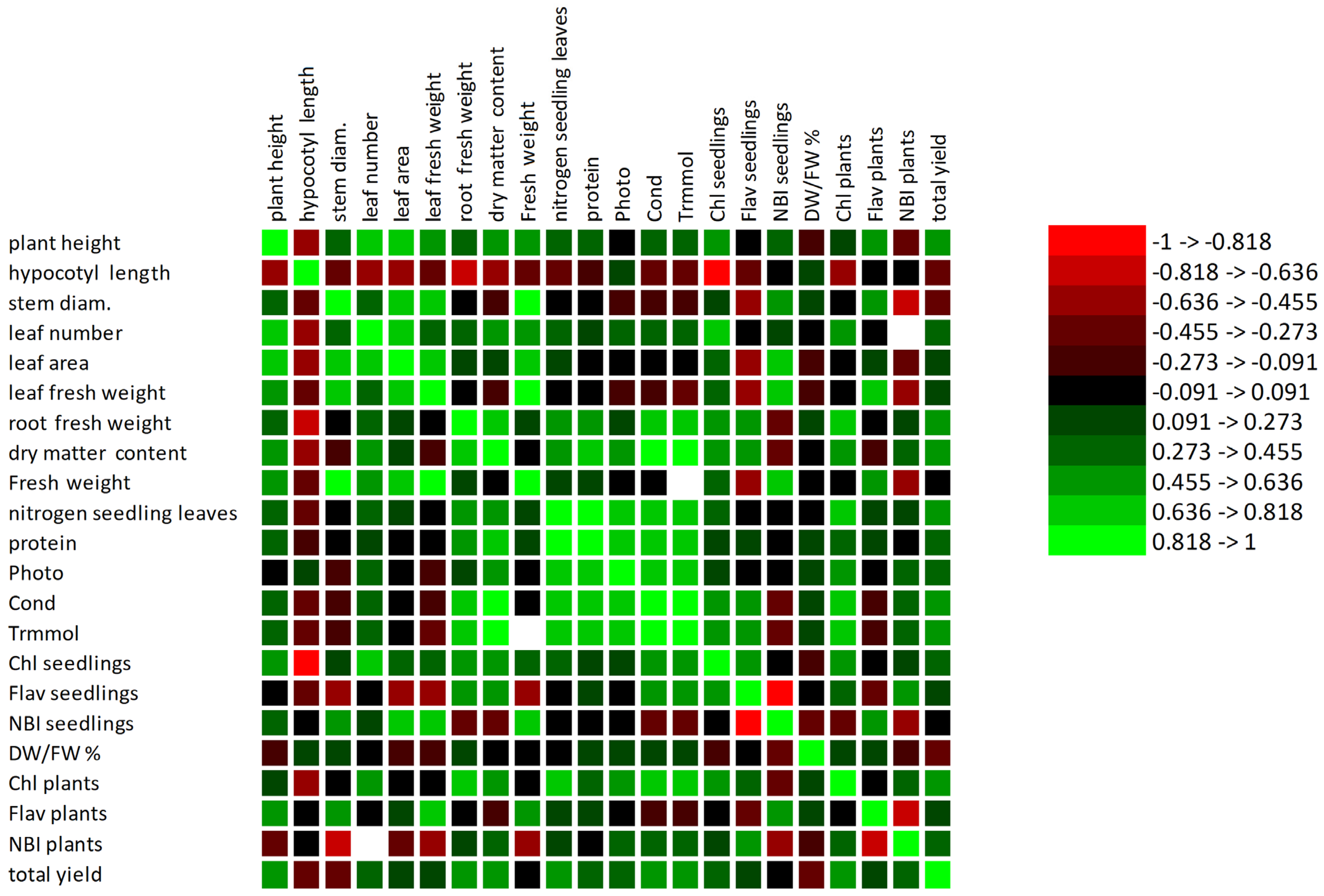
| Treatments | Plant Height, (cm) | Hypocotyl Length, (cm) | Stem Diameter, (mm) | Number of Leaves, (Unit) | Leaf Area, (cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peat | 30.13 ± 0.92 b | 2.91 ± 0.28 a | 5.73 ± 0.37 a | 13.82 ± 0.35 b | 597.94 ± 96.01 b |
| Peat+zeolite 1:1 | 33.27 ± 1.09 ab | 2.48 ± 0.07 bc | 5.55 ± 0.03 a | 14.67 ± 0.90 ab | 612.29 ± 47.83 b |
| Peat+zeolite 2:1 | 37.48 ± 0.14 a | 2.30 ± 0.10 c | 6.11 ± 0.26 a | 15.18 ± 0.31 a | 770.95 ± 25.60 a |
| Peat+zeolite 3:1 | 35.74 ± 3.27 a | 2.77 ± 0.12 ab | 6.03 ± 0.16 a | 15.10 ± 0.10 ab | 774.98 ± 5.09 a |
| Treatments | Photosynthetic Rate, (µmol CO2 m−2 s−1) | Stomatal Conductance, (H2O mol m −2 s−1) | Transpiration Rate, (mmol H2O m−2 s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peat | 8.39 ± 1.390 a | 0.005 ± 0.006 b | 0.08 ± 0.105 b |
| Peat+zeolite 1:1 | 9.83 ± 0.263 a | 0.04 ± 0.004 a | 0.57 ± 0.060 a |
| Peat+zeolite 2:1 | 8.80 ± 0.453 a | 0.03 ± 0.012 a | 0.37 ± 0.163 ab |
| Peat+zeolite 3:1 | 9.96 ± 0.803 a | 0.03 ± 0.008 a | 0.38 ± 0.118 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jankauskienė, J.; Laužikas, V.; Laužikė, K. Effect of Peat-Zeolite Substrates Used During Seedling Cultivation on the Growth, Physiology, and Yield of Sweet Peppers. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11121465
Jankauskienė J, Laužikas V, Laužikė K. Effect of Peat-Zeolite Substrates Used During Seedling Cultivation on the Growth, Physiology, and Yield of Sweet Peppers. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(12):1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11121465
Chicago/Turabian StyleJankauskienė, Julė, Vitalis Laužikas, and Kristina Laužikė. 2025. "Effect of Peat-Zeolite Substrates Used During Seedling Cultivation on the Growth, Physiology, and Yield of Sweet Peppers" Horticulturae 11, no. 12: 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11121465
APA StyleJankauskienė, J., Laužikas, V., & Laužikė, K. (2025). Effect of Peat-Zeolite Substrates Used During Seedling Cultivation on the Growth, Physiology, and Yield of Sweet Peppers. Horticulturae, 11(12), 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11121465








