Abstract
Norisoprenoids are important chemical compounds to grape and wine aroma, and their content in the grape berries can be greatly affected by varietal, terroir, and environmental factors. In this study, we investigate how major factors, such as genotype and climate conditions, influence the physicochemical properties of grape juice, volatile C13-norisoprenoid compounds, and gene expression profiles of three Vitis vinifera grape varieties: Muscat blanc à Petit grain, Muscat à petits grains rouges, and Gewürztraminer during the production period in 2010 and 2011. The total soluble solids (TSS) of both Muscat varieties were significantly higher in 2011 compared to 2010, reflecting interannual climatic variations, while Gewürztraminer showed no significant differences. At full maturity, total acid of all three cultivars was consistent between the years, indicating genetic determination. Thirteen norisoprenoids were identified, with Muscat varieties showing consistently higher levels than Gewürztraminer, irrespective of the production year. Varietal differences were significant for 13 out of 14 volatile compounds, and vintage effects were notable for 11 compounds, including key aroma contributors β-damascenone and β-ionone. OPLS-DA analysis highlighted distinct volatile profiles for each variety and vintage, influenced by climatic factors such as precipitation and sunlight hours. Gene expression analysis revealed strong correlations between VvCCD1, VvCCD4a, and VvCCD4b genes and C13-norisoprenoid accumulation, with these genes also implicated in the ABA biosynthesis pathway. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in VvCCD1, VvCCD4a, and VvCCD4b were linked to variations in norisoprenoid content among the cultivars. Altogether, these findings revealed the interaction of genetic and environmental factors in shaping the physicochemical properties for the grape, volatile profiles, and gene expression patterns of grape berries, with significant implications for viticulture and the winemaking process.
1. Introduction
Wine aroma is a complex mixture of more than 1300 different chemical compounds. Aroma compounds can be classified into eight categories based on their structure, including esters, alcohols, aldehydes, acids, C6/C9 compounds, aromatic compounds, terpenes, and norisoprenoids. Among these, norisoprenoids play a significant role in grape and wine aroma profiles, particularly in non-aromatic grape varieties such as Cabernet Sauvignon, Syrah, Sauvignon Blanc, and Pinot Noir [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Norisoprenoids are produced by the oxidative cleavage of carotenoids or terpenoids containing 40 carbon atoms. The synthesis of isoprene comes from the 2-C-methyl-D-erythrin-4-phosphate (MEP) pathway in plastids. The precursors, carotenoids, are C40 tetraterpenoid pigments formed by the condensation of 8 isoprene units and are metabolically unstable due to their double bonds. They undergo chemical or enzymatic degradation to form C9, C10, C11, and C13-norisoprenoids with carbonyl structures. These compounds are known for their volatility and aromatic properties [7]. For example, C9-norisoprenoids like 2,2,6-trimethyl cyclohexanone (TCH) impart a rock-rose-like aroma, while C13-norisoprenoids, including β-damascenone and β-ionone, contribute significantly to floral and fruity notes [8,9,10,11,12]. In addition, 1,1,6-trimethyldihydronaphthalene (TDN) is known for its “ petroleum-like” aroma with a threshold of 2 μg/L [13]. Although TDN can be detected in grape berries and young ‘Riesling’ wines, its concentration is typically below the threshold, thus not affecting the flavor. However, during bottle aging of some Riesling wines, TDN levels increase rapidly, impacting the wine’s flavor. [9,14,15]. C13-norisoprenoids, particularly β-damascenone (0.05 μg/L) and β-ionone (0.09 μg/L), are known to contribute to the fruity, honey, and violet aromas of the fruit [10].
Norisoprenoids are present throughout the grapes’ flowers, leaves, and berries, predominantly as odorless glycosidic conjugates. Research indicates that free norisoprenoids begin to accumulate in Cabernet Sauvignon grapes early during berry development, peak at the end of veraison, and decline at maturity [16,17,18]. These compounds, with their low sensory thresholds and distinct aromatic properties, are crucial for the characteristic aroma of wines, as they are not hydrolyzed by grape or yeast glycosidases during fermentation.
The accumulation of aroma compounds is influenced by numerous factors, including variety, regional characteristics, vintage, and climate [19,20]. Significant differences in the types and concentrations of aroma compounds among different grape varieties have been observed. For instance, in Chardonnay grapes, aromas such as “grassy”, “tea-like”, “honey”, and “pineapple” are derived from C13-norisoprenoids and their precursors [21,22]. In Riesling and Muscat grapes, high contents of norisoprenoids and substantial amounts of terpenes such as vitispirane, β-damascenone, TDN, and β-ionone are detected [23,24,25]. The gene expression patterns of norisoprenoids have been studied across various grape varieties, including Cabernet Sauvignon, Syrah, Riesling, Chardonnay, and Pinot Gris. In Riesling, the concentration of β-damascenone was found to be higher than in Chardonnay, followed by Pinot Gris, but lower than in Shiraz and Cabernet Sauvignon [26]. High levels of norisoprenoids are also reported in non-aromatic red and white wine grape varieties, such as Cabernet Sauvignon, Syrah Semillon, Sauvignon Blanc, and Chenin Blanc [19,22]. In recent years, five VvCCDs have been identified in grapes. VvCCD1 was first cloned and confirmed to produce C13-norisoprenoids in Vitis vinifera L. cv. Shiraz. VvCCD1, VvCCD4a, and VvCCD4b have been cloned from grapes, while VvCCD7 and VvCCD8 were predicted by software but found unrelated to the synthesis of C13-norisoprenoids [3]. VvCCD1, VvCCD4a, and VvCCD4b can cleave carotenoids into norisoprenoids with 9, 10, 11, and 13 carbon atoms, with specific substrate preferences. Lashbrooke’s research showed that VvCCD1, VvCCD4a, and VvCCD4b are functional with unique substrate specificities [27].
Wine grapes are often categorized into three groups based on the amount of free monoterpenoids they contain. These categories are defined as Muscat varieties, which are characterized by high levels of free monoterpenes; non-Muscat aromatic varieties, which contain moderate levels of free monoterpenes; and neutral varieties, which are distinguished by extremely low levels of free monoterpenes. The fragrance of Muscat and non-Muscat aromatic varietals is significantly influenced by terpenes and C13-norisoprenoids [28]. In recent years, attention has been focused on these varieties. However, it was found in our previous research that the levels of these compounds were also quite high in Muscat-flavored varieties. In this study, it was focused on three distinct Vitis vinifera L. grape varieties: Muscat blanc à Petit, Muscat à petits grains rouges, and Gewürztraminer. Our primary objective was to investigate how genotype and vintage influence the accumulation of C13-norisoprenoids and the expression of related genes in these varieties. These selected varieties are categorized into floral and non-Muscat aromatic based on their terpene levels. By analyzing these factors, we aimed to provide a comprehensive understanding of how genetic and environmental conditions affect norisoprenoid profiles and their role in wine aroma.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Grape Materials and Growth Conditions
Three Vitis vinifera L. wine grape varieties were used in this research: Muscat blanc à Petit, Muscat à petits grains rouges, and Gewürztraminer. Gewürztraminer is native to northern Italy and is grown in many wine-producing regions around the world. The typical flavor is described as lychee flavor, and the types of wine range from dry, semi-dry, to sweet. Muscat blanc à Petit is originally from Greece and is widely cultivated around the world as a versatile variety for both fresh food and wine. It can be brewed separately as dry white or sweet white wine, or mixed with other varieties to make sparkling wine. Muscat à petits grains rouges mainly produces sweet wines and can also be blended with other varieties. The berries were collected from the same vineyard located in Gaotai, Gansu Province, northwest China (39°14′ N, 99°84′ E). The vineyard was established in 2001, using self-rooted cuttings. The vineyard is located on the edge of the desert, with an average altitude of about 1400 m. According to the China Meteorological Science Data Sharing Service (https://data.cma.cn/, accessed no 10 July 2016), it is a cold and semi-arid area with an annual effective accumulated temperature of 2800–3000 °C, an average annual precipitation of 66.4–100 mm, and an average annual sunshine hours of 3120 h. The temperature difference between day and night is large, with an average daily temperature difference of 14.9 °C and an annual average temperature of 7.6 °C. An extreme high temperature of 38.7 °C was recorded in 1999. The soil type is sandy loam, and the vineyard is oriented north–south with a row spacing of 2.0 m and a plant spacing of 1.0 m. The vines were trained using the vertical shoot positioning (VSP) system, and vineyard management adhered to winery standards, including the use of a lime sulfur solution for pest and disease control and an application of base fertilizer and compound fertilizer. In vintage 2010, the flowering dates were as follows: Gewürztraminer: 11 June; Muscat blanc à Petit grain: 12 June; and Muscat à petits grains rouges: 14 June. In vintage 2011, the flowering dates were as follows: Gewürztraminer: 12 June; Muscat blanc à Petit grain: 14 June; and Muscat à petits grains rouges: 15 June. Berry sampling was conducted during the 2010 and 2011 growing seasons, starting 4 weeks after flowering and continuing at 6 and 8 (E-L35 Berries begin to color and enlarge), 10 (E-L36,Berrries with intermediate Brix values), 12 (E-L37, Berries not quite ripe), 14, and 15 (E-L38 Berries harvest-ripe) weeks (Figure S1), with three replicates and 2 rows per replicate (2 × 9 trees) collected at each stage, totaling 1000 berries [29]. To minimize edge effects, samples were not taken from the outer five rows or within seven meters from the row ends. Sampling accounted for sun-exposed and shaded berries, as well as berries from the inner and outer canopy. Berries were randomly collected from different parts of the cluster, including the shoulder, middle, and tip. The collected samples were immediately flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C.
2.2. Physicochemical Indexes
A total of 100 grape berries were used to determine the weight and volume of a hundred berries. After the berry weight was measured, the 100 grape berries were continued to be used to measure physical and chemical indicators. These grapes were compressed to extract grape juice following the removal of seeds. The grape juice was used for the examination of total soluble solids and total acids. The total soluble solids of the juices were quantified using a digital refractometer (Pocket Refractometer Pal1, Atago, Tokyo, Japan), and the sugar content was reported in Brix. The titratable acidity was determined following the previous study [1]. Each variety’s 50 mL grape juice sample was placed in a vacuum flask. The juice was vacuumed using a water pump for one to two minutes while shaking continuously. Next, 10 mL of processed grape juice was combined with 25 mL of boiled distilled water and 1 mL of bromothymol blue solution in a beaker. A 0.1 mol/L sodium hydroxide solution was added to the mixture until the color changed to blue–green. Then, 5 mL of the pH 7.0 buffer solution was added to the mixture. Next, 10 mL of processed grape juice was combined with 30 mL of boiled distilled water and 1 mL of bromothymol blue solution into a beaker. A 0.1 mol/L sodium hydroxide solution was added to the mixture until the same color was obtained as above.
2.3. Extraction and GC-MS Analysis of Volatile Compounds
One hundred g of grape berries were taken, de-seeded under liquid nitrogen protection, ground into powder, and 0.5 g of Glucono-δ-lactone USP26 FCCIV (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) and 2.0 g of PVPP (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) were added. The juice was extracted by soaking from the powder at 4 °C for 120 min, and then centrifuged at 4 °C at 5000× g for 15 min. The supernatant was collected [30]. Each variety’s 5 mL grape juice sample was combined with 10 µL of 4-methyl-2-pentanol (internal standard) (1.0388 g/L, Fluka, Buchs, Switzerland, and Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) and 1 g of NaCl (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Beijing Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) in a 20-mL vial with a PTFE–silicon septum and a magnetic stirrer. The mixture was agitated at 500 rpm for 30 min at 40 °C. A DVB/CAR/PDMS SPME fiber (12.50/30-μm DVB/Carboxen/PDMS, Supelco, Bellefonte, PA, USA) was preheated to 250 °C, then inserted into the vial headspace for 30 min at 40 °C to adsorb volatile compounds. The fiber was subsequently desorbed in the GC injector port for 8 min. The inlet temperature is 250 C, the ionization mode is EI, the ionization energy is 70 eV, the ion source temperature is 230 C, and the mass spectrum interface temperature is 280 C.
Volatile compounds were analyzed using an Agilent 7890N GC coupled with a 5975C MS, using an HP-INNOWAX capillary column (60 m × 0.25 mm, 0.25 µm) with helium as the carrier gas (1 mL/min). The oven temperature was programmed from 50 °C (1 min) to 220 °C at 3 °C/min, with a final hold of 5 min. Retention indices were calculated using n-alkanes (C6–C24, Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) and compared with the NIST05 library and the literature. Quantification was based on peak area ratios relative to the internal standard.
2.4. Real-Time PCR Analysis
For each variety, 10 berries without seeds were ground into powder, and 1 g of powder was used for RNA extraction. Total RNA was extracted using a Plant RNA Isolation Kit (Sigma RT-250, St. Louis, MO, USA). RNA integrity was verified using agarose gel electrophoresis. The RNA quantity and quality were evaluated using a Qubit 2.0 Fluorometer RNA Assay Kit (Invitrogen Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) and an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer RNA 6000 Nano Kit (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA), respectively. Additionally, 5 g total RNA was used to synthesize first-strand complementary DNA (cDNA) using the SuperScript First-Strand Synthesis System (Promaga, Madison, WI, USA). Gene-specific oligonucleotide primers for VvCCD1, VvCCD4a, and VvCCD4b were designed by Primer-Blast from NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/primer-blast/, accessed on 21 June 2018), and their sequences are listed in Table S1. Three grapevine reference genes were used for coding Ef (AT5G60390.1), actin (AF369524), GAPDH (CB975242), and ubiquitin (EC929411). Additionally, 10 µL of SYBR®Premix Ex TaqTM, 0.5 µL of ROX Reference Dye (50×) (Takara, Dalian, China), 1 µL of 10 mM primer mixture (forward primer and reverse primer), 4 µL of diluted template cDNA, and 4.5 µL of ddH2O were mixed to generate PCR solution. During the PCR cycling program, an initial denaturation was carried out at 95 °C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles of amplification at 95 °C for 10 s, and then at 60 °C for 31 s. Melt curve analysis from 65 °C to 95 °C was used to detect possible primer dimers or nonspecific amplification in the cDNA samples. The specificity of primers was confirmed using agarose gel electrophoresis. The expression level of the target gene was calculated using the equation below:
where CTref represents the geometric mean of three reference gene threshold cycles (CTs). The mean and standard deviation were estimated after 2−ΔCT calculations [31]. The q-PCR reaction for each replicate was carried out in triplicate.
The expression level = 2−ΔCT
ΔCT = CTtarget − CTref
ΔCT = CTtarget − CTref
2.5. Comparative Sequencing
The template for the experiment consisted of total RNA isolated from ripe grape berries, chosen for their high expression of VvCCD1, VvCCD4a, and VvCCD4b. Subsequently, AMV reverse transcriptase (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) and oligo d(T)18 (Takara, Dalian, China) were used to generate cDNA following the manufacturer’s instructions. The gene-coding region was cloned by performing full-length nucleotide sequence cloning using Master Mix (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The cloning process was conducted in a high-fidelity buffer under specific PCR conditions: 94 °C for 30 s, followed by 35 cycles consisting of 94 °C for 30 s, 56 °C for 60 s, and 72 °C for 30 s, and then a final elongation step of 72 °C for 5 min. The primer sequences are shown in Table S2. Afterwards, the PCR products were purified using the Wizard SV Gel PCR Clean-Up System (Takara, Dalian, China). The PCR products were purified and then subjected to A-tailing using Taq DNA Polymerase from ThermoFisher Scientific, located in Waltham, MA, USA. Subsequently, the PCR products with A-tails were joined to the pMD-19 vector (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) by ligation. The sequencing was carried out by Sangon (Shanghai, China). Correlation analysis is performed by R 4.3.2.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The data were presented as the average value ± standard deviation. A one-way analysis of variance [32,33] was conducted to assess the significance of the mean value using Duncan’s multiple range test at significance levels of 0.01 and 0.05, respectively. Hierarchical cluster analysis was conducted using the previously described approach, using MetaboAnalyst 3.0 (http://www.metaboanalyst.ca/, accessed on 21 June 2018) via the ‘Time Series Analysis’ interfaces [34]. Metabo-Analyst 3.0 was used for partial least squares discriminate analysis on a portion of normalized data. DNASTAR 2.0 was used to build nucleotide sequences (http://www.dnastar.com/).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparisons of Physicochemical Indexes among Different Varieties/Cultivations
The total soluble solids (TSS) and the total acid (TA) were compared among three varieties during berry development in 2010 and 2011 (Figure 1A). For Muscat blanc à Petit grain, from 12 weeks after flowering, the TSS in 2011 was higher than in 2010, while the TA in 2011 was lower than that in 2010. For Muscat à petits grains rouges, the TSS in 2011 was significantly higher than in 2010 from week 8 to week 14 after flowering, while the TA in 2011 was significantly lower than in 2010 from week 8 to week 10 after flowering. This interannual variation likely reflects differences in climatic conditions between the two vintages. Similar vintage effects on TSS have been reported in other grape varieties, such as Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot [35]. Compared to 2011, 2010 had a higher total acid during the whole grape development period for Muscat varieties, while the TA of Gewürztraminer in two consecutive years had almost identical trends during the grape development period.
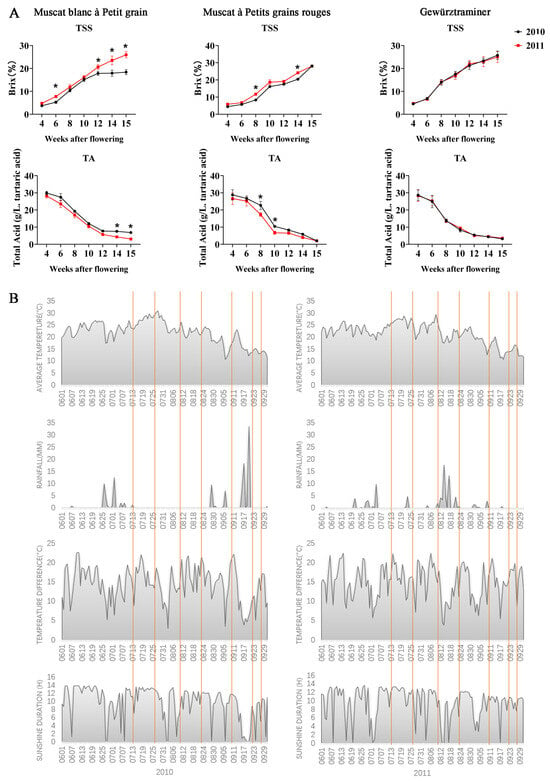
Figure 1.
Physicochemical indexes of three Vitis vinifera varieties during grape development and climatic data of Gaotai in 2011 and 2010. (A) Physicochemical indexes of three Vitis vinifera varieties during grape development. (B) Climatic data of Gaotai in 2011 and 2010, including average daily temperature, diurnal temperature difference, rainfall, and sunshine duration. Orange lines indicate 7 sampling days (7.13, 7.26, 8.10, 8.23, 9.10, 9.22, and 9.27), respectively. * Represents significant differences of parameters between 2010 and 2011 groups for the same stage (t test, p < 0.05).
Additionally, there are variations between varieties in the same vintage, especially in terms of TSS (Figure 1A). In 2011, the two Muscat varieties had a similar TSS, both higher than that of Gewürztraminer. This aligns with the general understanding that Muscat varieties tend to accumulate higher sugar levels compared to non-Muscat aromatic varieties like Gewürztraminer [36]. However, there was also a study on table grapes that found the total aroma content in the Jingya variety to be significantly higher than in other table grape varieties, while its TSS is significantly lower than that of the other varieties [37]. The observed differences in TSS accumulation patterns between the Muscat varieties and Gewürztraminer may be related to their distinct genetic backgrounds and metabolic processes. Muscat varieties are known for their high monoterpene content, which is closely linked to sugar metabolism [38]. The higher TSS in Muscat varieties could potentially be associated with their enhanced capacity for terpene synthesis. However, Muscat blanc à Petit grain had markedly lower TSS than the other two varieties in 2010, for reasons that will be discussed below. Interestingly, Gewürztraminer did not show significant differences in TSS and TA between 2010 and 2011, suggesting this variety may be less sensitive to year-to-year climate variations compared to the Muscat varieties, which were easily affected by environmental conditions [39].
In terms of climatic data of Gaotai (Figure 1B), the difference in average daily temperature of the 6 sampling days between 2010 and 2011 was in a state of fluctuation during the sampling period, resulting in two consecutive years close to each other regarding average daily temperature. Except for 13 July, the diurnal temperature difference of 6 sampling dates in 2010 was greater than that in 2011. For rainfall, 2010 barely witnessed rainfall in Gaotai, except for the first sampling day on 13 July, while the middle 3 sampling days in 2011 (10 August, 23 August, and 10 September) did not receive more than 2 mm of rainfall. For sunshine duration, the number of sunshine hours on 13 July, 10 August, and 22 August of the sampling period in 2010 was less than that in 2011, while the number of sunshine hours on 23 August and 10 September in 2010 was more than that in 2011.
It is widely recognized that water deficiency can negatively affect vine growth. However, some studies suggest that a certain level of water deficit during the ripening stage can promote maximum photosynthetic activity and minimize stomatal expansion, which in turn facilitates the ripening process and reduces berry size [40]. This could potentially result in more desirable sugar and acid levels at harvest. Nevertheless, in Figure 1A,B, it is observed that the sugar content in Muscat blanc was significantly lower in 2010 compared to 2011, while the acidity was notably higher in 2010 than in 2011 after 12 weeks. These outcomes may be attributed to other factors, such as temperature and soil conditions, which likely interacted with water availability to produce the observed differences. In terms of climate, there was a higher temperature difference between day and night and longer sunshine hours in 2010. The high temperature during the day is beneficial for plant photosynthesis to synthesize organic matter. The low temperature at night reduces the respiration of plants, which can decrease the decomposition of organic matter, thereby accumulating organic matter and converting it into sugar. And the effect of sunshine time on photosynthesis is also the same. These made the higher sugar content in 2011. For the acidity, we observed that grapes have lower TA at higher temperature differences. This is different with findings by Yan Y, Song C, Falginella L, et al. [41], who reported that a larger difference between day/night temperatures increased the TA level. This may be due to the significant difference in the climate and soil conditions in the two regions.
3.2. Volatile C13-Norisoprenoid Compounds
In all three varieties, 13 norisoprenoids were detected in grape berries (Table 1) [17], consistent with previous studies reporting these compounds as contributors to floral and fruity aromas in grapes. Furthermore, the analysis of total volatile norisoprenoid content across varieties and vintages (Figure 2) revealed consistently higher levels in Muscat berries compared to Gewurtztraminer, regardless of the year. This varietal difference persisted despite climatic variations, suggesting a strong genetic component in isoprenoid accumulation. This observation is supported by [42], who reported higher norisoprenoid concentrations in Muscat varieties compared to non-aromatic varieties.

Table 1.
Volatile C13-norisoprenoid compounds identified in this research.
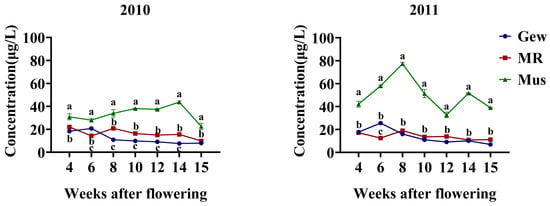
Figure 2.
Evolution of the concentrations of total volatile norisoprenoids in three grape cultivars during berry development. Mus: Muscat blanc à Petit grains; MR: Muscat à petits grains rouges; Gew: Gewürztraminer. Different letters on the line chart indicate statistically different values (p < 0.05) according to Duncan’s test; no letters indicate no statistical difference.
For the total degraded isoprenoid content in grape berries of different varieties from the years 2010 and 2011 (Figure 2), the aroma of Muscat blanc à Petit grain berries was significantly higher than that of the other two varieties throughout the entire development process. This pattern was consistent regardless of the year, indicating that climate variations do not affect the higher total degraded isoprenoid content in Muscat blanc à Petit grain berries compared to the other two varieties. In 2010, after the veraison stage, the total degraded isoprenoid content in Muscat à petits grains rouges was higher than in Gewürztraminer, while in 2011, there was no significant difference between Gewürztraminer and Muscat à petits grains rouges.
3.3. Volatile C13-Norisoprenoid Compounds between Vintage 2010 and 2011
In addition, the two-way ANOVA revealed significant varietal differences for 13 out of 14 compounds, while vintage effects were significant for 11 compounds, including key aroma contributors β-damascenone and β-ionone (Table 2). These findings are consistent with those of [46], who observed significant varietal and vintage effects on C13-norisoprenoid accumulation in Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, and Cabernet Gernischt grapes [46]. OPLS-DA analysis distinguished between 2010 and 2011 vintages for different varieties, with different compounds contributing to this distinction among varieties (Figure 3A,B). For Muscat varieties, β-ionone and cyclocitral were key differentiators, but there were not significant differences in Gewürztraminer, which is a non-Muscat aromatic variety, suggesting that these two compounds are more susceptible to climatic factors in Muscat varieties, albeit with opposite trends between Muscat blanc à Petit grain and Muscat à petits grains rouges (Figure 3C). This varietal-specific response to vintage conditions aligns with observations on the differential impact of climate on aroma compounds across grape varieties [47] (Figure 1B).

Table 2.
Two-factor variance analysis between variety and vintage.
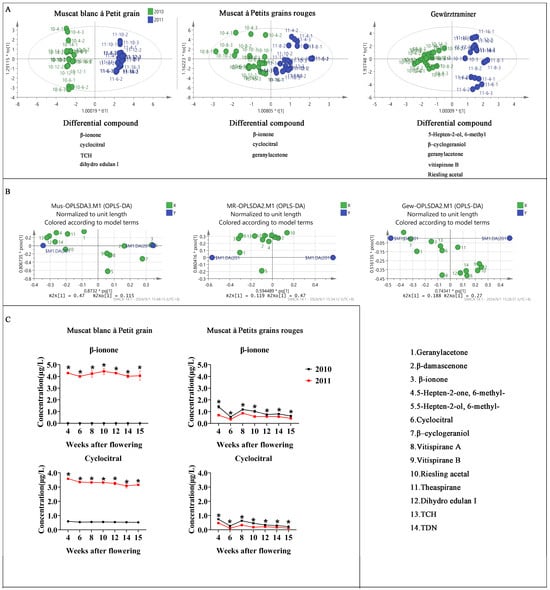
Figure 3.
Volatile C13-norisoprenoid compounds between vintage 2010 and 2011. Orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) score plot (A) and the loadings plot (B) obtained from grape berries between vintage 2010 and 2011. (C) Key volatile C13-norisoprenoid compounds between vintage 2010 and 2011. * Represents significant differences of parameters between 2010 and 2011 groups for the same stage (t test, p < 0.05).
Climatic analysis (Figure 1B) revealed significant differences in precipitation patterns and sunlight hours between 2010 and 2011. The higher monoterpene content observed in 2011 across all varieties may be attributed to lower precipitation and higher sunlight hours during the ripening period. This is consistent with studies by Talaverano et al. (2018) and Zhang et al. (2017), who reported increased aroma compound accumulation under water-limited conditions and higher light exposure, respectively [48,49]. Further varietal differentiation through OPLS-DA identified characteristic compounds for each variety: geranylacetone for Muscat à petits grains rouges, β-damascenone and β-cyclogeraniol for Muscat blanc à Petit grain, and TCH for Gewürztraminer. These findings highlight the unique aromatic profiles of each variety, supporting the work of Lambrechts [50] on the varietal-specific accumulation of aroma compounds in grapes [50,51].
Together, our findings demonstrate the complex interplay between genetic and envi-ronmental factors in determining the C13-norisoprenoid profile of grape berries. The consistent varietal differences observed, particularly the higher isoprenoid content in Muscat varieties, underscore the importance of genotype in aroma compound accumulation. Simultaneously, the significant vintage effects highlight the role of climatic conditions in modulating these compounds. These findings have important implications for viticulture and winemaking, particularly in the context of climate change, such as light, temperature difference, and rainfall, and suggest potential avenues for targeted breeding programs aimed at enhancing desirable aroma profiles in grapes.
3.4. Volatile C13-Norisoprenoid Compounds among Different Varieties
To further investigate the differential compounds among different grape varieties, we conducted OPLS-DA (orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis) on the changes in C13-norisoprenoids during the grape berry development process of three varieties in 2010 and 2011. As Figure 4A shows, we performed the score plot analysis for the berry development process; each point represents a sample, and different colors represent different grape varieties, and the three grape varieties could be completely separated. The analysis identified four key compounds with VIP (variable importance in projection) scores greater than 1: geranylacetone, β-damascenone, β-cyclogeraniol, and TCH (Figure 4B).
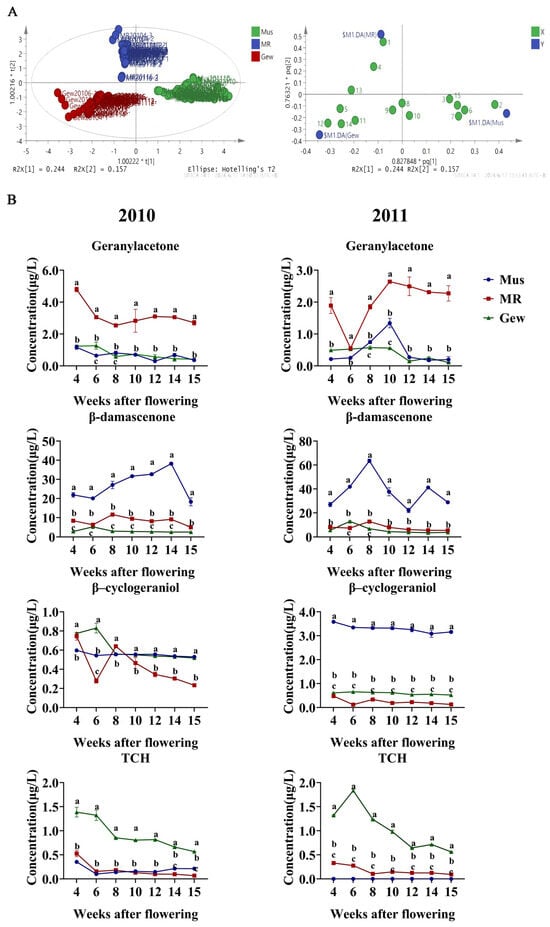
Figure 4.
Volatile C13-norisoprenoid compounds among different varieties. Orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) (A) score plot and variable correlation map obtained from grape berries among different varieties. (B) Key volatile C13-norisoprenoid compounds among different varieties. Different letters on the line chart indicate statistically different values (p < 0.05) according to Duncan’s test; no letters indicate no statistical difference.
Geranylacetone is known to contribute significantly to floral and fruity aromas, and its high content in the Muscat à petits grains rouges variety indicates a unique aromatic profile [3]. In the specific analysis, geranylacetone content was significantly higher in the Muscat à petits grains rouges variety compared to the other two varieties, making it a characteristic compound of the Muscat à petits grains rouges variety. β-damascenone and β-cyclogeraniol are characteristic compounds of the Muscat variety. These compounds significantly enhance the floral and fruity notes of the wine, particularly in the Muscat variety, indicating unique metabolic pathways for aromatic compound accumulation in this variety [17]. TCH is a characteristic compound of the Gewürztraminer variety, consistent with the unique aromatic profile of the Gewürztraminer variety, further supporting the differences in compound accumulation among varieties.
Differential compounds varied in different years and varieties. Further analysis showed significant differences in the accumulation patterns of C13-norisoprenoids among different years and varieties. As shown in the results, the accumulation pattern of geranylacetone in the Muscat variety was relatively stable, while it varied more in the other varieties during 2010 and 2011. In contrast, the accumulation of β-damascenone in the Muscat variety showed greater volatility in 2011 than that in 2010. Meanwhile, the β-cyclogeraniol content showed significant differences among varieties, especially in the Muscat à petits grains and Muscat à petits grains rouges varieties, with overall higher content in 2011 than that in 2010, and TCH showed distinct accumulation peaks in the Gewürztraminer variety, particularly between 6 and 10 days after flowering. These differences were related to the climates. β-damascenone was related to the sunlight hours and precipitation [35]. The TCH was associated with the high accumulation of its characteristic aromatic components [36]. Taken together, these results suggested that climate and grape variety affect the compound accumulation.
These findings indicate that grape varieties play a significant role in the accumulation of C13-norisoprenoids and related gene expression. Different varieties show significant genotypic differences in the accumulation of these compounds, which is crucial for understanding the aromatic characteristics of grapes and their wines. Specifically, the high accumulation of β-damascenone and β-cyclogeraniol in the Muscat blanc à Petit grain variety indicates unique metabolic pathways for the synthesis of aromatic compounds in this variety. These discoveries opened up new areas of study in chemicals found in different types of grapes and wines, which could help make them smell better.
3.5. Correlation Analysis of Volatile C13-Norisoprenoid Compounds and Their Synthesis-Related Genes
The correlation between gene expression levels and C13-norisoprenoid compound content during grape berry development from two vintages across different varieties is illustrated in Figure 5. A strong correlation between the expression of VvCCD1, VvCCD4a, and VvCCD4b genes and key C13-norisoprenoid compounds, including geranylacetone, β-damascenone, and β-ionone, in all three grape varieties studied was revealed by our analysis. These findings are consistent with previous research identifying VvCCD1, VvCCD4a, and VvCCD4b as crucial enzymes in the biosynthesis of C13-norisoprenoids. It was demonstrated that VvCCD4a and VvCCD4b are capable of cleaving various carotenoid substrates, producing important aroma compounds such as β-ionone and geranylacetone [27]. Similarly, it was shown that VvCCD1 is involved in the production of β-ionone from zeaxanthin [52]. The observed correlation between these genes and monoterpenoid compounds suggests a coordinated regulation of gene expression and metabolite production during berry development. This coordination is likely to be crucial for the accumulation of characteristic varietal aromas in grapes.
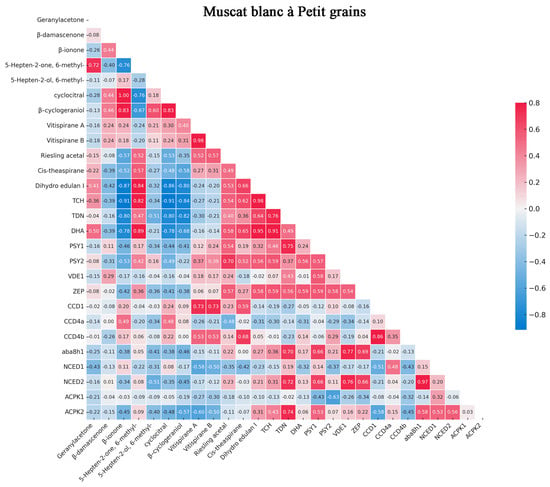
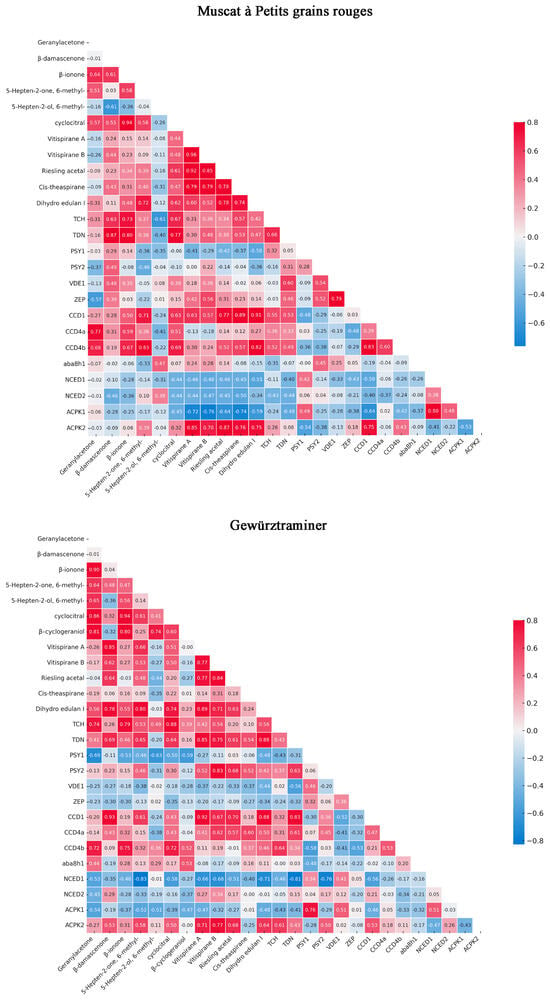
Figure 5.
The correlation between gene expression levels and monoterpenoid compound content in different varieties. The grape varieties were Muscat blanc à Petit grain, Muscat à petits grains rouges, and Gewürztraminer. Key volatile C13-norisoprenoid compounds were positively related gene expression levels (bright red) or negatively related gene expression levels (bright blue), and white represented no relation between compounds and gene expression levels.
The varietal differences in gene expression patterns and corresponding norisoprenoid levels observed in our study are indicative of genotype-specific regulation of aroma compound biosynthesis. This is in line with previous studies, which found varietal differences in CCD gene expression and corresponding differences in C13-norisoprenoid levels in different grape cultivars [53].
3.6. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism of VvCCD1, VvCCD4a, and VvCCD4b among Different Varieties
The sequences of VvCCD1, VvCCD4a, and VvCCD4b among different grape varieties are shown in Table S3. And the SNP analyses of VvCCD1, VvCCD4a, and VvCCD4b are displayed in Table 3. Despite these mutations, the overall similarity among the varieties was more than 99%. However, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were detected that could potentially influence the biosynthesis of C13-norisoprenoids. For instance, five SNPs were identified in VvCCD1 among the cultivars, with positions 44 and 239 being unique to Muscat à petits grains rouges. These specific mutations may be linked to the high concentrations of β-damascenone, TCH, β-cyclocitral, Vitispirane A, Vitispirane B, Riesling acetal, and α-cyclogeraniol in this variety. Previous studies, such as those by [54], have shown that SNPs can significantly alter enzyme activity and metabolite production, supporting the potential impact of these mutations on norisoprenoid synthesis [55]. Similarly, position 245 in VvCCD4a was unique to Gewürztraminer, which exhibited higher concentrations of 6-methyl-5-Hepten-2-one compared to other cultivars. This suggests that specific SNPs in VvCCD4a may influence the biosynthesis of certain norisoprenoids, consistent with findings by Lashbrooke et al. (2013) on the role of CCD genes in norisoprenoid production [27].

Table 3.
Comparison analysis of the open reading frame of VvCCD1, VvCCD4a, and VvCCD4b in three Vitis vinifera L. wine grape cultivars.
Unique SNPs at positions 252 and 387 in VvCCD4b were found in Gewürztraminer, while positions 231 and 357 were specific to Muscat à petits grains rouges. The latter variety showed the highest concentrations of TDN and dihydroedulan but lower levels of 5-Hepten-2-ol, 6-methyl-, geranylacetone, β-cyclocitral, and α-cyclogeraniol. These results align with the previous work, which reported varietal differences in CCD gene expression and corresponding norisoprenoid levels. The differential contribution of volatile compounds to the aroma profiles of different cultivars was evident. For instance, β-damascenone accounted for more than 50% of the aroma in Muscat à petits grains rouges grapes, but only 20–30% in Muscat à petits grains rouges and Gewürztraminer grapes. This highlights the significant role of genetic factors in determining the aromatic characteristics of grape varieties. Previous research by Battilana et al. [54] identified a mutation in the VvDXS gene that resulted in altered enzyme activity and increased monoterpene production [54]. Similarly, the SNPs identified in our study could potentially lead to varietal differences in norisoprenoid synthesis. Further studies are needed to confirm the functional impact of these mutations and their role in shaping the aroma profiles of different grape varieties.
4. Conclusions
This study provides valuable insights into the interaction between genotype and environmental factors in shaping the physicochemical properties, volatile C13-norisoprenoid profiles, and gene expression patterns of Vitis vinifera grape varieties. Our findings identified thirteen norisoprenoids, with Muscat varieties consistently showing higher levels than ‘Gewürztraminer’ across both years. Significant varietal differences were observed in 13 volatile compounds, while vintage effects were notable for 11 compounds, including key aroma contributors like β-damascenone and β-ionone, highlighting the complex interplay between genotype and environment. In addition, OPLS-DA analysis further highlighted the distinct volatile profiles for each variety and vintage, which were influenced by climatic factors such as precipitation and sunlight hours. Gene expression analysis revealed strong correlations between the accumulation of C13-norisoprenoids and the expression of genes such as VvCCD1, VvCCD4a, and VvCCD4b, which are also involved in the ABA biosynthesis pathway. Moreover, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in these genes were linked to variations in norisoprenoid content among the cultivars, providing further evidence of the genetic basis for these traits. These findings suggest fundamental information for improving selective breeding of grape varieties with desired aromatic qualities can be significantly enhanced, alongside the optimization of viticulture practices aimed at preserving and enhancing wine aroma under varying environmental conditions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae10090970/s1, Figure S1: Sample pictures of different varieties during grape development; Table S1: GenBank accession number and primers for quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR); Table S2: PCR primers used to clone the full length of VvCCD genes. Table S3: Data for the correlation between gene expression levels and concentration of C13-norisoprenoid compounds. Table S4: Sequences for the key genes from different varieties. Table S5: Climate data for vintage 2010 and 2011.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.G. and X.L.; methodology, Y.G.; software, X.L.; validation, Y.G. and X.L.; formal analysis, X.M.; investigation, Y.W.; resources, J.L.; data curation, X.L.; writing—original draft preparation, X.L.; writing—review and editing, N.A.; visualization, N.A.; supervision, C.D. and Q.P.; project administration, C.D.; funding acquisition, X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 32202416, the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China, grant number CSTB2023NSCQ-MSX0947, and Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences, grant number KJCX20220413.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article or Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Yuan, F.; Qian, M.C. Development of C13-norisoprenoids, carotenoids and other volatile compounds in Vitis vinifera L. Cv. Pinot noir grapes. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Wen, Y.Q.; Meng, N.; Qian, X.; Pan, Q.H. Monoterpenyl Glycosyltransferases Differentially Contribute to Production of Monoterpenyl Glycosides in Two Aromatic Vitis vinifera Varieties. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, S.; Terrier, N.; Procureur, J.; Bigey, F.; Gunata, Z. A carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase from Vitis vinifera L.: Functional characterization and expression during grape berry development in relation to C13-norisoprenoid accumulation. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 2721–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canuti, V.; Conversano, M.; Calzi, M.L.; Heymann, H.; Matthews, M.A.; Ebeler, S.E. Headspace solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for profiling free volatile compounds in Cabernet Sauvignon grapes and wines. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 3012–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Orte, P.; Concejero, B.; Astrain, J.; Lacau, B.; Cacho, J.; Ferreira, V. Influence of viticulture practices on grape aroma precursors and their relation with wine aroma. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 688–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryona, I.; Sacks, G.L. Behavior of Glycosylated Monoterpenes, C13>-Norisoprenoids, and Benzenoids in Vitis vinifera cv. Riesling during Ripening and Following Hedging. In Carotenoid Cleavage Products; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Volume 1134, pp. 109–124. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes-Pinto, M.M. Cartenoid breakdown products the-noisoprenoids-in win aroma. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 483, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, V.A.P.; Ramalho, P.S.; Azevedo, Z.; Macedo, A.; Chemistry, F. Identification of some volatile descriptors of the rock-rose-like aroma of fortified red wines from douro demarcated region. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 4327–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubelakis-Angelakis, K.A. (Ed.) Grapevine Molecular Physiology & Biotechnology; Springer Publishers: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; p. 612. ISBN 978-90-481-2304-9. [Google Scholar]
- Guth, H. Quantitation and Sensory Studies of Character Impact Odorants of Different White Wine Varieties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 3027–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Hou, L.; Ma, J.; Zhou, X.; Xia, H.; Wang, M.; Leal-Bertioli, S.; Zhao, S.; Tian, R.; Pan, J.; et al. Bulk RNA-Seq Analysis Reveals Differentially Expressed Genes Associated with Lateral Branch Angle in Peanut. Genes 2022, 13, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yufei, W.; Ahmad, N.; Jiaxin, C.; Lili, Y.; Yuying, H.; Nan, W.; Min, Z.; Libo, J.; Na, Y.; Xiuming, L. CtDREB52 transcription factor regulates UV-B-induced flavonoid biosynthesis by transactivating CtMYB and CtF3′H in Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.). Plant Stress. 2024, 11, 100384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, G.L.; Gates, M.J.; Ferry, F.X.; Lavin, E.H.; Kurtz, A.J.; Acree, T.E. Sensory threshold of 1,1,6-trimethyl-1,2-dihydronaphthalene (TDN) and concentrations in young Riesling and non-Riesling wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2998–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marais, J.; Van Wyk, C.; Rapp, A. Effect of Storage Time, Temperature and Region on the Levels of 1, l, 6-Trimethyl-1, 2-dihydronaphthalene and other Volatiles, and on Quality of Weisser Riesling Wines. South. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 1992, 13, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tarasov, A.; Giuliani, N.; Dobrydnev, A.; Müller, N.; Volovenko, Y.; Rauhut, D.; Jung, R. Absorption of 1,1,6-trimethyl-1,2-dihydronaphthalene (TDN) from wine by bottle closures. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 2343–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Qian, M.C. Accumulation of C13-Norisoprenoids and Other Aroma Volatiles in Glycoconjugate Form During the Development of Pinot Noir Grapes. In Flavor Chemistry of Wine and Other Alcoholic Beverages; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Volume 1104, pp. 101–115. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, N.; Wei, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yu, K.; Cheng, J.; Li, X.-Y.; Duan, C.-Q.; Pan, Q.-H. Characterization of Transcriptional Expression and Regulation of Carotenoid Cleavage Dioxygenase 4b in Grapes. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Ahmad, N.; Wang, N.; Jin, L.; Yao, N.; Liu, X. A Cinnamate 4-HYDROXYLASE1 from Safflower Promotes Flavonoids Accumulation and Stimulates Antioxidant Defense System in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marais, J. Viticulture: Sauvignon blanc Cultivar Aroma—A Review. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 1994, 15, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.Q.; Liu, B.; Zhu, B.Q.; Lan, Y.B.; Gao, Y.; Wang, D.; Reeves, M.J.; Duan, C.Q. Differences in volatile profiles of Cabernet Sauvignon grapes grown in two distinct regions of China and their responses to weather conditions. Plant Physiol. Biochem. PPB 2015, 89, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.J.; Sefton, M.A.; Francis, I.L. Glycosidic precursors of varietal grape and wine flavor. In Acs Symposium Series; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Sefton, M.A.; Francis, I.L.; Williams, P.J. Free and bound volatile secondary metabolites of Vitis Vhifera Grape cv. Sauvignon Blanc. J. Food Sci. 1994, 59, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterhalter, P.; Sefton, M.A.; Williams, P.; Chemistry, F. Two-dimensional GC-DCCC analysis of the glycoconjugates of monoterpenes, norisoprenoids, and shikimate-derived metabolites from Riesling wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Amin, N.; Ahmad, N.; Wu, N.; Pu, X.; Ma, T.; Du, Y.; Bo, X.; Wang, N.; Sharif, R.; Wang, P. CRISPR-Cas9 mediated targeted disruption of FAD2-2 microsomal omega-6 desaturase in soybean (Glycine max.L). BMC Biotechnol. 2019, 19, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandles, M.; Reynolds, A.G.; Khairallah, R.; Bowen, A. The effect of yeast strain on odor active compounds in Riesling and Vidal blanc icewines. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Brotchie, J.; Pang, M.; Marriott, P.J.; Howell, K.; Zhang, P. Free terpene evolution during the berry maturation of five Vitis vinifera L. cultivars. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lashbrooke, J.G.; Young, P.R.; Dockrall, S.J.; Vasanth, K.; Vivier, M.A. Functional characterisation of three members of the Vitis vinifera L. carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase gene family. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Xu, X.Q.; Yu, K.J.; Zhu, B.Q.; Lan, Y.B.; Duan, C.Q.; Pan, Q.H. Varietal Dependence of GLVs Accumulation and LOX-HPL Pathway Gene Expression in Four Vitis vinifera Wine Grapes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombe, B.G. Growth stages of the grapevine: Adoption of a system for identifying grapevine growth stages. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 1995, 1, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, L.; An, X.; Yu, K.; Meng, N.; Duan, C.; Pan, Q.H. VviWRKY40, a WRKY Transcription Factor, Regulates Glycosylated Monoterpenoid Production by VviGT14 in Grape Berry. Genes 2020, 11, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Zhang, K.; Ma, J.; Yuan, M.; Zhao, S.; Wang, M.; Deng, L.; Ren, L.; Gangurde, S.S.; Pan, J.; et al. Transcriptional networks orchestrating red and pink testa color in peanut. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilanova, M.; Genisheva, Z.; Bescansa, L.; Masa, A.; Oliveira, J.M. Changes in free and bound fractions of aroma compounds of four Vitis vinifera cultivars at the last ripening stages. Phytochemistry 2012, 74, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ahmad, N.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, C.; Zhong, W.; Wang, X.; Li, G. Effect of Salt Stress on Growth and Physiological Properties of Asparagus Seedlings. Plants 2022, 11, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Meng, N.; Castellarin, S.D.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Li, X.-Y.; Dong, Z.-G.; Tang, X.-P.; Duan, C.-Q.; Pan, Q.-H. Combined Metabolite and Transcriptome Profiling Reveals the Norisoprenoid Responses in Grape Berries to Abscisic Acid and Synthetic Auxin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.V.; Davis, R.E. Climate influences on grapevine phenology, grape composition, and wine production and quality for Bordeaux, France. Conf. Biometeorol. Aerobiol. 2000, 51, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribéreau-Gayon, P.; Glories, Y.; Maujean, A.; Dubourdieu, D. Handbook of Enology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yu, W.; Zhao, L.; Song, S.; Xu, W.; Zhang, C.; Ma, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, S. Study on the volatile composition of table grapes of three aroma types. LWT 2019, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund Steven, T.; Bohlmann Science, J.J. The Molecular Basis for Wine Grape Quality—A Volatile Subject. Science 2006, 311, 804–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buesa, I.; Intrigliolo, D.S.; Castel, J.R.; Vilanova, M. Influence of water regime on grape aromatic composition of Muscat of Alexandria in a semiarid climate. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 290, 110525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.C.; Ibáñez Jara, M.Á.; Rosillo, L.; Salinas, M.R. Effect of temperature and water availability on grape phenolic compounds and their extractability in Merlot grown in a warm area. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 337, 113475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Song, C.; Falginella, L.; Castellarin, S.D. Day Temperature Has a Stronger Effect Than Night Temperature on Anthocyanin and Flavonol Accumulation in ‘Merlot’ (Vitis vinifera L.) Grapes During Ripening. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenoll, J.; Manso, A.; Hellín, P.; Ruiz, L.; Flores, P. Changes in the aromatic composition of the Vitis vinifera grape Muscat Hamburg during ripening. Food Chem. 2009, 14, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.; Christensen, L.P.; Hansen, M.; Jørgensen, U.; Kaack, K. Olfactory and quantitative analysis of volatiles in elderberry (Sambucus nigra L) juice processed from seven cultivars. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.; Razungles, A.; Augier, C.; Baumes, R. Monoterpenic and norisoprenoidic glycoconjugates of Vitis vinifera L. cv. Melon, B. as precursors of odorants in Muscadet wines. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 936, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, S.; Nizet, S.; Claeys Bouuaert, T.; Despatures, P.M. Main odorants in Jura flor-sherry wines. Relative contributions of sotolon, abhexon, and theaspirane-derived compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorrain, B.; Chira, K.; Teissedre, P. Phenolic composition of Merlot and Cabernet-Sauvignon grapes from Bordeaux vineyard for the 2009-vintage: Comparison to 2006, 2007 and 2008 vintages. ScienceDirect 2011, 126, 1991–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasanta, C.; Caro, I.; Gómez, J.; Pérez, L. The influence of ripeness grade on the composition of musts and wines from Vitis vinifera cv. Tempranillo grown in a warm climate. Food Res. Int. 2014, 64, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talaverano, I.; Ubeda, C.; Cáceres-Mella, A.; Valdés, M.E.; Pastenes, C. Water stress and ripeness effects on the volatile composition of Cabernet Sauvignon wines. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Chai, F.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Liang, Z.; Fan, P. Effects of sunlight exclusion on the profiles of monoterpene biosynthesis and accumulation in grape exocarp and mesocarp. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrechts, M.G.; Pretorius, I.S. Yeast and its Importance to Wine Aroma—A Review. South. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2019, 21, 97–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Tian, R.; Lu, J.; Li, G.; Sun, J.; Lin, R.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, C.; Chang, H.; Zhao, S.; et al. DNA fingerprinting and genetic diversity analysis in Asparagus officinalis L. cultivars using microsatellite molecular markers. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2022, 70, 1163–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldermann, S.; Kato, M.; Kurosawa, M.; Kurobayashi, Y.; Fujita, A.; Fleischmann, P.; Watanabe, N. Functional characterization of a carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase 1 and its relation to the carotenoid accumulation and volatile emission during the floral development of Osmanthus fragrans Lour. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 2967–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Arneborg, N.; Toldam-Andersen, T.B.; Petersen, M.A.; Bredie, W.L. Effect of sequential fermentations and grape cultivars on volatile compounds and sensory profiles of Danish wines. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 9, 3594–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battilana, J.; Emanuelli, F.; Gambino, G.; Gribaudo, I.; Gasperi, F.; Boss, P.K.; Grando, M.S. Functional effect of grapevine 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase substitution K284N on Muscat flavour formation. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 5497–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Naeem, M.; Ali, H.; Alabbosh, K.F.; Hussain, H.; Khan, I.; Siddiqui, S.A.; Khan, A.A.; Iqbal, B. From challenges to solutions: The impact of melatonin on abiotic stress synergies in horticultural plants via redox regulation and epigenetic signaling. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 321, 112369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).