Techno-Economic Analysis of Macroalgae Biorefineries: A Comparison between Ethanol and Butanol Facilities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
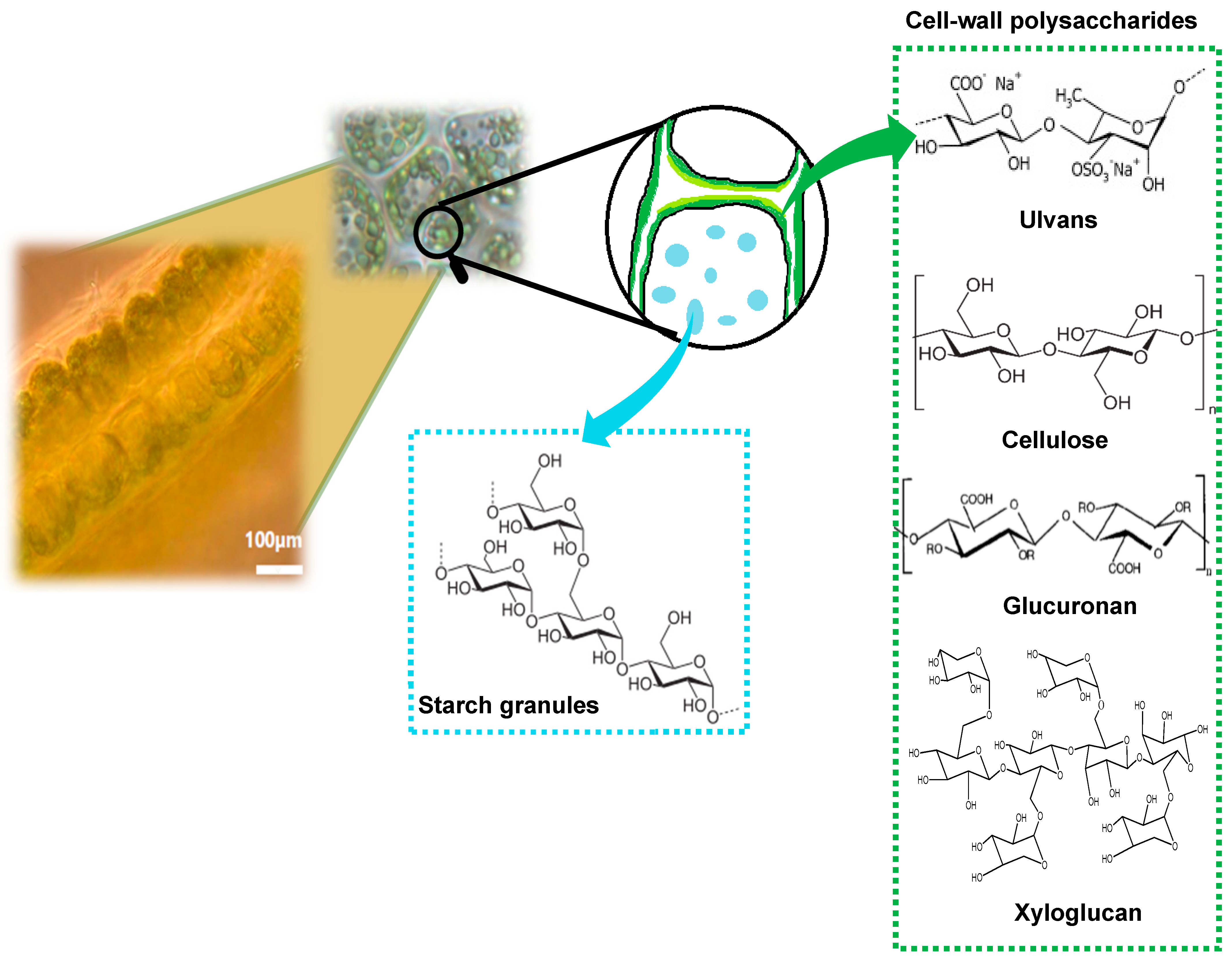
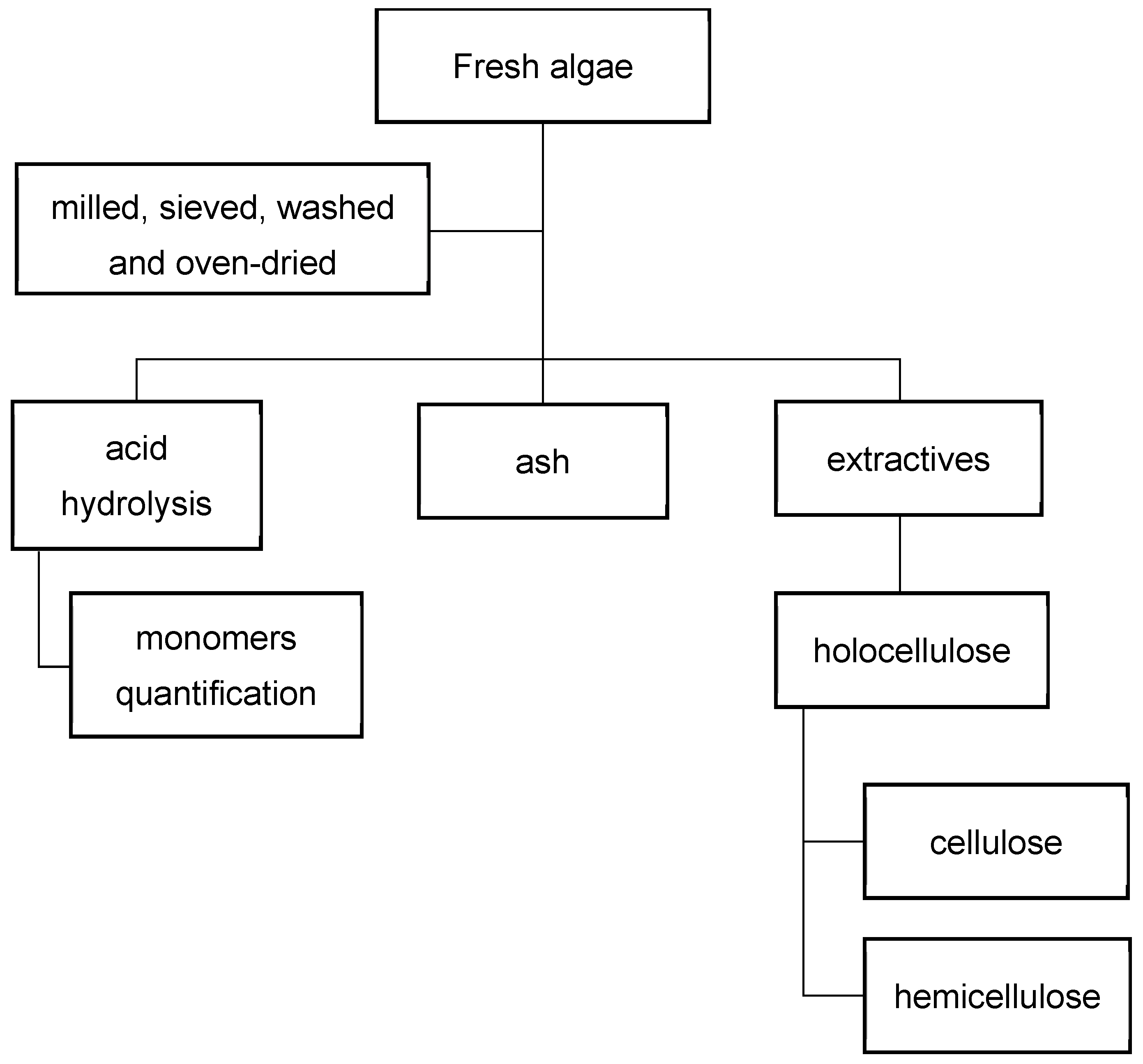
2.1. Seaweed Conditioning and Extractives Analysis
2.2. Holocellulose, Seifert Cellulose, and Alfa-Cellulose
2.3. Monomer Quantification
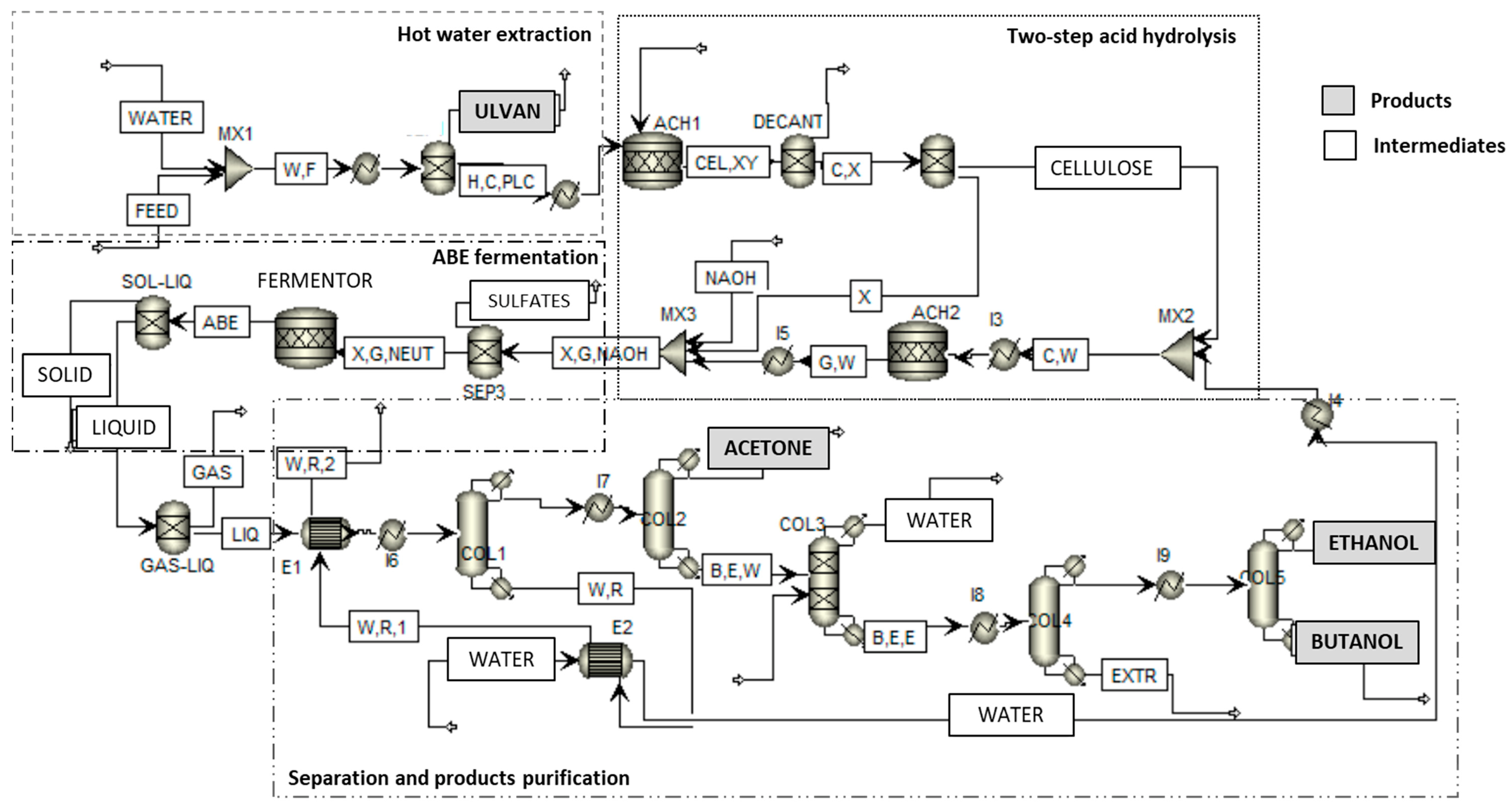
2.4. Aspen Plus Modelling of the ABE Process
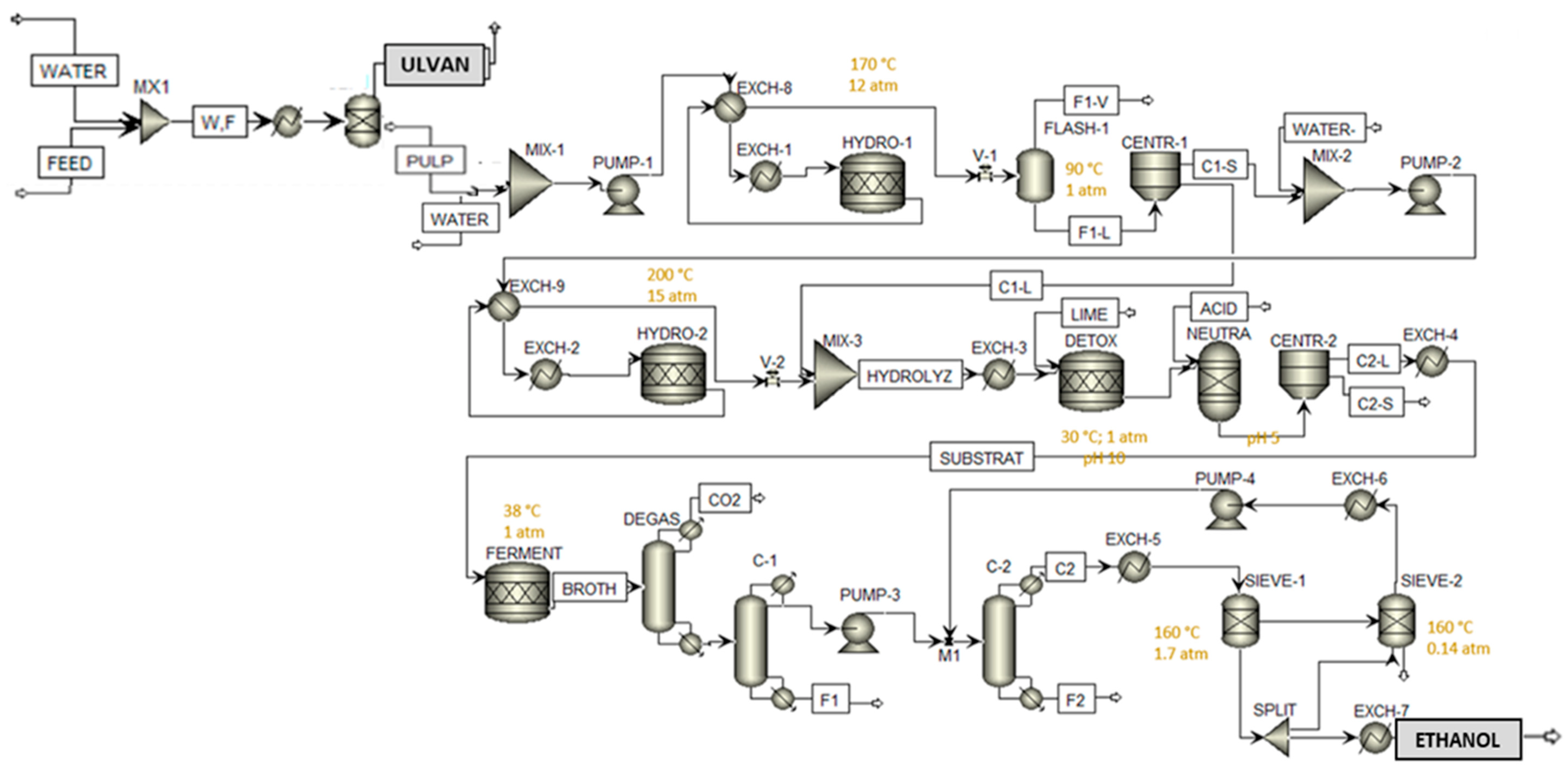
2.5. Aspen Plus Modelling of the Bioethanol Process
2.6. Economic Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Characterization Results of the Green Seaweed
3.2. Results of the Two Sugar Biorefinery Models
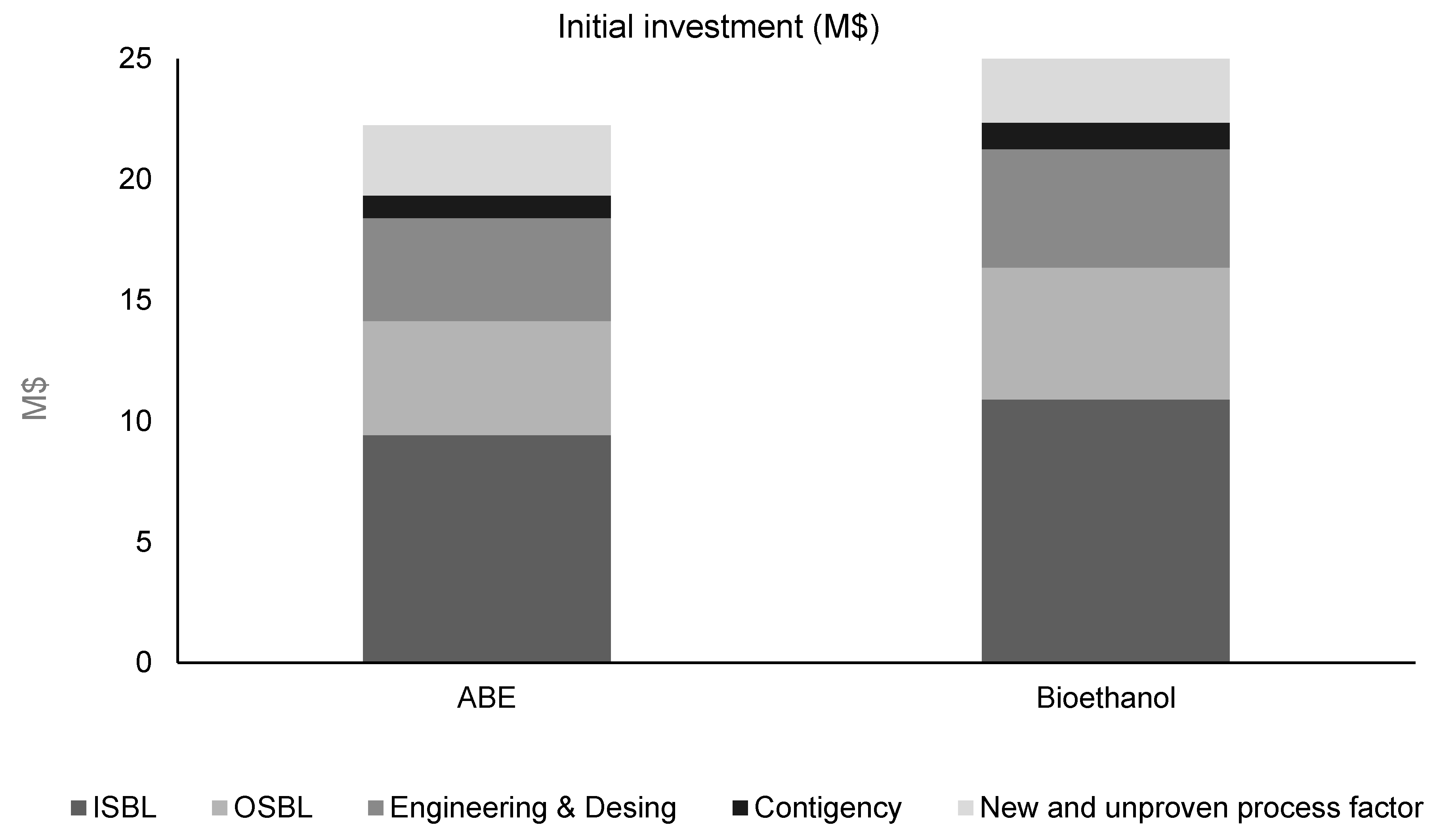
3.3. Economic Analysis
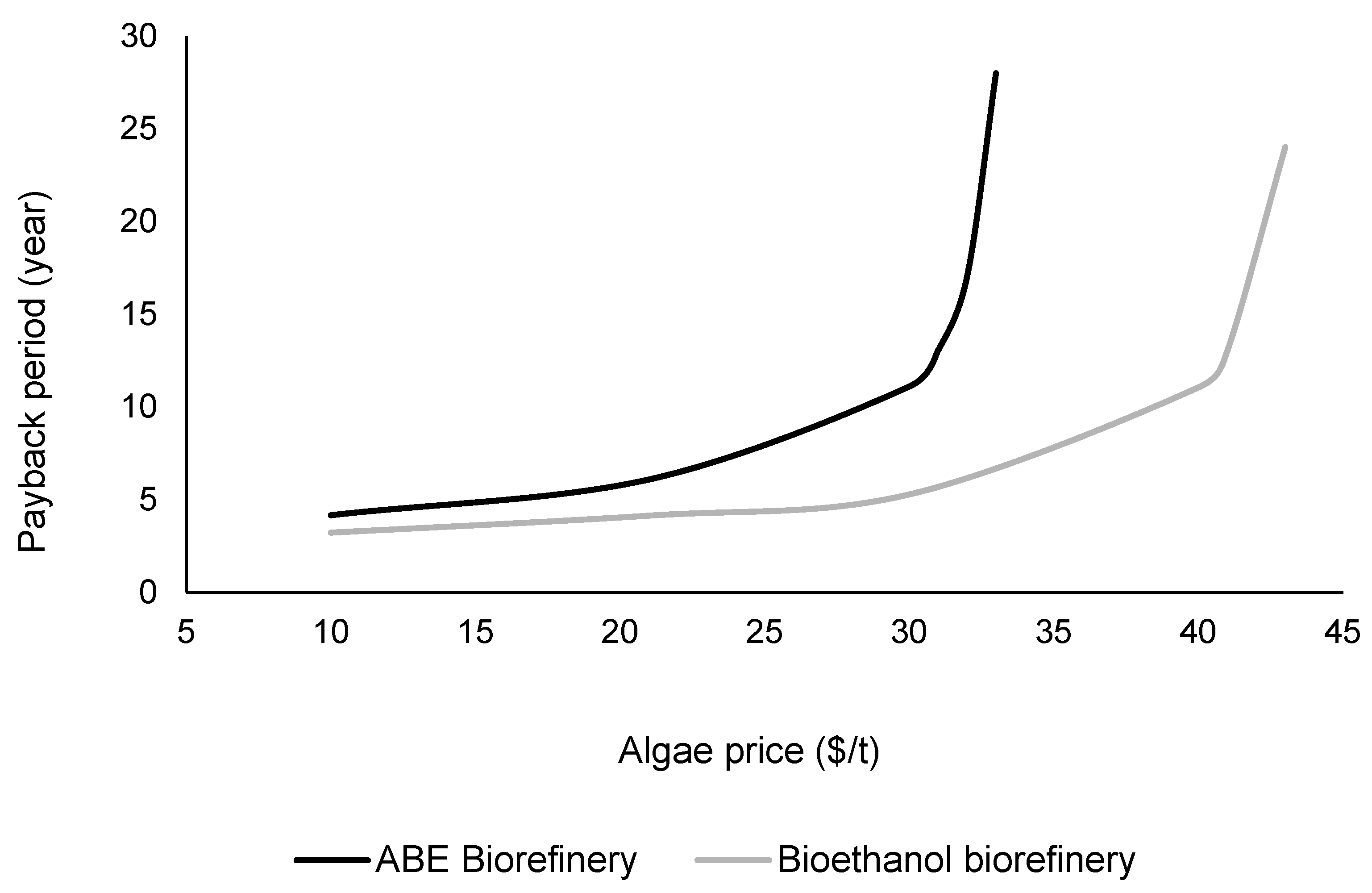
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. World Population. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/sections/issues-depth/population/ (accessed on 30 July 2019).
- Global Water Partnership GWP Perspective Papers. 2014, pp. 1–20. Available online: https://www.gwp.org/globalassets/global/toolbox/publications/perspective-papers/perspective_paper_landuse_and_groundwater_no6_english.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Jong, E.D.; Jungmeier, G. Biorefinery Concepts in Comparison to Petrochemical Refineries. In Industrial Biorefineries and White Biotechnology; Höfer, R., Pandey, A., Larroche, C., Eds.; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 3–33. ISBN 9780444634535. [Google Scholar]
- Geada, P.; Moreira, C.; Silva, M.; Nunes, R.; Madureira, L.; Rocha, C.M.R.; Pereira, R.N.; Vicente, A.A.; Teixeira, J.A. Algal proteins: Production strategies and nutritional and functional properties. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 332, 125125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subharda, B.G.; Edwards, M. Coproduct market analysis and water footprint of simulated commercial algal biorefineries. Appl. Energy 2011, 10, 3515–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balina, K.; Romagnoli, F.; Blumberga, D. Seaweed biorefinery concept for sustainable use of marine resources. Energy Procedia 2017, 128, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tako, M.; Tamanaha, M.; Tamashiro, Y.; Uechi, S. Structure of Ulvan Isolated from the Edible Green Seaweed, Ulva pertusa. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, L.; Grenha, A. Sulfated Seaweed Polysaccharides as Multifunctional Materials in Drug Delivery Applications. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezoa-Conte, R.; Leyton, A.; Baccini, A.; Ravanal, M.C.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Grénman, H.; Xu, C.; Willför, S.; Lienqueo, M.E.; Mikkola, J.P. Aqueous Extraction of the Sulfated Polysaccharide Ulvan from the Green Alga Ulva rigida—Kinetics and Modeling. Bioenergy Res. 2017, 10, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mis, L.; Ambroz, J.; Machu, L. Health Benefits of Algal Polysaccharides in Human Nutrition. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 66, 75–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, D.H.; Kim, S.K. Sulfated polysaccharides as bioactive agents from marine algae. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Liu, R. Overview on Biological Activities and Molecular Characteristics of Sulfated Polysaccharides from Marine Green Algaein Recent Years. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4984–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankiewicz, R.; Łę, B.; Messyasz, B.; Fabrowska, J.; So, M.; Pikosz, M. First isolation of polysaccharidic ulvans from the cell walls of freshwater algae. Algal Res. 2016, 19, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, M.; Chemodanov, A.; Gottlieb, R.; Kazir, M.; Nahor, O.; Gozin, M.; Israel, A.; Livney, Y.D.; Golberg, A. Starch from the sea: The green macroalga Ulva ohnoi as a potential source for sustainable starch production in the marine biorefinery. Algal Res. 2019, 37, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coste, O.B.N. Study of the Green Alga Ulva for Its Use as Functional Food in Aquaculture: Development of Biotechnologic Processes to Determine the Bioactivity of the Sulfated Polysaccharide Ulvan. Ph.D. Thesis, Escuela Internacional de Doctorado en estudios del mar (EIDEMAR), University of Cadiz, Cádiz, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wahab, R.; Mustafa, M.T.; Salam, M.A.; Sudin, M.; Samsi, H.W.; Rasat, M.S.M. Chemical Composition of Four Cultivated Tropical Bamboo in Genus Gigantochloa. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykiri-Acma, H.; Yaman, S.; Alkan, M.; Kucukbayrak, S. Mineralogical characterization of chemically isolated ingredients from biomass. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 77, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielewicz, D.; Surma-Ślusarska, B.; Żurek, G.; Martyniak, D. Selected Grass Plants as Biomass Fuels and Raw Materials for Papermaking. Part I. Calorific Value and Chemical Composition. BioResources 2015, 10, 8539–8551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, N.; Bustos, C.; Aguayo, M.G.; Cloutier, A.; Castillo, R. Impact of the chemical composition of Pinus radiata wood on its physical and mechanical properties following thermo-hygromechanical densification. BioResources 2018, 13, 2268–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llano, T.; Macías, C.; Trancho, A.; Robles, J.; Arroyo, N.L.; Coz, A. Acid depolymerization of cell wall polysaccharides from Ulvan-rich extracts of green seaweeds. In Proceedings of the II International Congress on Biorefineries and Renewable Energies Supported in ICTs: BRESICT, Bogotá, Colombia, 17–20 February 2020; pp. 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Llano, T.; Quijorna, N.; Andrés, A.; Coz, A. Sugar, acid and furfural quantification in a sulphite pulp mill: Feedstock, product and hydrolysate analysis by HPLC/RID. Biotechnol. Rep. 2017, 15, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasahati, P.; Liu, J.J. Process Simulation of Bioethanol Production from Brown Algae; IFAC: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 45, ISBN 9783902823052. [Google Scholar]
- Fasahati, P.; Woo, H.C.; Liu, J.J. Industrial-scale bioethanol production from brown algae: Effects of pretreatment processes on plant economics. Appl. Energy 2015, 139, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llano, T.; García-Quevedo, N.; Quijorna, N.; Viguri, J.R.; Coz, A. Evolution of lignocellulosic macrocomponents in the wastewater streams of a sulfite pulp mill: A preliminary biorefining approach. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 102534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, K.; Kankanala, H.R.; Lundin, M.; Taherzadeh, M.J. A novel process simulation model (PSM) for anaerobic digestion using Aspen Plus. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 168, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, J.A.; Cardona, C.A. Process simulation of fuel ethanol production from lignocellulosics using aspen plus. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 6205–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, M. Simulation of the process for producing butanol from corn fermentation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 5551–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigh, K.F.; Petersen, A.M.; Gottumukkala, L.; Mandegari, M.; Naleli, K. Simulation and comparison of processes for biobutanol production from lignocellulose via ABE fermentation. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2018, 12, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procentese, A.; Raganati, F.; Olivieri, G.; Russo, M.E.; Salatino, P.; Marzocchella, A. Continuous xylose fermentation by Clostridium acetobutylicum—Assessment of solventogenic kinetics. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, R.; Dehury, P.; Bharti, A.; Banerjee, T. Liquid-liquid extraction, COSMO-SAC predictions and process flow sheeting of 1-butanol enhancement using mesitylene and oleyl alcohol. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 265, 824–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, M.C.; Rehmann, M.S.; Zohaib, M. ABE Fermentation of Sugar in Brazil. Sr. Des. Rep. 2010, 4, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Llano, T.; Rueda, C.; Dosal, E.; Andrés, A.; Coz, A. Multi-criteria analysis of detoxification alternatives: Techno-economic and socio-environmental assessment. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 154, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llano, T.; Quijorna, N.; Coz, A. Detoxification of a LignocellulosicWaste from a Pulp Mill to Enhance Its Fermentation Prospects. Energies 2017, 10, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.; Grossmann, I.E. Energy Optimization of Bioethanol Production Via Hydrolysis of Switchgrass. AIChE J. 2011, 59, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, A.D.; Rojas Alfaro, D.M. Inmovilización de Lipasa candida Rugosa en Soporte de Quitosano. Ph. D. Thesis, Facultad de Ingeniería y Arquitectura, Universidad Nacional de Colombia (Sede Manizales), Manizales, Colombia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Towler, G.; Sinnot, R. Chemical Engineering Desing: Principles, Practice and Economics of Plant and Process Design; Elsevier: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-0-08-096659-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kutsay, A.; Kratky, L.; Jirout, T. Biogas Plant Upgrade to CO2-Free Technology: A Techno-Economic Case Study. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2020, 43, 1981–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutsay, A.; Kratky, L.; Jirout, T. Diversity of Biogas Plant Realizations. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2019, 42, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratky, L.; Zamazal, P. Economic feasibility and sensitivity analysis of fish waste processing biorefinery. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 243, 118677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoli, C.O.; Adams, R.A.; Brigljevic, B.; Liu, J.J. Design and economic analysis of a macroalgae-to-butanol process via a thermochemical route. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 123, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanzad, M.; Shafiei, M.; Karimi, K. Whole sweet sorghum plant as a promising feedstock for biobutanol production via biorefinery approaches: Technoeconomic analysis. Renew. Energy 2020, 158, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meramo-Hurtado, S.I.; González-Delgado, Á.; Rehmann, L.; Quinones-Bolanos, E.; Mehvar, M. Comparative analysis of biorefinery designs based on acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation under exergetic, techno-economic, and sensitivity analyses towards a sustainability perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Thomsen, M. Techno-economic and environmental assessment of novel biorefinery designs for sequential extraction of high-value biomolecules from brown macroalgae Laminaria digitata, Fucus vesiculosus, and Saccharina latissima. Algal Res. 2021, 60, 102499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gloria, K.D.; Rodríguez-Jasso, R.M.; Shiva; Aparicio, E.; Chávez González, M.L.; Kostas, E.T.; Ruiz, H.A. Macroalgal biomass in terms of third-generation biorefinery concept: Current status and techno-economic analysis—A review. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 16, 100863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, A.B.; Arasoglu, T.; Gulen, J.; Cheng, S.; Al-Shorgani, N.K.N.; Habaki, H.; Egashira, R.; Kalil, M.S.; Yusoff, W.M.W.; Cross, J.S. Techno-economic analysis of a two-step fermentation process for bio-butanol production from cooked rice. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2021, 5, 3705–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Gami, B.; Patel, P.; Patel, B. Biodiesel production from microalgae Dunaliella tertiolecta: A study on economic feasibility on large-scale cultivation systems. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023, 13, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harahap, A.F.P.; Ramadhan, M.Y.A.; Lestari, T.; Gozan, M.; Srinophakun, P. Preliminary Plant Design of Biofuel from Algae in Balikpapan, East Kalimantan. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 353, 012059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesijadi, G.; Jones, S.B.; Zhu, Y. Macroalgae as a Biomass Feedstock: A Preliminary Analysis; Report of the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, U.S. Department of Energy PNNL-19944; Pacific Northwest National Laboratory: Richland, WA, USA, 2010; pp. 1–50. [CrossRef]
- Echemi. Available online: https://www.echemi.com (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Servicio, T.D.E.L. La Factura del Agua para Suministros Comerciales/Industriales año 2016 La Factura del Agua para Suministros Comerciales/Industriales. 2016. Available online: https://www.aiguesdebarcelona.cat/documents/20126/0/triptico_factura_comercial_es_2019.pdf/c5066bb6-2bf8-fcc8-6b08-821ef649bc01?t=1549472793366 (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Intratec. Available online: https://www.intratec.us (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Gengiah, K.; Gurunathan, B.; Rajendran, N.; Han, J. Process evaluation and techno-economic analysis of biodiesel production from marine macroalgae Codium tomentosum. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 351, 126969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | Reactions of Hydrolysis | Extent of Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Hemicellulose | (C5H8O4)n + nH2O → nC5H10O5 | 0.60 |
| Hemicellulose | (C5H8O4)n + H2O → C2H4O2 | 0.40 |
| Protein | C13H25O7N3S + 6H2O → 6.5CO2 + 6.5CH4 + 3NH3 + H2S | 0.9 |
| Triolein | C57H104O6 + 3 H2O → C3H8O3 + 3 C18H34O2 | 0.9 |
| Tripalmitin | 16C51H98O6 + 135 H2O → 64C3H8O3 + 39 C16H34O | 0.9 |
| Cellulose | (C6H10O5)m + mH2O → mC6H12O6 | 0.29 (first reactor) |
| 0.9 (second reactor) | ||
| Glucose | C6H12O6 → C6H6O3 + 3H2O | 0.27 |
| Reactions of ABE Fermentation | Extent of Reaction | |
| C6H12O6 →C4H10O + 2CO2 + H2O | 0.629 | |
| C6H12O6 + H2O →C3H6O + 3CO2 + 4H2 | 0.322 | |
| C6H12O6 → 2C2H6O + 2CO2 + H2 | 0.014 | |
| C6H12O6 → C4H8O2 + 2CO2 + 2H2 | 0.018 | |
| C6H12O6 → 3C2H4O2 | 0.014 | |
| C5H10O5 → C4H10O + 2CO2 + H2O | 0.629 | |
| C5H10O5 → 2C2H5O + CO2 | 0.014 | |
| C5H10O5 → C4H8O2 + 2CO2 + 2H2 | 0.018 | |
| C5H10O5 → C2H4O2 + CO2 + H2 | 0.014 | |
| Compound | Reactions of the First Hydrolysis | Extent of Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Hemicellulose | (C5H8O4)n + nH2O → nC5H10O5 | 0.92 |
| Cellulose | (C6H10O5)m + mH2O → mC6H12O6 | 0.29 |
| Xylose | C5H10O5 → C5H4O2 + 3H2O | 0.0046 |
| Protein | C13H25O7N3S + 6H2O → 6.5CO2 + 6.5CH4 + 3NH3 + H2S | 0.90 |
| Triolein | C57H104O6 + 3 H2O → C3H8O3 + 3 C18H34O2 | 0.90 |
| Tripalmitin | 16 C51H98O6 + 135 H2O → 64 C3H8O3 + 39 C16H34O | 0.90 |
| Reactions of the Second Hydrolysis | ||
| Cellulose | (C6H10O5)m + mH2O → mC6H12O6 | 0.96 |
| Hemicellulose | (C5H8O4)n + nH2O → nC5H10O5 | 0.069 |
| Glucose | C6H12O6 → C6H6O3 + 3H2O | 0.27 |
| Xylose | C5H10O5 → C5H4O2 + 3H2O | 0.10 |
| Reactions of Bioethanol Fermentation | Extent of Reaction | |
| Glucose | C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 | 0.92 |
| Xylose | 3 C5H10O5 → 5 C2H5OH + 5CO2 | 0.80 |
| Production Costs (M$/Year) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Item | ABE | Bioethanol |
| Total personnel costs | 0.58 | 0.58 |
| Maintenance | 0.38 | 0.44 |
| Property taxes | 0.14 | 0.16 |
| Rent of land | 0.21 | 0.25 |
| Environmental charges | 0.14 | 0.16 |
| Materials | 6.04 | 2.74 |
| Utilities | 38.09 | 31.61 |
| Raw material | 8.42 | 8.42 |
| Total production costs | 54.00 | 44.35 |
| Revenues (M$/year) | ||
| Total | 67.43 | 61.45 |
| Pretax benefits | 13.43 | 17.10 |
| Depreciation and amortization | 1.11 | 1.29 |
| Interest charges and others | 0.83 | 0.96 |
| Profit before taxes | 11.48 | 14.85 |
| Income tax | 2.30 | 2.97 |
| Net profit | 10.30 | 13.17 |
| Plant | ABE | Bioethanol | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2SO4 ($/t) | 40 | [36] | |
| H2O ($/m3) | 1.9 | [37] | |
| NaOH ($/t) | 400 | [38] | |
| Ca(OH)2 ($/t) | 131.8 | [36] | |
| Algae ($/t) | 21 | [39] |
| Plant | ABE | Bioethanol |
|---|---|---|
| Biorefinery | VAN (M$) | IRR |
| ABE | 6.58 | 0.27 |
| Bioethanol | 15.90 | 0.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Llano, T.; Arce, C.; Gallart, L.E.; Perales, A.; Coz, A. Techno-Economic Analysis of Macroalgae Biorefineries: A Comparison between Ethanol and Butanol Facilities. Fermentation 2023, 9, 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040340
Llano T, Arce C, Gallart LE, Perales A, Coz A. Techno-Economic Analysis of Macroalgae Biorefineries: A Comparison between Ethanol and Butanol Facilities. Fermentation. 2023; 9(4):340. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040340
Chicago/Turabian StyleLlano, Tamara, Carlos Arce, Lien E. Gallart, Ana Perales, and Alberto Coz. 2023. "Techno-Economic Analysis of Macroalgae Biorefineries: A Comparison between Ethanol and Butanol Facilities" Fermentation 9, no. 4: 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040340
APA StyleLlano, T., Arce, C., Gallart, L. E., Perales, A., & Coz, A. (2023). Techno-Economic Analysis of Macroalgae Biorefineries: A Comparison between Ethanol and Butanol Facilities. Fermentation, 9(4), 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040340







