Metabolomic Analysis of Lycoris radiata across Developmental and Dormancy Stages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Sample Extraction
2.3. LC-MS Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
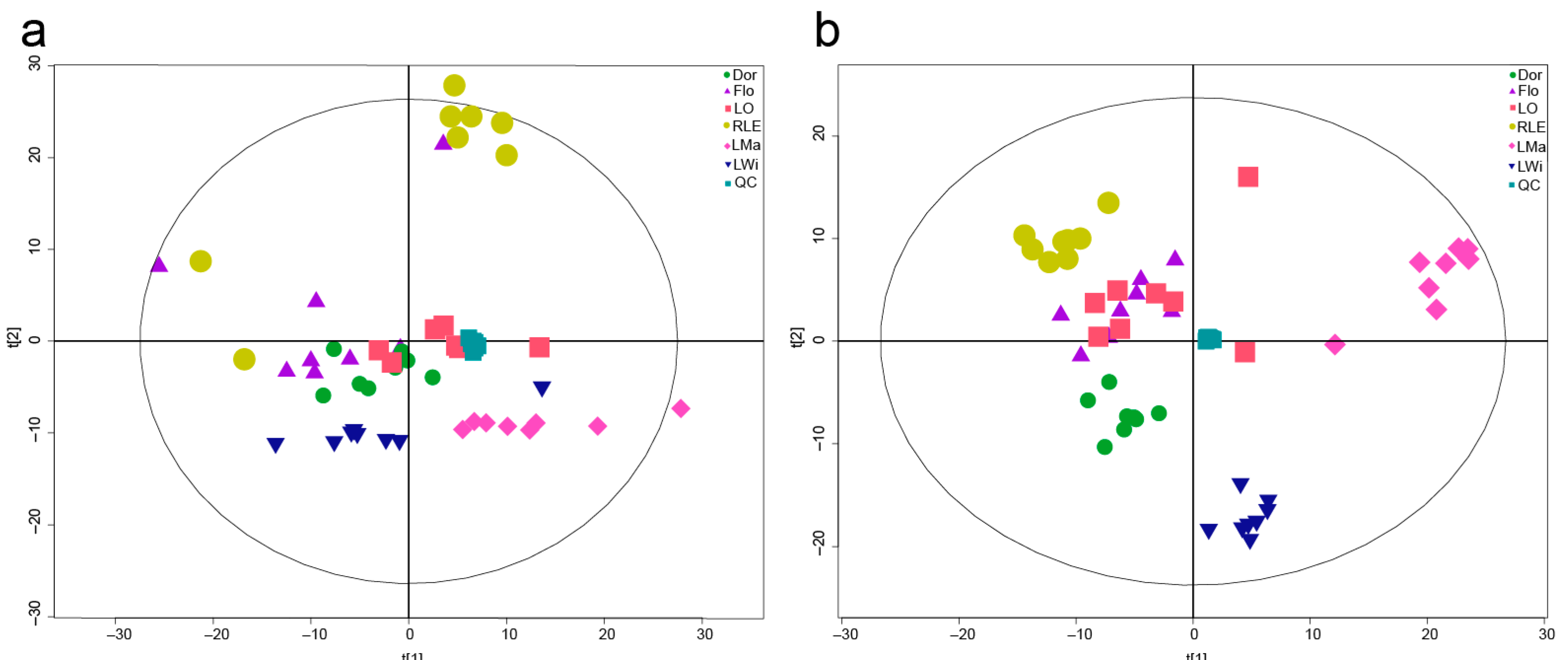
3.1. PCA of the Metabolites in Lycoris Bulb Samples
3.2. Orthogonal Projections to Latent Structures-Discrimination Analysis (OPLS-DA)
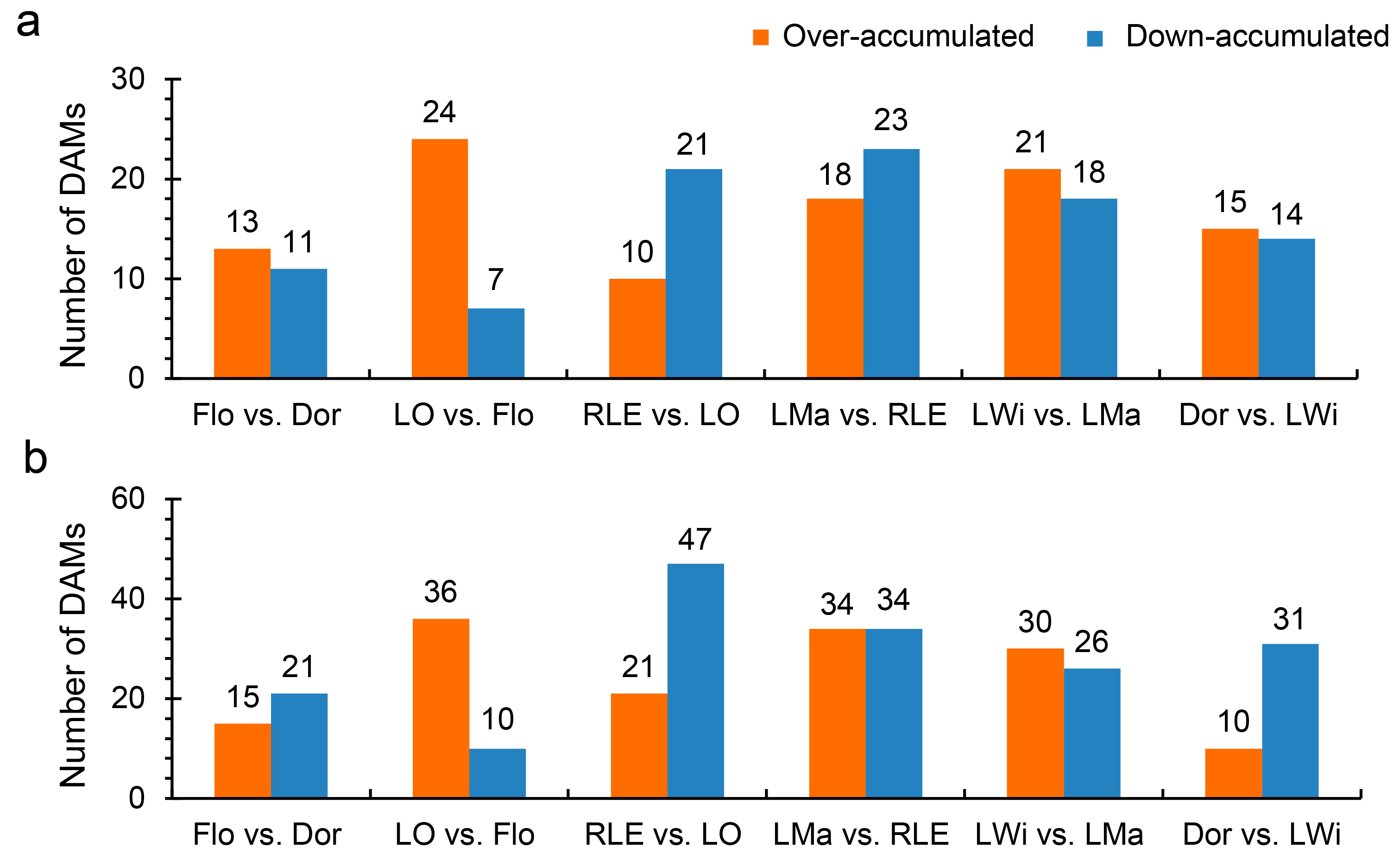
3.3. Differentially Accumulated Metabolites (DAMs) Analysis
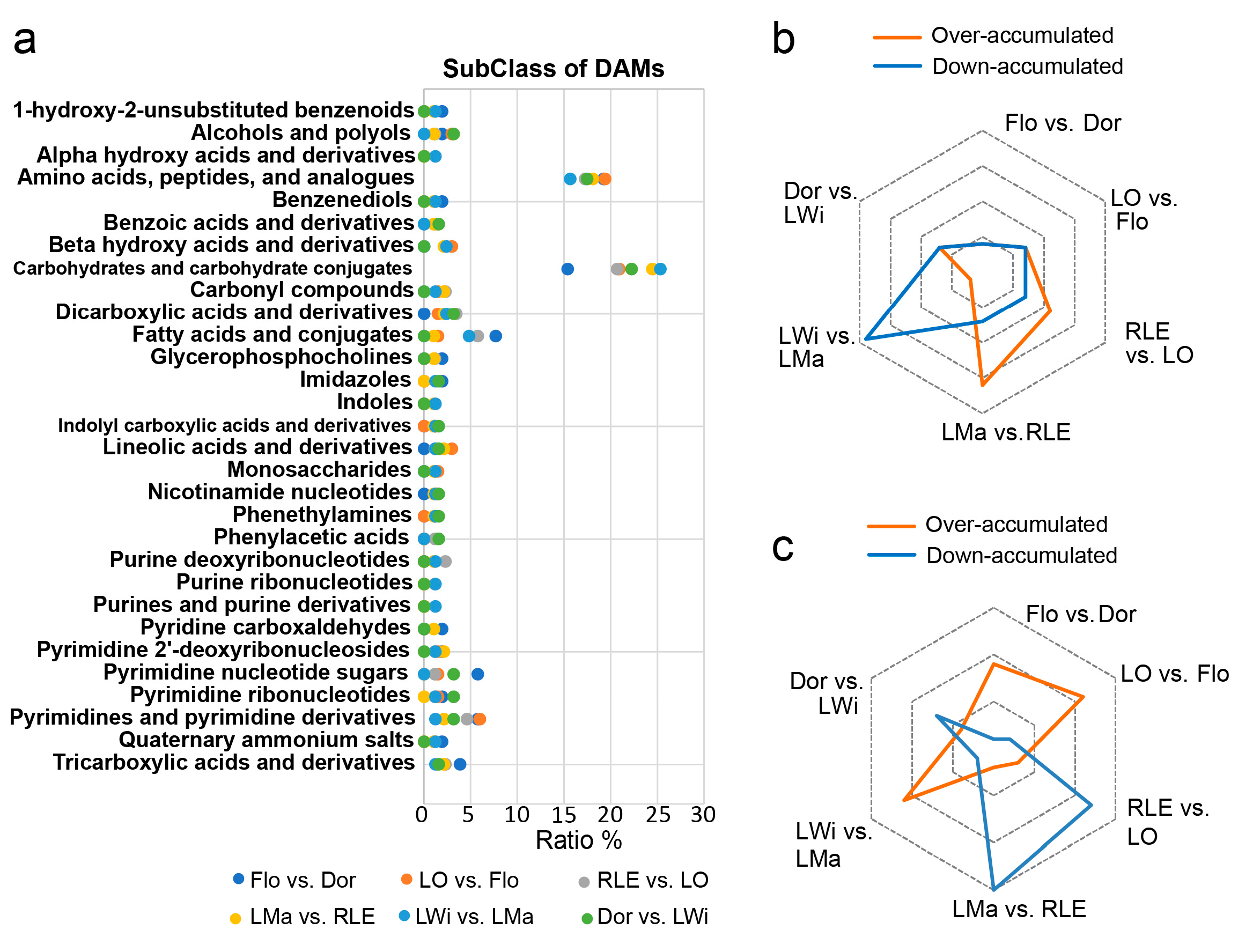
3.4. The KEGG Annotation Analysis of DAMs
4. Discussion
4.1. Stress Responses during Dormancy and Flowering Stages
4.2. Active Carbohydrate Metabolism during the Vegetative Growth Stages
4.3. Robust Amino Acid Metabolism during the Reproductive Stages
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cahlikova, L.; Breiterova, K.; Opletal, L. Chemistry and biological activity of alkaloids from the genus Lycoris (Amaryllidaceae). Molecules 2020, 25, 4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Xue, R.; Mao, Z.; Lu, W.; Jiang, Y. Lycorine hydrochloride suppresses stress-induced premature cellular senescence by stabilizing the genome of human cells. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, L.; Ji, Y.; Kennelly, E.J.; Long, C.; Di, R. Amaryllidaceae alkaloids from Lycoris suppress amyloid β-induced neurodegeneration in transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans CL2355. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 189, 115798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, S. Lycoris sanguinea Maxim. (Amaryllidaceae). Plant Spec. Biol. 2009, 24, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.H.; Wei, X.Y.; Li, J.F.; Zhang, L. The regulation and control of ambient temperature on growth rhythm of Lycoris radiata. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2018, 40, 24–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Fan, J.; Wei, X.; Zhang, L. A three-dimensional analysis of summer dormancy in the red spider lily (Lycoris radiata). Hortscience 2019, 54, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, Q.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Changes in starch synthesis and metabolism within developing bulbs of Lycoris radiata during the vegetative growth stage. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 39, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; He, L.; Wang, L. Relationships between flower bud differentiation in two kinds of Lycoris and the changes of carbohydrate, antioxidant enzymes and endogenous hormones. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2019, 46, 342–349. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Yan, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, L. Changes of endogenous hormones in 2 kinds of Lyroris plants at different growth stages. Mol. Plant Breed. 2022, 20, 6550–6558. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Cheng, G.; Shu, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z. Transcriptome analysis of Lycoris chinensis bulbs reveals flowering in the age-mediated pathway. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, A.; Dodd, M.S. Metabolism. Essays Biochem. 2020, 64, 607–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, S.A.; Rutter, J. Metabolites as signalling molecules. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Chen, H.; Wei, X.; Cai, J. Proteomic analysis provides an insight into the molecular mechanism of development and flowering in Lycoris radiata. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2021, 43, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Shu, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhuang, W.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z. Comparative transcriptome analysis identifies key regulatory genes involved in anthocyanin metabolism during flower development in Lycoris radiata. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 761862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Wei, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, M.; Cai, J. Transcriptome analysis of Lycoris radiata bulb tips at different developmental stages. Pak. J. Bot. 2023, 55, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.M.; Zhang, D.; Jiao, C.; Li, D.Q.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Gao, C.; Lin, Y.F.; Ruan, Y.L.; Xia, Y.P. Comparative transcriptome and metabolome analyses identified the mode of sucrose degradation as a metabolic marker for early vegetative propagation in bulbs of Lycoris. Plant J. 2022, 112, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Y. Transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses reveals that exogenous methyl jasmonate regulates galanthamine biosynthesis in Lycoris longituba seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 713795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Peng, J.T.; Klair, A.; Dickinson, A.J. Non-canonical and developmental roles of the TCA cycle in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2023, 74, 102382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailloux, R.J.; Beriault, R.; Lemire, J.; Singh, R.; Chenier, D.R.; Hamel, R.D.; Appanna, V.D. The tricarboxylic acid cycle, an ancient metabolic network with a novel twist. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.; Son, H.; Baek, J.H. Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle intermediates: Regulators of immune responses. Life 2021, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Harris, P.J.C. Potential biochemical indicators of salinity tolerance in plants. Plant Sci. 2004, 166, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, K.; Vijay Anand, K.G.; Kubavat, D.; Patidar, R.; Ghosh, A. Drought alleviatory potential of Kappaphycus seaweed extract and the role of the quaternary ammonium compounds as its constituents towards imparting drought tolerance in Zea mays L. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 2001–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenda, T.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Jin, H.; Liu, G.; Duan, H. Comparative proteomic and physiological analyses of two divergent maize inbred lines provide more insights into drought-stress tolerance mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramani, M.; Urrea, C.A.; Kalavacharla, V. Comparative analysis of untargeted metabolomics in tolerant and sensitive genotypes of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) seeds exposed to terminal drought stress. Metabolites 2022, 12, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Tan, P.; Huang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Zeng, C.; Tong, J.; Yan, M. Metabolic profiles in the xylem sap of Brassica juncea exposed to cadmium. Physiol. Plant 2023, 175, e13886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, G.; Zhu, H.; He, Y. Transcriptome of protoplasts reprogrammed into stem cells in Physcomitrella patens. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, M.; Jiang, X.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.; Yang, Y.; Cai, J. Changes of non-structured carbohydrate and starch metabolizing enzyme in bulbs of Lycoris radiata within the annual growth cycle. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 48, 106–114. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, Z.; Mashayekhi, K.; Mousavizadeh, S.J.; Nezhad, K.Z. Changes in carbohydrate and phytochemical content in the bulbs and leaves of ten onion accessions between two developmental stages. Italus Hortus 2022, 29, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, T.N.U.J.; Ikarashi, T.; Matsubara, T.; Baba, A. Behavior of carbohydrates in mother and daughter bulbs of tulips (Tulipa gesneriana). Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1988, 34, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naifeh, J.; Dimri, M.; Varacallo, M. Biochemistry, aerobic glycolysis. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470170/ (accessed on 9 April 2023).
- Copeland, L.; Turner, J.F. The regulation of glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway. In Biochemistry of Metabolism; Davies, D.D., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1987; pp. 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, H.S.; Sandwick, R.K. Purine biosynthetic intermediate-containing ribose-phosphate polymers as evolutionary precursors to RNA. J. Mol. Evol. 2014, 79, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawade, K.; Tabeta, H.; Ferjani, A.; Hirai, M.Y. The roles of functional amino acids in plant growth and development. Plant Cell Physiol. 2023, 64, 1482–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Li, X.; Huang, J. Morphological development and nutritional metabolism during floral bud differentiation in Acca Sellowiana (Feijoa). Int. J. Fruit. Sci. 2023, 23, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, Q.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Changes in carbohydrate metabolism and endogenous hormone regulation during bulblet initiation and development in Lycoris radiata. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 117–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamoral-Theys, D.; Andolfi, A.; Van Goietsenoven, G.; Cimmino, A.; Le Calve, B.; Wauthoz, N.; Megalizzi, V.; Gras, T.; Bruyere, C.; Dubois, J.; et al. Lycorine, the main phenanthridine Amaryllidaceae alkaloid, exhibits significant antitumor activity in cancer cells that display resistance to proapoptotic stimuli: An investigation of structure-activity relationship and mechanistic insight. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 6244–6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Du, Z.; Liao, M.; Feng, Y.; Ruan, H.; Jiang, H. Discovery and characterisation of lycorine-type alkaloids in Lycoris spp. (Amaryllidaceae) using UHPLC-QTOF-MS. Phytochem. Anal. 2019, 30, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, M.; Zhu, F.; Li, Q.; Li, K. SWATH-MS-Based proteomics reveals the regulatory metabolism of amaryllidaceae alkaloids in three Lycoris species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Yeo, H.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Nguyen, B.V.; Park, Y.E.; Sathasivam, R.; Kim, J.K.; Park, S.U. Profiles of secondary metabolites (phenolic acids, carotenoids, anthocyanins, and galantamine) and primary metabolites (carbohydrates, amino acids, and organic acids) during flower development in Lycoris radiata. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, X.; Wei, X.; Cheng, H.; You, X.; Cai, J. Metabolomic Analysis of Lycoris radiata across Developmental and Dormancy Stages. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10060636
Jiang X, Wei X, Cheng H, You X, Cai J. Metabolomic Analysis of Lycoris radiata across Developmental and Dormancy Stages. Horticulturae. 2024; 10(6):636. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10060636
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Xueru, Xuying Wei, Hua Cheng, Xin You, and Junhuo Cai. 2024. "Metabolomic Analysis of Lycoris radiata across Developmental and Dormancy Stages" Horticulturae 10, no. 6: 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10060636
APA StyleJiang, X., Wei, X., Cheng, H., You, X., & Cai, J. (2024). Metabolomic Analysis of Lycoris radiata across Developmental and Dormancy Stages. Horticulturae, 10(6), 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10060636







