Fragmentation Susceptibility of Controlled-Release Fertilizer Particles: Implications for Nutrient Retention and Sustainable Horticulture
Abstract
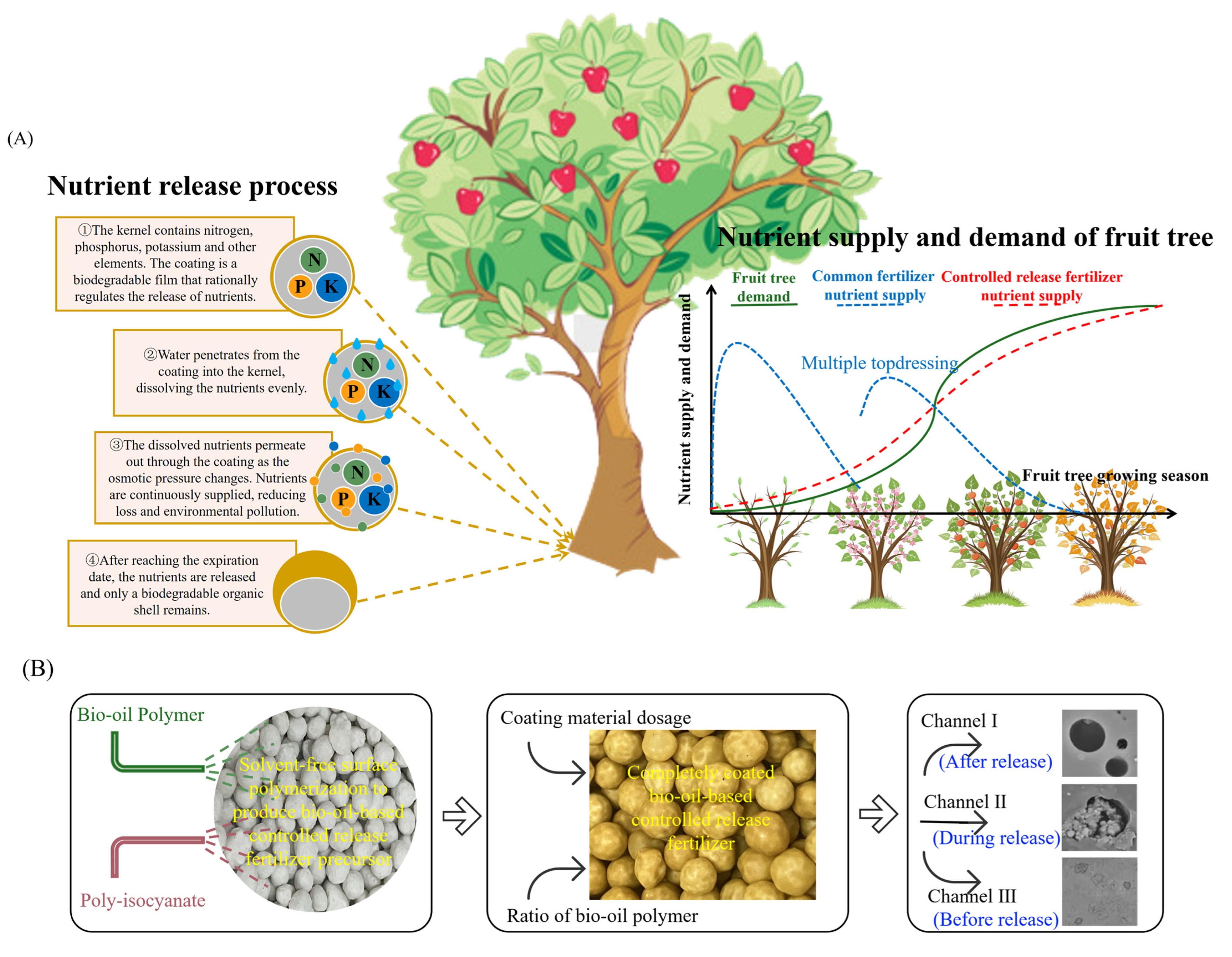
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
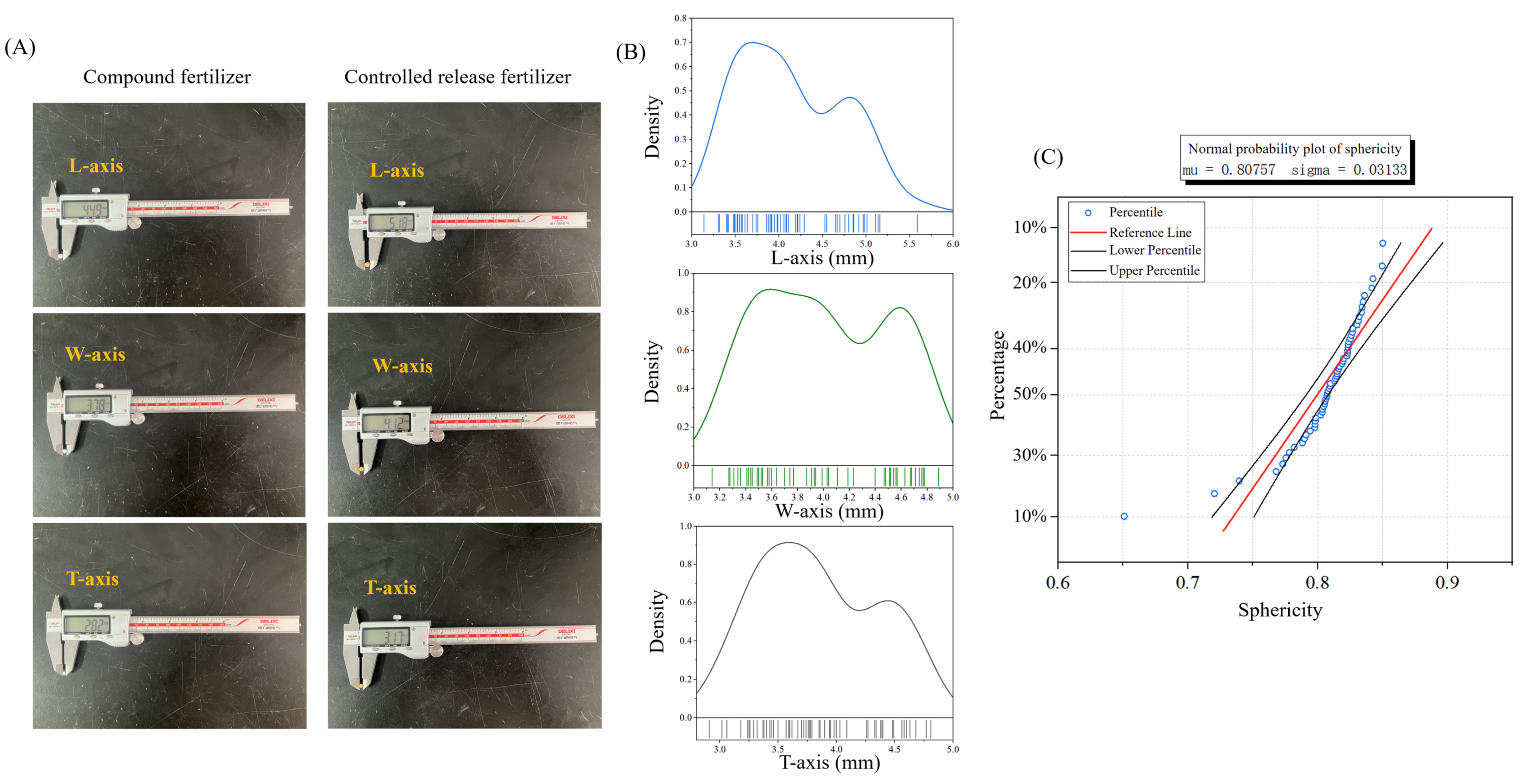
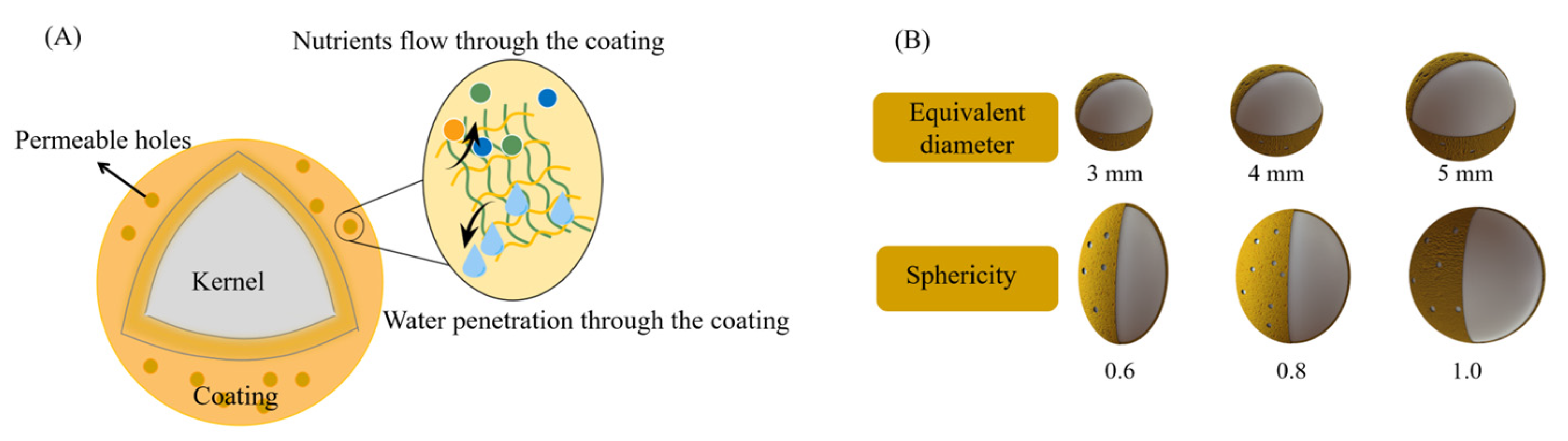
2.2. Morphological Parameter Determination
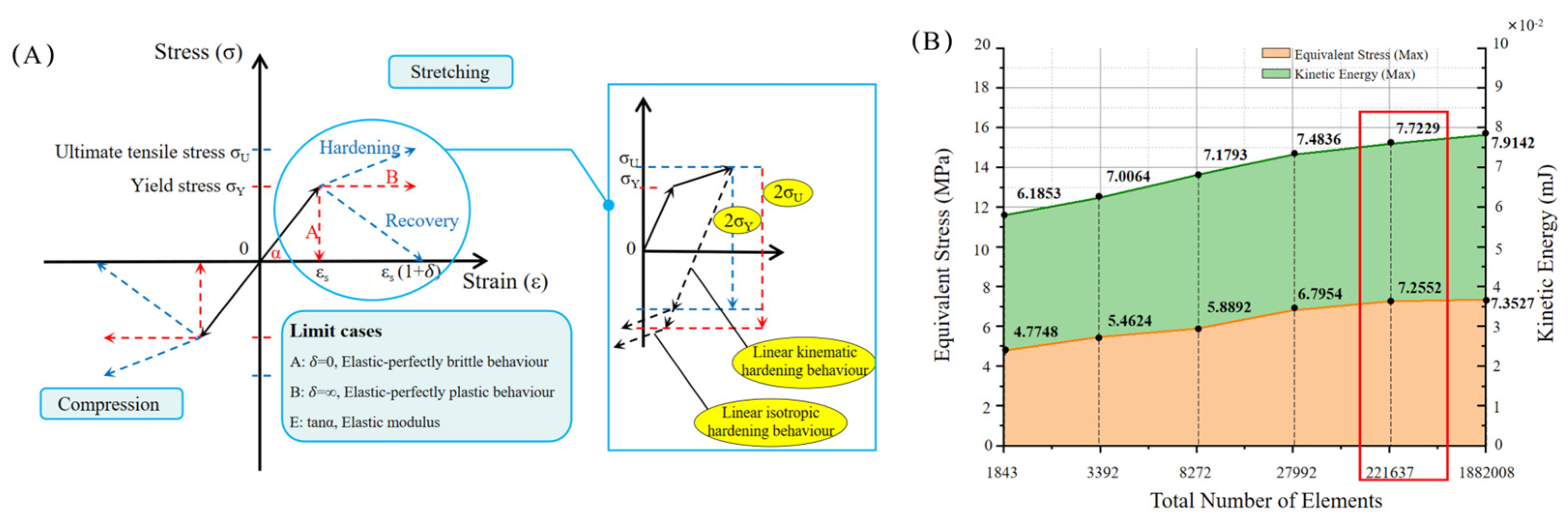
2.3. Material Parameter Determination
2.4. Geometry Model Construction
2.5. Finite Element Simulation Experiment
2.5.1. Material Properties and Meshing
2.5.2. Simulation Experiment
2.5.3. Quantification of Crushing Volume
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. The Effect of Impact Velocity on Crushing Characteristics
3.2. Effect of Equivalent Diameter and Sphericity on Crushing Characteristics
3.3. Effect of Impact Angle and Impacting Material on Crushing Characteristics
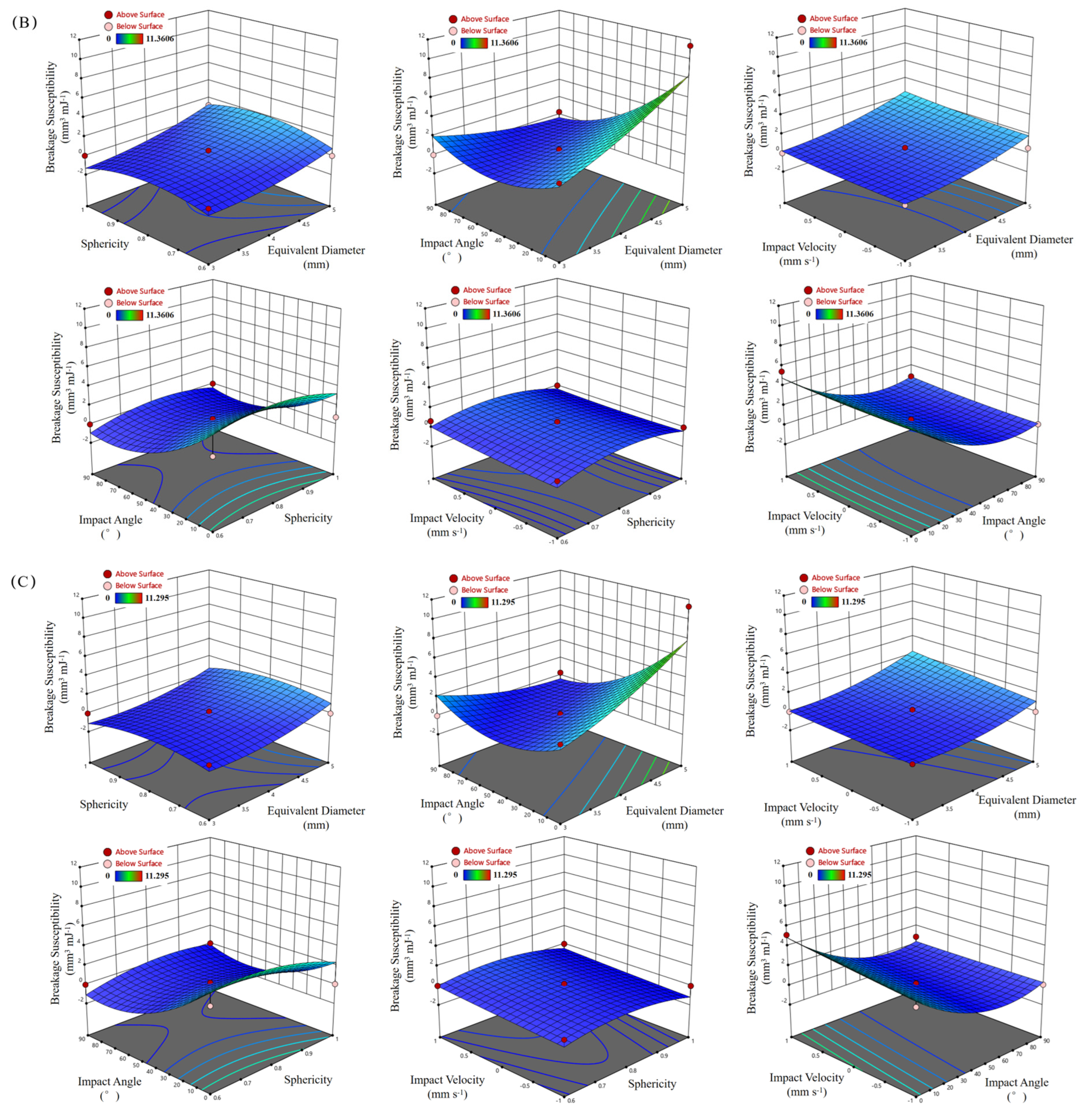
3.4. Results of Response Surface Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, L.; Zhao, S.; Song, Y.; Tang, M.; Li, H. Green Finance, Chemical Fertilizer Use and Carbon Emissions from Agricultural Production. Agriculture 2022, 12, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govil, S.; Long, N.; Escribà-Gelonch, M.; Hessel, V. Controlled-release fertiliser: Recent developments and perspectives. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 219, 119160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Bio-based materials for fabrication of controlled-release coated fertilizers to enhance soil fertility: A review. Next Mater. 2025, 8, 100701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Niu, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, W.; Tang, H.; Wang, J. Exploring sustainable agriculture: Investigating the impact of controlled release fertilizer damage through bonded particle modeling. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 468, 143095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horabik, J.; Molenda, M. Parameters and contact models for DEM simulations of agricultural granular materials: A review. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 147, 206–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Ooi, E.; Chan, A.; Fu, S. The combined scaled boundary finite-discrete element method: Grain breakage modelling in cohesion-less granular media. Comput. Geotech. 2017, 88, 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Cui, T.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Song, W. DEM study of particle motion in novel high-speed seed metering device. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 1438–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Bai, L.; Yao, Y.; Yue, B.; Fu, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, Y. Discrete element modelling (DEM) of fertilizer dual-banding with adjustable rates. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 152, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, G.; Xue, D. An approach to calibration of BPM bonding parameters for iron ore. Powder Technol. 2021, 381, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xie, G.; Xu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Lai, Q. Application of a staggered symmetrical spiral groove wheel on a quantitative feeding device and investigation of particle motion characteristics based on DEM. Powder Technol. 2022, 407, 117650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Jin, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Kanter, D.; Wu, B.; Xi, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; Xu, J.; et al. Fertilizer overuse in Chinese smallholders due to lack of fixed inputs. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sane, M.; Hajek, M.; Nwaogu, C.; Purwestri, R. Subsidy as an economic instrument for environmental protection: A case of global fertilizer use. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, K. Spatial patterns of fertilizer use and imbalances: Evidence from rice cultivation in India. Environ. Chall. 2022, 7, 100452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, Z.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y.; Gao, X. Development of a novel perforated type precision metering device for efficient and cleaner production of maize. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 443, 140928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Luo, J.; Sheng, T.; Xie, Y.; Xian, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, M. Diazotrophic communities shift with organic fertilizer substitution and growth stages in tomato field soil. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2025, 126, 103746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wu, L.; Qiu, G.; Yu, L. A novel slow-release urea fertiliser: Physical and chemical analysis of its structure and study of its release mechanism. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 115, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Ortiz, R.; Naranjo, M.Á.; Ruiz-Navarro, A.; Atares, S.; García, C.; Zotarelli, L.; San Bautista, A.; Vicente, O. Enhanced Agronomic Efficiency Using a New Controlled-Released, Polymeric-Coated Nitrogen Fertilizer in Rice. Plants 2020, 9, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrencia, D.; Wong, S.K.; Low, D.Y.S.; Goh, B.H.; Goh, J.K.; Ruktanonchai, U.R.; Soottitantawat, A.; Lee, L.H.; Tang, S.Y. Controlled Release Fertilizers: A Review on Coating Materials and Mechanism of Release. Plants 2021, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodki, B.; Kumar, K.; Goswami, T. Modeling breakage and motion of black pepper seeds in cryogenic mill. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 1055–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Effect of modeling parameters on the mechanical response of macroscopic crushing of agglomerate. Powder Technol. 2022, 408, 117720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Sakai, M. Recent progress on the discrete element method simulations for powder transport systems: A review. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayel, D.; Wiesehoff, M.; Özmerzi, A.; Müller, J. Laboratory measurement of seed drill seed spacing and velocity of fall of seeds using high-speed camera system. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2006, 50, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Gao, B.; Li, Y.; Xie, J. Bio-based elastic polyurethane for controlled-release urea fertilizer: Fabrication, properties, swelling and nitrogen release characteristics. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Zhao, Y. An experimentally validated coarse-grain DEM study of monodisperse granular mixing. Powder Technol. 2020, 361, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cong, J.; Liu, Z.; Liao, Q.; Liao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, X. Design and experimental analysis of the air-assisted fertilizer apparatus’s distributor using DEM-CFD and high-speed photography. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 237 Pt B, 110653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Liao, Q. Numerical simulation of seed motion characteristics of distribution head for rapeseed and wheat. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 150, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, W.; Gao, L.; Liao, Y.; Li, Q.; Liao, Q. An adaptive spacing of root-zone hole fertilization to improve production and fertilizer utilization of rapeseed. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 6276–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, X.; Liang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Li, B.; Guo, H. Mechanisation of ring-furrow fertiliser application for orchards: A multi-segment arc trajectory and its control method. Biosyst. Eng. 2025, 257, 104213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, J.; Leng, Y.; Xia, R. Concrete plastic-damage factor for finite element analysis: Concept, simulation, and experiment. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1687814017719642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partheniadis, I.; Terzi, V.; Nikolakakis, I. Finite element analysis and modeling in pharmaceutical tableting. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Sun, L.; Jing, L.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Predicting and quantifying damage characteristics in mechanized harvesting: A collision-based study of apples. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 227, 113586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yang, Z.; Karkee, M.; Han, X.; Duan, J.; He, Y. Dynamic finite element simulation of the collision behavior and multi-parameter quantitative characterization of the damage degree of banana fruit in the post-harvest operations. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 219, 113284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, H.; Rennie, A.; Akinci, I. Deformation behaviour simulation of an apple under drop case by finite element method. J. Food Eng. 2011, 104, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Park, B.; Li, C.; Wang, X. A multiscale computation study on bruise susceptibility of blueberries from mechanical impact. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 208, 112660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Miao, K.; Shan, W.; Tang, L.; Yu, H. Simulation and evaluation of tablet-coating burst based on finite element method. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, N.; Hayashi, Y.; Onuki, Y.; Miura, T.; Obata, Y.; Takayama, K. Mechanical stress simulation of scored tablets based on the finite element method and experimental verification. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 64, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, D.; Lei, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zheng, Y. The study on the constitutive model of concrete for explicit dynamic of ABAQUS based on damage energy. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 1914314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikins, K.; Ucgul, M.; Barr, J.; Awuah, E.; Antille, D.; Jensen, T.; Desbiolles, J. Review of Discrete Element Method Simulations of Soil Tillage and Furrow Opening. Agriculture 2023, 13, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, M.; Xiang, L.; Chen, D.; Zhuang, W.; Yin, X.; Li, Z. Foundation models in smart agriculture: Basics, opportunities, and challenges. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 222, 109032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, A.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, H.; Kaur, H. Chapter 5—Novel nanocomposite-based controlled-release fertilizer and pesticide formulations: Prospects and challenges. Multifunct. Hybrid Nanomater. Sustain. Agri-Food Ecosyst. 2020, 99–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejan, P.; Khadiran, T.; Abdullah, R.; Ahmad, N. Controlled release fertilizer: A review on developments, applications and potential in agriculture. J. Control. Release 2021, 339, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, I.; Ablouh, E.; Bouchtaoui, F.; Jaouahar, M.; Achaby, M. Polymer coated slow/controlled release granular fertilizers: Fundamentals and research trends. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2024, 144, 101269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, D.; Li, X.; Qin, X.; Li, H.; Hang, L. Investigating the jet comminuting process in cuttings transport by coupling the CFD/DEM method and bonded-particle model. SPE J. 2019, 24, 2020–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Ortiz, R.; Naranjo, M.; Ruiz-Navarro, A.; Caballero-Molada, M.; Atares, S.; García, C.; Vicente, O. New eco-friendly polymeric-coated urea fertilizers enhanced crop yield in wheat. Agronomy 2020, 10, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ain, N.; Naveed, M.; Hussain, A.; Mumtaz, M.; Rafique, M.; Bashir, M.; Alamri, S.; Siddiqui, M. Impact of coating of urea with bacillus-augmented zinc oxide on wheat grown under salinity stress. Plants 2020, 9, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcińczyk, M.; Oleszczuk, P. Biochar and engineered biochar as slow- and controlled-release fertilizers. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 339, 130685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertahi, S.; Ilsouk, M.; Zeroual, Y.; Oukarroum, A.; Barakat, A. Recent trends in organic coating based on biopolymers and biomass for controlled and slow release fertilizers. J. Control. Release 2021, 330, 341–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


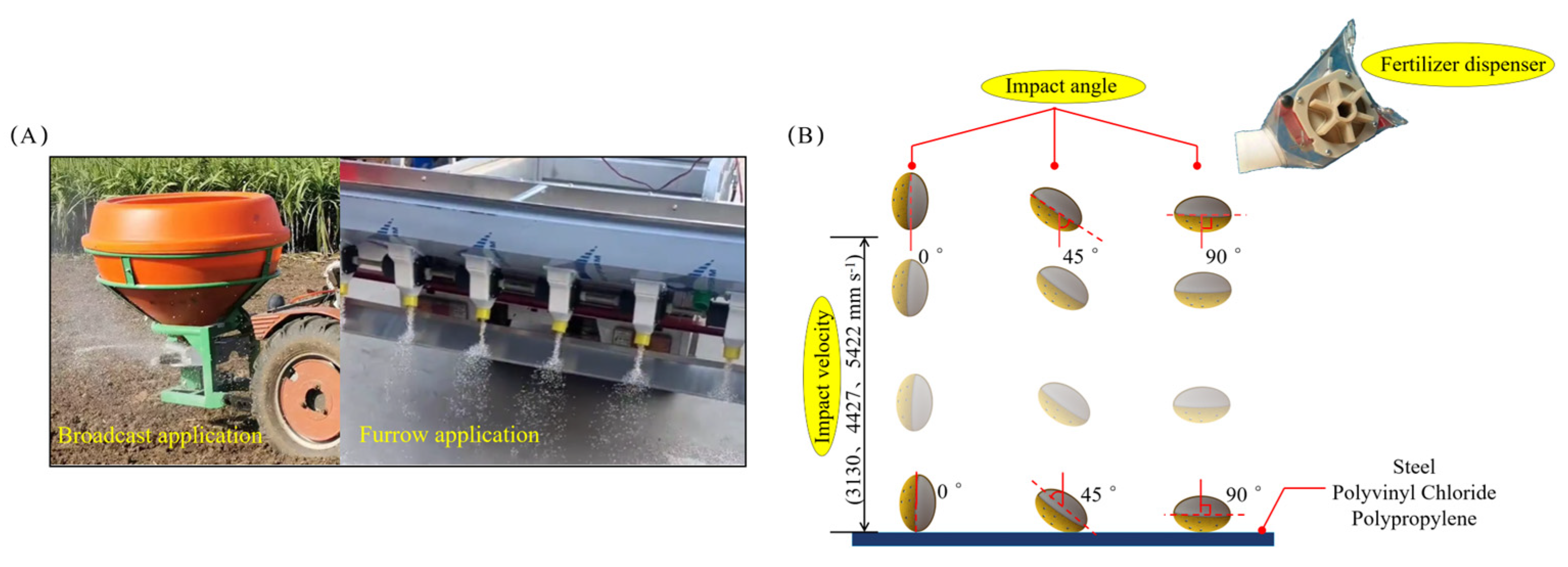
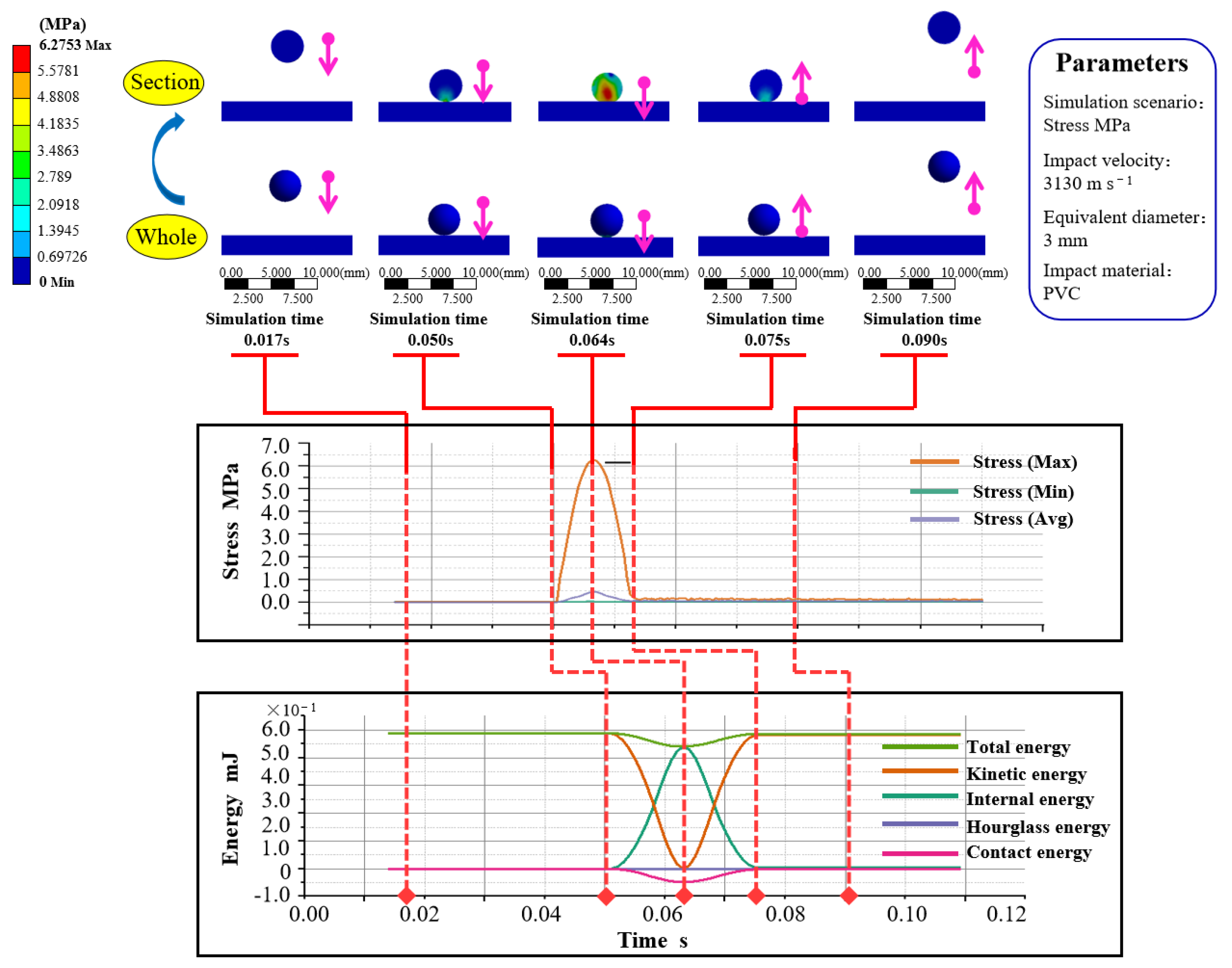
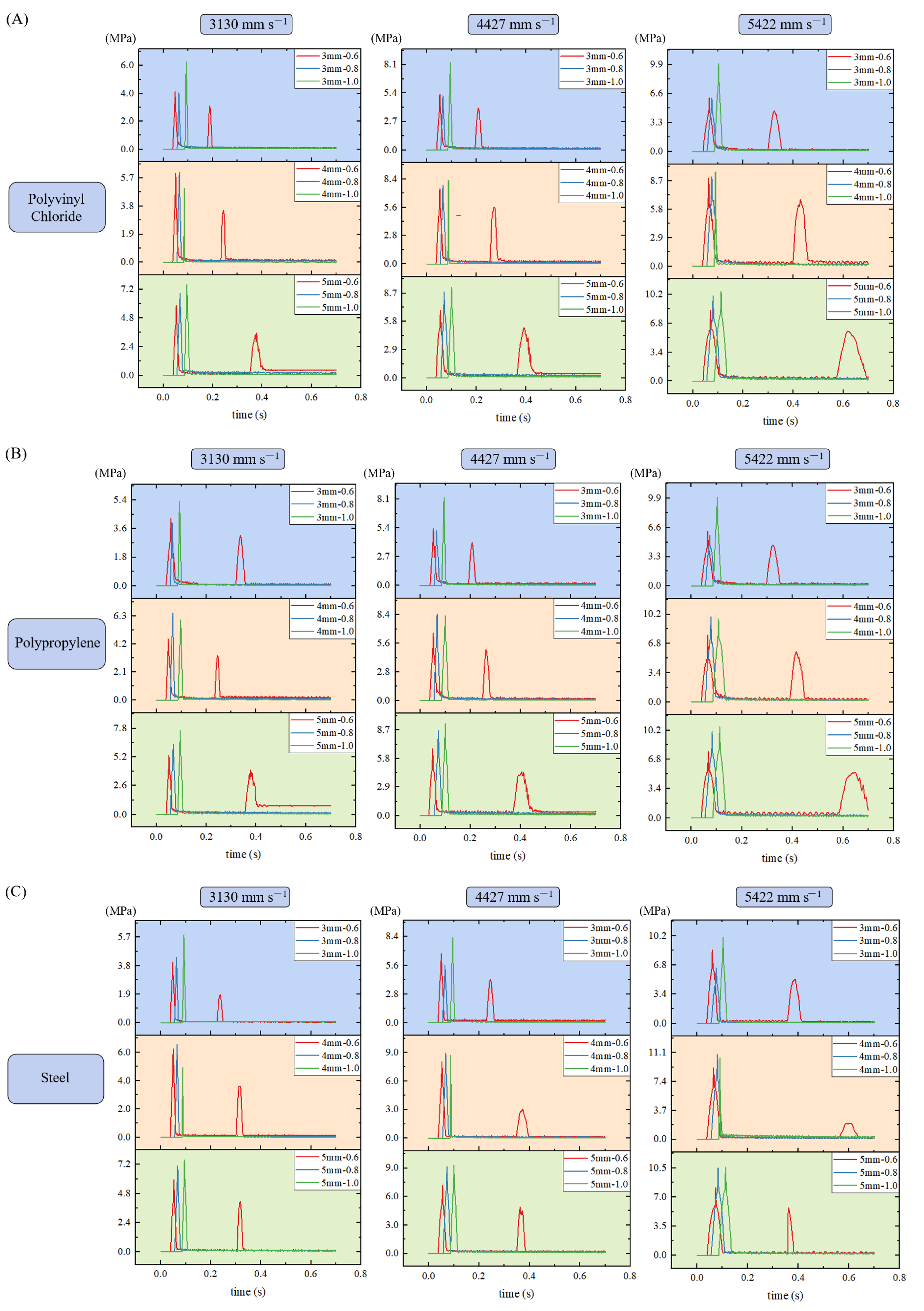

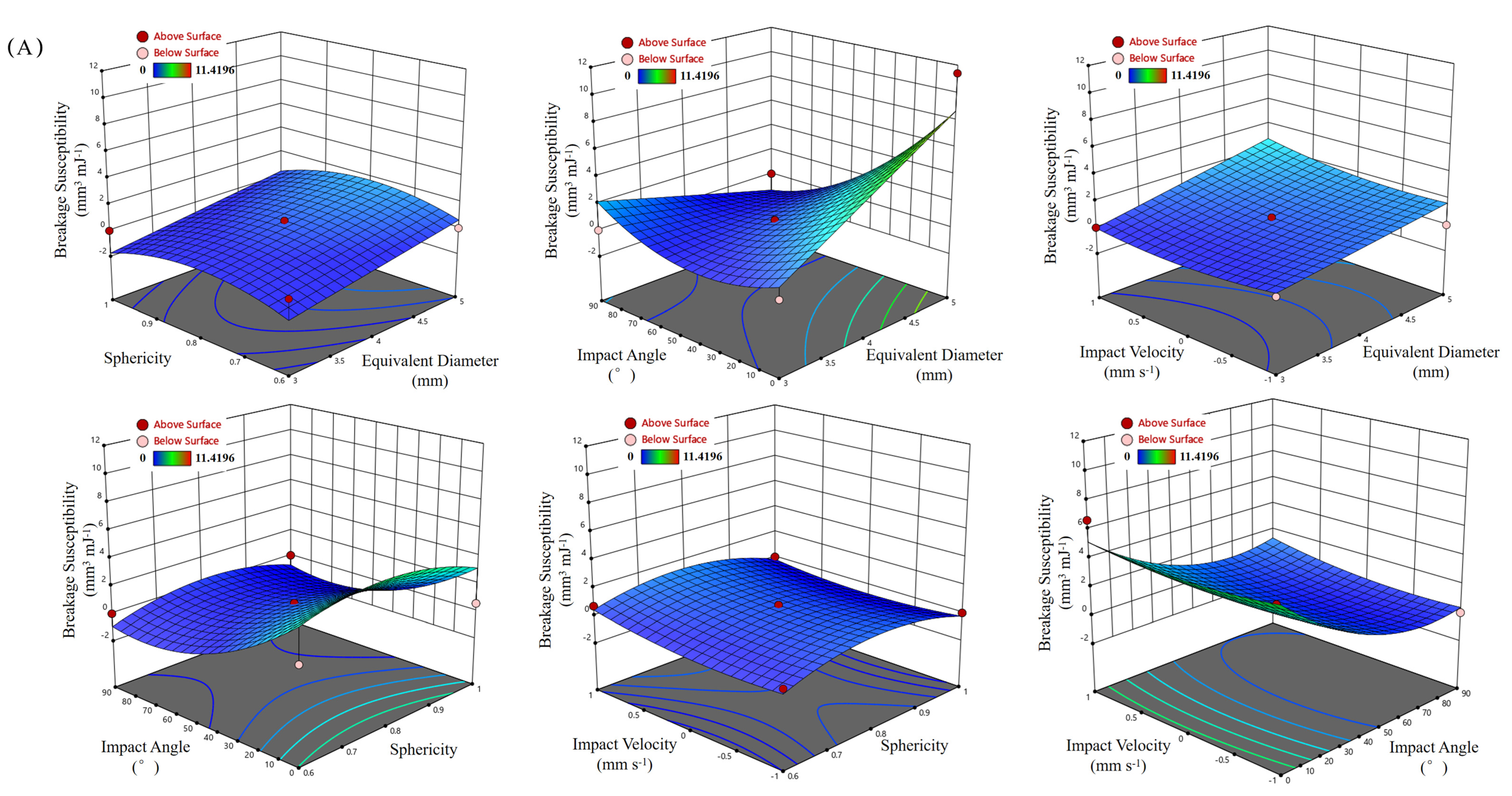

| Parameter | Sample | Mean |
|---|---|---|
| Elastic modulus | Controlled-release fertilizer | 36.23 MPa |
| Compound fertilizer | 29.81 MPa | |
| Strength limit | Controlled-release fertilizer | 11.74 MPa |
| Compound fertilizer | 8.25 MPa | |
| Density | Controlled-release fertilizer | 1250 kg m−3 |
| Compound fertilizer | 970 kg m−3 | |
| Moisture content | Controlled-release fertilizer | 5.7 ± 0.2% |
| Compound fertilizer | 1.1 ± 0.2% | |
| Poisson’s ratio | Controlled-release fertilizer | 0.33 |
| Compound fertilizer | 0.28 |
| Impact Material | Equivalent Diameter | Sphericity | Impact Angle | Impact Velocity | Equivalent Stress | Breakage Volume | Breakage Susceptibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mm) | (°) | (mm s−1) | (MPa) | (mm3) | (mm3 mJ−1) | ||
| Steel | 3 | 0.6 | 0 | 4427 | 8.7199 | 9.30 × 10−2 | 6.30 × 10−1 |
| 5422 | 9.7313 | 2.93 × 10−1 | 1.31 | ||||
| 45 | 5422 | 8.5313 | 5.56 × 10−2 | 3.00 × 10−1 | |||
| 0.8 | 0 | 5422 | 9.1669 | 1.81 × 10−1 | 1.25 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 4427 | 8.279 | 5.74 × 10−3 | 3.45 × 10−2 | ||
| 5422 | 9.9986 | 3.46 × 10−1 | 1.37 | ||||
| 4 | 0.6 | 0 | 4427 | 9.3127 | 4.98 × 10−1 | 1.4 | |
| 5422 | 11.0719 | 1.32 | 2.45 | ||||
| 45 | 5422 | 9.1564 | 4.25 × 10−1 | 7.07 × 10−1 | |||
| 0.8 | 0 | 3130 | 11.1074 | 1.34 | 7.04 | ||
| 4427 | 14.8909 | 3.11 | 8.1 | ||||
| 5422 | 16.6066 | 3.92 | 6.68 | ||||
| 45 | 4427 | 8.9082 | 3.09 × 10−1 | 6.86 × 10−1 | |||
| 5422 | 10.8589 | 1.22 | 1.83 | ||||
| 90 | 4427 | 8.3056 | 2.61 × 10−2 | 5.16 × 10−2 | |||
| 5422 | 9.5328 | 6.01 × 10−1 | 7.75 × 10−1 | ||||
| 1 | 0 | 4427 | 8.7196 | 2.20 × 10−1 | 5.57 × 10−1 | ||
| 5422 | 10.3931 | 1 | 1.48 | ||||
| 5 | 0.6 | 0 | 3130 | 11.4377 | 2.92 | 4.71 | |
| 4427 | 15.0954 | 6.27 | 5.09 | ||||
| 5422 | 17.353 | 8.34 | 4.41 | ||||
| 0.8 | 0 | 3130 | 14.2494 | 5.49 | 11.79 | ||
| 4427 | 19.746 | 10.53 | 11.42 | ||||
| 5422 | 22.3117 | 12.88 | 9.06 | ||||
| 45 | 4427 | 9.1308 | 8.07 × 10−1 | 7.91 × 10−1 | |||
| 5422 | 10.5394 | 2.1 | 1.37 | ||||
| 90 | 5422 | 9.2175 | 8.86 × 10−1 | 5.71 × 10−1 | |||
| 1 | 0 | 4427 | 9.2864 | 9.49 × 10−1 | 1.17 | ||
| 5422 | 10.5474 | 2.1 | 1.73 | ||||
| PVC | 3 | 0.6 | 0 | 4427 | 8.721 | 9.32 × 10−2 | 6.32 × 10−1 |
| 5422 | 9.7317 | 2.93 × 10−1 | 1.31 | ||||
| 0.8 | 0 | 5422 | 10.1369 | 3.73 × 10−1 | 2.29 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 4427 | 8.278 | 5.54 × 10−3 | 3.33 × 10−2 | ||
| 5422 | 9.994 | 3.45 × 10−1 | 1.37 | ||||
| 4 | 0.6 | 0 | 4427 | 9.8564 | 7.53 × 10−1 | 1.93 | |
| 5422 | 11.6225 | 1.58 | 2.81 | ||||
| 45 | 5422 | 8.9769 | 3.41 × 10−1 | 6.61 × 10−1 | |||
| 0.8 | 0 | 3130 | 10.4024 | 1.01 | 5.3 | ||
| 4427 | 13.7647 | 2.59 | 6.72 | ||||
| 5422 | 15.1857 | 3.25 | 5.52 | ||||
| 45 | 5422 | 9.1259 | 4.11 × 10−1 | 5.94 × 10−1 | |||
| 90 | 4427 | 8.3529 | 4.82 × 10−2 | 9.35 × 10−2 | |||
| 5422 | 9.5434 | 6.06 × 10−1 | 7.73 × 10−1 | ||||
| 1 | 0 | 5422 | 9.6135 | 6.39 × 10−1 | 1.15 | ||
| 5 | 0.6 | 0 | 3130 | 12.311 | 3.72 | 5.9 | |
| 4427 | 16.3742 | 7.44 | 6.07 | ||||
| 5422 | 18.5203 | 9.41 | 4.99 | ||||
| 45 | 5422 | 8.2729 | 2.10 × 10−2 | 1.67 × 10−2 | |||
| 0.8 | 0 | 3130 | 14.2494 | 5.49 | 11.79 | ||
| 4427 | 19.6597 | 10.45 | 11.36 | ||||
| 5422 | 22.2108 | 12.79 | 8.9 | ||||
| 45 | 4427 | 8.8301 | 5.31 × 10−1 | 5.35 × 10−1 | |||
| 5422 | 10.005 | 1.61 | 1.07 | ||||
| 90 | 4427 | 8.5722 | 2.95 × 10−1 | 2.84 × 10−1 | |||
| 5422 | 10.067 | 1.66 | 1.07 | ||||
| 1 | 0 | 4427 | 9.2856 | 9.48 × 10-1 | 1.17 | ||
| 5422 | 10.5464 | 2.1 | 1.73 | ||||
| PP | 3 | 0.6 | 0 | 4427 | 8.7214 | 9.33 × 10−2 | 6.32 × 10−1 |
| 5422 | 9.7318 | 2.93 × 10−1 | 1.31 | ||||
| 0.8 | 0 | 5422 | 10.1267 | 3.71 × 10−1 | 2.28 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 4427 | 8.2777 | 5.48 × 10−3 | 3.30 × 10−2 | ||
| 5422 | 9.9928 | 3.45 × 10−1 | 1.37 | ||||
| 4 | 0.6 | 0 | 4427 | 11.1431 | 1.36 | 2.99 | |
| 5422 | 13.3849 | 2.41 | 3.54 | ||||
| 0.8 | 0 | 3130 | 9.6172 | 6.41 × 10−1 | 3 | ||
| 4427 | 13.0812 | 2.27 | 5.24 | ||||
| 5422 | 15.677 | 3.48 | 5.2 | ||||
| 45 | 4427 | 8.4596 | 9.83 × 10−2 | 2.15 × 10−1 | |||
| 5422 | 9.879 | 7.64 × 10−1 | 1.13 | ||||
| 90 | 4427 | 8.3527 | 4.82 × 10−2 | 9.33 × 10−2 | |||
| 5422 | 9.5427 | 6.06 × 10−1 | 7.73 × 10−1 | ||||
| 1 | 0 | 4427 | 8.3046 | 2.56 × 10−2 | 7.04 × 10−2 | ||
| 5422 | 9.6457 | 6.54 × 10−1 | 1.18 | ||||
| 5 | 0.6 | 0 | 3130 | 11.1014 | 2.61 | 4.88 | |
| 4427 | 14.5429 | 5.76 | 5.27 | ||||
| 5422 | 16.8457 | 7.87 | 4.7 | ||||
| 0.8 | 0 | 3130 | 14.2906 | 5.53 | 11.78 | ||
| 4427 | 19.6903 | 10.48 | 11.3 | ||||
| 5422 | 22.2055 | 12.78 | 8.81 | ||||
| 45 | 4427 | 8.6392 | 3.56 × 10−1 | 3.65 × 10−1 | |||
| 5422 | 10.0191 | 1.62 | 1.1 | ||||
| 90 | 4427 | 8.5721 | 2.95 × 10−1 | 2.84 × 10−1 | |||
| 5422 | 10.0666 | 1.66 | 1.07 | ||||
| 1 | 0 | 4427 | 9.2852 | 9.48 × 10−1 | 1.17 | ||
| 5422 | 10.546 | 2.1 | 1.73 |
| Factors\Characteristics | FEM | RE | Error (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qo (g) | Qc (g) | Rc (%) | Qo (g) | Qc (g) | Rc (%) | ||
| ① 3 mm, 0.6, 4427 mm s−1 | 362.4 | 9.4 | 2.6 | 361.4 | 10.1 | 2.8 | 7.14 |
| ② 4 mm, 0.8, 5422 mm s−1 | 358.6 | 41.6 | 11.6 | 359.9 | 46.1 | 12.8 | 9.38 |
| ③ 5 mm, 0.8, 5422 mm s−1 | 346.9 | 73.9 | 21.3 | 348.5 | 80.9 | 23.2 | 8.19 |
| ④ 4 mm, 1.0, 3130 mm s−1 | 365.2 | 0 | 0 | 364.4 | 1.8 | 4.9 × 10−3 | —— |
| ⑤ 4 mm, 0.6, 4427 mm s−1 | 354.9 | 8.2 | 2.3 | 356.1 | 8.9 | 2.5 | 8.00 |
| ⑥ 3 mm, 0.8, 4427 mm s−1 | 360.5 | 10.5 | 2.9 | 359.9 | 11.5 | 3.2 | 9.38 |
| ⑦ 5 mm, 1.0, 4427 mm s−1 | 358.2 | 11.5 | 3.2 | 359.1 | 12.6 | 3.5 | 8.57 |
| ⑧ 3 mm, 1.0, 3130 mm s−1 | 342.4 | 0 | 0 | 341.5 | 0.6 | 1.8 × 10−3 | —— |
| ⑨ 4 mm, 0.6, 5422 mm s−1 | 367.7 | 15.1 | 4.1 | 368.3 | 16.6 | 4.5 | 8.88 |
| ⑩ 5 mm, 0.6, 5422 mm s−1 | 396.4 | 76.6 | 19.3 | 397.6 | 86.7 | 21.8 | 11.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Jing, L.; Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Fragmentation Susceptibility of Controlled-Release Fertilizer Particles: Implications for Nutrient Retention and Sustainable Horticulture. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11101215
Chen Z, Wang Y, Chen X, Jing L, Sun L, Zhang H, Wang J. Fragmentation Susceptibility of Controlled-Release Fertilizer Particles: Implications for Nutrient Retention and Sustainable Horticulture. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(10):1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11101215
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zixu, Yongxian Wang, Xiubo Chen, Linlong Jing, Linlin Sun, Hongjian Zhang, and Jinxing Wang. 2025. "Fragmentation Susceptibility of Controlled-Release Fertilizer Particles: Implications for Nutrient Retention and Sustainable Horticulture" Horticulturae 11, no. 10: 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11101215
APA StyleChen, Z., Wang, Y., Chen, X., Jing, L., Sun, L., Zhang, H., & Wang, J. (2025). Fragmentation Susceptibility of Controlled-Release Fertilizer Particles: Implications for Nutrient Retention and Sustainable Horticulture. Horticulturae, 11(10), 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11101215




