Abstract
The precise and automated diagnosis of apple leaf diseases is essential for maximizing apple yield and advancing agricultural development. Despite the widespread utilization of deep learning techniques, several challenges persist: (1) the presence of small disease spots on apple leaves poses difficulties for models to capture intricate features; (2) the high similarity among different types of apple leaf diseases complicates their differentiation; and (3) images with complex backgrounds often exhibit low contrast, thereby reducing classification accuracy. To tackle these challenges, we propose a three-residual fusion network known as MSCR-FuResNet (Fusion of Multi-scale Feature Extraction and Enhancements of Channels and Residual Blocks Net), which consists of three sub-networks: (1) enhancing detailed feature extraction through multi-scale feature extraction; (2) improving the discrimination of similar features by suppressing insignificant channels and pixels; and (3) increasing low-contrast feature extraction by modifying the activation function and residual blocks. The model was validated with a comprehensive dataset from public repositories, including Plant Village and Baidu Flying Paddle. Various data augmentation techniques were employed to address class imbalance. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms ResNet-50 with an accuracy of 97.27% on the constructed dataset, indicating significant advancements in apple leaf disease recognition.
1. Introduction
China is the largest apple producer in the world. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAOSTAT) statistics database [1], China’s apple production reached 47.57 million tons in 2022. As a result, apples hold significant economic value in the agricultural sector. However, the prevalence of apple diseases poses a major challenge to apple production, significantly reducing yield [2]. Leaves are among the primary indicators for identifying apple diseases. Therefore, accurate and rapid identification of apple leaf diseases is crucial not only for distinguishing among various disease types but also for minimizing the manual effort and related costs associated with disease scouting. However, the application of deep learning techniques to the identification of apple leaf diseases faces three significant challenges: (1) the small lesion areas on apple leaves make it difficult for models to capture detailed lesion features; (2) the high morphological similarity between different types of apple leaf diseases, particularly among certain fungal infections, complicates the differentiation process; and (3) images of apple leaf lesions taken in complex backgrounds often exhibit low contrast, which negatively impacts classification accuracy. These challenges significantly impede both research on the classification of apple leaf diseases and their practical application.
The accurate classification of apple leaf diseases is crucial for developing effective disease prevention and control measures. Traditional identification methods primarily depend on experts in the relevant fields who classify apple leaf diseases based on their experience [3]. While these methods can achieve high accuracy, they are susceptible to errors due to subjective judgment and individual differences. Consequently, spectral measurement techniques have been introduced to provide an objective diagnosis of apple leaf diseases [4]. Despite their objectivity, these techniques have drawbacks, including cumbersome equipment, slow recognition speed, high costs, and low efficiency. With the widespread use of smartphones and digital cameras, computer-based automatic classification of apple leaf diseases has been widely applied. This technological advancement not only improves the efficiency of disease diagnosis but also reduces the workload of researchers and agricultural workers, thereby offering somewhat notable research value and practical relevance.
To address these issues, many scholars have employed machine learning techniques to identify plant diseases and pests. For instance, Prasad et al. [5] proposed using the Gabor wavelet transform to extract texture information from the segmented diseased parts of plant leaves and classify them. Jian et al. [6] developed an improved Support Vector Machine (SVM) algorithm to classify cucumber leaf diseases using small samples. Liu et al. [7] introduced an enhanced Random Forest algorithm to extract color and texture features from diseased leaf areas, facilitating the classification of sunflower leaf diseases. Vaishnnave et al. [8] utilized the k-nearest neighbor (KNN) classifier to classify peanut leaf disease images. Shi et al. [9] proposed an apple disease identification method based on two-dimensional subspace learning dimensionality reduction (2DSLDR). They mapped observed sample points from high-dimensional space to low-dimensional subspace to achieve optimal classification features.
Traditional image processing methods primarily rely on expert experience to extract and handle features such as texture, color, structure, and shape. Machine learning approaches, on the other hand, typically utilize predefined datasets where disease characteristics are manually selected. Furthermore, the disease images used in these studies are often captured in controlled laboratory settings with optimal lighting and simple backgrounds. However, in real-world scenarios, images of apple leaf diseases present complex and variable backgrounds with lesions of different sizes, making them challenging to identify using conventional algorithms. Consequently, the disease detection models developed through these traditional methods lack generalizability and exhibit poor transferability.
In recent years, with the advent of deep learning [10] technology, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have become a popular research focus in the automated identification of plant diseases and pests. For example, Liu et al. [2] utilized an improved AlexNet deep convolutional neural network to detect apple leaf diseases, achieving an accuracy of 97.62%. This method offers higher accuracy, faster processing speed, and reduced time consumption compared with traditional methods. Yan et al. [11] proposed an enhanced VGG16 model incorporating global average pooling and batch normalization layers to identify apple leaf diseases, resulting in a 6.3% improvement in recognition accuracy and a reduction in training time to 0.56% of the original duration. The application of deep learning significantly enhances efficiency over traditional methods. Gao et al. [12] introduced BAM-Net, which employs an aggregate coordinate attention mechanism (ACAM) to boost the network’s focus on disease-specific regions, particularly in complex backgrounds, reaching an accuracy of 95.62%. Additionally, Bi et al. [13] presented a solution using the lightweight MobileNet model to implement the apple leaf disease identification system on mobile devices, achieving low cost, stable performance, and high accuracy.
Although the aforementioned research has largely addressed the limitations of traditional methods in handling small features, poor model generalizability, and the inability to process images with complex backgrounds, several challenges remain. Apple leaf lesions are typically small, and there is a high similarity between different disease types, which leads to low model recognition accuracy. Furthermore, the accuracy of identifying apple leaf images in complex backgrounds is still insufficient for practical application. Currently, the attention mechanism has become a key method for enhancing network performance and is a significant research focus [14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. The attention mechanism aids deep convolutional neural networks by suppressing less important pixels or channels, thus boosting performance. A notable approach for improving network performance through the suppression of irrelevant weights is the Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks (SENet) [15]. SENet enhances network performance by integrating spatial information into channel feature responses and computing attention via two Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) [21] layers. To further improve the network’s ability to extract channel and spatial features, the Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) [17] has been introduced. CBAM strengthens the network’s feature extraction capabilities by aggregating features using both average pooling and max-pooling layers.
In addition to enhancing the network’s ability to classify apple leaf disease images through the attention mechanism, integrating a multi-scale feature fusion pyramid sub-network into the backbone network has also been shown to significantly improve performance [22,23,24]. The Single Shot Detector (SSD) [25] demonstrated the effectiveness of feature pyramids in capturing fine details within the network. Consequently, such feature pyramid networks have gained prominence as a focal point in research [26,27]. Moreover, the winning models in the ImageNet [28] and COCO [29] challenges successfully employed multi-scale feature fusion pyramid networks. These findings collectively indicate that applying feature pyramid networks can substantially enhance the capability of deep convolutional neural networks in classifying apple leaf disease images.
Fusion models represent a significant approach to enhancing the performance of networks in classifying apple leaf disease images. In competitions such as Kaggle [30], numerous entries have successfully employed model fusion, yielding impressive results. Fusion models integrate the strengths of various models that excel in particular domains, leading to optimal classification outcomes [31]. The efficacy of model fusion has been well-documented in numerous studies [18], which highlight its superior performance in experimental results.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we introduce the data used for the experiments and describe the improvements made to the network methods in this study. Section 3 presents the experimental results and their analysis, which validate the superiority of MSCR-FuResNet. Section 4 provides the conclusions and outlines potential future work.
To address the challenges mentioned above, this paper introduces a three-residual network fusion model based on the ResNet-50 architecture, designed to accurately identify various types of apple leaf diseases. Moreover, we have constructed a new dataset with complex backgrounds by aggregating data related to apple leaf diseases from Plant Village [32], Baidu Flying Paddle [33,34], and various online sources. Training the model on this dataset is anticipated to significantly improve its generalization capability and robustness.
2. Dataset and Methodology
2.1. Dataset and Data Preprocessing
This paper presents an apple leaf disease image dataset containing a total of seven categories of images, including six different apple leaf diseases and images of healthy leaves. The categories are (a) Alternaria blotch (Alternaria mali), (b) brown spot (Marssonina coronaria), (c) gray spot (Didymella pomorum), (d) mosaic (caused by virus infections), (e) rust (Gymnosporangium juniperi-virginianae), and (f) scab (Venturia inaequalis) [35], as shown in Figure 1. These images are sourced from New Plant Village [32], Baidu Flying Paddle [33,34], and publicly available apple leaf disease datasets on the Internet. After a thorough filtering process, a total of 14,000 images were selected. The dataset was divided into training and test sets in a ratio of 80% to 20%, respectively.
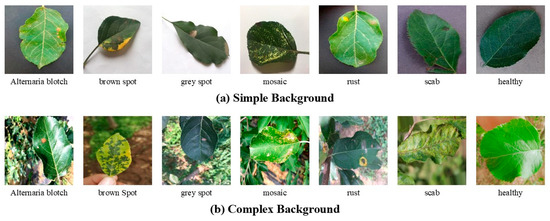
Figure 1.
Example images of six apple leaf diseases and asymptomatic (healthy) apple leaves.
The images of apple leaf diseases in the dataset can be categorized into two primary types. The first type consists of images with a simple background, typically captured in laboratory settings under favorable lighting conditions and without any background interference. The second type comprises images taken in actual production environments, such as orchards, where the backgrounds are often complex and contain significant interference. While these complex-background images can enhance the model’s robustness and generalization capabilities, they also introduce challenges to the training process. The presence of complex backgrounds can disrupt the model’s accuracy in recognizing the diseased leaves, even when the background is unrelated to the disease [36]. Moreover, such complexity can considerably extend the training time, leading to increased and unnecessary computational costs.
Considering the characteristics of the image background, this study employed the U-Net [37] neural network to segment the background and foreground of apple leaf disease images with complex backgrounds within the training set. The processed images, along with the generated weight files, were subsequently incorporated into the training set to enhance the dataset’s content. This approach helps reduce the influence of complex backgrounds and thereby improves the model’s accuracy, as illustrated in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
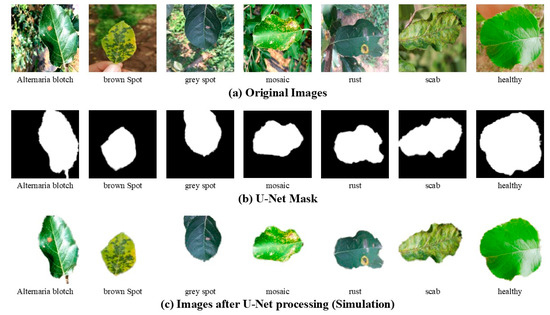
Figure 2.
Examples of apple leaf disease images with complex backgrounds processed by U-Net (Simulation).
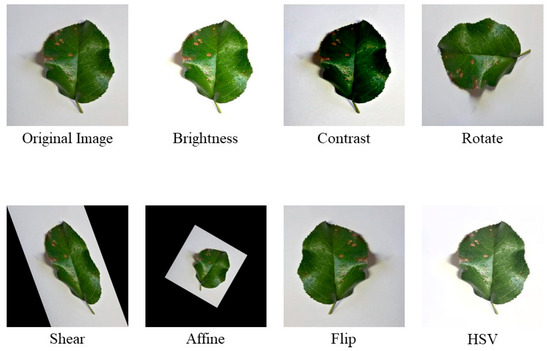
Figure 3.
Example images after applying seven data augmentation methods and the original image.
Additionally, the original dataset has issues with an uneven distribution of images for each type of apple leaf disease and low image diversity. These problems increase the difficulty of classification, making data preprocessing crucial [38]. Initially, the images are filtered, and redundant ones are removed. The redundant images refer to the duplicate images that were obtained from the New Plant Village and Baidu Flying Paddle datasets, and therefore, these duplicate images need to be deleted. Then, the dataset proportions are adjusted to a uniform level to allow the network model to extract features across different categories consistently. Finally, data augmentation is applied to the processed images to enhance their diversity. To prevent overfitting due to a limited number of images and to improve the network’s generalization capability, this study employs seven data augmentation methods: brightness enhancement, contrast enhancement, rotation, shearing, affine transformation, flipping, and HSV augmentation, resulting in a robust test dataset. The accuracy comparison of the model before and after image processing is provided in Section 3.5.
Each data augmentation method is applied to each image, thereby increasing the dataset size to seven times its original number of images (1600 training images and 400 test images for each disease and for healthy leaves). Potential anomalous samples in the dataset may negatively impact model performance. This study conducted preprocessing steps prior to inputting the images into the model. Initially, all images in the dataset were uniformly resized to 120 × 120 pixels. Subsequently, the images were converted to Tensor format, altering the data dimensions from height (H), width (W), channels (C) to channels (C), height (H), and width (W). Following this, pixel values were normalized by dividing by 255, standardizing the data within the range of [0, 1]. Finally, Z-Score normalization was applied to each channel of the images, as described by Equation (1).
In this formula, represents the standardized value of the i-th channel, denotes the original pixel value of this channel, indicates the mean pixel value of the channel, and signifies the standard deviation. Through this standardization process, we achieve image pixel data characterized by a zero mean and a unit variance. Consequently, the distribution of pixel values within each channel is normalized to have a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. This normalization ensures that the data falls within the range of [−1, 1].
2.2. Apple Leaf Disease Classification Model
This study introduces MSAR-FuResNet, a fusion model combining three distinct residual networks based on ResNet-50. The model leverages multi-scale feature fusion and enhances features through both channel and spatial domains to improve the classification accuracy of apple leaf disease images. The fusion model comprises three sub-networks: Network A, which is a multi-scale feature fusion pyramid network; Network B, which integrates a mechanism for enhancing channel features and spatial features and then reinforces channel features again; and Network C, a residual network optimized with modified residual blocks and activation functions.
2.2.1. Model Structure
The texture and structural information differences among apple leaf disease images are minimal; therefore, achieving fine-grained classification of these diseases necessitates more sophisticated deep recognition techniques. This study involves modifying the ResNet-50 architecture to enhance its depth. The aim is to improve the performance of the three sub-networks within the fusion model, thereby enabling more accurate classification of apple leaf disease images.
The overall structure of the fusion model is illustrated in Figure 4. Initially, the dataset comprising images of apple leaf diseases undergoes data augmentation. Subsequently, these augmented images are processed by three sub-networks, labeled A, B, and C (as depicted in Figure 4). The final classification outcome for the apple leaf disease images is derived from the joint output of these three sub-networks.
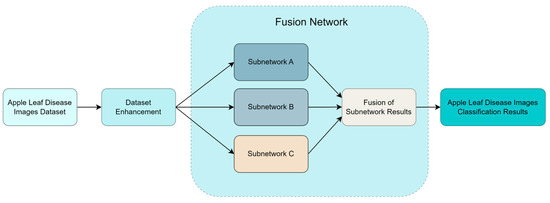
Figure 4.
Overall network architecture, which illustrates how the network operates.
To address the issue of varying classification difficulty among samples, this study employs the loss function specified in Equation (2). This loss function assigns weights to the samples based on the classification difficulty: it allocates a smaller weight to easily classified samples and a larger weight to samples that are difficult to classify.
In this context, represents the loss function for easily classified samples, while represents the loss function for difficult-to-classify samples. Given that is relatively smaller and is relatively larger, becomes the dominant loss function. Consequently, the primary focus of the loss function is directed toward the difficult-to-classify samples. The corresponding expression for the loss function is given by Equation (3).
Here, denotes the probability of positive samples, serves as the modulation factor, and acts as the tunable focusing parameter. As increases, the loss associated with easily classified samples decreases. This adjustment encourages the model to concentrate more on the harder-to-classify samples, thereby mitigating the issue of class imbalance in the dataset.
2.2.2. Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Mechanism of SubNetwork A
To tackle the challenge posed by the small lesion areas on apple leaves, we incorporated a multi-scale fusion pyramid into subnetwork A. This modification aims to enhance the model’s ability to capture the detailed features of the disease. The detailed architecture of the multi-scale fusion pyramid is illustrated in Figure 5.
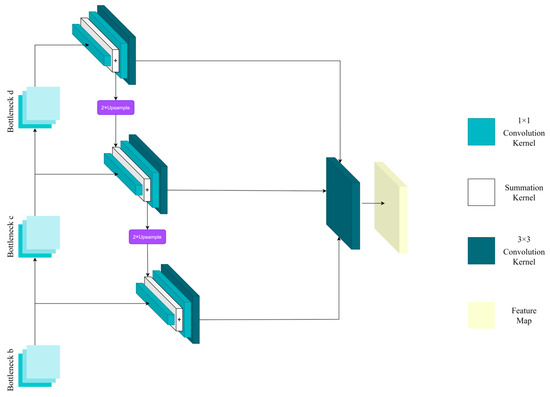
Figure 5.
Mechanism of multi-scale feature fusion.
This mechanism operates by applying convolutions with kernels of varying sizes to obtain feature maps at different scales. Smaller kernels are effective at capturing fine details in the image, which helps in accurately identifying small lesions. In contrast, larger kernels are better suited for capturing the overall structure of the image, making them more effective for recognizing larger objects. For a comprehensive description of the architecture of subnetwork A and the specific technical details of this mechanism, please refer to Appendix A.
2.2.3. Channel and Spatial Feature Enhancement and Subsequent Channel Feature En-Hancement Mechanism of SubNetwork B
To address the challenge of distinguishing apple leaf diseases due to their high visual similarity, we implemented a channel feature enhancement mechanism within subnetwork B, aimed at strengthening channel features after image compression. Following this, we developed mechanisms for spatial feature enhancement and channel feature re-enhancement at the end of the residual block to reduce the loss of channel-specific features. These two strategies help the model more effectively differentiate between various types of diseases.
Subnetwork B, shown in Figure 6, enhances the structure of image channel features, while Figure 7 illustrates the enhancement of spatial features and the re-enhancement of channel features.
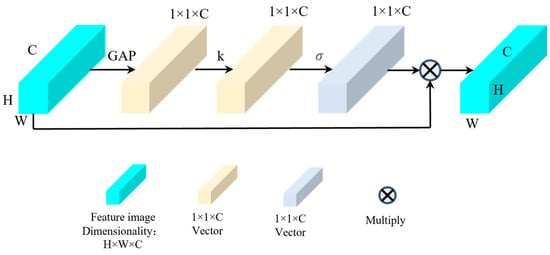
Figure 6.
Structural diagram of image channel feature enhancement.
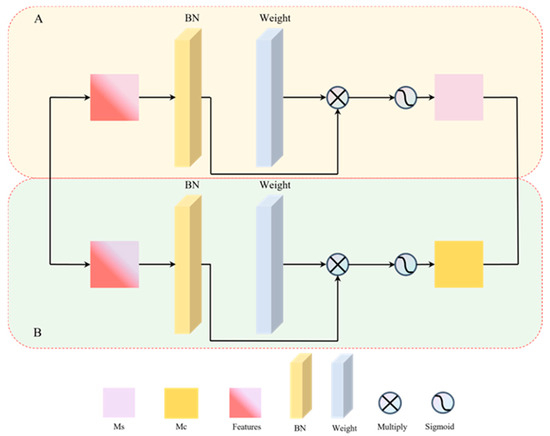
Figure 7.
Structure for enhancing image spatial and channel features. (A) represents the structure designed to enhance the spatial features, while (B) focuses on enhancing the channel features of the image.
As illustrated in Figure 6, when enhancing the features of image channels, the feature map first undergoes global average pooling. This operation transforms the feature map from a matrix of [H, W, C] (height (H), width (W), channels (C)) to a vector of [1, 1, C] (channels (C)). This approach not only avoids dimension reduction but also captures cross-channel interactions.
As illustrated in Figure 7, the upper section labeled A depicts the structure designed to enhance the spatial features of an image. Following the application of batch normalization (BN) [39] to the feature image, a scaling factor is computed. Subsequently, the weights for each spatial dimension are determined. These weights are then multiplied with the image that has been adjusted using the scaling factor, and the result is processed through a Sigmoid function to yield a spatially weighted feature map, denoted as Ms. The lower section labeled B in the figure represents the structure for enhancing image channel features, which is analogous to the structure of section A. The key difference lies in the fact that, in section B, the computation is performed on the channels rather than the spatial dimensions, resulting in a channel-weighted feature map, Mc.
For a comprehensive description of the architecture of subnetwork B and the specific technical details of this mechanism, please refer to Appendix B.
2.2.4. Optimization of Convolution Kernels and Activation Functions of SubNetwork C
Due to the low contrast of apple leaf spot images against complex backgrounds, which adversely affects classification accuracy, we have optimized the convolution kernels and activation functions in sub-network C to improve its sensitivity in detecting fine features. This enhancement effectively increases the classification accuracy. The underlying rationale of this optimization mechanism is detailed as follows.
As shown in Figure 8, configuration a represents the unmodified structure, while configuration b represents the modified structure. The residual block in configuration a follows the standard ResNet-50 structure. In contrast, configuration b introduces a 7 × 7 convolutional kernel in the first layer of the residual structure. This modification allows the residual block to retain more image information during the initial stages of processing, thereby reducing information loss.
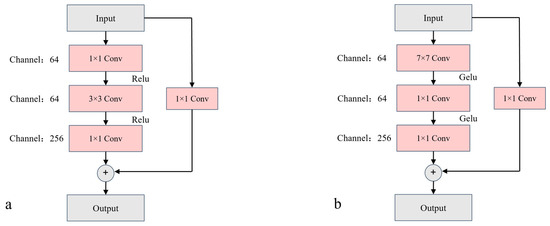
Figure 8.
Diagrams of Residual Block Structures: Before and After Modification. Part (a) of the image illustrates the residual block structure of ResNet-50, while Part (b) shows the structure of the modified residual block.
In the residual block a, ResNet-50’s convolution sequence is 1 × 1 convolution → depthwise convolution → 1 × 1 convolution. For the residual block b, the sequence is altered to depthwise convolution → 1 × 1 convolution → 1 × 1 convolution, inspired by the design of the Swin Transformer [40], where the MSA [40] module precedes the MLP [21] module. This adjustment enhances model accuracy.
Furthermore, unlike the ReLU activation function used in Figure 8a, the residual blocks in subnetwork C employ the GELU activation function. The GELU activation function mitigates the neuron death issue that ReLU may cause during training when the activation input is negative, thereby improving gradient flow.
For a comprehensive description of the architecture of subnetwork C and the specific technical details of this mechanism, please refer to Appendix C.
2.2.5. Fusion Model
Although the three methods discussed above have been integrated into ResNet, each still presents certain limitations. Thus, there is a pressing need for an approach that synthesizes the strengths of these methods, effectively offsetting their weaknesses, to further improve network performance. To this end, we implemented a network fusion strategy. Research indicates that network fusion is a key approach for enhancing model performance. In fact, in Kaggle and other data science competitions [30], ensemble models consistently outperform individual models, demonstrating superior overall performance. By integrating the three improved sub-networks, A, B, and C, we aim to achieve a fusion model that outperforms individual sub-networks in the classification of apple leaf diseases.
Fusion models are used to enhance model accuracy. Within a fusion model, different sub-models might produce varying predictions for the same image due to their distinct focus areas determined by their design mechanisms and structures. The essence of a fusion model lies in selecting the best or most accurate prediction from these sub-models to serve as the final output. This study employs a fusion model strategy to optimize subnetworks, aiming to enhance the classification performance of apple leaf disease images within a deep learning framework. The fusion method used in this research is illustrated in Figure 9.
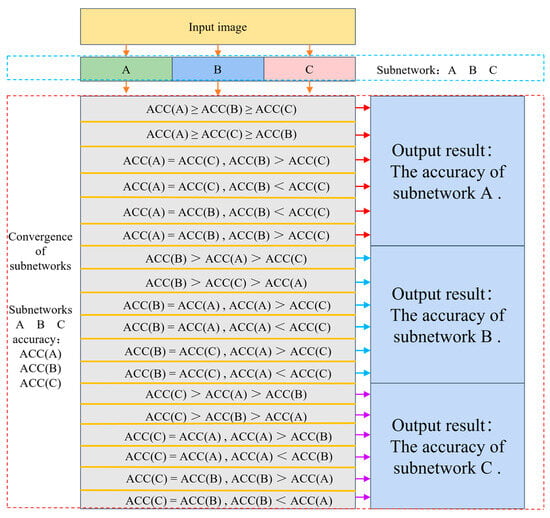
Figure 9.
Fusion methods of subnetworks, detailing the model fusion mechanism and its operation.
As illustrated in Figure 9, the image is fed into three sub-networks: A, B, and C. These sub-networks classify the image and yield their respective accuracies: ACC(A), ACC(B), and ACC(C). The fusion model compares these accuracies and, if they differ, it employs the highest accuracy among the subnetworks as the output of MSCR-FuResNet. In cases where two subnetworks have identical accuracies that differ from the third, the fusion model adopts the accuracy of the two matching subnetworks. This fusion strategy ensures that the optimal or most accurate prediction is retained when predicting the same image, thereby enhancing image recognition performance compared to using independent sub-models.
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
In all the experiments in this chapter, accuracy refers to the ratio of correct predictions to total predictions without considering whether the predictions are for positive or negative cases. As shown in Equation (4) below.
If an instance is positive and is predicted as positive, it is classified as a True Positive (TP). If an instance is negative and is predicted as negative, it is classified as a True Negative (TN). If an instance is negative and is predicted as positive, it is classified as a False Positive (FP). If an instance is positive and is predicted as negative, it is classified as a False Negative (FN).
3.1. Environmental Configuration and Experimental Setup
The methodology presented in this study utilizes the Pytorch 1.12.1 deep learning framework. Experiments were executed on a system equipped with an Intel Core i9-7960X CPU (Intel Corporation, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and an NVIDIA GeForce RTX3080Ti GPU (NVIDIA Corporate, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The operating system employed was Windows 10, version 22H2. For our experimental setup, the learning rate (RL) was configured to 0.0001, with a batch size of 16 and seven distinct sample categories. To optimize model performance, the number of epochs was set to 280. Detailed configuration parameters are provided in Table 1.

Table 1.
System configuration and experimental setup.
3.2. Sub-Network Fusion Comparison Experiment
To verify the effectiveness of subnet fusion in this study, we employed ablation experiments. According to the characteristics of the fusion model, it must contain three or more subnets; fusion is not possible with only two subnets. Thus, our experiments are divided into four parts: Part A, a model with only subnet A; Part B, a model with only subnet B; Part C, a model with only subnet C; and Part D, a fusion model incorporating subnets A, B, and C. The experimental results are presented in Figure 10 and Figure 11.
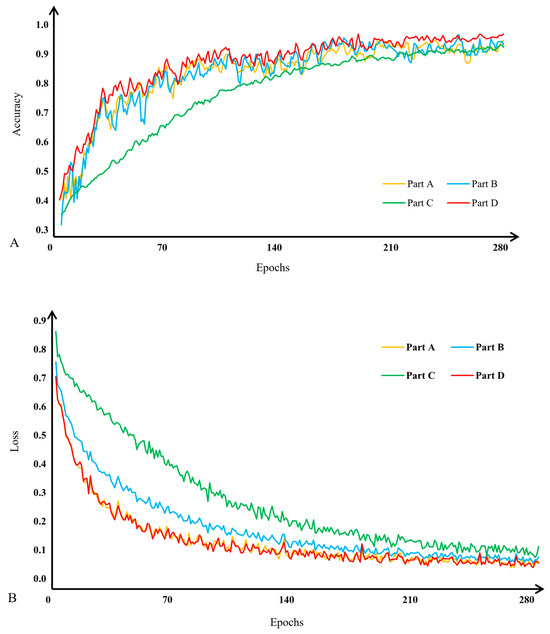
Figure 10.
Comparison of validation accuracy (A) and training loss (B) for apple leaf disease image classification. Part A: a model with only subnet A. Part B: a model with only subnet B. Part C: a model with only subnet C. Part D: a fusion model incorporating subnets A, B, and C.
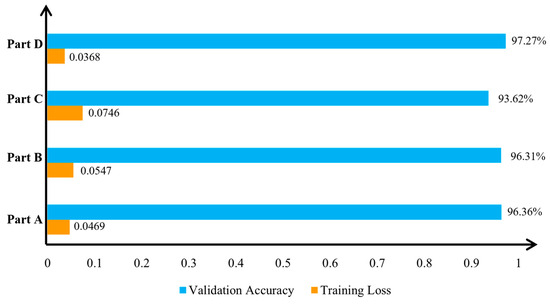
Figure 11.
Comparison of subnetwork fusion results in terms of accuracy for apple leaf disease image classification. Part A: a model with only subnet A. Part B: a model with only subnet B. Part C: a model with only subnet C. Part D: a fusion model incorporating subnets A, B, and C.
The results of the subnetwork fusion comparison experiments are illustrated in Figure 10 and Figure 11. The fused model demonstrates a higher validation accuracy in classifying apple leaf disease images compared with individual subnetworks. Additionally, as shown in Figure 10B, the fused model also converges faster during training.
The highest classification accuracy achieved by the fused model was 97.27%. This was superior to the accuracy of subnetwork A at 96.36%, subnetwork B at 96.31%, and subnetwork C at 93.62%. These results underscore the enhanced effectiveness of sub-network fusion.
3.3. Ablation Study
To assess the impact of the modified network mechanisms on the performance of MSCR-FuResNet, we conducted a series of ablation experiments. As the fusion model must include three or more distinct subnetworks, the experiments were divided into four parts: Part A, Part B, Part C, and Part D. These are defined as follows: Part A integrates the improved subnetworks A, B, and C, forming MSCR-FuResNet; Part B combines the improved subnetworks A and B with the original, unimproved residual block network C; Part C merges subnetwork A, which lacks a multi-scale feature fusion mechanism, with the improved subnetworks B and C; and Part D fuses the improved subnetworks A and C with subnetwork B, which does not include spatial feature enhancement or the mechanism for secondary enhancement of channel features at the end of the residual block within the residual structure. The results of the ablation experiments are shown in Figure 12 and Figure 13.
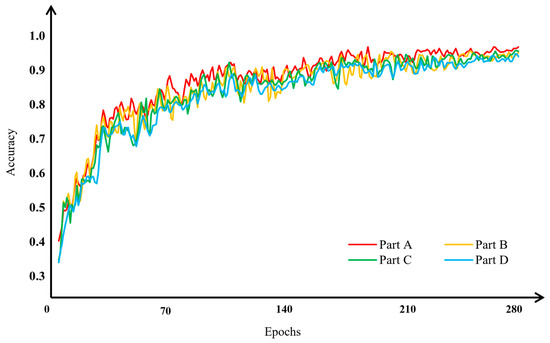
Figure 12.
Ablation experiments verify classification accuracy for apple leaf disease image classification. Part A integrates the improved subnetworks A, B, and C, forming MSCR-FuResNet; Part B combines the improved subnetworks A and B with the original, unimproved residual block network C; Part C merges subnetwork A, which lacks a multi-scale feature fusion mechanism, with the improved subnetworks B and C; Part D fuses the improved subnetworks A and C with subnetwork B, which does not include spatial feature enhancement or the mechanism for secondary enhancement of channel features at the end of the residual block within the residual structure.
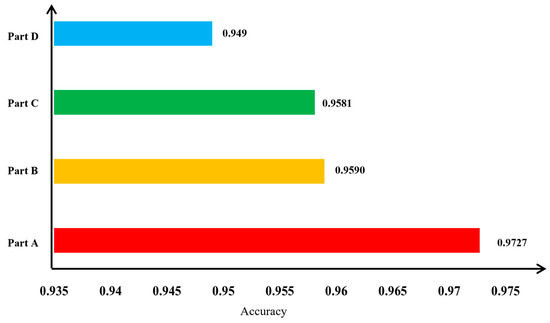
Figure 13.
Comparison of ablation experiment results in terms of accuracy for apple leaf disease image classification. Part A integrates the improved subnetworks A, B, and C, forming MSCR-FuResNet; Part B combines the improved subnetworks A and B with the original, unimproved residual block network C; Part C merges subnetwork A, which lacks a multi-scale feature fusion mechanism, with the improved subnetworks B and C; and Part D fuses the improved subnetworks A and C with subnetwork B, which does not include spatial feature enhancement or the mechanism for secondary enhancement of channel features at the end of the residual block within the residual structure.
As shown in Figure 12, the Part A fusion model achieves the best classification performance for apple leaf disease images and converges faster during training compared with the other fusion models (Part B, Part C, Part D) in the experiment. The ablation experiment results, shown in Figure 13, further illustrate this point. The accuracy of the Part B fusion model is 1.37% lower than that of the Part A model, indicating that subnetwork C, after processing with residual blocks, significantly impacts the fusion model. The Part C fusion model’s accuracy is 1.46% lower than the Part A model, highlighting the importance of the multi-scale feature fusion mechanism in classifying apple leaf disease images. The Part D fusion model has an accuracy that is 2.37% lower than the Part A model, showing that the spatial feature enhancement and secondary enhancement mechanism for channel features at the end of the residual block are beneficial for the fusion model’s classification performance on apple leaf disease images. The ablation experiments confirm the effectiveness of the mechanisms introduced in the modified network on the overall fusion model.
3.4. Comparison Experiment between Sub-Networks and the Original ResNet-50 Network
To ensure that each subnetwork that was improved based on the ResNet-50 network demonstrates higher accuracy in classifying apple leaf disease images compared with the original ResNet-50 network, we conducted comparative experiments. These experiments compared the performance of subnetworks A, B, and C against the original ResNet-50 network. The results, highlighting the comparative accuracy, are illustrated in Figure 14 and detailed in Table 2.
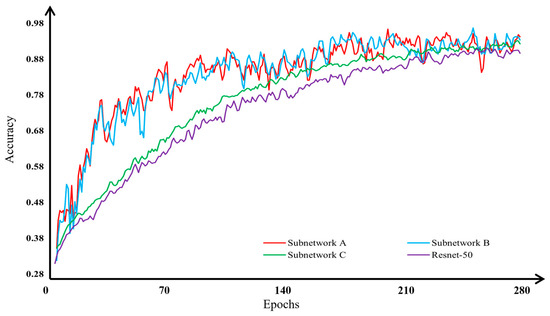
Figure 14.
Comparative analysis of subnetworks and the original Resnet-50 network in terms of accuracy for apple leaf disease image classification.

Table 2.
Comparative analysis of subnetworks and the original Resnet-50 network in terms of accuracy for apple leaf disease image classification.
The analysis indicates that subnetwork A increased the accuracy by 4.59%, subnetwork B by 4.54%, and subnetwork C by 1.85% over the original ResNet-50 network. Consequently, the modified subnetworks A, B, and C not only achieve higher accuracy in apple leaf disease recognition but also demonstrate faster convergence during training compared with the original ResNet-50 network.
3.5. Data Enhancement Experiment on Apple Leaf Disease Images
Due to the uneven distribution and limited diversity of the apple leaf disease image dataset, classifying these images has become more challenging. To address this issue, we applied seven data augmentation techniques: enhancing brightness, enhancing contrast, rotating images, applying shear transformations, using affine transformations, flipping images, and augmenting HSV data. Additionally, we utilized U-Net to process the regions of the images with varying levels of importance. Following these augmentations, our model’s accuracy in classifying apple leaf disease images significantly improved. The experimental results before and after data augmentation are illustrated in Figure 15 and Figure 16.
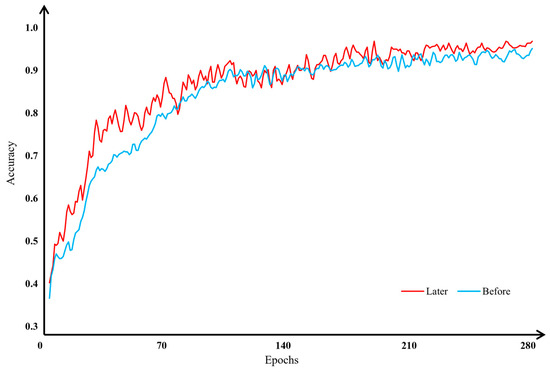
Figure 15.
Accuracy of apple leaf disease image classification before and after data augmentation.
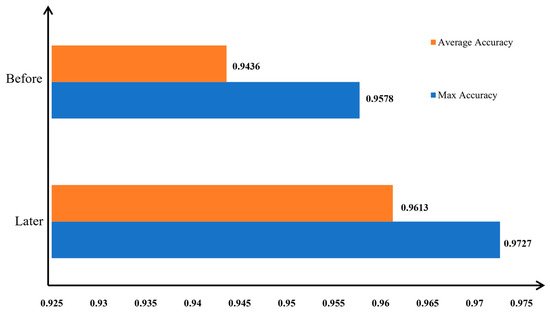
Figure 16.
Accuracy of apple leaf disease image classification before and after data augmentation.
Figure 15 clearly demonstrates that both the model’s convergence speed and its classification accuracy for apple leaf disease images improved post-data augmentation compared with the pre-augmentation results. Figure 16 further corroborates these findings, indicating that the highest and average classification accuracies after data augmentation exceeded those before augmentation. Specifically, the highest accuracy improved by 1.49%, and the average accuracy improved by 1.77% after data augmentation. These experiments confirm that augmenting apple leaf disease images enhances the model’s classification accuracy.
3.6. Comparison Experiment of Network Methods
To evaluate the classification performance of the improved model in this study on the preprocessed apple leaf disease image dataset, we conducted comparative experiments using MSCR-FuResNet, conventional ResNet-50 [41], Vgg16 [42], MobilenetV2 [43], and Swin Transformer [44] networks. The average, highest, and lowest accuracies of these networks are presented in Table 3. The results confirm that the improved, optimized model developed in this study demonstrates superior performance in classifying apple leaf disease images. Detailed experimental results are illustrated in Figure 17.

Table 3.
Comparison of average, highest, and lowest network accuracy for apple leaf disease image classification.
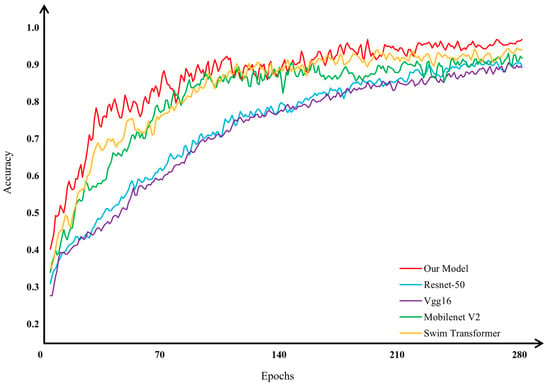
Figure 17.
Comparison of network methods in terms of accuracy for apple leaf disease image classification.
Moreover, to conduct a more comprehensive comparison of MSAR-FuResNet’s performance, we applied our model to the apple leaf disease dataset provided by New Plant Village. On this dataset, our model achieved an average accuracy of 98.97%, with a peak accuracy of 99.35% and an average loss of 0.073. Compared with a 2023 study [45] that also classified apple leaf diseases using the New Plant Village dataset [32], the accuracy of our proposed model improved by 1.19%, demonstrating relatively enhanced classification performance and generalization capability.
As illustrated in Figure 18, the results of the network method comparison experiments indicate that our model outperforms other networks in terms of both convergence speed and the accuracy of classifying apple leaf disease images. In Figure 18, the network accuracy results show that our model surpasses others in average, maximum, and minimum accuracy. The closer the blue, red, and yellow lines in the figure are to the outer black line, the higher the model’s accuracy. These findings confirm that our improved model exhibits superior classification performance on the preprocessed apple leaf disease image dataset compared with other networks, showcasing enhanced competitiveness.
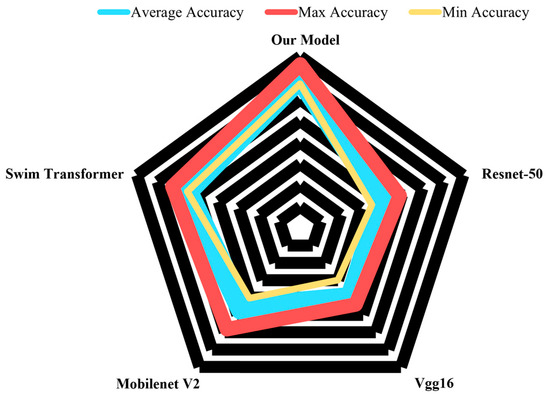
Figure 18.
Comparison of network accuracy for apple leaf disease image classification.
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
4.1. Conclusions
In order to facilitate the rapid identification of apple leaf diseases and thereby enhance apple production, we introduce MSAR-FuResNet. This model is a fusion of three-residual networks based on ResNet-50, specifically designed to address the limitations of traditional methods, which often struggle with low accuracy in disease detection, particularly in complex backgrounds. To further improve the model’s performance, we restructured the ResNet-50 backbone, integrating the benefits of multi-scale feature fusion with enhanced channel spatial features, which boosts the extraction of similar features while minimizing the risk of feature loss.
Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed MSAR-FuResNet model achieves impressive recognition performance. Trained and tested on a processed, self-constructed apple leaf disease dataset, the model attained a classification accuracy of 97.27%. When evaluated on the apple leaf disease dataset provided by New Plant Village, our model achieved an average accuracy of 98.97%. In comparison with other approaches, our model not only maintains high accuracy but also significantly improves the ability to recognize apple leaf diseases in complex backgrounds.
The primary contribution of this study is its capability to automatically and efficiently detect apple leaf diseases in natural environments. This reduces the need for manual labor and associated costs in disease identification, thereby enhancing the efficiency of agricultural informatics in the research of apple leaf diseases.
4.2. Future Directions
Our model has shown excellent classification performance, generalization capabilities, and robustness on the apple leaf disease dataset. However, there is still room for improvement in the current network architecture. Future research will focus on the following three aspects:
- Model Efficiency: The suitability of the model is closely linked to its size and the number of parameters. Future work will aim to develop lightweight models that maintain high performance while being easily deployable on resource-constrained mobile platforms.
- Dataset Enhancement: Increasing the diversity and complexity of the dataset by incorporating images that depict multiple types of apple leaf diseases within a single image.
- Algorithm Optimization: Enhancing the underlying algorithms to ensure that the model operates with greater speed and lower complexity. This will involve developing more efficient algorithms to improve the model’s computational efficiency.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.L., L.L., L.T. and R.G.; Methodology, R.L., L.L., L.T., Z.S. and R.G.; Software, X.C., R.Z. and Z.S.; Validation, R.Z.; Formal analysis, H.Z. and J.D.; Investigation, L.T., H.Z., R.G. and J.D.; Resources, L.T., H.Z. and J.D.; Data curation, R.Z., L.T., H.Z. and J.D.; Writing—original draft, X.C. and X.X.; Writing—review & editing, Y.Z. and R.L.; Visualization, X.C. and Z.S.; Supervision, L.L.; Project administration, Y.Z. and L.L.; Funding acquisition, X.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request. If you need data please contact xili0623@gmail.com
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. SubNetwork A
To address the challenge of detecting small lesion areas on apple leaves, we employed ResNet-50, a variant of the ResNet model, as the backbone network. ResNet is particularly advantageous because it mitigates the degradation issue commonly encountered in deep neural networks, where merely increasing the number of layers does not necessarily lead to performance improvements. In our study, deepening the network is crucial for enhancing the model’s capability to extract fine-grained features. The effectiveness of ResNet in addressing degradation stems from its use of a residual learning mechanism, which strengthens the network’s ability to learn by incorporating skip connections. These connections help preserve information flow through the deeper layers of the network, reducing the risk of information loss. Therefore, we integrated a multi-scale feature fusion mechanism into ResNet-50, allowing the model to more effectively predict features across images of varying sizes, thereby significantly enhancing its overall performance.
Subnetwork A builds upon the ResNet-50 architecture. It is modified to incorporate multi-scale feature fusion capabilities, which enhances the network’s ability to capture fine details and improves its performance in classifying apple leaf disease images. The three-dimensional structure of subnetwork A is illustrated in Figure A1.
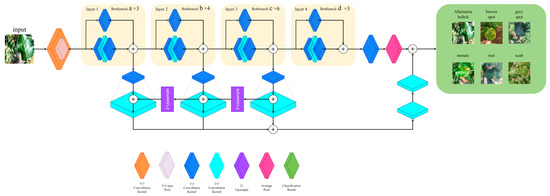
Figure A1.
Diagram of the three-dimensional structure of subnetwork A.
In subnetwork A, the input images of apple leaf diseases are first processed by a 7 × 7 convolutional kernel. The output is then passed to a 3 × 3 max-pooling layer, followed by a residual block labeled as a. The residual block a consists of three smaller residual blocks. Each smaller residual block includes two 1 × 1 convolutional kernels, one 3 × 3 convolutional kernel, and a shortcut structure. The shortcut structure, which uses a 1 × 1 convolutional kernel, connects directly to the output section of the smaller residual block to facilitate dimensionality reduction. The output of the shortcut structure is combined with the output of the smaller residual block, which helps to minimize image loss during the convolution process and allows the downsampled image to propagate further in the network. The residual blocks labeled as b, c, and d in Figure 5 share the same configuration as residual block a. However, they differ in the number of smaller residual blocks they contain. This design enhances the network’s depth while simultaneously reducing image loss during compression.
After the b, c, and d residual blocks in subnetwork A, each layer connects to a 1 × 1 convolutional kernel. Subsequently, a multi-scale feature fusion mechanism is incorporated into the network, as illustrated in Figure 6. Following the multi-scale feature fusion, the feature maps are input into the average pooling layer, ultimately yielding the classification results for subnetwork A. The technical details of the multi-scale feature fusion mechanism are described below.
The multi-scale feature fusion mechanism is located directly beneath the residual blocks labeled a, b, c, and d. The procedure is detailed here. In the original ResNet-50 network, a 1 × 1 convolutional layer is added after each residual block to standardize the channel dimensions of the feature maps. This ensures consistent channel dimensions during feature fusion. The modified feature maps are then summed and upsampled by a factor of two. Subsequently, they are combined with lower-level feature maps that have been reduced in dimension using a 1 × 1 convolutional layer. The resulting feature maps from this addition and fusion process are further processed through a 3 × 3 convolutional layer to enhance the integration of the fused feature maps, creating a pyramid-like structure. The utilization of this feature fusion pyramid structure significantly enhances the network’s ability to extract fine-grained details in images of apple leaf diseases.
Appendix B. SubNetwork B
Subnetwork B, an improved version of ResNet-50, enhances the residual structure’s capability in extracting image channel features. Moreover, the processing by the residual structure not only strengthens the analysis of spatial features but also further enhances the channel features. These improvements significantly boost the network’s efficiency in handling both spatial and channel features, demonstrating better performance. The 3D structure of subnetwork B is illustrated in Figure A2.
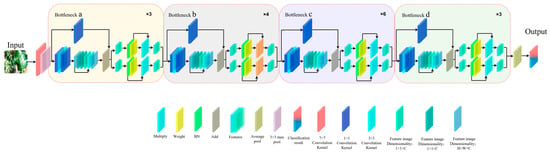
Figure A2.
Diagram of the three-dimensional structure of subnetwork B.
As shown in Figure A2, the apple leaf disease image is first input into the network through a 7 × 7 convolution kernel and then output to the 3 × 3 max-pooling layer. After that, the image undergoes a 3 × 3 max-pooling process before entering residual block a. Residual block a consists of 3 smaller residual blocks, each made up of two 1 × 1 convolution kernels and one 3 × 3 convolution kernel. The image is processed sequentially by the 1 × 1, 3 × 3, and 1 × 1 convolution kernels, entering the channel feature enhancement stage. The enhanced image is then added to a shortcut structure that has been dimensionally reduced by a 1 × 1 convolution kernel, helping to minimize information loss during the convolution process.
To further improve the model’s capability in processing subtle features, this study implements a channel and spatial attention mechanism. Since different regions of an image contribute unequally to the task, the spatial attention mechanism targets and processes task-relevant important regions to enhance the network’s spatial feature extraction ability. The Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM), a representative of such mechanisms, has been widely utilized in various neural networks.
The structure diagram of the small residual block designed for enhancing spatial features and re-enhancing channel features is illustrated in Figure A3. In subnetwork B, there are four similar residual block structures, denoted as a, b, c, and d. This process is stacked and repeated three times within subnetworks B to construct a complete residual block a. Residual blocks b, c, and d are processed similarly to block a, with the difference being that the number of small residual blocks in blocks b, c, and d is 4, 6, and 3, respectively.
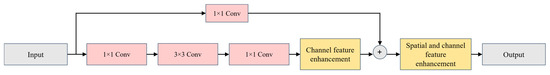
Figure A3.
Structural diagram of stacked small residual blocks in a, b, c, and d.
To enhance the generalization of the network, it is necessary to determine the size of the adaptive 1D convolution kernel () based on the number of channels in the feature map. The calculation method for is presented in Equation (A1). After determining , it is applied in the one-dimensional convolution to obtain the weights for each channel of the feature map, as calculated through and shown in Equation (A3). These weights are then normalized and multiplied with the original input feature map on a per-channel basis, resulting in the weighted feature map.
In Equation (A1), denotes the channel dimension, and rounding down to the nearest odd number is indicated by , resulting in the value , which determines the size of the one-dimensional convolution kernel. The channel dimension is influenced by , the size of the convolution kernel. The relationship between and is illustrated in Equation (A2).
Here, the size of the convolution kernel is directly proportional to the channel dimension . As the convolution kernel size increases, the range of interaction within the channels expands, leading to an increase in the channel dimension.
In Equation (A3), denotes the Sigmoid function, stands for one-dimensional convolution, and indicates the channel. The term refers to the interaction information between the k-th channel and its adjacent layer. This method of cross-channel information interaction ensures both the performance and efficiency of the model, thereby enabling the calculation of the weight for each channel.
The equation for determining the extent of variation in both spatial and channel dimensions is presented in Equation (A4). The symbol represents the variance across spatial dimensions or channels, and denote the trainable parameters of the affine transformation, including scale and shift, and indicates the mean value computed over the spatial dimensions or channels.
In Equation (A5), represents the scale parameter for each of the spatial dimensions, also known as channels. Additionally, refers to the th channel, while serves as the summation index, summing the values from the 0-th channel up to the th channel. The expression denotes the cumulative sum of all values, which is used to normalize the individual , thereby determining its relative proportion with respect to the total sum.
Appendix C. SubNetwork C
Subnetwork C is built upon the ResNet-50 architecture and modifies the number of residual blocks and the size of convolution kernels to achieve better performance compared with the original network. The three-dimensional structure of subnetwork C is depicted in Figure A4.
In subnetwork C, a convolution kernel with a size of 7 × 7 is applied to the residual structure to minimize the loss of image features related to apple leaf disease. Additionally, inspired by the structure of the Swin Transformer, we adjusted the convolution kernel placement within the residual structure. To further enhance performance, we replaced the original ReLU activation function with a GELU activation function. This modification aims to prevent neuron death and mitigate issues related to gradient vanishing. These enhancements have consequently improved the network’s performance in classifying apple leaf disease images compared to the original ResNet-50 model.
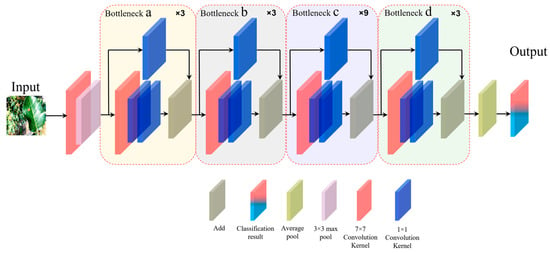
Figure A4.
Diagram of the three-dimensional structure of subnetwork C.
As illustrated in Figure A4, the input image undergoes convolution using a 7 × 7 convolutional kernel. The resulting feature map is then processed by a 3 × 3 max-pooling layer. After max pooling, the feature map is sequentially passed through the residual blocks labeled a, b, c, and d. Finally, an average pooling layer outputs the feature map, which is used for classification. The residual blocks a, b, c, and d contain different numbers of smaller residual blocks, specifically 3, 3, 9, and 3, respectively. Each small residual block consists of one 7 × 7 convolutional kernel and two 1 × 1 convolutional kernels. Additionally, the input and output of the residual block are combined using a 1 × 1 convolution kernel in a shortcut connection to achieve dimensionality reduction.
Equation (A6) provides the mathematical expression of the GELU activation function.
In Equation (A6), represents the mean, represents the variance, and represents the activation input value of the neuron. The term here refers to the Gaussian Error Linear Unit (GELU), which describes the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the Gaussian normal distribution. The CDF of the Gaussian distribution varies with changes in ; it increases as increases by and decreases as decreases by . Specifically, when is small, the probability of the activation result being 0 increases, leading to a higher likelihood of neuron pruning. Conversely, larger values of increase the probability of neuron retention. This function effectively preserves active neurons and mitigates the issue of the network’s inability to learn due to negative activation inputs.
References
- FAOSTAT. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; He, D.; Li, Y. Identification of Apple Leaf Diseases Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Symmetry 2018, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predicting the spread of postharvest disease in stored fruit, with application to apples. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2013, 85, 45–56. [CrossRef]
- Mahlein, A.-K.; Rumpf, T.; Welke, P.; Dehne, H.-W.; Plümer, L.; Steiner, U.; Oerke, E.-C. Development of Spectral Indices for Detecting and Identifying Plant Diseases. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Kumar, P.; Hazra, R.; Kumar, A. Plant Leaf Disease Detection Using Gabor Wavelet Transform. In Proceedings of the Swarm, Evolutionary, and Memetic Computing, Bhubaneswar, India, 20–22 December 2012; Panigrahi, B.K., Das, S., Suganthan, P.N., Nanda, P.K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 372–379. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, Z.; Wei, Z. Support Vector Machine for Recognition of Cucumber Leaf Diseases. In Proceedings of the 2010 2nd International Conference on Advanced Computer Control, Shenyang, China, 27–29 March 2010; Volume 5, pp. 264–266. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Lv, F.; Di, P. Identification of Sunflower Leaf Diseases Based on Random Forest Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Automation and Systems (ICICAS), Chongqing, China, 6–8 December 2019; pp. 459–463. [Google Scholar]
- Vaishnnave, M.P.; Devi, K.S.; Srinivasan, P.; Jothi, G.A.P. Detection and Classification of Groundnut Leaf Diseases Using KNN Classifier. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on System, Computation, Automation and Networking (ICSCAN), Pondicherry, India, 29–30 March 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhang, S. Apple disease recognition based on two-dimensionality subspace learning. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2017, 53, 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep Learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; Yang, B.; Wang, W.; Wang, B.; Chen, P.; Zhang, J. Apple Leaf Diseases Recognition Based on An Improved Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors 2020, 20, 3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Cao, Z.; Cai, W.; Gong, G.; Zhou, G.; Li, L. Apple Leaf Disease Identification in Complex Background Based on BAM-Net. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Wang, J.; Duan, Y.; Fu, B.; Kang, J.-R.; Shi, Y. MobileNet Based Apple Leaf Diseases Identification. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2022, 27, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Jiang, M.; Qian, C.; Yang, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Residual Attention Network for Image Classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3156–3164. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J. BAM: Bottleneck Attention Module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06514. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, X.; Deng, W.; Gu, C.; Zhou, H.; Li, C.; Sun, F. Model Ensemble for Click Prediction in Bing Search Ads. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on World Wide Web Companion, Perth, Australia, 3–7 April 2017; International World Wide Web Conferences Steering Committee: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 689–698. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Channel Locality Block: A Variant of Squeeze-and-Excitation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.01493. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual Attention Network for Scene Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, P.O.; Lin, T.-Y.; Collobert, R.; Dollár, P. Learning to Refine Object Segments. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 75–91. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, A.; Yang, K.; Deng, J. Stacked Hourglass Networks for Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 483–499. [Google Scholar]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2014, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–7 and 12 September 2014; Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Tariq, Z.; Shah, S.K.; Lee, Y. Feature-Based Fusion Using CNN for Lung and Heart Sound Classification. Sensors 2022, 22, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New Plant Diseases Dataset. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/vipoooool/new-plant-diseases-dataset (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Apple Leaf Pathology Images_Dataset-Flying Paddle AI Studio Star River Community. Available online: https://aistudio.baidu.com/datasetdetail/11591/0 (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Apple Leaf Diseases Dataset.Zip. Available online: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1KudYvGcAwnwHX6_ioeyPKrFjRVldHF-7/view (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Jiang, P.; Chen, Y.; Liu, B.; He, D.; Liang, C. Real-Time Detection of Apple Leaf Diseases Using Deep Learning Approach Based on Improved Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 59069–59080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Engstrom, L.; Ilyas, A.; Madry, A. Noise or Signal: The Role of Image Backgrounds in Object Recognition. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.09994. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- ConvPatchTrans: A Script Identification Network with Global and Local Semantics Deeply Integrated—ScienceDirect. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0952197622001427 (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; ICML: Lille, France, 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer Using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Two-Stream Convolutional Networks for Action Recognition in Videos. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.-Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A ConvNet for the 2020s. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 11976–11986. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Pan, J.; Wu, Q. Apple Leaf Disease Identification via Improved CycleGAN and Convolutional Neural Network. Soft Comput. 2023, 27, 9773–9786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).