A Multi-Fruit Recognition Method for a Fruit-Harvesting Robot Using MSA-Net and Hough Transform Elliptical Detection Compensation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2. MSA-Net
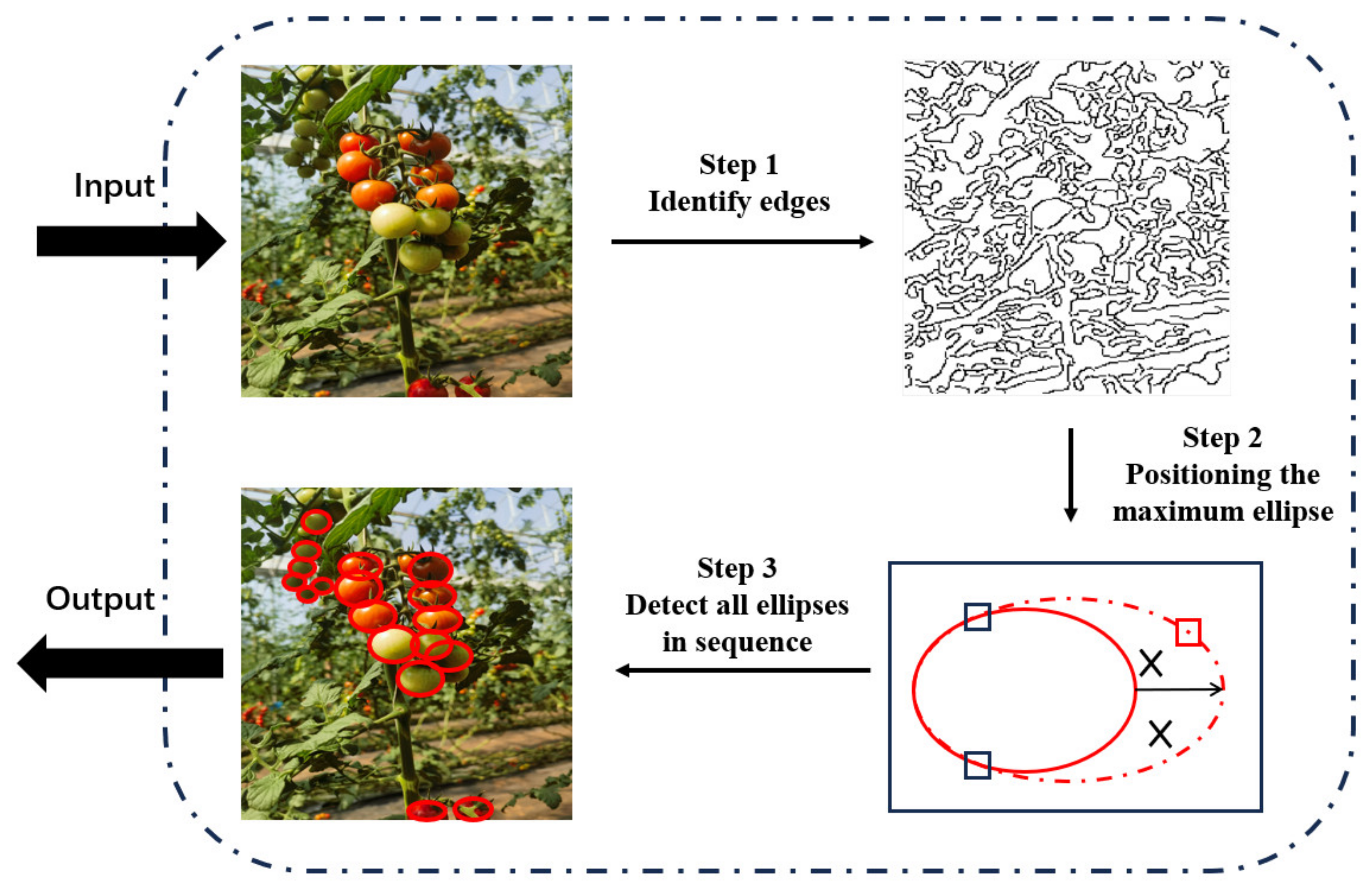
2.3. Hough Transform Compensation Mechanism
2.4. Experimental Design
3. Results and Discussion
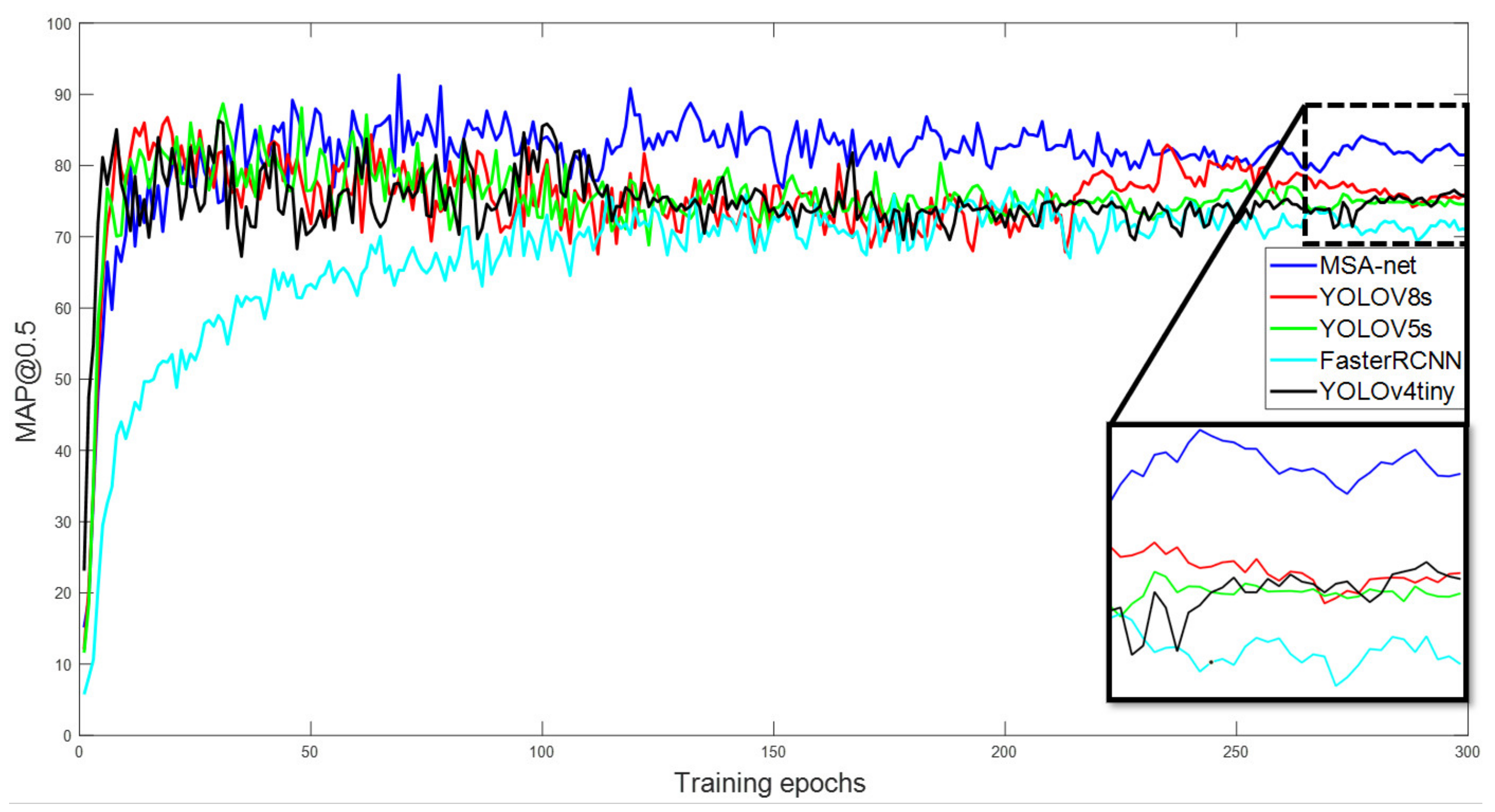
3.1. Detection Performance of the MSA-Net Model
3.2. Analysis of MSA-Net Recognition Results
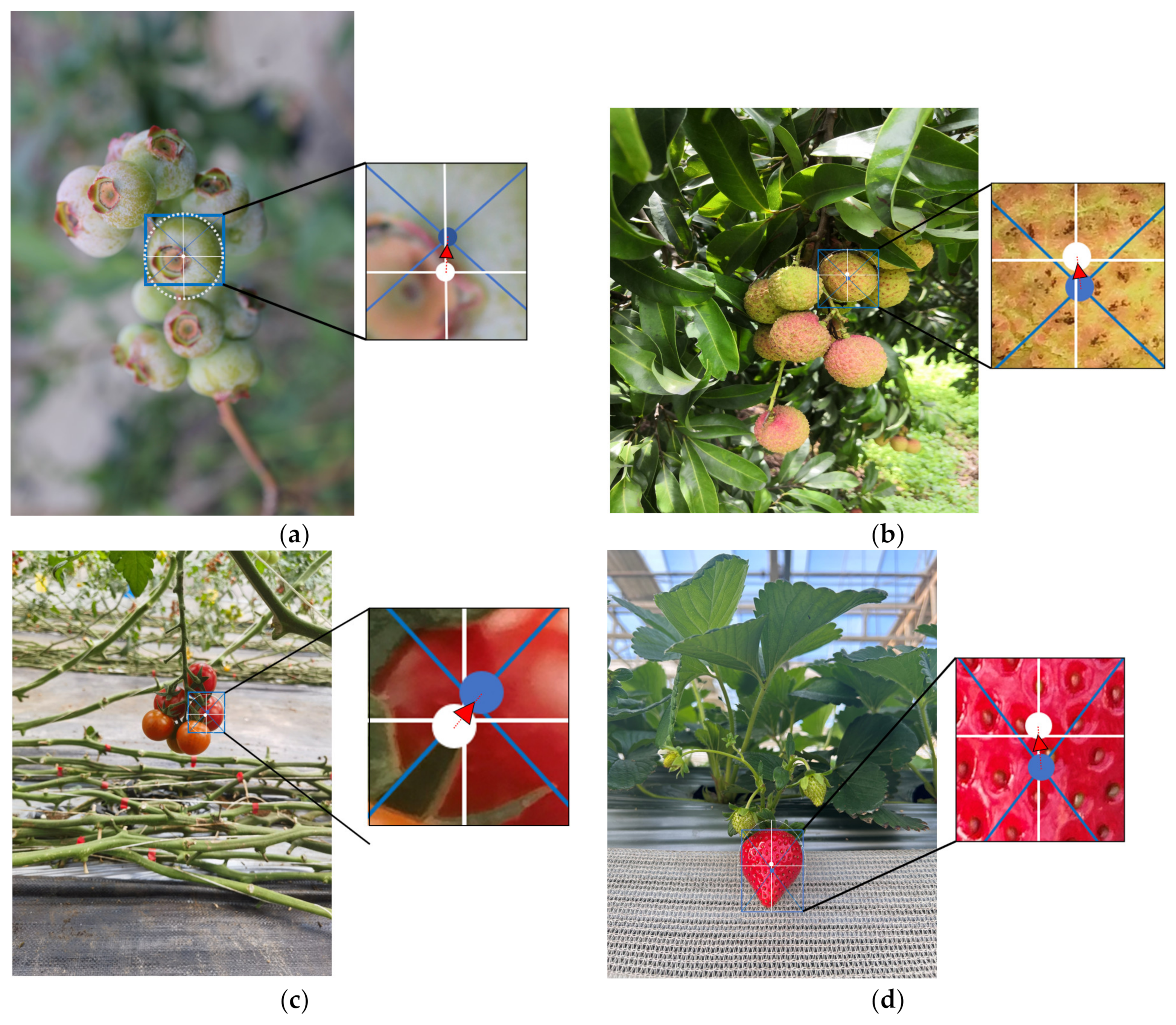
3.3. Analysis of Hough Transform Compensation Results
4. Conclusions
- MSA-Net can effectively learn the features of different types of fruits. For a comprehensive dataset including blueberries, lychees, strawberries, and tomatoes, the model achieved a precision of 97.56, a recall of 92.21, and an mAP@0.5 of 94.81, accurately identifying various fruits in the environment.
- The introduction of the Hough Transform ellipse detection compensation mechanism further refines the initial localization of spherical fruits. For close-up fruit images, the average localization error for different fruits decreased by 8.8 pixels. For distant fruit images, the average localization error for different fruits decreased by 3.5 pixels, further improving the accuracy of fruit localization.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Osorio, L.; Flórez-López, E.; Grande-Tovar, C. The Potential of Selected Agri-Food Loss and Waste to Contribute to a Circular Economy: Applications in the Food, Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Industries. Molecules 2021, 26, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Río-Celestino, M.; Font, R. The Health Benefits of Fruits and Vegetables. Foods 2020, 9, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andaryani, S.; Sloan, S.; Nourani, V.; Keshtkar, H. The utility of a hybrid GEOMOD-Markov Chain model of land-use change in the context of highly water-demanding agriculture in a semi-arid region. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 64, 101332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Igathinathane, C.; Li, J.; Cen, H.; Lu, Y.; Flores, P. Technology progress in mechanical harvest of fresh market apples. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 175, 105606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Han, Q.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Kong, D.; Wang, F.; Zou, X. Assisting the Planning of Harvesting Plans for Large Strawberry Fields through Image-Processing Method Based on Deep Learning. Agriculture 2024, 14, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Han, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, D.; Zou, X. Strawberry Detection and Ripeness Classification Using YOLOv8+ Model and Image Processing Method. Agriculture 2024, 14, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Fang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Pan, Y. A Sustainable Economic System to Face the Fluctuation of Fruit Prices: Based on a Small-Region DSGE Model. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2021, 2021, 6693709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, R. Fruit Detection and Recognition Based on Deep Learning for Automatic Harvesting: An Overview and Review. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussi, A.; Zero, E.; Sacile, R.; Trinchero, D.; Fossa, M. Smart Sensors and Smart Data for Precision Agriculture: A Review. Sensors 2024, 24, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, I.M.; Bibi, A.; Shah, J.H.; Khan, M.A.; Sharif, M.; Iqbal, K.; Nam, Y.; Kadry, S. Deep learning-based classification of fruit diseases: An application for precision agriculture. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 66, 1949–1962. [Google Scholar]
- Duong, L.T.; Nguyen, P.T.; Di Sipio, C.; Di Ruscio, D. Automated fruit recognition using EfficientNet and MixNet. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 171, 105326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, D.; Hussain, I.; Ismail, M.; Alabrah, A.; Ullah, S.; Alaghbari, H. A Simple and Efficient Deep Learning-Based Framework for Automatic Fruit Recognition. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 35237311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachmawati, E.; Supriana, I.; Khodra, M.L.; Firdaus, F. Integrating semantic features in fruit recognition based on perceptual color and semantic template. Inf. Process. Agric. 2022, 9, 316–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuong, N.; Luong, A.; Trinh, T.; Ho, P.; Meesad, P.; Nguyen, T. Intelligent Fruit Recognition System Using Deep Learning. Lect. Notes Netw. Syst. 2021, 251, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Han, Q.; Li, C.; Zou, T.; Zou, X. Fusion of fruit image processing and deep learning: A study on identification of citrus ripeness based on R-LBP algorithm and YOLO-CIT model. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1397816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Han, Q.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Zou, X. YOLO-BLBE: A Novel Model for Identifying Blueberry Fruits with Different Maturities Using the I-MSRCR Method. Agronomy 2024, 14, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Xia, K.; Pan, H. Fruit Recognition Using Color Statistics. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Automation, Robotics and Computer Engineering, Wuhan, China, 16–17 December 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qin, M.; Lei, J.; Wang, X.; Tan, K. Blueberry maturity recognition method based on improved YOLOv4-Tiny. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 170–178. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Gui, G.; Khattak, A.M.; Wang, M.; Gao, W.; Jia, J. Multi-Task Cascaded Convolutional Networks Based Intelligent Fruit Detection for Designing Automated Robot. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 56028–56038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbasi, E.; Mostafa, N.; AlArnaout, Z.; Aymen, I.Z.; Cina, E.; Varghese, G.; Shdefat, A.; Topcu, A.E.; Abdelbaki, W.; Mathew, S.; et al. Artificial Intelligence Technology in the Agricultural Sector: A Systematic Literature Review. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 171–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, J.; Wang, K. Automatic cucumber recognition algorithm for harvesting robots in the natural environment using deep learning and multi-feature fusion. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 170, 105254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheiralipour, K.; Kazemi, A. A new method to determine morphological properties of fruits and vegetables by image processing technique and nonlinear multivariate modeling. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 23, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saedi, S.; Khosravi, H. A deep neural network approach towards real-time on-branch fruit recognition for precision horticulture. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 159, 113594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Image Type | Number of Blueberry Images | Number of Strawberry Images | Number of Lychee Images | Number of Tomato Images | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distant fruit image | 158 | 214 | 174 | 131 | |
| Close-range-exposure fruit image | 179 | 194 | 216 | 184 | |
| Close-range natural-light fruit image | 314 | 337 | 402 | 367 | |
| Close-range backlit fruit image | 144 | 95 | 138 | 84 | |
| Total | 795 | 840 | 930 | 766 | 3331 |
| Model | Precision | Recall | F1 | mAP@0.5 | mAP@0.5:0.95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSA-Net | 97.56 | 92.21 | 94.81 | 92.72 | 61.85 |
| YOLOV8s | 97.84 | 83.57 | 90.14 | 86.77 | 56.14 |
| YOLOV5s | 96.51 | 84.97 | 90.37 | 88.69 | 58.79 |
| FasterRCNN | 93.19 | 90.48 | 91.82 | 76.88 | 50.77 |
| YOLOV4tiny | 90.86 | 87.74 | 89.27 | 86.31 | 55.98 |
| Image Type | Initial Positioning Average Error (Close Range)/Pixel | Initial Positioning Average Error (Close Range)/Pixel | Positioning Accuracy Improvement (Close Range)/Percentage | Initial Positioning Average Error (Distant Range)/Pixel | Average Error after Compensation (Distant Range)/Pixel | Positioning Accuracy Improvement (Distant Range)/Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blueberry | 29 | 18 | 37.93% | 18 | 17 | 5.55% |
| Lychee | 34 | 30 | 11.76% | 25 | 23 | 8.00% |
| Tomato | 41 | 22 | 46.34% | 30 | 22 | 26.67% |
| Strawberry | 26 | 25 | 3.84% | 19 | 16 | 15.79% |
| Average | 33 | 24 | 24.97% | 23 | 20 | 14.01% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Luo, T. A Multi-Fruit Recognition Method for a Fruit-Harvesting Robot Using MSA-Net and Hough Transform Elliptical Detection Compensation. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10101024
Wang S, Luo T. A Multi-Fruit Recognition Method for a Fruit-Harvesting Robot Using MSA-Net and Hough Transform Elliptical Detection Compensation. Horticulturae. 2024; 10(10):1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10101024
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shengxue, and Tianhong Luo. 2024. "A Multi-Fruit Recognition Method for a Fruit-Harvesting Robot Using MSA-Net and Hough Transform Elliptical Detection Compensation" Horticulturae 10, no. 10: 1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10101024
APA StyleWang, S., & Luo, T. (2024). A Multi-Fruit Recognition Method for a Fruit-Harvesting Robot Using MSA-Net and Hough Transform Elliptical Detection Compensation. Horticulturae, 10(10), 1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10101024





