Exploring the PpEXPs Family in Peach: Insights into Their Role in Fruit Texture Development through Identification and Transcriptional Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Measurement of Peach Fruit Firmness
2.3. Identification of PpEXPs in Peach Genome
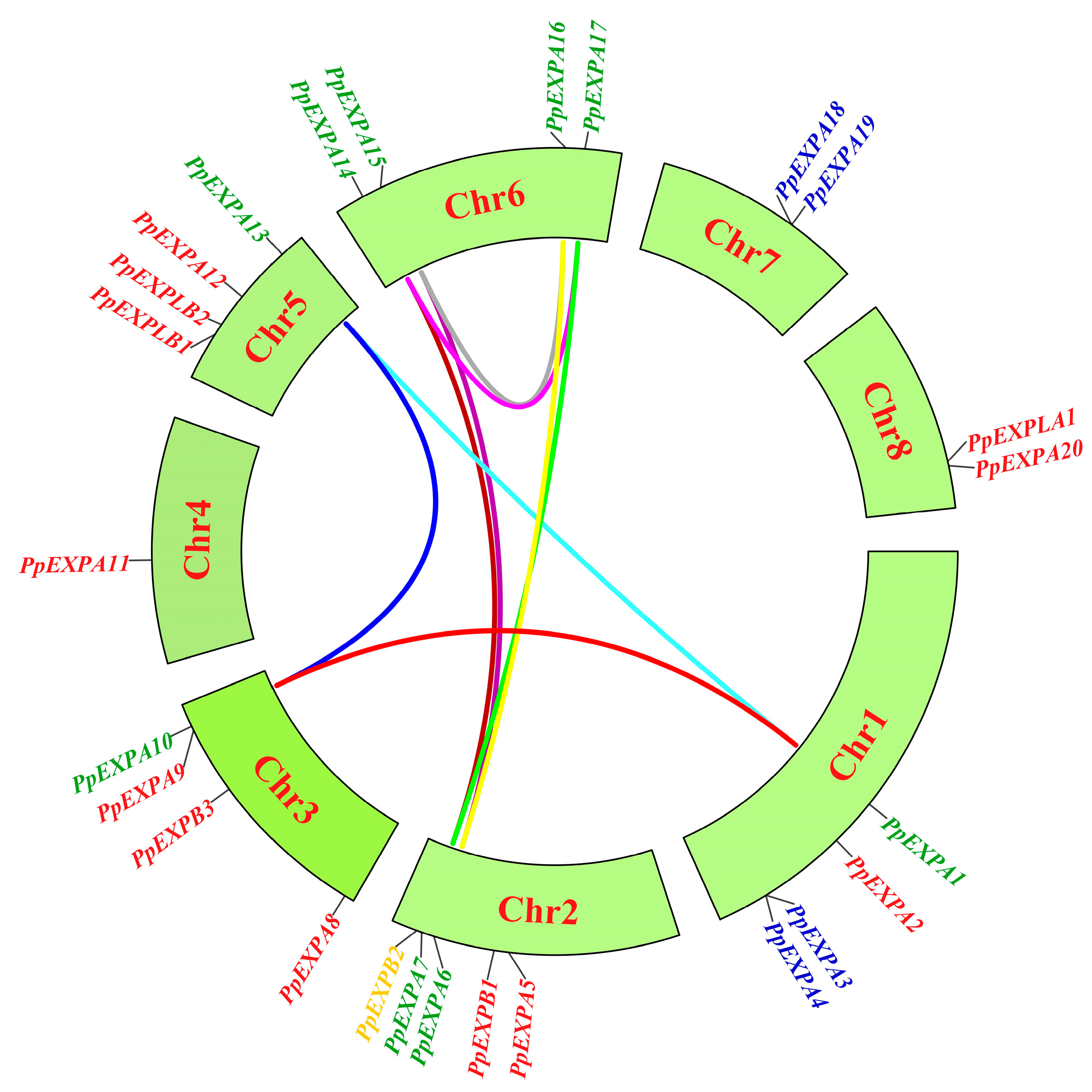
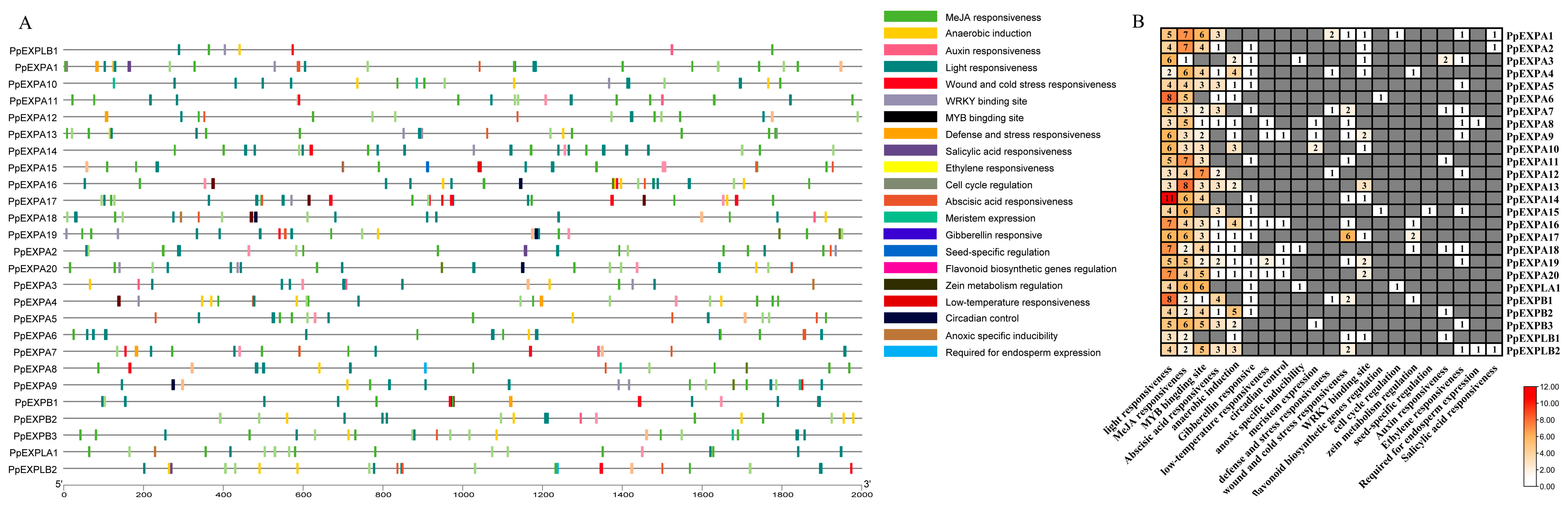
2.4. Chromosome Location, Gene Structure and cis-Elements Analysis of the PpEXP Genes
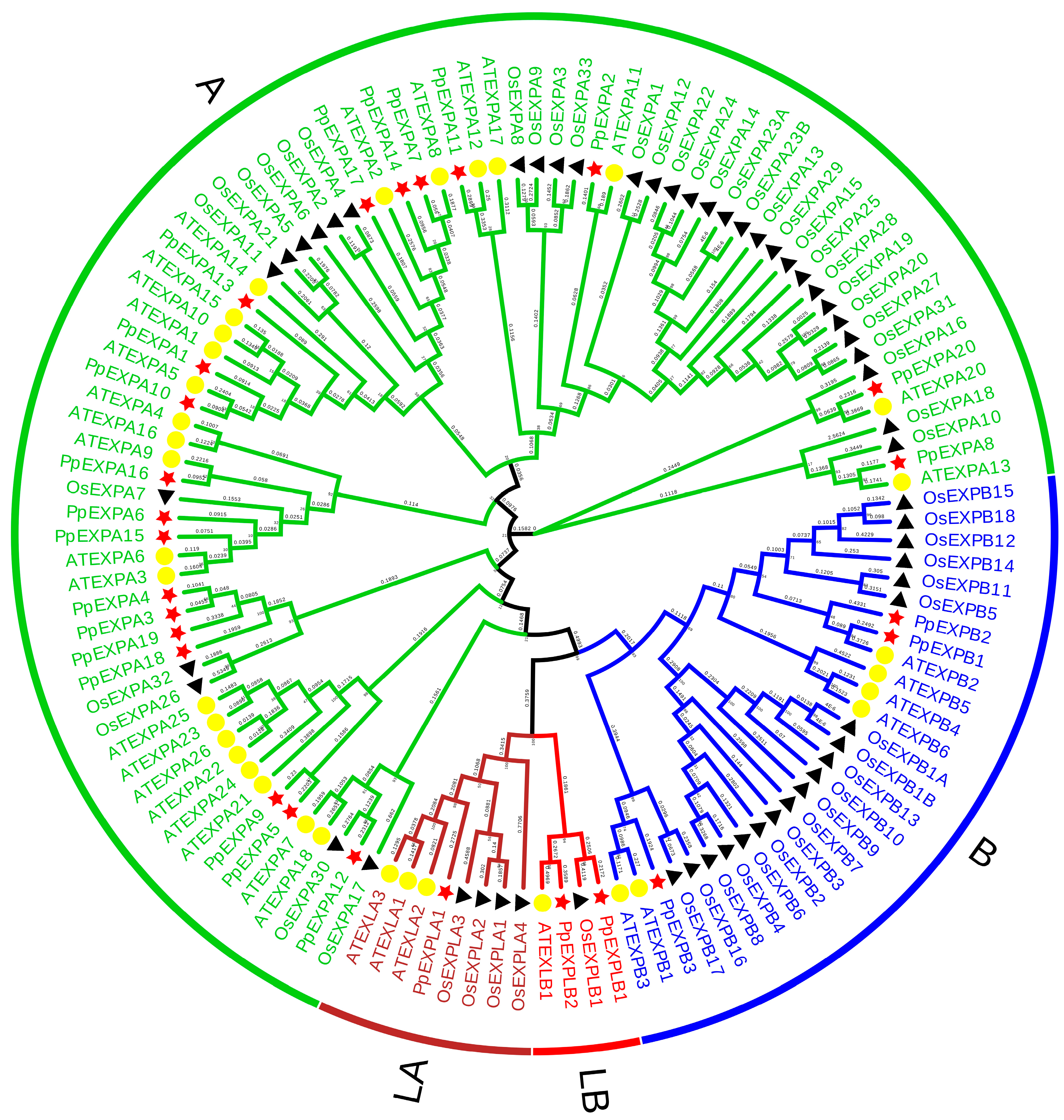
2.5. Phylogeny Analysis of PpEXPs
2.6. Transcriptomic Analysis
2.7. Expression Pattern Analysis of PpEXP Genes in Peach Fruit and qRT-PCR Analysis
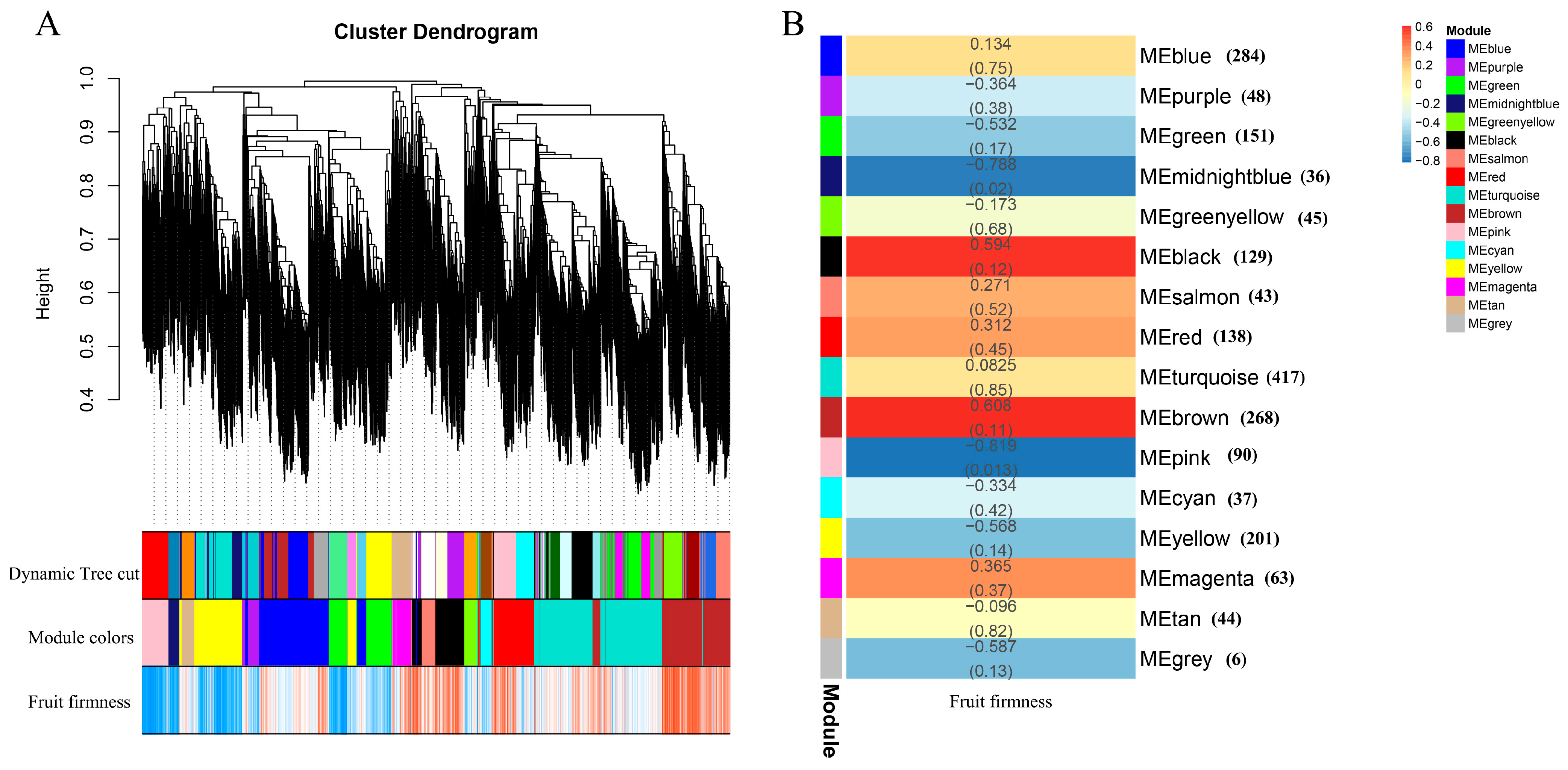
2.8. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA)
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of the PpEXPs Family in Peaches
3.2. Gene Structure and Motif Analysis of PpEXPs
3.3. Chromosome Distribution and Gene Duplication
3.4. Cis-Acting Elements Detection in the Promoter Regions of PpEXPs
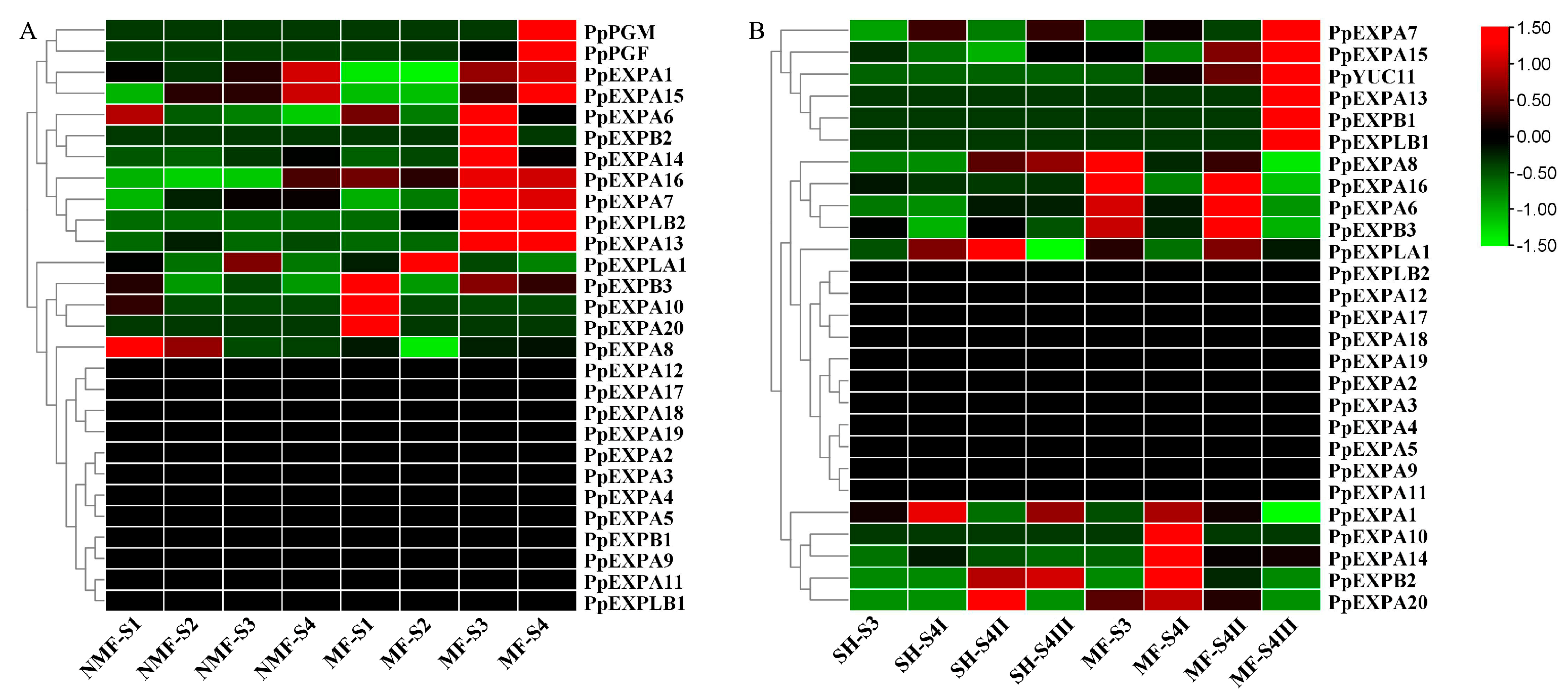
3.5. Expression Analysis of PpEXPs during Fruit Ripening in MF, NMF and SH Peach
3.6. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) of Fruit Development
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoshida, M. Genetical studies on the fruit quality of peach varieties. III. Texture and keeping quality. Bull. Fruit Tree Res. Sta. 1976, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Haji, T.; Yaegaki, H.; Yamaguchi, M. Inheritance and expression of fruit texture melting, non-melting and stony hard in peach. Sci. Hortic. 2005, 105, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Zhou, H.; Ma, B.; Zheng, H.; Fang, T.; Ogutu, C.; Vimolmangkang, S.; Han, Y. Copy number variation of a gene cluster encoding endopolygalacturonase mediates flesh texture and stone adhesion in peach. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 1993–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Zeng, W.; Niu, L.; Lu, Z.; Liu, H.; Cui, G.; Zhu, Y.; Chu, J.; Li, W.; Fang, W.; et al. PpYUC11, a strong candidate gene for the stony hard phenotype in peach (Prunus persica L. Batsch), participates in IAA biosynthesis during fruit ripening. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 7031–7044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, C.; Korban, S.S.; Chen, K. Regulatory Mechanisms of Textural Changes in Ripening Fruits. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2010, 29, 222–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yeats, T.H.; Uluisik, S.; Rose, J.K.C.; Seymour, G.B. Fruit Softening: Revisiting the Role of Pectin. Trends Plant Sci 2018, 23, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Seymour, G.B. Molecular and biochemical basis of softening in tomato. Mol. Hortic. 2022, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, R.G.; Sutherland, P.W.; Johnston, S.L.; Gunaseelan, K.; Hallett, I.C.; Mitra, D.; Brummell, D.A.; Schroder, R.; Johnston, J.W.; Schaffer, R.J. Down-regulation of POLYGALACTURONASE1 alters firmness, tensile strength and water loss in apple (Malus × domestica) fruit. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada, M.A.; Blanco-Portales, R.; Posé, S.; García-Gago, J.A.; Jiménez-Bermúdez, S.; Muñoz-Serrano, A.S.; Caballero, J.L.; Pliego-Alfaro, F.; Mercado, J.A.; Muñoz-Blanco, J. Antisense Down-Regulation of the FaPG1 Gene Reveals an Unexpected Central Role for Polygalacturonase in Strawberry Fruit Softening. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paniagua, C.; Blanco-Portales, R.; Barcelo-Munoz, M.; Garcia-Gago, J.A.; Waldron, K.W.; Quesada, M.A.; Munoz-Blanco, J.; Mercado, J.A. Antisense down-regulation of the strawberry beta-galactosidase gene FabetaGal4 increases cell wall galactose levels and reduces fruit softening. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.W.; Zhao, S.Q.; Gu, S.; Cao, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, J.F.; Liu, L.; Li, A.R.; Jia, W.S.; Qi, B.X.; et al. FvWRKY48 binds to the pectate lyase FvPLA promoter to control fruit softening in Fragaria vesca. Plant Physiol. 2022, 189, 1037–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, G.B.; Østergaard, L.; Chapman, N.H.; Knapp, S.; Martin, C. Fruit Development and Ripening. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2013, 64, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.J.S.; Watson, C.F.; Ray, J.; Bird, C.R.; Morris, P.C.; Schuch, W.; Grierson, D. Antisense RNA inhibition of polygalacturonase gene expression in transgenic tomatoes. Nature 1988, 334, 724–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieman, D.M.; Harriman, R.W.; Ramamohan, G.; Handa, A.K. An Antisense Pectin Methylesterase Gene Alters Pectin Chemistry and Soluble Solids in Tomato Fruit. Plant Cell 1992, 4, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uluisik, S.; Chapman, N.H.; Smith, R.; Poole, M.; Adams, G.; Gillis, R.B.; Besong, T.M.D.; Sheldon, J.; Stiegelmeyer, S.; Perez, L.; et al. Genetic improvement of tomato by targeted control of fruit softening. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 950–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Huang, W.; Xiong, F.; Xian, Z.; Su, D.; Ren, M.; Li, Z. Silencing of SlPL, which encodes a pectate lyase in tomato, confers enhanced fruit firmness, prolonged shelf-life and reduced susceptibility to grey mould. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 1544–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozzi, G.O.; Fraschina, A.A.; Navarro, A.A.; Cascone, O.; Greve, L.C.; Labavitch, J.M. α-L-arabinofuranosidase activity during development and ripening of normal and ACC synthase antisense tomato fruit. Hortscience 2002, 37, 564–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Lin, Y.; Wang, C.; Lu, J.; Liu, Z.; He, Z.; Shu, X.; Chen, W.; Wu, R.; Li, B.; et al. Expansin SlExp1 and endoglucanase SlCel2 synergistically promote fruit softening and cell wall disassembly in tomato. Plant Cell 2023, 36, 709–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQueen-Mason, S.; Durachko, D.M.; Cosgrove, D.J. Two endogenous proteins that induce cell wall extension in plants. Plant Cell 1992, 4, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar]
- Cosgrove, D.J. Plant expansins: Diversity and interactions with plant cell walls. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2015, 25, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yan, H.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Jiang, C.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, S.; Cheng, B. Genome-wide identification and characterization of maize expansin genes expressed in endosperm. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2014, 289, 1061–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampedro, J.; Carey, R.E.; Cosgrove, D.J. Genome histories clarify evolution of the expansin superfamily: New insights from the poplar genome and pine ESTs. J. Plant Res. 2006, 119, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal Santo, S.; Vannozzi, A.; Tornielli, G.B.; Fasoli, M.; Venturini, L.; Pezzotti, M.; Zenoni, S. Genome-Wide Analysis of the Expansin Gene Superfamily Reveals Grapevine-Specific Structural and Functional Characteristics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, R.; Gao, Z.; Chen, C.; Jiang, Z.; Shu, H. A genome-wide analysis of the expansin genes in Malus × Domestica. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2014, 289, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampedro, J.; Lee, Y.; Carey, R.E.; DePamphilis, C.; Cosgrove, D.J. Use of genomic history to improve phylogeny and understanding of births and deaths in a gene family. Plant J. 2005, 44, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.-M.; Zuo, D.-Y.; Wang, X.-F.; Cheng, H.-L.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Wang, Q.-L.; Song, G.-L.; Ma, Z.-Y. Genome-wide identification of the expansin gene family reveals that expansin genes are involved in fibre cell growth in cotton. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minoia, S.; Boualem, A.; Marcel, F.; Troadec, C.; Quemener, B.; Cellini, F.; Petrozza, A.; Vigouroux, J.; Lahaye, M.; Carriero, F.; et al. Induced mutations in tomato SlExp1 alter cell wall metabolism and delay fruit softening. Plant Sci. 2016, 242, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Lopez, A.; Jeon, S.; de Freitas, S.T.; Yu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Labavitch, J.M.; Tian, S.; Powell, A.L.T.; Mitcham, E. Disassembly of the fruit cell wall by the ripening-associated polygalacturonase and expansin influences tomato cracking. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Xie, B.; An, X.-H.; Ma, R.-P.; Zhao, D.-Y.; Cheng, C.-G.; Li, E.-M.; Zhou, J.-T.; Kang, G.-D.; Zhang, Y.-Z. Overexpression of the apple expansin-like gene MdEXLB1 accelerates the softening of fruit texture in tomato. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 3578–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Li, X.; Luo, J.; Pan, Q.; Li, Y.; Gu, T. Characterization of expansin genes and their transcriptional regulation by histone modifications in strawberry. Planta 2021, 254, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A "one for all, all for one"; bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.; Lian, X.; Cheng, J.; Zeng, W.; Zheng, X.; Wang, W.; Ye, X.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; et al. Genome-wide identification and transcriptome profiling reveal that E3 ubiquitin ligase genes relevant to ethylene, auxin and abscisic acid are differentially expressed in the fruits of melting flesh and stony hard peach varieties. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Liu, Y.-X.; Huang, L. ImageGP: An easy-to-use data visualization web server for scientific researchers. Imeta 2022, 1, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenn, M.A.; Giovannoni, J.J. Phytohormones in fruit development and maturation. Plant J. 2021, 105, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, D.J. Loosening of plant cell walls by expansins. Nature 2000, 407, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgelis, N.; Yennawar, N.H.; Cosgrove, D.J. Structural basis for entropy-driven cellulose binding by a type-A cellulose-binding module (CBM) and bacterial expansin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14830–14835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yennawar, N.H.; Li, L.-C.; Dudzinski, D.M.; Tabuchi, A.; Cosgrove, D.J. Crystal structure and activities of EXPB1 (Zea m 1), a β-expansin and group-1 pollen allergen from maize. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14664–14671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccardi, T.L.; Barthe, G.A.; Derrick, K.S. A novel protein associated with citrus blight has sequence similarities to expansin. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 38, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampedro, J.; Cosgrove, D.J. The expansin superfamily. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rafudeen, S.; Gxaba, G.; Makgoke, G.; Bradley, G.; Pironcheva, G.; Raitt, L.; Irving, H.; Gehring, C. A role for plant natriuretic peptide immuno-analogues in NaCl- and drought-stress responses. Physiol. Plant 2003, 119, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, N.; Song, W.; Yin, G.; Qin, Y.; Yan, Y.; Hu, Y. Soybean (Glycine max) expansin gene superfamily origins: Segmental and tandem duplication events followed by divergent selection among subfamilies. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, P.; Hong, J.K.; Kim, J.A.; Jeong, M.-J.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lee, S.I. Genome-wide analysis of the expansin gene superfamily reveals Brassica rapa-specific evolutionary dynamics upon whole genome triplication. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2015, 290, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampedro, J.; Guttman, M.; Li, L.C.; Cosgrove, D.J. Evolutionary divergence of beta-expansin structure and function in grasses parallels emergence of distinctive primary cell wall traits. Plant J. 2015, 81, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Yan, L.; Li, H.; Lian, X.; Cheng, J.; Wang, W.; Zheng, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Ye, X.; et al. Genome-wide identification of HSF family in peach and functional analysis of PpHSF5 involvement in root and aerial organ development. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Gao, F.; Li, T.; Chen, T.; Zheng, X.; Lian, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, J.; Wang, W.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of the GRAS transcription factor gene family in peach (Prunus persica) and ectopic expression of PpeDELLA1 and PpeDELLA2 in Arabidopsis result in dwarf phenotypes. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 298, 111003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Evolution by gene duplication: An update. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Peach Genome, I.; Verde, I.; Abbott, A.G.; Scalabrin, S.; Jung, S.; Shu, S.; Marroni, F.; Zhebentyayeva, T.; Dettori, M.T.; Grimwood, J.; et al. The high-quality draft genome of peach (Prunus persica) identifies unique patterns of genetic diversity, domestication and genome evolution. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 487–494. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Han, Y.; Feng, Y.; Xing, S.; Zhao, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W. Expression of wheat expansin driven by the RD29 promoter in tobacco confers water-stress tolerance without impacting growth and development. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 163, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, A.; Marowa, P.; Kong, Y. Genome-wide identification of the expansin gene family in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Mol Genet Genom. 2016, 291, 1891–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, G.; Feng, C.; Li, H. Genome-wide identification of expansin genes in Brachypodium distachyon and functional characterization of BdEXPA27. Plant Sci. 2020, 296, 110490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Walk, T.C.; Liao, H. Characterization of soybean beta-expansin genes and their expression responses to symbiosis, nutrient deficiency, and hormone treatment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 2805–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.-T.; Cosgrove, D.J. Regulation of Root Hair Initiation and Expansin Gene Expression in Arabidopsis[W]. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 3237–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Choi, H.-S.; Cho, H.-T. Root Hair-Specific EXPANSIN A7 Is Required for Root Hair Elongation in Arabidopsis. Mol. Cells 2011, 31, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Thorne, E.T.; Sharp, R.E.; Cosgrove, D.J. Modification of Expansin Transcript Levels in the Maize Primary Root at Low Water Potentials. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Xu, X.; Shi, Y.; Xu, J.; Huang, B. Transgenic Tobacco Plants Overexpressing a Grass PpEXP1 Gene Exhibit Enhanced Tolerance to Heat Stress. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, H.-H.; Sloan, J.; Dorca-Fornell, C.; Fleming, A. Inducible Repression of Multiple Expansin Genes Leads to Growth Suppression during Leaf Development. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Shi, T.; Liu, J.; Tian, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, L. Genomic, metabonomic and transcriptomic analyses of sweet osmanthus varieties provide insights into floral aroma formation. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 306, 111442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Fang, W.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Cao, K. Mining Genes Related to Single Fruit Weight of Peach (Prunus persica) Based on WGCNA and GSEA. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Diretto, G.; Pirrello, J.; Roustan, J.-P.; Li, Z.; Giuliano, G.; Regad, F.; Bouzayen, M. The chimeric repressor version of an Ethylene Response Factor (ERF) family member, Sl-ERF.B3, shows contrasting effects on tomato fruit ripening. New Phytol. 2014, 203, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.C.; Kuang, J.F.; Chen, J.Y.; Liu, X.C.; Xiao, Y.Y.; Fu, C.C.; Wang, J.N.; Wu, K.Q.; Lu, W.J. Banana Transcription Factor MaERF11 Recruits Histone Deacetylase MaHDA1 and Represses the Expression of MaACO1 and Expansins during Fruit Ripening. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 1070–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.C.; Han, Y.C.; Qi, X.Y.; Shan, W.; Chen, J.Y.; Lu, W.J.; Kuang, J.F. Papaya CpERF9 acts as a transcriptional repressor of cell-wall-modifying genes CpPME1/2 and CpPG5 involved in fruit ripening. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 2341–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, K.; Zhao, P.; Zhu, G.; Fang, W.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. Expansin genes are candidate markers for the control of fruit weight in peach. Euphytica 2016, 210, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayama, H.; Ito, A.; Moriguchi, T.; Kashimura, Y. Identification of a new expansin gene closely associated with peach fruit softening. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2003, 29, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene ID | Gene Name | No. of Amino Acid (aa) | Molecular Weight(KDa) | Predicted Isoelectric Point (PI) | Subcellular Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prupe.1G276700 | PpEXPA1 | 252 | 26.74 | 9.33 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.1G360700 | PpEXPA2 | 257 | 27.78 | 9.14 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.1G516600 | PpEXPA3 | 253 | 28.13 | 9.10 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.1G516700 | PpEXPA4 | 262 | 29.35 | 9.18 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.2G121800 | PpEXPA5 | 260 | 28.74 | 8.59 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.2G136500 | PpEXPB1 | 272 | 28.52 | 4.72 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.2G237000 | PpEXPA6 | 259 | 27.83 | 9.41 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.2G263600 | PpEXPA7 | 252 | 26.74 | 6.92 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.2G274400 | PpEXPB2 | 277 | 29.55 | 6.58 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.3G014800 | PpEXPA8 | 265 | 28.67 | 8.60 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.3G155600 | PpEXPB3 | 266 | 28.58 | 8.83 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.3G256600 | PpEXPA9 | 259 | 28.51 | 8.89 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.3G265800 | PpEXPA10 | 241 | 26.12 | 9.32 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.4G183400 | PpEXPA11 | 265 | 29.11 | 9.83 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.5G047300 | PpEXPLB1 | 255 | 27.70 | 4.69 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.5G057900 | PpEXPLB2 | 252 | 27.98 | 7.46 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.5G087100 | PpEXPA12 | 263 | 28.99 | 9.39 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.5G195200 | PpEXPA13 | 249 | 26.22 | 9.08 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.6G042000 | PpEXPA14 | 254 | 27.27 | 8.43 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.6G075100 | PpEXPA15 | 260 | 28.02 | 9.58 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.6G256500 | PpEXPA16 | 258 | 27.96 | 8.59 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.6G292300 | PpEXPA17 | 257 | 27.51 | 8.92 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.7G124900 | PpEXPA18 | 266 | 29.50 | 8.84 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.7G125000 | PpEXPA19 | 288 | 31.56 | 8.57 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.8G174500 | PpEXPLA1 | 261 | 28.22 | 8.84 | Cell wall |
| Prupe.8G182000 | PpEXPA20 | 259 | 28.57 | 8.28 | Cell wall |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Song, C.; Gao, F.; Zhi, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Hou, N.; Cheng, J.; Wang, W.; et al. Exploring the PpEXPs Family in Peach: Insights into Their Role in Fruit Texture Development through Identification and Transcriptional Analysis. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10040332
Guo Y, Song C, Gao F, Zhi Y, Zheng X, Wang X, Zhang H, Hou N, Cheng J, Wang W, et al. Exploring the PpEXPs Family in Peach: Insights into Their Role in Fruit Texture Development through Identification and Transcriptional Analysis. Horticulturae. 2024; 10(4):332. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10040332
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yakun, Conghao Song, Fan Gao, Yixin Zhi, Xianbo Zheng, Xiaobei Wang, Haipeng Zhang, Nan Hou, Jun Cheng, Wei Wang, and et al. 2024. "Exploring the PpEXPs Family in Peach: Insights into Their Role in Fruit Texture Development through Identification and Transcriptional Analysis" Horticulturae 10, no. 4: 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10040332
APA StyleGuo, Y., Song, C., Gao, F., Zhi, Y., Zheng, X., Wang, X., Zhang, H., Hou, N., Cheng, J., Wang, W., Zhang, L., Ye, X., Li, J., Tan, B., Lian, X., & Feng, J. (2024). Exploring the PpEXPs Family in Peach: Insights into Their Role in Fruit Texture Development through Identification and Transcriptional Analysis. Horticulturae, 10(4), 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10040332







