Calafate (Berberis microphylla G. Forst) Populations from Chilean Patagonia Exhibit Similar Structuring at the Genetic and Metabolic Levels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
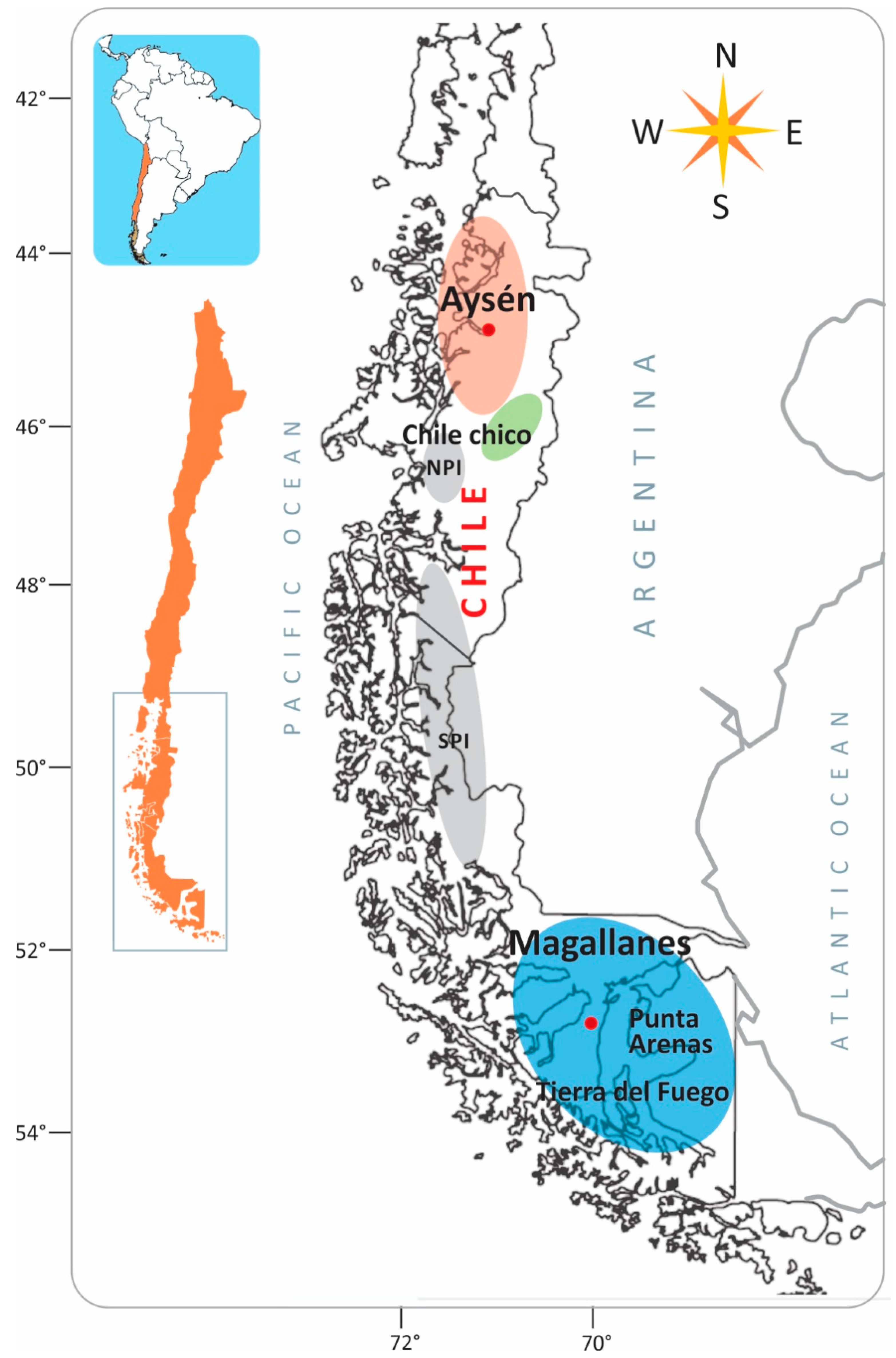
2.1. Sampling
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. SSR Analysis
2.4. Genetic Data Analyses
2.5. Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity Determinations
2.6. Chemometric Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
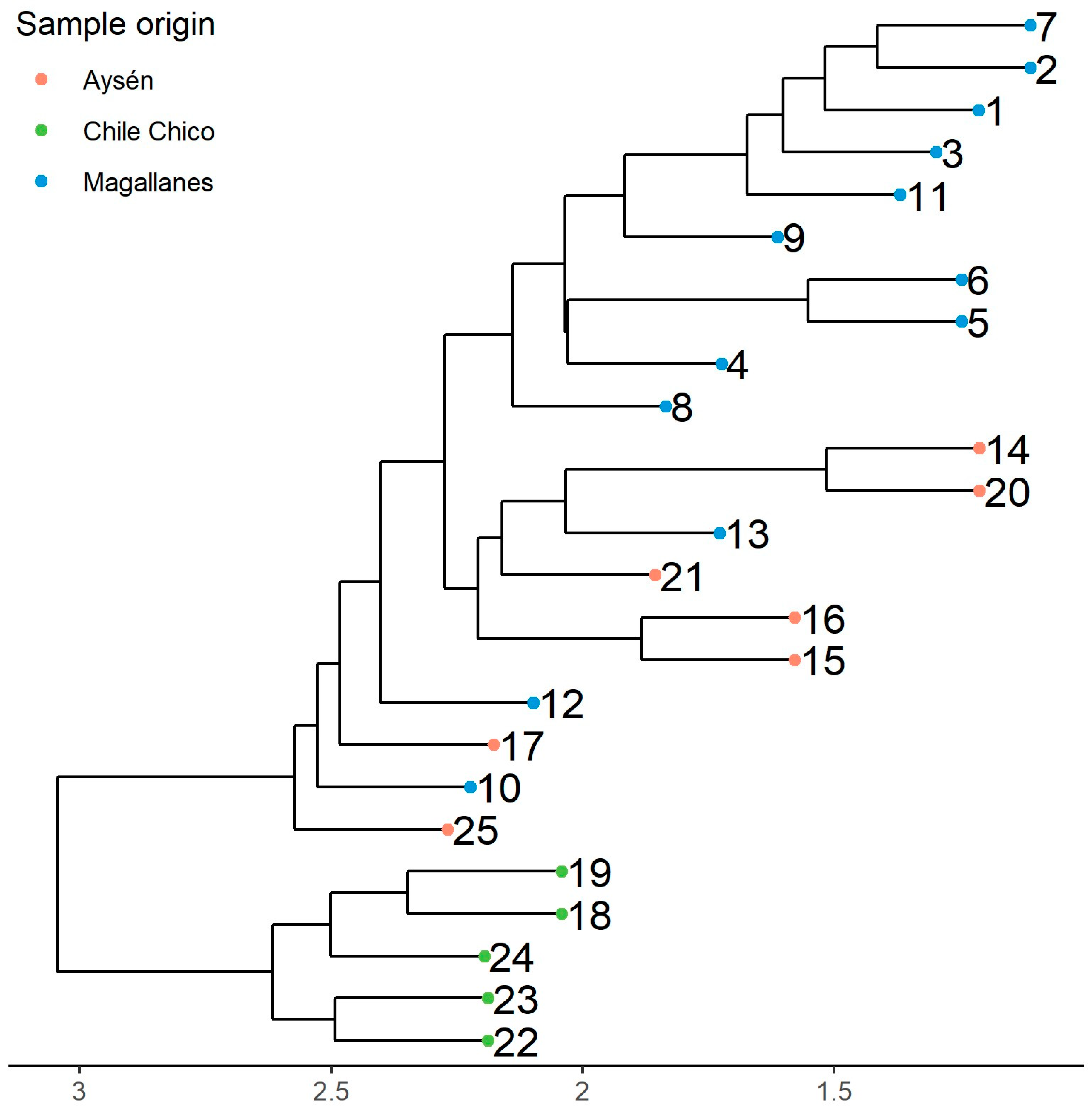
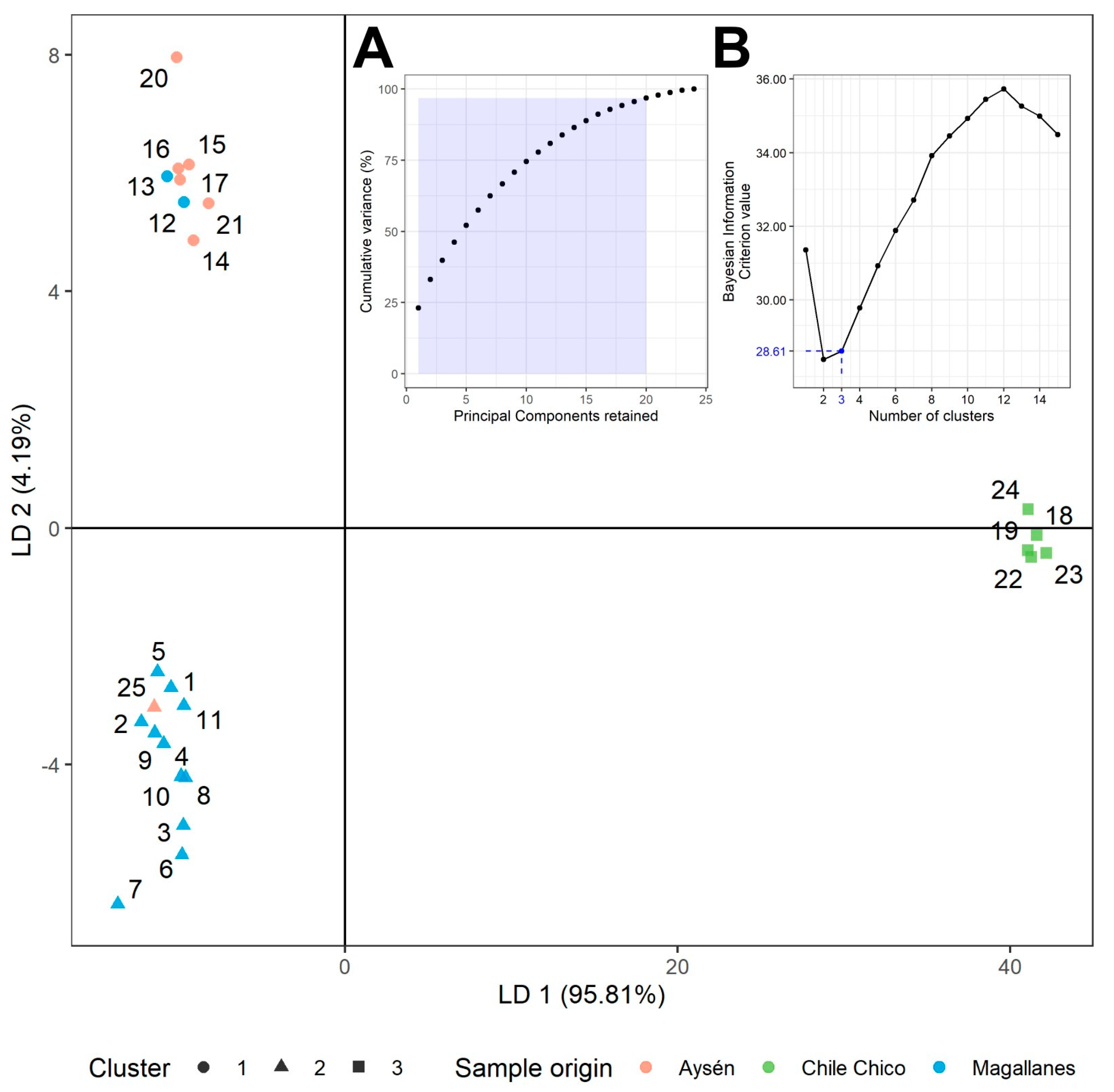
3.1. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure Based on SSR Marker Analysis
3.2. Phenolic Compound Profiles of Calafate Fruits
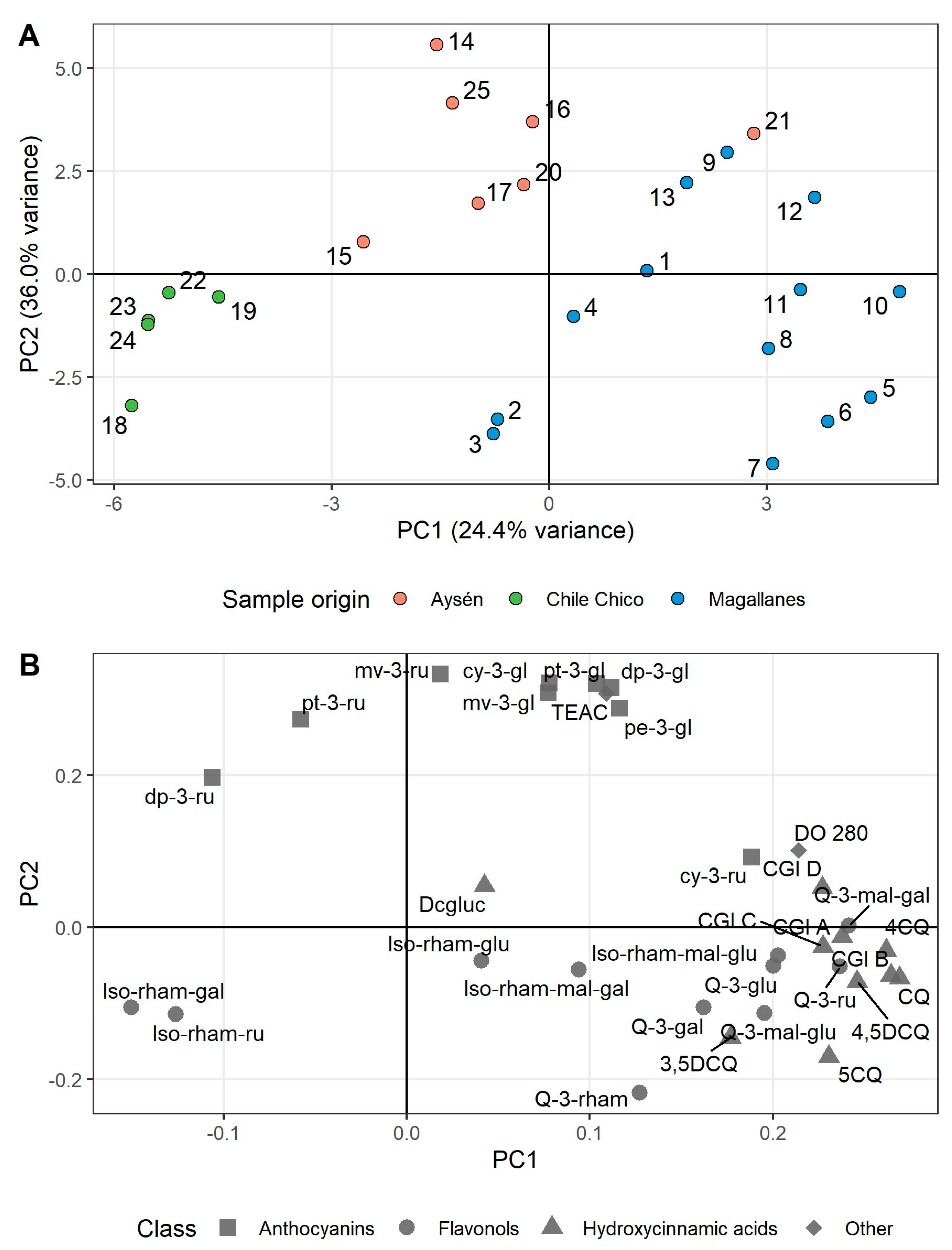
3.3. Principal Component Analysis of Phenolic Compounds in Calafate Berries
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Landrum, L.R. Revision of Berberis (Berberidaceae) in Chile and adjacent southern Argentina. Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard. 1999, 86, 793–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi, M.C. Berbiradeceae. In Flora Patagónica; Correa, M.N., Ed.; INTA: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1984; Section 4; pp. 325–348. [Google Scholar]
- Bottini, M.C.J.; De Bustos, A.; Sanso, A.M.; Jouve, N.; Poggio, J. Relationships in Patagonian species of Berberis (Berberidaceae) based on the characterization of rDNA internal transcribed spacer sequences. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2007, 153, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrendt, L.W.A. Berberis and Mahonia: A taxonomic revision. Bot. J. Linn. 1961, 57, 1–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marticorena, C.; Rodríguez, R. Flora de Chile, 2(2) Berberidaceae-Betulaceae; Universidad de Concepción: Concepción, Chile, 2003; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.; Jiménez-Aspee, F.; Theoduloz, C.; Ladio, A. Patagonian berries as native food and medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 241, 111979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredes, C.; Parada, A.; Salinas, J.; Robert, P. Phytochemical and traditional use of two southernmost Chilean berry fruits: Murta(Ugni molinae Turcz) and calafate (Berberis buxifolia Lam ASS). Foods 2020, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega-Galvez, A.; Rodriguez, A.; Stucken, K. Antioxidant, functional prpoerties and health-promoting potential of native South American berries: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Diaz, D.F.; Jimenez, P.; Reyes-Farias, M.; Soto-Covasich, J.; Costa, A.G.V. A Review of the potential of Chilean native berries in the treatment of obesity and its related features. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2019, 74, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidi, F.; Vamadevan, V.; Young Oh, W.; Peng, H.J. Phenolic compounds in agri-food by-products. Food Bioact. 2019, 5, 57–119. [Google Scholar]
- Dini, I.; Grumetto, L. Recent advances in polyphenol research. Molecules 2022, 27, 8777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medda, S.; Fadda, A.; Mulas, M. Climate variables of the sites of origin and genotype influence on phenolic compounds accumulation in cultivars of Myrtus communis L. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordani, E.; Müller, M.; Gambineri, F.; Paffetti, D.; Arena, M.; Radice, S. Genetic and morphological analysis of Berberis microphylla G. Forst. accessions in southern Tierra del Fuego. Plant Biosyst. 2017, 151, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottini, M.C.J.; De Bustos, A.; Jouve, N.; Poggio, L. AFLP characterization of natural populations of Berberis (Berberidaceae) in Patagonia, Argentina. Plant Syst. Evol. 2002, 231, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varas, B.; Castro, M.; Rodriguez, R.; von Baer, D.; Mardones, C.; Hinrichsen, P. Identification and characterization of microsatellites from calafate (Berberis microphylla, Berberidaceae). Appl. Plant Sci. 2013, 1, 1200003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, R.; Rai, M.; Kalia, S.; Singh, R.; Dhawan, A. Microsatellite markers: An overview of the recent progress in plants. Euphytica 2011, 177, 309–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, R. Chemometrics: Data Analysis for the Laboratory and Chemical Plant; Applied Chemometrics for Scientists; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bosque-Sendra, J.; Cuadros-Rodriguez, L.; Ruiz-Samblas, C.; de la Mata, P. Combining chromatography and chemometrics for the characterization and authentication of fats and oils from triacylglycerol compositional data—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 724, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodhi, M.; Ye, G.N.; Weeden, N.; Reisch, B. A simple and efficient method for DNA extraction from grapevine cultivars and Vitis species. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 1994, 12, 6–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasieniuk, M. polysat: An R Package for Polyploid Microsatellite Analysis. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2011, 11, 562–566. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G. Using Ggtree to Visualize Data on Tree-Like Structures. Curr. Prot. Bioinform. 2020, 69, e9622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jombart, T.; Adegenet , A.R. Package for the Multivariate Analysis of Genetic Markers. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1403–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, L.; Pastene, E.; Duran-Sandoval, D.; Vergara, C.; von Baer, D.; Mardones, C. Pharmacokinetics of low molecular weight phenolic compounds in gerbil plasma after the consumption of calafate berry (Berberis microphylla) extract. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.; Zapata, M.; Sabando, C.; Bustamante, L.; von Baer, D.; Vergara, C.; Mardones, C. Flavonols, alkaloids and antioxidant capacity of edible wild Berberis species from Patagonia. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 12407–12417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.M.; Obae, S.G.; Brand, M.H.; Silander, J.A.; Jones, K.L.; Nunziata, S.O.; Lance, S.L. Development and characterization of microsatellite markers for Berberis thunbergii (Berberidaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2012, 99, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, C.; Durka, W. Isolation and characterization of microsatellite markers in the invasive shrub Mahonia aquifolium (Berberidaceae) and their applicability in related species. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 948–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gago, P.; Boso, S.; Santiago, J.-L.; Martínez, M.-C. Identification and characterization of relict olive varieties (Olea europaea L.) in the Northwest of the Iberian Peninsula. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.V.; Gómez-Silva, V.; Ramírez, M.J.; Fontúrbel, F.E. Meta-analysis of the differential effects of habitat fragmentation and degradation on plant genetic diversity. Conserv. Biol. 2020, 34, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testolin, R.; Messina, R.; Cipriani, G.; De Mori, G. SSR-based DNA fingerprinting of fruit crops. Crop Sci. 2023, 63, 390–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, D.L.; Clark, A.G. Principles of Population Genetics, 2nd ed.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 1989; p. 677. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, M.; Ebadi, A.; Reim, S.; Fatahi, R.; Balandary, A.; Farrokhi, N.; Hanke, M.V. Molecular analysis of Iranian seedless barberries via SSR. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 129, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Martino, L.; Manavella, F.A.; García, D.A.; Salato, G. Phenology and fruit quality of nine sweet cherry cultivars in South Patagonia. Acta Hortic. 2008, 795, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M. Viñateros más Australes del Mundo ya Tienen sus Primeros Vinos. WIP 2023. Available online: https://wip.cl/vinateros-mas-australes-del-mundo-ya-tienen-sus-primeros-vinos (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Fitzgerald, T.L.; Shapter, F.M.; McDonald, S.; Waters, D.L.E.; Chivers, I.H.; Drenth, A.; Nevo, E.; Henry, R.J. Genome diversity in wild grasses under environmental stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 21140–21145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cona, M.; Chávez, A.; León-Lobos, P.; Marín, J.C.; Hinrichsen, P. Genetic structure and north-south decrease of genetic diversity in the Patagonian maqui berry (Aristotelia chilensis [Molina] Stuntz): Implications for its conservation and use. Conserv. Genet. 2023, 24, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thole, V.; Bassard, J.E.; Ramírez-González, R.; Trick, M.; Afshar, B.G.; Breitel, D.; Hill, L.; Foito, A.; Shepherd, L.; Freitag, S.; et al. RNA-seq, de novo transcriptome assembly and flavonoid gene analysis in 13 wild and cultivated berry fruit species with high content of phenolics. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamorro, M.; Reiner, G.; Theduloz, C.; Ladio, A.; Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.; Gómez-Alonso, S.; Jimenez-Aspee, F. Polyphenol composition and (bio)activity of Berberis species and wild strawberry from the Argentinean Patagonia. Molecules 2019, 24, 3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodarte-Castrejon, A.D.; Eichholz, I.; Rohn, S.; Kroh, L.W.; Huyskens-Keil, S. Phenolic profile and antioxidant activity of highbush blueberry Vaccinium corymbosum L. during fruit maturation and ripening. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, M.E.; Giordani, E.; Bustamante, G.; Radice, S. Variability in fruit traits and anthocyanin content among populations of underutilized Patagonian species Berberis microphylla G. Forst. J. Berry Res. 2021, 11, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, S.; Alonso, M.; Arena, M.E. Berberis microphylla: A Species with Phenotypic Plasticity in Different Climatic Conditions. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2018, 20, 2221–2229. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto-Morales, F.; Retamal-Salgado, J.; López, M.D.; Zapata, N.; Vergara-Retamales, R.; Palma, D. Variation in Physical-Chemical Parameters and Phenolic Compounds in Fruits of Four Calafate Clones. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| SSR Marker 1 | A 2 | Ae | He | Ho | Cj | GenBank Accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BmLP05 * | 5 | 3.308 | 0.698 | 0.92 | 0.273 | JX481194 |
| BmLP07 | 5 | 3.186 | 0.686 | 0.96 | 0.285 | JX481196 |
| BmLP09 * | 6 | 3.377 | 0.704 | 1.00 | 0.267 | JX481198 |
| BmLP11 * | 5 | 2.808 | 0.644 | 0.56 | 0.329 | JX481200 |
| BmLP19.2 * | 6 | 2.616 | 0.618 | 0.68 | 0.356 | JX481207 |
| BmLP26 * | 4 | 3.684 | 0.729 | 0.80 | 0.241 | JX481214 |
| BmLP30 | 6 | 2.654 | 0.623 | 0.80 | 0.351 | JX481218 |
| BmLP36 | 8 | 3.769 | 0.735 | 0.92 | 0.235 | JX481224 |
| BmLP38 | 7 | 3.366 | 0.703 | 0.84 | 0.268 | JX481226 |
| BmLP39 * | 4 | 1.337 | 0.252 | 0.24 | 0.738 | JX481227 |
| BmLP46 | 6 | 2.420 | 0.587 | 0.52 | 0.389 | JX481234 |
| BmLP49 * | 5 | 3.591 | 0.722 | 0.56 | 0.248 | JX481238 |
| BmLP53 | 2 | 1.713 | 0.416 | 0.24 | 0.566 | JX481241 |
| BmLP54 | 7 | 4.931 | 0.797 | 1.00 | 0.170 | JX481243 |
| BmLP58.2 * | 3 | 1.764 | 0.433 | 0.60 | 0.549 | JX481248 |
| BmLP59 * | 6 | 3.631 | 0.725 | 0.84 | 0.245 | JX481249 |
| BmLP65 * | 12 | 4.778 | 0.791 | 0.96 | 0.176 | JX481255 |
| BmLP71 | 11 | 4.702 | 0.787 | 1.00 | 0.180 | JX481261 |
| Mean | 6 ± 2.47 | 3.202 ± 1.025 | 0.647 ± 0.145 | 0.747 ± 0.246 | 0.326 ± 0.151 |
| Phenolic Compound Class | Compound | Abbreviation | Concentration Range * (µmol/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anthocyanins | Delphinidin-3-glucoside | Dp-3-glu | 1.50–12.21 |
| Delphinidin-3-rutinoside | Dp-3-ru | 0.25–1.57 | |
| Cyanidin-3-glucoside | Cy-3-glu | 0.35–1.88 | |
| Cyanidin-3-rutinoside | Cy-3-ru | n.d.–0.37 | |
| Petunidin-3-glucoside | Pt-3-glu | 0.68–7.64 | |
| Petunidin-3-rutinoside | Pt-3-ru | 0.04–1.92 | |
| Peonidin-3-glucoside | Pe-3-glu | n.d.–0.88 | |
| Peonidin-3-rutinoside | Pe-3-ru | n.d.–0.10 | |
| Malvidin-3-glucoside | Mv-3-glu | 0.31–7.29 | |
| Malvidin-3-rutinoside | Mv-3-ru | 0.12–1.06 | |
| Flavonols | Quercetin-3-rutinoside | Q-3-ru | 0.07–0.74 |
| Quercetin-3-galactoside | Q-3-gal | 0.04–0.71 | |
| Quercetin.3-glucoside | Q-3-glu | 0.03–0.22 | |
| Quercetin-3-malonylgalactoside | Q-3-mal-gal | n.d.–0.11 | |
| Quercetin-3-malonylglucoside | Q-3-mal-glu | n.d.–0.49 | |
| Isorhamnetin-3-rutinoside | Isorham-3-ru | n.d.–0.43 | |
| Isorhamnetin-3-galactoside | Isorham-3-gal | n.d.–0.17 | |
| Quercetin-3-rhamnoside | Quer-3-rham | n.d.–0.58 | |
| Isorhamnetin-3-glucoside | Isorham-3-glu | n.d.–0.06 | |
| Isorhamnetin-3-malonylgalactoside | Isorham-3-mal-gal | n.d.–0.13 | |
| Isorhamnetin-3-malonylglucoside | Isorham3-mal-glu | n.d–0.12 | |
| Hydroxycinnamic acids | Caffoeoyl glucaric acid isomer A | CGI A | 0.02–1.07 |
| Caffoeoyl glucaric acid isomer B | CGI B | 0.06–1.88 | |
| Caffoeoyl glucaric acid isomer C | CGI C | 0.06–1.25 | |
| Caffoeoyl glucaric acid isomer D | CGI D | 0.02–0.29 | |
| Caffeoyquinic acid | CQ | 0.02–0.51 | |
| 5-Caffeoylquinic acid | 5-CQ | 0.04–2.33 | |
| 4-Caffeoylquinic acid | 4-CQ | 0.03–0.38 | |
| Dicaffeoylglucaric acid | DCgluc | n.d.–0.67 | |
| 3,5-dicaffeoylglucaric acid | 3,5-DCQ | 0.02–0.64 | |
| 4,5-dicaffeoylglucaric acid | 4,5-DCQ | n.d–0.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz, A.; Meneses, M.; Varas, B.; Araya, J.; Vergara, C.; von Baer, D.; Hinrichsen, P.; Mardones, C. Calafate (Berberis microphylla G. Forst) Populations from Chilean Patagonia Exhibit Similar Structuring at the Genetic and Metabolic Levels. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10050458
Ruiz A, Meneses M, Varas B, Araya J, Vergara C, von Baer D, Hinrichsen P, Mardones C. Calafate (Berberis microphylla G. Forst) Populations from Chilean Patagonia Exhibit Similar Structuring at the Genetic and Metabolic Levels. Horticulturae. 2024; 10(5):458. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10050458
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz, Antonieta, Marco Meneses, Benjamín Varas, Juan Araya, Carola Vergara, Dietrich von Baer, Patricio Hinrichsen, and Claudia Mardones. 2024. "Calafate (Berberis microphylla G. Forst) Populations from Chilean Patagonia Exhibit Similar Structuring at the Genetic and Metabolic Levels" Horticulturae 10, no. 5: 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10050458
APA StyleRuiz, A., Meneses, M., Varas, B., Araya, J., Vergara, C., von Baer, D., Hinrichsen, P., & Mardones, C. (2024). Calafate (Berberis microphylla G. Forst) Populations from Chilean Patagonia Exhibit Similar Structuring at the Genetic and Metabolic Levels. Horticulturae, 10(5), 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10050458






