Abstract
As a typical sucrose-accumulating fruit, longan commonly experiences sugar receding during on-tree preservation, leading to quality deterioration. To investigate the mechanism of sucrose degradation in longan fruit, we conducted genome-wide identification and analysis of key genes involved in sucrose synthesis and catabolism based on the ‘Shixia’ (SX) genome. The results revealed that longan contained 8 sucrose synthases (SUSs), 4 sucrose phosphate synthases (SPSs), and 26 invertases (INVs). Notably, members of the longan SUS, SPS, and cell wall invertase (CWINV) families all contained the motif 10 sequence, while cytoplasmic invertase (CINV) members exhibited diverse motif combinations. Similarity analysis revealed that sequence similarity was reliable only when the sequence lengths of the compared genes were comparable. Cis-acting elements and miRNA prediction showed that these genes were enriched in MYB elements and regulated by miR156/827/171. Additionally, the expansion of SUS, SPS, and INV genes was driven by segmental duplication events under purifying selection. Furthermore, the ‘Chuliang’ (CL) cultivar exhibited slower on-tree sucrose degradation than SX, with sucrose accounting for 72.2% of total sugars at maturity, which is 33.4% higher than SX. Enzyme activity assay during the sucrose decline stage revealed that SUS, SPS, and INV activities were generally higher in SX pulp than in CL. Furthermore, correlation analysis showed that the activities of AINV and A/N-INV were both significantly negatively correlated with TSS and sucrose content, respectively. Additionally, the expression of DlCWINV10 exhibited a negative correlation with TSS (p < 0.05) and sucrose content (r = −0.6, p = 0.07), suggesting that DlCWINV10 may play an important role in the sucrose degradation process. In summary, this study elucidates the characteristics of SUS, SPS, and INV gene families in longan and their potential roles in sucrose metabolism, providing a theoretical foundation for understanding the on-tree sucrose degradation mechanism.
1. Introduction
Longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.), as a typical subtropical and tropical fruit, is widely cultivated in Southeast Asia and other regions. Its fruit is rich in sugar, various vitamins, and antioxidant compounds, serving both as a fresh food and for medicinal purposes, making it highly popular among consumers [1]. However, whether during postharvest storage or on-tree preservation, longan fruit commonly experiences a rapid decline in sugar content after ripening, leading to quality deterioration and significant economic losses [2,3]. As a sucrose-accumulating fruit, sucrose metabolism is the core physiological process determining the sweetness, quality, and preservation of longan fruit [4]. Therefore, investigating the key enzymes involved in sucrose synthesis and catabolism in longan holds significant scientific and practical value.
Sucrose, the primary product of plant photosynthesis, serves as the main carbon transport form between source and sink organs, with its metabolism involving two key processes: synthesis and degradation [5]. In source organs, SPS catalyzes the reaction of UDP-glucose with fructose-6-phosphate to produce sucrose-6-phosphate, which is subsequently dephosphorylated by sucrose phosphate phosphatase to form free sucrose. Notably, SPS acts as the pivotal enzyme in sucrose synthesis [5,6]. The sucrose degradation pathway comprises two principal mechanisms: (1) INV-mediated hydrolysis of sucrose into glucose and fructose [5] and (2) SUS-catalyzed cleavage of sucrose into UDP-glucose and fructose using UDP, a reaction that predominantly occurs in sink organs such as fruit, seeds, and tubers. Importantly, this SUS-catalyzed reaction is reversible, meaning SUS can also facilitate sucrose synthesis under specific conditions [5,7].
Different protein families are typically distinguished by their conserved domains. SUS proteins generally contain two core structural domains: glycosyl transferase group 1 and sucrose synthase. Phylogenetic analysis reveals that the SUS gene family has already formed three major evolutionary clades (Groups I–III) prior to the divergence of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants [8]. The SPS gene family encodes proteins that not only share the conserved domains of SUS but also possess a highly conserved sucrose-6F-phosphate phosphohydrolase domain. The SPS gene family exhibits significant evolutionary diversity in plants. In dicots, SPS is classified into three subfamilies (A, B, and C), whereas in monocots (e.g., Poaceae), an additional subfamily D has emerged [9,10]. INV are classified based on their optimal pH for enzyme activity into acid invertase (AINV) and neutral/alkaline invertase (A/N-INV). Furthermore, they are also categorized by their subcellular localization into CWINV, vacuolar invertase (VINV), and CINV. Typically, CWINV and VINV are classified as AINV, while CINV belongs to A/N-INV. Structurally, AINV and A/N-INV are members of the glycoside hydrolase family 32 and glycoside hydrolase family 100, respectively [11].
Sucrose serves not only as a primary storage substance that influences fruit and vegetable quality, but also functions as a signaling molecule regulating plant growth, development, and stress responses [6]. SUS, SPS, and INV are key enzymes that regulate sucrose synthesis and degradation, directly affecting the dynamics of sugar accumulation. The phylogenetic relationship, expression pattern, and functional diversification of their gene family members have garnered considerable attention in recent years. With the advancement of whole-genome sequencing technology, systematic identification of SUS, SPS, and INV gene families in multiple species has provided new perspectives for elucidating their biological functions [7,12]. The number of gene family members and their functions in key sucrose metabolic enzymes exhibit diversity across different plant species. For instance, the SUS gene family in tobacco [13], Arabidopsis [14], rice [15], and tomato [16] contains 14, 6, 6, and 6 members, respectively, and is associated with sucrose degradation and stress. Gene expression analysis indicates that Ntab0259170 and Ntab0259180 play major roles in sucrose metabolism during tobacco leaf development. The expression of Ntab0288750 and Ntab0234340 is significantly induced under low temperature and virus treatment [13]. Furthermore, AtSUS1/4 maintains root metabolism under hypoxia [14]. This suggests that SUS plays a crucial role in the increased glycolysis during abiotic and biotic stresses.
The SPS gene family has been identified to contain four members in Arabidopsis [9], five members in wheat [10], seven members in apple [16], and four members in tomato [12], and these members are associated with sucrose synthesis and stress responses. For instance, MdSPSA2.3 in apple regulates fruit sucrose accumulation [16]. Under stress treatments with PEG, NaCl, H2O2, ABA, and SA, SlSPS3 in tomato is down-regulated in leaves during early stress stages, while SlSPS1 is significantly up-regulated in roots, indicating the involvement of SPS in stress responses [12].
INV family members in tobacco [17], Arabidopsis [18,19], and tomato [12] are comprised of 36 (20 CINVs, 4 VINVs, and 12 CWINVs), 17 (9 CINVs, 2 VINVs, and 6 CWINVs), and 19 (8 CINVs, 2 VINVs, and 9 CWINVs) members, respectively, participating in sucrose degradation, stress responses, and growth and development. For instance, the inhibition of NtNINV10 expression reduces glucose and fructose content in tobacco leaves. Furthermore, NtNINV, NtVINV, and NtCWINV respond to various stresses and hormone treatments [17]. In tomato, SlINVVR1 is highly expressed in multiple tissues (e.g., parenchyma, fruit) and may influence fruit ripening and sugar metabolism, while SlINVAN5 and SlINVAN7 are generally down-regulated under stress, potentially by inhibiting sucrose degradation to conserve energy [12]. Overall, these enzymes play crucial roles in plant development, adaptation to adversity, and agronomic traits by regulating sugar metabolic balance.
As a sucrose-accumulating fruit, longan exhibits sugar degradation during both postharvest storage and on-tree preservation, particularly in the latter process, which provides excellent experimental material for studying fruit sugar degradation. However, there have been no reports on genome-wide identification and expression analysis of key enzymes (SUS, SPS, and INV) involved in sucrose metabolism in longan to date. Therefore, identifying the gene family members of key sucrose-metabolizing enzymes in longan and analyzing their conserved motifs, physicochemical properties, evolutionary relationships, promoter cis-acting elements, gene expression patterns, and enzymatic activities is of great significance. This research helps uncover critical genes involved in sugar metabolism in longan fruit and lays a molecular foundation for addressing sugar degradation issues and extending shelf life.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of SUS, SPS, and INV in Longan
The SX longan genome was downloaded from the SapBase database [20]. Simultaneously, protein sequences for members of the SUS, SPS, and INV gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana were obtained from the Tair database. HMM files for SUS (PF00534 and PF00862), SPS (PF00534, PF00862, and PF05116), and INV (CWINV: PF00251 and PF08244; VINV: PF00251, PF08244, and PF11837; and CINV: PF12899) families were downloaded from the Pfam database (http://pfam.xfam.org/). Candidate genes were identified through BLAST (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 14 January 2025)) and HMMER (v3.4) searches performed using TBtools [21]. Subsequently, these candidate genes were subjected to conserved domain confirmation using Pfam (https://pfam.xfam.org/ (accessed on 11 February 2025)), SMART (https://smart.embl.de/ (accessed on 12 February 2025)), and NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 12 February 2025)) domain searches to obtain the final members of the longan SUS, SPS, and INV gene families. The conserved domains of these identified genes were then visualized using TBtools (v2.030) software.
2.2. Bioinformatic Characterization of SUS, SPS, and INV Family Members
The gene structures, CDS similarity, collinearity, and Ka/Ks analyses of the longan SUS, SPS, and INV family members were all performed using the TBtools software. Phylogenetic analysis was constructed using MEGA 12.0, with alignments performed in ClustalW mode. For Maximum Likelihood tree construction, the Adaptive Bootstrap (fast) mode was employed with a bootstrap value of 100. Finally, the resulting phylogenetic trees were beautified using Chiplot (https://www.chiplot.online/ (accessed on 23 February 2025)). Conserved motifs were predicted using the MEME (https://web.mit.edu/meme/current/share/doc/overview.html (accessed on 12 February 2025)) website and visualized with TBtools. Further, the number of motifs was set to 15, and all other parameters remained default settings. Physicochemical properties were calculated using the Expasy (https://web.expasy.org (accessed on 14 February 2025)) website, while transmembrane domains and signal peptides were predicted by TMHMM-2.0 and SignalP-6.0, respectively. Subcellular localization was predicted using Cell-PLoc 2.0. Cis-acting elements were predicted using the PlantCARE (https://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/ (accessed on 18 February 2025)) website and visualized with TBtools and Origin 21.0. Using the longan SUS, SPS, and INV gene family members as target genes, upstream miRNA regulatory genes were predicted by selecting the longan miRNA library from the SapBase database.
2.3. Determination of TSS and Sugar Content
Fresh fruits of the fast sugar receding cultivar ‘Shixia’ and the slow sugar receding cultivar ‘Chuliang’ longan [4] were selected as experimental materials. Fruits at different stages were harvested from Hejie Orchard in Hezhou city, Guangxi Province, and transported to the laboratory within 1 h. Fruits were collected from 15-year-old longan trees, with three trees per cultivar. To cover developmental, maturity, and sugar receding stages (on-tree preservation), sampling was conducted on 24 July (S1, 240 fruit), 13 August (S2, 180 fruit), 27 August (S3, commercial maturity stage, 150 fruit), 10 September (S4, 150 fruit), and 24 September (S5, 150 fruit), 2023, for each cultivar, using total soluble solids (TSS) content as the reference indicator. Additionally, the collected fruits from the three trees were placed in one bag. The arils were separated, flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen, and immediately stored at −80 °C for subsequent assays.
TSS content (%) was measured using a handheld refractometer (ATAGO, Tokyo, Japan). Fresh longan pulp powder was used to determine the sugar contents (mg·g−1) of sucrose, glucose, and fructose. The procedures were conducted as described in our previous study [2], including the use of the HPLC system, column, mobile phase, and flow rate. Specifically, the Waters SugarPak1 column (Waters, MA, USA) was used for sugar quantification, with ultra-pure water as the mobile phase. The injection volume was 10 µL, and the flow rate was 0.6 mL min−1. A refractive index detector was employed for detection, with no specific detection wavelength. The calibration curves for sucrose, glucose, and fructose were as follows: sucrose: y = 0.0000079911x + 0.0524386820 (R2 = 0.9966), glucose: y = 0.0000077454x + 0.0119526238 (R2 = 0.9998), and fructose: y = 0.0000070367x − 0.0006726081 (R2 = 0.9999). The contents detection range for all three sugars was from 0.01 to 1 mg·mL−1.
2.4. Determination of SUS, SPS, AINV, and A/N-INV Activity
The extraction and activity determination of SUS, SPS, AINV, and A/N-INV followed our previously published methods for longan aril analysis [2]. One unit (U) of enzyme activity was defined as the amount of sucrose or glucose generated by tissue protein per minute. All enzyme activities were expressed as U·g−1.
Enzyme extraction from longan aril was performed using a buffer containing 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mm EDTA, 2.5 mm DTT, 0.05% Triton X-100, 0.5 g·L−1 BSA, and 10% glycerol (Shanghai Yuanye Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). The powder was mixed with the buffer and centrifuged at 13,000× g for 15 min at 4 °C to obtain the supernatant. One milliliter aliquot of the supernatant was used to remove sugar via a PD-10 column. Finally, the collected rinse solution was the crude enzyme extract.
AINV activity was assessed by incubating 0.3 mL of crude extract with 0.7 mL of 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) containing 1% sucrose, 5 mM MgCl2, and 1 mm EDTA at 34 °C for 1 h. The reaction was terminated by adding 2.0 mL of 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid, followed by boiling for 5 min. Absorbance was measured at 540 nm. A/N-INV activity was measured similarly, with 0.1 M acetate buffer (pH 5.5) replacing the phosphate buffer.
SUS activity was determined by incubating 0.1 mL of crude extract with 0.1 mL of reaction solution (80 mm MES buffer, pH 5.5, 5 mm NaF, 100 mm sucrose, and 5 mm UDP) at 37 °C for 3 h. Glucose production was quantified using the DNS method.
SPS activity was assessed by incubating 0.1 mL of crude extract with 0.1 mL of reaction solution (100 mm Hepes–NaOH, pH 8.0, containing 10 mm UDP-glucose, 5 mm fructose-6-phosphate, 15 mM glucose-6-phosphate, 15 mm MgCl2, and 1 mm EDTA) at 34 °C for 1 h. The reaction was terminated with 0.2 mL of 30% KOH, followed by boiling for 10 min. After cooling, 3.5 mL of anthrone solution (0.15 g anthrone in 100 mL 81% sulfuric acid) was added to the reaction mixture, and sucrose production was determined.
2.5. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) Assay
Total RNA was extracted using the FastPure® Universal Plant Total RNA Isolation Kit (Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China), with RNA quality verified by 1.0% agarose gel electrophoresis. First-strand cDNA synthesis was carried out using the HiScript® Ⅲ 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Nanjing Novogene Bioinformatics Technology Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China). The qRT-PCR experiment was conducted following our previous methods [2]. Gene-specific primers were designed using TBtools software based on the SX longan genome database. Primer sequences are listed in Table S1.
2.6. Data Analysis
All experiments were conducted with three replicates. Data significance analysis was performed using the Dunn–Sidak method, and graphical plotting was completed with Origin 21.0 software. Correlation analysis was performed using the Pearson method on the Chiplot website. Asterisks *, **, and *** denote significant differences at p ≤ 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001, respectively, between different cultivars at the same time point.
3. Results
3.1. SUS, SPS, and INV Family Members and Phylogenetic Analysis
Using the SX longan genome as a reference database, a total of 8 DlSUS, 4 DlSPS, and 26 DlINV (DlCINVs: 14, DlVINVs: 2, and DlCWINVs: 10) sucrose metabolism genes were identified through conserved domain confirmation (Figure 1C), which were named DlSUS1-DlSUS8, DlSPS1-DlSPS4, DlCINV1-DlCINV14, DlVINV1-DlVINV2, and DlCWINV1-DlCWINV10, respectively. Within the SUS family, all members except DlSUS6 possessed a sucrose synthase N-terminal domain. Intraspecies phylogenetic analysis (Figure 1A) revealed that the SUS, SPS, and INV gene families in longan were distinctly separated, with SUS and SPS families exhibiting closer evolutionary relationships. Among the INV family, CWINV and VINV subgroups shared greater phylogenetic affinity. Gene structure visualization analysis (Figure 1B) demonstrated that, compared to INV family members, SUS and SPS gene family members in longan generally contained more exons, with relatively uniform distribution. Similarly, CWINV and VINV subgroup members showed comparable exon numbers. Among INV subgroups, CWINV and VINV members showed comparable exon numbers, whereas striking structural diversity was observed in the CINV family. Specifically, DlCINV6 contained only one exon, while DlCINV14 comprised 10 exons. This variation may reflect their functional differentiation and adaptability to different physiological processes.
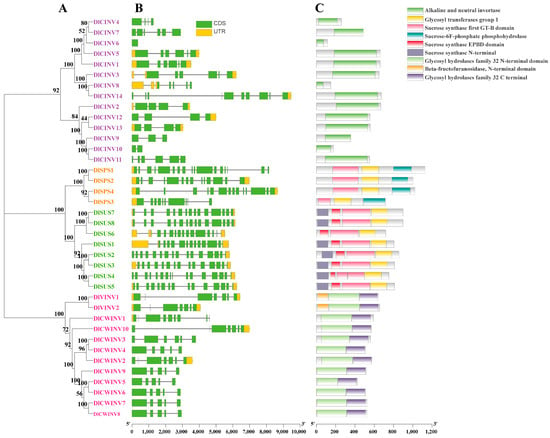
Figure 1.
Phylogeny (A), gene structure (B), and conserved domains (C) of SUS, SPS, and INV family members in longan.
The MEME conserved motif analysis (Figure 2) revealed that all members of the longan SUS family contained motifs 10/6/15/9/3. Additionally, DlSUS6/7/8 possessed an extra motif 6 at the C-terminus. Members of the SPS family universally harbored motifs 10/9/3, suggesting their potential evolutionary divergence from the SUS family. All members of the CWINV family contained motifs 10/8/5/4/7. Meanwhile, the VINV family members shared motifs 8/5/7 with the CWINV family, with DlVINV1 additionally containing motif 10 and DlVINV2 containing motif 4. Regarding CINV members, DlCINV5/1/3/14/2/12/13/11 all carried motifs 12/13/1/6/14/2/11, while other CINV members possessed one or multiple of these motifs. Significantly, motif 10 was conserved in the SUS, SPS, and CWINV families, as well as in DlVINV1, highlighting potential functional or evolutionary connections among these enzyme families.
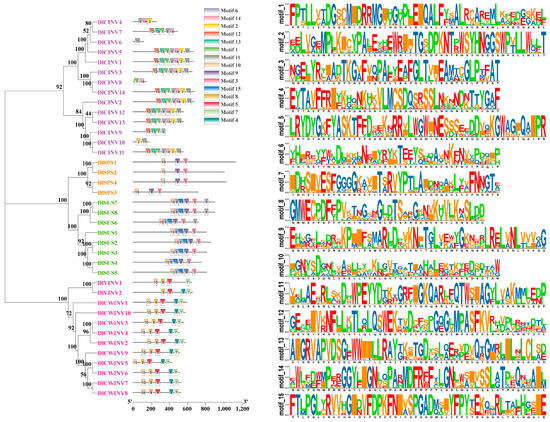
Figure 2.
Conserved motifs of SUS, SPS, and INV family members in longan.
To gain a better understanding of the phylogeny of longan SUS, SPS, and INV gene family members, phylogenetic trees were constructed with tomato and Arabidopsis. Figure 3 shows that the SUS family members were divided into three subfamilies: I, II, and III. The SPS family members were classified into three subfamilies: A, B, and C. The INV family members were clearly separated into two major branches: CINV and the combined CWINV-VINV subgroups. Following the classification by Duan et al. [12], DlSUS1 belonged to the SUS subfamily I, DlSUS2/3/4/5 were members of the SUS subfamily II, and DlSUS6/7/8 constituted the SUS subfamily III. In the SPS family, DlSPS1/2 were members of the SUS subfamily A, DlSPS3 belonged to the SUS subfamily B, and DlSPS4 was part of the SUS subfamily C. Notably, DlSPS3 and DlSPS4 exhibited closer evolutionary relationships. Within the INV family, VINV and CWINV were grouped into a single major branch. However, VINV members did not exhibit a dispersed or interspersed pattern within the CWINV members. Specifically, DlVINV1 showed a closer relationship with SlINVVR1, while DlVINV2 was more closely related to SlINVVR2 and AtVINVs. DlCWINV1, DlCWINV10, and DlCWINV2-9 independently formed three distinct small branches. CINV formed an independent major branch, which was further divided into two small branches. DlCINV2/12/13/9/10/11 formed one lineage, and DlCINV8/14/3/1/4/7/5/6 constituted another lineage.
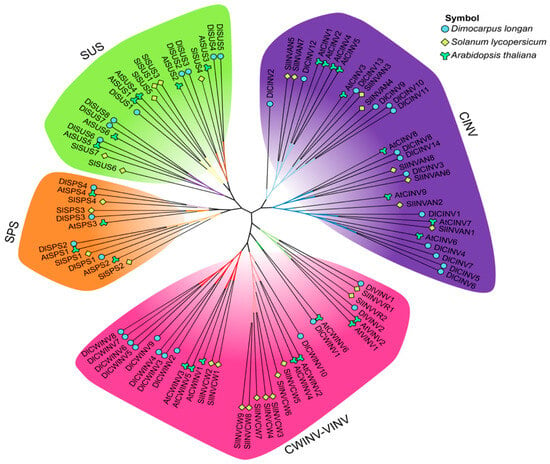
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of SUS, SPS, and INV family members in longan, tomato, and Arabidopsis. Gene names and corresponding IDs for tomato are consistent with Duan et al. [12]. Arabidopsis members are detailed in Table S2.
3.2. Similarity and Physicochemical Properties Analysis
To understand the similarity among members of the longan SUS, SPS, and INV gene families for better selection of key genes for future functional validation, we performed a similarity analysis on their CDS sequences. The results presented in Figure 4 indicate that the similarities between DlSUS7 and DlSUS8, DlSUS2 and DlSUS3, and DlSUS4 and DlSUS5 reached 99.9%, 94.5%, and 87.3%, respectively. Notably, the CDS sequence of DlSUS3 was entirely a part of DlSUS2 (Figure S1). The similarities between DlCWINV8 and DlCWINV7, DlCWINV6, and DlCWINV9 were 97.8%, 91.6%, and 89.6%, respectively. Furthermore, DlCWINV7 showed similarities of 91.1% and 89.7% with DlCWINV6 and DlCWINV9, respectively, while the similarity between DlCWINV6 and DlCWINV9 was 89.9%. Although the sequence similarity between DlCWINV8 and DlCWINV5 was only 76.4%, the CDS sequence of DlCWINV5 was almost entirely contained within DlCWINV8, with only 1–2 base differences scattered at different positions (Figure S4). A similar situation was observed between DlCINV10 and DlCINV11, with only 31.2% similarity between them (Figure S3). The similarity between DlCINV6 and DlCINV5 was only 17.0%; however, aside from the initial 13 differing bases at the beginning of DlCINV6, the remaining sequence was identical to DlCINV5 (Figure S2).
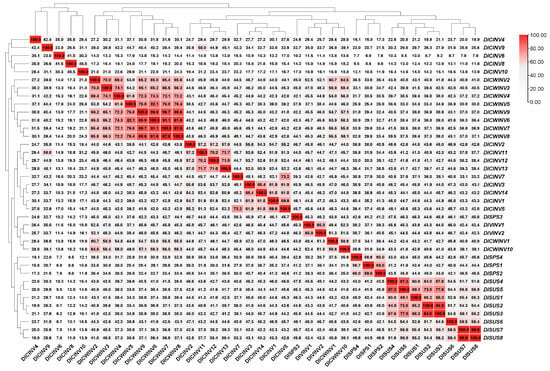
Figure 4.
CDS sequence similarity matrix of SUS, SPS, and INV gene family members in longan. Note: The matrix displays the pairwise sequence similarity of the CDS for the SUS, SPS, and INV gene family members in longan. Each cell in the matrix represents the similarity percentage between two gene family members, with darker colors indicating higher sequence similarity.
To better infer the biological functions of the longan SUS, SPS, and INV family members, their physicochemical and other properties were predicted. The gene ID results showed that DlSUS1-3, DlSPS1-3, DlCWINV1, and DlCINV1 were located on chromosome (Chr) 1. DlCWINV2-9 was located on Chr 3. DlSUS4/5 and DlCINV2/3 were located on Chr 4. DlCINV4-7 was located on Chr 5. DlCINV8 was located on Chr 7. DlSUS6 and DlVINV1 were located on Chr 8. DlSPS4 and DlCINV9-12 were located on Chr 9. DlCINV13, DlCINV14, and DlCWINV10 were located on Chr 11, 13, and 14, respectively. DlSUS7/8 and DlVINV2 were located on Chr 15 (Table 1).

Table 1.
Characteristic analysis of SUS/SPS/INV.
Furthermore, Table 1 shows that the protein molecular weights of longan SUSs ranged from 85.50 to 101.79 KDa, SPSs from 79.51 to 126.27 KDa, CINVs from 13.19 to 75.84 KDa, and CWINV-VINVs from 48.11 to 72.41 KDa. The theoretical isoelectric points of SUS, SPS, CINV, and CWINV-VINV proteins were between 5.89~8.05, 6.40~6.92, 5.17~8.71, and 5.10~9.54, respectively. Regarding the instability index, aliphatic index, and GRAVY, the values for SUS protein family members were 35.39~37.98, 85.04~97.63, and −0.32 to −0.10, respectively; for SPS family members, 43.92~48.22, 86.92~89.37, and −0.37 to −0.38; for CINV family members, 37.94~61.97, 79.32~107.33, and −0.34 to −0.01; and for CWINV-VINV family members, 28.05~41.21, 75.39~85.82, and −0.57 to −0.28. Notably, except for DlVINV1 and DlCWINV1, all CWINV-VINV and SUS family members were predicted to be stable proteins. In contrast, except for DlCINV1/5/6, the remaining CINV and SPS family members were unstable. Furthermore, all longan SUS, SPS, and INV family proteins exhibited negative GRAVY values, indicating an overall hydrophilic tendency.
Transmembrane domain prediction suggested that only DlSUS2/7/8, DlCINV4, DlVINV1/2, and DlCWINV2 possessed transmembrane helices (Table 1). Signal peptide analysis indicated that only DlCWINV1/2/3/10 contained signal peptides, with cleavage sites detailed in Table 1. Subcellular localization prediction showed that in the SUS and SPS families, all members were localized to the chloroplast, except for DlSUS6, which may reside in the chloroplast or cytoplasm. The CINV family exhibited diverse localization patterns: DlCINV3 and DlCINV11 may localize to the chloroplast or cytoplasm; DlCINV6 to the chloroplast, cytoplasm, or peroxisome; DlCINV8 and DlCINV9 to the nucleus; DlCINV10 to the cell membrane, chloroplast, cytoplasm, or nucleus; DlCINV14 to the cytoplasm or nucleus; and the remaining to the chloroplast. VINV and CWINV family members were predicted to localize to the vacuole and cell wall, respectively.
3.3. Collinearity and Ka/Ks Analysis
To investigate homologous gene segments within the same species or across different species, we performed collinearity analysis. The intraspecies collinearity results revealed that there were nine collinear gene pairs among SUS, SPS, and INV family members in longan, including DlSUS2/DlSUS3, DlSUS2/DlSUS5, DlSUS3/DlSUS4, DlSUS4/DlSUS5, DlSPS2/DlSPS1, DlCINV4/DlCINV7, DlCINV13/DlCINV11, DlCINV14/DlCINV3, and DlVINV2/DlVINV1, all of which were attributed to segmental duplication events (Table 2). Furthermore, Ka/Ks ratio calculations indicated that all gene pairs, except DlSUS2/DlSUS3, exhibited Ka/Ks values less than 1. However, we observed that both Ka and Ks values for the DlSUS2/DlSUS3 gene pair were 0, indicating that the gene duplication event occurred very recently.

Table 2.
Homologous gene pairs of SUS, SPS, and INV family members in longan and their Ka/Ks analysis.
The results of the collinearity analysis of SUS, SPS, and INV gene families in litchi, longan, and lemon revealed that there were 37 pairs of collinear genes between litchi and longan, and 63 pairs between longan and lemon (Figure 5). Specifically, between litchi and longan, DlSUS1/6/7/8 each had one pair; DlSUS2/3/5 each had two pairs; DlSPS1 and DlSPS2 each had two pairs, while DlSPS3 and DlSPS4 each had one pair; DlCINV1/2/5/7/9/12/13 each had one pair; DlCINV3/11/14 each had two pairs; DlCWINV1/2/9/10 each had one pair; and DlVINV1 and DlVINV2 each had two pairs. Between longan and lemon, DlSUS1 had two pairs located on lemon Chr 04A and 04B, respectively; DlSUS2 had four pairs on lemon Chr 05/09A and 05/09B, with DlSUS3/5 exhibiting the same syntenic pairs as DlSUS2. Additionally, DlSUS4 had one pair co-localized with DlSUS2 on lemon Chr 05A; DlSUS6 had two pairs; DlSPS1 had four pairs, sharing the same syntenic pairs as DlSPS2; DlSPS3 had two pairs; DlCINV1 and DlCINV2 each had two pairs; DlCINV3 and DlCINV14 shared identical syntenic pairs (four pairs each); similarly, DlCINV5 and DlCINV6 each had two pairs; DlCINV4 syntenic pairs coincided with DlCINV5 on Chr 03B; DlCINV12/13 each had two pairs; DlCINV10 had one pair; DlCWINV1/2/10 each had two pairs; and DlVINV1 and DlVINV2 shared identical syntenic pairs (four pairs each). These results indicate that DlSUS1/2/3/5/6, DlSPS1/2/3, DlCINV1/2/3/5/12/13/14, DlCWINV1/2/10, and DlVINV1/2 exhibit highly conserved gene segments in both sweet and sour fruit.
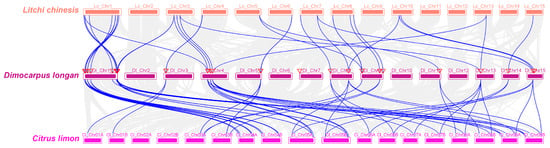
Figure 5.
Collinearity analysis of SUS, SPS, and INV gene family members among Dimocarpus longan, Litchi chinensis, and Citrus limon. Note: Gene family members are represented by colored lines, with each color corresponding to a specific species. Genes conserved across multiple species are connected by lines. The inverted triangle chart indicates that the chromosome contains members of the DlSUS, DlSPS, and DlINV gene families. The analysis was conducted using TBtools, and includes comparisons between litchi, longan, and lemon. The syntenic regions highlight the conserved gene order and structural relationships among the species.
3.4. Cis-Acting Elements Analysis
Prediction of cis-acting elements in a gene promoter region allows for the inference of the factors that may regulate it. The cis-acting elements of the longan SUS, SPS, and INV gene family members were primarily classified into four major categories: light-responsive (454 elements), biotic and abiotic stress (837 elements), phytohormone-responsive (421 elements), and plant growth and development (211 elements) elements (Figure 6B). Gene clustering based on the number of cis-elements revealed that members of each family grouped together (Figure 6A). Additionally, the promoter regions of SUS, SPS, and INV gene family members all contained numerous MYB elements. Furthermore, these promoter regions also harbored abundant Box 4, G-box, ARE (anaerobic induction), MYC, ABRE (abscisic acid), ERE (ethylene), and MeJA (methyl jasmonate) regulatory elements, indicating that the SUS, SPS, and INV gene family members are regulated by light, abiotic stress, and hormones. Figure 6B shows that DlCINV13 possessed the highest total number of cis-acting elements, followed by DlCINV12 and DlSUS4, while DlCWINV4 had the fewest, followed by DlCWINV8 and DlCWINV3. The gene with the most light-responsive elements was DlVINV1 (21 elements), while the fewest were found in DlCWINV5/6 and DlCINV6 (five elements each). For biotic and abiotic stress elements, DlCINV8 had the most (40 elements), whereas DlVINV1 and DlCINV5 had the fewest (12 elements each). The highest number of phytohormone-responsive elements was observed in DlCINV13 (38 elements), while DlCWINV4 had the fewest (four elements). Regarding plant growth and development elements, DlCINV13 again ranked highest (19 elements), whereas DlCWINV3 had none (0 elements).
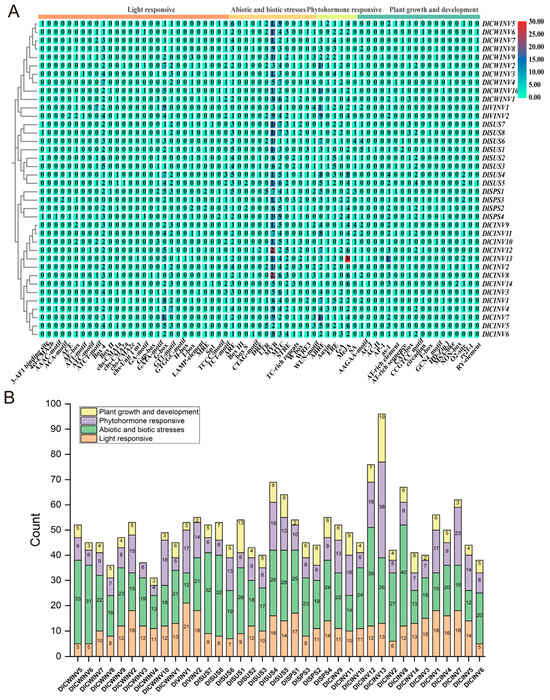
Figure 6.
Cis-acting elements in the promoters of SUS, SPS, and INV gene family members in longan (A) and their classification count (B). Note: In panel (A), green represents a low quantity (0–5); light green represents a medium quantity (7–12); dark green represents a high quantity (13–18); brown represents a higher quantity (19–24); red represents an extremely high quantity (25–30).
3.5. miRNA Prediction
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small non-coding RNAs, typically 18–21 nucleotides in length, which regulate gene expression through two primary mechanisms: mRNA cleavage and translational repression, depending on their degree of complementarity with target mRNAs [22]. Table 3 shows that among the SUS, SPS, and INV gene family members in longan, only DlSUS2/3, DlSPS2, and DlVINV1 were potentially regulated by miRNAs. Specifically, DlSUS2 and DlSUS3 may be targeted by miR156c, DlSPS2 may be regulated by miR827, and DlVINV1 may be modulated by miR171a/b/d/e/f. Furthermore, based on the penalty score analysis, these miRNAs were likely to exert their regulatory effects primarily through translational repression rather than mRNA cleavage on DlSUS2/3, DlSPS2, and DlVINV1.

Table 3.
Prediction of miRNA targeting members of the SUS/SPS/INV gene family.
3.6. TSS and Main Sugar Content
As a sugar-accumulating fruit, the changes in sugar content play a crucial role in the quality of longan fruit. In this study, fruits at different developmental (S1~S2), ripening (S3), and sugar receding (S4~S5) stages were used as materials to measure the contents of TSS, sucrose, glucose, and fructose in the pulp. As shown in Figure 7, during the S3~S5 stages, the TSS and sucrose contents of the CL cultivar were significantly higher than those of SX, while the glucose and fructose contents showed the opposite trend. Furthermore, within the corresponding stages, sucrose content in each cultivar was higher than glucose and fructose. Additionally, the content of these four indicators in both the SX and CL cultivars showed a trend of initially increasing and then decreasing. However, the timing of their peak accumulation differed. Across the five stages, the CL cultivar’s TSS and sucrose reached their highest levels at S3 and subsequently declined, indicating sucrose degradation. Glucose and fructose peaked at S4 and then decreased, but remained higher than in the S1~S3 stages. In SX, TSS peaked at S3 and then declined, while sucrose peaked earlier at S2 before decreasing and stabilizing. The peak stages for glucose and fructose in SX were the same as in CL. When considering the sum of the three sugar contents as the total sugar, the proportions of sucrose, glucose, and fructose in SX at S3 were 38.8%, 34.7%, and 26.5%, respectively, and at S5 were 40.5%, 33.2%, and 26.3%. For CL, these proportions at S3 were 72.2%, 15.0%, and 12.8%, respectively, and at S5 were 55.6%, 24.3%, and 20.1%. Moreover, at the S3 stage, the sucrose content of CL was 2.75 times higher than that of SX. These results suggest that a higher proportion of sucrose during the mature stage is beneficial for delaying the onset of on-tree sugar reduction.
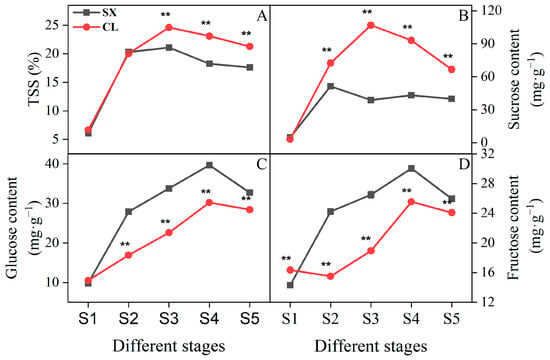
Figure 7.
TSS and main sugar contents in longan pulp at different stages. (A) TSS; (B) sucrose content; (C) glucose content; (D) fructose content. Asterisks ** denote significant differences at p ≤ 0.01.
3.7. Activities of Sucrose Metabolic Enzymes
As shown in Figure 8, during the S1, S2, and S3 stages, the activities of SUS, SPS, and AINV in the aril of SX longan were higher than those in CL. A/N-INV also exhibited higher activity in these periods, except for S1, with a particularly significant difference observed in S3. During the S4~S5 stages, the activities of SPS, AINV, and A/N-INV remained higher than those in CL, whereas SUS activity exhibited the opposite trend. Throughout the S1~S5 stages, the activities of SUS and SPS in SX generally showed an increasing trend followed by a decrease, peaking in S3 and S4, respectively. In contrast, the SUS activity in CL exhibited less fluctuation and peaked in S5. SPS activity in CL peaked in S2, with activities in other stages being similar to those of SX in the S1 and S5 stages. The overall trend for AINV activity in both SX and CL was a decline. A/N-INVI activity showed a trend similar to AINV activity. These findings suggest that sucrose synthesis and degradation occur throughout the developmental, ripening, and sugar receding stages of longan pulp. The SX cultivar exhibits high activities of both synthesis and degradation enzymes, which may be the reason for its faster rate of sugar decline.
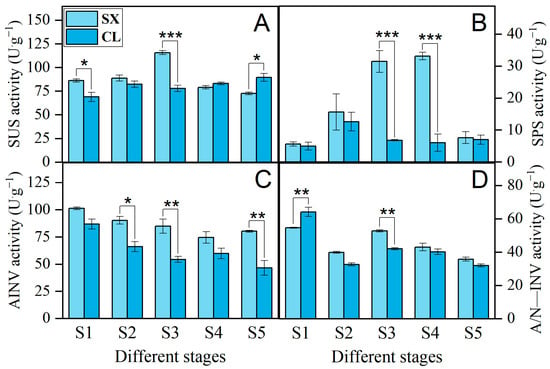
Figure 8.
Sucrose metabolism-related enzymatic activities in longan pulp at different stages. (A) SUS activity; (B) SPS activity; (C) AINV activity; (D) A/N—INV activity. Asterisks *, **, and *** denote significant differences at p ≤ 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001, respectively.
3.8. Gene Expression
Based on our research group’s transcriptome data (unpublished) from developmental to sugar receding stages of longan pulp, some SUS, SPS, and INV genes were selected for the qRT-PCR experiment, with the values of the S1 stage in SX as the reference. Figure 9 shows that among these genes, DlSUS2/6, DlVINV2, and DlCWINV2 exhibited relatively high expression levels, reaching dozens of copies at their peak, while the other genes remained below 10. Additionally, DlSUS5/6, DlSPS2, and DlVINV1 were consistently more highly expressed in SX than in CL across all stages, whereas DlSUS2 showed the opposite trend. In SX, DlCWINV2, DlCINV1/12, and DlSUS8 were expressed at lower levels during stages S1~S3 than S4~S5, particularly DlCWINV2 and DlSUS8, which showed 9.37-fold and 2.37-fold higher expression, respectively, at S5 compared to S3. Conversely, DlCWINV3/10, DlSPS1/3/4, DlSUS5, and DlVINV1 were more highly expressed during stages S1~S3 than S4~S5. In CL, DlSPS1/2/3, DlCWINV2, DlSUS2/8, and DlCINV3/5/12/13/14 were expressed at lower levels during stages S1~S3 than S4~S5, with DlCWINV2 showing an 18.91-fold increase at S5 compared to S3. Meanwhile, DlCWINV3/10, DlVINV1, and DlSPS4 were generally more highly expressed during stages S1~S3 than S4~S5.
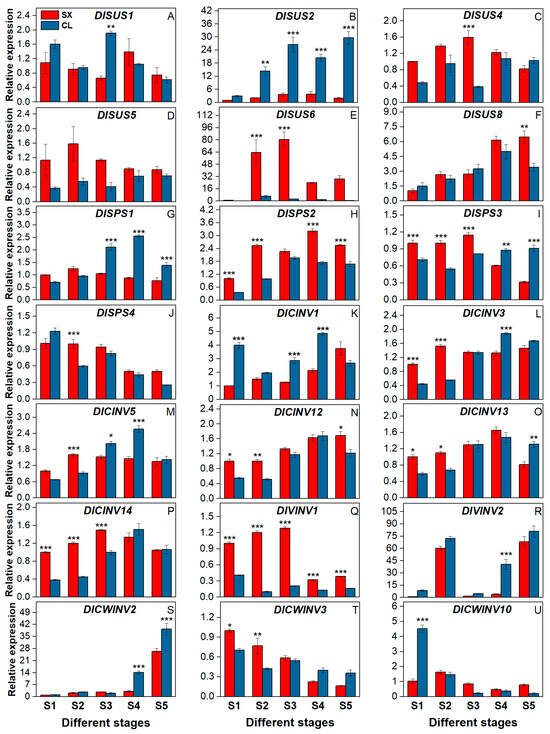
Figure 9.
The expression of sucrose metabolism-associated genes in longan pulp at different stages. (A) DlSUS1; (B) DlSUS2; (C) DlSUS4; (D) DlSUS5; (E) DlSUS6; (F) DlSUS8; (G) DlSPS1; (H) DlSPS2; (I) DlSPS3; (J) DlSPS4; (K) DlCINV1; (L) DlCINV3; (M) DlCINV5; (N) DlCINV12; (O) DlCINV13; (P) DlCINV14; (Q) DlVINV1; (R) DlVINV2; (S) DlCWINV2; (T) CWINV3; (U) CWINV10. Asterisks *, **, and *** denote significant differences at p ≤ 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001, respectively.
3.9. Correlation Analysis
The TSS content is a simple and direct indicator for assessing the sweet taste of longan. A correlation analysis (Figure 10) of physiological and gene expression indicators related to sucrose metabolism in longan pulp at different stages of SX and CL longan was conducted. The results revealed a significant positive correlation between TSS content and the contents of glucose and sucrose (p < 0.05), while a significant negative correlation was observed with the expression of DlCWINV10, AINV activity, and A/N-INV activity (p < 0.05). Furthermore, we also observed a negative correlation between sucrose content and the expression of DlCWINV10 (r = −0.6, p = 0.07), AINV activity (p < 0.05), and A/N-INV activity (p < 0.05).
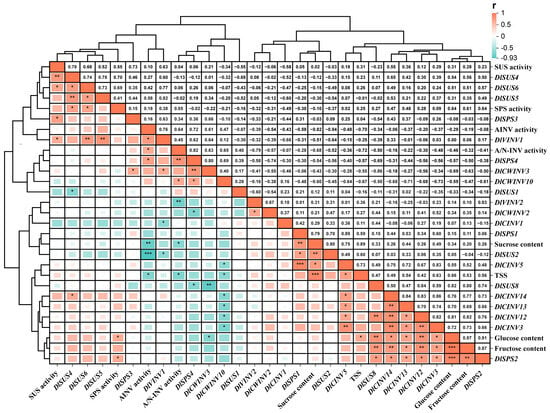
Figure 10.
Correlation analysis of physiological indices and gene expression related to sucrose metabolism in longan pulp at different stages. Asterisks *, **, and *** denote significant differences at p ≤ 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001, respectively. Red represents a positive correlation, blue represents a negative correlation, and the color intensity from dark to light indicates the absolute value of the correlation from 1 to 0.
Moreover, the correlation analysis (Figure 10) revealed that SUS activity is positively correlated with the expression of all DlSUS genes measured in this study, with particularly significant positive correlations observed for the expression of DlSUS4 and DlSUS6 (p < 0.05). Similar results were found in the SPS, AINV, and AN-INV families. For example, SPS activity was significantly positively correlated with DlSPS2 expression (p < 0.05); AINV activity was significantly positively correlated with DlVINV1 expression (p < 0.05). These correlations suggest that the activity of sugar-metabolizing enzymes is under the regulatory control of corresponding genes.
4. Discussion
This study represents the first comprehensive identification and characterization of the key sucrose metabolic gene families in longan, including 8 DlSUS, 4 DlSPS, and 26 DlINV (14 DlCINVs, 2 DlVINVs, and 10 DlCWINVs) members (Figure 1). Notably, the number of members in the SUS and SPS families showed minor variations across fruit with sour, neutral, and sweet tastes. For instance, lemon [23] contains six SUS and four SPS members; grape has five [24] and four [25], respectively; apple has five [26] and seven [16]; rice has six [15] and five [27]; tomato [12] has six and four; kiwifruit [28] has six and six; litchi has five [29] and four [30]; and sugarcane has seven [31] and eight [32]. In contrast, a considerable difference in the number of INV family members was observed. For example, tomato [12] possesses 19 INVs (8 CINVs, 2 VINVs, and 9 CWINVs), lemon [22] has 15 (8 CINVs, 2 VINVs, and 5 CWINVs), rice [18] has 19 (8 CINVs, 2 VINVs, and 9 CWINVs), apple [33] has 17 (11 CINVs, 3 VINVs, and 3 CWINVs), grape [34] has 18 (10 CINVs, 3 VINVs, and 5 CWINVs), and sugarcane [35] has 14 (6 CINVs, 1 VINVs, and 7 CWINVs). These findings suggest that the INV family might be a primary determinant for the distinct sweet flavors observed in different fruits, particularly the CINV and CWINV subfamilies. This aligns with the crucial role of soluble AINV in regulating the sucrose/hexose ratio during sugar receding in longan pulp [3]. Furthermore, research in passion fruit has indicated that PeCWINV5 participates in hexose accumulation [36].
Gene structure analysis revealed differences among the gene families. Longan SUS and SPS members possessed a relatively high number of uniformly distributed exons, whereas CINV members exhibit substantial variation in exon numbers (Figure 1B). This suggests functional conservation in SUS and SPS, while CINV family members may generate isoforms through alternative splicing to adapt longan fruit to different physiological environments [12,23]. Phylogenetic analysis within species revealed (Figure 1A) that the SUS and SPS families were closely related, while CWINV and VINV within the INV family cluster together, suggesting a potential common evolutionary origin. This finding is consistent with observations in lemon [23], apple [33], and sugarcane [35]. Based on the phylogenetic tree constructed with dicotyledonous plants (Figure 3), members of the longan SUS, SPS, and INV families are consistent with the classification of tomato and Arabidopsis species [12]. This corroborates the division of dicotyledonous SUS into subfamilies I-III, SPS family members into subfamilies A-C, and INV family members into AINV and A/N-INV subfamilies, implying functional coupling of genes involved in sucrose synthesis and degradation pathways during the evolution of dicots.
MEME motif analysis (Figure 2) revealed that all SUS family members contained motifs 10/6/15/9/3, whereas SPS members retained motifs 10/9/3 (lacking motif 6/15). This suggests that the SPS lineage may have evolved from an ancestral SUS gene through motif loss. This finding aligns with the notion that “functional domain differentiation is a key mechanism in gene family evolution” [6,37]. Notably, VINV family members completely encompassed the CWINV motifs 8/5/7, implying that VINV evolved and diverged from CWINV. The cross-family motif conservation, such as the widespread presence of motif 10 in SUS/SPS/CWINV family members and DlVINV1, indicates its potential role in encoding core catalytic function. In contrast, family-specific motifs (e.g., the C-terminal motif 6 in the SUS III subfamily) may be responsible for sub-functionalization. CDS sequence similarity analysis unveiled potential gene duplication or alternative splicing events. The high similarity of 94.5% between DlSUS2 and DlSUS3 (Figure 4), coupled with the complete inclusion of DlSUS3 within the DlSUS2 sequence (Figure S1), suggests that these two may originate from recent gene duplication or represent alternative splicing isoforms of the same gene [38]. Furthermore, the Ka/Ks calculation analysis supports this conclusion (Table 2). Similar phenomena were also observed in DlCWINV5 and DlCWINV8 (76.4% similarity but highly overlapping sequences) and DlCINV5 and DlCWINV6 (17% similarity but with shared sequence segments), underscoring that similarity analysis is only reliable when sequence lengths are comparable. These sequence anomalies could stem from mutations in splice sites or selective exon skipping, thereby contributing to protein functional diversification.
Physicochemical property prediction showed that the SUS and CWINV families predominantly exhibited stable protein properties (instability index < 40), whereas most SPS and CINV members were unstable proteins (Table 1). This is consistent with findings in pineapple [39], pomegranate [40], kiwi fruit [28], and apple [33]. All members displayed negative GRAVY values (−0.57 to −0.01), indicating their preference for hydrophilic environments, consistent with the known functional role of sucrose metabolic enzymes in hydrolysis reactions [6]. Analysis of specific domain structures revealed that only a few members contained transmembrane structures (DlSUS2/7/8, DlCINV4, DlVINV1/2, and DlCWINV2) or signal peptides (DlCWINV1/2/3/10). This suggests their potential involvement in membrane-bound transport or extracellular secretion, corroborating experimental results by Zhang et al. [41], where the PbrvacInv1-GFP fusion protein accumulated at the vacuolar membrane. Furthermore, signal peptide prediction results for maize INV family members also indicate that signal peptides are found only in CWINV members [42], which is consistent with the findings of the current study.
Subcellular localization predictions indicated that longan SUS/SPS proteins were primarily localized to chloroplasts, while the CINV family exhibited diverse localization patterns, predominantly in chloroplasts, cytoplasm, and nucleus. CWINV and VINV members were predicted to localize to the cell wall and vacuole, respectively (Table 1). However, discrepancies were observed among different subcellular prediction tools. For example, PSORT predicted that SUS members in sweet potato are mainly localized to the cytoplasm and chloroplasts [43], whereas ExPASy predicted nuclear localization for both SUS and SPS family members [44]. Additionally, YLoc predictions for INV family members in maize revealed that most CWINV proteins localize to vacuoles, while CINV members are primarily localized to the cytoplasm and chloroplasts [42]. PSORT predictions for apple CWINV and VINV members align with the results of this study, whereas CINV members are predominantly predicted in the cytoplasm and mitochondria. Experimental validation of subcellular localization demonstrated that one CINV member predicted to localize to mitochondria was actually found in the cytoplasm [33]. In tomato, functional studies confirmed that a CWINV member localizes to the cell wall and a CINV member resides in the cytoplasm [12]. Moreover, the Arabidopsis CINV member At-A/N-InvE was experimentally verified to localize to chloroplasts [45]. Zhang et al. [41] reported that the PbrvacInv1-GFP fusion protein accumulated in the vacuolar membrane, with a minor fraction detected in the vacuolar lumen, consistent with predictions, further supporting vacuolar localization of VINV members. These findings collectively suggest that subcellular localization predictions should be interpreted with caution and serve primarily as references. Nevertheless, Cell-PLoc 2.0 demonstrates relatively higher accuracy in predicting subcellular localization for CWINV and VINV members compared to other tools.
Intraspecies analysis identified nine collinear gene pairs in longan (Table 2), all resulting from segmental duplication events, indicating that segmental duplication serves as the primary driver for the expansion of sucrose metabolism gene families in this species. Ka/Ks ratio analysis demonstrated that all gene pairs except DlSUS2/DlSUS3 exhibited values less than 1 (Table 2), suggesting strong purifying selection on these genes. This reflects the stability and evolutionary conservation of sucrose metabolism genes, which is consistent with findings in lemon [23]. Cross-species collinearity comparisons revealed more homologous genes between longan–lemon than longan–litchi. This discrepancy may be attributed to the AB-type Chr in lemon, formed by ancestral polyploidization events, which facilitates the retention of duplicated gene pairs [46]. Notably, DlSUS1/2/3/5/6, DlSPS1/2/3, DlCINV1/2/3/5/12/13/14, DlCWINV1/2/10, and DlVINV1/2 exhibited high collinearity across species. This conservation highlights their critical roles in sucrose metabolism, suggesting their orthologs may represent core genes regulating fruit sugar accumulation in multiple species [26,47]. Collectively, these results demonstrate that core sucrose metabolism genes in fruit are under strong selective constraints, likely due to their critical functions in carbon allocation and stress adaptation [6].
Analysis of cis-acting elements in the promoter regions of longan sucrose metabolism genes revealed a multi-layered regulatory network, wherein MYB binding sites were ubiquitously enriched (Figure 6). This finding is consistent with previous studies in lemon [23], melon [44], pear [48], and sweet potato [43]. In addition, research suggests that MYB may mediate the involvement of SPS in longan sucrose accumulation [49]. Furthermore, Gao et al. [50] reported that the up-regulation of CmMYB44 could inhibit the expression of CmSPS1, thereby reducing sucrose accumulation in eastern melon fruit. Concurrently, the widespread presence of hormonal elements such as ABRE and MeJA indicates the significance of abscisic acid and jasmonic acid signaling in longan stress responses, analogous to ABRE-mediated drought responses in tobacco [17]. Additionally, the high frequency of light-responsive elements underscores the crucial role of light signals in sucrose synthesis [51]. These results suggest that MYB transcription factors may be central regulators of sucrose synthesis and degradation in longan, coordinating sucrose metabolism alongside light, stress, and hormone response elements. The bioinformatic predictions identified that among the longan SUS, SPS, and INV gene families, only DlSUS2/3, DlSPS2, and DlVINV1 might be regulated by specific miRNAs (miR156, miR827, and miR171) (Table 3). However, this is inconsistent with the miRNAs that regulate SUS and SPS in melon [44] and tobacco [52], but congruent with miRNAs regulating certain INV family members in tobacco [17], indicating the diversity of miRNAs involved in sucrose metabolism regulation.
Sucrose is the most abundant sugar accumulated in mature longan fruits, and its content is closely related to fruit quality [4]. Longan fruits that remain on the tree and maintain their freshness after entering the mature stage can extend their market supply period for greater economic value. However, fruit retention on trees for preservation may lead to a phenomenon of sugar decline, characterized by a decrease in TSS and sucrose degradation [3]. In this study, from stage S3 onwards, both the TSS and sucrose contents of CL were higher than those of SX (Figure 7), which is consistent with SX longan being a rapid sugar-declining cultivar and CL being a slow sugar-declining cultivar [4]. Furthermore, the proportion of sucrose in the CL cultivar was higher than in SX, aligning with research on sucrose as a stable carbon reserve in citrus [53]. Sucrose homeostasis is intricately linked to the activities of SUS, SPS, and INV [5]. For instance, Zhang et al. [16] found that the expression level of the MdSPS gene in apple showed a significant positive correlation with sucrose content. In this work, Figure 8 shows that the SX cultivar likely exhibited an enzyme activity pattern of high synthesis–high degradation of sucrose. For instance, during stage S3, the activities of sucrose synthesis (SPS) and degradation (SUS, AINV, and A/N-INV) enzymes were significantly higher in SX than in CL, thereby driving rapid sugar decrease through accelerated sucrose-to-hexose conversion [3]. In contrast, higher AINV and A/N-INV activities in early longan fruit development promoted sucrose degradation, leading to increased accumulation of glucose and fructose to meet the higher metabolic and energy demands of early fruit development. This finding is consistent with the results reported by Shi et al. [54] and Tan et al. [55]. The increase in SPS activity during stages S3~S4 (SX) and S2 (CL) indicates that SPS is a major factor in sucrose accumulation in longan, which is in agreement with the findings of Li et al. [49] and Fang et al. [56]. qRT-PCR analysis revealed that the high expression of DlSPS2 in SX (Figure 9) coincided with the peak of SPS activity (Figure 8), corroborating the direct regulation of enzyme activity by SPS gene expression. Furthermore, correlation analysis (Figure 10) also supported these results. Notably, we found that the expression of DlCWINV10 was negatively correlated with TSS (p < 0.05) and sucrose (r = −0.6, p = 0.07), while both TSS and sucrose showed significant negative correlations with AINV and A/N-INV activities, suggesting that AINV may play a vital role in promoting sucrose hydrolysis. This finding is consistent with the results reported by Luo et al. [3]. Research has indicated that transient overexpression of PeCWINV5 in passion fruit leads to a more pronounced accumulation of fructose and glucose compared to sucrose, while showing no significant difference in sucrose accumulation compared to the control [36]. Additionally, INV family members primarily function in the process of sucrose degradation in plants [5]. These results suggest that DlCWINV10 may play a crucial role in the sucrose degradation process of longan fruit.
In addition, an interesting phenomenon was observed in this study (Figure 7): the peak of TSS content (S3) and the peak of sucrose content (S2) in the SX variety of longan occurred at different times. In contrast, both the TSS and sucrose peaks in the CL variety occurred simultaneously at S3. This discrepancy with previous studies may be attributed to regional climatic differences. Past research on longan sugar degradation has primarily focused on regions in China, such as Guangzhou city (23°16′ N, 113°23′ E) [3,4], Guangdong Province, and Fuzhou city (26°08′ N, 119°28′ E) [49], Fujian Province, both of which are in typical subtropical climates with higher average temperatures. In contrast, the longan in this study were grown in Hezhou city (25°09′ N, 111°05′ E), Guangxi Province, where the temperature is relatively lower, and the longan matures later (with fruit still being commercially harvestable as late as the end of August). As a result, the SX variety, which experiences rapid sugar degradation, began sucrose loss before reaching commercial maturity (Figure 7). This is consistent with higher AINV activity and lower SPS activity in the SX variety at this period (Figure 8). Furthermore, correlation analysis also indicates that AINV is the main enzyme for sucrose degradation, which is consistent with the findings of Luo et al. [3]. However, intense sugar accumulation continued at stages S3~S4 (with higher SPS activity in SX compared to CL), leading to the observed discrepancy between sucrose and TSS peak timings in this study. This suggests that sugar degradation in tree-retained longan may result from the combined actions of both sucrose synthesis and degradation, which is consistent with the findings of Huang et al. [57].
5. Conclusions
This study conducted a comprehensive identification and analysis of the SUS, SPS, and INV gene family members in longan, revealing their basic characteristics, phylogenetic relationships, and potential roles in the sugar receding process of fruit. The research revealed significant differences among these gene family members in terms of gene structure, conserved motifs, physicochemical properties, and subcellular localization, especially in INV families. Moreover, the expression patterns of different family members from fruit development to sucrose degradation showed close correlations with enzymatic activity changes, among which certain genes, DlCWINV10, were identified as potentially playing crucial roles in sucrose degradation. These findings provide critical molecular insights into the mechanism of sugar receding in longan fruit during on-tree preservation and establish a foundation for subsequent functional validation and cultivar improvement.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae11101270/s1: Figure S1: Comparison of the CDS sequences between DlSUS2 and DlSUS3; Figure S2: Comparison of the CDS sequences between DlCINV5 and DlCINV6; Figure S3: Comparison of the CDS sequences between DlCINV10 and DlCINV11; Figure S4: Comparison of the CDS sequences between DlCWINV5 and DlCWINV8; Table S1: The sequences of specific primers used for qRT-PCR assay; and Table S2: Gene names and corresponding IDs for Arabidopsis members used in phylogenetic analysis.
Author Contributions
M.H.: investigation, funding acquisition, writing—original draft; L.S.: writing—original draft, funding acquisition; Y.Z.: formal analysis, funding acquisition; M.S.: visualization; F.Y.: investigation, writing—review and editing; Y.L.: conceptualization, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (2024GXNSFBA010323), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 32260611 and 32460611), the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by GXAST (GXYESS2025025), and the Guangdong Provincial Young Innovative Talents Program for Higher Education Institutions (2024KQNCX280).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lin, Y.; Min, J.; Lai, R.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L.; Cheng, C.; Jin, Y.; Tian, Q.; Liu, Q.; et al. Genome-wide sequencing of longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.) Provides insights into molecular basis of its polyphenol-rich characteristics. Gigascience 2017, 6, gix023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, L.; Xue, P.; Liao, L.; Guo, X.; Liu, Y.; Song, M.; Cai, W.; Yin, F.; He, M. Methyl jasmonate improves pulp flavor by modulating sugar metabolism in postharvest longan fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 219, 113268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Shuai, L.; Liao, L.; Li, J.; Duan, Z.; Guo, X.; Xue, X.; Han, D.; Wu, Z. Soluble acid invertases act as key factors influencing the sucrose/hexose ratio and sugar receding in longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.) Pulp. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2019, 67, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, L.; Gu, L.; Liu, W.; Han, D.; Wu, Z. Characteristic analysis of sugar returning in the fruit of different longan cultivars. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2016, 10, 1900–1907. [Google Scholar]
- Lunn, J.E. Sucrose metabolism. els 2016, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.L. Sucrose metabolism: Gateway to diverse carbon use and sugar signaling. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 33–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Chi, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ma, A.; Vanitha, J.; Ramachandran, S. Sucrose metabolism gene families and their biological functions. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, O.; Granot, D. An overview of sucrose synthases in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langenkämper, G.; Fung, R.W.M.; Newcomb, R.D.; Atkinson, R.G.; Gardner, R.C.; Macrae, E.A. Sucrose phosphate synthase genes in plants belong to three different families. J. Mol. Evol. 2002, 54, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castleden, C.K.; Aoki, N.; Gillespie, V.J.; Macrae, E.A.; Quick, W.P.; Buchner, P.; Foyer, C.H.; Furbank, R.T.; Lunn, J.E. Evolution and function of the sucrose-phosphate synthase gene families in wheat and other grasses. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 1753–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coculo, D.; Lionetti, V. The plant invertase/pectin methylesterase inhibitor superfamily. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 863892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, J.; Sun, H.; Gong, H. Structure and expression analysis of sucrose phosphate synthase, sucrose synthase and invertase gene families in Solanum lycopersicum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wei, P.; Wu, M.; Xu, Y.; Li, F.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, A.; Xie, X.; Cao, P.; et al. Analysis of the sucrose synthase gene family in tobacco: Structure, phylogeny, and expression patterns. Planta 2015, 242, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baud, S.; Vaultier, M.N.; Rochat, C. Structure and expression profile of the sucrose synthase multigene family in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, T.; Scofield, G.N.; Terao, T. An expression analysis profile for the entire sucrose synthase gene family in rice. Plant Sci. 2008, 174, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, L.; Xu, Y.; Lv, L.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Liu, W.; Ma, F.; Li, M.; Han, D. Genome-wide identification and function analysis of the sucrose phosphate synthase MdSPS gene family in apple. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 2080–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Jin, J.; He, X.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Xu, X. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the invertase gene family in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) reveals NtNINV10 participating the sugar metabolism. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1164296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; van den Ende, W.; van Laere, A.; Cheng, S.; Bennett, J. Structure, evolution, and expression of the two invertase gene families of rice. J. Mol. Evol. 2005, 60, 615–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherson, S.M.; Alford, H.L.; Forbes, S.M.; Wallace, G.; Smith, S.M. Roles of cell-wall invertases and monosaccharide transporters in the growth and development of Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2003, 54, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, C.; Zeng, Z.; Wu, F.; Feng, J.; Liu, B.; Mai, Y.; Chu, X.; Wei, W.; Li, X.; et al. Sapbase: A central portal for functional and comparative genomics of sapindaceae species. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2024, 66, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. Tbtools-ii: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Kong, X.; Jiang, Y.; Qu, H.; Zhu, H. Micrornas: Emerging regulators in horticultural crops. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 936–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, C.; Yang, Y.; Tang, T.; Yan, X.; Huang, G. Identification and expression analysis of key enzyme gene family in lemon sucrose metabolism. J. South Agric. 2023, 5, 1327–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Jiu, S.; Wang, C.; Fang, J. Genome-wide analysis of the sucrose synthase gene family in grape (Vitis vinifera): Structure, evolution, and expression profiles. Genes 2017, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, X. Identification, characterization and expression analysis of the sucrose phosphate synthase gene family in Vitis vinifera. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2022, 16, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Feng, F.; Cheng, L. Expression patterns of genes involved in sugar metabolism and accumulation during apple fruit development. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, M.; Aoki, N.; Hirose, T.; Yonekura, M.; Ohto, C.; Ohsugi, R. Tissue specificity and diurnal change in gene expression of the sucrose phosphate synthase gene family in rice. Plant Sci. 2011, 181, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhong, M.; Jia, D.; Huang, C.; Xu, X. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling analysis of sucrose synthase (SUS) and sucrose phosphate synthase (SPS) genes family in Actinidia chinensis and A. eriantha. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, J.; Qin, Y.; Qin, Y.; Hu, G. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression profile of the sucrose synthase gene family in litchi chinensis. Hortic. Plant J. 2021, 7, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, J.; Hu, B.; Li, J.; Qin, Y.; Chen, L.; Qin, Y.; Hu, G. Identification and expression profile analysis of the sucrose phosphate synthase gene family Litchi chinensis Sonn. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirugnanasambandam, P.P.; Mason, P.J.; Hoang, N.V.; Furtado, A.; Botha, F.C.; Henry, R.J. Analysis of the diversity and tissue specificity of sucrose synthase genes in the long read transcriptome of sugarcane. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Hua, X.; Wang, Z.; Tang, H.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, M.; et al. Comparative analysis of sucrose phosphate synthase (SPS) gene family between Saccharum officinarum and Saccharum spontaneum. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhu, L.; Tian, R.; Wang, L.; Su, J.; Yuan, Y.; Ma, F.; Li, M.; Ma, B. Genome-wide identification, characterization and evolutionary dynamic of invertase gene family in apple, and revealing its roles in cold tolerance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 229, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Cai, C.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xie, Z. Identification and expression analysis of invertase family genes during grape (Vitis vinifera L.) Berry development under cppu and ga treatment. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2023, 298, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Ding, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J. Molecular cloning, structure, phylogeny and expression analysis of the invertase gene family in sugarcane. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Wu, B.; Chen, G.; Xing, W.; Xu, Y.; Ma, F.; Li, H.; Hu, W.; Huang, H.; Yang, L.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of the passion fruit invertase gene family reveals involvement of PeCWINV5 in hexose accumulation. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, K. Sucrose metabolism: Regulatory mechanisms and pivotal roles in sugar sensing and plant development. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Lin, K. The distribution pattern of genetic variation in the transcript isoforms of the alternatively spliced protein-coding genes in the human genome. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 1378–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, M.; Yao, Y.; Fu, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, X. Identification, characterisation, and expression profile analysis of the sucrose phosphate synthase gene family in pineapple (Ananas comosus). J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 97, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zheng, J. Identification and expression analysis of the sucrose synthase gene family in pomegranate (Punica granatum L.). PeerJ 2022, 10, e12814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, X.; Liu, Z.; Ma, M.; Fan, J.; Luo, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S. Identification and characterization of invertase family genes reveal theirroles in vacuolar sucrose metabolism during Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd. fruit development. Genomics 2021, 113, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Colunga, S.; López-González, C.; Morales-Elías, N.C.; Massange-Sánchez, J.A.; Trachsel, S.; Tiessen, A. Genome-wide analysis of the invertase gene family from maize. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 97, 385–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gao, S.; Zhai, H.; He, S.; Zhao, N.; Liu, Q. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the sucrose synthase gene family in sweet potato and its two diploid relatives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, I.H.; Manzoor, M.A.; Azam, M.; Jinhui, W.; Li, X.; Rehman, A.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Q.; Chang, L. Comprehensive characterization and expression profiling of sucrose phosphate synthase (SPS) and sucrose synthase (SUS) family in Cucumis melo under the application of nitrogen and potassium. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, W.A.; Pontis, H.G.; Salerno, G.L. New insights on sucrose metabolism: Evidence for an active A/N-INV in chloroplasts uncovers a novel component of the intracellular carbon trafficking. Planta 2008, 227, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.A.; Terol, J.; Ibanez, V.; López-García, A. Genomics of the origin and evolution of citrus. Nature 2018, 554, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, A.; Moriguchi, T.; Koyama, K.; Omura, M.; Akihama, T. Analysis of sucrose synthase genes in citrus suggests different roles and phylogenetic relationships. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.; Cao, Y.; Cheng, X.; Meng, D.; Chen, Y.; Shakoor, A.; Gao, J.; Cai, Y. The sucrose synthase gene family in chinese pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.): Structure, expression, and evolution. Molecules 2018, 23, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ren, R.; Pan, R.; Bao, Y.; Xie, T.; Zeng, L.; Fang, T. Comparative transcriptome analysis identifies candidate genes related to sucrose accumulation in longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.) Pulp. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1379750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Yang, F.; Wang, C.; Duan, X.; Li, M.; Ma, Y.; Wang, F.; Qi, H. The transcription factor CmERFI-2 represses CmMYB44 expression to increase sucrose levels in oriental melon fruit. Plant Physiol. 2023, 192, 1378–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieniawska, Z.; Paul Barratt, D.H.; Garlick, A.P.; Thole, V.; Kruger, N.J.; Martin, C.; Zrenner, R.; Smith, A.M. Analysis of the sucrose synthase gene family in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2007, 49, 810–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Su, H.; Wang, S.; Gao, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Xu, X. Identification of the sucrose phosphate synthase (SPS) gene family reveals the positive role of NtSPS5 and NtSPS6 in drought stress tolerance of tobacco. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2025, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.Z.; Hu, X.; Jin, L.; Liu, Y.; Peng, S. Genome-wide identification and expression profile analysis of citrus sucrose synthase genes: Investigation of possible roles in the regulation of sugar accumulation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Shu, B.; Wei, Y.; Jue, D.; Fu, J.; Xie, J.; Liu, C. Physico-chemical properties of longan fruit during development and ripening. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 207, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Xie, J.; Wang, W.; Shi, S. Effects of exogenous plant hormones on sugar accumulation and related enzyme activities during the development of longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.) Fruits. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Li, Y.; Xie, T.; Xian, H.; Bao, Y.; Zeng, L. The bHLH transcription factor DlbHLH68 positively regulates DlSPS1 expression to promote sucrose biosynthesis in longan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 296, 139594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Lv, X.; Han, Y.; Han, D.; Wei, J.; Li, J.; Guo, D. Disrupted sugar transport and continued sugar consumption lead to sugar decline in ripe ‘Shixia’ longan fruit. LWT 2024, 191, 115620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).