Microbial Community and Fermentation Quality of Alfalfa Silage Stored in Farm Bunker Silos in Inner Mongolia, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Sample Collection
2.2. Chemical Composition, Fermentation Products, and Microbial Composition Analysis
2.3. Bacterial Community Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Chemical and Microbial Composition of Pre-Ensiling Alfalfa
3.2. Fermentation Products of Alfalfa Silages Produced in Farm Bunker Silos
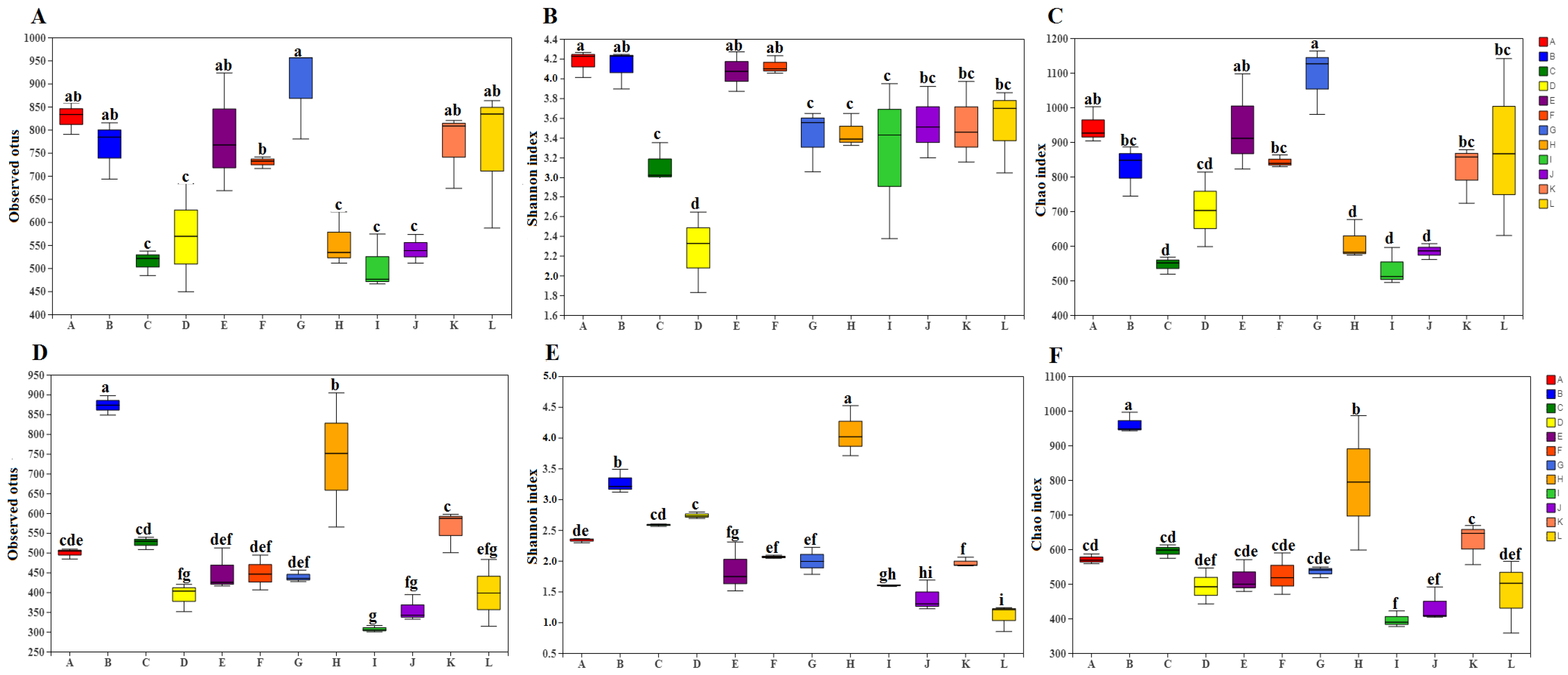
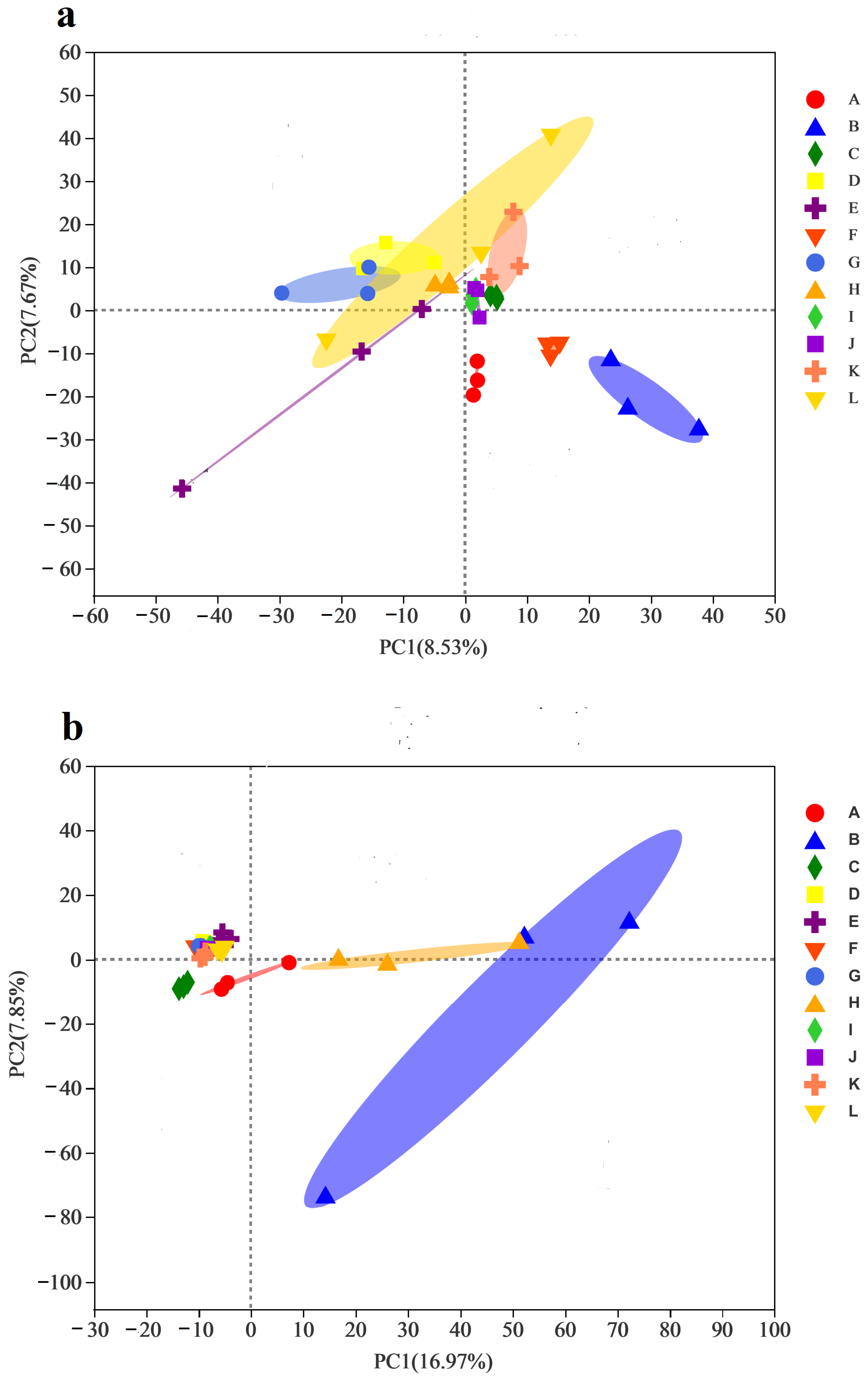
3.3. Bacterial Diversity of Fresh Material and Silage
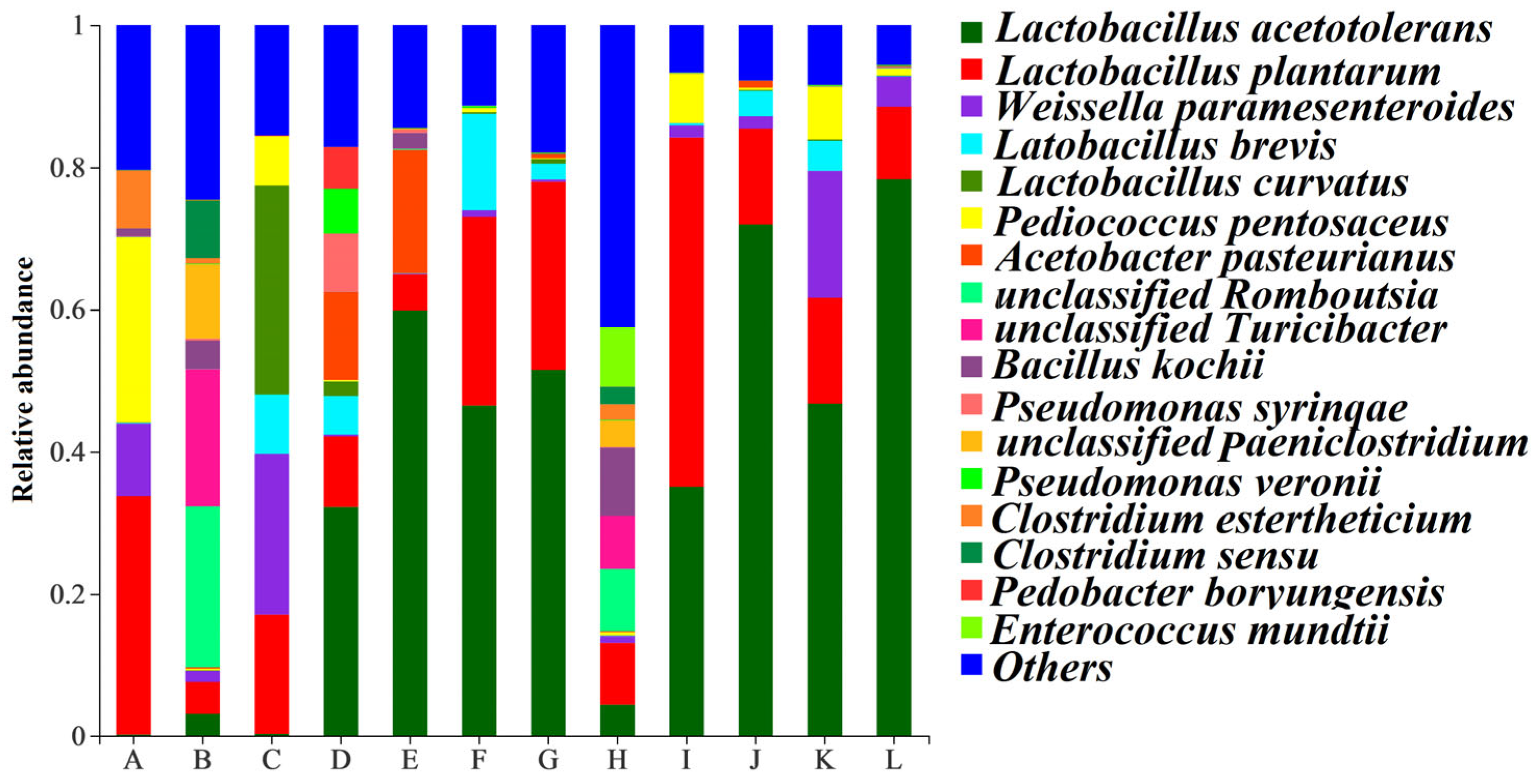
3.4. Bacterial Community Dynamics in Fresh Material and Silage
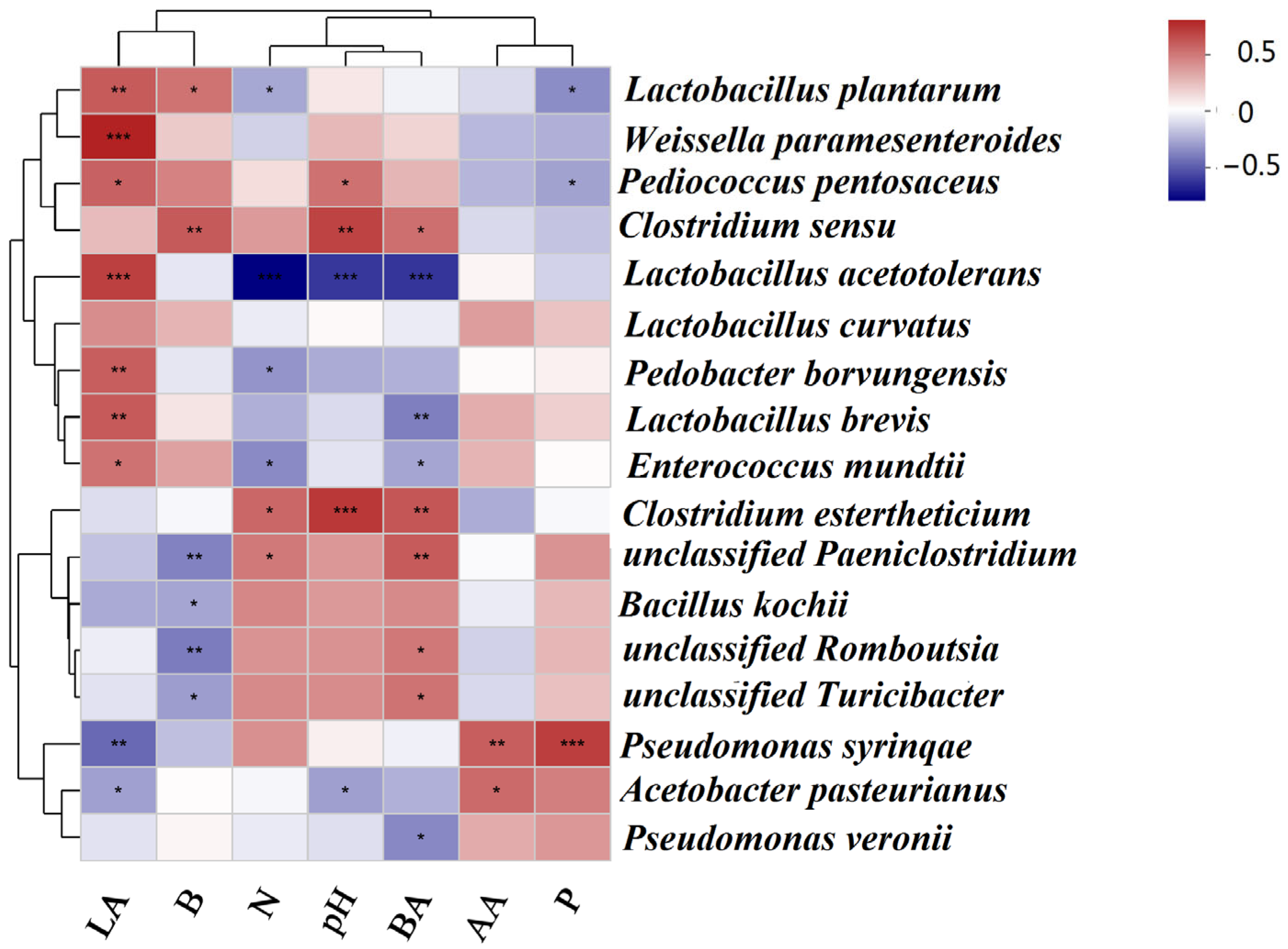
3.5. Association of the Bacterial Microflora with the Fermentation Products
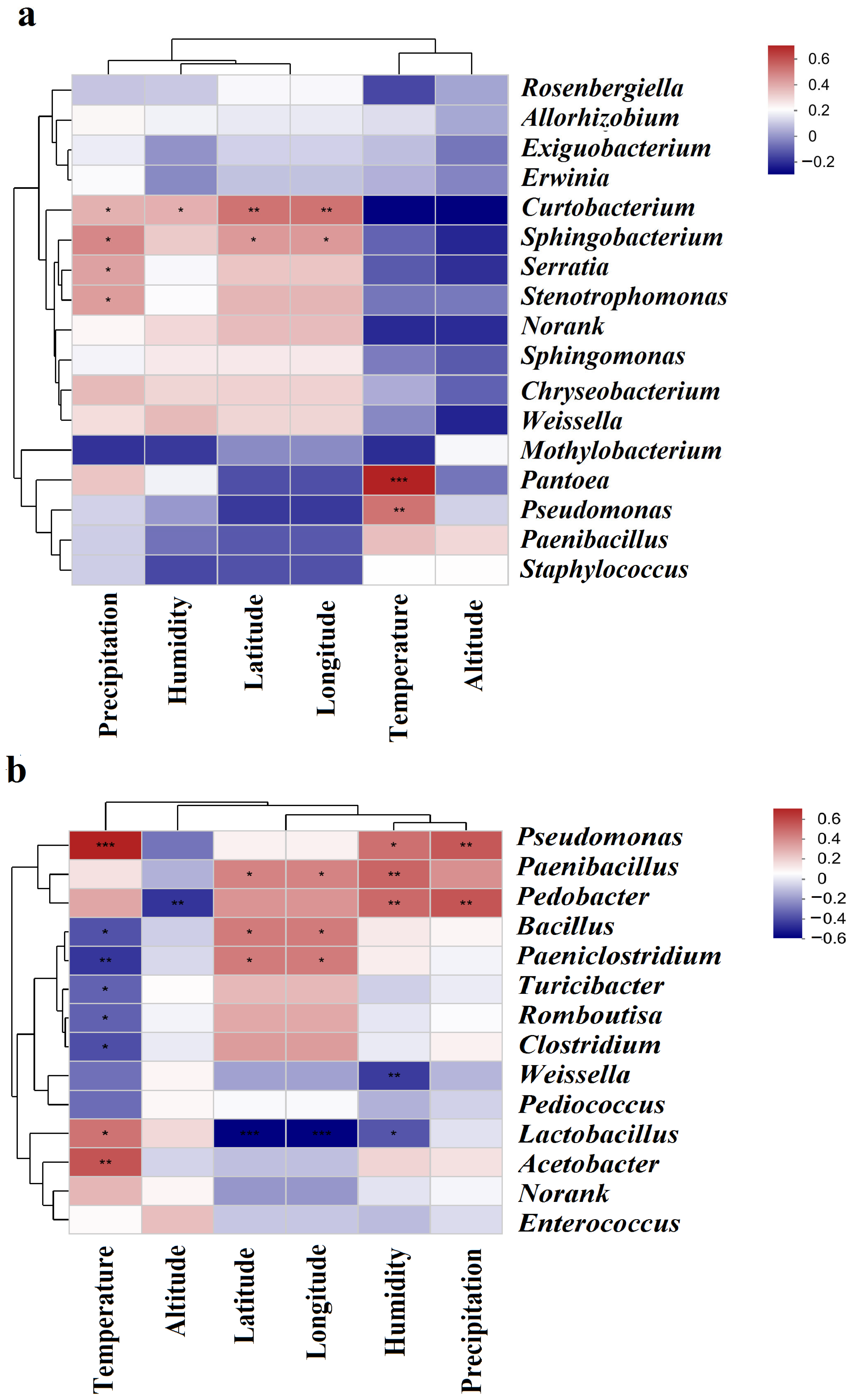
3.6. Correlations between Bacterial Communities and Environmental Factors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pahlow, G.; Muck, R.E.; Driehuis, F.; Elferink, S.J.W.H.O.; Spoelstra, S.F. Microbiology of ensiling. In Silage Science and Technology; Buxton, D.R., Muck, R.E., Harrison, R.E., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy; Crop Science Socioty of America Inc.; Soil Science Society of America, Inc. Publications: Madison, WI, USA, 2003; pp. 31–93. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Niu, H.; Tong, Q.; Chang, J.; Yu, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Ma, D. The microbiota dynamics of alfalfa silage during ensiling and after air exposure, and the metabolomics after air exposure are affected by Lactobacillus casei and cellulase addition. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 519121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardes, T.F.; Daniel, J.L.P.; Adesogan, A.T.; McAllister, T.A.; Drouin, P.; Nussio, L.G.; Huhtanen, P.; Tremblay, G.F.; Bélanger, G.; Cai, Y. Silage review: Unique challenges of silages made in hot and cold regions. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4001–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, V.A.; Pereyra, C.M.; Keller, L.A.; Dalcero, A.M.; Rosa, C.A.; Chiacchiera, S.M.; Cavaglieri, L.R. Fungi and mycotoxins in silage: An overview. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 115, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Jiang, D.; Zheng, M.; Tian, P.; Zheng, M.; Xu, C. Microbial community dynamics during alfalfa silage with or without clostridial fermentation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, P.; Chen, C. Effects of LAB Inoculants on the Fermentation Quality, Chemical Composition, and Bacterial Community of Oat Silage on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, E.B.; Liu, X.; Mellinger, C.; Gressley, T.F.; Stypinski, J.D.; Moyer, N.A.; Kung, L., Jr. Effect of dry matter content on the microbial community and on the effectiveness of a microbial inoculant to improve the aerobic stability of corn silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 5024–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.M.; Jiang, D.D.; Yuan, B.J.; Ni, K.K. Effect of Low-Temperature-Tolerant Lactic Acid Bacteria on the Fermentation Quality and Bacterial Community of Oat Silage at 5 °C vs. 15 °C. Fermentation 2022, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Nishino, N. Identification and isolation of Lactobacillus fructivorans from wilted alfalfa silage with and without molasses. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nishino, N. Effects of inoculation of Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus buchneri on fermentation, aerobic stability and microbial communities in whole crop corn silage. Grassl. Sci. 2011, 57, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.S.; Ke, W.C.; Ding, W.R.; Ding, L.M.; Xu, D.M.; Wang, W.W.; Zhang, P.; Yang, F.Y. Profiling of metabolome and bacterial community dynamics in ensiled Medicago sativa inoculated without or with Lactobacillus plantarum or Lactobacillus buchneri. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 15th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Arlington, AV, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, G.A.; Kang, J.H. Automated simultaneous determination of ammonia and total amino acids in ruminal fluid and in vitro media. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Dong, Z.; Shao, T. Dynamics of microbial community and fermentation quality during ensiling of sterile and nonsterile alfalfa with or without Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloveras, J.; Ferran, J.; Alvarez, A.; Torres, L. Harvest management effects on alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) production and quality in Mediterranean areas. Grass Forage Sci. 1998, 53, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdonald, P.; Henderson, A.R.; Heron, S.J.E. The Biochemistry of Silage, 2nd ed.; Chalcombe Publications: Bucks, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Otero, A.; Castro, M. Variability of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Seasonal forage production in the southwest of Uruguay. Agrociencia Urug. 2019, 23, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wen, A.; Desta, S.T.; Dong, Z.; Shao, T. Effects of four short–chain fatty acids or salts on the dynamics of nitrogen transformations and intrinsic protease activity of alfalfa silage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2759–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, X.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Ni, K.; Yang, F. Innovative utilization of herbal residues: Exploring the diversity of mechanisms beneficial to regulate anaerobic fermentation of alfalfa. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Minh, T.T.; Tu, T.T.; Tsuruta, T.; Pang, H.; Nishino, N. Comparative microbiota assessment of wilted Italian ryegrass, whole crop corn, and wilted alfalfa silage using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and next-generation sequencing. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Hu, Z.; Wei, M.; Yong, M.; Niu, H. Effects of inoculation of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Lentilactobacillus buchneri on fermentation quality, aerobic stability, and microbial community dynamics of wilted Leymus chinensis silage. Front Microbiol. 2022, 13, 928731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, S.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Nishino, N. Effects of inoculation with lactic acid bacteria on the bacterial communities of Italian ryegrass, whole crop maize, guinea grass and rhodes grass silages. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2010, 160, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, Z.; Wang, X.; Na, R. Effects of chlorpyrifos and chlorantraniliprole on fermentation quality of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) silage inoculated with or without Lactobacillus plantarum LP. Anim. Sci. J. 2017, 88, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Sun, L.; Lin, Y.; Yang, F.; Cai, Y. The use of PacBio SMRT technology to explore the microbial network and fermentation characteristics of woody silage prepared with exogenous carbohydrate additives. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 2193–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Nishino, N. Bacterial communities in alfalfa and corn silages produced in large-scale stack and bunker silos in China. Grassl. Sci. 2014, 60, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Shuai, Y.; Feng, G.; Ran, Q.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Microbial communities and natural fermentation of corn silages prepared with farm bunker-silo in Southwest China. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Kumai, S.; Ogawa, M.; Benno, Y.; Nakase, T. Characterization and Identification of Pediococcus Species Isolated from Forage Crops and Their Application for Silage Preparation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 2901–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.M.; Davies, D.R. The aerobic stability of silage: Key findings and recent developments. Grass Forage Sci. 2013, 68, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Han, H.; Gu, X.; Yu, Z.; Nishino, N. A survey of fermentation products and bacterial communities in corn silage produced in a bunker silo in China. Anim. Sci. J. 2014, 85, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, X.J.; Zhao, M.M.; Yu, Z. Isolating and evaluating lactic acid bacteria strains for effectiveness of Leymus chinensis silage fermentation. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 59, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Benno, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Ohmomo, S.; Nakase, T. Influence of Lactobacillus spp. from an Inoculant and of Weissella and Leuconostoc spp. from forage crops on silage fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2982–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nishino, N. Bacterial and fungal communities of wilted Italian ryegrass silage inoculated with and without Lactobacillus rhamnosus or Lactobacillus buchneri. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 52, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, O.C.M.; Arriola, K.G.; Daniel, J.L.P.; Adesogan, A.T. Effects of 8 chemical and bacterial additives on the quality of corn silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 5836–5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trcek, J.; Toyama, H.; Czuba, J.; Misiewicz, A.; Matsushita, K. Correlation between acetic acid resistance and characteristics of PQQ-dependent ADH in acetic acid bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 70, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, K.; Daniel, J.L.P.; Jobim, C.C.; Nussio, L.G. A data analysis on the effect of acetic acid on dry matter intake in dairy cattle. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2021, 272, 114782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L., Jr.; Shaver, R.D.; Grant, R.J.; Schmidt, R.J. Silage review: Interpretation of chemical, microbial, and organoleptic components of silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Adesogan, A.T. Influence of ensiling temperature, simulated rainfall, and delayed sealing on fermentation characteristics and aerobic stability of corn silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 3122–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, Z.G.; Muck, R.E. New trends and opportunities in the development and use of inoculants for silage. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 19, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulfam, A.; Guo, G.; Tajebe, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, X.; Bai, Y.; Saho, T. Characteristics of lactic acid bacteria isolates and their effect on the fermentation quality of Napier grass silage at three high temperatures. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1931–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
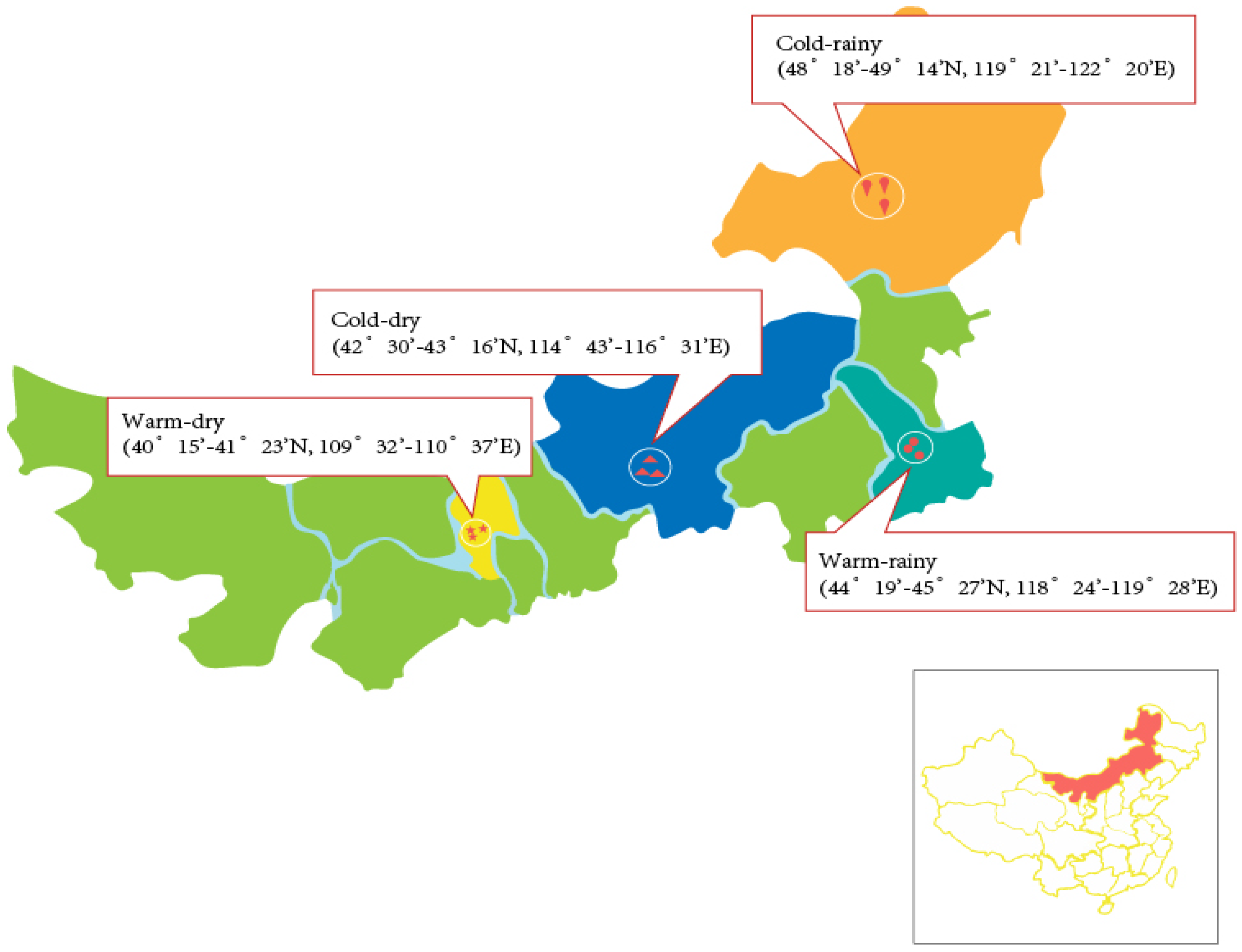


| Region | Cold–Rainy | Warm–Rainy | Cold–Dry | Warm–Dry | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bunker Silo | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | SEM | p-Value |
| DM (g/kg) | 236 fg | 244 fg | 274 cd | 286 bc | 314 a | 293 b | 262 de | 229 g | 264 de | 295 b | 273 cd | 321 a | 6.36 | <0.01 |
| pH | 6.01 abc | 5.93 bcd | 6.13 ab | 5.89 cd | 5.93 cd | 6.14 ab | 5.83 d | 5.93 cd | 6.03 abc | 6.15 a | 5.83 d | 6.03 abc | 0.06 | <0.01 |
| WSC (g/kg DM) | 43.2 d | 46.2 bc | 41.9 d | 45.1 c | 39.7 e | 42.1 d | 47.9 ab | 48.3 a | 46.2 bc | 38.9 e | 43.2 d | 38.7 e | 0.60 | <0.01 |
| CP (g/kg DM) | 212 de | 197 f | 218 bcd | 228 ab | 231 a | 216 cd | 193 fg | 217 bcd | 184 g | 214 cde | 204 ef | 225 abc | 3.81 | <0.01 |
| NDF (g/kg DM) | 365 abc | 372 ab | 368 bc | 359 bc | 383 a | 374 ab | 356 bc | 349 c | 362 bc | 367 abc | 349 c | 372 ab | 6.43 | <0.05 |
| ADF (g/kg DM) | 263 a | 257 a | 248 ab | 242 bcd | 256 ab | 263 a | 238 cd | 241 bcd | 258 a | 253 abc | 237 d | 258 a | 5.22 | <0.01 |
| LAB (log cfu/g) | 5.24 cd | 6.24 a | 4.18 f | 5.38 c | 5.25 cd | 5.69 b | 4.83 e | 5.17 d | 5.39 c | 5.82 b | 5.32 cd | 6.15 a | 0.06 | <0.01 |
| Yeasts (log cfu/g) | 4.29 e | 4.89 d | 4.21 e | 4.93 d | 5.83 a | 5.28 c | 3.84 f | 3.58 g | 4.25 e | 5.39 bc | 4.85 d | 5.51 b | 0.07 | <0.01 |
| Enterobacter (log cfu/g) | 4.29 e | 4.83 a | 4.58 bc | 4.87 a | 4.49 cd | 4.73 ab | 3.83 f | 3.73 f | 4.28 e | 4.37 de | 4.52 cd | 4.63 bc | 0.06 | <0.01 |
| Region | Cold-Rainy | Warm-Rainy | Cold-Dry | Warm-Dry | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bunker Silo | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | SEM | p-Value |
| pH | 5.74 a | 5.52 b | 4.84 cd | 4.75 cd | 4.38 e | 4.82 cd | 4.72 d | 5.63 ab | 4.86 c | 4.71 d | 4.87 c | 4.47 e | 0.05 | <0.01 |
| NH3-N (g/kg DM) | 6.38 c | 7.13 a | 3.47 e | 3.98 d | 2.86 g | 3.13 f | 2.64 g | 6.78 b | 3.17 ef | 2.74 g | 2.83 g | 2.29 h | 0.08 | <0.01 |
| Lactic acid (g/kg DM) | 16.75 h | 17.84 g | 23.74 b | 13.87 k | 14.74 i | 21.38 e | 22.64 d | 14.25 j | 19.75 f | 24.21 a | 23.17 c | 24.27 a | 0.07 | <0.01 |
| Acetic acid (g/kg DM) | 12.31 h | 13.43 g | 18.96 c | 24.86 a | 23.67 b | 17.34 e | 16.45 f | 23.75 b | 18.54 d | 16.45 f | 17.53 e | 16.28 f | 0.09 | <0.01 |
| Butyric acid (g/kg DM) | 8.03 c | 9.14 b | 2.36 d | 1.86 g | 1.74 g | 1.86 g | 2.31 d | 10.36 a | 2.27 d | 2.14 e | 2.07 e | 2.03 ef | 0.06 | <0.01 |
| 2,3-Butanediod (g/kg DM) | 2.07 a | 1.78 d | 1.54 f | 1.86 c | 1.24 g | 1.75 d | 1.95 b | 1.76 d | 2.08 a | 1.84 c | 1.92 b | 1.69 e | 0.01 | <0.01 |
| 1,2-Propanediod (g/kg DM) | 1.09 i | 2.74 c | 6.85 b | 7.23 a | 6.85 b | 1.93 e | 1.32 gh | 2.54 d | 1.49 g | 1.25 hi | 1.74 f | 1.46 g | 0.06 | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, B.; Sui, H.; Qin, W.; Hu, Z.; Wei, M.; Yong, M.; Wang, C.; Niu, H. Microbial Community and Fermentation Quality of Alfalfa Silage Stored in Farm Bunker Silos in Inner Mongolia, China. Fermentation 2023, 9, 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9050455
Wu B, Sui H, Qin W, Hu Z, Wei M, Yong M, Wang C, Niu H. Microbial Community and Fermentation Quality of Alfalfa Silage Stored in Farm Bunker Silos in Inner Mongolia, China. Fermentation. 2023; 9(5):455. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9050455
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Baiyila, Humujile Sui, Weize Qin, Zongfu Hu, Manlin Wei, Mei Yong, Chao Wang, and Huaxin Niu. 2023. "Microbial Community and Fermentation Quality of Alfalfa Silage Stored in Farm Bunker Silos in Inner Mongolia, China" Fermentation 9, no. 5: 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9050455
APA StyleWu, B., Sui, H., Qin, W., Hu, Z., Wei, M., Yong, M., Wang, C., & Niu, H. (2023). Microbial Community and Fermentation Quality of Alfalfa Silage Stored in Farm Bunker Silos in Inner Mongolia, China. Fermentation, 9(5), 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9050455




